Abstract
The eco-sustainable use of materials derived from agricultural and food processing waste will represent one of the most stimulating challenges shortly. Chitin and chitosan are two remarkable examples of how molecules with high added value can be extracted from food waste, such as crustaceans’ shells, fungi, mollusks, etc. This Perspective summarizes the current state of knowledge about chitin extraction, chitosan production, and hydrogel formation, highlighting the environmental critical steps in the common route (use of strong acids and basis, toxic solvents, and not eco-friendly crosslinkers). At the same time, promising green alternatives are described and analyzed. Examples are the employment of NADESs or DESs (such as choline chloride: urea or choline chloride: organic acids mixtures) for chitin extraction and dissolution, use of citric acid both in chitin extraction and hydrogel formation or utilization of natural extracts, like genipin, as green cross-linkers under mild conditions (heating at 37 °C for 12 h). In particular, this perspective aims to provide a stimulating basis for the development of processes based on the recycling and reusing of chemicals, during the different preparation steps, in line with “system chemistry” and “circular economy” principles.
1. Introduction
One of the consequences of the increasing world population is food waste increment. A report from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimated that 1/3 of agriculture production is discarded [1], corresponding to 1.6 Gtonnes of “primary product equivalents” and 1.3 Gtonnes of the edible part of the food. This is a major problem in terms of environmental impact, not only for the waste of valuable resources but also for greenhouse gas emissions (measured in tons of CO2 equivalent) linked to product disposal at the end of their life [2].
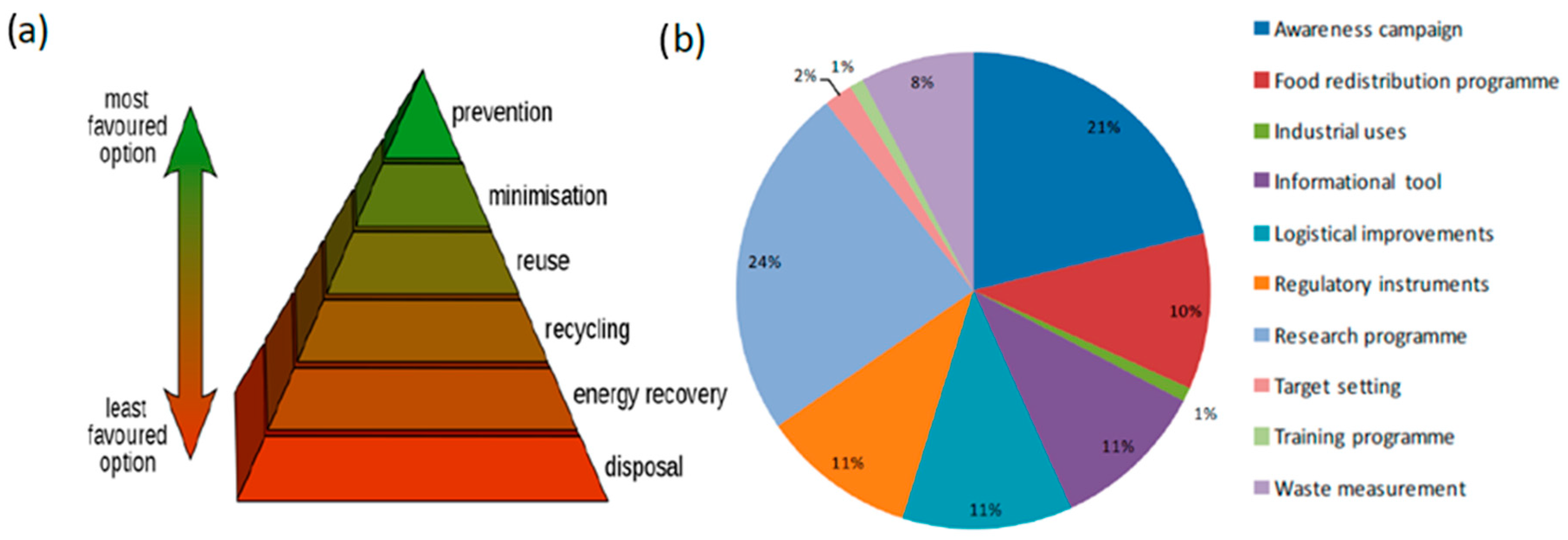
For this reason, searching for new routes for minimizing food waste is a paramount goal for scientists and policymakers. In 2008, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) presented a hierarchical pyramid showing the preferable strategies that should be actuated to reduce food waste [3] (Figure 1).
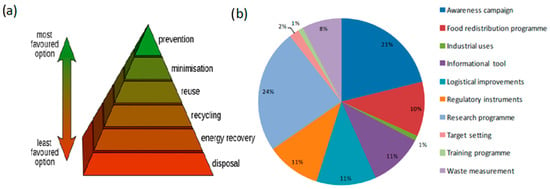
Figure 1.
(a) Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) food waste recovery hierarchical pyramid; (b) types of strategies used to prevent food waste. Adapted and reprinted with permission from Ref. [2,3].
At present, industrial use represents only 1% of residue reduction [2].
However, in the last few years, scientific interest seems to move precisely in this direction. The so-called “Food Supply Chain Waste” (FSCW), which includes agricultural and processing residues generated in the food production/utilization chain, is considered as an exciting new frontier for recycling. Even though most of the research in this area has been focused so far on the production of biofuels, fertilizers, animal feed, and packaging, food waste can be an endless source of molecules, including proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, and so on, which can be exploited for fabricating a variety of functional materials.
For example, vegetable and fruit waste is an extremely rich source of functional molecules, including carboxylic acids (e.g., ascorbic, citric, arachidic acids), biogenic amines, phenols and polyphenols, flavonoids, carotenoids, limonene, as well as starch, pectin, cellulose, and other biopolymers [4]. In addition to calcium carbonate, eggshells contain key structural proteins (ovocleidins, ovolayxins, osteopontins), uronic, hyaluronic, and sialic acids [5]. The surplus in milk production can open the door to a viable extraction of casein and amyloid proteins [6].
A rational combination of those molecules has driven recent research towards new types of applications. In particular, environmental monitoring and remediation, which are strategic areas in sustainable development, can have major benefits [7].
For example, many toxic heavy metal cations [8] and oxoanions (chromate, arsenite/arsenate) have been captured and immobilized on either cellulose or eggshell-based membranes functionalized with carboxylic acids that can be easily extracted from vegetable and fruit waste [9]. β-lactoglobulin amyloid proteins extracted from milk have been successfully utilized to fabricate membranes that absorb arsenic ions from water [10].
Another major breakthrough in developing value-added products from FSCW is represented by food-based electronics [11]. This approach entails the selection and functional characterization of food waste, to create versatile toolkits for producing electronic components (antennas, resistors, capacitors, inductors, sensing elements, conductive and insulating substrates, etc.) that can be assembled into functional devices. A good example is described in a very recent patent [12] in which a chitin hydrogel is used into supercapacitors as electrolyte membrane.
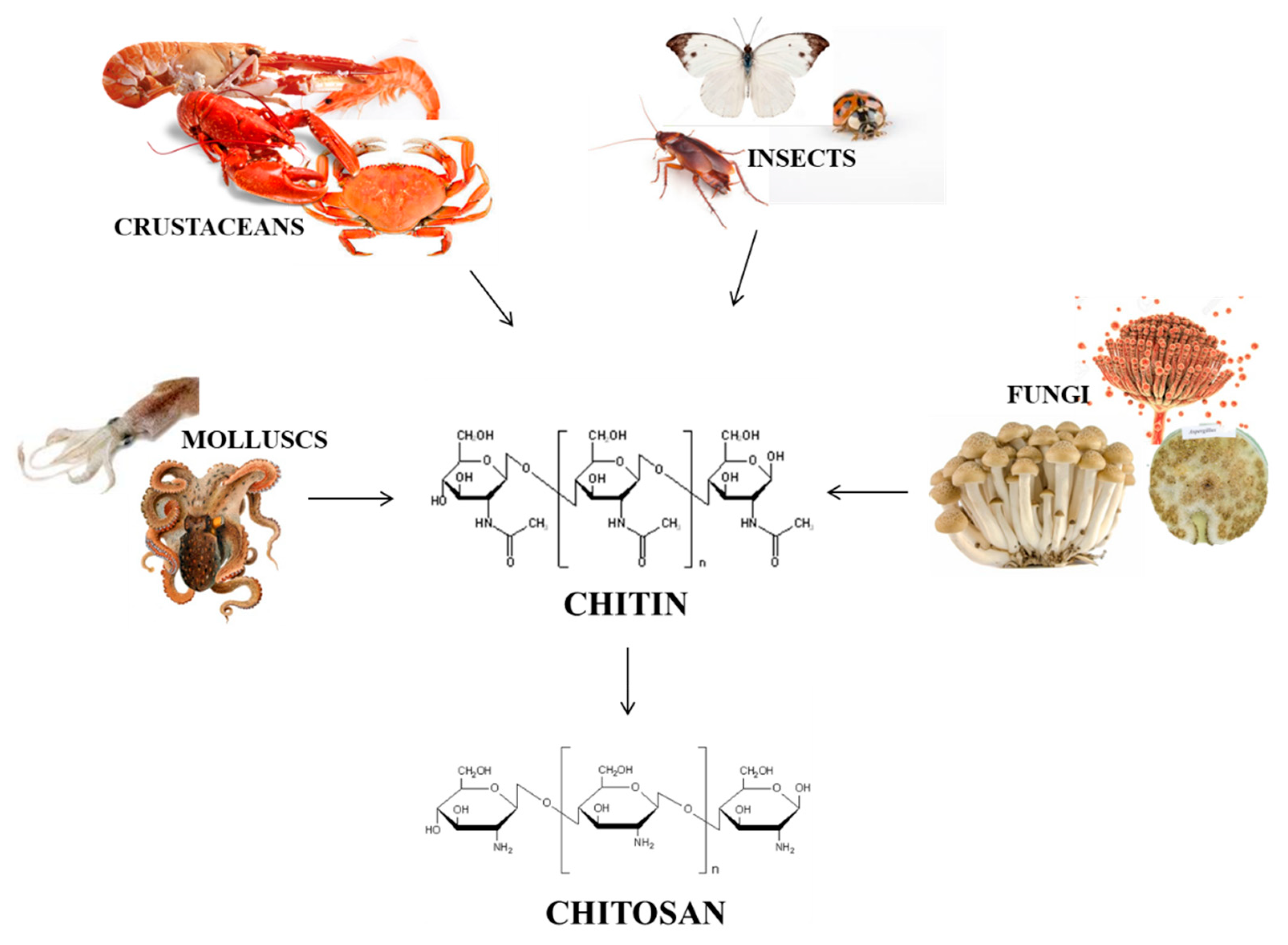
In this perspective, we will focus our attention on chitin and chitosan, two closely-related polysaccharides, that are finding a number of applications in several fields of materials science and bio-engineering (Figure 2). In particular, we will focus on their use in the production of food waste-based hydrogels, which is one of the hottest topics in the field of food recycling for technology applications [13]. Chitin can be extracted from the exoskeleton of insects, crustaceans (more generally, arthropods) [14], from mollusks, and it is also present in the fungi cell wall [15,16] (Figure 2).
