Intrinsic Functional Connectivity Alterations of the Fusiform Face Area in Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Face Memory Assessments
2.3. MRI Data Acquisition
2.3.1. Anatomical Scan
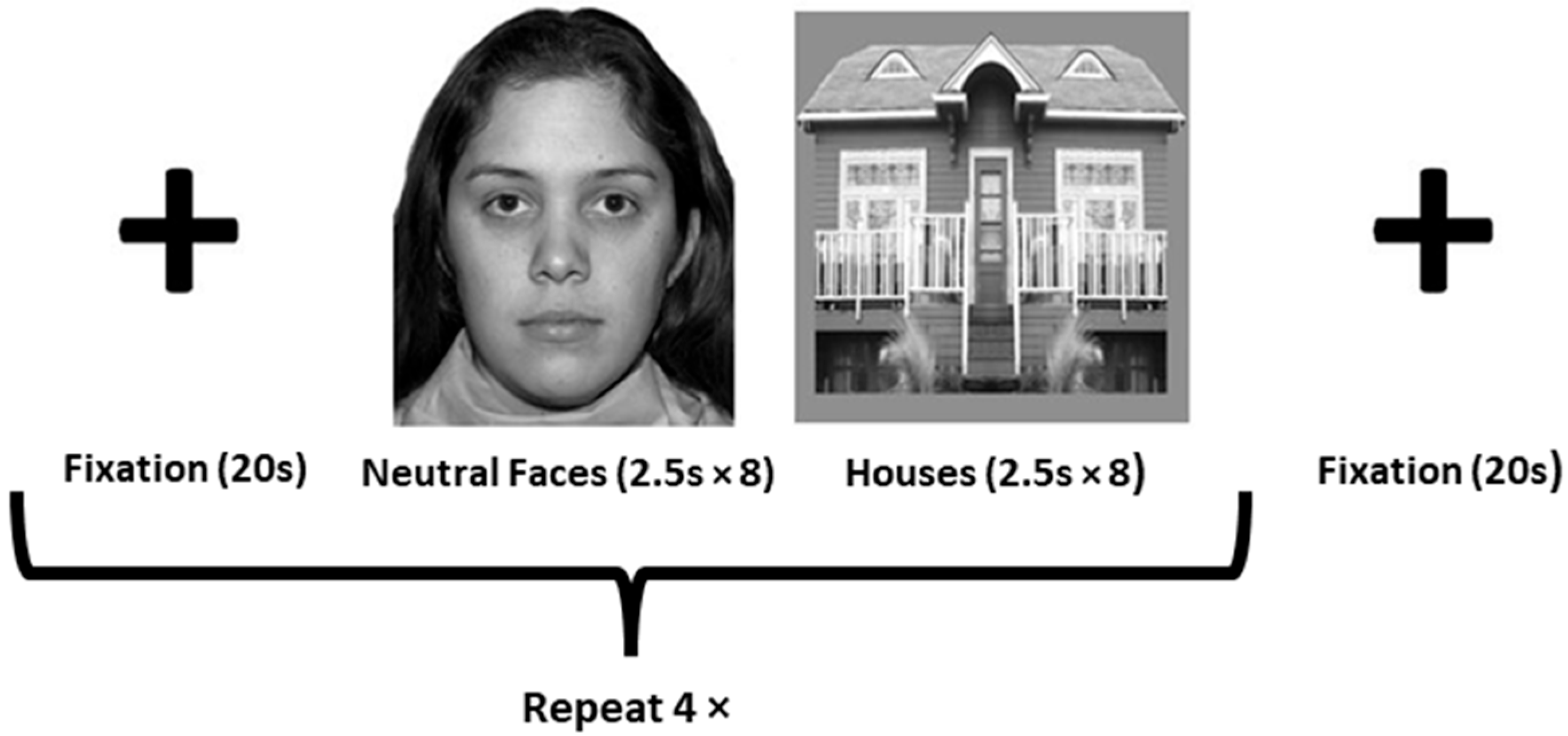
2.3.2. Functional Localizer Scan
2.3.3. Resting State Scans
2.4. Physiological Monitoring
2.5. fMRI Preprocessing
2.6. fMRI Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Face Memory Performance
3.2. fMRI Results
3.2.1. Motion Parameters
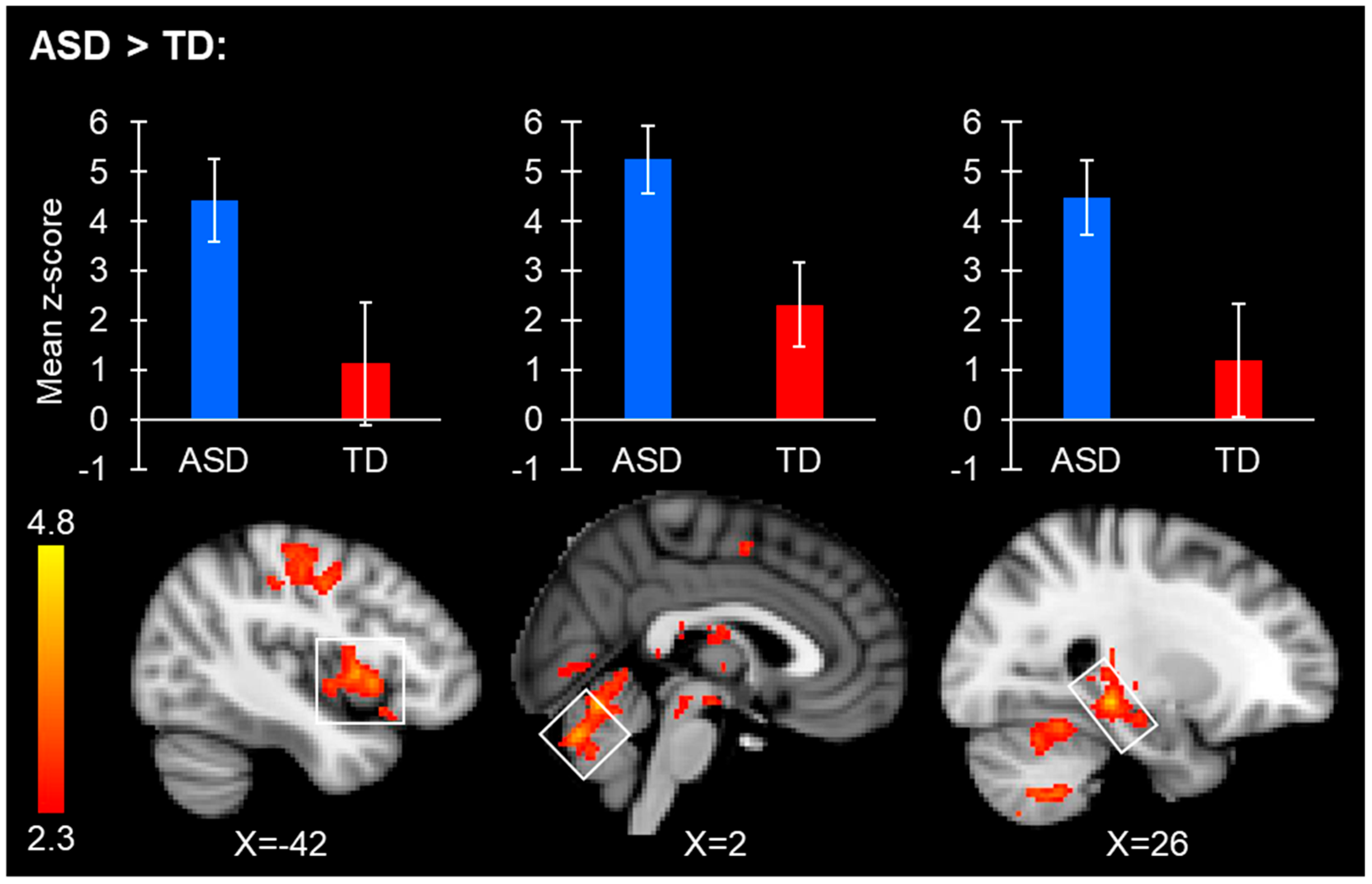
3.2.2. Intrinsic Connectivity Group Difference Analyses
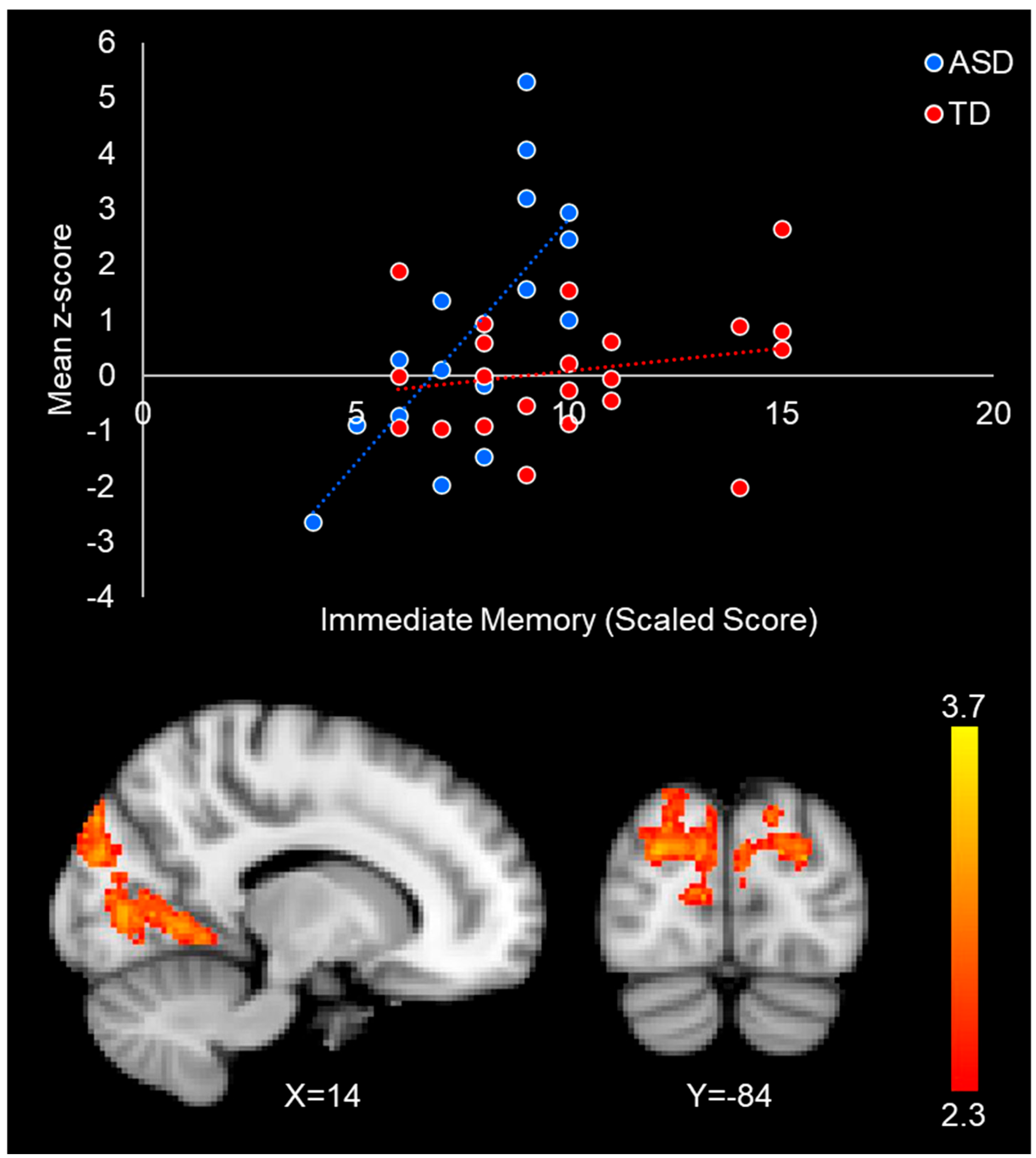
3.2.3. Relationship Between Connectivity and Immediate Face Memory Performance
3.2.4. Group–Performance Interaction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, E.J.; Venema, K.; Earl, R.; Lowy, R.; Barnes, K.; Estes, A.; Dawson, G.; Webb, S.J. Reduced engagement with social stimuli in 6-month-old infants with later autism spectrum disorder: A longitudinal prospective study of infants at high familial risk. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2016, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawarska, K.; Macari, S.; Shic, F. Decreased spontaneous attention to social scenes in 6-month-old infants later diagnosed with autism spectrum disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelt, S.; Koldewyn, K.; Kanwisher, N. Face identity recognition in autism spectrum disorders: A review of behavioral studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 1060–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobson, R.P.; Ouston, J.; Lee, A. What’s in a face? The case of autism. Br. J. Psychol. 1988, 79 Pt 4, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, F.E.; Lincoln, A.J.; Lai, Z.; Ene, M.; Searcy, Y.M.; Bellugi, U. Orientation and affective expression effects on face recognition in Williams syndrome and autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2007, 37, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.W.; Azu, M.A.; Cramer-Benjamin, S.; Franke, C.J.; Herman, N.; Iqbal, R.; Keifer, C.M.; Rosenthal, L.H.; McPartland, J.C. Investigating the Face Inversion Effect in Autism Across Behavioral and Neural Measures of Face Processing: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2023, 80, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klin, A.; Jones, W.; Schultz, R.; Volkmar, F.; Cohen, D. Visual fixation patterns during viewing of naturalistic social situations as predictors of social competence in individuals with autism. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2002, 59, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, K.; Moriuchi, J.M.; Jones, W.; Klin, A. Parsing heterogeneity in autism spectrum disorders: Visual scanning of dynamic social scenes in school-aged children. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2012, 51, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.W.; Naples, A.; Bernier, R.; Chawarska, K.; Dawson, G.; Dziura, J.; Faja, S.; Jeste, S.; Kleinhans, N.; Sugar, C.; et al. Spatiotemporal Eye Movement Dynamics Reveal Altered Face Prioritization in Early Visual Processing Among Autistic Children. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2024, 10, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haxby, J.V.; Hoffman, E.A.; Gobbini, M.I. The distributed human neural system for face perception. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2000, 4, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, R.T.; Gauthier, I.; Klin, A.; Fulbright, R.K.; Anderson, A.W.; Volkmar, F.; Skudlarski, P.; Lacadie, C.; Cohen, D.J.; Gore, J.C. Abnormal ventral temporal cortical activity during face discrimination among individuals with autism and Asperger syndrome. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, K.; Haist, F.; Sedaghat, F.; Courchesne, E. The brain response to personally familiar faces in autism: Findings of fusiform activity and beyond. Brain 2004, 127, 2703–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubl, D.; Bölte, S.; Feineis-Matthews, S.; Lanfermann, H.; Federspiel, A.; Strik, W.; Poustka, F.; Dierks, T. Functional imbalance of visual pathways indicates alternative face processing strategies in autism. Neurology 2003, 61, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, K.M.; Nacewicz, B.M.; Johnstone, T.; Schaefer, H.S.; Gernsbacher, M.A.; Goldsmith, H.H.; Alexander, A.L.; Davidson, R.J. Gaze fixation and the neural circuitry of face processing in autism. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjikhani, N.; Joseph, R.M.; Snyder, J.; Chabris, C.F.; Clark, J.; Steele, S.; McGrath, L.; Vangel, M.; Aharon, I.; Feczko, E.; et al. Activation of the fusiform gyrus when individuals with autism spectrum disorder view faces. Neuroimage 2004, 22, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjikhani, N.; Joseph, R.M.; Snyder, J.; Tager-Flusberg, H. Abnormal activation of the social brain during face perception in autism. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2007, 28, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapretto, M.; Davies, M.S.; Pfeifer, J.H.; Scott, A.A.; Sigman, M.; Bookheimer, S.Y.; Iacoboni, M. Understanding emotions in others: Mirror neuron dysfunction in children with autism spectrum disorders. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinhans, N.M.; Richards, T.; Sterling, L.; Stegbauer, K.C.; Mahurin, R.; Johnson, L.C.; Greenson, J.; Dawson, G.; Aylward, E. Abnormal functional connectivity in autism spectrum disorders during face processing. Brain 2008, 131, 1000–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piggot, J.; Kwon, H.; Mobbs, D.; Blasey, C.; Lotspeich, L.; Menon, V.; Bookheimer, S.; Reiss, A.L. Emotional attribution in high-functioning individuals with autistic spectrum disorder: A functional imaging study. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2004, 43, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, K.; Redcay, E. Fusiform function in children with an autism spectrum disorder is a matter of “who”. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, J.; Milleville, S.C.; Kenworthy, L.; Wallace, G.L.; Gotts, S.J.; Beauchamp, M.S.; Martin, A. Social perception in autism spectrum disorders: Impaired category selectivity for dynamic but not static images in ventral temporal cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2014, 24, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, L.Q.; Castellanos, F.X.; Menon, V. Resting state functional brain connectivity in child and adolescent psychiatry: Where are we now? Neuropsychopharmacology 2024, 50, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tian, J.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Lee, K. Intrinsically organized network for face perception during the resting state. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 454, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk-Browne, N.B.; Norman-Haignere, S.V.; McCarthy, G. Face-Specific Resting Functional Connectivity between the Fusiform Gyrus and Posterior Superior Temporal Sulcus. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- O’Neil, E.B.; Hutchison, R.M.; McLean, D.A.; Köhler, S. Resting-state fMRI reveals functional connectivity between face-selective perirhinal cortex and the fusiform face area related to face inversion. NeuroImage 2014, 92, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Y.L.L.; Dilks, D.D.; Liu, J. Resting-State Neural Activity across Face-Selective Cortical Regions Is Behaviorally Relevant. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, A.; Yan, C.G.; Li, Q.; Denio, E.; Castellanos, F.X.; Alaerts, K.; Anderson, J.S.; Assaf, M.; Bookheimer, S.Y.; Dapretto, M.; et al. The autism brain imaging data exchange: Towards a large-scale evaluation of the intrinsic brain architecture in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammons, C.J.; Winslett, M.-E.; Kana, R.K. Neural responses to viewing human faces in autism spectrum disorder: A quantitative meta-analysis of two decades of research. Neuropsychologia 2021, 150, 107694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, J.V.; Dokovna, L.B.; Jacokes, Z.J.; Torgerson, C.M.; Irimia, A.; Van Horn, J.D. Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Review. Front. Psychiatry 2016, 7, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuilleumier, P.; Pourtois, G. Distributed and interactive brain mechanisms during emotion face perception: Evidence from functional neuroimaging. Neuropsychologia 2007, 45, 174–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishai, A.; Haxby, J.V.; Ungerleider, L.G. Visual imagery of famous faces: Effects of memory and attention revealed by fMRI. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 1729–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovács, G. Getting to Know Someone: Familiarity, Person Recognition, and Identification in the Human Brain. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2020, 32, 2205–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.; Rutter, M.; Le Couteur, A. Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised: A revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1994, 24, 659–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.; Risi, S.; Lambrecht, L.; Cook, E.H., Jr.; Leventhal, B.L.; DiLavore, P.C.; Pickles, A.; Rutter, M. The autism diagnostic observation schedule-generic: A standard measure of social and communication deficits associated with the spectrum of autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2000, 30, 205–223. [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler, D. The Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI); The Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler, D. The Wechsler Memory Scale Third Edition; The Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tottenham, N.; Tanaka, J.W.; Leon, A.C.; McCarry, T.; Nurse, M.; Hare, T.A.; Marcus, D.J.; Westerlund, A.; Casey, B.J.; Nelson, C. The NimStim set of facial expressions: Judgments from untrained research participants. Psychiatry Res. 2009, 168, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birn, R.M.; Diamond, J.B.; Smith, M.A.; Bandettini, P.A. Separating respiratory-variation-related fluctuations from neuronal-activity-related fluctuations in fMRI. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1536–1548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shmueli, K.; van Gelderen, P.; de Zwart, J.A.; Horovitz, S.G.; Fukunaga, M.; Jansma, J.M.; Duyn, J.H. Low-frequency fluctuations in the cardiac rate as a source of variance in the resting-state fMRI BOLD signal. Neuroimage 2007, 38, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M. Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2002, 17, 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson, M.; Bannister, P.R.; Brady, J.M.; Smith, S. Improved optimisation for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage 2002, 17, 825–841. [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann, C.F.; Jenkinson, M.; Smith, S.M. General multilevel linear modeling for group analysis in FMRI. Neuroimage 2003, 20, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Woolrich, M.W.; Behrens, T.E.; Beckmann, C.F.; Jenkinson, M.; Smith, S.M. Multilevel linear modelling for FMRI group analysis using Bayesian inference. Neuroimage 2004, 21, 1732–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worsley, K.J. 14 Statistical analysis of activation images. In Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Introduction to Methods; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 2001; Volume 251. [Google Scholar]
