Characterization of Anti-GAD65-Associated Neurological Syndromes: Clinical Features and Antibody Titers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Setting
2.2. Clinical Data
2.3. Anti-GAD65 Antibody Assays
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Approval
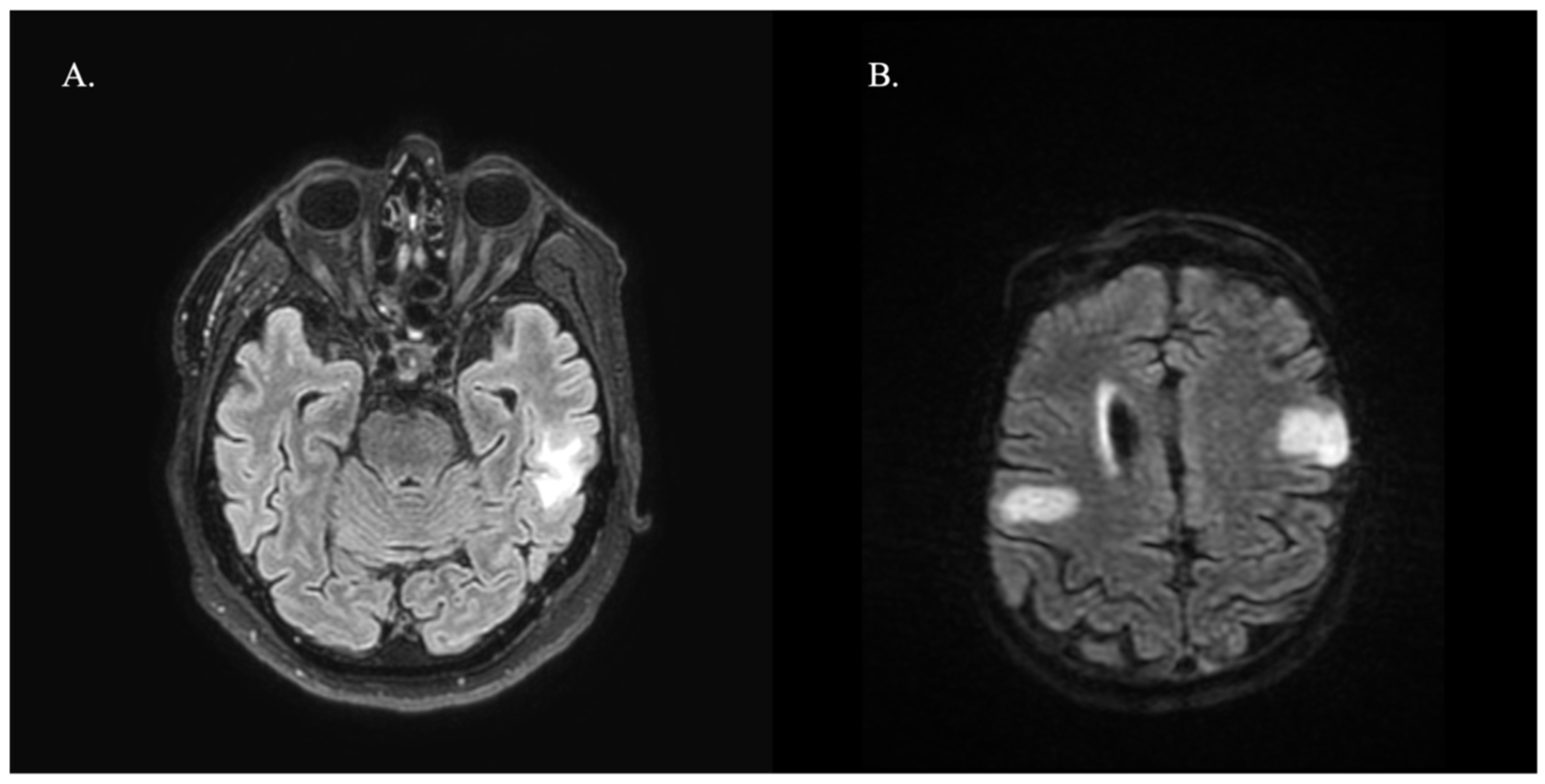
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fenalti, G.; Buckle, A.M. Structural biology of the GAD autoantigen. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanone, M.M.; Petersen, J.S.; Vergani, D.; Peakman, M. Expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase in nervous tissue structures targeted by autoantibodies in patients with diabetic autonomic neuropathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 78, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solimena, M.; De Camilli, P. Autoimmunity to glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) in stiffman syndrome and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Trends Neurosci. 1991, 14, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malter, M.P.; Helmstaedter, C.; Urbach, H.; Vincent, A.; Bien, C.G. Antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase define a form of limbic encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltola, J.; Kulmala, P.; Isojärvi, J.; Saiz, A.; Latvala, K.; Palmio, J.; Savola, K.; Knip, M.; Keränen, T.; Graus, F. Autoantibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase in patients with therapy-resistant epilepsy. Neurology 2000, 55, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giometto, B.; Miotto, D.; Faresin, F.; Argentiero, V.; Scaravilli, T.; Tavolato, B. Anti-gabaergic neuron autoantibodies in a patient with stiff-man syndrome and ataxia. J. Neurol. Sci. 1996, 143, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, L.L.; Fernandez-Fournier, M.; Muñoz, I.P.; Fraga, O.R.; Fernandez-Escandon, C.L.; Garrido, F.J.R.d.R.; Suarez, E.M.A.; Barranco, A.T. Serum glutamate decarboxylase antibodies and neurological disorders: When to suspect their association? Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manto, M.U.; Laute, M.A.; Aguera, M.; Rogemond, V.; Pandolfo, M.; Honnorat, J. Effects of anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies associated with neurological diseases. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.R.; Baquet, Z.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Tisch, R.; Smeyne, R.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A.A. Central Nervous System Destruction Mediated by Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase-Specific CD4+ T Cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 4863–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Vogrig, A.; Muniz-Castrillo, S.; Antoine, J.-C.G.; Desestret, V.; Dubey, D.; Giometto, B.; Irani, S.R.; Joubert, B.; Leypoldt, F.; et al. Updated Diagnostic Criteria for Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndromes. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Lopetegi, A.; de Bruijn, M.A.; Boukhrissi, S.; Bastiaansen, A.E.; Nagtzaam, M.M.; Hulsenboom, E.S.; Boon, A.J.; Neuteboom, R.F.; de Vries, J.M.; Smitt, P.A.S.; et al. Neurologic syndromes related to anti-GAD65: Clinical and serologic response to treatment. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanri, K.; Niwa, H.; Mitoma, H.; Takei, A.; Ikeda, J.; Harada, T.; Okita, M.; Takeguchi, M.; Taguchi, T.; Mizusawa, H. Low-titer anti-GAD-antibody-positive cerebellar ataxia. Cerebellum 2013, 12, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Guo, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, S. Immune-mediated epilepsy with GAD65 antibodies. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 341, 577189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhram, A.; Sechi, E.; Flanagan, E.P.; Dubey, D.; Zekeridou, A.; Shah, S.S.; Gadoth, A.; Naddaf, E.; McKeon, A.; Pittock, S.J.; et al. Clinical spectrum of high-titre GAD65 antibodies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalakas, M.C.; Fujii, M.; Li, M.; McElroy, B. The clinical spectrum of anti-GAD antibody-positive patients with stiff-person syndrome. Neurology 2000, 55, 1531–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkari, M.; Messelmani, M.; Souissi, W.; Derbali, H.; Mrissa, R. Subacute dementia revealing a limbic encephalitis with anti-GAD 65 antibodies in a young woman. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2021, 122, 1651–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanoni, G.; Formenti, A.; Tremolizzo, L.; Stabile, A.; Appollonio, I.; Ferrarese, C. Atypical parkinsonism and intrathecal anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies—An unusual association: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 14, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belém, A.D.; Vasconcelos, T.d.M.F.; Paula, R.C.d.A.d.; da Costa, F.B.S.; Rodrigues, P.G.B.; Pereira, I.d.S.; Tavares, P.R.d.A.; Galdino, G.S.; Dias, D.A.; Santos, C.d.F.; et al. Stiff-eye syndrome—Anti-gad ataxia presenting with isolated ophthalmoplegia: A case report. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, B.M.; Bhat, N.; Bindiganavile, S.H.; Lee, A.G. Convergence spasm with horizontal nystagmus in anti-GAD65 antibody syndrome. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 56, e20–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Ambati, A.; Dubois, V.; Vogrig, A.; Joubert, B.; Rogemond, V.; Picard, G.; Lin, L.; Fabien, N.; Mignot, E.; et al. Primary DQ effect in the association between HLA and neurological syndromes with anti-GAD65 antibodies. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 1906–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, H.; Zhou, R.; Huang, W.; Lin, W.; Chen, T.; Long, Y. Clinical Heterogeneity in Patients with Glutamate Decarboxylase Antibody. Neuroimmunomodulation 2019, 26, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalakas, M.C.; Fujii, M.; Li, M.; Lutfi, B.; Kyhos, J.; McElroy, B. High-Dose Intravenous Immune Globulin for Stiff-Person Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1870–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalakas, M.C.; Rakocevic, G.; Dambrosia, J.M.; Alexopoulos, H.; McElroy, B. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of rituximab in patients with stiff person syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiortou, P.; Alexopoulos, H.; Dalakas, M.C. GAD antibody-spectrum disorders: Progress in clinical phenotypes, immunopathogenesis and therapeutic interventions. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chengyu, L.; Weixiong, S.; Chao, C.; Songyan, L.; Lin, S.; Zhong, Z.; Hua, P.; Fan, J.; Na, C.; Tao, C.; et al. Clinical features and immunotherapy outcomes of anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 antibody-associated neurological disorders. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 345, 577289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Case | Age of Onset | Sex | Clinical Presentation | Clinical Presentation | Anti-GAD65 Serum (U/mL) and Method | Anti-GAD65 CSF (U/mL) * | FU | mRS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 63 | M | LE | Subacute altered mental status, personality changes, and working memory impairment | 22,178.70 ELISA | - | 12 | 6 |
| 2 | 52 | F | CA | Gait unsteadiness, falls | 104,234.40 ELISA | - | 36 | 4 |
| 3 | 49 | F | CA | Gait unsteadiness, dysmetria | 2.26 RIA | 2.61 ELISA | 16 | 4 |