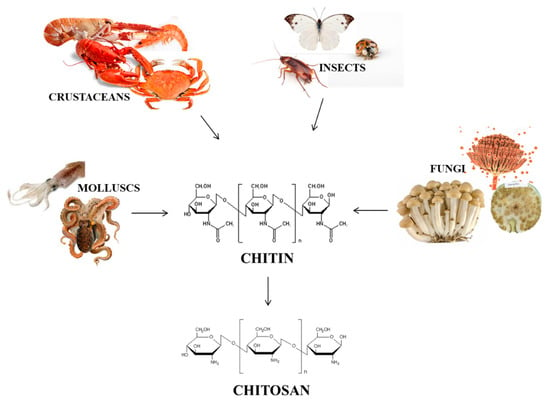
Figure 2.
Examples of chitin and chitosan sources.
Extractions from crustaceans and fungi are the most common ones thanks to the large availability of raw materials in food waste and due to the satisfactory percentages of extraction. It is estimated that about 2.0 × 1010 kg of chitin is produced in a year by freshwater arthropods and about 1.3 × 1012 kg by marine arthropods [17,18].
However, this polysaccharide is insoluble in water, and this fact seriously limits its use.
On the contrary, chitosan, which can be obtained by deacetylation of chitin and is present in fungi cell walls too, is water-soluble and is protonated [19] in neutral water solutions.
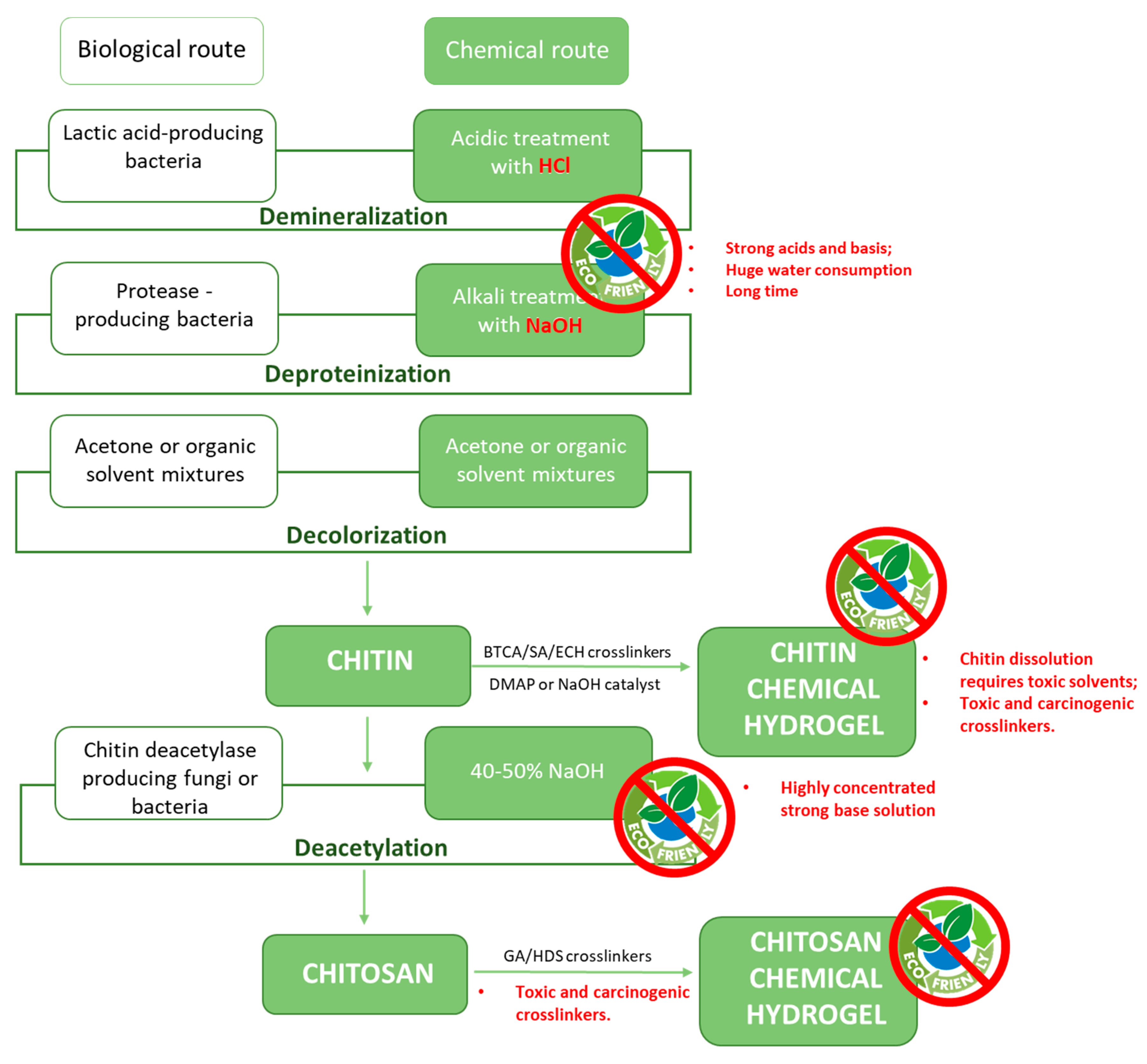
The advantages of using chitin and its derivatives are linked not only to their natural abundance but also to renewability, biodegradability, and non-toxicity. For these reasons, they find application in a large variety of fields, for example as anti-bacterial and anti-tumoral agents [20] in medicine, as constituents of artificial bones and skin [21] or for drug delivery in the biomedical field [22,23] and the detection and removal of organic and inorganic pollutants for environmental remediation [24,25,26]. However, conventional extraction and processing of chitin and chitosan pass through the use of chemicals with significant environmental impacts, such as highly concentrated acidic and basic solutions and toxic chemical cross-linkers (Figure 3). Even if in literature it is already possible to find different reviews regarding chitin, chitosan, and their derivatives, especially as regards the analysis of their properties and their possible applications [7,27,28,29,30,31,32,33], in this perspective we want to bring to light the critical points that can be encountered during the process of conversion of chitin-rich raw materials into functional advanced systems. In particular, we will compare conventional routes for extraction/processing of chitin and chitosan with the most recent green alternative processes, highlighting from the point of view of environmental sustainability the drawbacks and limitations encountered during the production process following conventional well-established routes. We will propose some alternative environmentally-friendly solutions that have been already proposed in the literature and we will discuss the challenges that remain on the road towards the development of a sustainable production chain of functional hydrogels.
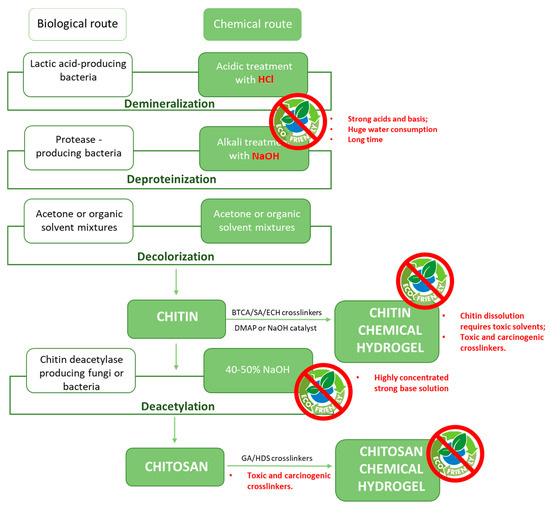
Figure 3.
Conventional steps for chitin and chitosan extraction from crustacean shells to fabricate functional hydrogels.
2. Chitin Extraction
Chitin is the most abundant natural polymer after cellulose, discovered for the first time by the French pharmacist Henri Braconnot [34] in 1811. In 1843 the chemist Jean Louis Lassaigne, working on the possibility to qualitatively determine heterogeneous elements in organic compounds, demonstrated the presence of N in chitin. Nowadays, we know that chitin consists of multiple units of N-acetyl-d-glucos-2-amine bonded together by a β-1,4 bond. The units are the same as cellulose with the difference that chitin has an acetylamine group instead of hydroxyl.
Chitin occurs in nature as ordered crystalline microfibrils. X-ray diffraction and solid-state NMR spectroscopy revealed two main crystalline forms, namely α and β [35]. The α structure is the most common and stable form. It occurs in fungi cell walls, shrimp cells, and insect cuticle. The chains in α-chitin are arranged in anti-parallel strands, responsible for the characteristic resistance of insect and crustacean exoskeleton.
The less stable and rarer β structure is found in squid pens [36], spines and annelids; the chains are parallelly distributed, which justifies its higher degree of softness.
Finally, an additional allomorph is known, ɣ-chitin, which is probably just a variant of α-structure [37].
In its stable form, chitin presents itself as white or pale-pink, odorless, and tasteless solid. The strong intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds make chitin extremely aggregated, which makes it insoluble in common solvents such as water, organic solvents, and mild acidic or basic solutions [38]. This drawback represents a major limitation for many applications. Conversely, it can be solubilized in strongly polar solvents, such as hexafluoroisopropyl alcohol and hexafluoracetone, lithium thiocyanate [39], dimethylacetamide (DMA)/LiCl mixture [40], etc.
