Abstract
Herein, an inexpensive commercially available sensor is presented for the detection of 4-nitrophenol (4NP) pollutant. Sodium fluorescein (NaFl) is used as a sensor to detect trace amounts of 4NP in acetonitrile (MeCN). The photophysical properties of NaFl were studied in two different solvents, MeCN (aprotic) and water (protic), with varying concentrations of different nitroaromatics using UV-visible absorption and fluorescence spectrophotometry. In an aqueous medium, photophysical properties of NaFl did not change in the presence of nitroaromatics. However, examination of the photodynamics in MeCN demonstrated that NaFl is extremely sensitive to 4NP (limit of detection: 0.29 µg/mL). This extreme specificity of NaFl towards 4NP when dissolved in MeCN, as compared to other nitroaromatics, is attributed to hydrogen bonding of 4NP with NaFl in the absence of water, resulting in both static and dynamic quenching processes. Thus, NaFl is demonstrated as a simple, inexpensive, sensitive, and robust optical turn off sensor for 4NP.
1. Introduction
Nitroaromatics are a class of industrial chemicals generally used in dyes, polyurethane foams (material found in mattresses and other furniture items), herbicides, insecticides, nuclear weapons, and explosives [1]. As a result of widespread industrial usage, nitroaromatic pollutants are quite common and found primarily as derivatives of nitrotoluenes, nitrophenols, and nitrobenzenes [2]. Due to their widespread use, the detection of such compounds is extremely vital in many areas including military and civilian safety, the chemical industry, and environmental monitoring [3,4]. Among the various derivatives of nitroaromatics, the pollutant 4-Nitrophenol (4NP), is especially harmful to the human body [5]. This pollutant can irritate and cause inflammation of the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract as well as trigger allergic responses. When ingested, 4NP can cause abdominal pain and vomiting [6]. Furthermore, it can also cause confusion and unconsciousness due to 4NP-induced methemoglobinemia [2]. Hence, 4NP has been listed as a priority pollutant by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) due to its toxicity and environmental persistence [7]. Consequently, it is very important to detect 4NP in the environment.
Based on the arguments mentioned earlier, there is a great need for the development of a highly sensitive sensor for 4NP in order to protect the environment, human health, homeland security, and civilian safety [3]. Techniques such as liquid chromatography [8], gas chromatography–mass spectrometry [9], 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance [10], energy dispersive X-ray diffraction [11], and surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy [12] have been employed for the detection of 4NP with high sensitivity. However, these methods are often expensive and inconvenient for use outside of the laboratory. Therefore, an easy and prompt method is needed for 4NP detection.
Simple optical methods have also been applied for nitroaromatic detection. In this regard, numerous studies have been devoted towards examining the photophysical properties of novel fluorescent materials such as Zn (salicylaldimine) complexes [13], N,N’-bis(3-pentyl)perylene-3,4,9,10-bis(dicarboximide) [12], quantum dots [5,14,15], etc., for nitroaromatics detection. Synthesis of such optical organic sensors often involves multistep and time-consuming protocols that result in costly materials with low product yields. In contrast, herein, a reliable approach is introduced using the well-known, low-cost, and commercially available compound, sodium fluorescein (NaFl), for the detection of 4NP with high sensitivity and selectivity. We note that NaFl is one of the most widely studied fluorescent compounds. However, to the best of our knowledge, it has never been reported as a sensor for nitroaromatics [3].
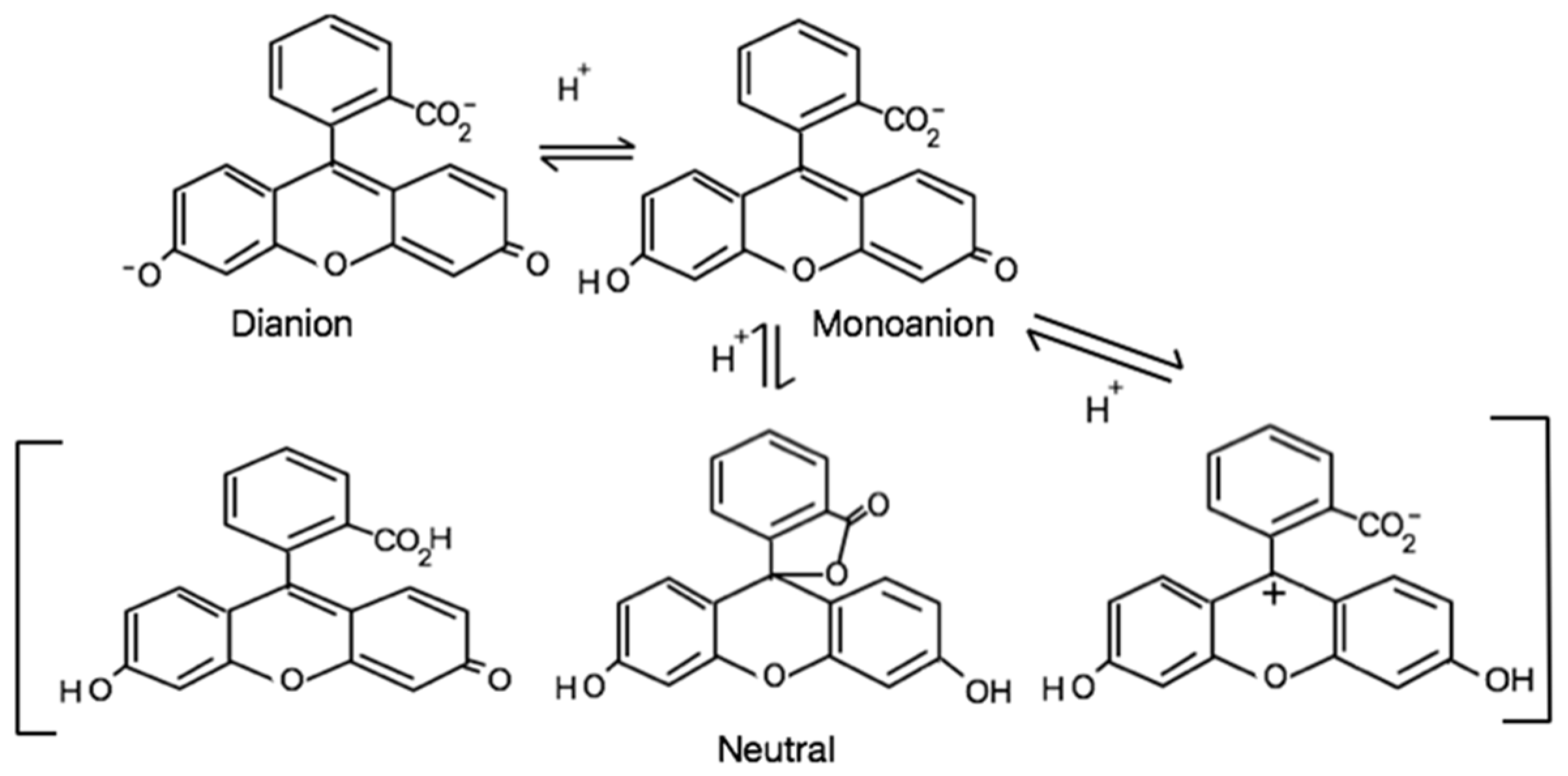
NaFl is a highly fluorescent, reasonably photostable, and biocompatible xanthene dye [16,17,18]. Since the late 1900s, NaFl has been widely employed to locate tumors or abnormal tissues using the naked eye with UV light in ophthalmic [19] and neuro-oncologic surgery [20]. In aqueous solution, fluorescein exists in different prototropic forms (as depicted in Scheme 1) under various pH conditions that exhibit very different photophysical properties [18,21]. The spectral properties of the dianion species significantly depends on the hydrogen bonding environment [22]. The dianion form of fluorescein is highly fluorescent as compared to the monoanionic form while the neutral form is nonfluorescent [23]. However, there is at least one report that concludes that among three conformations of the neutral form, one neutral fluorescein specie exhibits some fluorescence characteristics with a quantum yield value of 0.29 [24]. Significant changes in the photophysical properties of NaFl are directly correlated to the neutral, monoanionic, and dianionic forms of fluorescein. Therefore, these properties have been previously used to create a wide variety of optical pH sensors employing fluorescein [25,26].
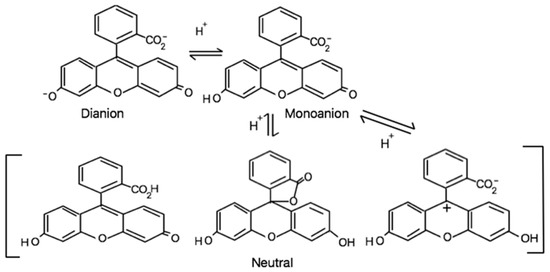
Scheme 1.
Different structural forms of fluorescein (NaFl).
In this study, an affordable and commercially available NaFl compound was selected for the development of an optical sensor selective for 4NP, as compared to other nitroaromatics, due to the possibility of (1) π-π and (2) hydrogen bonding interactions between these two molecules. The intermolecular hydrogen bond between 4NP and NaFl may play a key role in tailoring the photophysical response of NaFl, while alteration of charge distribution upon excitation of NaFl can affect this hydrogen bond formation [27]. Finally, the formation of protonated (monoanionic or neutral) forms directly affects the fluorescence intensity of NaFl [28]. ln general, a slight change is expected in the absorption and fluorescence emission spectra of NaFl in the presence of nitroaromatics due to π-π interactions. It has been shown that hydrogen bonding can cause fluorescence quenching in coumarin and PRODAN-based dyes [29,30]. Herein, the same hydrogen bonding concept is used to tailor the photophysical properties of fluorescein in the presence of 4NP for a unique sensor application.
