Mitigating Head Position Bias in Perivascular Fluid Imaging: LD-ALPS, a Novel Method for DTI-ALPS Calculation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Classification
- ‘Original-ALPS’—this group includes research that sufficiently adheres to the original DTI-ALPS specification, which is characterized by an anatomically aligned slice prescription, tensor calculation, and index calculation performed in native space.
- ‘Unrotated-ALPS’—this group includes DTI-ALPS analyses in which the authors did not specify that the slice specification was aligned with the subjects’ anatomical orientation, and make no mention of vector registration or similar techniques.
- ‘VECREG-ALPS’—this group includes DTI-ALPS analyses in which tensor metrics are rotated and registered to a template space with canonical orientation for interpretation.
- ‘Not-Applicable’—this group includes non-primary research or other research not amenable to the classification scheme outlined above.
2.3. Participants
2.4. Diffusion Processing
- Tensor model was fit to the eddy-corrected data using FSL’s dtifit.
- These data were then nonlinearly warped to FSL’s JHU-ICBM-FA-1mm template using fnirt.
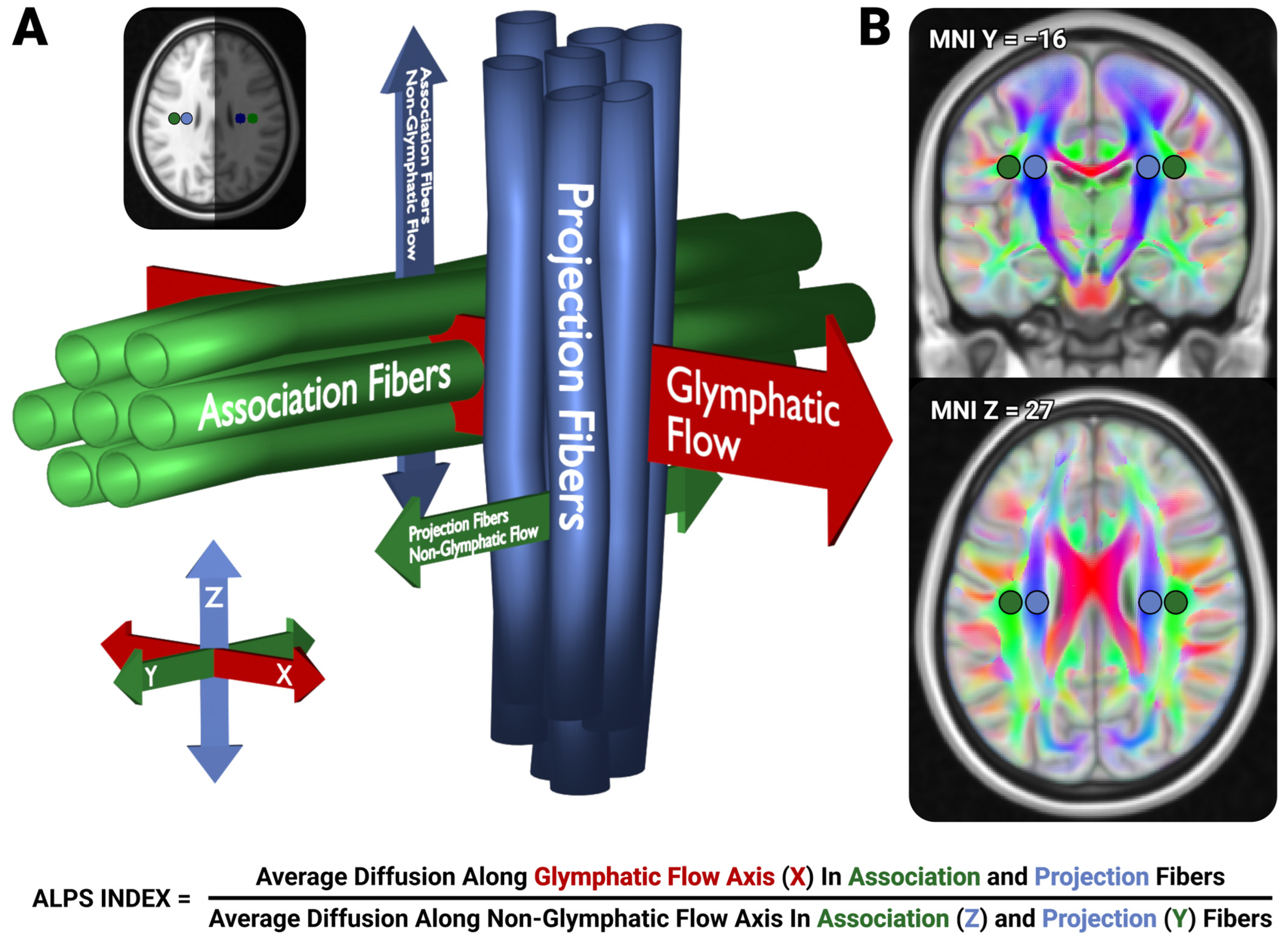
2.5. LD-ALPS
- We inverted the warps computed in preprocessing (4) and moved the predefined ALPS ROIs into native space
- Within each of the native-space ROIs, we clustered the primary diffusion vector (i.e., the V1 vectors) using the DBSCAN algorithm [32], with ε = 0.5, min_samples = 5–20. Outlier vectors with great-circle distances exceeding z = 3.5 from the primary cluster center are excluded to ensure primary diffusion direction consistency within each ROI.
- For each ROI, we select the primary diffusion direction of the voxel passed from (2) with the smallest distance to the cluster center to represent that ROI’s primary diffusion direction.
- For each passed voxel in each ROI, we utilize that voxel’s primary diffusion direction, and the median diffusion direction computed from (3) from the neighboring ROI (i.e., the median primary diffusion direction from the Right Association ROI would be used for voxels in the Right Projection ROI), to identify the orthogonal vector to these two vectors, representing the axis of glymphatic flow.
- We compute the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of each of these directions for each passed voxel, using a Clough-Tocher 2D interpolator from a half-sphere orthographic projection of the eddy-corrected vector’s ADCs. To handle half-shell diffusion acquisitions, we presume that the diffusion values are equivalent for the polarity-flipped vectors to allow for continuous interpolation the entire sphere.
- We compute the mean ADC from each ROI for each of the component ALPS values.
- These values are used to compute the LD-ALPS index using the typical ALPS formula (Figure 1).
2.6. Technique Comparison
