Post-Mortem 7.0-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Hippocampus in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy with and without Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kovacs, G.G. Tauopathies. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 145, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scaravilli, T.; Tolosa, E.; Ferrer, I. Progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration: Lumping versus splitting. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20 (Suppl. S12), 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, O.; Davidson, Y.; Bigio, E.H.; Ishizu, H.; Terada, S.; Arai, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Akiyama, H.; Sikkink, S.; Pickering-Brown, S.M. Phosphorylated TDP-43 pathology and hippocampal sclerosis in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropath. 2010, 120, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, J.; Bagepally, B.S.; Sandhya, M.; Pasha, S.A.; Yadav, R.; Thennarasu, K.; Pall, P.K. Subcortical structures in progressive supranuclear palsy: Vertex-based analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2013, 20, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Wu, J.; Peng, S.; Wu, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Guan, Y.; Eidelberg, D.; Zuo, C.; Ma, Y. Reproducible network and regional topographies of abnormal glucose metabolism associated with progressive supranuclear palsy: Multivariate and univariate analyses in American and Chinese patient cohorts. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 2842–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reuck, J.; Auger, F.; Durieux, N.; Deramecourt, V.; Maurage, C.A.; Pasquier, F.; Cordonnier, C.; Leys, D.; Bordet, R. Cerebrovascular lesions during normal aging: A neuropathological study with 7.0-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging. EC Neurol. 2018, 10, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- De Reuck, J.; Auger, F.; Durieux, N.; Maurage, C.A.; Deramecourt, V.; Cordonnier, C.; Pasquier, F.; Leys, D.; Bordet, R. The impact of cerebral amyloid angiopathy in progressive supranuclear palsy: A neuropathological study with magnetic resonance imaging correlations. EC Neurol. 2019, 11, 807–812. [Google Scholar]
- De Reuck, J.; Auger, F.; Durieux, N.; Maurage, C.A.; Deramecourt, V.; Cordonnier, C.; Pasquier, F.; Leys, D.; Bordet, R. Post-mortem 7.0-tesla magnetic resonance imaging of the hippocampus during normal aging and in neurodegenerative dementias. SunText Rev. Neurosci. Psychol. 2020, 1, 108. [Google Scholar]