- Klin, A. Three things to remember if you are a functional magnetic resonance imaging researcher of face processing in autism spectrum disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 549–551. [Google Scholar]
- Kanwisher, N.; McDermott, J.; Chun, M.M. The fusiform face area: A module in human extrastriate cortex specialized for face perception. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 4302–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotshtein, P.; Henson, R.N.; Treves, A.; Driver, J.; Dolan, R.J. Morphing Marilyn into Maggie dissociates physical and identity face representations in the brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitcher, D.; Walsh, V.; Duchaine, B. The role of the occipital face area in the cortical face perception network. Exp. Brain Res. 2011, 209, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, A.J.; Beaver, J.D.; Winston, J.S.; Dolan, R.J.; Jenkins, R.; Eger, E.; Henson, R.N. Separate coding of different gaze directions in the superior temporal sulcus and inferior parietal lobule. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puce, A.; Allison, T.; Bentin, S.; Gore, J.C.; McCarthy, G. Temporal cortex activation in humans viewing eye and mouth movements. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 2188–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.A.; Shih, P.; Keehn, B.; Deyoe, J.R.; Leyden, K.M.; Shukla, D.K. Underconnected, but how? A survey of functional connectivity MRI studies in autism spectrum disorders. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 2233–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, M.G.; Park, J.; Gonzalez, R.; Polk, T.A.; Gehrke, A.; Knaffla, S.; Jonides, J. Evaluating functional localizers: The case of the FFA. Neuroimage 2010, 50, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghatol-Eslami, V.C.; Maximo, J.O.; Ammons, C.J.; Libero, L.E.; Kana, R.K. Hyperconnectivity of social brain networks in autism during action-intention judgment. Neuropsychologia 2020, 137, 107303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supekar, K.; Uddin, L.Q.; Khouzam, A.; Phillips, J.; Gaillard, W.D.; Kenworthy, L.E.; Yerys, B.E.; Vaidya, C.J.; Menon, V. Brain hyperconnectivity in children with autism and its links to social deficits. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Chang, H.; Rudoler, J.; Al-Zughoul, A.B.; Kang, J.B.; Abrams, D.A.; Menon, V. Replicable Patterns of Memory Impairments in Children With Autism and Their Links to Hyperconnected Brain Circuits. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2023, 8, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Song, Y.; Liu, J. Developmental Reorganization of the Core and Extended Face Networks Revealed by Global Functional Connectivity. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 3521–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stantić, M.; Brown, K.; Ichijo, E.; Pounder, Z.; Catmur, C.; Bird, G. Independent measurement of face perception, face matching, and face memory reveals impairments in face perception and memory, but not matching, in autism. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2023, 30, 2240–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, K.; Lewis, M.; Minar, N.; Willson, E.; Ace, J. Face Memory Deficits in Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 2021, 43, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trontel, H.G.; Duffield, T.C.; Bigler, E.D.; Froehlich, A.; Prigge, M.B.D.; Nielsen, J.A.; Cooperrider, J.R.; Cariello, A.N.; Travers, B.G.; Anderson, J.S.; et al. Fusiform Correlates of Facial Memory in Autism. Behav. Sci. 2013, 3, 348–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill-Spector, K.; Kourtzi, Z.; Kanwisher, N. The lateral occipital complex and its role in object recognition. Vis. Res. 2001, 41, 1409–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolls, E.T. Functions of the Primate Temporal Lobe Cortical Visual Areas in Invariant Visual Object and Face Recognition. Neuron 2000, 27, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazlett, H.C.; Gu, H.; Munsell, B.C.; Kim, S.H.; Styner, M.; Wolff, J.J.; Elison, J.T.; Swanson, M.R.; Zhu, H.; Botteron, K.N.; et al. Early brain development in infants at high risk for autism spectrum disorder. Nature 2017, 542, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ASD | TD | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group Size | 17 | 22 | |
| Age (SD) | 25.1 (4.78) | 27.22 (8.19) | =0.35 |
| WASI Full-Scale IQ | 112.00 (13.25) | 112.57 (12.04) | =0.89 |
| WASI Verbal IQ | 109.35 (18.26) | 111.67 (11.04) | =0.63 |
| WASI Performance IQ | 112.41 (11.01) | 110.43 (12.72) | =0.62 |
| ADI-R Social Score | 19.41 (5.64) | ||
| ADI-R Communication Score | 15.65 (3.66) | ||
| ADOS Severity Score | 5.38 (1.75) | ||
| ADOS Social Interaction | 5.71 (1.69) | ||
| ADOS Comm. and Language | 3.06 (1.48) |
| Immediate Face Memory | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ASD | TD | ||
| M(SD) | M(SD) | p-Value | |
| Total (Scaled Score) | 7.67 (1.78) | 10.05 (2.97) | <0.001 |
| Hits | 15.71 (3.10) | 18.14 (3.20) | 0.02 |
| Misses | 8.29 (3.10) | 5.86 (3.20) | 0.02 |
| Correct Rejections | 18.47 (2.43) | 19.50 (3.00) | 0.26 |
| False Alarms | 5.53 (2.43) | 4.50 (3.00) | 0.26 |
| Seed | Contrast | Voxels | Peak Region | p-Values | z-Max | MNI (mm) | Other Regions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | Z | |||||||
| R FFA+ | ASD > TD | 6596 | Left VI | <0.001 | 4.87 | −24 | −70 | −22 | Right Thalamus; Lingual Gyrus; Bilateral Hippocampus; Left Amygdala; Ventral Tegmental Area; Right VIIIa; Right VI |