As many of these solvents are toxic or mutagenic, seeking safer alternatives is vital for this field of research. An example of a good “green” alternative for chitin dissolution is reported in the patent “Dissolution method of chitin” [41]. The protocol foresees the use of a mixture of NaOH and carbamide where chitin is held for 3–10 h. The solution is stirred at room temperature after a freeze of 7 days at −18 °C/−10 °C. The great advantage of this method is that the waste liquid can be reused more times by reducing toxic by-products, but the required dissolution time (10 h + 7 days) is too high and remains an open issue.
2.1. Conventional Chitin Extraction from Crustaceans
Thanks to the abundance of waste crustacean exoskeletons (6–8 million tons are produced globally per year) [17], the extraction from crustaceans are the most common procedure, and two routes can be followed: biological and chemical methods.
Both of them involve two fundamental steps: demineralization and deproteinization.
In the biological method, demineralization occurs thanks to lactic acid produced by lactic acid bacteria. Lactic acid reacts with calcium carbonate in the crustacean exoskeleton and induces the formation of calcium lactate, which precipitates and can be removed. Moreover, lactic acid creates the necessary low pH to activate the protease present in the biowaste that is responsible for the deproteinization step [42].
Even though the biological method is eco-friendly, the use of lactic acid bacteria (for demineralization) and protease (for deproteinization) make it a time-consuming route (an average of 6 to 7 days, up to a maximum of 14 days for Parapenaeus longirostris [42]).
As a result, the chemical method is still the most commonly used.
The chemical method consists of different steps. In the beginning, the powdered raw material is processed with an acidic solution (generally HCl 1–2 M at 100 °C) for up to 48 h. The purpose is to remove exoskeleton mineral constituents (calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate). Subsequent alkali treatment is performed for achieving a deproteinization of the demineralized shells. Proteins are removed with NaOH (typically 1 M; 3–6 h at 65–100 °C), leading to the production of chitin [42]. An additional decolorization step can be performed, if a colorless product is wanted. Acetone, 10% H2O2 solution, NaClO, or organic solvent mixtures are used to remove the pigments. All these steps can be performed consecutively, by interposing washing steps with fresh water to achieve neutralization. Unfortunately, these washing steps require huge amounts of water, which further limits the sustainability of the whole process (Figure 3).
2.2. Conventional Chitin Extraction from Fungi
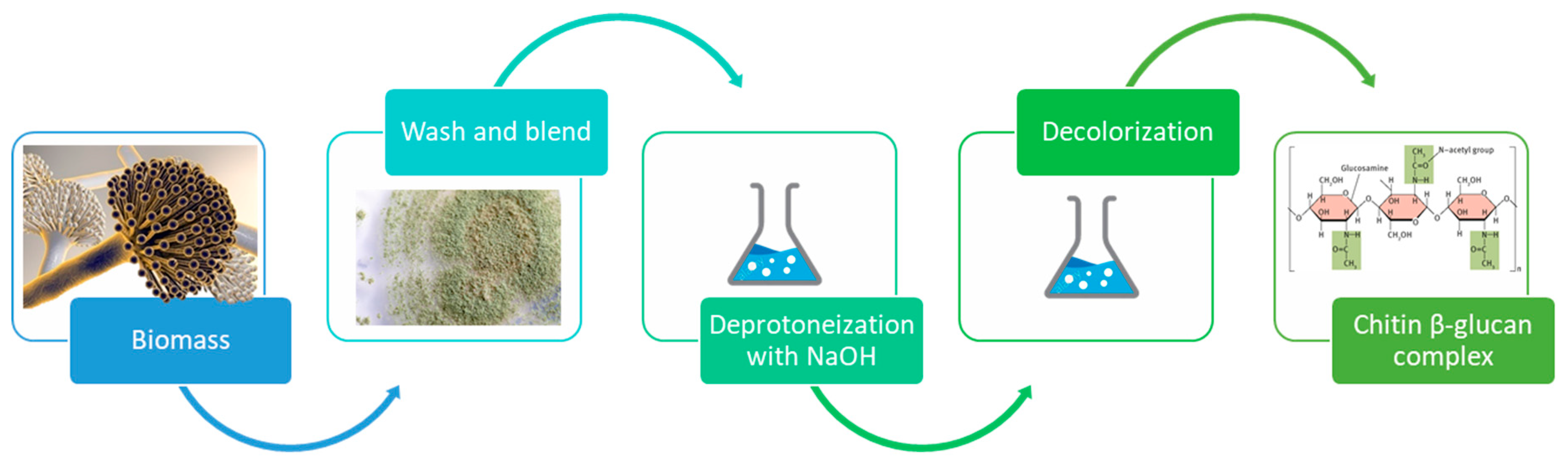
Fungi could be valid alternative sources of chitin [18]. Unlike crustaceans, in this case, the demineralization step is not necessary [43,44]. The starting materials are mycelial biomass that, after a washing step, can be homogenized in a common kitchen blender and directly subjected to deproteinization.
This step is the same as that previously described for crustaceans and it can be done with NaOH 1 M.
This way provides an alternative to crustacean chemical methods characterized by several advantages: for example, unlike crustaceans, fungi are not subject to seasonal or regional variations. Moreover, fungi do not need HCl treatment, which is otherwise requested by crustaceans to achieve demineralization (Figure 4).
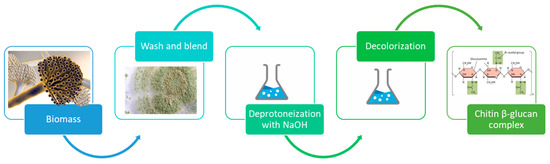
Figure 4.
Conventional steps for chitin extraction from fungi.
However, the lower chitin content (from 9 to 42% for fungi, compared to 30–70% in crustaceans [14]) and the fact that fungal chitin sources yield to a chitin-β-glucan complex [14] rather than pure chitin, makes this way unpractical for industrial and commercial purposes.
Pure chitin could be derived from the chitin-β-glucan complex introducing an acidic treatment to degrade glucan [16], but this would mean to waste one of the main advantages taken from fungi extraction.
2.3. Green Extraction Methods
The employment of strong acids or alkali solutions, huge amounts of water for neutralization steps between acid and alkali treatments, and the lengthy times are the main limitations for the reported conventional extraction protocols. In the last few years, the need to find a valid eco-friendly alternative for chitin extraction, adopting a circular economy approach, became an unavoidable challenge.
Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADESs), in particular, have aroused scientific interest for their ability to dissolve and extracting materials from natural sources [45,46].
DESs are a mixture formed by a hydrogen bond donor (HBD) and a hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA), characterized by a melting temperature lower than the melting temperatures of each pure component, thanks to the charge delocalization between HBD and HBA [47].
For their physical properties, they can be defined as a new class of ionic liquids with the advantage of easy preparation and availability from low-cost components.
Nowadays the use of DESs in a wide range of fields is promoted by their low price, non-toxicity, low flammability, and biodegradability. DESs are already used in catalysis and organic synthesis [48,49], in electrochemistry, analytical chemistry [50], and they are getting space in dissolution and extraction procedures [51,52].
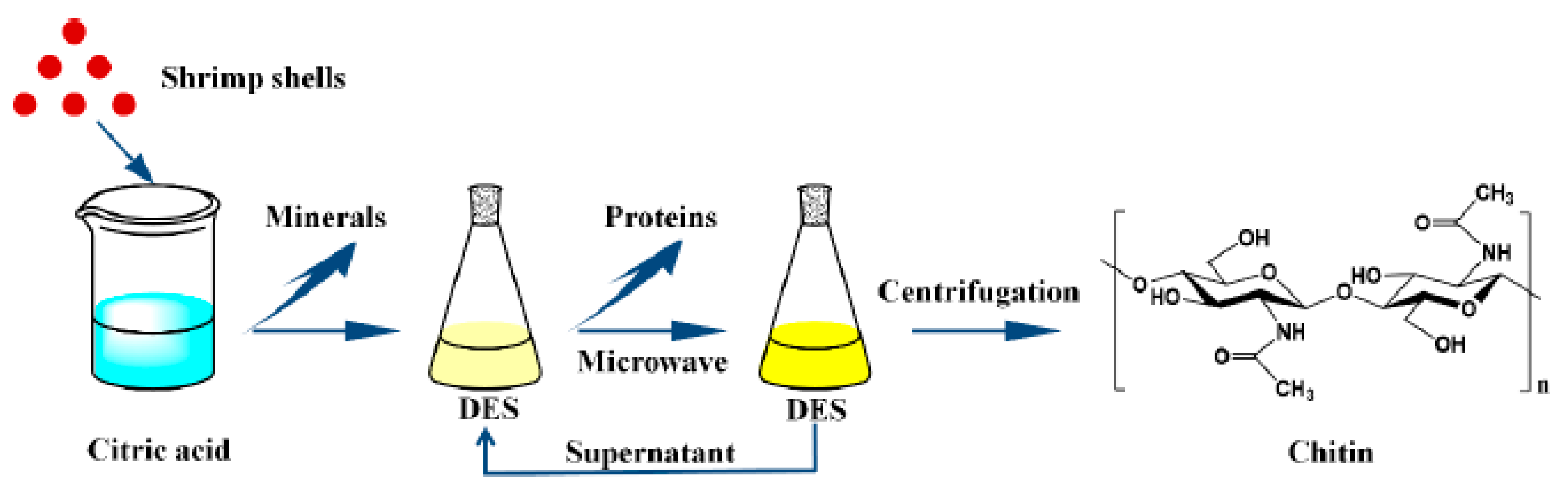
In particular, Zhao et al. reported an interesting two-steps method for chitin extraction using different DESs and citric acid, in combination with microwave heating [53] (Figure 5).
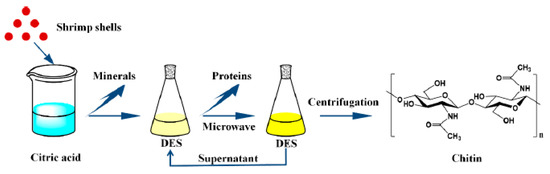
Figure 5.
