Metal and Molecular Vapor Separation Analysis for Direct Determination of Mn and Cu by Atomic Absorption Detection, Free of Background Absorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus
2.2. Reagents and Procedures
3. Results
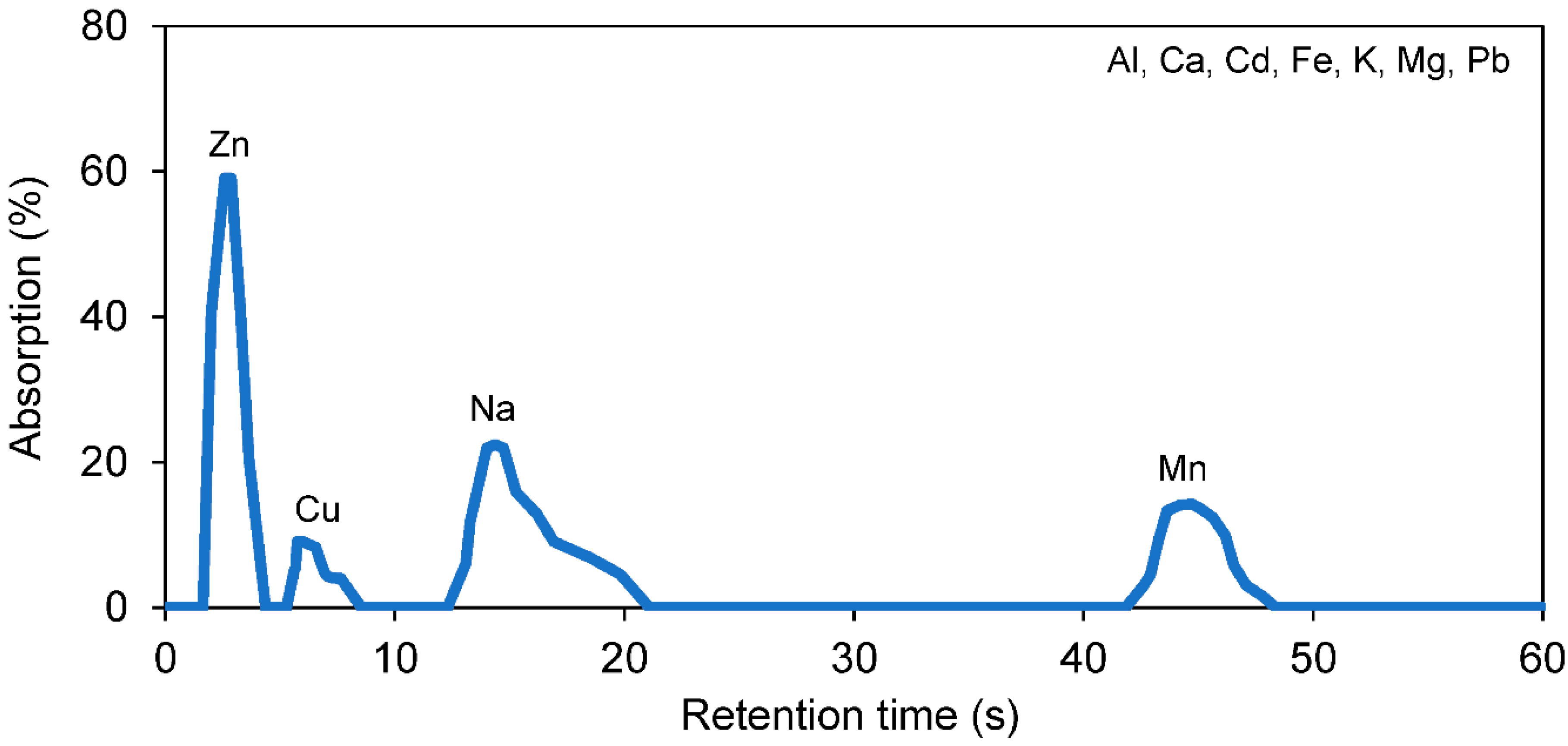
3.1. Separation of Cu and Mn by MMVSA
3.2. Effect of Ultrasonic Agitation
3.3. Direct Determination of Mn and Cu
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kriegerova, K.; Prochazkova, S.; Tucek, J.; Halko, R. Direct solid sampling in atomic absorption spectrometry with electrothermic atomization. Chem. Listy 2020, 114, 644–650. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, Z.; Yu, T.; Hou, Q.; Xia, X.; Gao, G.; Yang, R. Determination of Pb in geological materials by heat extraction slurry sampling ET-AAS. At. Spectrosc. 2020, 41, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Xing, P.; Zheng, H.; Hu, S. Plasma induced chemical vapor generation for atomic spectrometry: A review. Spectrochim. Acta B 2020, 167, 105822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserfalvi, T.; Mezei, P. Investigations on the element dependency of sputtering process in the electrolyte cathode atmospheric discharge. J. Anal. At. Spectom. 2005, 20, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chan, G.C.-Y.; Ray, S.J.; Zhang, X.; Hieftj, G.M. Use of a solution cathode glow discharge for cold vapor generation of mercury with determination by ICP-atomic emission spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 7043–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiderski, K.; Welna, M.; Greda, K.; Pohl, P.; Jamroz, P. Hanging drop cathode-atmospheric pressure glow discharge as a new method of sample introduction for inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 4211–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Bao, Z.; Zheng, H.; Hu, S. Determination of trace cadmium in rice by liquid spray dielectric barrier discharge induced plasma—Chemical vapor generation coupled with atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta B 2018, 141, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Peng, H.; Liu, Z.; Guo, W.; Hu, S. Cold vapor generation of Zn based on dielectric barrier discharge induced plasma chemical process for the determination of water samples by atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7523–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A.J.; Kelsey, L.; Williams, K.L.; Hieftjea, J.T. Atmospheric-pressure solution-cathode glow discharge: A versatile ion source for atomic and molecular mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 15, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, C. A portable solution cathode glow discharge-atomic emission spectrometer for the rapid determination of thallium in water samples. Talanta 2017, 173, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, K.; Uegomori, H.; Kaneco, S.; Mizuno, T. Sequential metal vapor elution analysis for the determination of Cu and Mn in biological materials and waters. Talanta 1999, 48, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, K.; Kawaguchi, K.; Uegomori, H.; Mizuno, T. Lead and zinc determination in copper alloys by sequential metal vapor elution analysis with an improved column. Chem. Anal. 1999, 44, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Daminelli, G.; Katskov, D.A.; Mofolo, R.M.; Tittarelli, P. Atomic and molecular spectra of vapors evolved in a graphite furnace. Part 1. Alkali halides. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 1999, 54, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J. Bioinformatics of metalloproteins and metalloproteomes. Molecules 2020, 25, 3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, A.W.; Young, T.R.; Chivers, P.T.; Robinson, N.J. Protein metalation in biology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2022, 66, 102095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lide, D. (Ed.) Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 85th ed.; CRC Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kulek de Andrade, C.; Klack de Brito, P.; Egea dos Anjos, V.; Quinaia, S. Determination of Cu, Cd, Pb and Cr in yogurt by slurry sampling electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry: A case study for Brazilian yogurt. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoog, D.; Holler, F.; Crouch, S. Principles of Instrumental Analysis, 7th ed.; Brooks/Cole Publishing Company: Devon, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
| Separation |
| MMVSA column: molybdenum column (250 mm long, 1.22 mm i.d.) |
| Transformer: YAMABISHI S-130-30, Cap. 3k VA, Tokyo, Japan |
| Power supply: KIKUSUI PAD 35–60L, Kikusui Denki Co., Yokohama, Japan |
| Detector (atomic absorption spectrometry) |
| Monochromator: Nippon Janell–Ash 0.5 m Ebert-type, Kyoto, Japan |
| Lock-in amplifier: NF LI-575, NF Circuit Design Block Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan |
| Storage oscilloscope: Kikusui 5516ST, Kikusui Denki Co., Yokohama, Japan |
| Computer: Dell Latitude 3310, Dell Japan Inc., Kanagawa, Japan. |
| Experimental conditions |
| Column temperature: 2170 K |
| Drying temperature: 350 K for 40 s |
| Pyrolysis temperature: 480 K for 10 s |
| Vaporization temperature: 2220 K |
| Purge gas: Ar 3000 mL min−1 + 200 mL min−1 H2 |
| Carrier gas: Ar 4.0 mL min−1 |
| Agitating time for solid sample: 5 min |
| Light source: Hollow cathode lamp (Hamamatsu photonics Co., Shizuoka, Japan) |
| Al 309.3 nm, Ca 422.7 nm, Cd 228.8 nm, Cu 324.8 nm, Fe 248.3 nm, K 766.5 nm |
| Mg 285.2 nm, Mn 279.5 nm, Na 589.0 nm, Pb 217.0 nm, Zn 213.9 nm |
| Sample | Element | Concentration (μg g−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Found | Certified Value | ||
| Apple leaves (SRM 1515) | Mn | 48.9 ± 6.0 | 53 ± 3 |
| Bovine liver (SRM 1577a) | Cu | 140 ± 22 | 158 ± 7 |
| Oyster tissue | Mn | 17.1 ± 1.4 | 17.5 ± 1.2 |
| (SRM 1566) | Cu | 60.9 ± 8.7 | 63.0 ± 3.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tateishi, I.; Furukawa, M.; Katsumata, H.; Kaneco, S. Metal and Molecular Vapor Separation Analysis for Direct Determination of Mn and Cu by Atomic Absorption Detection, Free of Background Absorption. Sustain. Chem. 2022, 3, 475-481. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem3040029
Tateishi I, Furukawa M, Katsumata H, Kaneco S. Metal and Molecular Vapor Separation Analysis for Direct Determination of Mn and Cu by Atomic Absorption Detection, Free of Background Absorption. Sustainable Chemistry. 2022; 3(4):475-481. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem3040029
Chicago/Turabian StyleTateishi, Ikki, Mai Furukawa, Hideyuki Katsumata, and Satoshi Kaneco. 2022. "Metal and Molecular Vapor Separation Analysis for Direct Determination of Mn and Cu by Atomic Absorption Detection, Free of Background Absorption" Sustainable Chemistry 3, no. 4: 475-481. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem3040029
APA StyleTateishi, I., Furukawa, M., Katsumata, H., & Kaneco, S. (2022). Metal and Molecular Vapor Separation Analysis for Direct Determination of Mn and Cu by Atomic Absorption Detection, Free of Background Absorption. Sustainable Chemistry, 3(4), 475-481. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem3040029





