Compound Heterozygous PNKP Variants Causing Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy with Severe Microcephaly: Natural History of Two New Cases and Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Recruitment
2.2. Genetic Analyses
2.3. Data Collection
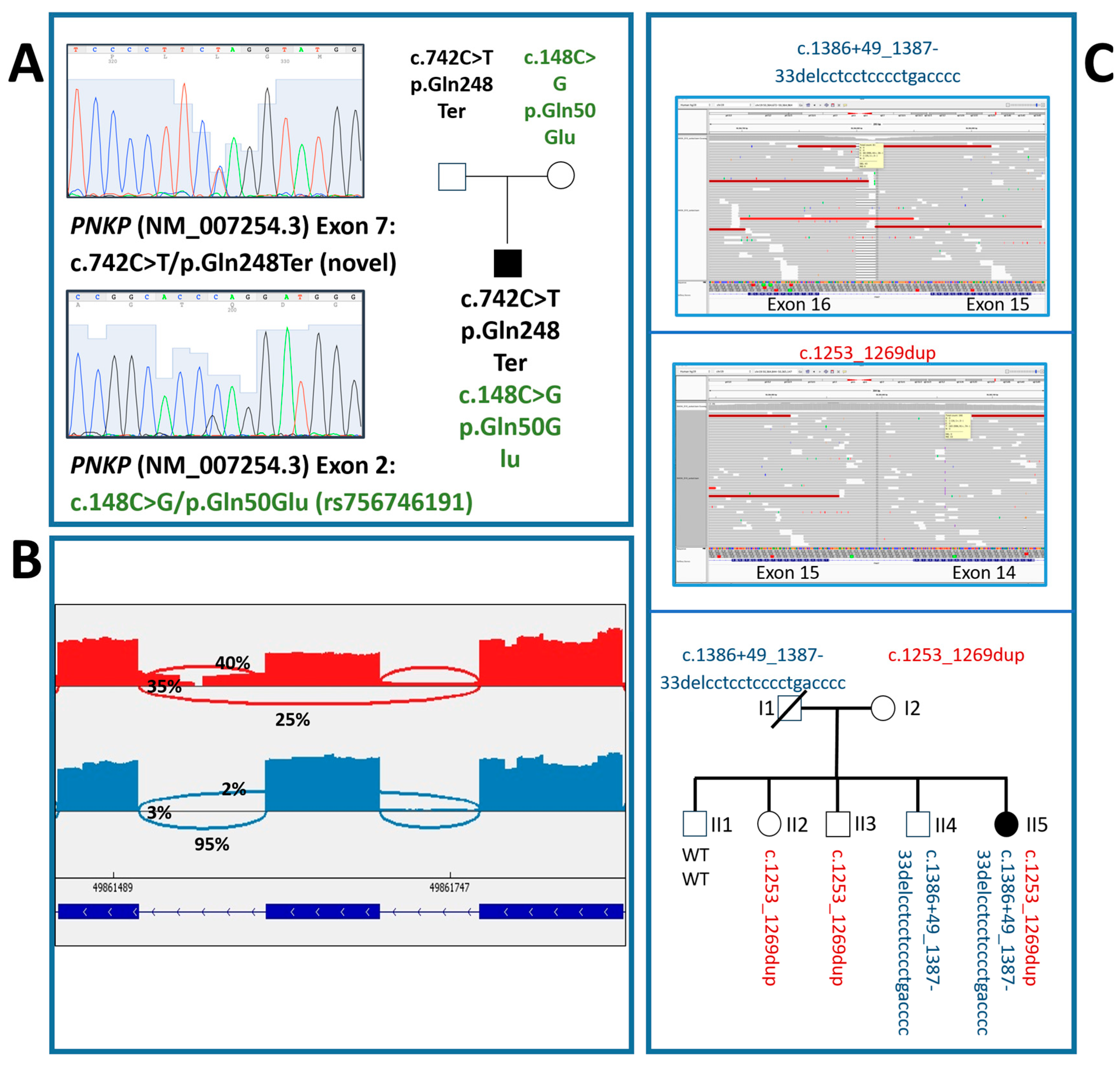
3. Results
3.1. Case Descriptions
3.1.1. Case #1
3.1.2. Case #2
3.2. Literature Review
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jilani, A.; Ramotar, D.; Slack, C.; Ong, C.; Yang, X.M.; Scherer, S.W.; Lasko, D.D. Molecular Cloning of the Human Gene, PNKP, Encoding a Polynucleotide Kinase 3’-Phosphatase and Evidence for Its Role in Repair of DNA Strand Breaks Caused by Oxidative Damage. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 24176–24186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Penney, J.; Tsai, L.-H. Chromatin Regulation of DNA Damage Repair and Genome Integrity in the Central Nervous System. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 3376–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Gilmore, E.C.; Marshall, C.A.; Haddadin, M.; Reynolds, J.J.; Eyaid, W.; Bodell, A.; Barry, B.; Gleason, D.; Allen, K.; et al. Mutations in PNKP Cause Microcephaly, Seizures and Defects in DNA Repair. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, M.; Magri, S.; Nanetti, L.; Sarto, E.; Di Bella, D.; Salsano, E.; Pantaleoni, C.; Mariotti, C.; Taroni, F. From Congenital Microcephaly to Adult Onset Cerebellar Ataxia: Distinct and Overlapping Phenotypes in Patients with PNKP Gene Mutations. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2019, 179, 2277–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, J.L.; Rocha, C.R.R.; Macedo-Souza, L.I.; De Mario, V.; Marques, W.; Barsottini, O.G.P.; Bulle Oliveira, A.S.; Menck, C.F.M.; Kok, F. Mutation in PNKP Presenting Initially as Axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. Neurol. Genet. 2015, 1, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputi, C.; Tolve, M.; Galosi, S.; Inghilleri, M.; Carducci, C.; Angeloni, A.; Leuzzi, V. PNKP Deficiency Mimicking a Benign Hereditary Chorea: The Misleading Presentation of a Neurodegenerative Disorder. Park. Relat. Disord. 2019, 64, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellotti, B.; Ragona, F.; Freri, E.; Messina, G.; Magri, S.; Previtali, R.; Solazzi, R.; Franceschetti, S.; Taroni, F.; Canafoglia, L.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing in Pediatric-Onset Epilepsies: Analysis with Target Panels and Personalized Therapeutic Approach. Epilepsia Open 2024, 9, 1922–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.; Capovilla, G.; Connolly, M.B.; French, J.; Guilhoto, L.; Hirsch, E.; Jain, S.; Mathern, G.W.; Moshé, S.L.; et al. ILAE Classification of the Epilepsies: Position Paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirrell, E.C.; Nabbout, R.; Scheffer, I.E.; Alsaadi, T.; Bogacz, A.; French, J.A.; Hirsch, E.; Jain, S.; Kaneko, S.; Riney, K.; et al. Methodology for Classification