Green chitin extraction process with citric acid and Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES). Adapted and reprinted with permission from Ref. [53].
In this extraction procedure, shrimp shells, properly washed, dried, and ground, are treated with 10% citric acid for demineralization. In this case, citric acid (an edible, weak acid that can be extracted from natural sources) takes the place of HCl in the classic chemical extraction.
The step of deproteinization is performed by suspending the pretreated sample in different DES solutions and heating by means of microwave irradiation. Finally, simple centrifugation allows for the separation of chitin from DES.
Betaine hydrochloride-urea, choline chloride (ChCl)-urea, ChCl-ethylene glycol, and ChCl-glycerol mixtures have been tested as DESs and the best results in terms of yield and chitin purity are obtained in the case of ChCl:urea 1:2 mixture.
The recovered DES can be reused without purification until five times. This protocol provides a double advantage: (i) the utilization of environmental-friendly solvent (DES mixture), which, combined with microwaves, avoids the use of concentrated NaOH solution, with the possibility of recycling and reusing the extracting solvent; (ii) in the preliminary demineralization step, HCl has been substituted by citric acid, which is more eco-friendly. It can be naturally extracted from a variety of fruits and vegetables [54,55]; moreover, it can be biochemically produced by fungi like Aspergillus niger [56]. In this way, fungi can be at the same time source of chitin, chitosan, and citric acid.
However, it is necessary to point out that the performance of DESs during deproteinization decreases from the third cycle.
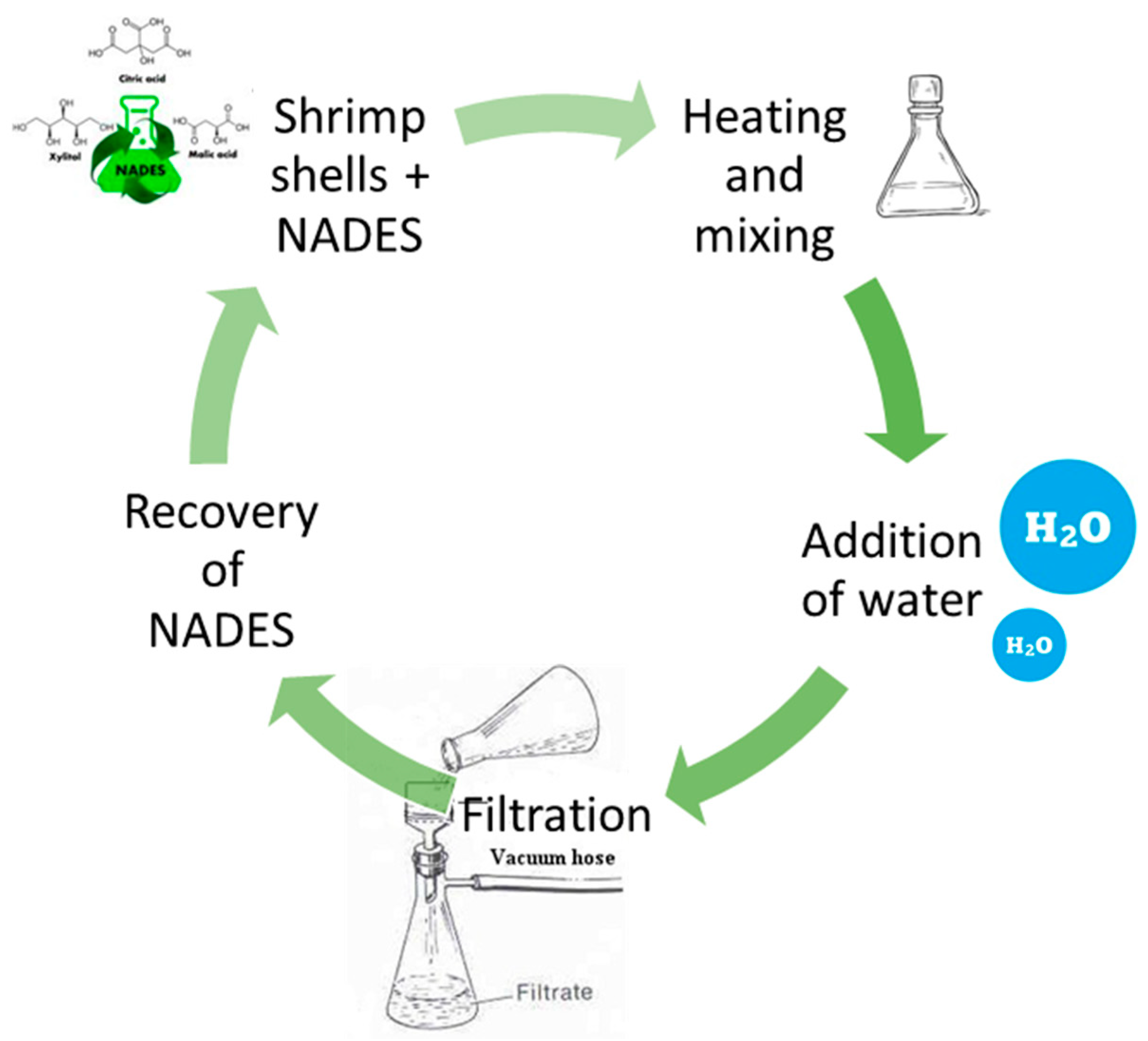
In this regard, Bradić et al. [57] developed a zero-waste method to convert shrimp shell waste into chitin. In this case, shrimp shells are solubilized in NADESs rather than in DESs. Natural DESs (NADESs) are deep eutectic solvents that are composed of two or more compounds that are generally primary metabolites of plants, i.e., organic acids, sugars, alcohols, amines, and amino acids. In this process, chitin can be separated from minerals and proteins in one step at elevated temperatures (60–90 °C). Four different NADES have been tested: ChCl:lactic acid, ChCl:malonic acid, ChCl:citric acid, and ChCl:urea, and the best results are obtained in the case of ChCl:lactic acid mixture, combined with a heating treatment at 70 °C. Once again, minerals and protein separations are achieved and NADES can be recycled (Figure 6).
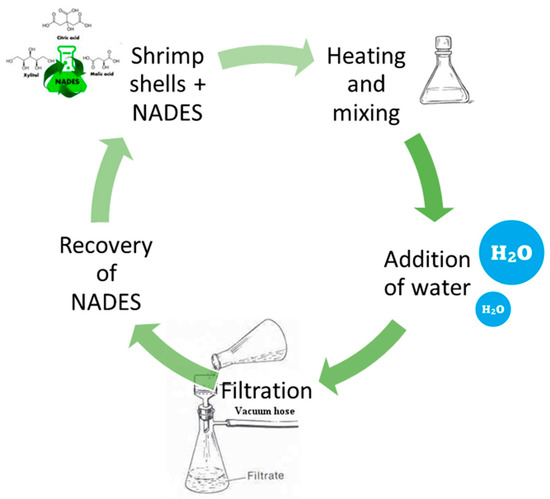
Figure 6.
Green chitin extraction process with Natural Deep Eutetic Solvents (NADES). See text and Ref. [57] for details.
The great potential of this method compared to the classical one is that not only chitin but also the chemicals (NADESs) used during extraction can be recovered from food waste, vegetables, and natural sources.
Moreover, the possibility to recycle NADESs more times makes this approach in line with the principles of the circular economy.
Other examples of chitin extraction with DES can be found in the literature. For example, Zhu et al. [51] reported the possibility to extract chitin from lobster shell using ChCl:urea, ChCl:thiourea, and ChCl:malonic acid. Interestingly, in the case of ChCl:malonic acid (1:2) mixture mild working conditions (heating at 50 °C for 2 h) are enough, which represents the most sustainable protocol for this type of extractions. A comprehensive summary of chitin extraction procedures reported in the literature can be found in Table 1.

Table 1.
Synoptic summary of chitin extraction methods discussed in the text.
3. Chitin Conversion into Chitosan
The most important derivative of chitin is chitosan. Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed β-(1 → 4)-linked D-glucosamine and N-acetyl-d-glucosamine.
Chitosan was discovered in 1859 when the physiologist Charles Rouget discovered that by boiling chitin in KOH under reflux, it was possible to get a new product soluble in aqueous acidic media [27]. Its solubility is linked to the presence of positive charges on the amino groups in the C-2 position in d-glucosamine.
In the solid-state, this biopolymer is semi-crystalline with a wide range of polymorphs depending on formation conditions [58].
Chitosan is obtained by deacetylation of chitin when the degree of acetylation (the ratio between glucosamine and N-acetyl glucosamine) is lower than 50%.
In Table 2, different chitosan production methods reported in the literature are summarized and compared. The common method to deacetylate chitin requires treatment with highly concentrated (40–50%) NaOH solution for 6 h at 107 °C [14].

Table 2.
Synoptic summary of chitosan production methods discussed in the text.
The concentrated alkali treatment makes this process with high environmental impact and with high cost, not to mention that it is necessarily a huge amount of water in the neutralization step. All these drawbacks limit chitosan scale-up and industrial applications.
For this reason, environmentally sustainable, inexpensive alternatives have been investigated.
An enzymatic method could seem a valid option. In this case, the deacetylation occurs thanks to the Chitin Deacetylase (CD) enzyme produced by fungi or bacteria [59]. CD can catalyze the hydrolysis of N-acetamido bonds in chitin. This option is eco-friendly also for mild reaction conditions. Kim et al. [60] managed to obtain chitosan at 60 °C and pH 5.5 using extracellular CD.
However, the enzymatic way might not be affordable for industrial use due to the high cost of CD and too long reaction time [61].