3. Results
3.1. Literature Review
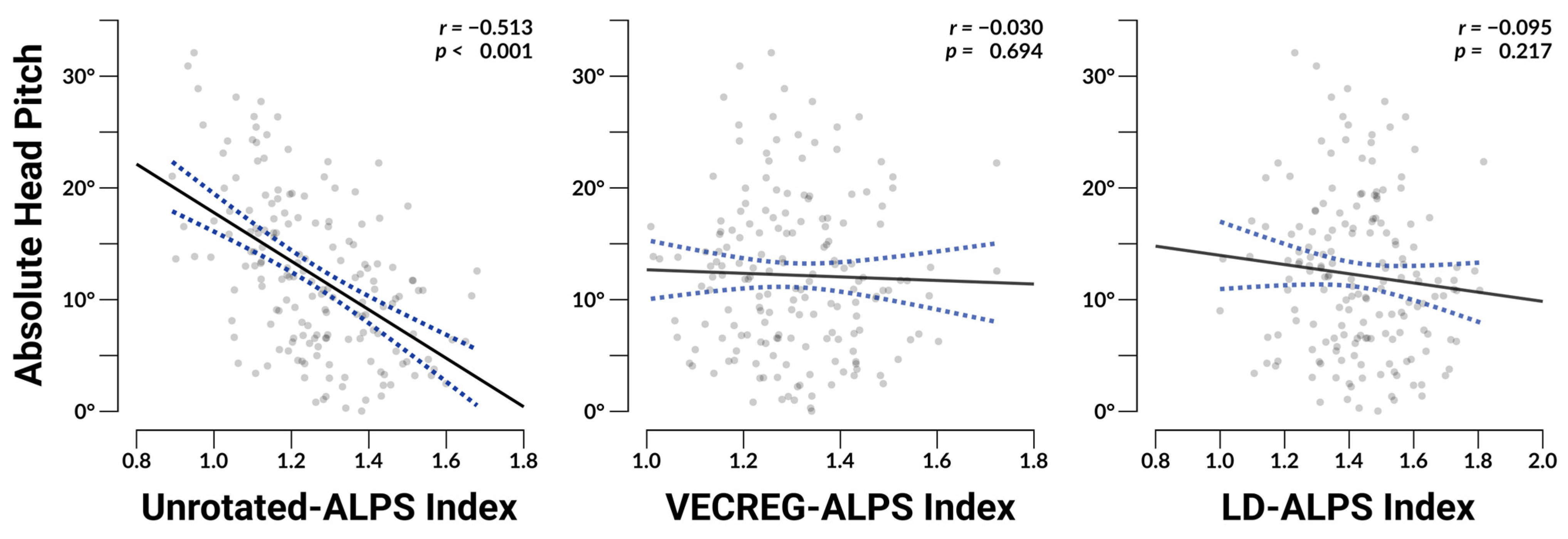
3.2. Head Orientation
3.3. ALPS Indices
3.4. ALPS Associations with Head Orientation
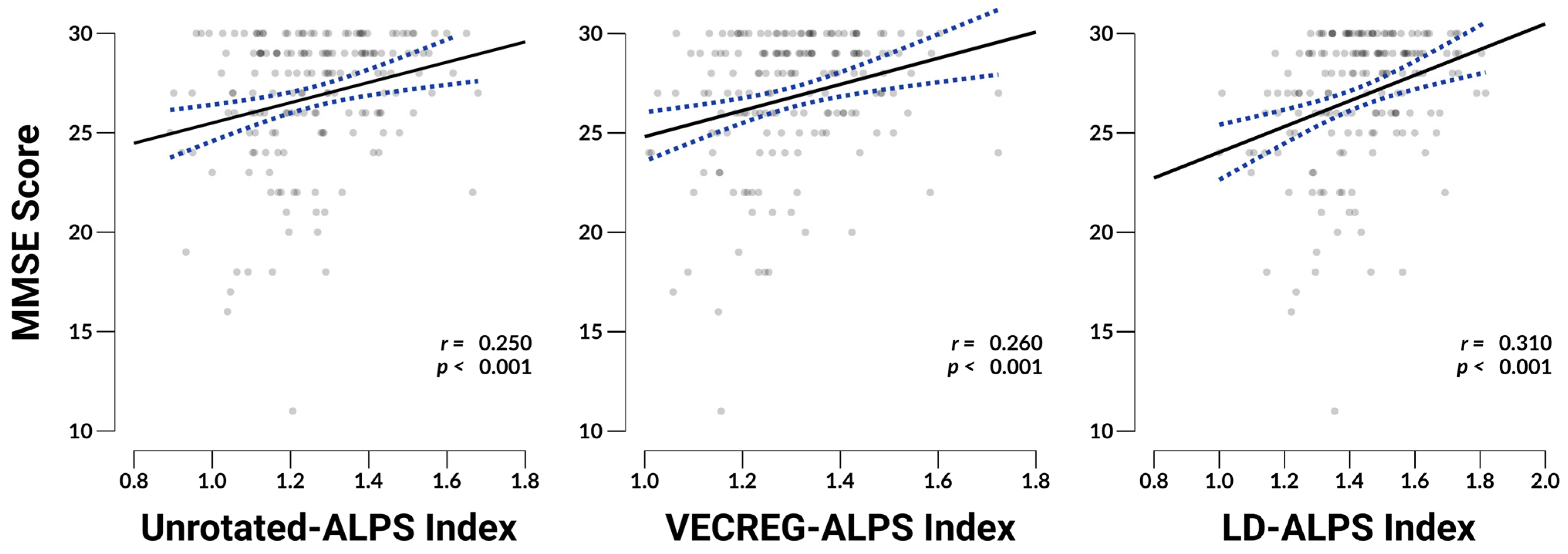
3.5. ALPS Associations with MMSE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADNI | Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative |
| AC | Anterior Commissure |
| ADC | Apparent Diffusion Coefficient |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| DBSCAN | Density Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise |
| DTI | Diffusion tensor imaging |
| DTI-ALPS | Diffusion tensor imaging analysis along the perivascular space |
| FA | Fractional Anisotropy |
| GBCA | Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent |
| LD-ALPS | Local diffusion analysis along the perivascular space |
| MD | Mean Diffusivity |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
| MNI | Montreal Neurological Institute |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| PC | Posterior Commissure |
References
- Jessen, N.A.; Munk, A.S.F.; Lundgaard, I.; Nedergaard, M. The Glymphatic System: A Beginner’s Guide. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 2583–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busche, M.A.; Hyman, B.T. Synergy between Amyloid-β and Tau in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspelund, A.; Antila, S.; Proulx, S.T.; Karlsen, T.V.; Karaman, S.; Detmar, M.; Wiig, H.; Alitalo, K. A Dural Lymphatic Vascular System That Drains Brain Interstitial Fluid and Macromolecules. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louveau, A.; Smirnov, I.; Keyes, T.J.; Eccles, J.D.; Rouhani, S.J.; Peske, J.D.; Derecki, N.C.; Castle, D.; Mandell, J.W.; Lee, K.S.; et al. Structural and Functional Features of Central Nervous System Lymphatic Vessels. Nature 2015, 523, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliff, J.J.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.; Plogg, B.A.; Peng, W.; Gundersen, G.A.; Benveniste, H.; Vates, G.E.; Deane, R.; Goldman, S.A.; et al. A Paravascular Pathway Facilitates CSF Flow Through the Brain Parenchyma and the Clearance of Interstitial Solutes, Including Amyloid β. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 147ra111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedergaard, M.; Goldman, S.A. Glymphatic Failure as a Final Common Pathway to Dementia. Science 2020, 370, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plog, B.A.; Nedergaard, M. The Glymphatic System in Central Nervous System Health and Disease: Past, Present, and Future. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2018, 13, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasoff-Conway, J.M.; Carare, R.O.; Osorio, R.S.; Glodzik, L.; Butler, T.; Fieremans, E.; Axel, L.; Rusinek, H.; Nicholson, C.; Zlokovic, B.V.; et al. Clearance Systems in the Brain—Implications for Alzheimer Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, B.T.; Iliff, J.J.; Xia, M.; Wang, M.; Wei, H.S.; Zeppenfeld, D.; Xie, L.; Kang, H.; Xu, Q.; Liew, J.A.; et al. Impairment of Paravascular Clearance Pathways in the Aging Brain. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliff, J.J.; Lee, H.; Yu, M.; Feng, T.; Logan, J.; Nedergaard, M.; Benveniste, H. Brain-Wide Pathway for Waste Clearance Captured by Contrast-Enhanced MRI. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre, H.; Tithof, J.; Du, T.; Song, W.; Peng, W.; Sweeney, A.M.; Olveda, G.; Thomas, J.H.; Nedergaard, M.; Kelley, D.H. Flow of Cerebrospinal Fluid Is Driven by Arterial Pulsations and Is Reduced in Hypertension. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Kang, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, M.J.; Liao, Y.; Thiyagarajan, M.; O’Donnell, J.; Christensen, D.J.; Nicholson, C.; Iliff, J.J.; et al. Sleep Drives Metabolite Clearance from the Adult Brain. Science 2013, 342, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlstrom, L.P.; Eltanahy, A.; Perry, A.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Elder, B.D.; Morris, J.M.; Meyer, F.B.; Graffeo, C.S.; Lundgaard, I.; Burns, T.C. A Clinical Primer for the Glymphatic System. Brain 2022, 145, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylkilahti, T.M.; Berends, E.; Ramos, M.; Shanbhag, N.C.; Töger, J.; Markenroth Bloch, K.; Lundgaard, I. Achieving Brain Clearance and Preventing Neurodegenerative Diseases—A Glymphatic Perspective. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2021, 41, 2137–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, S.B.; Rane, S.; Hanson, M.R.; Albayram, M.; Iliff, J.J.; Kernagis, D.; Rosenberg, J.T.; Seidler, R.D. Quantification Approaches for Magnetic Resonance Imaging Following Intravenous Gadolinium Injection: A Window into Brain-wide Glymphatic Function. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2023, 57, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringstad, G.; Vatnehol, S.A.S.; Eide, P.K. Glymphatic MRI in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Brain 2017, 140, 2691–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia Bara, M.T.; Gallardo-Higueras, A.; Moreno, E.M.; Laffond, E.; Muñoz Bellido, F.J.; Martin, C.; Sobrino, M.; Macias, E.; Arriba-Méndez, S.; Castillo, R.; et al. Hypersensitivity to Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 813927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Molen, A.J.; Quattrocchi, C.C.; Mallio, C.A.; Dekkers, I.A.; European Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Biology Gadolinium Research, Educational Committee (ESMRMB-GREC). Ten Years of Gadolinium Retention and Deposition: ESMRMB-GREC Looks Backward and Forward. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 34, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taoka, T.; Naganawa, S. Neurofluid Dynamics and the Glymphatic System: A Neuroimaging Perspective. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 21, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringstad, G. Glymphatic Imaging: A Critical Look at the DTI-ALPS Index. Neuroradiology 2024, 66, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taoka, T.; Ito, R.; Nakamichi, R.; Nakane, T.; Kawai, H.; Naganawa, S. Diffusion Tensor Image Analysis ALong the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS): Revisiting the Meaning and Significance of the Method. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2024, 23, 268–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, K.G.; Newton, A.; Tax, C.; Nilsson, M.; Chamberland, M.; Anderson, A.; Landman, B.; Descoteaux, M. White Matter Geometry Confounds Diffusion Tensor Imaging Along Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) Measures. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2025, 46, e70282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Barisano, G.; Shao, X.; Jann, K.; Ringman, J.M.; Lu, H.; Arfanakis, K.; Caprihan, A.; DeCarli, C.; Gold, B.T.; et al. Cross-Vendor Test-Retest Validation of Diffusion Tensor Image Analysis along the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) for Evaluating Glymphatic System Function. Aging Dis. 2023, 15, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taoka, T.; Ito, R.; Nakamichi, R.; Kamagata, K.; Sakai, M.; Kawai, H.; Nakane, T.; Abe, T.; Ichikawa, K.; Kikuta, J.; et al. Reproducibility of Diffusion Tensor Image Analysis along the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) for Evaluating Interstitial Fluid Diffusivity and Glymphatic Function: CHanges in Alps Index on Multiple conditiON acquIsition eXperiment (CHAMONIX) Study. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2022, 40, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taoka, T.; Masutani, Y.; Kawai, H.; Nakane, T.; Matsuoka, K.; Yasuno, F.; Kishimoto, T.; Naganawa, S. Evaluation of Glymphatic System Activity with the Diffusion MR Technique: Diffusion Tensor Image Analysis along the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) in Alzheimer’s Disease Cases. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2017, 35, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Kamagata, K.; Andica, C.; Uchida, W.; Takabayashi, K.; Yoshida, S.; Nakaya, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Kamiyo, S.; Sato, K.; et al. Reproducibility of Automated Calculation Technique for Diffusion Tensor Image Analysis along the Perivascular Space. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2023, 41, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatekawa, H.; Matsushita, S.; Ueda, D.; Takita, H.; Horiuchi, D.; Atsukawa, N.; Morishita, Y.; Tsukamoto, T.; Shimono, T.; Miki, Y. Improved Reproducibility of Diffusion Tensor Image Analysis along the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) Index: An Analysis of Reorientation Technique of the OASIS-3 Dataset. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2023, 41, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. Mini-Mental State. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, J.-D.; Smith, R.; Raffelt, D.; Tabbara, R.; Dhollander, T.; Pietsch, M.; Christiaens, D.; Jeurissen, B.; Yeh, C.-H.; Connelly, A. MRtrix3: A Fast, Flexible and Open Software Framework for Medical Image Processing and Visualisation. NeuroImage 2019, 202, 116137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, J.L.R.; Sotiropoulos, S.N. An Integrated Approach to Correction for Off-Resonance Effects and Subject Movement in Diffusion MR Imaging. NeuroImage 2016, 125, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.J.; Woolrich, M.W.; Smith, S.M. FSL. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.-P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A Density-Based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise; AAAI: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bouffard, M.A.; Avanaki, M.A.; Ford, J.N.; Jaafar, N.; Brook, A.; Abbasi, B.; Torun, N.; Alsop, D.; Comeau, D.S.; Chang, Y.-M. MRI Indices of Glymphatic Function Correlate With Disease Duration in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. J. Neuro-Ophthalmol. Off. J. N. Am. Neuro-Ophthalmol. Soc. 2024, 45, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Su, S.; Dai, Y.; Zou, M.; Lin, L.; Qian, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, M.; et al. Assessment of the Glymphatic Function in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-L.; Chen, P.-C.; Lu, C.-H.; Tsai, N.-W.; Yu, C.-C.; Chou, K.-H.; Lai, Y.-R.; Taoka, T.; Lin, W.-C. Associations among Cognitive Functions, Plasma DNA, and Diffusion Tensor Image along the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 4034509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Chang, F.; Huang, Z.; Peng, D.; Zhou, X.; Liu, W. Evaluation of Glymphatic System Activity by Diffusion Tensor Image Analysis along the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) in Dementia Patients. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20220315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-P.; Su, S.; Hou, W.; Huang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zou, M.; Qian, L.; Cui, W.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Y.; et al. Glymphatic System Dysfunction in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia without Clinically Diagnosed Central Nervous System Infiltration: A Novel DTI-ALPS Method. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 3726–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, S.; Li, C.; Wang, R.; Chen, M.; Chen, H.; Su, W. Diffusion Tensor Imaging Along the Perivascular Space Index in Different Stages of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 773951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Yu, H.; Li, X.; Bu, S.; Zhao, M.