Adsorptive Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solution Utilizing Activated Carbon Developed from Spathodea campanulata
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
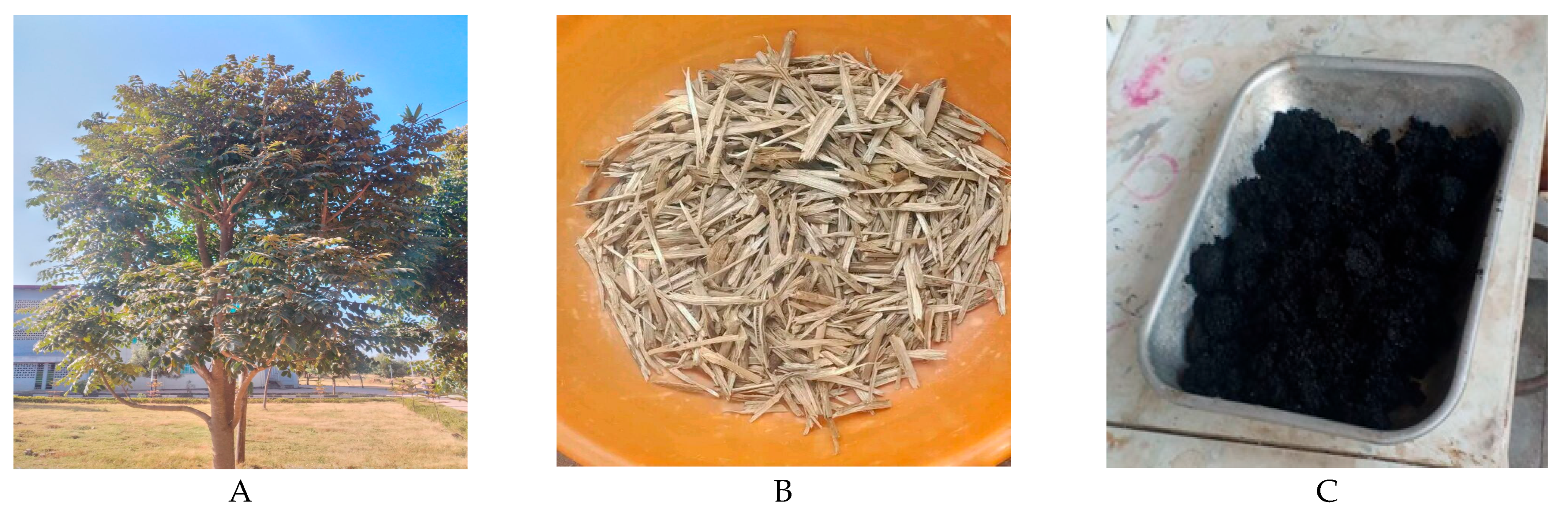
2.1. Adsorbent Preparation
2.2. Adsorbent Characterization
2.3. Batch Adsorption Experimental Design
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Adsorption Isotherm
2.6. Adsorption Kinetics
2.7. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3. Results and Discussion
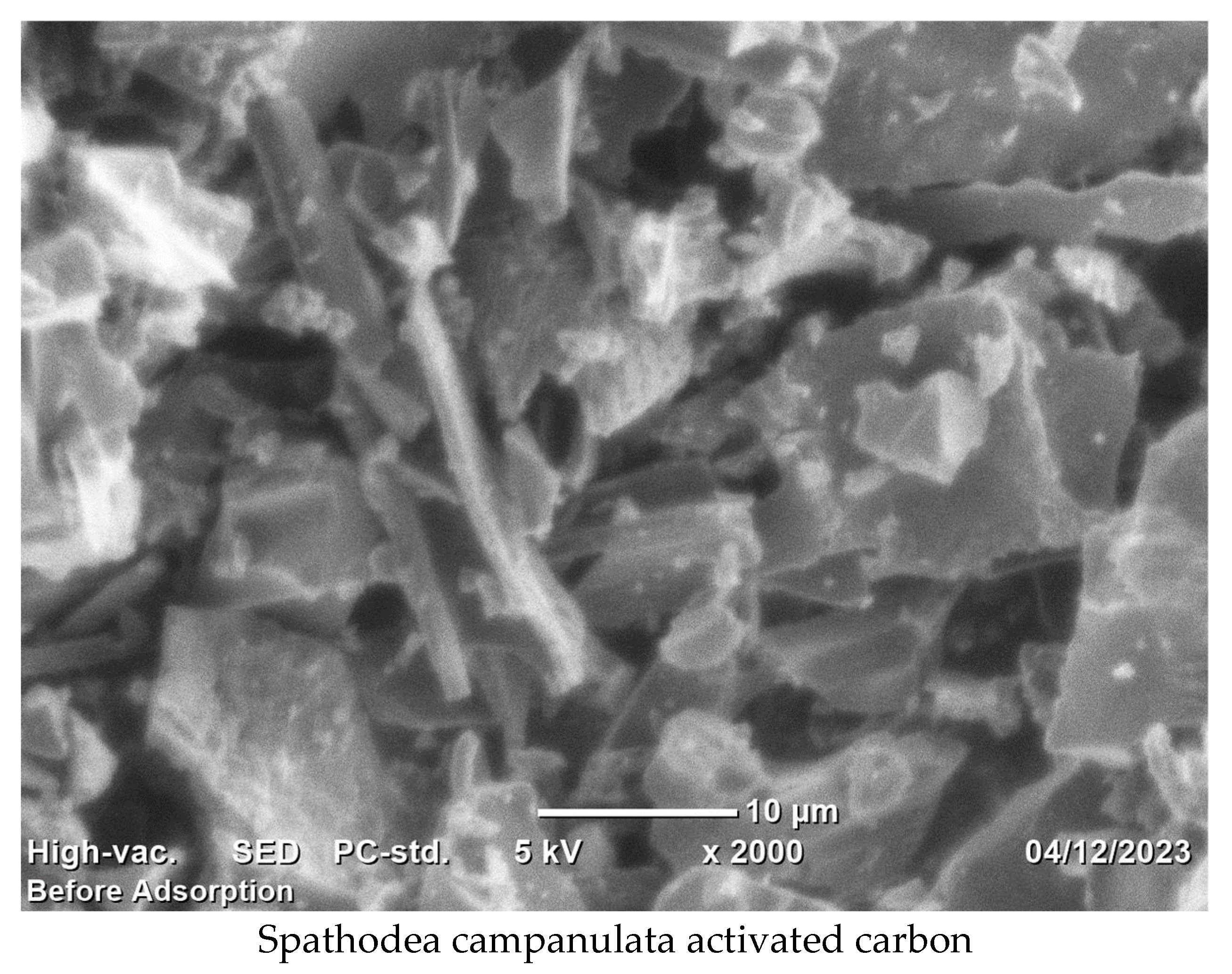
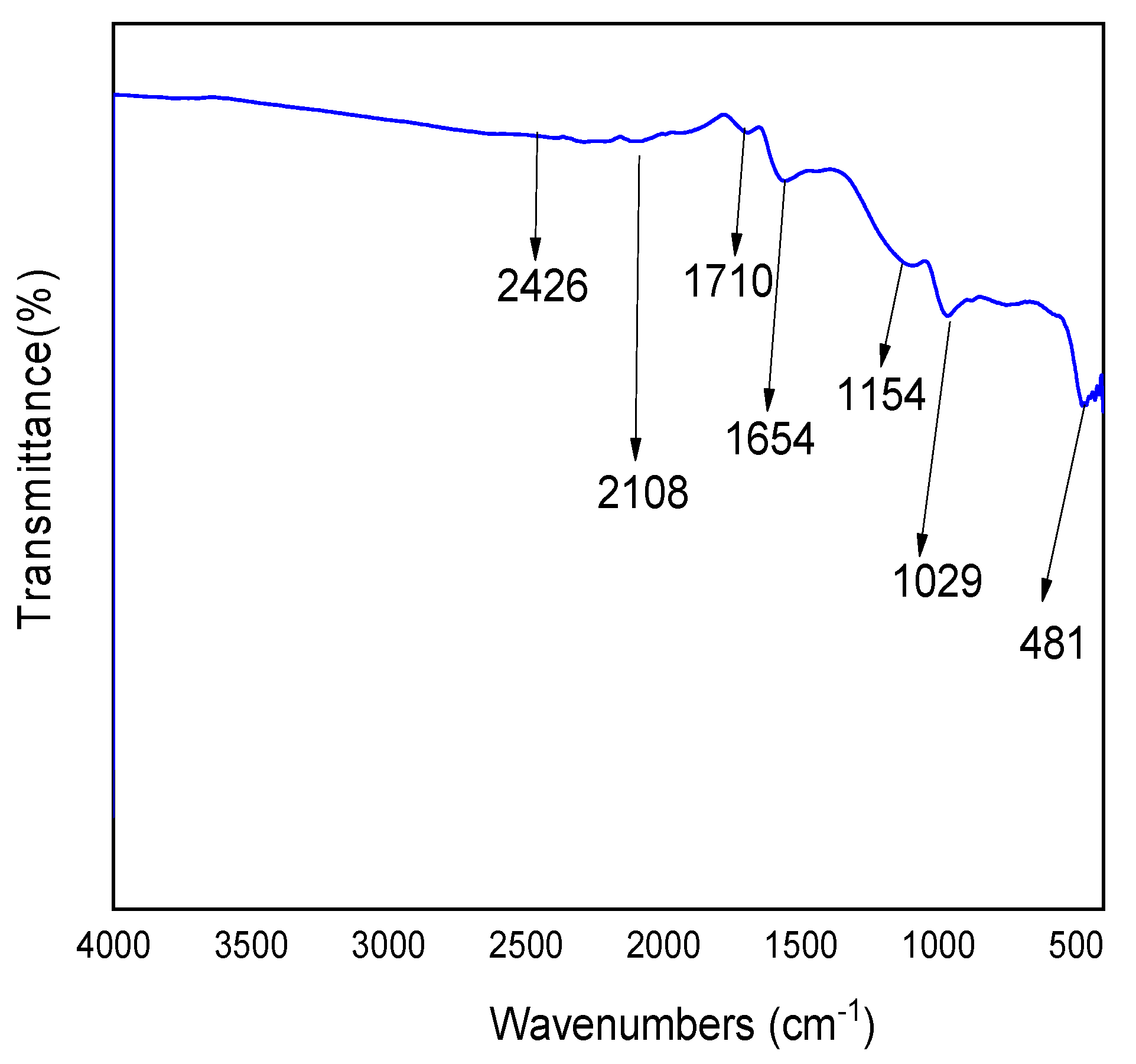
3.1. Adsorbent Characteristics
3.2. Batch Adsorption Performance
3.3. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and Fit Summary
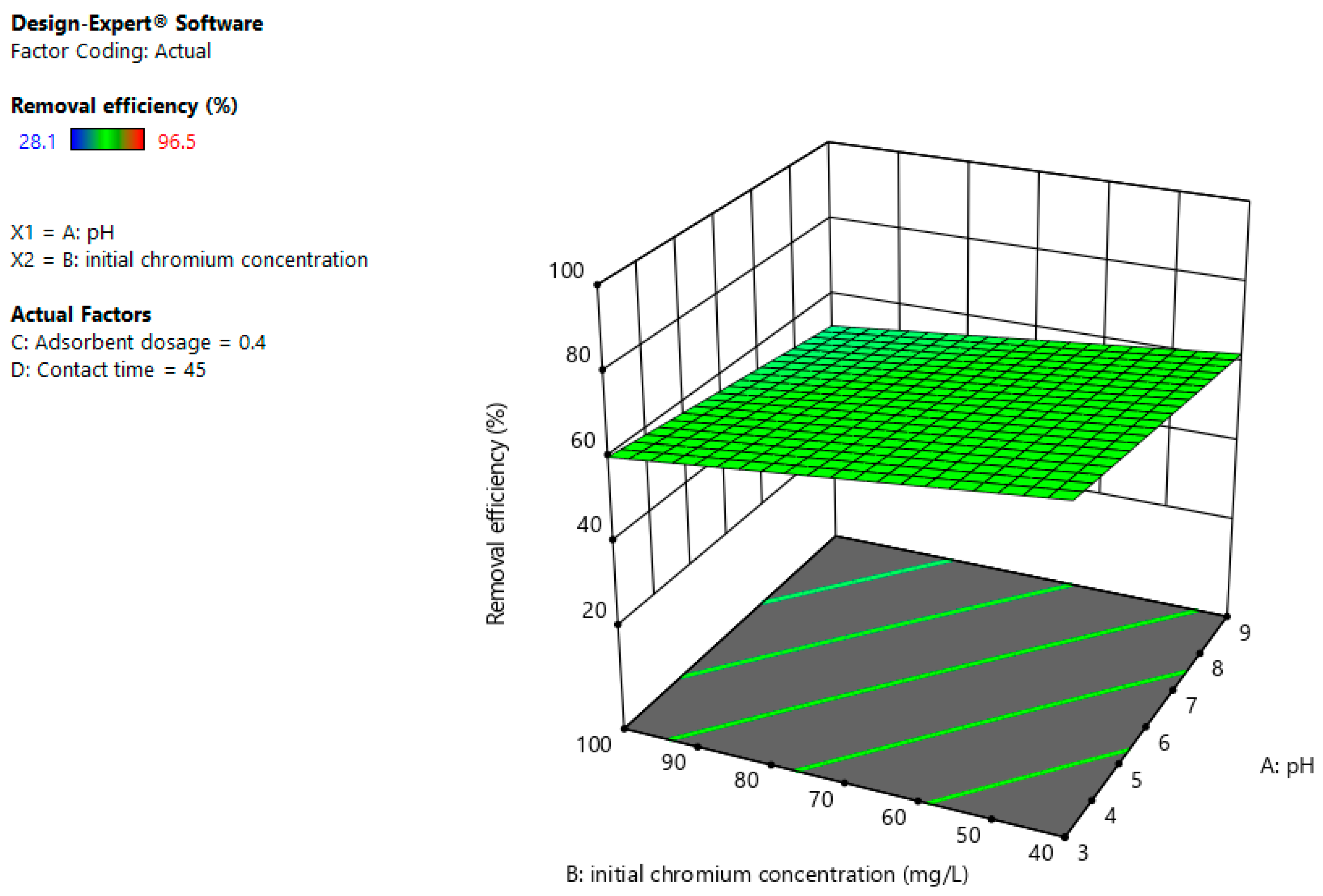
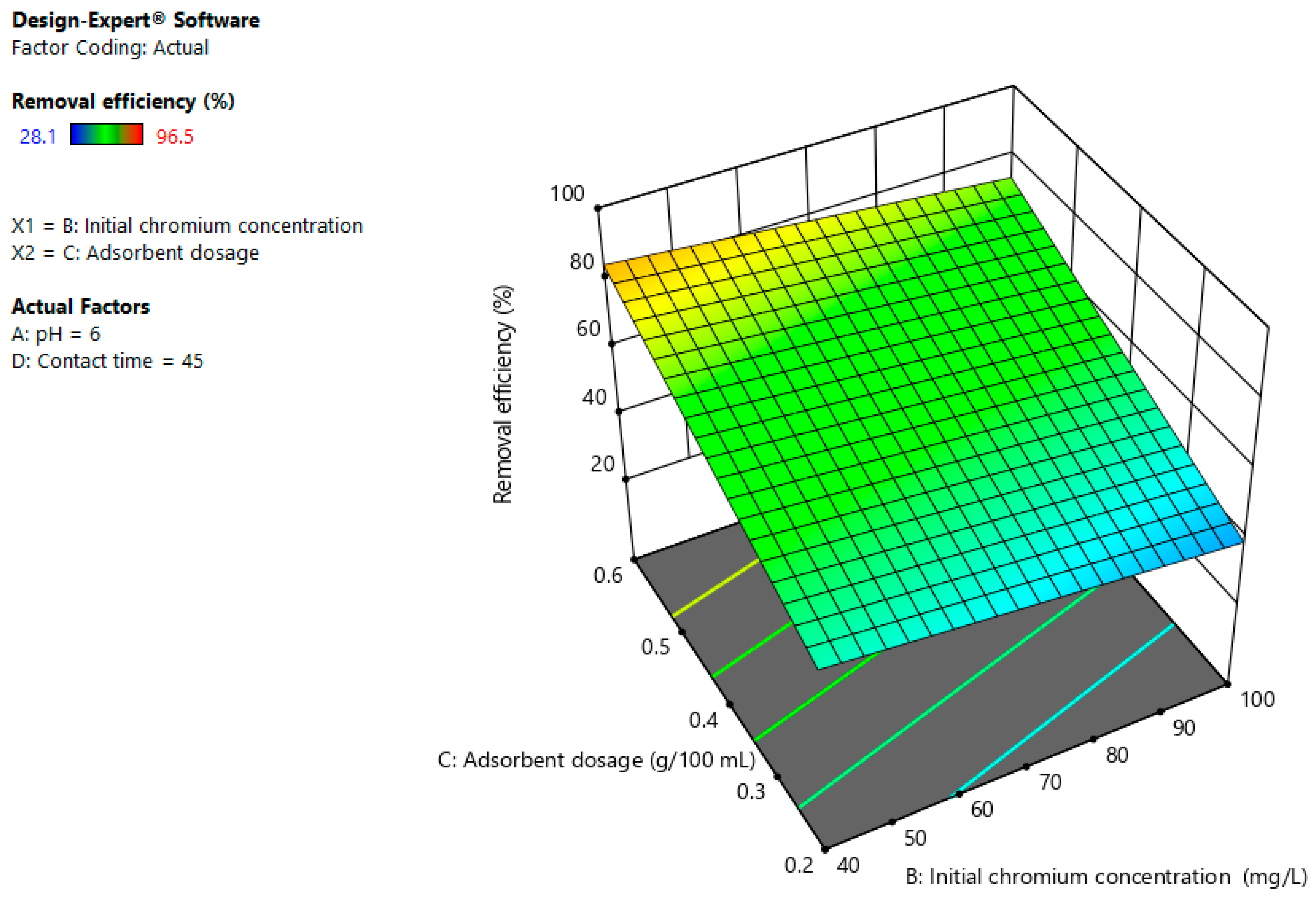
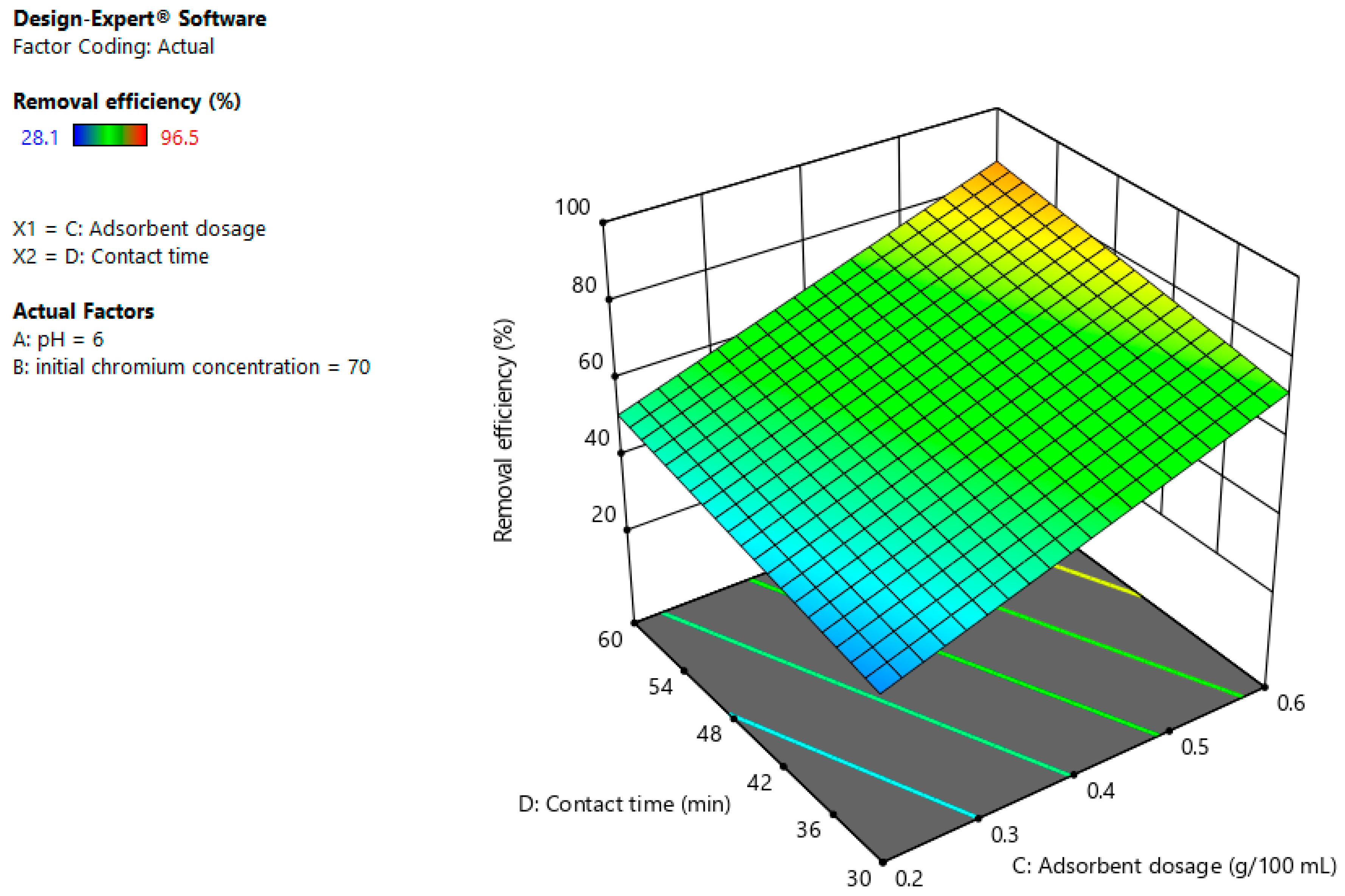
3.4. Interaction Effects
3.4.1. pH and Adsorbent Dosage
3.4.2. Initial Chromium Concentration and Adsorbent Dosage
3.4.3. Adsorbent Dosage and Contact Time