and Definition of Epilepsy Syndromes with List of Syndromes: Report of the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1333–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campostrini, G.; DiFrancesco, J.C.; Castellotti, B.; Milanesi, R.; Gnecchi-Ruscone, T.; Bonzanni, M.; Bucchi, A.; Baruscotti, M.; Ferrarese, C.; Franceschetti, S.; et al. A Loss-of-Function HCN4 Mutation Associated With Familial Benign Myoclonic Epilepsy in Infancy Causes Increased Neuronal Excitability. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previtali, S.C.; Zhao, E.; Lazarevic, D.; Pipitone, G.B.; Fabrizi, G.M.; Manganelli, F.; Mazzeo, A.; Pareyson, D.; Schenone, A.; Taroni, F.; et al. Expanding the Spectrum of Genes Responsible for Hereditary Motor Neuropathies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, M.; Takano, K.; Osaka, H.; Aida, N.; Tsurusaki, Y.; Miyake, N.; Saitsu, H.; Matsumoto, N. Causative Novel PNKP Mutations and Concomitant PCDH15 Mutations in a Patient with Microcephaly with Early-Onset Seizures and Developmental Delay Syndrome and Hearing Loss. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 59, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, K.M.; da Silva, C.; Alexander, J.J.; Hegde, M.; Escayg, A. Diagnostic Yield From 339 Epilepsy Patients Screened on a Clinical Gene Panel. Pediatr. Neurol. 2017, 77, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindy, A.S.; Stosser, M.B.; Butler, E.; Downtain-Pickersgill, C.; Shanmugham, A.; Retterer, K.; Brandt, T.; Richard, G.; McKnight, D.A. Diagnostic Outcomes for Genetic Testing of 70 Genes in 8565 Patients with Epilepsy and Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi-Ikeda, M.; Morisada, N.; Inagaki, H.; Ouchi, Y.; Takami, Y.; Tachikawa, M.; Satake, W.; Kobayashi, K.; Tsuneishi, S.; Takada, S.; et al. Two Patients with PNKP Mutations Presenting with Microcephaly, Seizure, and Oculomotor Apraxia. Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 931–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entezam, M.; Razipour, M.; Talebi, S.; Beiraghi Toosi, M.; Keramatipour, M. Multi Affected Pedigree with Congenital Microcephaly: WES Revealed PNKP Gene Mutation. Brain Dev. 2019, 41, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalasova, I.; Hanzlikova, H.; Gupta, N.; Li, Y.; Altmüller, J.; Reynolds, J.J.; Stewart, G.S.; Wollnik, B.; Yigit, G.; Caldecott, K.W. Novel PNKP Mutations Causing Defective DNA Strand Break Repair and PARP1 Hyperactivity in MCSZ. Neurol. Genet. 2019, 5, e320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.-C.C.; Yu, H.-C.; Martin, R.; Cirulli, E.T.; Schenker-Ahmed, N.M.; Hicks, M.; Cohen, I.V.; Jönsson, T.J.; Heister, R.; Napier, L.; et al. Precision Medicine Integrating Whole-Genome Sequencing, Comprehensive Metabolomics, and Advanced Imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3053–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcilla Vázquez, C.; Carrascosa Romero, M.D.C.; Martínez Gutiérrez, A.; Baquero Cano, M.; Alfaro Ponce, B.; Dabad Moreno, M.J. A Novel c.968C > T Homozygous Mutation in the Polynucleotide Kinase 3′ - Phosphatase Gene Related to the Syndrome of Microcephaly, Seizures, and Developmental Delay. J. Pediatr. Genet. 