Protein Kinase Expression of the AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Peripheral Mononuclear Cells of Schizophrenia Patients: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. The Main Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Expression of Protein Kinases of the AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDNF | brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| TrkB | the receptor tyrosine kinase B |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| PLCγ | phosphoinositide phospholipase C |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| AKT | also known as protein kinase B |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| p70S6K | ribosomal protein S6 kinase |
| 4E-BP1 | initiation factor 4E binding protein 1 |
| GSK3 | glycogen synthase kinase 3 |
| PANSS | Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale |
| MFI | median fluorescence intensity |
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases 10 |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
References
- Shmukler, A.B. Schizophrenia; GJeOTAR-Media: Moscow, Russia, 2017; 176p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kornetov, A.N.; Kornetova, E.G.; Golenkova, A.V.; Kozlova, S.M.; Arzhanik, M.B.; Samoylenko, Z.A.; Boiko, A.S.; Semke, A.V. Neurocognitive deficits in clinical polymorphism of schizophrenia: Typology, expression and syndromal overlaps. Bull. Sib. Med. 2019, 18, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornetova, E.G.; Goncharova, A.A.; Dmitrieva, E.M.; Kornetov, A.N.; Gerasimova, V.I.; Ivanova, S.A.; Semke, A.V. The effectiveness of treatment and features of adverse events in patients with schizophrenia receiving risperidone and haloperidol depending on the duration of illness. Med. News N. Cauc. 2021, 16, 285–289. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Amooeian, V.G.; Rashidi, E. Dysfunction in Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Signaling Pathway and Susceptibility to Schizophrenia, Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Diseases. Curr. Gene Ther. 2018, 18, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, S.A.; Losenkov, I.S.; Bokhan, N.A. Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3β in the pathogenesis of mental disorders. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. Im. S. S. Korsakova 2014, 114, 93–100. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Zahid, S.; Hasan, B.; Asif, A.R.; Ahmed, N. Mass Spectrometry based identification of site-specific proteomic alterations and potential pathways underlying the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 4931–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchenko, A.; Kanapin, A.; Samsonova, A.; Fedorenko, O.Y.; Kornetova, E.G.; Nurgaliev, T.; Mazo, G.E.; Semke, A.V.; Kibitov, A.O.; Bokhan, N.A.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies a gene network associated with paranoid schizophrenia and antipsychotics-induced tardive dyskinesia. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 105, 110134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, K.R.; Law, A.J. Neurodevelopmental concepts of schizophrenia in the genome-wide association era: AKT/mTOR signaling as a pathological mediator of genetic and environmental programming during development. Schizophr. Res. 2020, 217, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGorry, P.; Keshavan, M.; Goldstone, S.; Amminger, P.; Allott, K.; Berk, M.; Lavoie, S.; Pantelis, C.; Yung, A.; Wood, S.; et al. Biomarkers and clinical staging in psychiatry. World Psychiatry 2014, 13, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorofeeva, M.Y.; Sakharova, O.V. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway as a target for pathogenetic therapy of tuberous sclerosis. Med. Counc. 2012, 1, 90–103. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Düvel, K.; Yecies, J.L.; Menon, S.; Raman, P.; Lipovsky, A.I.; Souza, A.L.; Triantafellow, E.; Ma, Q.; Gorski, R.; Cleaver, S.; et al. Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream of mTOR complex 1. Mol. Cell. 2010, 39, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, A.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Mahoney, S.J.; Vu, H.; Yoon, S.O.; Cantley, L.C.; Blenis, J. Glucose addiction of TSC null cells is caused by failed mTORC1-dependent balancing of metabolic demand with supply. Mol. Cell. 2010, 38, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.M.; Ackerman, D.; Quinn, Z.L.; Mancuso, A.; Gruber, M.; Liu, L.; Giannoukos, D.N.; Bobrovnikova-Marjon, E.; Diehl, J.A.; Keith, B.; et al. Dysregulated mTORC1 renders cells critically dependent on desaturated lipids for survival under tumor-like stress. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 1115–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhitko, A.A.; Favorova, O.O.; Khabibullin, D.I.; Anisimov, V.N.; Henske, E.P. Kinase mTOR: Regulation and role in maintenance of cellular homeostasis, tumor development and aging. Biochemistry 2014, 79, 128–143. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hers, I.; Vincent, E.E.; Tavaré, J.M. Akt signalling in health and disease. Cell Signal 2011, 23, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.C.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, C.H.; Liu, S.C.; Ho, C.J.; Shen, W.W.; Leu, S.J. Alterations of serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in early alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol Alcohol. 2008, 43, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochhead, P.A.; Kinstrie, R.; Sibbet, G.; Rawjee, T.; Morrice, N.; Cleghon, V. A chaperone-dependent GSK3beta transitional intermediate mediates activation-loop autophosphorylation. Mol Cell. 2006, 24, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, C.; Cohen, P. The alpha-isoform of glycogen synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal muscle is inactivated by p70 