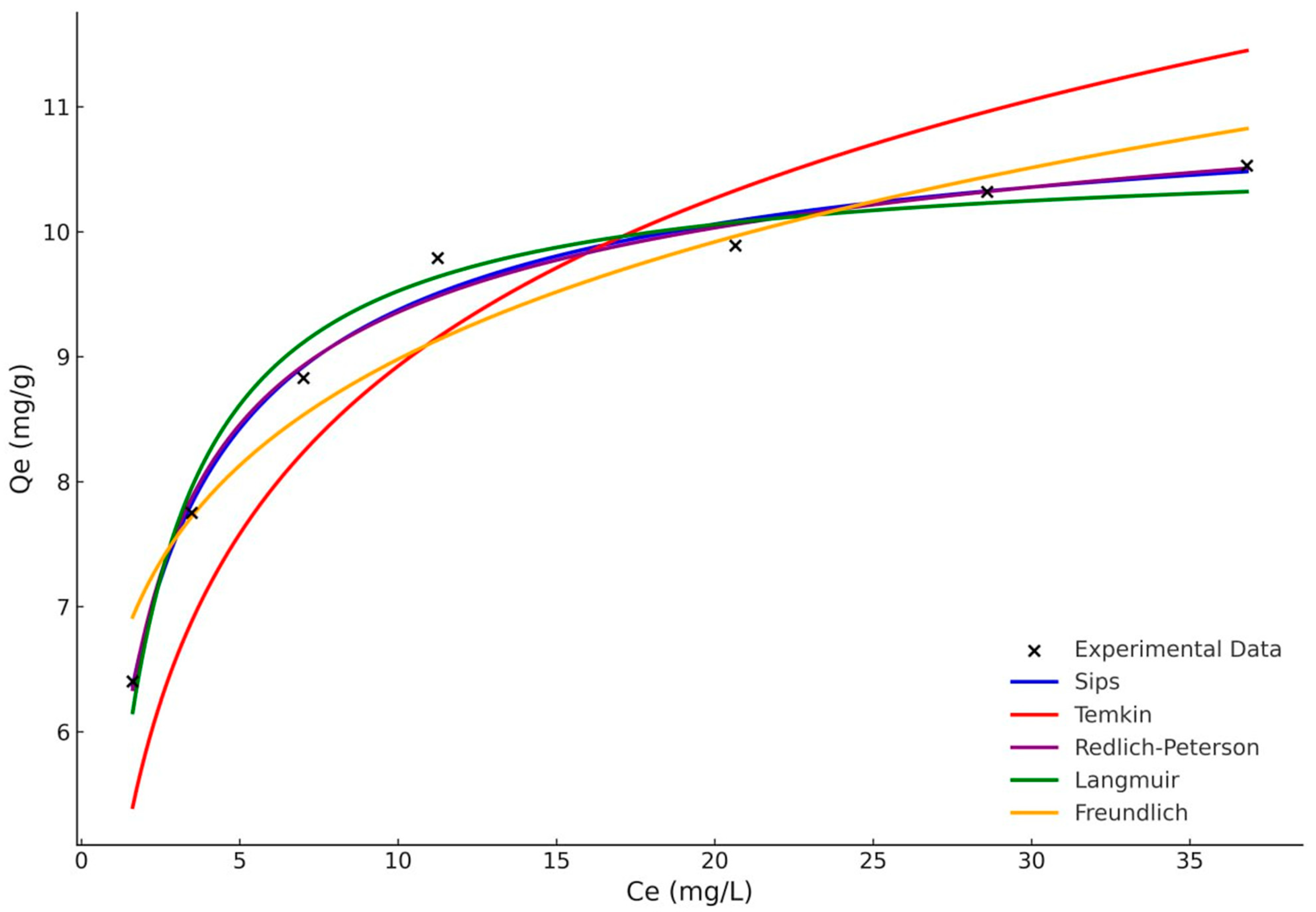
3.5. Adsorption Isotherm
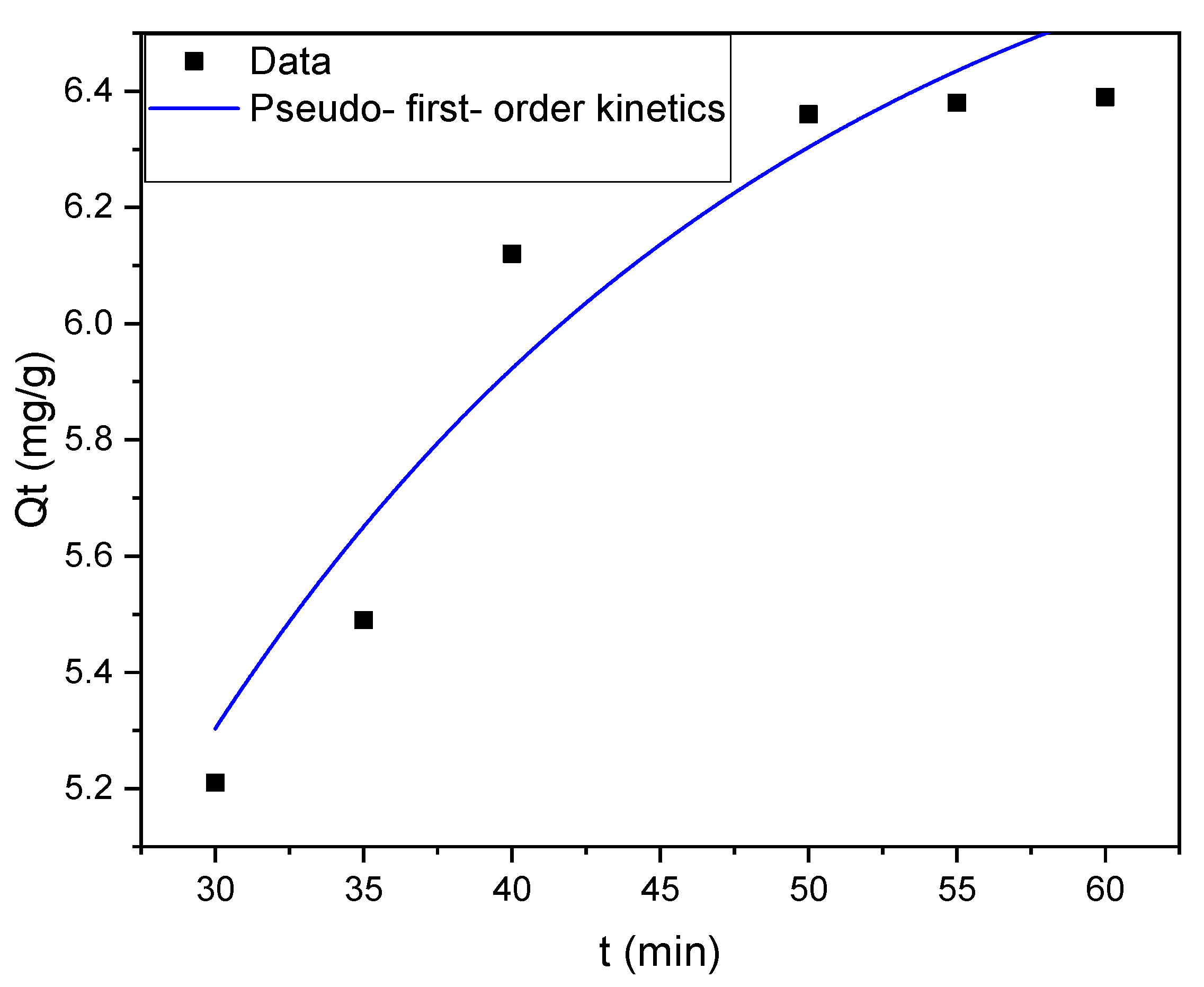
3.6. Adsorption Kinetics
3.7. Adsorption Thermodynamics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khatua, S.; Kumar Dey, S. The Chemistry and Toxicity of Chromium Pollution: An Overview. Asian J. Agric. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, G.R.; Pokhre, G. The Effect of Chromium on Human-Health: A Review. BMC J. Sci. Res. 2022, 5, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsania, P.; Dar, M.A.; Kaushik, G. Bioremediation Strategies for Removal of Chromium from Polluted Environment. In Bioremediation of Toxic Metal (loid) s; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 216–236. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, A.; Sinha, A. Fate and Transport of Chromium Contaminant in Environment. In Persistent Pollutants in Water and Advanced Treatment Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 283–297. [Google Scholar]