2021, 10, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitarafan, F.; Khodaeian, M.; Almadani, N.; Kalhor, A.; Sardehaei, E.A.; Garshasbi, M. Compound Heterozygous Mutations in PNKP Gene in an Iranian Child with Microcephaly, Seizures, and Developmental Delay. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2021, 40, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Murray, C.; Cole, B.L.; Glover, J.N.M.; Chan, G.K.; Deschenes, J.; Mani, R.S.; Subedi, S.; Nerva, J.D.; Wang, A.C.; et al. Mutations of the DNA Repair Gene PNKP in a Patient with Microcephaly, Seizures, and Developmental Delay (MCSZ) Presenting with a High-Grade Brain Tumor. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.-L.; Jiang, C.-Y.; Sun, P.-P.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, N.; Luan, S.-X. Prenatal Phenotype of PNKP-Related Microcephaly, Seizures, and Developmental Delay: A Case Report and Literature Review. Medicine 2025, 104, e41300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, U.; Baschiera, E.; Desbats, M.A.; Zuffardi, O.; Salviati, L.; Cassina, M. Characterization of Two Novel PNKP Splice-Site Variants in a Proband With Microcephaly, Intellectual Disability, and Multiple Malformations. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Psychiatr. Genet. 2025, 198, e33013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrelfs, M.R.; Takada, S.; Kamsteeg, E.-J.; Pegge, S.; Mancini, G.; Engelen, M.; van de Warrenburg, B.; Rennings, A.; van Gaalen, J.; Peters, I.; et al. The Phenotypic Spectrum of PNKP-Associated Disease and the Absence of Immunodeficiency and Cancer Predisposition in a Dutch Cohort. Pediatr. Neurol. 2020, 113, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez-Guzmán, L.; Leal, A. DNA Repair Deficiency in Neuropathogenesis: When All Roads Lead to Mitochondria. Transl. Neurodegener. 2019, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Case # | Genetic Characteristics | Clinical-Instrumental Characteristics | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleotide Variant (Inheritance) | Protein Change | Variant Type | Transmission Pattern | gnomAD Frequency | In Silico Prediction and ACMG Classification | Gender | Neurological Features | Syndromic Aspects | Microcephaly | Developmental Delay | Age at Seizure Onset | Type of Seizures | EEG Background | EEG Epileptic Activity | Brain MRI | Ineffective ASMs | Actual ASMs | |
| 1 | c.148C>G (mother); c.742C>T (father) | p.Gln50Glu; p.Gln248Ter | missense; nonsense | compound heterozygosity | ƒ = 0.00000796 (rs756746191) ƒ = Not found (novel) | Pathogenic (PM3; PM2; PP5; PP2); Pathogenic (PM3; PM2; PVS1) | Male | growth deficiency, pyramidal signs, clumsiness, apraxic gait | large ear pads, arched eyebrows, flat nasal saddle, short philtrum, thin upper lip, microretrognathy, large incisors | yes | severe | 6 years | focal | poor organization | multifocal | microcephaly, simplification of cortical convexities, thin corpus callosum, dysmorphic hippocampi, enlarged and dysmorphic lateral ventricles | VPA, LEV | CBZ, CLB, LCM |