S6 kinase or MAP kinase-activated protein kinase-1 in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1994, 338, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadha, R.; Meador-Woodruff, J.H. Downregulated AKT-mTOR signaling pathway proteins in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadha, R.; Alganem, K.; Mccullumsmith, R.E.; Meador-Woodruff, J.H. mTOR kinase activity disrupts a phosphorylation signaling network in schizophrenia brain. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 6868–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Lecue, I.; Diez-Alarcia, R.; Morentin, B.; Meana, J.J.; Callado, L.F.; Urigüen, L. Ribosomal Protein S6 Hypofunction in Postmortem Human Brain Links mTORC1-Dependent Signaling and Schizophrenia. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamian, E.S.; Hall, D.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Karayiorgou, M.; Gogos, J.A. Convergent evidence for impaired AKT1-GSK3beta signaling in schizophrenia. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrikis, P.; Polyzou, A.; Premeti, K.; Roumelioti, A.; Karampas, A.; Georgiou, G.; Grigoriadis, D.; Leondaritis, G. GSK3β and mTORC1 Represent 2 Distinct Signaling Markers in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Drug-Naive, First Episode of Psychosis Patients. Schizophr Bull. 2022, 48, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joaquim, H.P.G.; Zanetti, M.V.; Serpa, M.H.; Van de Bilt, M.T.; Sallet, P.C.; Chaim, T.M.; Busatto, G.F.; Gattaz, W.F.; Talib, L.L. Increased platelet glycogen sysnthase kinase 3beta in first-episode psychosis. Schizophr Res. 2018, 195, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadri, C.; Kozlovsky, N.; Agam, G.; Bersudsky, Y. GSK-3 parameters in lymphocytes of schizophrenic patients. Psychiatry Res. 2002, 112, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.R.; Opler, L.A.; Fiszbein, A. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1987, 13, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorieva, J.A.; Dainiak, M.B.; Katrukha, A.G.; Muronetz, V.I. Antibodies to the nonnative forms of d-glyceraldehyde3-phosphate dehydrogenase: Identification, purification, and influence on the renaturation of the enzyme. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 369, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Murakami, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tsuji, A.; Kitagishi, Y. Roles of PI3K/AKT/GSK3 Pathway Involved in Psychiatric Illnesses. Diseases 2019, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Qiao, X.; Wu, H.; Yin, F.