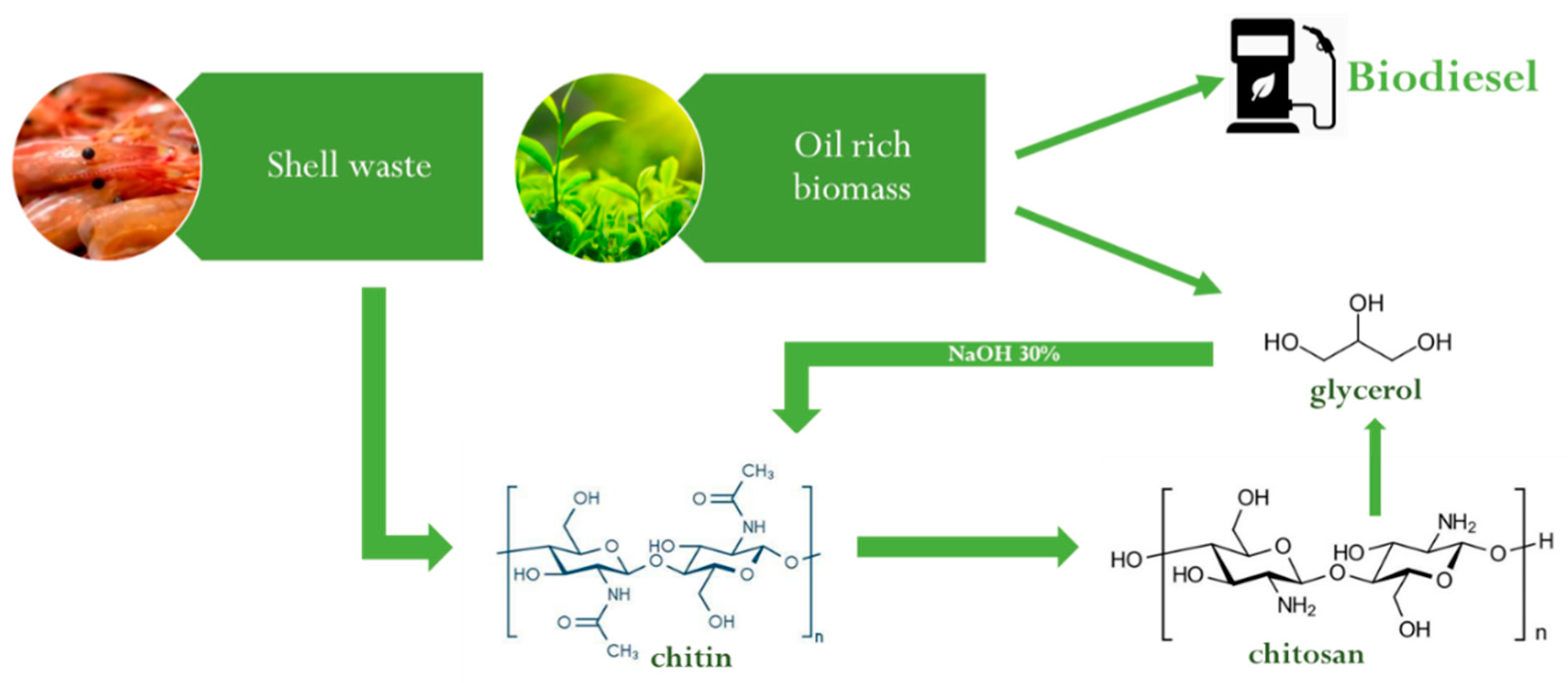
Liu et al. [62] tried to develop an efficient and green chemical process by using glycerol as a reaction solvent at 180 °C, enabling to lower the NaOH concentration needed for the deacetylation reaction. Glycerol is a recyclable, stable, green solvent that can be obtained as a by-product of biodiesel (Figure 7). Thus, the idea to use it for producing chitosan offers the opportunity to show a perfect example of circular economy and by-product recycling.
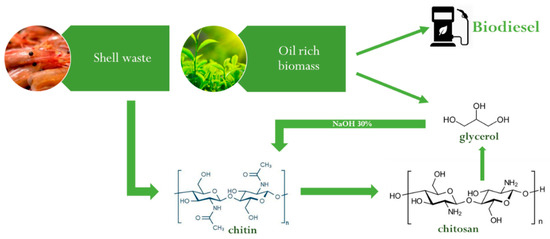
Figure 7.
Optimized green procedure to deacetylate chitin in chitosan. See text and Ref. [62] for details.
The optimized procedure involves the treatment of chitin with 30% NaOH and glycerol, keeping a 1:40 chitin/glycerol ratio. During the process, 1% of water was added to avoid the polymerization of glycerol catalyzed in an alkaline environment.
This new deacetylation route allows, at the same time, to obtain chitosan with lower NaOH concentration and to employ a by-product of another fundamental chemical process. Moreover, glycerol and NaOH can be recovered and reused for another deacetylation reaction.
Again, the concepts of “eco-sustainability”, “reuse” and “recycling” become the basis of the research.
4. Production of Chitin- and Chitosan-Based Hydrogels
Hydrogels are 3D hydrophilic polymeric networks that do not dissolve but can swell, in water.
In the last few years, there is increasing interest in these materials thanks to their solid and liquid-like properties, high biocompatibility, easy preparation, and versatile applications.
Hydrogels can be classified depending on their sources, pore size, nature of swelling, ionic charge, chain composition, and type of cross-linking [63,64]. In particular, according to their inter-chain interactions, they can be divided into physical and chemical hydrogels.
Physical hydrogels are cross-linked by physical interactions, such as entangled chains, hydrophobic or electronic interactions, van der Waals forces, or hydrogen bonds, which can be reversibly created and destroyed [65], setting the basis for stimuli-responsive “smart” materials.
Despite physical hydrogel can adsorb water, it is not uncommon finding some little defects in their network due to the presence of free chains [66,67].
Sometimes, to guarantee a stable structure and effective swelling, a covalent bond between polymeric chains, achieved by adding chemical cross-linkers, is required. These types of materials are referred to as chemical hydrogels [65].
Hydrogel formation is one of the most appreciated applications for chitin and chitosan [68,69,70]. They are classified as natural gels according to sources and have a great potential in various fields. Chitin and chitosan hydrogels, for example, are used in drug delivery [71,72] where the small pore in chitin, is exploited for a slow release of drug [73]. Tissue engineering wound dressing [74] and water purification [75] are other interesting applications, that make these hydrogels increasingly studied.
4.1. Common Chitin and Chitosan Physical Hydrogel
Most hydrogels based on chitosan and chitin required a two-step process: polymer dissolution and cross-linking (or gelation).
In both cases, the starting materials are chitin and chitosan powders.
While for chitosan the dissolution step is relatively easy and commonly takes place with an acidic aqueous solution (generally, acetic acid 5%) at room temperature, for chitin it is more complicated, due to its insolubility in water and the high number of inter- and intramolecular interactions between polymeric chains.
Therefore, in this step, finding a good solvent for this polymer is mandatory. The commonly used solvents include lithium chloride/dimethylacetamide (LiCl/DMAc) [76,77], Lithium chloride/N-Methyl-2-pyrolidone (LiCl/NMP) [78] and CaCl2·2H2O/MeOH [79].
In these cases, the gelation begins when the chitin concentration exceeds a certain threshold value. The polymer increasing concentration leads to an increase of entanglements between chains and, therefore, to a passage from a liquid isotropic structure to a solid gel with an anisotropic structure.
By pouring the obtained gel in a specific mold or in vials at a temperature between 5–60 °C for a certain time it is possible to facilitate the interaction between chains and increase the hydrogel stability. A similar effect can be obtained thanks to a process of coagulation, which consists of immerging gels in anti-solvents (water, methanol, ethanol, etc.) [77,78,79,80]. It is worth remembering that despite the fact that these solvents are still commonly used, they are toxic and not eco-friendly. In Table 3, a summary of different methods conventionally used for the preparation of hydrogels from chitin is reported.

Table 3.
Synoptic summary of common methods for the preparation of chitin-based hydrogels.
Chitosan-based physical hydrogels (as summarized in Table 4) are normally obtained by combining its acidic solution with an alkaline medium containing a physical cross-linker, such as Sodium Citrate (SC), Tripolyphosphate (TPP), and β-Glycerophosphate (β-GP) [81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89].

Table 4.
Overview of chitosan physical hydrogel production methods.
In particular, SC and TPP are negatively charged (SC contains COO− groups, while TPP contains P3O105− units) and can establish electronic interactions with –NH3+ units of chitosan in alkaline media, while β-GP is defined “hydrophobic cross-linker” and promotes a favorable environment to form hydrogel thanks to GP-polymer electrostatic interactions and polymer-polymer hydrophobic interactions. Despite the fact that these physical hydrogels are obtained with a greener approach thanks to the use of a non-toxic cross-linker, their application is still quite limited due to their low stability.
4.2. Common Routes for Chitin and Chitosan Chemical Hydrogels
In chemical hydrogels, the gelation step requires a chemical cross-linker that enables to achieve covalent bonds between polymeric chains.
As summarized in Table 5, for chitin, cross-linkers can be classified into two groups: those which lead to esterification reactions and those which lead to etherification reactions.

Table 5.
Overview of common chitin chemical hydrogel production methods.
The first ones, including butane tetracarboxylic dianhydride (BTCA) and succinic anhydride (SA) [90,91,92], create an ester bond with the chitin hydroxyl group.
Curing or coagulation are required, alongside the presence of a nucleophilic catalyst, such as dimethyl aminopyridine (DMAP) [93].
In the case of etherification, epichlorohydrin is commonly used [94,95]. In this case, nucleophilic catalysis induced by DMAP is not necessary, but alkali catalysis induced by solvents, such as NaOH or urea, is required.
For chitosan (Table 6), instead, gelation generally is obtained by using chemical cross-linkers glutaraldehyde (GA) and hexamethylene-1,6-di (aminocaroxysulfonate) (HDS) [96,97,98]. In these cases, nucleophilic or alkali catalysis is not required, but the cross-linkers can be added during or after curing. Alternatively, a gel solution can be soaked in the cross-linker solution through the use of a syringe.

Table 6.
Overview of common chitosan chemical hydrogel production methods.
4.3. Green Hydrogels
Both physical and chemical illustrated processes required the use of solvents and cross-linkers that are not environmentally or human health-friendly.
This perspective aims to show a valid sustainable alternative and, where possible, tries to recycle by-products of chitin and chitosan extraction.