- Iskra, R.Y.; Fedoruk, R.S. Chromium, its properties, transformation, and impact on humans. Fiziol. Zhurnal (Physiol. J.) 2022, 68, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, A.; Nkambule, T.T.I.; Fito, J. The application of GO-Fe3O4 nanocomposite for chromium adsorption from tannery industry wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedda, G.; Balakrishnan, K.; Devi, R.U.; Shah, K.J.; Gandhi, V.; Gandh, V.; Shah, K.L. Introduction to conventional wastewater treatment technologies: Limitations and recent advances. Mater. Res. Found. 2021, 91, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Abuhasel, K.; Kchaou, M.; Alquraish, M.; Munusamy, Y.; Jeng, Y.T. Oily wastewater treatment: Overview of conventional and modern methods, challenges, and future opportunities. Water 2021, 13, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poornima, S.; Manikandan, S.; Karthik, V.; Balachandar, R.; Subbaiya, R.; Saravanan, M.; Chi, N.T.L.; Pugazhendhi, A. Emerging nanotechnology based advanced techniques for wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, J.; Lodh, B.K.; Sharma, R.; Mahata, N.; Shah, M.P.; Mandal, S.; Ghanta, S.; Bhunia, B. Advanced oxidation process for the treatment of industrial wastewater: A review on strategies, mechanisms, bottlenecks and prospects. Chemosphere 2023, 345, 140473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, P.Y.; Velizarov, S.; Volkov, A.V.; Eliseeva, T.V.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Parshina, A.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Popov, K.I.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Fouling and membrane degradation in electromembrane and baromembrane processes. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2022, 4, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, R.; Shafiq, I.; Akhter, P.; Iqbal, M.J.; Hussain, M. A state-of-the-art review on wastewater treatment techniques: The effectiveness of adsorption