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, G. Glymphatic Function from Diffusion-Tensor MRI to Predict Conversion from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Dementia in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 5598–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Ruan, Z.; Gao, L.; Lv, D.; Sun, D.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J. Structural Network Efficiency Mediates the Association between Glymphatic Function and Cognition in Mild VCI: A DTI-ALPS Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 974114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taoka, T.; Ito, R.; Nakamichi, R.; Nakane, T.; Kawamura, M.; Ishihara, S.; Ichikawa, K.; Kawai, H.; Naganawa, S. Evaluation of Alterations in Interstitial Fluid Dynamics in Cases of Whole-Brain Radiation Using the Diffusion-Weighted Image Analysis along the Perivascular Space Method. NMR Biomed. 2024, 37, e5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taoka, T.; Ito, R.; Nakamichi, R.; Nakane, T.; Sakai, M.; Ichikawa, K.; Kawai, H.; Naganawa, S. Diffusion-Weighted Image Analysis along the Perivascular Space (DWI-ALPS) for Evaluating Interstitial Fluid Status: Age Dependence in Normal Subjects. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2022, 40, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdolizadeh, A.; Torres-Carmona, E.; Kambari, Y.; Amaev, A.; Song, J.; Ueno, F.; Koizumi, T.; Nakajima, S.; Agarwal, S.M.; De Luca, V.; et al. Evaluation of the Glymphatic System in Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorder Using Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Measurement of Brain Macromolecule and Diffusion Tensor Image Analysis Along the Perivascular Space Index. Schizophr. Bull. 2024, 50, 1396–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, W.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, K.; He, Y.; Luo, Z.; Ran, W.; Sun, J.; et al. Choroid Plexus Enlargement Exacerbates White Matter Hyperintensity Growth through Glymphatic Impairment. Ann. Neurol. 2023, 94, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, L.; D’Agata, F.; Campisi, C.; Arcaro, M.; Carandini, T.; Örzsik, B.; Dal Maschio, V.P.; Fenoglio, C.; Pietroboni, A.M.; Ghezzi, L.; et al. A “Glympse” into Neurodegeneration: Diffusion MRI and Cerebrospinal Fluid Aquaporin-4 for the Assessment of Glymphatic System in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2024, 45, e26805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siow, T.Y.; Toh, C.H.; Hsu, J.-L.; Liu, G.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Chen, N.-H.; Fu, C.J.; Castillo, M.; Fang, J.