| 1207 | Precentral Gyrus | <0.001 | 3.94 | −14 | −10 | 58 | Postcentral Gyrus; Juxtapositional Lobule Cortex (formerly Supplementary Motor Cortex) | ||
| 915 | Central Opercular Cortex | <0.001 | 3.91 | −42 | 6 | 4 | Insular Cortex; Left Putamen; Frontal Orbital Cortex; Precentral Gyrus | ||
| Seed | Group | Voxels | Peak Region | p-Values | z-Max | MNI (mm) | Other Regions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||||||
| R FFA+ | ASD | 6606 | Occipital pole | <0.001 | 4.12 | 20 | −94 | 28 | Lateral Occipital Cortex, superior division; Cuneal Cortex; Intracalcarine Cortex; Lingual Gyrus; Precuneous Cortex |
| R FFA+ | TD | 1528 | Lateral Occipital Cortex | <0.001 | 5.02 | 58 | −28 | 6 | Occipital Pole; Supramarginal Gyrus, posterior division; Angular Gyrus |
| 985 | Superior Temporal Gyrus | <0.001 | 3.95 | −34 | −68 | 34 | Central Opercular Cortex; Planum Temporale; Middle Temporal Gyrus, posterior division | ||
| 844 | Lateral Occipital Cortex | <0.001 | 4.04 | 56 | −22 | 2 | none | ||
| 520 | Planum Temporale | 0.01 | 3.94 | 46 | −82 | 12 | Superior Temporal Gyrus, posterior division; Central Opercular Cortex | ||
| 393 | Middle Temporal Gyrus | 0.047 | 3.87 | −50 | −30 | 4 | Temporal Occipital Fusiform Cortex; Inferior Temporal Gyrus, temporooccipital part; Temporal Fusiform Cortex, posterior division | ||
| L FFA+ | ASD | 538 | Precuneus Cortex | 0.016 | 3.79 | −14 | −62 | 18 | Intracalcarine Cortex; Cuneal Cortex; Supracalcarine Cortex; Lingual Gyrus; |
| L FFA+ | TD | 907 | Lateral Occipital Cortex | <0.001 | 3.63 | 48 | −84 | 14 | Temporal Occipital Fusiform Cortex; Occipital Fusiform Gyrus |
| Seed | Contrast | Voxels | Peak Region | p-Values | z-max | MNI (mm) | Other Regions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||||||
| R FFA+ | Group x Face Memory | 2583 | Cuneal Cortex | <0.001 | 3.78 | −20 | −78 | 30 | Lateral Occipital Cortex; Occipital Pole; Intracalcarine Cortex; Lingual Gyrus; Precuneous Cortex |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kleinhans, N.; Larsen, S.F.; Estes, A.; Aylward, E. Intrinsic Functional Connectivity Alterations of the Fusiform Face Area in Autism Spectrum Disorder. NeuroSci 2025, 6, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6020029
Kleinhans N, Larsen SF, Estes A, Aylward E. Intrinsic Functional Connectivity Alterations of the Fusiform Face Area in Autism Spectrum Disorder. NeuroSci. 2025; 6(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleKleinhans, Natalia, Sarah F. Larsen, Annette Estes, and Elizabeth Aylward. 2025. "Intrinsic Functional Connectivity Alterations of the Fusiform Face Area in Autism Spectrum Disorder" NeuroSci 6, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6020029
APA StyleKleinhans, N., Larsen, S. F., Estes, A., & Aylward, E. (2025). Intrinsic Functional Connectivity Alterations of the Fusiform Face Area in Autism Spectrum Disorder. NeuroSci, 6(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6020029