In order to assess the contribution of the π-π and hydrogen bonding interactions of nitroaromatics on the photophysical properties of NaFl, two different solvents, specifically water (H2O) (protic, hydrogen bonding solvent) and acetonitrile (MeCN) (aprotic, no hydrogen bonding), were used. The photophysical properties of NaFl were investigated in the presence of different concentrations of four different nitroaromatics separately in two solvents. The photodynamics of NaFl in contact with different nitroaromatics were examined to investigate the selectivity and sensitivity of the NaFl sensor towards nitroaromatics. In addition, a portable and disposable paper-based sensor was developed and tested for nitroaromatics. This approach proved to be unique, simple, and inexpensive as compared to other existing methods and technologies currently available for the detection of toxic nitroaromatic compounds. Thus, this approach may be useful for distinguishing other pollutants using NaFl as a sensor.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
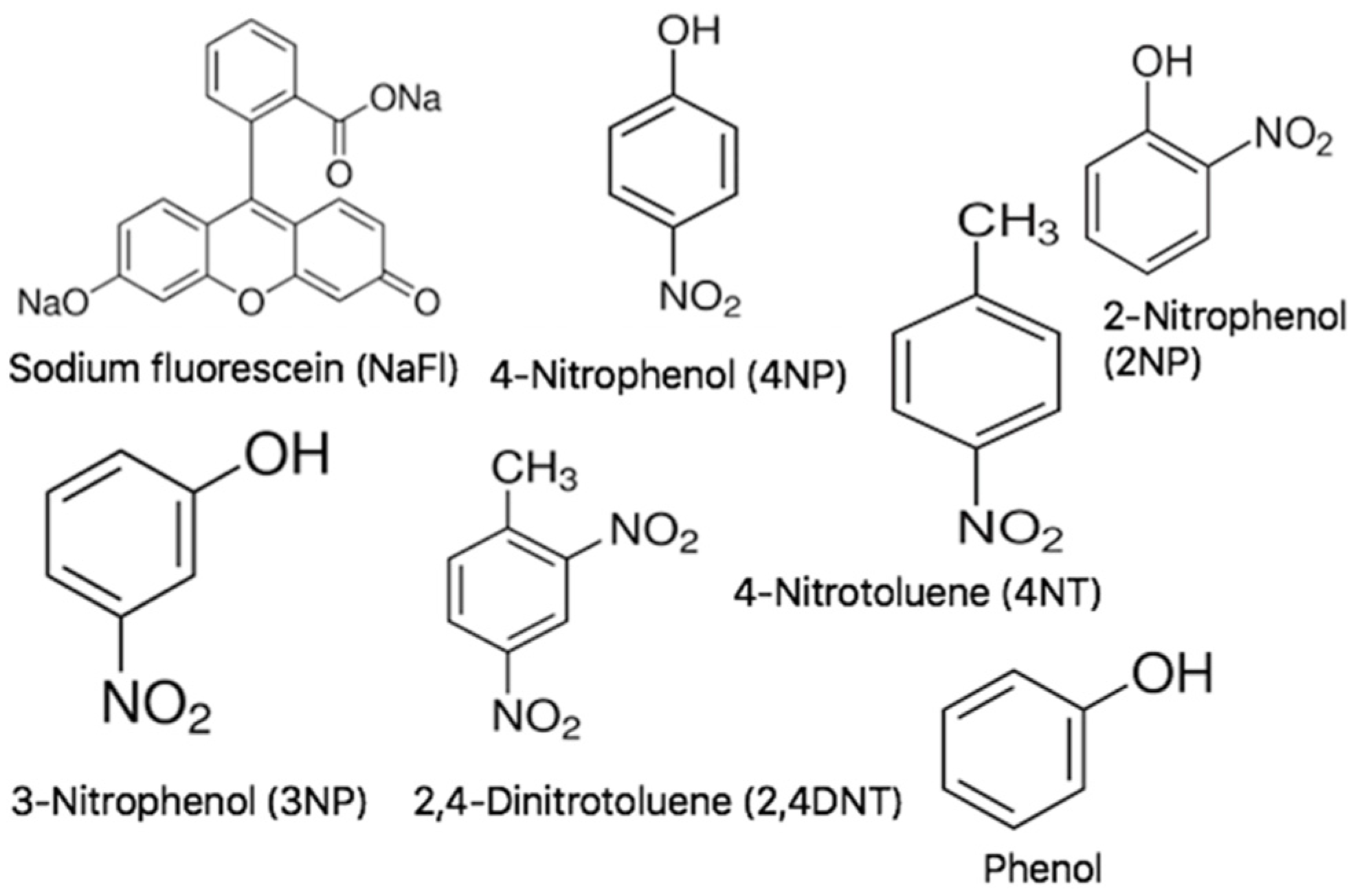
NaFl, four nitroaromatic pollutants, i.e., 4-NP, 3-nitrophenol (3NP), 4-nitrotoluene (4NT), 2-nitrophenol (2NP), phenol, and 2,4-dinitrotoluene (2,4DNT) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and used as received. The structures of NaFl and the nitroaromatics are given below in Scheme 2. MeCN was purchased from J.T. Baker. Triply deionized (DI) water (18.2 MΩ cm) was obtained by use of an Elga model PURELAB ultra water-filtration system. Laboratory grade hydrochloric acid (HCl), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and chloroform were purchased from VWR. N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) was obtained from Alfa Aesar. Tetrahydrofuran (THF) and chloroform were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
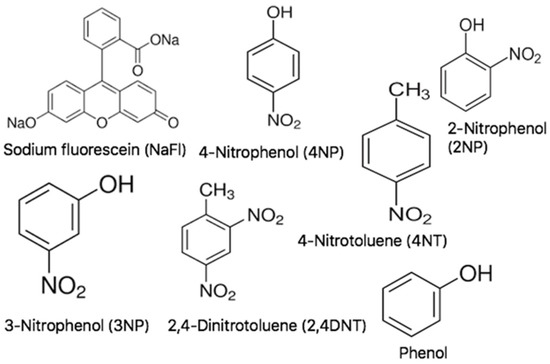
Scheme 2.
Structure of NaFl and nitroaromatics and phenol.
2.2. Optical Measurements
Cary 5000 UV-VIS-NIR spectrophotometer was used for absorbance measurements. All fluorescence measurements were performed using a Spex Fluorolog-3 spectrofluorometer (model FL3-22TAU3); Jobin Yvon, Edison, NJ, USA). A 1 cm pathlength quartz cuvette (Starna Cells from Atascadero, CA, USA) was used for fluorescence measurements. All fluorescence studies were performed using right angle geometry. A 1 cm pathlength quartz cuvette was used for absorbance measurements, while referencing against an identical cell filled with water or MeCN as the blank solvent.
A UV lamp model UVG-54 Mineralight® lamp (short wave UV-254 nm, 115 volts 60 Hz, 0.16 amps) was used to investigate fluorescence quenching on portable paper-based sensor when exposed to nitroaromatics.
2.3. Sensitivity of NaFl to Nitroaromatics in Aqueous Solution
Initially, stock solutions of 1 mM of NaFl and nitroaromatics (4NP, 3NP; 4NT, 2,4DNT) solutions were prepared separately in water. To test the sensitivity of NaFl towards nitroaromatics in aqueous solution, a total of 66 sample vials were prepared using a constant 50 µM NaFl solution and 10 different concentrations of the five nitroaromatic and phenol solutions. Each concentration was tested in triplicate, for an aggregate test data set of 198 sample vials (66 × 3). The composition of each sample vial tested is presented in Table S1 of Supporting Information. Absorption and fluorescence emission spectra of NaFl in the presence of selected nitroaromatics were recorded.
2.4. Sensitivity of NaFl to Nitroaromatics in MeCN Solution
The absorption and fluorescence emission of NaFl were studied in the presence of different nitroaromatics in MeCN medium. A Branson 3510RDTH bath ultrasonicator (40 kHz) was used to prepare NaFl solutions in MeCN. Since NaFl is partially soluble (not highly soluble) in MeCN, a small aliquot of NaFl stock solution prepared in water was rapidly added to 5 mL of MeCN under sonication and allowed to sonicate for an additional 30 min. Similar to earlier tests in aqueous media, three trials of 10 test solutions were prepared in MeCN, where NaFl concentration was held constant while the concentrations of nitroaromatics varied.
2.5. Sensitivity of NaFl to Nitroaromatics on an Economical Filter Paper (as a Solid Phase Sensor)
In order to develop a portable sensor, ashless filter paper and glass fiber paper were cut into small rectangular strips (0.5 in × 1.75 in). A NaFl solution was prepared in MeCN solvent. A paper strip was then immersed in the NaFl solution for 5 min and air dried for 15 min. Subsequently, 10 µL aliquots comprised of varying concentrations of individual nitroaromatics were tested on the paper strips containing NaFl to observe changes in fluorescence under UV lamp illumination.
2.6. Electrochemical Analysis
Cyclic voltammetry experiments were performed using a silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) reference electrode and platinum working and reference electrodes at a scan rate of 50 mV/s from −1 V to 0 V. A solution of 0.1 M tetrabutylammonium hexafluorophosphate was used as supporting electrolyte. A 0.1 mM solution of 4NP was prepared in MeCN and 1 mM solution of NaFl was prepared in water. The cyclic voltammogram was recorded for 4NP in the absence of NaFl. After adding a few microliters of 1 mM NaFl into the 4NP and supporting electrolyte solution, the cyclic voltammogram was recorded in order to investigate proton transfer from 4NP to NaFl.
3. Results and Discussion
In order to develop a colorimetric sensor for nitroaromatics on the basis of hydrogen bonding interactions, solvent choice is very important. In this regard, a solvent that can dissolve nitroaromatics and is miscible with NaFl aqueous solution is most desirable. In addition, the chosen solvent should avoid hydrogen bonding interactions with nitroaromatics. For this reason, Kamlet and Taft parameters of different solvents were investigated prior to experimentation. A list of Kamlet and Taft parameters for different solvents are tabulated in Table S2 of Supporting Information. A solvent with high alpha values acts as a hydrogen bonding donor and a solvent with high beta values serves as a hydrogen bond acceptor. In this study, NaFl was used to develop an inexpensive ratiometric and fluorescent sensor for 4NP due to possible π-π and hydrogen bonding interactions between these two molecules. Absorption spectra of 4NP were also recorded in different solvents (Figure S1 of the Supporting Information). The peak in the region of 400 nm was assigned to hydrogen bonding interactions of 4NP with a solvent. Examination of the spectra revealed hydrogen bonding interactions of the phenolic group of 4NP with all other solvents except MeCN. Therefore, all solvents with hydrogen bond donor and acceptor capabilities were avoided to achieve the best response upon interactions of NaFl with 4NP. Thus, MeCN was used for additional experiments. Absorption and fluorescence spectra of NaFl and 4NP were also recorded in water as an example of a hydrogen bonding solvent, in order to validate that hydrogen bonding interactions were playing a key role in developing this turn off fluorescent sensor for 4NP.
Initially, absorption and fluorescence spectra of each compound, NaFl and nitroaromatics, were recorded at various concentrations in a hydrogen bonding solvent (water) as well as in a non-hydrogen bonding solvent (MeCN), separately, using a UV-Vis absorption spectrophotometer and a fluorescence spectrophotometer. Absorption wavelength maxima, molar absorptivity, and fluorescence emission maxima for NaFl and nitroaromatics in different solvents are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Absorption and fluorescence emission maxima and the molar extinction coefficient of all compounds in water and MeCN.