For the preparation of physical chitin hydrogels, the use of the cited solvents in the dissolution steps is the main concern, due to their toxicity. For this reason, finding eco-substitutes is a primary issue.
Chen et al. [99] show a new dissolution process based on the simple treatment of chitin powder with low-concentrated NaOH solution at low temperature.
The protocol provides for the dispersion of chitin powder in a 20% NaOH aqueous solution under stirring. This NaOH concentration is not enough to deacetylate chitin, but after soaking the chitin/NaOH solution in a refrigerator at −18 °C, chitin undergoes dissolution. In these conditions, in fact, NaOH uptake is maximized, which promotes the formation of hydrogen bonds with chitin, destroying its original structure. After 12 h, the chitin solution can be recovered and heated at 60 °C. At this temperature, polymer chains establish hydrogen bonds forming entanglements that lead to the formation of the desired gel.
Valid alternatives for complete chitin dissolution are also other alkali solutions, such as 2.5 M KOH/0.67 M urea, 2.5 M NaOH/0.7 M urea, and 2.5 M LiOH/0.l67 M urea [100,101]. In these cases, the suspensions are frozen at −30 °C overnight and, then, cured at 0 °C.
Other interesting methods to dissolve chitin with green solvents have been reported by Sharma et al. [102] and Vicente et al. [103]. In these cases, DESs are used as solvents. In particular, ChCl:urea 1:2 dissolves chitin at 100 °C in 10 h, while ChCl:thiourea 1:2 dissolves the biopolymer at the same temperature in 6 h. In both cases, it is possible to reduce the required temperature for dissolution from 100 °C to 80 °C through ultrasonication for 1 h or microwaves irradiation for 2 h. ChCl: lactic acid 1:1 mixture (2 h) is evaluated as a further valid alternative.
As reported in Section 2.3, it is possible to extract chitin from crustaceans by using the same DESs, and these DESs can be recovered and reused a certain number of times. Therefore, the potential of these last methods consists in the employment of the same green chemicals used for chitin extraction and the recycling of subsequent chitin dissolution. This is a good example of a circular process.
A summary of different methods that can be used to achieve chitin-based hydrogels following green protocols can be found in Table 7.

Table 7.
Overview of chitin green hydrogel production methods.
In human health and the environment, the aforementioned glutaraldehyde, for example, can be toxic for humans, environment, and some species of animals [105,106,107] in certain conditions, so green alternatives are appreciated (summarized in Table 8).

Table 8.
Overview of chitosan green hydrogel production methods.
Agu et al. [108] demonstrated that citric acid can be used as a cross-linker for chitosan at room temperature, stirring the obtained chitosan dispersion for 40 min at 400 rpm.
Again, it is worthy of noticing that citric acid can be extracted by fungi [56], which can be at the same time source of chitin and hence of chitosan.
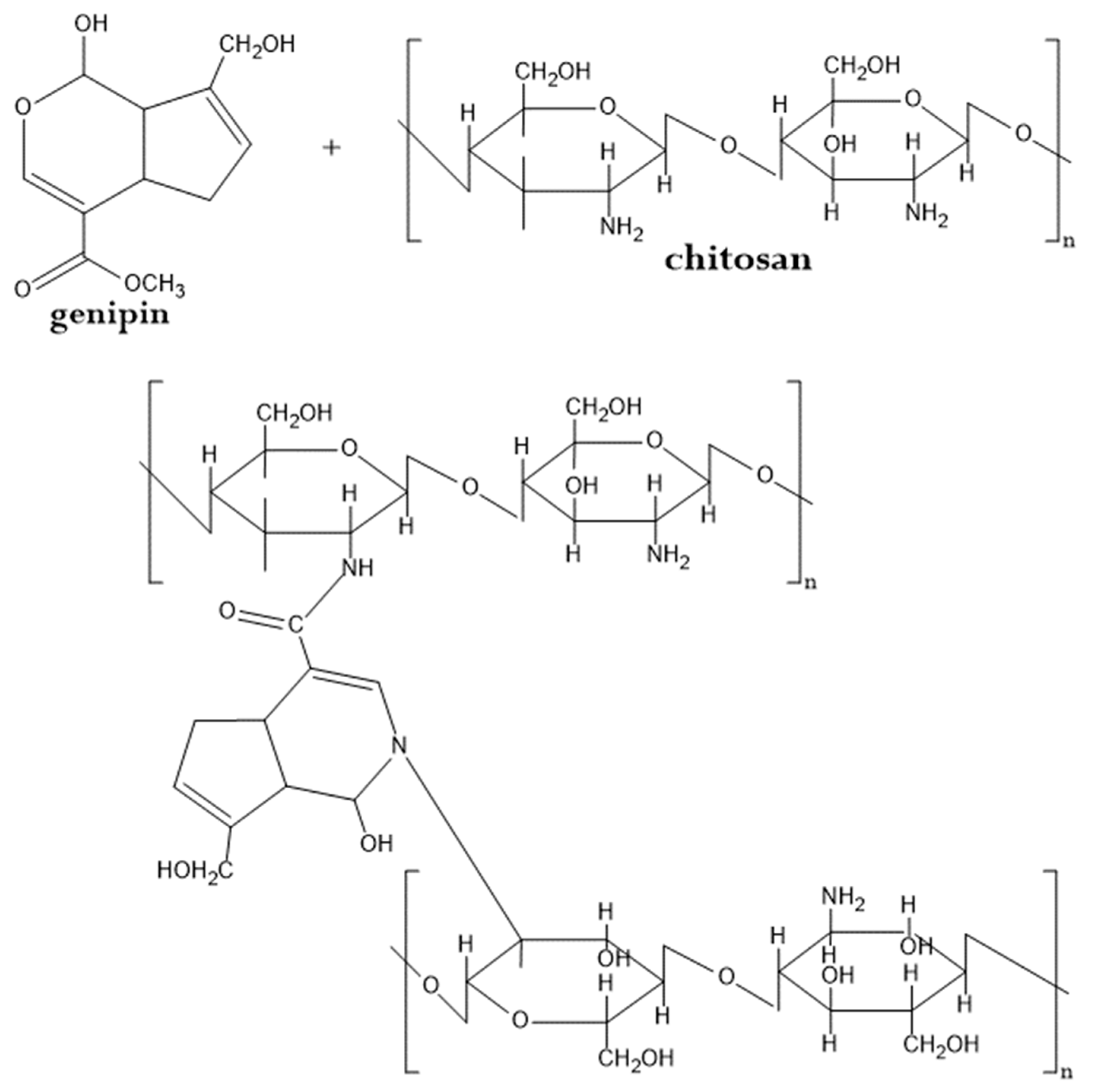
Genipin can replace more aggressive chemical cross-linkers [109,110,111,112]. Genipin is a natural chemical compound extracted from the fruit of Genipa americana. In the extraction process, the fruit of gardenia are washed, ground, and dried at 60 °C. Then, the obtained material is boiled with water for 30 min and the extract is recovered. Genipin works as a cross-linker for chitosan, by interacting with its amine groups and producing peptide bonds and tertiary amines. To obtain an optimal hydrogel, genipin (0.10 wt%) is added to the chitosan solution at pH = 5, followed by curing for 12 h at 37 °C (Figure 8).
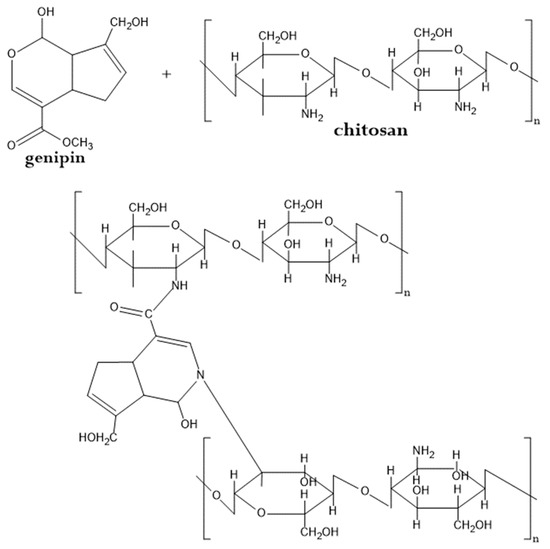
Figure 8.
Suggested crosslinking reaction mechanism between chitosan and genipin. See text and Ref. [111] for details.
The use of another molecule of natural origin, limonene, instead has been tested for the preparation of chitosan-based microspheres, using limonene as an emulsifier [113].
Another alternative is represented by the formation of a double crosslinking [114]. This process requires the reaction between alpha-beta unsaturated acylated chitosan and sulphydrilated chitosan to obtain a single-cross-linked hydrogel. The double cross-linking is lastly obtained by soaking the hydrogel in an ethanol solution. This route has the advantage to be fast, safe and it doesn’t require the use of toxic compounds.
Moreover, it has been proved that the use of chemical cross-linkers can be avoided by exploiting photo-crosslinking to induce the formation of a covalent bond between polymer chains [115]. In this case, it is necessary to make the starting chitosan solution photoreactive, by introducing inside the chitosan structure an azide group. This can be done by means of alkalization in isopropanol (a reaction between chitosan and propylene oxide in the presence of tetramethylammonium hydroxide as a catalyst). Then, the azide group is obtained by making the derived hydroxypropyl chitosan react with 4-azidobenzoic acid.
The newly described routes allow for minimizing of impacts on the environment thanks to the use of chemicals of natural origin. In addition, they allow the reuse of by-products of chitin and chitosan extraction, minimizing waste originated from the synthesis processes.