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Y.; Wei, S.; Lai, J. An Association Study Between Genetic Polymorphisms in Functional Regions of Five Genes and the Risk of Schizophrenia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 59, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapogiannis, D.; Dobrowolny, H.; Tran, J.; Mustapic, M.; Frodl, T.; Meyer-Lotz, G.; Schiltz, K.; Schanze, D.; Rietschel, M.; Bernstein, H.G.; et al. Insulin-signaling abnormalities in drug-naïve first-episode schizophrenia: Transduction protein analyses in extracellular vesicles of putative neuronal origin. Eur. Psychiatry 2019, 62, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijtenburg, S.A.; Kapogiannis, D.; Korenic, S.A.; Mullins, R.J.; Tran, J.; Gaston, F.E.; Chen, S.; Mustapic, M.; Hong, L.E.; Rowland, L.M. Brain insulin resistance and altered brain glucose are related to memory impairments in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2019, 208, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, S.H.; Folsom, T.D.; Thuras, P.D. Altered subcellular localization of fragile X mental retardation signaling partners and targets in superior frontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia. NeuroReport 2017, 28, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.P.; Romano-Silva, M.A.; Lieberman, J.A.; Meltzer, H.Y.; Wong, A.H.; Kennedy, J.L. Association study of GSK3 gene polymorphisms with schizophrenia and clozapine response. Psychopharmacology 2008, 200, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inkster, B.; Nichols, T.E.; Saemann, P.G.; Auer, D.P.; Holsboer, F.; Muglia, P.; Matthews, P.M. Association of GSK3beta polymorphisms with brain structural changes in major depressive disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladkevich, A.; Kauffman, H.F.; Korf, J. Lymphocytes as a neural probe: Potential for studying psychiatric disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 28, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, J.; Morrens, M.; Coppens, V. The Potential Use of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells as Biomarkers for Treatment Response and Outcome Prediction in Psychiatry: A Systematic Review. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2021, 25, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mednova, I.A.; Boiko, A.S.; Kornetova, E.G.; Semke, A.V.; Bokhan, N.A.; Ivanova, S.A. Cytokines as Potential Biomarkers of Clinical Characteristics of Schizophrenia. Life 2022, 12, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornetova, E.G.; Kornetov, A.N.; Mednova, I.A.; Goncharova, A.A.; Gerasimova, V.I.; Pozhidaev, I.V.; Boiko, A.S.; Semke, A.V.; Loonen, A.J.M.; Bokhan, N.A.; et al. Comparative Characteristics of the Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence in Patients With Schizophrenia in Three Western Siberia Psychiatric Hospitals. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 661174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arihisa, W.; Kondo, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Matsumoto, J.; Nakanishi, H.; Kunii, Y.; Akatsu, H.; Hino, M.; Hashizume, Y.; Sato, S.; et al. Lipid-correlated alterations in the transcriptome are enriched in several specific pathways in the postmortem prefrontal cortex of Japanese patients with schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2023, 43, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, E.A.; Imami, A.S.; Eby, H.; Sahay, S.; Hamoud, A.R.; Golchin, H.; Ryan, W.; Shedroff, E.A.; Arvay, T.; Joyce, A.W.; et al. Neuronal alterations in AKT isotype expression in schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2025, 30, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Lin, J.; Little, P.J.; Srivastava, L.K.; Quirion, R. The possible role of the Akt signaling pathway in schizophrenia. Brain Res. 2012, 1470, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, J.L.; Depasquale, E.A.; Funk, A.J.; O’Donnovan, S.M.; Hasselfeld, K.; Marwaha, S.; Hammond, J.H.; Hartounian, V.; Meador-Woodruff, J.H.; Meller, J.; et al. Abnormalities of signal transduction networks in chronic schizophrenia. NPJ Schizophr. 2017, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa Abreu, R.; Penalva, L.O.; Marcotte, E.M.; Vogel, C. Global signatures of protein and mRNA expression levels. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 5, 1512–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.; Marcotte, E.M. Insights into the regulation of protein abundance from proteomic and transcriptomic analyses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boiko, A.; Pozhidaev, I.; Mikhalitskaya, E.; Paderina, D.; Vyalova, N.; Kornetova, E.; Bokhan, N.; Ivanova, S. The Role of Polymorphic Variants of Neuroplasticity Genes and Protein Kinases in the Formation of an Unfavorable Course of Schizophrenia. Psychiatry Psychother. Clin. Psychol. 2025, 16, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rok-Bujko, P. Molecular mechanisms of antipsychotics—Their influence on intracellular signaling pathways, and epigenetic and post-transcription processes. Postep. Psychiatr Neurol. 2022, 31, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koros, E.; Dorner-Ciossek, C. The role of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in schizophrenia. Drug. News Perspect. 2007, 20, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Lee, J.G.; Ha, E.K.; Choi, S.M.; Cho, H.Y.; Seo, M.K.; Kim, Y.H. Differential effects of aripiprazole and haloperidol on BDNF-mediated signal changes in SH-SY5Y cells. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 19, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
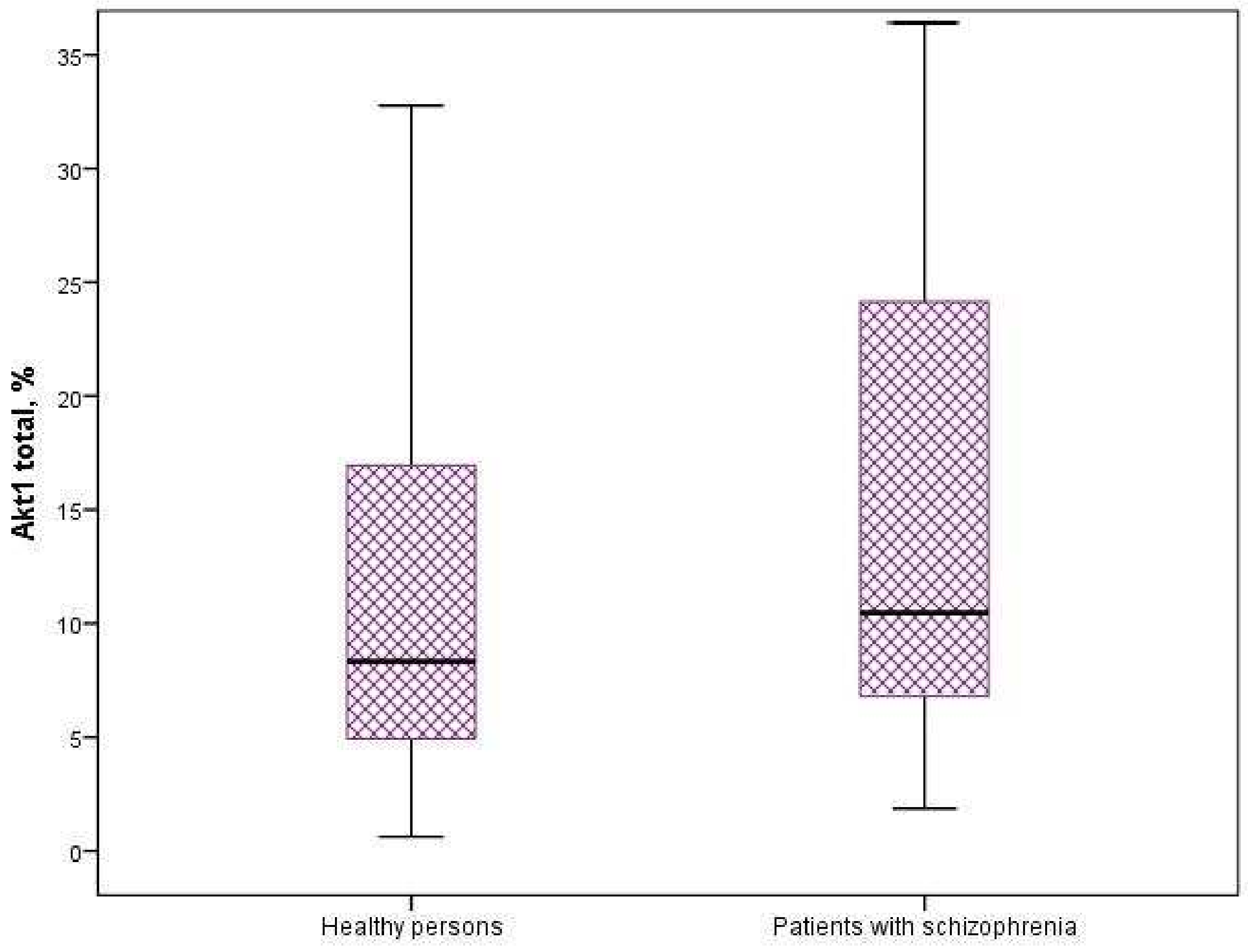
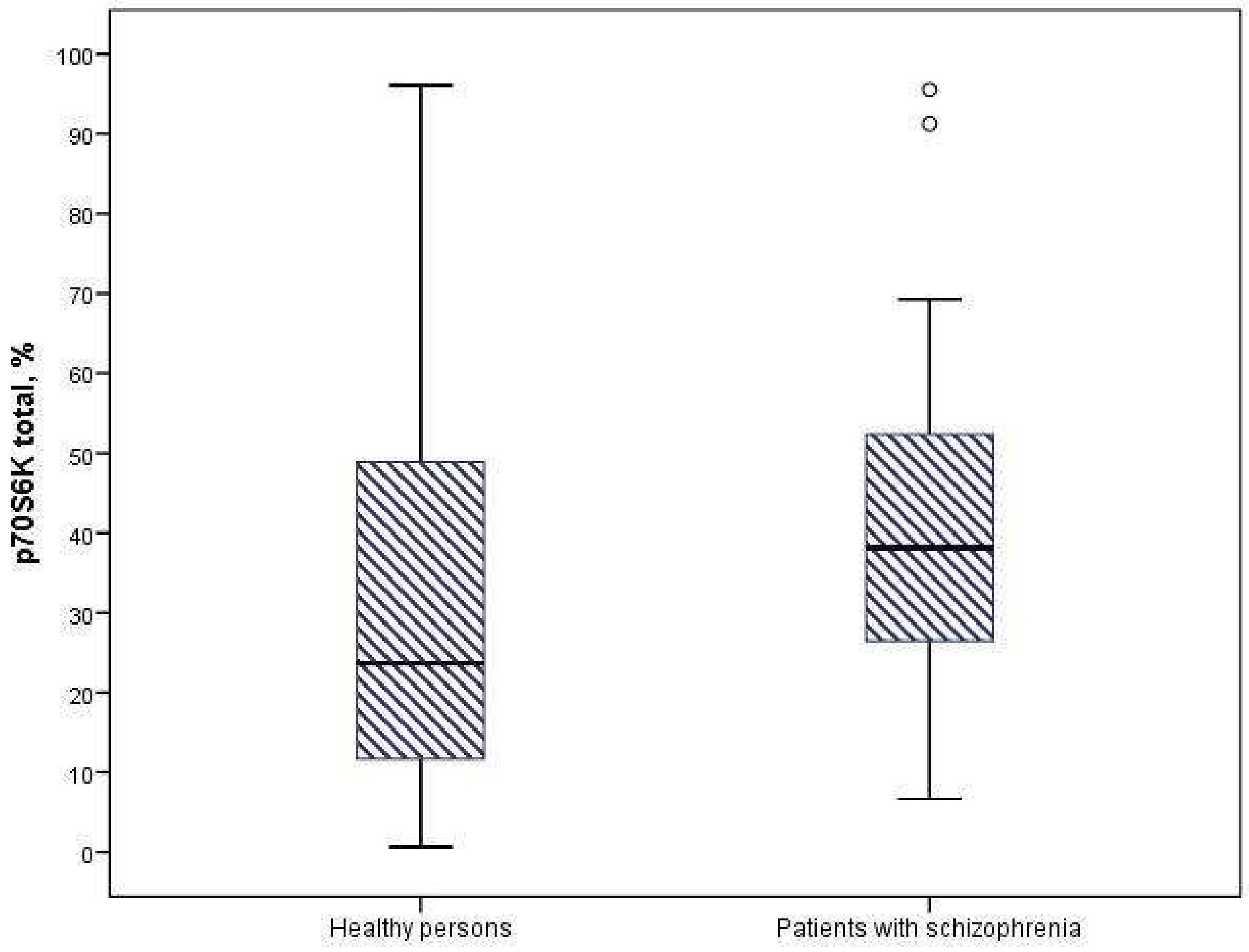
| Parameter | Healthy Persons (n = 60) | Patients with Schizophrenia (n = 58) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 43 [30; 55] | 35 [28; 42] | |
| Gender, n (%) | Male | 25 (41.7%) | 32 (53.3%) |
| Female | 35 (58.3%) | 28 (46.7%) | |
| Duration of disorder, years | - | 9 [5; 16] | |
| Clinical course, n (%) | Episodic course | - | 20 (34.5%) |
| Continuous course | - | 33 (56.9%) | |
| Not defined | 5 (8.6%) | ||
| Leading symptomatology, n (%) | Negative | - | 34 (58.6%) |
| Positive | - | 24 (41.4%) | |