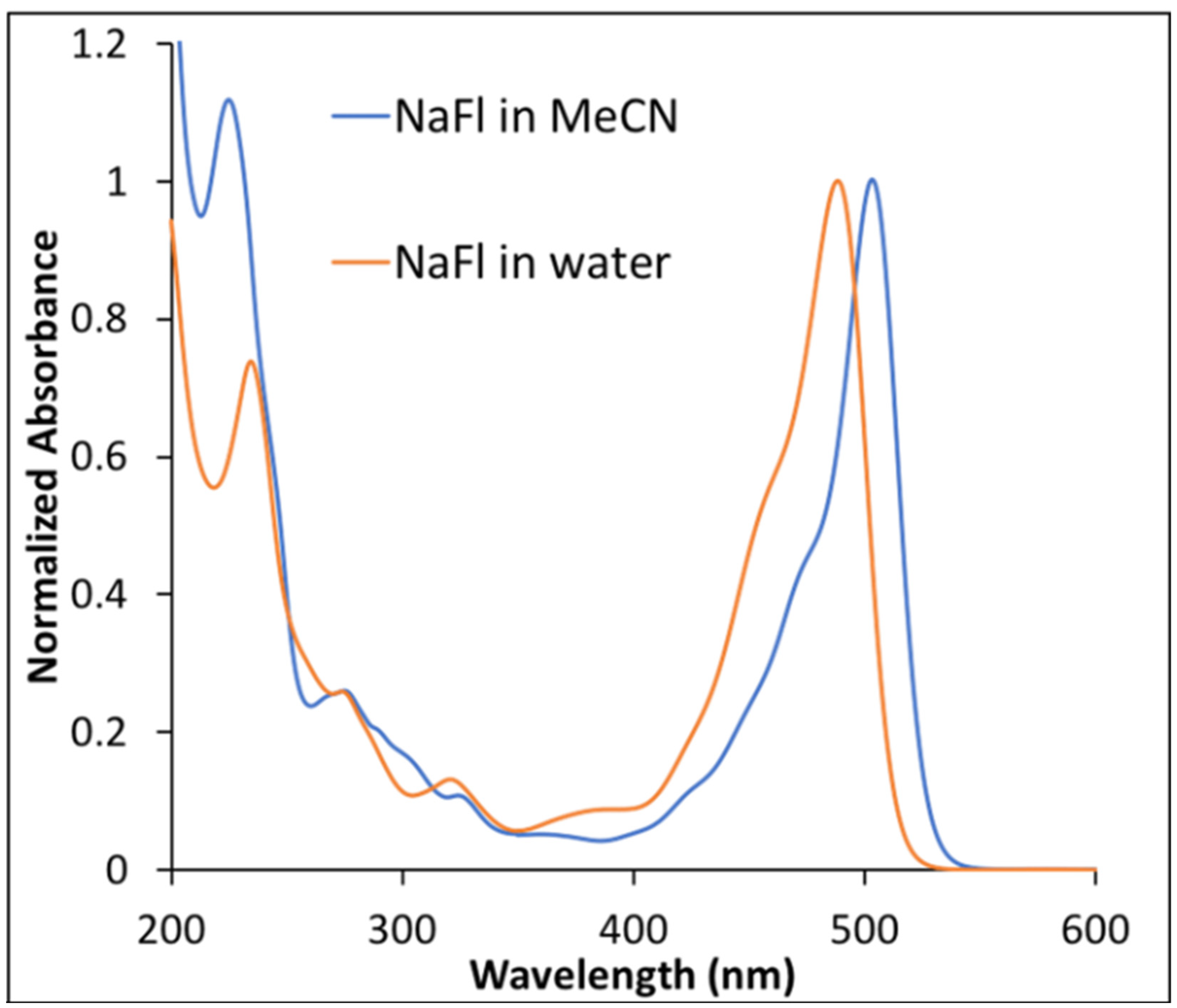
Examination of absorption spectra for NaFl, recorded in two different solvents, revealed a shift of approximately 10 nm at peak maxima (Figure 1). A bathochromic shift of NaFl peak maxima in MeCN was observed, which is consistent with previously reported work [16]. This shift is very well correlated with the α and β parameters of Kamlet and Taft [31,32]. The absorption spectra of NaFl in water, a protic solvent, exhibited an absorption peak maxima at shorter wavelength, which was attributed to hydrogen bonding in comparison to MeCN, an aprotic solvent with no tendency to hydrogen bond [18].
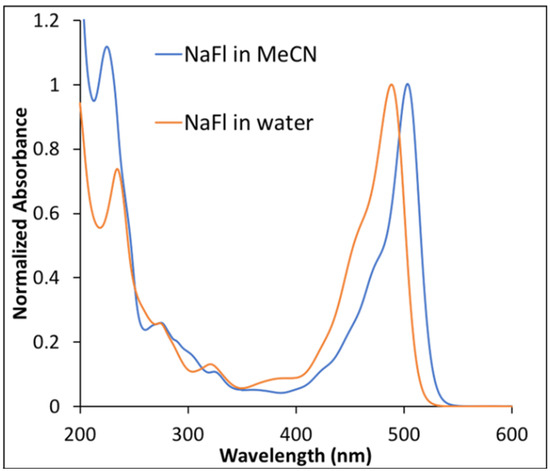
Figure 1.
Normalized absorption spectra of NaFl in water and in MeCN.
NaFl was excited at 490 nm and 510 nm for water and the MeCN solvent, respectively. The fluorescence emission spectra of NaFl in the two solvents were similar in shape, with a difference in peak maxima of 10 nm (Figure S2 of the Supporting Information), as observed for the absorption spectra (Figure 1).
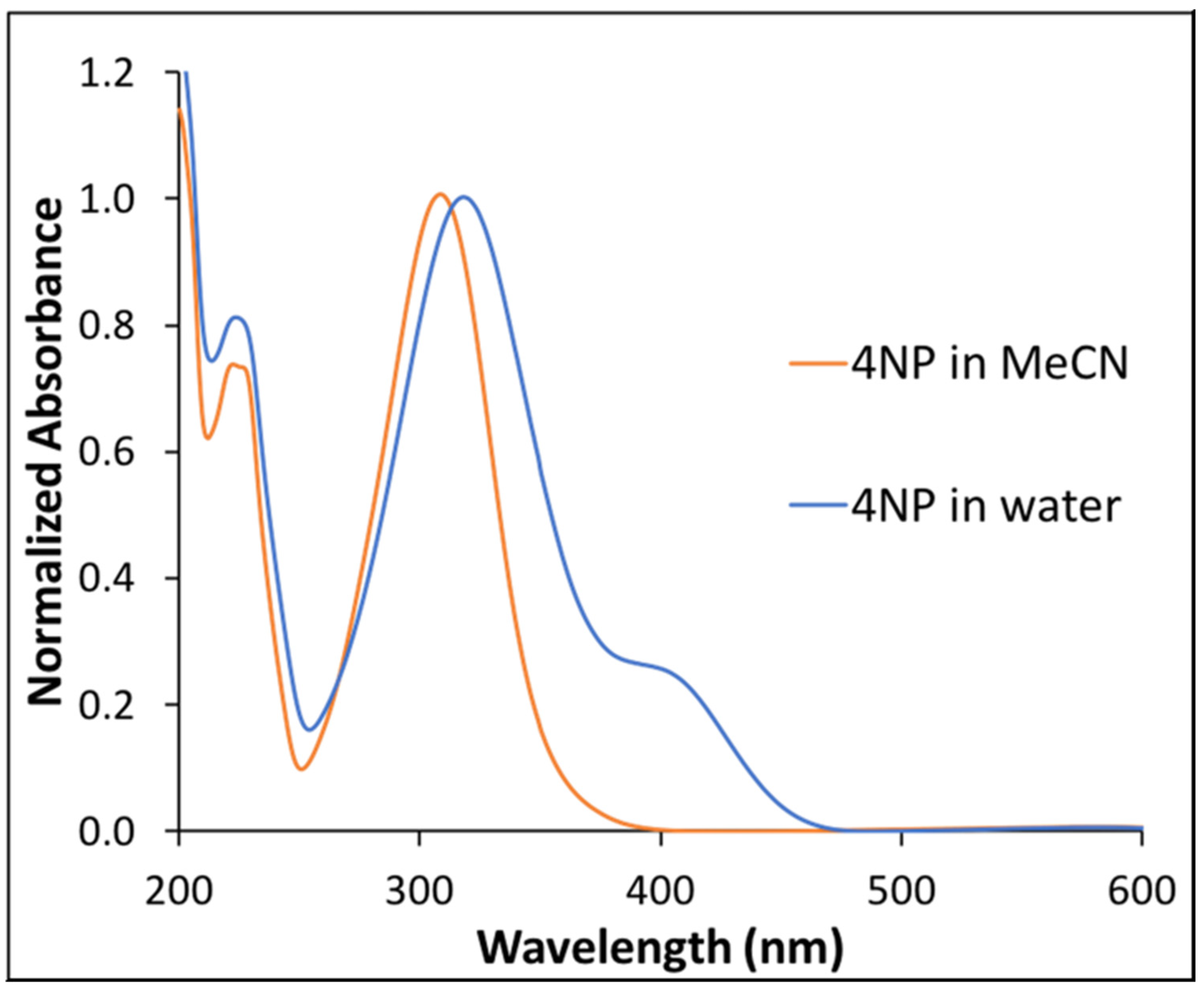
A very interesting change in absorption spectra of the solvated 4NP was observed when comparing the two different solvents. Notably, a single peak for 4NP at 312 nm (peak maxima) was observed in MeCN (Figure 2) while a broad absorption spectrum was observed in water. As shown in Figure 2, a bathochromic shift of peak maxima (322 nm) was observed in water. In addition, a shoulder at 410 nm was observed in the absorption spectrum of 4NP in water, which was not observed in MeCN. The additional shoulder peak was attributed to hydrogen bonding interactions between the phenolic hydrogen of 4NP and water. The red shift of the 4NP absorption peak suggests that the excited state of 4NP is more polar as compared to the ground state [33].
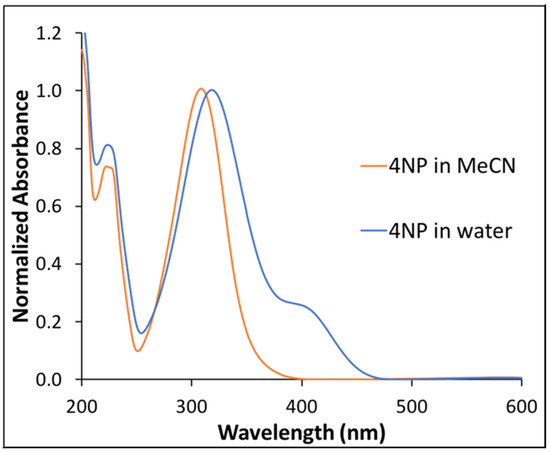
Figure 2.
Normalized absorption spectra of 4NP in water and in MeCN.