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
The increase in world population has led to the research of new methods for the sustainable disposal and reuse of food waste. In particular, the awareness that food waste can be a source of molecules with high added value (e.g., proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, etc.) has resulted in new investigations in the field of material science and bio-engineering. Chitin, and its derivative chitosan, are key examples of polysaccharides that can be extracted from food waste, in particular crustaceans and fungi. Renewability, biodegradability, and non-toxicity are the main advantages of their employment in the preparation of functional advanced materials for different applications. However, the processes at the basis of their production are not always paired with the same environmentally-sustainability. In fact, both molecule extraction and hydrogel production show some points of criticism. In the extraction process, the use of strong bases and acids, high temperatures, and a large amount of water for washing steps represent major limitations that still need to be addressed. In the case of hydrogel formation, instead, the major concerns come from the use of toxic and not eco-friendly solvents and cross-linkers. This Perspective summarizes most of the work that can be found in recent literature, aimed at the exploitation of eco-friendly alternative routes. These unconventional strategies are based on the employment of green solvents for chitin extraction and dissolution (DES-based on choline chloride, urea, organic acids), alternative sources of heating (microwave), and/or the use of non-toxic and natural crosslinkers (citric acid, genipin or limonene). In this regard, we would like to highlight that citric acid and DESs/NADES can combine good results during chitin extraction, with the possibility of reusing them in subsequent processing steps: DES can be reused for chitin dissolution before its conversion into chitosan, while citric acid shows the interesting application as cross-linker in hydrogel production. The opportunity of purifying and recycling these extraction chemicals introduces the possibility of developing a whole circular process in which by-products of a single step can be used as reagents in the following one, creating inner loops that are associated with the concepts of “system chemistry” and “circular economy”. We want also to underline that most of the chemicals proposed an alternative “green” procedures (choline chloride, urea, organic acids, glycerol, limonene, or genipin) can be extracted from natural sources, and, in some cases, they are by-products of other chemical processes, leading to the development of interconnected sustainable systems. Anyway, these are only a limited number of examples and a huge amount of work has still to be done in this framework. In the future, more attention should be focused on (a) intensive study of DES and NADES and their application in the extraction of chitin (b) low temperature and low energy process for extraction of chitin and chitosan and production of hydrogel (c) evaluation of the cost of production and disposal of chemicals used in the green routes. In addition, to obtain a truly sustainable system, it is necessary to evaluate not only the toxicity of the involved chemicals but also the embodied energy linked to their production, the CO2 footprint of the whole process, and the life cycle assessment of the final product. This information can be scarcely found in literature, but the new analysis could be performed, also with the support of machine learning and artificial intelligence-based algorithms.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out with the support of Ministero Italiano delle Politiche Agricole, Alimentari, Forestali e del Turismo (MIPAAFT) in the framework of the RESTART project. M. M. acknowledges ENEA for supporting her grant, in the framework of the program “Smart agriculture for the sustainability of the agro-food system”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- FAO. Food Wastage Footprint Impacts on Natural Resources; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; ISBN 9789251077528. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Preparatory Study on Food Waste Across Eu 27; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2010; Volume 33, ISBN 9789279221385. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Food Recovery Hierarchy; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Weiss, J.; Takhistov, P.; McClements, D.J. Functional materials in food nanotechnology. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Ikawa, N.I.; Ozimek, L. Chemical composition of chicken eggshell and shell membranes. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patni, N.; Tripathi, N.; Bosmia, S. Casein Extraction from various milk samples and its role as a viable substitute for conventional plastics. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2013, 8, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, V.K.; Voicu, S.I. Recent advances in cellulose and chitosan based membranes for water purification: A concise review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 146, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Ma, S.; Wang, C. Chitosan-Based Hydrogel for Removing Silver Ions in Water and Preparation Method Thereof. Chinese Patent CN108948381A, 7 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vassalini, I.; Litvinava, M.; Alessandri, I. All food waste-based membranes for Chromium(VI) removal. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peydayesh, M.; Suter, M.K.; Bolisetty, S.; Boulos, S.; Handschin, S.; Nyström, L.; Mezzenga, R. Amyloid Fibrils Aerogel for Sustainable Removal of Organic Contaminants from Water. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muskovich, M.; Bettinger, C.J. Biomaterials-Based electronics: Polymers and interfaces for biology and medicine. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 248–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Deng, L. Chitin Regenerated Hydrogel as Well as Preparation Method and Application Thereof. Chinese Patent CN111312528A, 19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Mezzenga, R. Design principles of food gels. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, I.; Özogul, F.; Regenstein, J.M. Industrial applications of crustacean by-products (chitin, chitosan, and chitooligosaccharides): A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 48, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Huang, H. Magnetic chitin hydrogels prepared from Hericium erinaceus residues with tunable characteristics: A novel biosorbent for Cu2+ removal. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 220, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Kujundzic, M.; John, S.; Bismarck, A. Crab vs. Mushroom: A review of crustacean and fungal chitin in wound treatment. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Chen, X. Don’t waste seafood waste: Turning cast-off shells into nitrogen-rich chemicals would benefit economies and the environment. Nature 2015, 524, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauchie, H.M. Chitin production by arthropods in the hydrosphere. Hydrobiologia 2002, 470, 63–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Tan, E.; Kim, H.J.; Zhang, A.; Bhattacharya, R.; Yarema, K.J. Comparative evaluation of chitosan, cellulose acetate, and polyethersulfone nanofiber scaffolds for neural differentiation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Lu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, C.; Lu, L.; Zhang, S. Direct conversion of shrimp shells to: O -acylated chitin with antibacterial and anti-tumor effects by natural deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Bhuiyan, M.A.R.; Islam, M.N. Chitin and Chitosan: Structure, Properties and Applications in Biomedical Engineering. J. Polym. Environ. 2017, 25, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, M.P.C.; Sábio, R.M.; de Ribeiro, T.C.; dos Santos, A.M.; Meneguin, A.B.; Chorilli, M. Highlighting the impact of chitosan on the development of gastroretentive drug delivery systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 804–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.M.; Silva, S.S.; Reis, R.L. Exploring the use of Choline Acetate on the sustainable development of α-chitin-based sponges. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 13507–13516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, D.G.; Peixoto, L.P.F.; Sánchez-Cortés, S.; Andrade, G.F.S. Chitosan-based improved stability of gold nanoparticles for the study of adsorption of dyes using SERS. Vib. Spectrosc. 2016, 87, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukhadra, M.R.; Adlii, A.; Bakry, B.M. Green fabrication of bentonite/chitosan@cobalt oxide composite (BE/CH@Co) of enhanced adsorption and advanced oxidation removal of Congo red dye and Cr (VI) from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xia, Y. Facile synthesis of chitosan-gold nanocomposite and its application for exclusively sensitive detection of Ag+ ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 226, 115290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Historical review on chitin and chitosan biopolymers. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1623–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi Kumar, M.N.V. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar, V.; Asghari, M.; Dashti, A. A Review on Chitin and Chitosan Polymers: Structure, Chemistry, Solubility, Derivatives, and Applications. ChemBioEng Rev. 2015, 2, 204–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Berton, P.; Rogers, R.D. Advances in Functional Chitin Materials: A Review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6444–6457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barikani, M.; Oliaei, E.; Seddiqi, H.; Honarkar, H. Preparation and application of chitin and its derivatives: A review. Iran. Polym. J. 2014, 23, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, B.; Koytepe, S.; Ulu, A.; Gurses, C.; Thakur, V.K. Chemistry, structures, and advanced applications of nanocomposites from biorenewable resources. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 9304–9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.K.; Thakur, M.K. Recent advances in graft copolymerization and applications of chitosan: A review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2637–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A.; Boudrant, J.; Meyer, D.; Manno, N.; Demarchis, M.; Paoletti, M.G. Current views on fungal chitin/chitosan, human chitinases, food preservation, glucans, pectins and inulin: A tribute to Henri Braconnot, precursor of the carbohydrate polymers science, on the chitin bicentennial. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 995–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavall, R.L.; Assis, O.B.G.; Campana-Filho, S.P. β-Chitin from the pens of Loligo sp.: Extraction and characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, E. Conformations in polysaccharides and complex carbohydrates. J. Biosci. 1985, 8, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.C.; Salaün, F.; Giraud, S.; Ferri, A.; Chen, G.; Guan, J. Solubility of Chitin: Solvents, Solution Behaviors and Their Related Mechanisms. Solubility Polysacch. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Liu, Y.; Kennedy, J.F.; Nie, J. Synthesize and properties of photosensitive organic solvent soluble acylated chitosan derivatives (2). Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboh, O.C.; Qin, Y. Chitin and Chitosan Fibers. Polym. Adv. Technol. 1997, 8, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsunori, I.; Hiroshi, S.; Seiichi, T. Chitin Solution. Japonese Patent JPH06179702A, 28 June 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Arbia, W.; Arbia, L.; Adour, L.; Amrane, A. Chitin extraction from crustacean shells using biological methods—A review. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 51, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Di Mario, F.; Rapanà, P.; Tomati, U.; Galli, E. Chitin and chitosan from Basidiomycetes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 43, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassainia, A.; Satha, H.; Boufi, S. Chitin from Agaricus bisporus: Extraction and characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents in natural products research: Mixtures of solids as extraction solvents. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2162–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Munro, H.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Preparation of novel, moisture-stable, lewis-acidic ionic liquids containing quaternary ammonium salts with functional side chains. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1, 2010–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sert, M. Catalytic effect of acidic deep eutectic solvents for the conversion of levulinic acid to ethyl levulinate. Renew. Energy 2020, 153, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, T.J.; Singh, T.P.; Singh, O.M. The one-pot four-component eco-friendly synthesis of spirooxindoles in deep eutectic solvent. J. Chem. Sci. 2020, 132, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Bulatov, A.; Locatelli, M.; Carradori, S.; Andruch, V. Application of deep eutectic solvents in analytical chemistry. A review. Microchem. J. 2017, 135, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Gu, Z.; Hong, S.; Lian, H. One-pot production of chitin with high purity from lobster shells using choline chloride–malonic acid deep eutectic solvent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravana, P.S.; Ho, T.C.; Chae, S.J.; Cho, Y.J.; Park, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Chun, B.S. Deep eutectic solvent-based extraction and fabrication of chitin films from crustacean waste. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Huang, W.C.; Guo, N.; Zhang, S.; Xue, C.; Mao, X. Two-step separation of chitin from shrimp shells using citric acid and deep eutectic solvents with the assistance of microwave. Polymers 2019, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Fernández, R.; López-Martínez, J.C.; Romero-González, R.; Martínez-Vidal, J.L.; Alarcón Flores, M.I.; Garrido Frenich, A. Simple LC-MS determination of citric and malic acids in fruits and vegetables. Chromatographia 2010, 72, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penniston, K.L.; Nakada, S.Y.; Holmes, R.P.; Assimos, D.G. Quantitative assessment of citric acid in lemon juice, lime juice, and commercially-available fruit juice products. J. Endourol. 2008, 22, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Show, P.L.; Oladele, K.O.; Siew, Q.Y.; Aziz Zakry, F.A.; Lan, J.C.W.; Ling, T.C. Overview of citric acid production from Aspergillus niger. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradić, B.; Novak, U.; Likozar, B. Crustacean shell bio-refining to chitin by natural deep eutectic solvents. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baklagina, Y.G.; Klechkovskaya, V.V.; Kononova, S.V.; Petrova, V.A.; Poshina, D.N.; Orekhov, A.S.; Skorik, Y.A. Polymorphic Modifications of Chitosan. Crystallogr. Rep. 2018, 63, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigos, I.; Martinou, A.; Kafetzopoulos, D.; Bouriotis, V. Chitin deacetylases: New, versatile tools in biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.; Oh, K.T.; Nguyen, V.N.; Park, R.D. Enzymatic deacetylation of chitin by extracellular chitin deacetylase from a newly screened Mortierella sp. DY-52. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 759–766. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Park, R.D.; Muzzarelli, R.A.A. Chitin deacetylases: Properties and applications. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, G.; Sui, W.; An, L.; Si, C. Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan by a Novel Deacetylation Approach Using Glycerol as Green Reaction Solvent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4690–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Othman, M.B.H.; Javed, F.; Ahmad, Z.; Akil, H.M. Classification, processing and application of hydrogels: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 57, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Garg, A.; Vishwavidyalaya, R.D. Hydrogel: Classification, Properties, Preparation and Technical Features. Asian J. Biomater. Res. 2016, 2, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Maitra, J.; Shukla, V.K. Cross-linking in Hydrogels—A Review. Am. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 4, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.T.; West, J.L. Photopolymerizable hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4307–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.S. Self-dissolving chitosan, I: Preparation, characterization and evaluation for drug delivery system. Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1998, 259, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akakuru, O.U.; Isiuku, B.O. Chitosan Hydrogels and their Glutaraldehyde-Crosslinked Counterparts as Potential Drug Release and Tissue Engineering Systems—Synthesis, Characterization, Swelling Kinetics and Mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. Biophys. 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta Ramos, M.L.; González, J.A.; Albornoz, S.G.; Pérez, C.J.; Villanueva, M.E.; Giorgieri, S.A.; Copello, G.J. Chitin hydrogel reinforced with TiO2 nanoparticles as an arsenic sorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Shamshina, J.L.; Berton, P.; Gurau, G.; Rogers, R.D. Hydrogels based on cellulose and chitin: Fabrication, properties, and applications. Green Chem. 2015, 18, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, R. Drug delivery applications of chitin and chitosan: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 577–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazi, R.; Amiji, M. Chitosan-based gastrointestinal delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2003, 89, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Impacts of nanowhisker on formation kinetics and properties of all-cellulose composite gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Furuike, T.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Biomedical applications of chitin hydrogel membranes and scaffolds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Bai, H.; Li, L. Graphene oxide-chitosan composite hydrogels as broad-spectrum adsorbents for water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1992–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, D.; Tatsumi, D.; Matsumoto, T.; Murata, K.; Hayashi, H.; Yoshitani, H. Investigation of the structure of cellulose in LiCl/DMAc solution and its gelation behavior by small-angle X-ray scattering measurements. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Bengisu, M. Preparation and characterization of physical gels and beads from chitin solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 54, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, D.; Vachoud, L.; Chakrabandhu, Y.; Pochat-Bohatier, C. Influence of mass transfer on gelation time using VIPS-gelation process for chitin dissolved in LiCl/NMP solvent-Modelling and experimental study. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Nagahama, H.; Tokura, S. Preparation of chitin hydrogel under mild conditions. Cellulose 2006, 13, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsioptsias, C.; Panayiotou, C. Foaming of chitin hydrogels processed by supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2008, 47, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.Z.; Zhu, K.J.; Song, W. Novel pH-sensitive citrate cross-linked chitosan film for drug controlled release. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 212, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, H.; Yerlikaya, Ç.; Uzan, S. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of copper (II) ion uptake by modified wheat shells. Desalin. Water Treat. 2012, 44, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, W.S.W.; Fatinathan, S. Adsorption characterization of Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions onto chitosan-tripolyphosphate beads: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureshkumar, M.K.; Das, D.; Mallia, M.B.; Gupta, P.C. Adsorption of uranium from aqueous solution using chitosan-tripolyphosphate (CTPP) beads. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csaba, N.; Köping-Höggård, M.; Alonso, M.J. Ionically crosslinked chitosan/tripolyphosphate nanoparticles for oligonucleotide and plasmid DNA delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 382, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Nishimoto, S.K.; Bumgardner, J.D.; Haggard, W.O.; Gaber, M.W.; Yang, Y. A chitosan/β-glycerophosphate thermo-sensitive gel for the delivery of ellagic acid for the treatment of brain cancer. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4157–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenite, A.; Chaput, C.; Wang, D.; Combes, C.; Buschmann, M.D.; Hoemann, C.D.; Leroux, J.C.; Atkinson, B.L.; Binette, F.; Selmani, A. Novel injectable neutral solutions of chitosan form biodegradable gels in situ. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.M.; Hughes, N.; Hunt, J.A.; Freemont, A.J.; Hoyland, J.A. Human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to NP-like cells in chitosan-glycerophosphate hydrogels. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, H.; Fujita, S. Biodegradable superabsorbent hydrogels derived from cellulose by esterification crosslinking with 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxylic dianhydride. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2582–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, H.; Zakimi, M. Preparation, water absorbency, and enzyme degradability of novel chitin- and cellulose/chitin-based superabsorbent hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T.; Matsuo, K.; Fujioka, R. Novel biodegradable superabsorbent hydrogels derived from cotton cellulose and succinic anhydride: Synthesis and characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 99, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T.; Uchikoshi, I.; Yoshiura, Y.; Fujioka, R. Synthesis and characterization of novel biodegradable superabsorbent hydrogels based on chitin and succinic anhydride. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 61, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakura, A.; Kawajiri, K.; Ohkubo, T.; Kosugi, Y.; Ishihara, K. Widely useful DMAP-catalyzed esterification under auxiliary base- and solvent-free conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 14775–14779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chang, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L. Hydrogels prepared from unsubstituted cellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L. Novel hydrogels prepared via direct dissolution of chitin at low temperature: Structure and biocompatibility. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3865–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierszewska-Drużyńska, M.; Ostrowska-Czubenko, J. Structural and swelling properties of hydrogel membranes based on chitosan crosslinked with glutaraldehyde and sodium tripolyphosphate. Prog. Chem. Appl. Chitin Deriv. 2015, 20, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, J.; Yamanaka, Y.; Ohkawa, K. Chitin-chitosan nanocomposite gels: Reinforcement of chitosan hydrogels with rod-like chitin nanowhiskers. Polym. J. 2012, 44, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kildeeva, N.R.; Perminov, P.A.; Vladimirov, L.V.; Novikov, V.V.; Mikhailov, S.N. About mechanism of chitosan cross-linking with glutaraldehyde. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2009, 35, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, D.; Yano, H.; Abe, K. Dissolution and gelation of α-chitin nanofibers using a simple NaOH treatment at low temperatures. Cellulose 2014, 21, 3339–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Zhao, D.; Song, J.; Gao, H.; Xu, D.; Xu, M.; Cao, X.; Zhang, L.; Cai, J. Light weight, mechanically strong and biocompatible α-chitin aerogels from different aqueous alkali hydroxide/urea solutions. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 59, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Huang, J.C.; Zhang, L.N. Solvent Composition for Dissolving Chitin. Chinese Patent CN103059320A, 24 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.; Mukesh, C.; Mondal, D.; Prasad, K. Dissolution of α-chitin in deep eutectic solvents. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 18149–18155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, F.A.; Bradić, B.; Novak, U.; Likozar, B. α-Chitin dissolution, N-deacetylation and valorization in deep eutectic solvents. Biopolymers 2020, 111, e23351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, L.N.; Zhong, Y. Preparation Method of Chitosan Gel Series Material. Chinese Patent CN106800662A, 6 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger, E.; Gollapudi, B.; Spencer, P. Genetic toxicity and carcinogenicity studies of glutaraldehyde—A review. Mutat. Res.—Rev. Mutat. Res. 2005, 589, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, H.W. Ecotoxicology of glutaraldehyde: Review of environmental fate and effects studies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2001, 49, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takigawa, T.; Endo, Y. Effects of glutaraldehyde exposure on human health. J. Occup. Health 2006, 48, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, A.B.S.; Benablo, P.J.L.; Mesias, V.S.D.; Penaloza, D.P. Synthesis and characterization of a chitosan-based citric acid-crosslinked encapsulant system. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2019, 64, 4610–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A. Genipin-crosslinked chitosan hydrogels as biomedical and pharmaceutical aids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, M.J.; Figueiredo, M.M.; Gil, M.H. Rheological study of genipin cross-linked chitosan hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3823–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.R.; Hsu, L.H.; Xiao, E.S.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X. Using genipin as a “green” crosslinker to fabricate chitosan membranes for pervaporative dehydration of isopropanol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 244, 116843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, F.L.; Tan, Y.C.; Liang, H.F.; Sung, H.W. In vivo biocompatibility and degradability of a novel injectable-chitosan-based implant. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H. Method for Preparing Chitosan Microspheres by Limonene Emulsification. Chinese Patent CN109046194A, 21 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L.; Chu, J. Double-Crosslinked Chitosan Hydrogel as Well as Preparation Method and Application Thereof. Chinese Patent CN111333878A, 26 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Chen, J.; Ling, K.; Xu, Z. Method for Preparing Photo-Crosslinking Chitosan Hydrogel Film. Chinese Patent CN101530629A, 16 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).