| 2 | c.1253_1269dup (mother); c.1386+49_1387-33del (father) | p.Thr424GlyfsTer49; exon 15 skipping | nonsense; nonsense | compound heterozygosity | ƒ = 0.000169 (rs587784365) ƒ = 0.0000699 (rs752902474) | Pathogenic (PM3; PM2; PVS1; PP5; PP3); Pathogenic (PM3; PM2; PP5) | Female | reduced weight growth, delayed psycho-motor development | receding forehead, hypertelorism, epicanthus, enlarged nasal root, wide mouth, micrognathia | yes | severe | 13 months | focal | diffuse slowing | right occipital focal activity | microcephaly, simplified cortical gyration, a previous left occipital vascular lesion, thin corpus callosum, small cerebellar vermis, moderate enlargement of lateral ventricles, diffuse thickening of the bilateral skull vault | PB, CBZ, GVG | VPA, CLB |
| Nucleotide Variant | Protein Change | Genetic Effect | Transmission | Clinical Features | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM_007254.4:c.1386+49_1387-33delCCTCCTCCCCTGACCCC | Intron deletion | heterozygous compound | microcephaly, seizures, developmental delay | [3] | |
| NM_007254.4:c.1253_1269dupGGGTCGCCATCGACAAC | NP_009185.2:p.Thr424GlyfsTer49 | Frameshift | |||
| NM_007254.4:c.976G>A | NP_009185.2:p.Glu326Lys | Missense | homozygous | microcephaly, seizures, developmental delay | [3] |
| NM_007254.4:c.1250_1266dup | NP_009185.2:Thr424GlyfsTer48 | Frameshift | homozygous | ||
| NM_007254.4:c.1250_1266dup | NP_009185.2:Thr424GlyfsTer48 | Frameshift | heterozygous compound | ||
| NM_007254.4:c.526C>T | NP_009185.2:p.Leu176Phe | Missense | |||
| NM_007254.4:c.874G>A | NP_009185.2:p.Gly292Arg | Missense | heterozygous compound | microcephaly, early-onset seizures, developmental delay, hearing loss | [13] |
| NM_007254.4:c.163G>T | NP_009185.2:p.Ala55Ser | Missense | |||
| NM_007254.4:c.1324G>A | NP_009185.2:p.Gly442Ser | Missense | homozygous | epilepsy | [14] |
| NM_007254.4:c.1293_1298+2dupCGCCAGGT | Splicing | heterozygous | epilepsy and/or neurodevelopmental disorders | [15] | |
| NM_007254.4:c.1029+2T>C | Splicing | heterozygous compound | |||
| NM_007254.4:c.968C>T | NP_009185.2:p.Thr323Met | Missense | |||
| NM_007254.4:c.1028C>T | NP_009185.2:p.Pro343Leu | Missense | heterozygous compound | microcephaly, seizures, oculomotor apraxia | [16] |
| NM_007254.4:c.1313_1318delGCCCGA | NP_009185.2:p.Ala438_Arg439del | In-frame deletion | |||
| NM_007254.4:c.1028C>T | NP_009185.2:p.Pro343Leu | Missense | homozygous | ||
| NM_007254.4:c.1274_1284dupACCCAGACGCC | NP_009185.2:p.Ala429ThrfsTer42 | Frameshift | homozygous | Microcephaly, developmental delay | [4] |
| NM_007254.4:c.1133A>C | NP_009185.2:p.Lys378Thr | Missense | homozygous | microcephaly, congenital | [17] |