The absorption spectra for four other nitroaromatics and phenol in two different solvents (water and MeCN) are presented in Figure S3 of Supporting Information. Similar to 4NP, a slight bathochromic shift was observed for other nitroaromatics in water. No significant changes in the shape of the absorption spectra for other nitroaromatics were observed in protic and aprotic solvents. In contrast to 4NP, no additional peak was observed in other nitroaromatics due to hydrogen bonding. Since all nitroaromatics are nonfluorescent molecules, no fluorescence emission results are presented for these nitroaromatics.
3.1. NaFl Sensor for Nitroaromatics in Aqueous Media
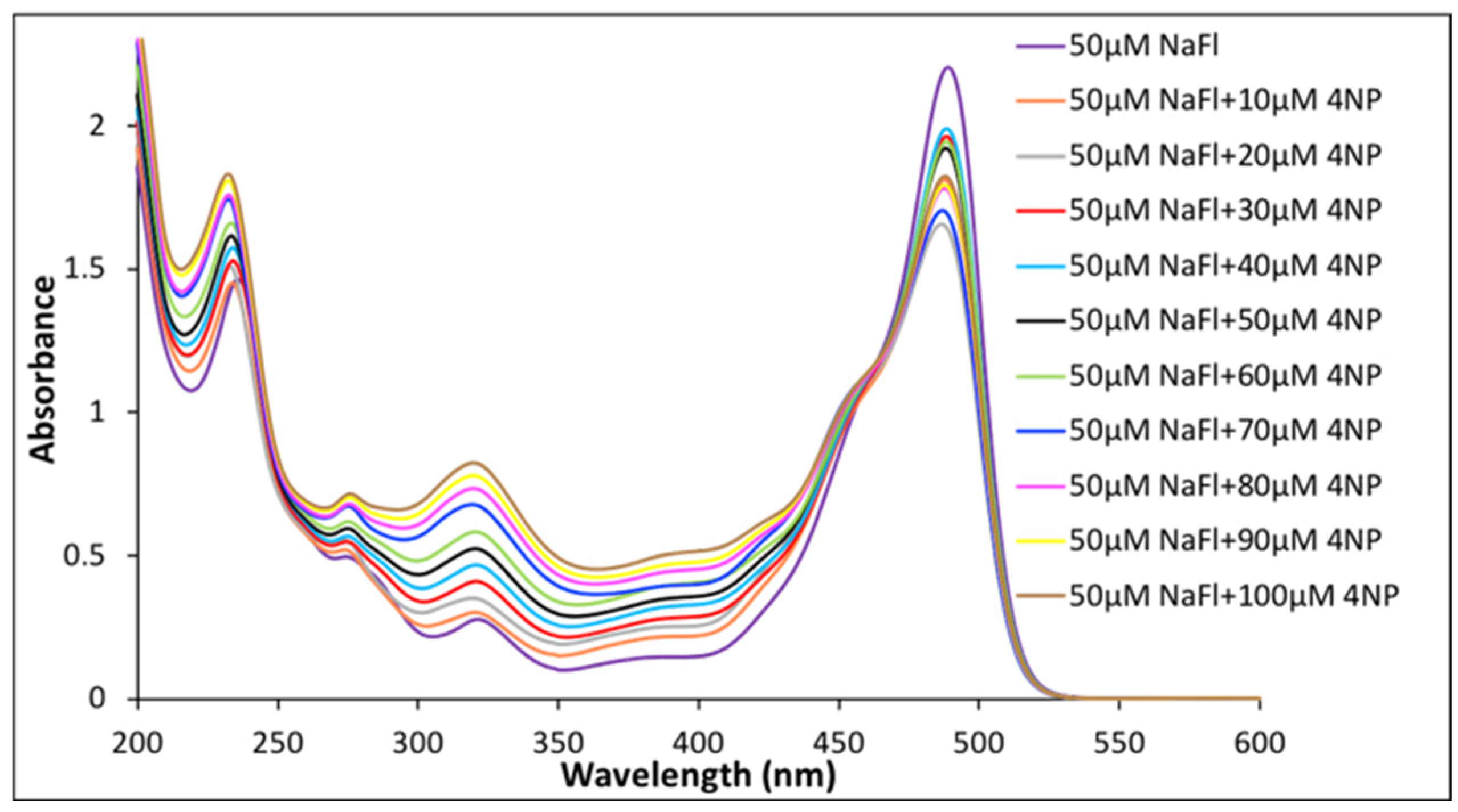
The photophysical properties for a fixed concentration of NaFl in the presence of different concentrations of nitroaromatics in aqueous media were studied. First, NaFl was exposed to 10 different concentrations of 4NP. Similar to the pure aqueous solution of NaFl, the absorption peak maxima for NaFl was observed at 490 nm in the presence of 4NP (Figure 3). The peak intensity of 4NP at 320 nm increased as the concentration of 4NP increased in the solution mixture, while a slight decrease was observed for absorbance of NaFl. The observed decrease in absorbance of the peak maxima of NaFl is attributed to weak interactions between 4NP and NaFl in aqueous media.
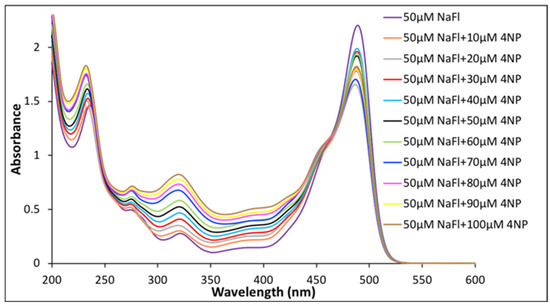
Figure 3.
Absorbance spectrum of 50 µM of NaFl in presence of different concentrations of 4NP in water.
Fluorescence emission spectra were recorded for the aforementioned solutions presented in Table S1 of Supporting Information. No change was observed in fluorescence emission intensity with increases in the concentration of 4NP in water (Figure S4 of the Supporting Information). Similarly, absorption and fluorescence spectra of NaFl were recorded in the presence of four other nitroaromatic compounds (3NP, 4NT, 2,4DNT, 2NP) and phenol in aqueous media. As with 4NP, no significant alterations in the photophysical properties of NaFl were observed in the presence of these nitroaromatics in aqueous media. Absorbance and fluorescence emission spectra for NaFl in the presence of other nitroaromatics in aqueous solution are not presented here.
3.2. Testing of Nitroaromatics Using NaFl in MeCN
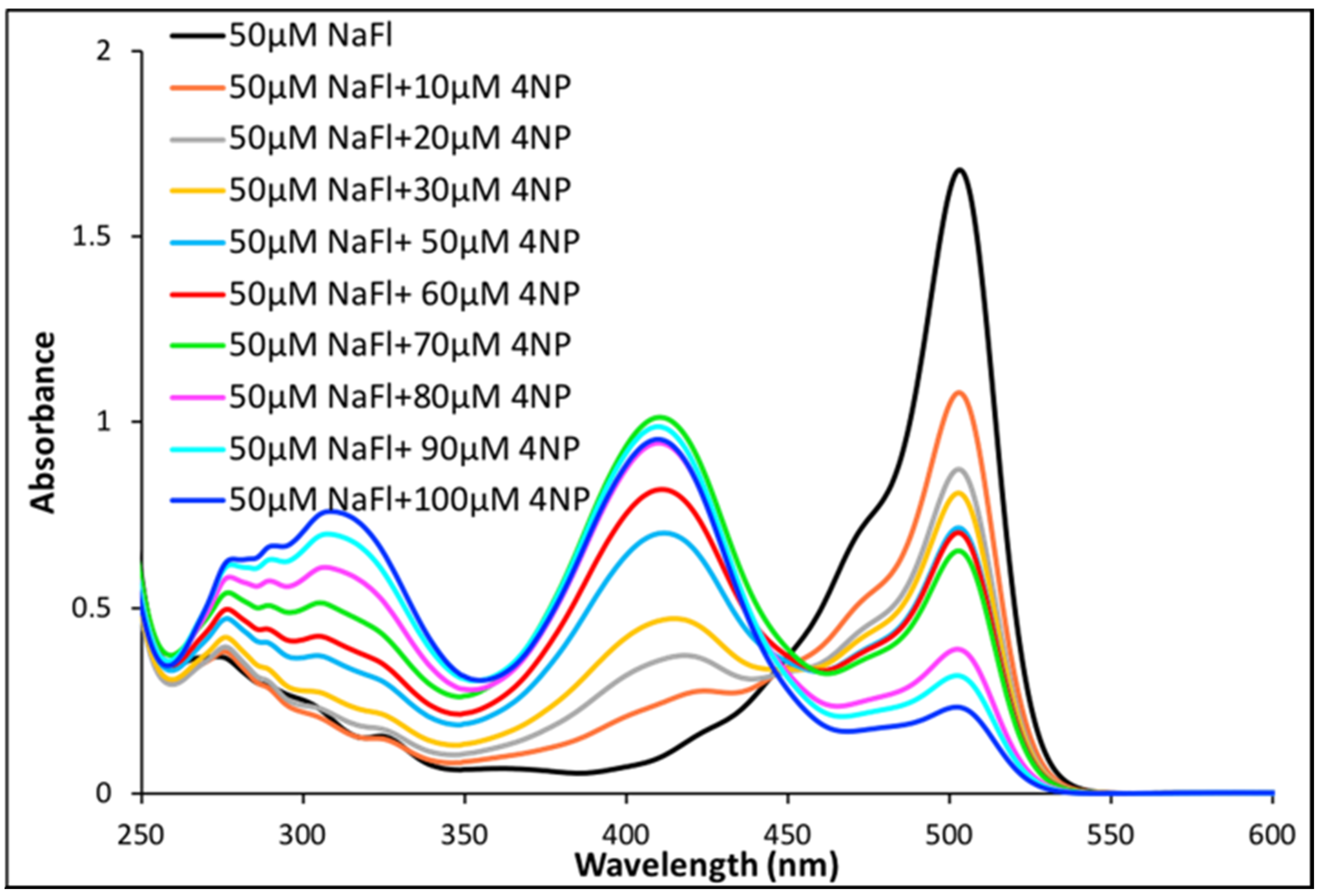
In order to investigate the photophysical properties of NaFl in the presence of nitroaromatics in MeCN solutions, absorption and emission spectra were acquired. Three distinct peaks were observed in the absorption spectra when different concentrations of 4NP in MeCN were mixed with a fixed concentration of 50 µM NaFl solution (Figure 4). The peak maxima at 515 nm was ascribed to NaFl (as observed in Figure 1) while the two peaks, approximately at 315 nm and 410 nm, were attributed to 4NP (Figure 4). Notably, a very strong peak at 410 nm is observed in the mixture of 4NP and NaFl in MeCN, as compared to a weak peak signal at 410 nm observed for pure 4NP solvated in water (Figure 2). The change in peak intensity is attributed to hydrogen bonding (Figure 2). In MeCN media, pure 4NP exhibited only one peak due to the absence of hydrogen bonding with the solvent (Figure 2). Additionally, the strong 410 nm peak was not observed for mixtures of NaFl and 4NP in the aqueous medium (Figure 3) due to the peak overlap of NaFl and 4NP. The very strong peak at 410 nm observed in MeCN media is attributed to hydrogen bonding interactions between the phenolic hydrogen of 4NP and the oxygen of NaFl. Strong interaction between NaFl and 4NP is only possible in the absence of a hydrogen bonding solvent (e.g., water). In an aqueous medium, both 4NP and NaFl are more likely to exhibit hydrogen bonding interactions with the aqueous solvent. Furthermore, interesting spectral behavior was observed when a constant concentration of NaFl solution in MeCN was used for 4NP sensing. A continuous decrease in NaFl absorption intensity was observed with increased concentrations of 4NP (Figure 4). As expected, a continuous increase in absorbance intensity of 4NP at 315 nm was observed with increased concentration of 4NP. Observation of the absorbance results suggest a ratiometric trend between the absorption peaks of NaFl and 4NP, which demonstrates that increased amounts of 4NP concentration have significant effects on NaFl absorbance. These results contradict with the observation recorded in the NaFl aqueous solution in the presence of 4NP. In that study, the absorption intensity of the NaFl aqueous solution remained negligible, while it significantly reduced for the NaFl solution in MeCN at different concentrations of 4NP. Based on these results, it is obvious that MeCN media (a non-hydrogen bonding solvent) is more suitable for the detection of 4NP. This unique observation led us to investigate the intermolecular interactions between NaFl and 4NP in MeCN media.