- De Reuck, J.; Caparros-Lefebvre, D.; Deramecourt, V.; Defebvre, L.; Auger, F.; Durieux, N.; Bordet, R.; Pasquier, F.; Maurage, C.-A. Prevalence of small cerebral bleeds in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy: A neuropathological study with 7.0-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging correlates. Folia Neuropathol. 2014, 52, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglinger, G.U.; Respondek, G.; Stamelou, M.; Kurz, C.; Josephs, K.A.; Lang, A.E.; Mollenhauer, B.; Müller, U.; Nilsson, C.; Whitwell, J.L.; et al. Clinical diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy: The movement disorder society criteria. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Martin, P.R.; Botha, H.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Bower, J.H.; Masumoto, J.Y.; Maraganore, D.; Hassan, A.; Eggers, S.; Boeve, B.F.; et al. Sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic criteria for progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, S.; Chalmers, K.; Ince, P.; Esiri, M.; Attems, J.; Jellinger, K.; Yamada, M.; McCarron, M.; Minett, T.; Matthews, F.; et al. Development, appraisal, validation and implementation of a consensus protocol for assessment of cerebral amyloidal angiopathy in post-mortem brain tissue. Am. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2014, 3, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scheltens, P.; Leys, D.; Barkhof, F.; Huglo, D.; Weinstein, H.C.; Vermersch, P.; Kuiper, M.; Steinling, M.; Wolters, E.C.; Valk, J. Atrophy of medial temporal lobes on MRI in “probable” Alzheimer’s disease and normal aging: Diagnostic value and neuropsychological correlates. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1992, 55, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlund, L.O.; Julin, P.; Johansson, S.E.; Scheltens, P. Visual rating and volumetry of the medial temporal lobe on magnetic resonance imaging: A comparative study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000, 69, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reuck, J. Histopathological stainings and definitions of vascular disruptions in the elderly brain. Exp. Gerontol. 2012, 47, 834–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reuck, J.; Auger, F.; Cordonnier, C.; Deramecourt, V.; Durieux, N.; Pasquier, F.; Bordet, R.; Maurage, C.; Leys, D. Comparison of 7.0-T T2*-magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral bleeds in post-mortem brain sections of Alzheimer patients with their neuropathological correlates. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2011, 31, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotte, A.A.J.D.; Koning, W.; Hartog, A.G.D.; Bovens, S.M.; Zwanenburg, J.J.M.; Klomp, D.W.J.; Pasterkamp, G.; Moll, F.L.; Luijten, P.R.; De Borst, G.J.; et al. 7.0 t MRI detection of cerebral microinfarcts in patients with symptomatic high-grade carotid artery stenosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 34, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.E.; Schneider, J.A.; Wardlaw, J.M.; Greenberg, S.M. Cerebral microinfarcts: The invisible lesions. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, S.; Kouri, N.; Walton, R.L.; Ebbert, M.T.W.; Josephs, K.A.; Litvan, I.; Graff-Radford, N.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Uitti, R.J.; Van Gerpen, J.A.; et al. Corticobasal degeneration with TDP-43 pathology presenting with progressive supranuclear palsy syndrome: A distinct clinicopathologic subtype. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, M.S.; Blauwendraat, C.; Ahmed, S.; Serrano, G.E.; Beach, T.G.; Perkins, M.; Rice, A.C.; Masliah, E.; Morris, C.M.; Pihlstrøm, L.; et al. Assessment of APOE in atypical parkinsonism syndromes. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 127, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, Y.; Jozephs, K.A.; Cookson, N.; Dickson, D.W. APAE E4 is a determinant for Alzheimer type of pathology in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 2003, 60, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reuck, J.; Auger, F.; Cordonnier, C.; Deramecourt, V.; Durieux, N.; Pasquier, F.; Bordet, R.; Maurage, C.A.; Leys, D. Comparison of post-mortem 7.0-tesla magnetic resonance imaging of the hippocampus in Alzheimer brains with and without cerebral amyloid angiopathy. OBM Geriatr. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- De Reuck, J.; Auger, F.; Durieux, N.; Maurage, C.A.; Deramecourt, V.; Cordonnier, C.; Pasquier, F.; Leys, D.; Bordet, R. Comparison of post-mortem 7.0-tesla magnetic resonance imaging of the hippocampus in Lewy body dementia brains with and without cerebral amyloid angiopathy. EC Neurol. 2020, 12, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- De Reuck, J. The impact of cerebral amyloid angiopathy in various neurodegenerative dementia syndromes: A neuropathological study. Neurol. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7247325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
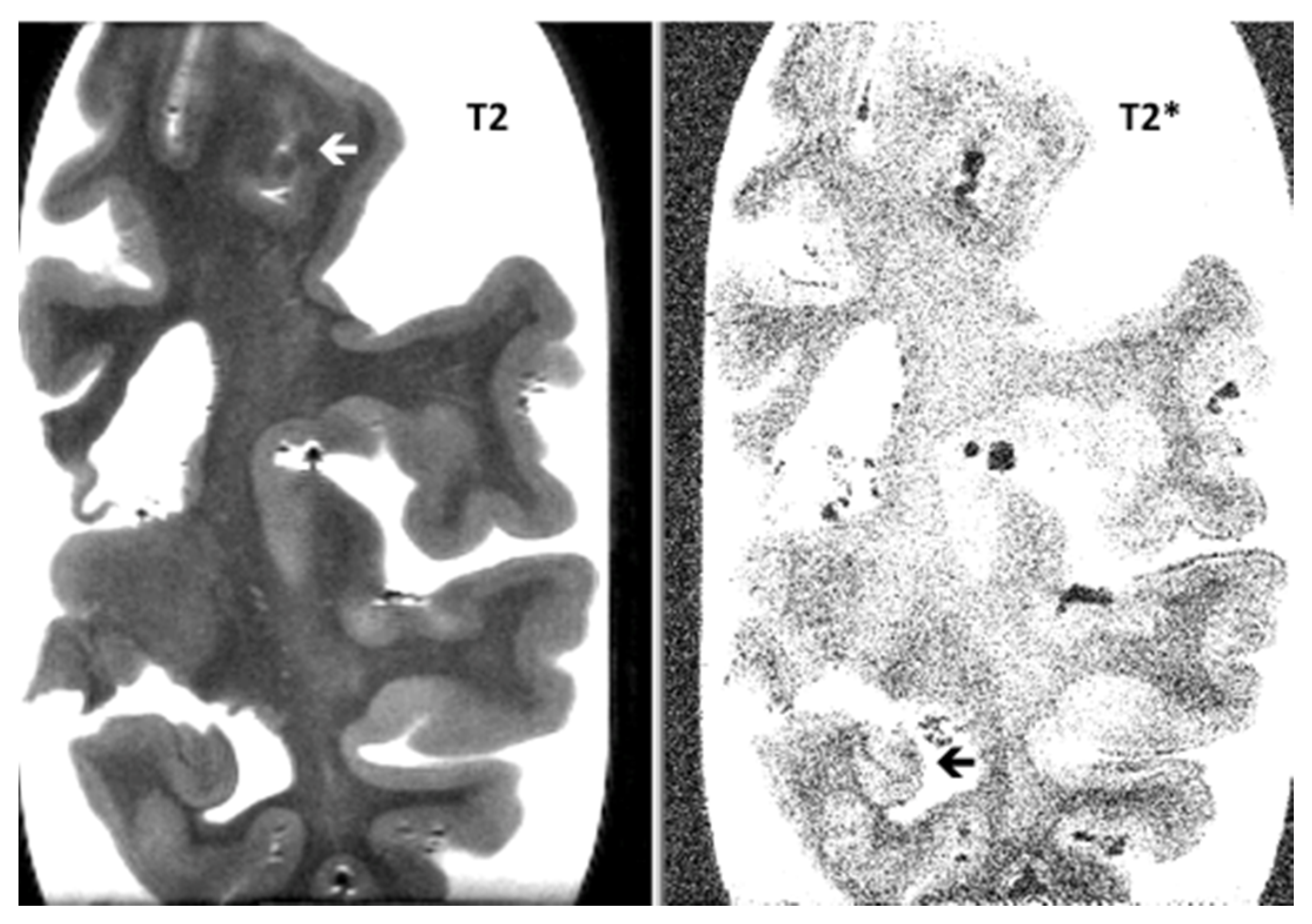
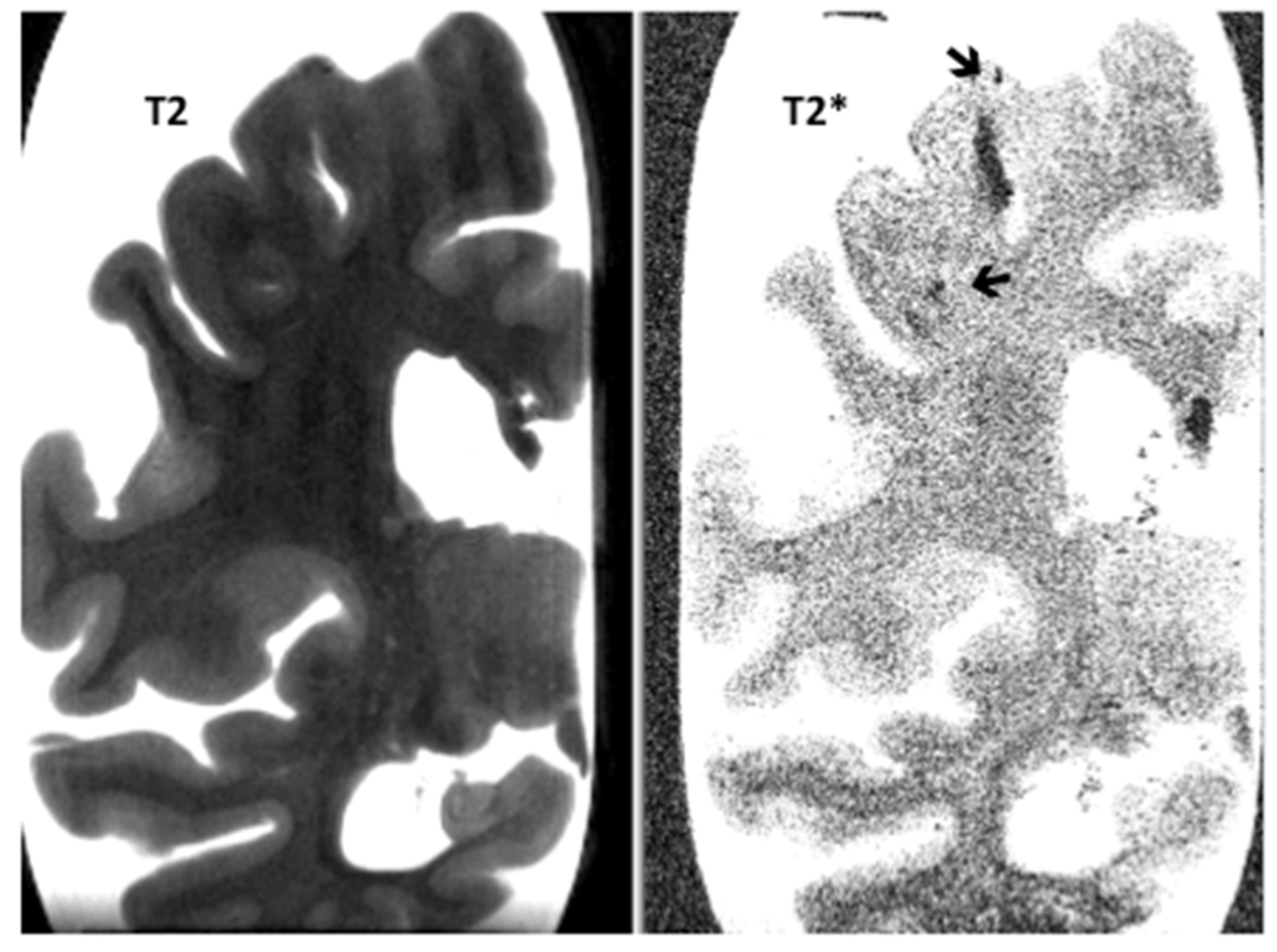
