Phenol Recovery from Aromatic Solvents by Formation of Eutectic Liquids with Trialkyl-2,3-dihydroxypropylammonium Chloride Salts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials And Methods
2.1. Materials
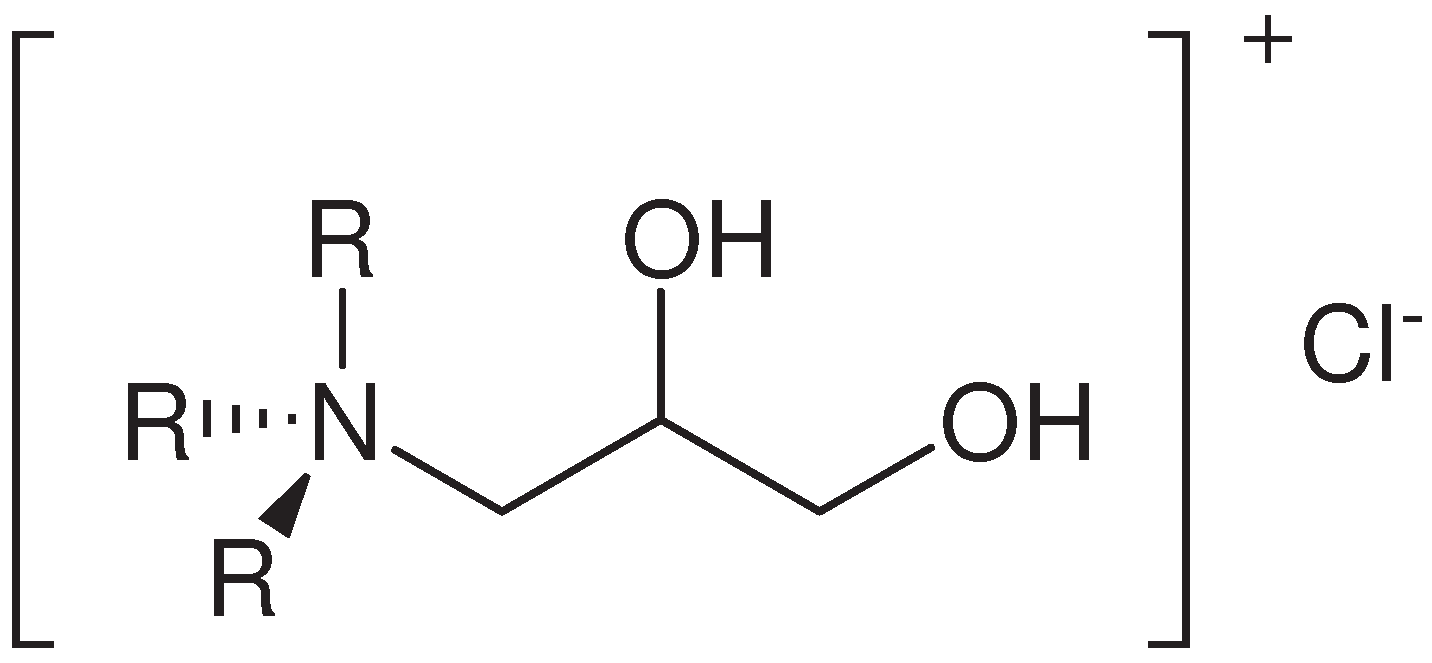
2.1.1. Trimethyl-2,3-dihydroxypropylammonium Chloride, [Me3NCH2CH(OH)CH2(OH)]Cl (1)
2.1.2. Triethyl-2,3-dihydroxypropylammonium Chloride, [Et3NCH2CH(OH)CH2(OH)]Cl (2)
2.1.3. Tributyl-2,3-dihydroxypropylammonium Chloride, [Bu3NCH2CH(OH)CH2(OH)]Cl (3)
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. Characterisation
2.2.2. Phenol Extraction Screening
3. Results and Discussion
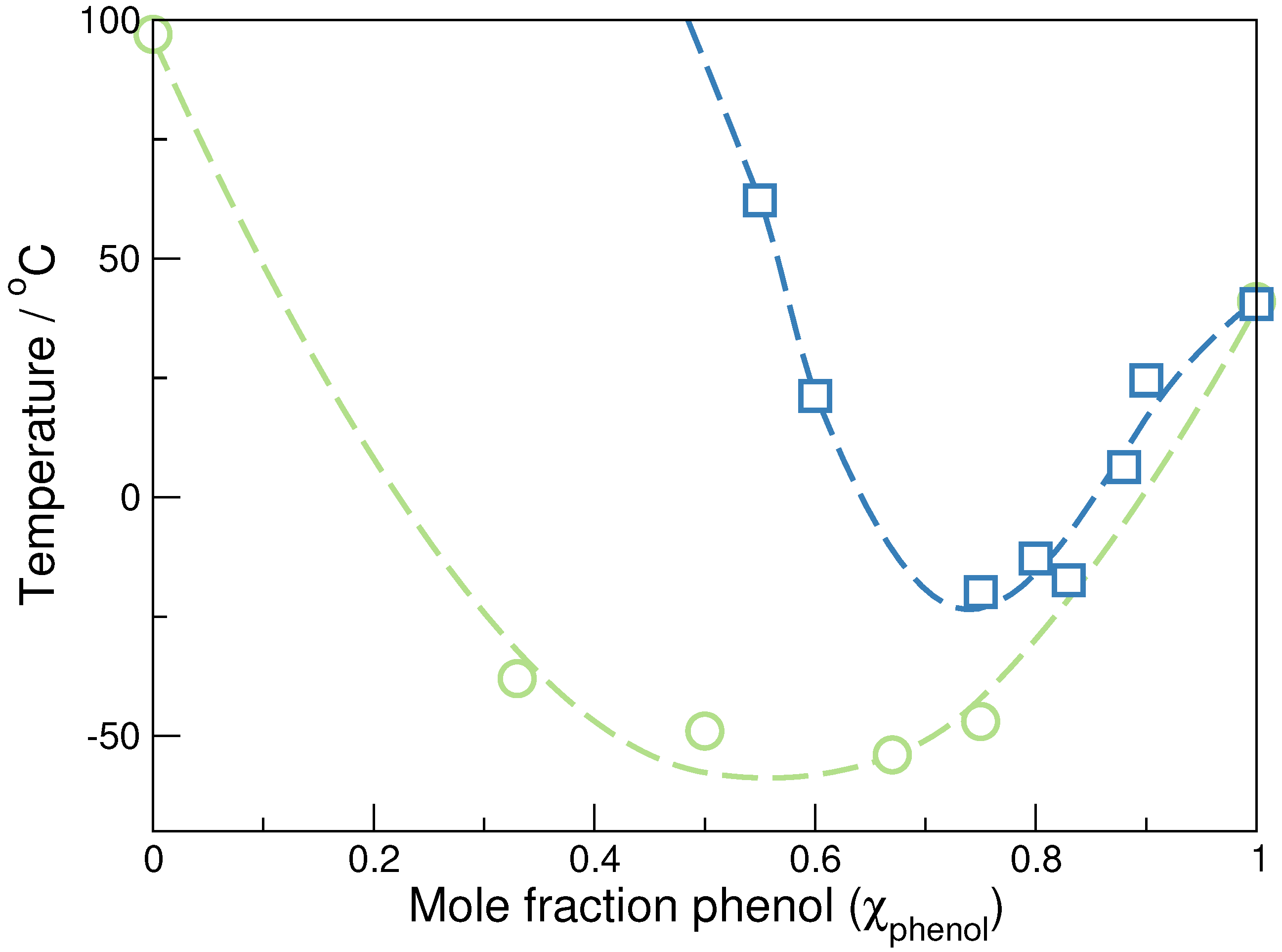
3.1. Formation of [Et3NCH2CH(OH)CH2(OH)]Cl/phenol Eutectic Mixtures
3.2. Extraction of Phenol from Hexane and Toluene
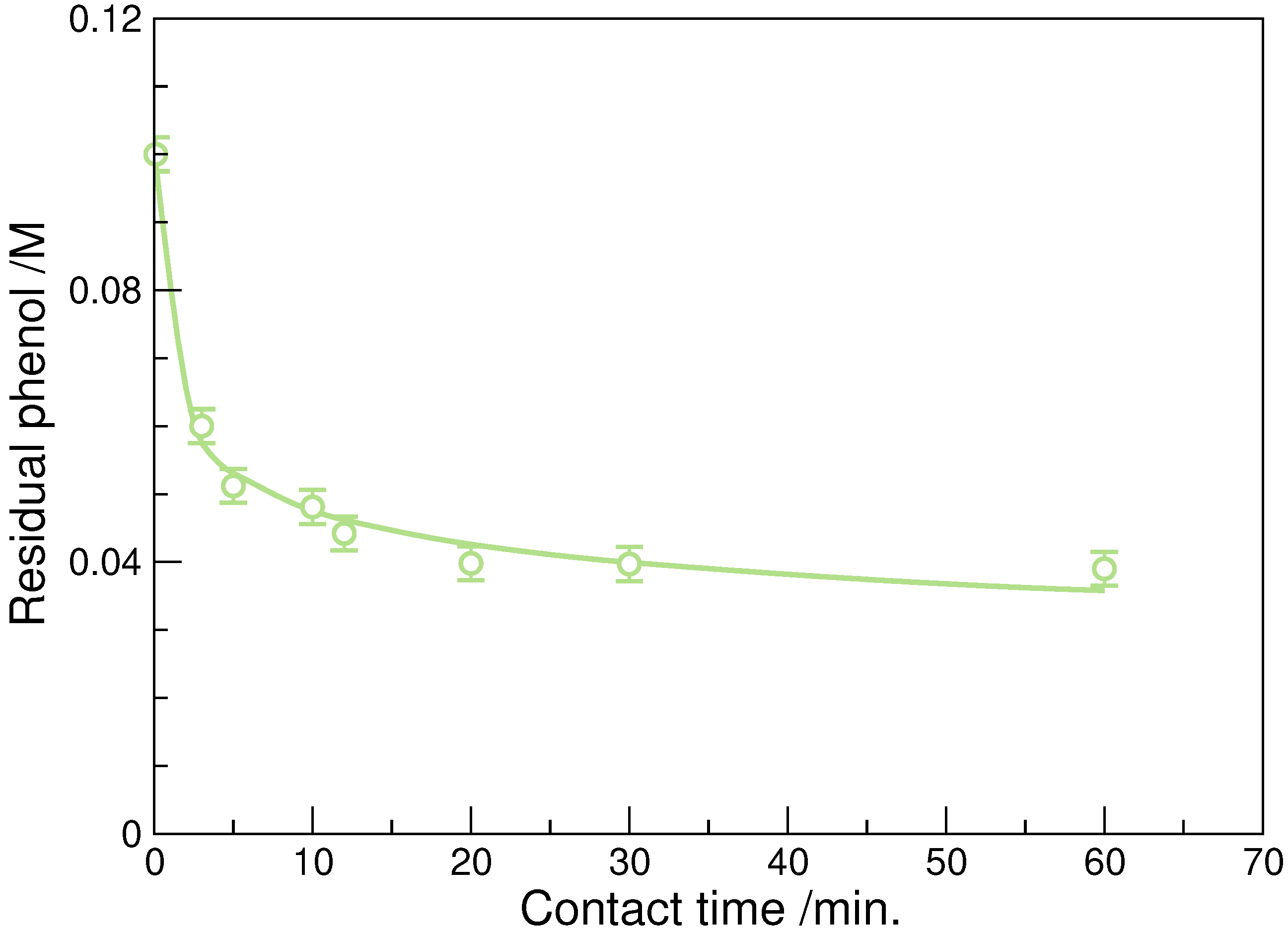
3.3. Effect of Mixing Time
3.4. Effect of Extractant Mole Ratio
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weissermel, K.; Arpe, H.J. Industrial Organic Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rappoport, Z. The Chemistry of Phenols; Patai’s Chemistry of Functional Groups; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R.J. Industrial catalytic processes—Phenol production. Industrial Catalytic Processes. Appl. Catal. A 2005, 280, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Schobert, H.H. Non-fuel uses of coals and synthesis of chemicals and