method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9050–9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Lan, J.; Bo, C.; Gong, B.; Ou, J. Adsorption of heavy metal onto biomass-derived activated carbon. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 4275–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, C.; Robledo-Cabrera, A.; López-Valdivieso, A. Highly surface activated carbon to remove Cr (VI) from aqueous solution with adsorbent recycling. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Kassimi, A.; Naboulsi, A.; Yazid, H.; Achour, Y.; Regti, A.; El Himri, M.; Lazar, S.; Laamari, R.; El Haddad, M. Adsorption of chromium (VI) on low-cost adsorbents derived from agricultural waste material: A comparative study and experimental design. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 104, 8376–8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, L.R.; Mukunda, P.A.; Bapu, D.S.; Vijay, B.P.; Jain, P.P. A Case Study over Adsorption of Removal of CR(VI) by Prepared Activated Carbon. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 11, 6711–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, M.R.; Alkali, M.I. Removal of Chromium (VI) from Aqueous Solution Using Activated Carbon Derived from Modified Bambara Nut Shells (Vignasubterranea (L.) verdc.). J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2023, 27, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleye, A.T.; Akande, A.A.; Odoh, C.K.; Philip, M.; Fidelis, T.T.; Amos, P.I.; Banjoko, O.O. Efficient synthesis of bio-based activated carbon (AC) for catalytic systems: A green and sustainable approach. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 96, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tri, C.L.; Tung, V.H.; Hong, N.T.; Tuan, L.; Nguyen, D.D.; Nguyen, X.C.; La, D.D.; Le, D.K. Optimization of Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Eichhornia crassipes-Derived Adsorbents Through a Response Surface Methodology. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-4593512/v1 (accessed on 27 January 2024).