-T. Association of Sleep, Neuropsychological Performance, and Gray Matter Volume With Glymphatic Function in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Neurology 2022, 98, e829–e838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, J.; Raghavan, P.; Li, J.; Roys, S.; Njonkou Tchoquessi, R.L.; Chen, H.; Wickwire, E.M.; Parikh, G.Y.; Schwartzbauer, G.T.; Grattan, L.M.; et al. Longitudinal Assessment of Glymphatic Changes Following Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: Insights from Perivascular Space Burden and DTI-ALPS Imaging. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1443496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yao, Y.; Liu, C.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W. Enlarged Choroid Plexus in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis May Lead to Brain Structural Changes through the Glymphatic Impairment. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2024, 85, 105550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccellato, F.R.; D’Anca, M.; Serpente, M.; Arighi, A.; Galimberti, D. The Role of Glymphatic System in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.; Silva, J.; Ferreira, R.; Trigo, D. Glymphatic System, AQP4, and Their Implications in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2021, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagirov, A.F.; Sergeev, T.V.; Shabrov, A.V.; Yurov, A.Y.; Guseva, N.L.; Agapova, E.A. Postural Influence on Intracranial Fluid Dynamics: An Overview. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2023, 42, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burles, F.; Sallis, E.; Kopala-Sibley, D.C.; Iaria, G., on behalf of the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Mitigating Head Position Bias in Perivascular Fluid Imaging: LD-ALPS, a Novel Method for DTI-ALPS Calculation. NeuroSci 2025, 6, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040101
Burles F, Sallis E, Kopala-Sibley DC, Iaria G on behalf of the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Mitigating Head Position Bias in Perivascular Fluid Imaging: LD-ALPS, a Novel Method for DTI-ALPS Calculation. NeuroSci. 2025; 6(4):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040101
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurles, Ford, Emily Sallis, Daniel C. Kopala-Sibley, and Giuseppe Iaria on behalf of the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. 2025. "Mitigating Head Position Bias in Perivascular Fluid Imaging: LD-ALPS, a Novel Method for DTI-ALPS Calculation" NeuroSci 6, no. 4: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040101
APA StyleBurles, F., Sallis, E., Kopala-Sibley, D. C., & Iaria, G., on behalf of the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. (2025). Mitigating Head Position Bias in Perivascular Fluid Imaging: LD-ALPS, a Novel Method for DTI-ALPS Calculation. NeuroSci, 6(4), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6040101