| 4 | 74 | M | CA, P | Gait unsteadiness, parkinsonism | 41.79 RIA | 3.13 ELISA | 16 | 6 |
| 5 | 24 | F | LE | Refractory status epileptic, altered mental status, dystonic posture of the left arm | 2000.00 ELISA | - | 18 | 1 |
| 6 | 79 | M | LE | Subacute working memory impairment and frontal syndrome | 35,419.20 RIA | 2610.20 ELISA | 12 | 2 |
| 7 | 65 | M | LE | This patient had a history of perinatal strokes. By age 55, he had started developing seizures and cognitive dysfunction | 14.10 RIA | - | 108 | 4 |
| 8 | 58 | F | SpS, D | Stiffness, muscle spasms, diplopia | 274.64 RIA | - | 132 | 3 |
| 9 | 75 | F | LE | Personality changes and seizures, subacute onset | 123.68 RIA | - | 24 | 6 |
| 10 | 69 | F | Ep | Generalized seizures | 110,530.30 ELISA | 19,964.00 ELISA | 48 | 1 |
| 11 | 45 | F | SpS, D | Stiffness, muscle spasms, diplopia | 0.50 RIA | 10.64 ELISA | 24 | 2 |
| 12 | 56 | M | Ep | Generalized seizures | 0.50 RIA | 0.57 ELISA | 32 | 2 |
| 13 | 49 | M | CA, D | Gait unsteadiness, dysmetria, diplopia | 2.34 RIA | - | 96 | 4 |
| 14 | 52 | F | SpS | Stiffness, muscle spasms | - | - | 32 | 2 |
| 15 | 52 | F | LE | Subacute altered mental status, personality changes, and working memory impairment | 101,572.00 ELISA | 11,993.00 ELISA | 12 | 1 |
| 16 | 62 | F | Dementia | Altered mental status and working memory impairment | 174,740.10 ELISA | - | 11 | 1 |
| 17 | 56 | F | Dementia | Personality changes and working memory impairment | 155.70 RIA | - | 4 | 2 |
| 18 | 59 | F | Ep | Focal motor seizures | 209,461.70 ELISA | 1735.91 ELISA | 24 | 1 |
| 19 | 39 | M | Ep | Generalized seizures | 0.50 RIA | 14.38 ELISA | 60 | 2 |
| Characteristics | Sample |
|---|---|
| Demographic | |
| Female, number (%) | 12 (63.2) |
| Age of onset, mean (SD) | 56.0 (13.3) |
| Age of diagnosis, mean (SD) | 54.4 (14.6) |
| Clinical phenotype | |
| Ep, number (%) | 6 (31.6) |
| LE, number (%) | 6 (31.6) |
| CA, number (%) | 4 (21.1) |
| SpS, number (%) | 3 (15.8) |
| Serostatus | |
| Anti-GAD65 positive, serum, number (%) | 17 (89.5) |
| Anti-GAD65 positive, CSF, number (%) | 15 (78.9) |
| Therapeutic regimen | |
| MPD, number (%) | 8 (42.1) |
| IVIG, number (%) | 7 (36.8) |
| RTX, number (%) | 5 (26.3) |
| AZA, number (%) | 3 (15.8) |
| MTX, number (%) | 1 (5.3) |
| CYC, number (%) | 1 (5.3) |
| Maintenance PD, number (%) | 7 (36.8) |
| Follow-up time (months), median (IQR) | 24.0 (14.0–42.0) |
| Final mRS, median (IQR) | 1.0 (1.0–4.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moura, J.; Sambayeta, F.; Sousa, A.P.; Carneiro, P.; Neves, E.; Samões, R.; Silva, A.M.; Santos, E. Characterization of Anti-GAD65-Associated Neurological Syndromes: Clinical Features and Antibody Titers. NeuroSci 2024, 5, 201-208. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5020015
Moura J, Sambayeta F, Sousa AP, Carneiro P, Neves E, Samões R, Silva AM, Santos E. Characterization of Anti-GAD65-Associated Neurological Syndromes: Clinical Features and Antibody Titers. NeuroSci. 2024; 5(2):201-208. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoura, João, Firmina Sambayeta, Ana Paula Sousa, Paula Carneiro, Esmeralda Neves, Raquel Samões, Ana Martins Silva, and Ernestina Santos. 2024. "Characterization of Anti-GAD65-Associated Neurological Syndromes: Clinical Features and Antibody Titers" NeuroSci 5, no. 2: 201-208. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5020015
APA StyleMoura, J., Sambayeta, F., Sousa, A. P., Carneiro, P., Neves, E., Samões, R., Silva, A. M., & Santos, E. (2024). Characterization of Anti-GAD65-Associated Neurological Syndromes: Clinical Features and Antibody Titers. NeuroSci, 5(2), 201-208. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5020015