- Vidhya, L.; Pradeeba, S.J.; Jeyagowri, B.; Sivakumar, K.; Devi, V.N. Evaluation of Sustainable and Renewable Agro-Waste Adsorbent for the Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Wastewater. J. Environ. Nanotechnol. 2024, 13, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhari, P.I.; Dhote, S.S.; Lanjewar, M.R. Sequestration of Hexavalent Chromium in Aqueous Media Using Chitosan-Modified Biochar. Orient. J. Chem. 2024, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dalahmeh, Y.; Hamadneh, I.; Aburumman, G.; Al-Mobydeen, A.; Alkhawaldeh, M.; Abu Shawer, A.; Ahmed, R.; Esaifan, M.; Al-Dujaili, A.H. Biosorption of hexavalent chromium by biochar prepared from the Ceratonia siliqua pod: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamics studies. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2024, 42, 02636174241241946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakye, M.K.; Agyemang, A.O.; Gbadegbe, R.S.; Quashie, M.; Turkson, B.K.; Adanu, K.K.; Wiafe, E.D. Ethnobotanical applications of Spathodea campanulata P. Beauv. (African tulip tree) in Ghana. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2023, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Umaru, I. Evaluation of Antifungal Potential and Gastroprotective Effect of Ethanol Seed Extract of Spathodea Campanulata of Indomethacin Induced Gastric Ulcer, A Possible Application for Veterinary Animal. Res. Gastric Manag. Hepatol. 2023, 1, 01–05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrue, S.; Baray, J.; Chadeyron, J.; Meyer, J.; Mazal, L.; Daehler, C.C.; Fumanal, B. Modeling long-distance seed dispersal of the invasive tree Spathodea campanulata in the Society Islands. Ecol. Appl. 2023, 33, e2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omale, J.M.; Mutai, P.; Njogu, P.; Mukungu, N.; Mwangi, J.; Odongo, E. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants used in Emuhaya Subcounty, Vihiga County in Western Kenya. Appl. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shandilya, K.; Arora, N.; Goyel, S. Phytochemical Screening and Characterization of Active Component of Spathodea Campanulata (Raktura) for Their Anti-Arthritic Activity. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2021, 12 (Suppl. S2), 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, M.; King, P. Application of response surface optimization on biosorption of congo red dye onto Spathodea Campanulata leaves. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 182, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimbo, D.; Abewaa, M.; Adino, E.; Mengistu, A.; Takele, T.; Oro, A.; Rangaraju, M. Methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution using activated carbon of Spathodea campanulate. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abewaa, M.; Mengistu, A.; Takele, T.; Fito, J.; Nkambule, T. Adsorptive removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution using Rumex abyssinicus derived activated carbon. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bithi, I.J.; Mottalib, M.A.; Miran, M.S.; Ehsan, M.F.; Rahman, M.M. Removal of Cr (VI) from wastewater by impregnated activated carbon generated from vegetable tanned leather waste with aluminium oxide. Results Surf. Interfaces 2024, 14, 100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamacı, U.D.; Kamacı, M. Hydrogel beads based on sodium alginate and quince seed nanoparticles for the adsorption of methylene blue. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 160, 111919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkin, M.I. Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalysts. Acta Physiochim. URSS 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Sips, R. On the structure of a catalyst surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redlich, O.; Peterson, D.L. A useful adsorption isotherm. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Rethinking of the intraparticle diffusion adsorption kinetics model: Interpretation, solving methods and applications. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Tsuchikane, K.; Inoue, J.; Arai, S. Selective Zn/Na ions Insertion into FePO4 Positive Electrode Tuned by Counter Anions in Aqueous Zn-Based Rechargeable Batteries. ChemElectroChem 2024, 11, e202300540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, Z.; Tibebu, S.; Nure, J.F.; Tibebu, S.; Moyo, W.; Ambaye, A.D.; Nkambule, T.T.I. Adsorption of chromium from electroplating wastewater using activated carbon developed from water hyacinth. BMC Chem. 2023, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Chang, F.; Zhang, H.; Wågberg, T.; Hu, G. Mesopore-rich badam-shell biochar for efficient adsorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegunde, S.M.; Idowu, K.S.; Adejuwon, O.M.; Adeyemi-Adejolu, T. A review on the influence of chemical modification on the performance of adsorbents. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, D.; Saal, L.; Zietzschmann, F.; Mai, M.; Altmann, K.; Al-Sabbagh, D.; Schumann, P.; Ruhl, A.S.; Jekel, M.; Braun, U. Characterization of activated carbons for water treatment using TGA-FTIR for analysis of oxygen-containing functional groups. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temesgen Abeto, A.; Beyan, S.M.; Abreham Bekele, B.; Worku Firomsa, K. Optimization and Modeling of Cr (VI) Removal from Tannery Wastewater onto Activated Carbon Prepared from Coffee Husk and Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4) as Activating Agent by Using Central Composite Design (CCD). J. Environ. Public Health 2023, 2023, 5663261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loulidi, I.; Jabri, M.; Amar, A.; Kali, A.; A. Alrashdi, A.; Hadey, C.; Ouchabi, M.; Abdullah, P.S.; Lgaz, H.; Cho, Y.; et al. Comparative Study on Adsorption of Crystal Violet and Chromium (VI) by Activated Carbon Derived from Spent Coffee Grounds. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedada, D.; Angassa, K.; Tiruneh, A.; Kloos, H.; Fito, J. Chromium removal from tannery wastewater through activated carbon produced from Parthenium hysterophorus weed. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2020, 5, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, S.U.R.; Shah, S.A. Adsorption of Cr (VI) by NaOH-modified microporous activated carbons derived from the wastes of Amaranthus retroflexus, Magnolia soulangeana, and Tanacetum vulgar L.: Mechanism, isotherms, and kinetic studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 35808–35837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, L.T. Efficient Cr (VI) sequestration from aqueous solution by chemically modified Garcinia kola hull particles: Characterization, isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 109751–109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beksissa, R.; Tekola, B.; Ayala, T.; Dame, B. Investigation of the adsorption performance of acid treated lignite coal for Cr (VI) removal from aqueous solution. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, A.; Sahu, S.; Pahi, S.; Singh, S.K.; Mahapatra, B.; Patel, R.K. Polypyrrole modified zirconium (IV) phosphate nanocomposite: An effective adsorbent for Cr (VI) removal by adsorption-reduction mechanism. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 290, 126540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.K.; Naiya, T.K.; Mandal, S.N.; Das, S.K. Adsorption, kinetics and equilibrium studies on removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions using different low-cost adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 137, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Huang, H. Adsorption of chromium (III) on lignin. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7709–7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fito, J.; Abewaa, M.; Mengistu, A.; Angassa, K.; Ambaye, A.D.; Moyo, W.; Nkambule, T. Adsorption of methylene blue from textile industrial wastewater using activated carbon developed from Rumex abyssinicus plant. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fito, J.; Mengistu, A.; Abewaa, M.; Angassa, K.; Moyo, W.; Phiri, Z.; Mafa, P.J.; Kuvarega, A.T.; Nkambule, T.T.I. Adsorption of Black MNN reactive dye from tannery wastewater using activated carbon of Rumex abysinicus. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 151, 105138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takele, T.; Angassa, K.; Abewaa, M.; Kebede, A.M.; Tessema, I. Adsorption of methylene blue from textile industrial wastewater using activated carbon developed from H3PO4-activated khat stem waste. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrutha; Jeppu, G.; Girish, C.R.; Prabhu, B.; Mayer, K. Multi-component adsorption isotherms: Review and modeling studies. Environ. Process. 2023, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, A.M.; Arowo, M.N.; Selele, M.I.; Houndedjihou, D.; Nayem, Z. Jovanovic and Sips Isotherm Parameters of Mango Seed Shell Cadmium Ion Sorption from Aqueous Solution. Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 6, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hossain, M.F.; Duan, C.; Lu, J.; Tsang, Y.F.; Islam, M.S.; Zhou, Y. Isotherm models for adsorption of heavy metals from water—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andelescu, A.; Nistor, M.A.; Muntean, S.G.; Rădulescu-Grad, M.E. Adsorption studies on copper, cadmium, and zinc ion removal from aqueous solution using magnetite/carbon nanocomposites. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2352–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teweldebrihan, M.D.; Gnaro, M.A.; Dinka, M.O. The application of magnetite biochar composite derived from parthenium hysterophorus for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1375437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, A.; Abewaa, M.; Adino, E.; Gizachew, E.; Abdu, J. The application of Rumex abyssinicus based activated carbon for Brilliant Blue Reactive dye adsorption from aqueous solution. BMC Chem. 2023, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslim, W.A.; Albayati, T.M.; Al-Nasri, S.K. Decontamination of actual radioactive wastewater containing 137Cs using bentonite as a natural adsorbent: Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | Unit | Lower (−) | Higher (+) |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 3 | 9 |
| Contact time | min | 30 | 60 |
| Initial Cr concentration | mg/L | 40 | 100 |
| Adsorbent dosage | g/100 mL | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| Run | pH | Initial Chromium Concentration (mg/L) | Adsorbent Dosage (g/100 mL) | Contact Time (min) | Actual Removal Efficiency (%) | Predicted Removal Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 3 | 40 | 0.6 | 30 | 81.5 | 81.85 |
| 2. | 9 | 40 | 0.2 | 60 | 52.6 | 52.30 |
| 3. | 9 | 40 | 0.6 | 60 | 86.5 | 87.00 |
| 4. | 3 | 40 | 0.2 | 30 | 47.4 | 47.15 |
| 5. | 9 | 100 | 0.2 | 60 | 41.6 | 41.60 |
| 6. | 3 | 40 | 0.6 | 60 | 96.5 | 95.77 |
| 7. | 9 | 100 | 0.6 | 60 | 76.6 | 76.30 |
| 8. | 9 | 100 | 0.6 | 30 | 62.1 | 62.38 |
| 9. | 9 | 40 | 0.2 | 30 | 38.1 | 38.37 |
| 10. | 3 | 100 | 0.6 | 30 | 71.4 | 71.15 |
| 11. | 9 | 100 | 0.2 | 30 | 28.1 | 27.68 |
| 12. | 3 | 100 | 0.2 | 30 | 36.4 | 36.45 |
| 13. | 3 | 100 | 0.6 | 60 | 84.9 | 85.08 |
| 14. | 3 | 40 | 0.2 | 60 | 60.9 | 61.08 |
| 15. | 3 | 100 | 0.2 | 60 | 49.9 | 50.38 |
| 16. | 9 | 40 | 0.6 | 30 | 73.1 | 73.08 |
| S.No | Activated Carbon Precursor Material | Maximum Removal Efficiency (%) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Coffee husk | 97.65 | 23.2 | [42] |
| 2. | Spent coffee grounds | 95 | 187.6 | [43] |
| 3. | Parthenium hysterophorus | 90 | 1 | [44] |
| 4. | Water hyacinth | 90.4 | 6.02 | [38] |
| 5. | Amaranthus retroflexus | 81 | 108.14 | [45] |
| 6. | Garcinia kola hull | 96.25 | 3.86 | [46] |
| 7. | Spathodea campanulata | 96.5 | 10.65 | This work |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 6357.95 | 4 | 1589.49 | 9580.47 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A–pH | 308.00 | 1 | 308.00 | 1856.45 | <0.0001 | |
| B–Initial chromium concentration | 457.96 | 1 | 457.96 | 2760.31 | <0.0001 | |
| C–Adsorbent dose | 4816.36 | 1 | 4816.36 | 29,030.12 | <0.0001 | |
| D–Contact time | 775.62 | 1 | 775.62 | 4674.98 | <0.0001 | |
| Residual | 1.82 | 11 | 0.1659 | |||
| Cor Total | 6359.77 | 15 |
| Source | Std. Dev. | R2 | Adjusted R2 | Predicted R2 | PRESS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | 0.4073 | 0.9997 | 0.9996 | 0.9994 | 3.86 | Suggested |
| 2FI | 0.4806 | 0.9998 | 0.9995 | 0.9981 | 11.83 | |
| Quadratic | * | Aliased |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teweldebrihan, M.D.; Dinka, M.O. Adsorptive Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solution Utilizing Activated Carbon Developed from Spathodea campanulata. Sustain. Chem. 2025, 6, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem6010008
Teweldebrihan MD, Dinka MO. Adsorptive Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solution Utilizing Activated Carbon Developed from Spathodea campanulata. Sustainable Chemistry. 2025; 6(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem6010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeweldebrihan, Meseret Dawit, and Megersa Olumana Dinka. 2025. "Adsorptive Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solution Utilizing Activated Carbon Developed from Spathodea campanulata" Sustainable Chemistry 6, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem6010008
APA StyleTeweldebrihan, M. D., & Dinka, M. O. (2025). Adsorptive Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solution Utilizing Activated Carbon Developed from Spathodea campanulata. Sustainable Chemistry, 6(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem6010008