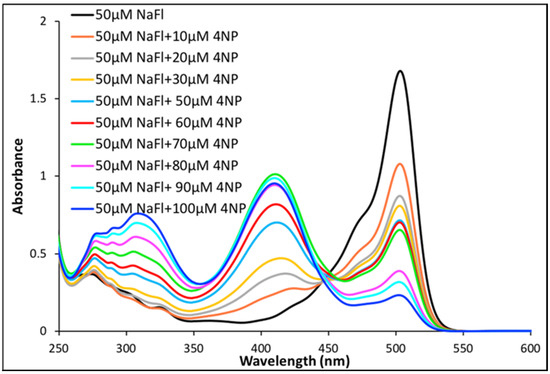
Figure 4.
Absorption spectra of NaFl in the presence of different concentration of 4NP in MeCN.
As indicated in Table S1 of Supporting Information, the solution mixture of NaFl and 4NP contain a fixed 250 µL of water in each 5 mL solution of MeCN. In order to determine if the peak observed at 410 nm is due to interactions between 4NP and water or between 4NP and NaFl, another experiment was performed where the volume of water was altered in the microliter range, while the total volume of the solution was held constant at 5 mL MeCN. As displayed in Figure S5 of Supporting Information, the peak at 410 nm was not observed in pure MeCN, while an increase in intensity at 410 nm was observed as the amount of water increased in the constant concentration of 4NP (50 µM) in MeCN due to hydrogen bonding interactions of the phenolic group of 4NP with water. The volume of water was constant in the mixture of NaFl and 4NP solution in MeCN. Thus, the continuous increase in intensity at 410 nm is attributed to hydrogen bonding interactions between 4NP and fluorescein (Fl).
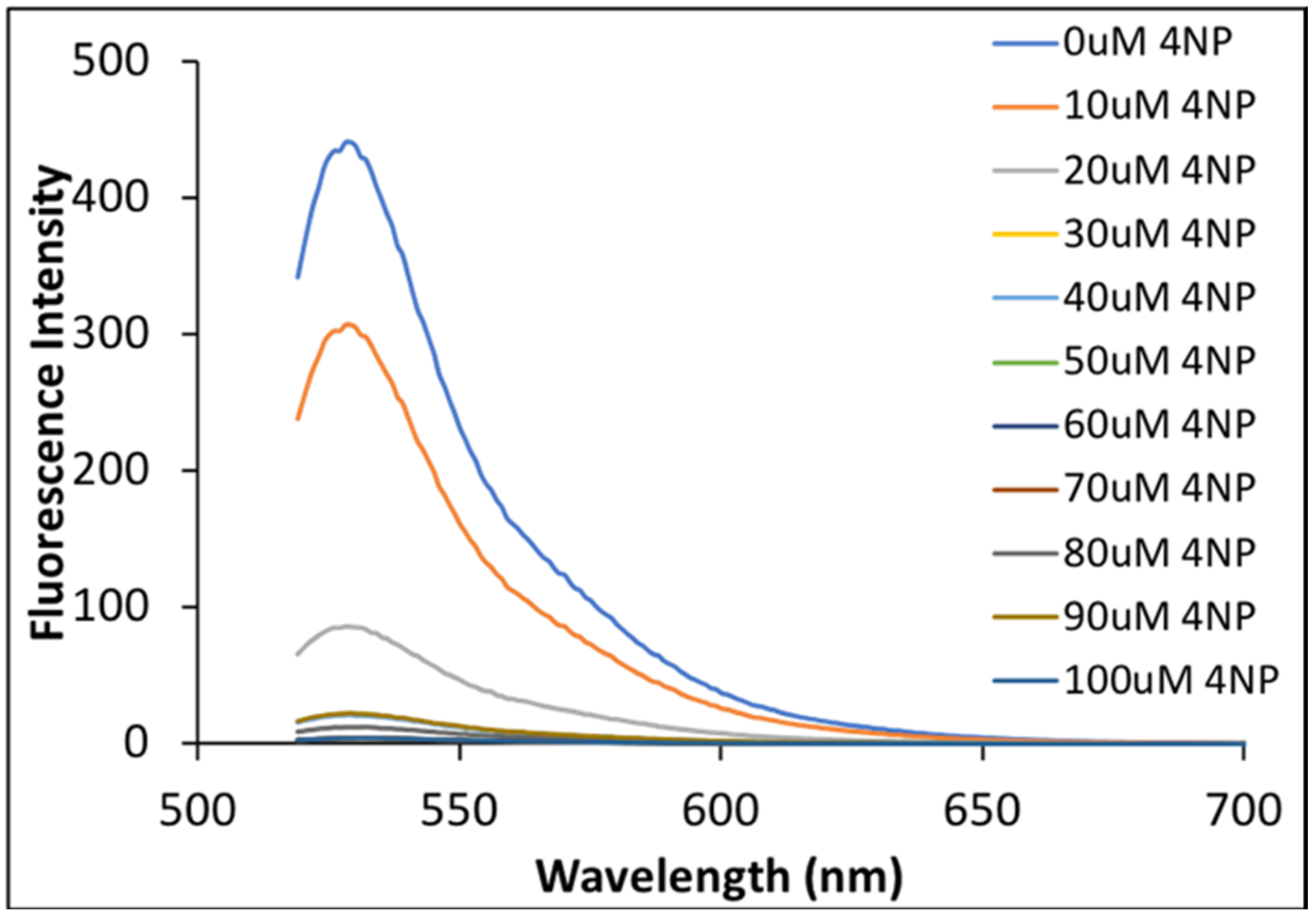
Fluorescence spectra for all solutions of NaFl in the presence of varying concentrations of 4NP in MeCN were recorded. Fluorescence emission of NaFl decreased significantly as the concentration of 4NP increased (Figure 5). A slight decrease in NaFl fluorescence emission signal was expected since the absorption intensity of NaFl was also lowered. However, the fluorescence emission of NaFl was completely quenched at higher concentrations of 4NP. This significant quenching of absorption and fluorescence intensities is attributed to enhanced hydrogen bonding and π-π interaction of 4NP with NaFl in MeCN media in the ground state. Ratiometric behavior in absorption spectra, and substantial changes in fluorescence intensities were not observed in aqueous media. Experiments were conducted in triplicate and reproducibility confirmed for these measurements. Thus, we conclude that NaFl can be used to selectively detect 4NP in MeCN media.
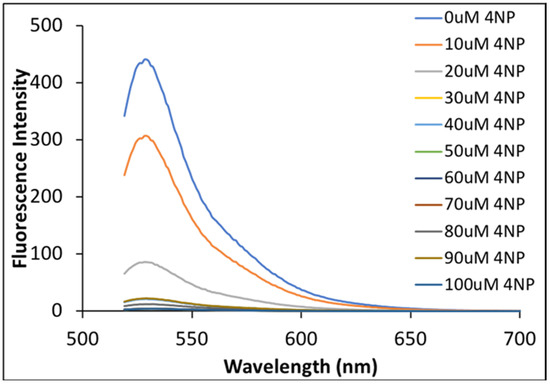
Figure 5.
Fluorescence emission spectra of NaFl in the presence of different concentrations of 4NP in MeCN at an excitation wavelength of 510 nm.
Neither the ratiometric response in absorption spectra, nor significant trends in the quenching of NaFl fluorescence emission spectra in the presence of other nitroaromatics (2NP, 3NP, 2,4DNT, 4NT and phenol in MeCN was observed (Figures S6 and S7 of the Supporting Information). While all nitroaromatics exhibit π-π interactions, examination of data suggests that π-π interactions are not likely playing a key role in tailoring the photophysical properties of NaFl observed in the presence of 4NP since π-π interactions are possible with all nitroaromatics. Therefore, hydrogen bonding must be a crucial parameter for diminishing the absorption and fluorescence emission intensity of NaFl for developing a selective turn off NaFl sensor for 4NP.
Nitroaromatic compounds such as 2,4DNT and 4NT do not have polar hydrogen atoms that can participate in hydrogen bonding, making it impossible to observe ratiometric turn off behavior for these compounds via this mechanism. However, 3NP and 2NP possess a phenolic group that could facilitate similar ratiometric behavior or quenching of NaFl. However, no changes were observed in NaFl spectral responses with 4NT, 2,4,DNT, 3NP, 2NP, and phenol (Figures S6 and S7 in the Supporting Information). The dissimilar spectral response of NaFl in the presence of 4NP, 2NP, and 3NP solvated in MeCN is explained by the hydrogen bonding donor abilities of 4NP, 2NP, and 3NP. The electron withdrawing nitro group at the ortho and para position enhances the acidic character of hydrogen in 2NP and 4NP. This is supported by observing the pka values of 4NP, 2NP, and 3NP, which were 7.15, 7.23, and 8.40 respectively [34,35]. Observation of the pka values suggests that 4NP and 2NP have a better tendency to donate a proton as compared to 3NP. The observed tremendous changes in the absorption as well as fluorescence intensity of NaFl is attributed to the stronger hydrogen donating ability of 4NP. However, 2NP did not exhibit similar behavior as 4NP due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding [36]. No changes in the absorption and fluorescence intensity of NaFl were detected for 3NP due to its poor hydrogen donor ability. Exploitation of hydrogen bonding ability to prepare selective sensors is well supported in the literature [29,30].