| Protein Kinases, % | Healthy Persons (n = 60) | Patients with Schizophrenia (n = 58) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| mTOR | 3.99 [3.48; 5.23] | 4.76 [3.28; 5.28] | 0.56 |
| GSK3-α | 75.71 [56.15; 119.03] | 86.21 [42.46; 209.99] | 0.918 |
| GSK3-β | 39.55 [33.54; 71.7] | 67.13 [19.65; 159.62] | 0.732 |
| Protein Kinases, % | Continuous Course | Episodic Course | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| AKT1 | 12.85 [6.17; 35.67] | 11.67 [7.04; 21.16] | 0.576 |
| p70S6K | 40.13 [26.41; 59.7] | 37.59 [25.58; 44.74] | 0.44 |
| mTOR | 4.81 [4.01; 6.82] | 4.5 [2.09; 4.95] | 0.2 |
| GSK3-α | 113.33 [54.27; 258.71] | 83.14 [29.26; 150.3] | 0.277 |
| GSK3-β | 80.2 [22.74; 191.01] | 47.02 [16.13; 91] | 0.423 |
| Protein Kinases, % | Negative Symptomatology | Positive Symptomatology | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| AKT1 | 9.7 [6.16; 22.92] | 10.94 [7.66; 38.53] | 0.41 |
| p70S6K | 40.46 [27.63; 55.39] | 37.53 [24.17; 50.41] | 0.543 |
| mTOR | 4.77 [4.55; 5.33] | 4.02 [2.27; 5.11] | 0.237 |
| GSK3-α | 107.81 [64.43; 176.28] | 62.34 [17.87; 226.23] | 0.237 |
| GSK3-β | 74.66 [40.32; 99.82] | 25.82 [9.65; 170.08] | 0.203 |
| Protein Kinases, % | Less than 5 Year | More than 5 Years | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| AKT1 | 8.37 [6.31; 21.16] | 15.55 [6.62; 35.67] | 0.345 |
| p70S6K | 39.56 [27.13; 57.32] | 37.51 [24.73; 54.3] | 0.588 |
| mTOR | 4.02 [3.05; 4.93] | 4.77 [2.8; 5.31] | 0.443 |
| GSK3-α | 46.21 [30.47; 96.69] | 154.25 [85.44; 275.51] | 0.019 * |
| GSK3-β | 21.48 [12.32; 29.82] | 93.27 [47.02; 201.48] | 0.018 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boiko, A.S.; Mikhalitskaya, E.V.; Kornetova, E.G.; Bokhan, N.A.; Ivanova, S.A. Protein Kinase Expression of the AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Peripheral Mononuclear Cells of Schizophrenia Patients: A Pilot Study. NeuroSci 2025, 6, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040116
Boiko AS, Mikhalitskaya EV, Kornetova EG, Bokhan NA, Ivanova SA. Protein Kinase Expression of the AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Peripheral Mononuclear Cells of Schizophrenia Patients: A Pilot Study. NeuroSci. 2025; 6(4):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040116
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoiko, Anastasiia S., Ekaterina V. Mikhalitskaya, Elena G. Kornetova, Nikolay A. Bokhan, and Svetlana A. Ivanova. 2025. "Protein Kinase Expression of the AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Peripheral Mononuclear Cells of Schizophrenia Patients: A Pilot Study" NeuroSci 6, no. 4: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040116
APA StyleBoiko, A. S., Mikhalitskaya, E. V., Kornetova, E. G., Bokhan, N. A., & Ivanova, S. A. (2025). Protein Kinase Expression of the AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Peripheral Mononuclear Cells of Schizophrenia Patients: A Pilot Study. NeuroSci, 6(4), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040116