| Items | PSP-CAA | PSP | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| White matter changes | 1.3 (0.5) | 0.8 (0.9) | NS |
| Territorial infarcts | 0.3 (0.5) | 0.2 (0.4) | NS |
| Lacunar infarcts | 0.8 (0.5) | 0.1 (0.2) | <0.01 |
| Lobar haematomas | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.1 (0.2) | NS |
| Cortical micro-infarcts | 0.5 (0.6) | 0.6 (0.8) | NS |
| Cortical micro-bleeds | 1.3 (0.5) | 1.2 (0.9) | NS |
| Items | PSP-CAA | PSP | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hippocampal atrophy | 0.6 (0.7) | 0.9 (0.6) | NS |
| Hippocampal micro-infarcts | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.2 (0.4) | NS |
| Hippocampal micro-bleeds | 0.9 (0.6) | 0.4 (0.5) | NS |
| Neocortical micro-infarcts | 0.4 (0.7) | 0.4 (0.6) | NS |
| Neocortical micro-bleeds | 1.0 (0.9) | 1.1 (1.2) | NS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Reuck, J.; Auger, F.; Durieux, N.; Maurage, C.-A.; Deramecourt, V.; Cordonnier, C.; Pasquier, F.; Leys, D.; Bordet, R. Post-Mortem 7.0-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Hippocampus in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy with and without Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy. NeuroSci 2020, 1, 115-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci1020011
De Reuck J, Auger F, Durieux N, Maurage C-A, Deramecourt V, Cordonnier C, Pasquier F, Leys D, Bordet R. Post-Mortem 7.0-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Hippocampus in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy with and without Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy. NeuroSci. 2020; 1(2):115-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci1020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Reuck, Jacques, Florent Auger, Nicolas Durieux, Claude-Alain Maurage, Vincent Deramecourt, Charlotte Cordonnier, Florence Pasquier, Didier Leys, and Regis Bordet. 2020. "Post-Mortem 7.0-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Hippocampus in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy with and without Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy" NeuroSci 1, no. 2: 115-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci1020011
APA StyleDe Reuck, J., Auger, F., Durieux, N., Maurage, C.-A., Deramecourt, V., Cordonnier, C., Pasquier, F., Leys, D., & Bordet, R. (2020). Post-Mortem 7.0-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Hippocampus in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy with and without Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy. NeuroSci, 1(2), 115-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci1020011