| NM_007254.4:c.63dupC | NP_009185.2:p.Ile22HisfsTer37 | Frameshift | heterozygous compound | microcephaly, early-onset seizures, developmental delay, hearing loss | [18] |
| NM_007254.4:c.1295_1298+6delCCAGGTAGCG | Splicing | ||||
| NM_007254.4:c.876delA | NP_009185.2:p.Arg293AlafsTer69 | Frameshift | homozygous | early infantile epileptic encephalopathy 10 | [19] |
| NM_007254.3:c.968C>T | NP_009185.2:p.Thr323Met | Missense | homozygous | syndrome of microcephaly, seizures, developmental delay | [20] |
| NM_007254.4: c.1298+33_1299-24del | Intron deletion | heterozygous compound | microcephaly, seizures, developmental delay | [21] | |
| NM_007254.4: c.1253_1269dup | NP_009185.2: p.Thr424Glyfs*4 | Frameshift | |||
| NM_007254.3:c.968C>T | NP_009185.2:p.Thr323Met | Missense | heterozygous compound | microcephaly, seizures, developmental delay, high-grade brain tumor | [22] |
| NM_007254.3:c.302C>T | NP_009185.2:p.Pro101Leu | Missense | |||
| NM_007254.4: c.976G>A | NP_009185.2:p.Glu326Lys | Missense | heterozygous compound | microcephaly, seizures, developmental delay | [23] |
| NM_007254.4: c.1188+1G>A | Splicing | ||||
| NM_007254.4: c.1448+1G>A | Splicing | heterozygous compound | microcephaly, intellectual disability, multiple malformations | [24] | |
| NM_007254.4: c.199-8_199-5del |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ragona, F.; Messina, G.; Magri, S.; Doniselli, F.M.; Freri, E.; Canafoglia, L.; Solazzi, R.; Gellera, C.; Granata, T.; DiFrancesco, J.C.; et al. Compound Heterozygous PNKP Variants Causing Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy with Severe Microcephaly: Natural History of Two New Cases and Literature Review. NeuroSci 2025, 6, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040110
Ragona F, Messina G, Magri S, Doniselli FM, Freri E, Canafoglia L, Solazzi R, Gellera C, Granata T, DiFrancesco JC, et al. Compound Heterozygous PNKP Variants Causing Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy with Severe Microcephaly: Natural History of Two New Cases and Literature Review. NeuroSci. 2025; 6(4):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040110
Chicago/Turabian StyleRagona, Francesca, Giuliana Messina, Stefania Magri, Fabio Martino Doniselli, Elena Freri, Laura Canafoglia, Roberta Solazzi, Cinzia Gellera, Tiziana Granata, Jacopo C. DiFrancesco, and et al. 2025. "Compound Heterozygous PNKP Variants Causing Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy with Severe Microcephaly: Natural History of Two New Cases and Literature Review" NeuroSci 6, no. 4: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040110
APA StyleRagona, F., Messina, G., Magri, S., Doniselli, F. M., Freri, E., Canafoglia, L., Solazzi, R., Gellera, C., Granata, T., DiFrancesco, J. C., & Castellotti, B. (2025). Compound Heterozygous PNKP Variants Causing Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy with Severe Microcephaly: Natural History of Two New Cases and Literature Review. NeuroSci, 6(4), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040110