To further prove that the stronger acidic property of 4NP is the primary cause of quenching, NaFl spectral responses were also recorded in the presence of HCl and NaOH. In the presence of NaOH, no change in the photophysical properties of NaFl was observed as shown in Figure S8 of Supporting Information. However, the absorption spectra of NaFl recorded in the presence of HCl showed a hypsochromic shift as depicted in Figure S9 of Supporting Information. The absorption wavelength maxima in the presence of HCl is the same as for the neutral fluorescein molecule [23]. Moreover, the fluorescence is completely quenched in the presence of HCl due to the protonation of fluorescein. This observation aids in explaining the results observed for NaFl fluorescence emission with increased concentrations of 4NP in MeCN.
The pure spectrum of NaFl absorption recorded in water did not show any peak shift. However, there was hydrogen bonding between NaFl and water. Moreover, the peak shift in the absorption spectra of NaFl was not observed with 4NP as observed in HCl, which indicates that complete proton transfer did not occur in the ground state. However, it is loosely bonded to 4NP through hydrogen bonding as bonded in water. Conversely, in the excited state, complete transfer occurred, which quenched the fluorescence emission of fluorescein. Under aqueous and basic conditions, NaFl did not show any fluorescence quenching of emission. However, it showed significant quenching in acidic media. Thus, it can be concluded that significant fluorescence quenching of NaFl by 4NP occurred due to complete proton transfer.
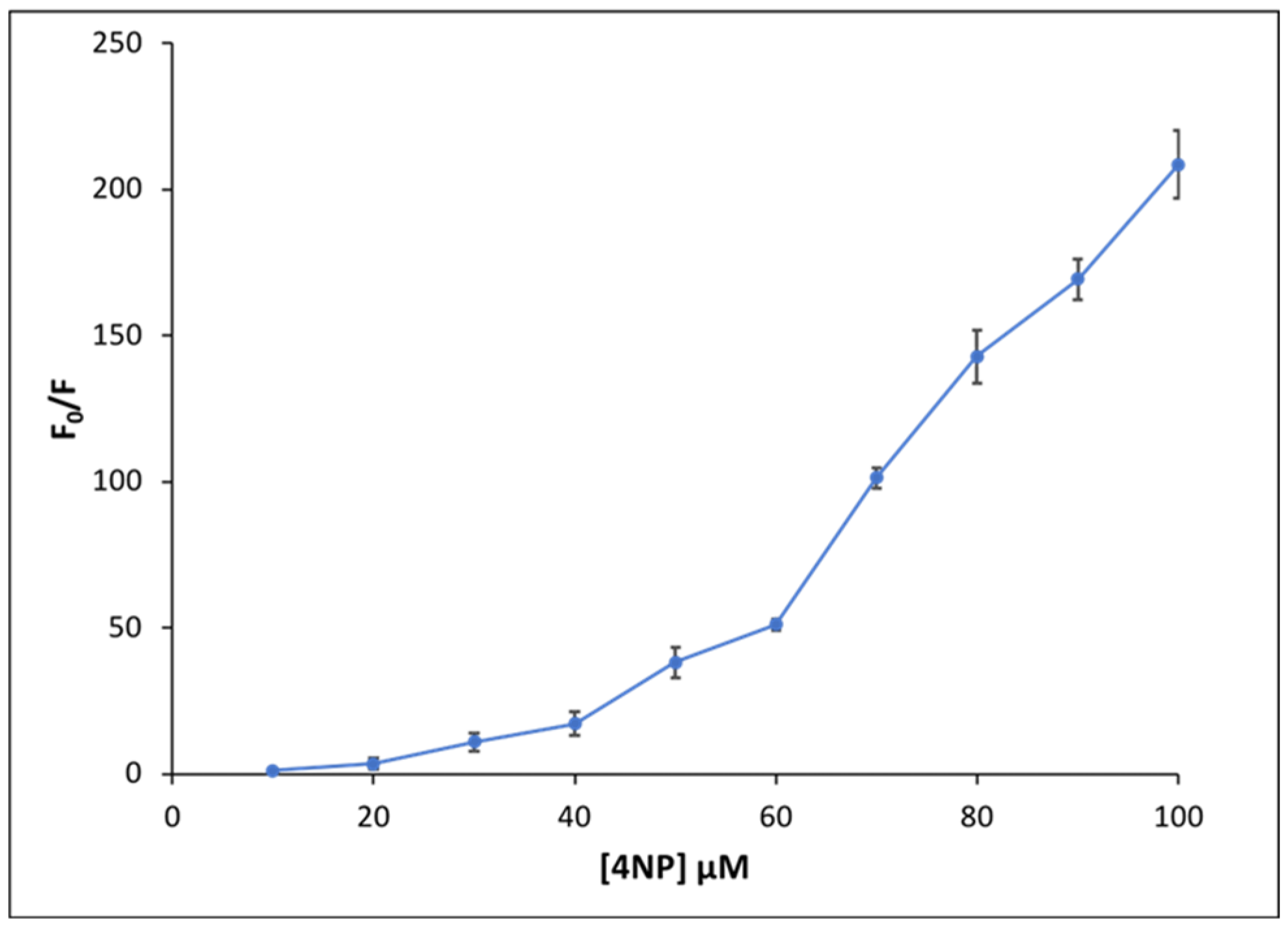
To further elucidate the quenching mechanism of NaFl in the presence of 4NP in MeCN, fluorescence emission data were analyzed in detail using the Stern–Volmer Equation (1) below.
where F0 is the fluorescence emission intensity in the absence of quencher, F is the fluorescence emission intensity in the presence of quencher, ksv is the Stern–Volmer constant, and Q is the concentration of quencher. A graph of F0/F versus 4NP concentration is plotted and is shown in Figure 6. Examination of the upward curvature suggests both static and dynamic quenching between NaFl and 4NP [37]. This behavior is attributed to hydrogen bonding interactions between NaFl and 4NP that occur in the ground state as well as the possibility that NaFl accepts a proton from 4NP in the excited state, which completely diminished the fluorescence signal of NaFl. In the Stern–Volmer plot, the ratio of F0/F gradually increases for low concentrations of 4NP. However, after ~50 μM concentration of 4NP, a steeper slope is observed. Since for all experiments the concentration of NaFl was held constant at 50 μM, the concentration of 4NP up to 50 μM can only donate one proton to NaFl and produce monoanion fluorescein. It is well known that the monoprotonated (monoanionic) form of fluorescein is fluorescent with low quantum yield, while the neutral fluorescein (diprotonated form) is nonfluorescent [23]. It is possible that at a low concentration of 4NP, only the monoprotonated form of NaFl is formed, which is weakly fluorescent as compared to dianionic fluorescein. Therefore, a slight decrease in fluorescence intensity is observed. At higher concentrations (100 µM) of 4NP, NaFl is neutral (diprotonated), and, thus, the signal is completely quenched resulting in a drastic decrease in intensity.
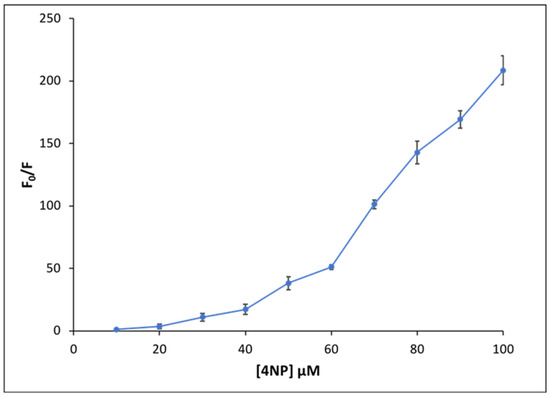
Figure 6.
Stern–Volmer plot for fluorescence emission quenching of NaFl at different 4NP concentrations.
The limit of detection (LOD) of NaFl towards 4NP was calculated from the fluorescence emission data using the following Equation (2) [38]
where K is the slope of the fluorescence spectra of various concentrations of 4NP, 3 is the confidence factor, and σ is the standard deviation. The calculated value for the limit of detection is 2.07 µM for 4NP. This lower limit of detection suggests that NaFl is a highly sensitive sensor for 4NP and can be used to detect concentrations of 4NP lower than the reported EPA toxicity limit (see Table S3 of Supporting Information). Hence, this detection method is a very promising tool for environmental analyses of 4NP.
The quenching percentage for all nitroaromatics was calculated using Equation (3)
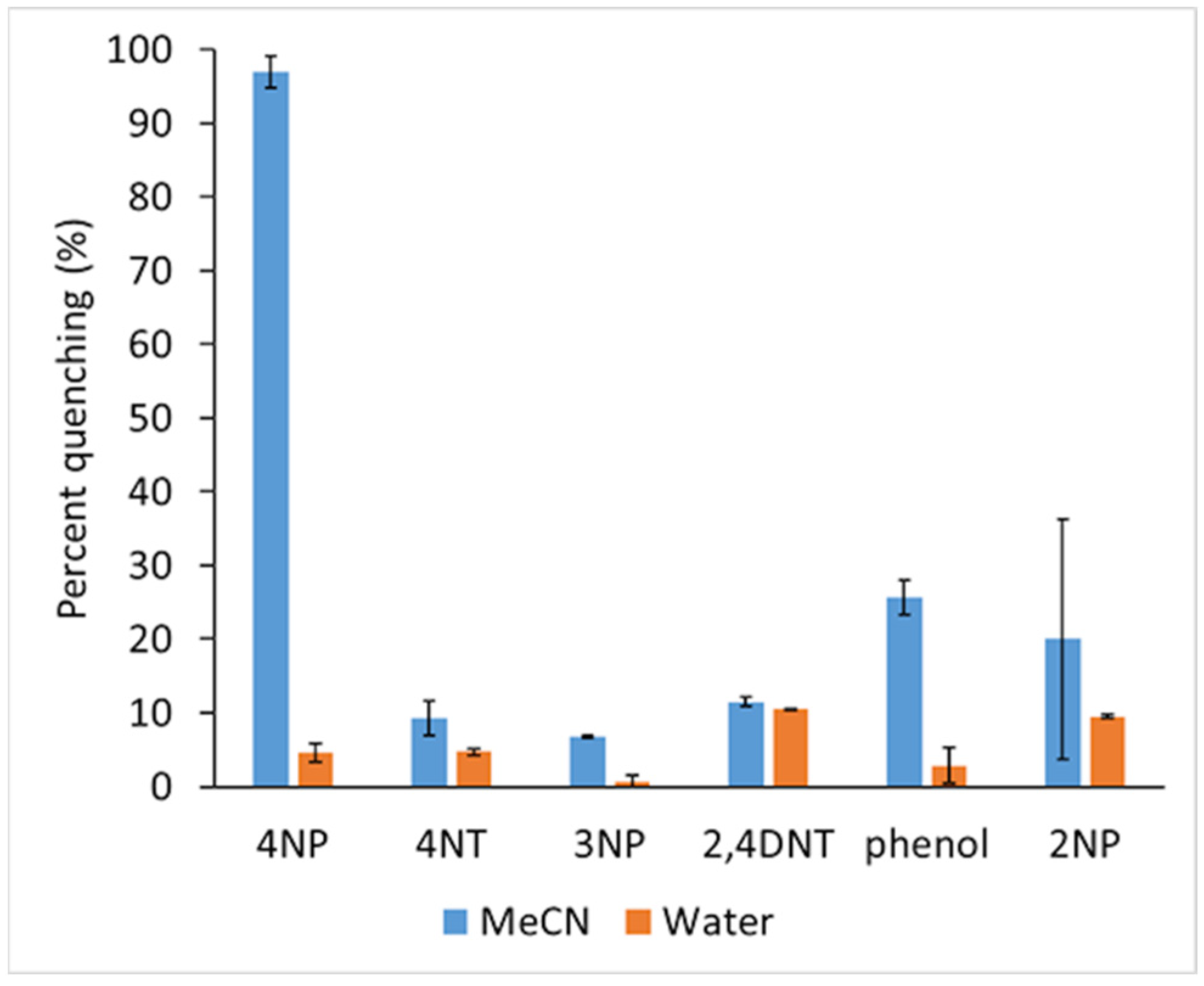
where Io is the fluorescence intensity of NaFl in the absence of quencher and I is the fluorescence intensity in the presence of quencher. The graph for the percentage of quenching efficiency for all nitroaromatics in both water and MeCN using NaFl is shown in Figure 7.
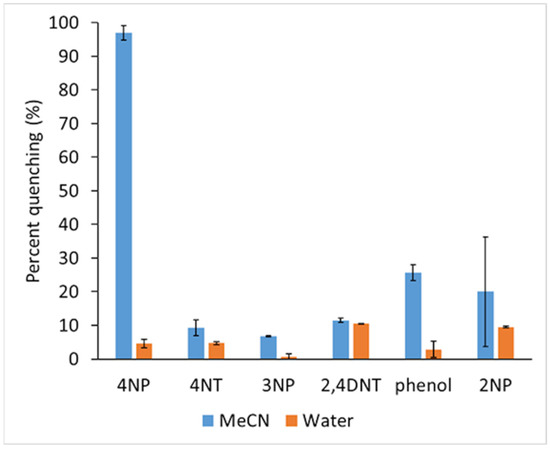
Figure 7.
Percentage of fluorescence quenching of NaFl in presence of nitroaromatic in MeCN and in water.
The sensitivity of the present sensor was compared with other reported sensors for 4NP in Table S4 of the Supporting Information. The present low-cost NaFl sensor in MeCN is very sensitive and selective towards 4NP with a high quenching efficiency of ~98% in comparison to other expensive materials, metallic compounds which required complex synthesis. Moreover, the other sensors are not just selective for 4NP.
Since the turn off response was so evident in the solution, a portable inexpensive paper-based solid sensor was explored. Other studies have shown that fluorescent paper strips can be developed to have high selectivity and sensitivity towards nitroaromatic pollutants due to π-π stacking [39]. In this study, a paper-based sensor approach was explored for accelerating the turn off fluorescence quenching of NaFl in the presence of nitroaromatic pollutants. MeCN was used to dissolved nitroaromatic compounds since it can enhance the hydrogen bonding between NaFl and nitroaromatic compounds. Thus, filter paper could serve as a simple, inexpensive, and portable sensor for the detection of 4NP. NaFl was adsorbed onto the filter paper and tested for each nitroaromatic. Then, each nitroaromatic was applied onto the paper coated with NaFl and placed under UV light. Figure S10 of Supporting Information shows the filter paper response under UV light. Clear quenching is displayed for 4NP, but much less quenching is shown for the other nitroaromatics and phenol. In fact, the quenching response of 3NP is slightly better than nitrotoluene but less than for 4NP. This exercise demonstrates that 3NP (weak proton donor) can also be detected in the solid state. Thus, use of this portable and disposable NaFl filter paper sensor demonstrates a simplistic and cost-effective method for the detection of 4NP.
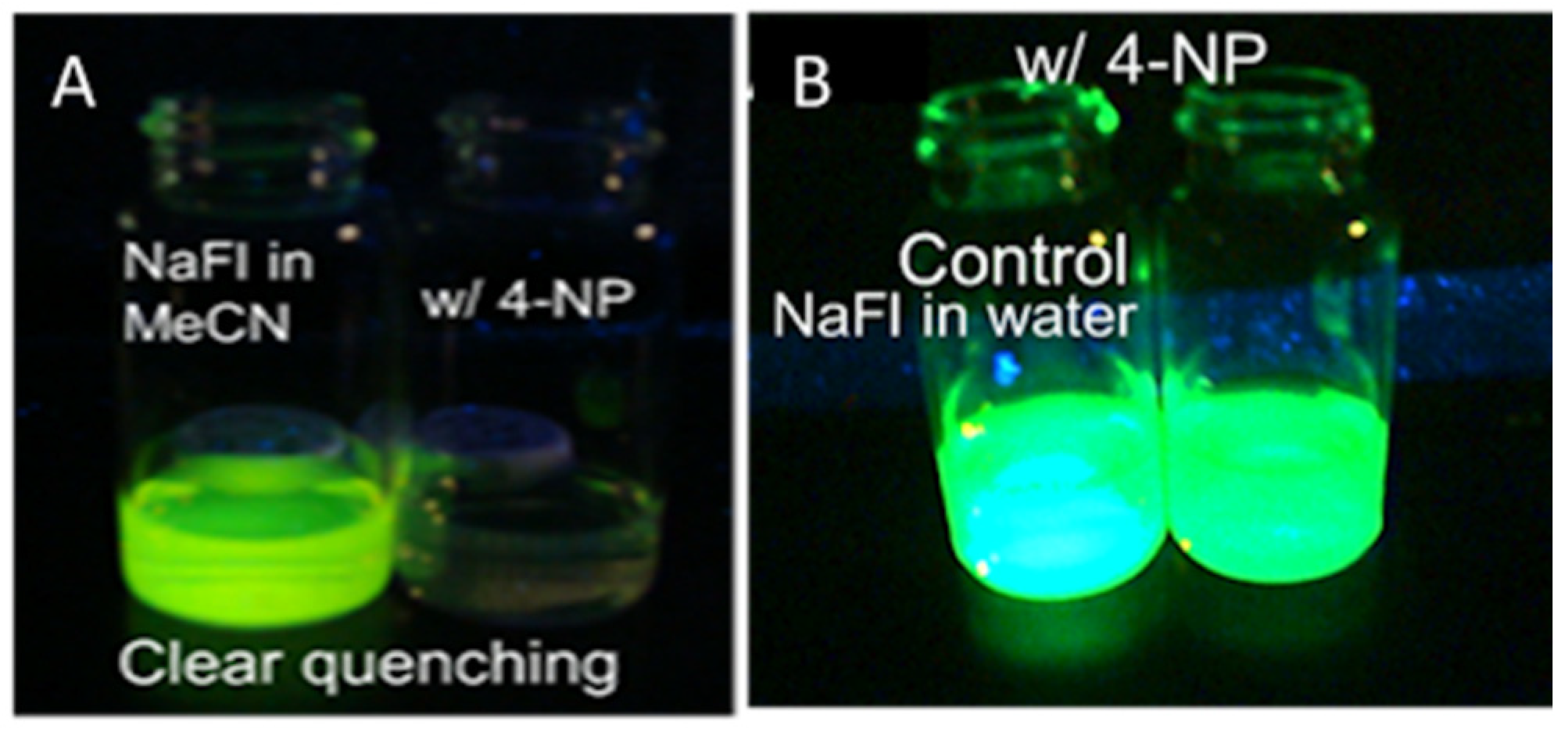
Since quenching of NaFl by 4NP showed such extreme selectivity for 4NP (Figure 7), a visual testing experiment was also conducted. In this regard, two vials with NaFl in MeCN were prepared. In one vial, 5 mL of the 4NP solution was added. As shown in Figure 8a, NaFl exhibited fluorescence under UV lamp illumination, while no fluorescence of NaFl was observed via the naked eye from the solution when 4NP was added in MeCN. In contrast, this same test was performed in an aqueous medium and no visual change was observed (Figure 8b).
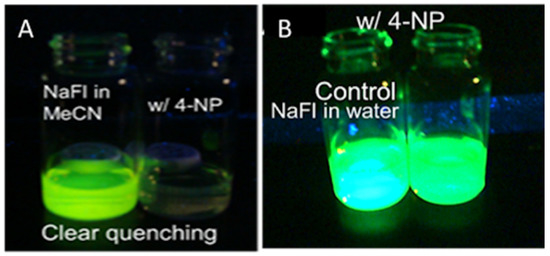
Figure 8.
The fluorescence emission of NaFl under UV lamp in MeCN (A) and water media (B) when 4NP was added.
An electrochemical experiment was also performed to validate the proton transfer mechanism between 4NP and NaFl [40,41]. A cyclic voltammogram of 4NP in MeCN showed an oxidation peak at −0.735 V versus an Ag/AgCl electrode as depicted in Figure S11 of Supporting Information. The addition of a few drops of NaFl into the 4NP solution diminished the oxidation peak and, finally, the peak disappeared due to strong hydrogen bonding with NaFl. This experiment demonstrates that the 4NP hydrogen is not available for oxidation in the presence of NaFl. The aggregate of all of the results confirms that there is a strong hydrogen bonding interaction between 4NP and NaFl in MeCN media that generates a unique optical response for NaFl.
4. Conclusions
A reliable and inexpensive optical sensor using NaFl in MeCN media for detection of the nitroaromatic pollutant, 4NP, is presented. Results obtained in this study confirm that this NaFl sensor is quite selective and highly sensitive towards 4NP. The critical interaction between 4NP and NaFl is determined to be a strong hydrogen bonding interaction that produces a significant decrease in absorption and the fluorescence emission signal intensity of NaFl. Both dynamic and static quenching occur simultaneously between 4NP and NaFl in MeCN due to hydrogen bonding in the ground state and complete proton transfer in the excited state. An electrochemical experiment also supports a proton transfer mechanism between 4NP and NaFl. A paper-based portable sensor is demonstrated for the simple, facile detection of 4NP. Thus, in this manuscript, we have presented a novel, inexpensive, and portable turn off fluorescent sensor using a hydrogen bonding mechanism that may be exploited for a variety of other applications.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/suschem2030028/s1, Table S1: Concentration and volume of NaFl and nitroaromatics solution in the reaction vials, Table S2: Kamlet–Taft Parameters which measures separately the acidity or proticity or Hydrogen bond donating ability (α), basicity or hydrogen bond accepting ability (β) and dipolarity/polarizability (π*) properties of solvents, Figure S1: Normalized absorption spectra of 4NP in different solvents, Figure S2: Normalized fluorescence emission spectra of NaFl in two different solvents, Figure S3: Normalized absorption spectra of nitroaromatics in MeCN and in water, Figure S4: Fluorescence emission spectra of NaFl at the excitation wavelength of 490 nm in the presence of 4NP in water, Figure S5: Absorption spectra of 4NP in MeCN and upon addition of different volumes (µL) of water, Figure S6: Absorption spectra of NaFl in the presence of different concentrations of other nitroaromatics in MeCN, Figure S7: Fluorescence emission spectra of NaFl at the excitation wavelength of 510 nm in the presence of different concentrations of other nitroaromatics in MeCN, Figure S8: Absorption and fluorescence emission spectra of NaFl in alkaline media, Figure S9: Absorption and fluorescence emission spectra of NaFl in acidic media, Table S3: 4NP toxic concentration reported by EPA, Figure S10: filter paper-based NaFl sensor for nitroaromatic detection, Figure S11: Cyclic voltammogram of 4NP in the presence of NaFl.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S. (Noureen Siraj), N.S. (Nicholas Speller), Y.K. and I.W.; methodology, N.S. (Noureen Siraj), and Y.K.; validation, N.S. (Noureen Siraj); formal analysis, Y.K., T.L., M.B. and N.S. (Noureen Siraj); investigation, N.S. (Noureen Siraj), T.L., Y.K. and M.B.; resources, N.S. (Noureen Siraj) and I.W.; writing—original draft preparation, T.L.; writing—review and editing, M.B., S.M. and N.S. (Noureen Siraj); visualization, N.S. (Noureen Siraj); supervision, N.S. (Noureen Siraj); project administration, N.S. (Noureen Siraj); funding acquisition, N.S. (Noureen Siraj). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Datasets generated during this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under grant no. RII Track-4 1833004. We are thankful to Mavis Forson for her help. We would like to express our gratitude to the University of Arkansas at Little Rock Signature Experience Grant, the University of Arkansas at Little Rock McNair Scholar Program for funding our project, the University of Arkansas at Little Rock Center for Integrative Nanotechnologies Sciences and the University of Arkansas at Little Rock Chemistry Department for supporting us with instrumentation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Snellinx, Z.; Nepovím, A.; Taghavi, S.; Vangronsveld, J.; Vanek, T.; van der Lelie, D. Biological remediation of explosives and related nitroaromatic compounds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2002, 9, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roper, W. Toxicological Profile for Nitrophenols: 2-Nitrophenol 4-Nitrophenol (CAS#: 2-Nitrophenol 88-75-5; 4-Nitrophenol 100-02-7). Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/ToxProfiles/ToxProfiles.aspx?id=880&tid=172 (accessed on 26 August 2021).
- Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Y. Fluorescence based explosive detection: From mechanisms to sensory materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8019–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diaz, Y.J.; Page, Z.A.; Knight, A.S.; Treat, N.J.; Hemmer, J.R.; Hawker, C.J.; Read de Alaniz, J. A Versatile and Highly Selective Colorimetric Sensor for the Detection of Amines. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 3562–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Peng, R.; Zhou, H.; Liu, H. Sensitive determination of 4-Nitrophenol based on its enhancement of a peroxyoxalate chemiluminescence system containing graphene oxide quantum dots and fluorescein. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, D.V. Adsorption of phenol and 4-Nitrophenol on granular activated carbon in basal salt medium: Equilibrium and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA Title 40: Protection of Environment. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/text-idx?SID=fff5d53a14e2217cc5713bcd589a28c7&mc=true&tpl=/ecfrbrowse/Title40/40tab_02.tpl (accessed on 26 August 2021).
- Jáuregui, O.; Moyano, E.; Galceran, M.T. Liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometry for the determination of chloro- and nitrophenolic compounds in tap water and sea water. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 787, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alber, M.; Böhm, H.B.; Brodesser, J.; Feltes, J.; Levsen, K.; Schöler, H.F. Determination of nitrophenols in rain and snow. Fresenius’ Zeitschrift für Anal. Chemie 1989, 334, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiß, A.; Lewin, U.; Wennrich, L.; Findeisen, M.; Efer, J. Analysis of nitrophenols and other polar nitroaromatic compounds in ammunition wastewater by high-field proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) spectroscopy and chromatographic methods. Fresenius. J. Anal. Chem. 1997, 357, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbitskiy, E.V.; Baranova, A.A.; Yakovleva, Y.A.; Chuvashov, R.D.; Khokhlov, K.O.; Dinastiya, E.M.; Rusinov, G.L.; Chupakhin, O.N.; Charushin, V.N. New “turn-off” fluorescence sensors to detect vapors of nitro-explosives on the basis of 4,6-bis[5-(heteroaryl)thiophen-2-yl] substituted 5-(4-tert-butylphenyl)pyrimidines. Arkivoc 2017, 2017, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maity, A.; Maiti, A.; Satpati, B.; Patsha, A.; Dhara, S.; Chini, T.K. Probing Localized Surface Plasmons of Trisoctahedral Gold Nanocrystals for Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 27003–27012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Germain, M.E.; Knapp, M.J. Optical explosives detection: From color changes to fluorescence turn-on. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2543–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Gao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Su, R.; Huang, R.; Qi, W.; He, Z. Molecularly Imprinted Core-Shell CdSe@SiO2/CDs as a Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for 4-Nitrophenol Sensing. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geng, S.; Lin, S.M.; Liu, S.G.; Li, N.B.; Luo, H.Q. A new fluorescent sensor for detecting p-nitrophenol based on ß-cyclodextrin-capped ZnO quantum dots. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 86061–86067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonis, N.; Clayton, A.H.; Voss, E.W.; Sawyer, W.H. Spectral properties of fluorescein in solvent-water mixtures: Applications as a probe of hydrogen bonding environments in biological systems. Photochem. Photobiol. 1998, 67, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. Fluorescence Properties of Twenty Fluorescein Derivatives: Lifetime, Quantum Yield, Absorption and Emission Spectra. J. Fluoresc. 2014, 24, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klonis, N.; Sawyer, W.H. Effect of solvent-water mixtures on the prototropic equilibria of fluorescein and on the spectral properties of the monoanion. Photochem. Photobiol. 2000, 72, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikalje, A. Nanotechnology and its Applications in Medicine. Med. Chem. 2015, 94, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schebesch, K.; Brawanski, A.; Hohenberger, C.; Hohne, J. Fluorescein sodium-guided surgery of malignant brain tumors: History, current concepts, and future projects. Turk. Neurosurg. 2016, 26, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togashi, D.M.; Szczupak, B.; Ryder, A.G.; Calvet, A.; O’Loughlin, M. Investigating Tryptophan Quenching of Fluorescein Fluorescence under Protolytic Equilibrium. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 2757–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.-J.; Han, K.-L. Hydrogen Bonding in the Electronic Excited State. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.M.; Lindqvist, L. The pH dependence of fluorescein fluorescence. J. Lumin. 1975, 10, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonis, N.; Sawyer, W.H. Spectral properties of the prototropic forms of fluorescein in aqueous solution. J. Fluoresc. 1996, 6, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; He, S.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Optical pH Sensor with Rapid Response Based on a Fluorescein-Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxide. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 3856–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, C.; Cen, J.; Bai, Y.; He, W.; Guo, Z. Ratiometric detection of pH fluctuation in mitochondria with a new fluorescein/cyanine hybrid sensor. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 3187–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Peng, X.; Fan, J.; Gao, S.; Tian, M.; Zhao, J.; Sun, S. Fluorescence Sensing of Anions Based on Inhibition of Excited-State Intramolecular Proton Transfer. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräuer, M.; Mosquera, M.; Luis Pérez-Lustres, J.; Rodríguez-Prieto, F. Ground-State Tautomerism and Excited-State Proton-Transfer Processes in 4,5-Dimethyl-2-(2’-hydroxyphenyl)imidazole in Solution: Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Quantum Mechanical Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 10736–10745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, N.; Singha, D.; Sahu, K. Fluorescence Quenching of Hydrogen-Bonded Coumarin 102-Phenol Complex: Effect of Excited-State Hydrogen Bonding Strength. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 3945–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alty, I.G.; Cheek, D.W.; Chen, T.; Smith, D.B.; Walhout, E.Q.; Abelt, C.J. Intramolecular Hydrogen-Bonding Effects on the Fluorescence of PRODAN Derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 3518–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Taft, R.W. The Solvatochromic Comparison Method. I. The β-Scale Of Solvent Hydrogen-Bond Acceptor (HBA) Basicities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taft, R.W.; Kamlet, M.J. The Solvatochromic Comparison Method. 2. The α-Scale of Solvent Hydrogen-Bond Donor (HBD) Acidities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 2886–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, C. Solvatochromic Dyes as Solvent Polarity Indicators. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 2319–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoleti, C.R.; Marini, V.G.; Zimmermann, L.M.; Machado, V.G. Anionic chromogenic chemosensors highly selective for fluoride or cyanide based on 4-(4-Nitrobenzylideneamine)phenol. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liptak, M.D.; Gross, K.C.; Seybold, P.G.; Feldgus, S.; Shields, G.C. Absolute pKa determinations for substituted phenols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6421–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.H.; Walker, S. Dipole moment and infra-red studies of solvent effects on intramolecular hydrogen bonding. Part 4.—Nitroanilines and nitronaphthylamines. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1961, 57, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, W.R.; Contino, P.B. [21] Fluorescence quenching studies: Analysis of nonlinear Stern-Volmer data. Methods Enzymol. 1992, 210, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Q.; Shi, Y.; Hua, Q.; Tong, B. Phosphorescent chemosensor for Hg2+ based on an iridium(iii) complex coordinated with 4-phenylquinazoline and carbazole dithiocarbamate. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 74924–74931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daglar, B.; Demirel, G.B.; Bayindir, M. Fluorescent Paper Strips for Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Nitroaromatic Analytes in Water Samples. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 7735–7740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ai, S.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Lu, L. Electrochemical oxidative determination of 4-Nitrophenol based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with a hydroxyapatite nanopowder. Microchim. Acta 2010, 169, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Lei, W.; Xia, X.; Xia, M.; Hao, Q. Electrochemical determination of 4-Nitrophenol at polycarbazole/N-doped graphene modified glassy carbon electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 146, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).