materials. Fuel 1996, 75, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schobert, H.H.; Song, C. Chemicals and materials from coal in the 21st century. Fuel 2002, 81, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.P.P.; Arauzo, J.; Fonts, I.; Domine, M.E.; Fernandez Arroyo, A.; Estrella Garcia-Perez, M.; Montoya, J.; Chejne, F.; Pfromm, P.; Garcia-Perez, M. Challenges and opportunities for bio-oil refining: A review. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 4683–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.; Hou, Y.; Wu, W.; Guo, W.; Peng, W.; Marsh, K.N. Efficient separation of phenols from oils via forming deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2398–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Hou, Y.; Wu, W.; Ren, S.; Tian, S.; Marsh, K.N. Separation of phenol from model oils with quaternary ammonium salts via forming deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubalo, M.C.; Ćurko, N.; Tomašević, M.; Ganić, K.K.; Redovniković, I.R. Green extraction of grape skin phenolics by using deep eutectic solvents. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Rodríguez-Juan, E.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, G.; Rios, J.J.; Fernández-Bolaños, J. Extraction of phenolic compounds from virgin olive oil by deep eutectic solvents (DESs). Food Chem. 2016, 197, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruesgas-Ramón, M.; Figueroa-Espinoza, M.C.; Durand, E. Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) for Phenolic Compounds Extraction: Overview, Challenges, and Opportunities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, O.G.; Castro, M.; Domínguez, Á.; González, B. Removing phenolic pollutants using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 115703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, D.; Ji, Y.; Ren, S. Roles of a hydrogen bond donor and a hydrogen bond acceptor in the extraction of toluene from n-heptane using deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3089–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Hou, Y.; Ren, S.; Yao, C.; Wu, W. Tetraethylammonium amino acid ionic liquids and CO2 for separation of phenols from oil mixtures. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 11046–11054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Ren, Y.; Peng, W.; Ren, S.; Wu, W. Separation of phenols from oil using imidazolium-based ionic liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 18071–18075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidek, N.; Manan, N.S.A.; Mohamad, S. Efficient removal of phenolic compounds from model oil using benzyl imidazolium-based ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 240, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Hou, Y.; Ren, S.; Yao, C.; Wu, W. Highly efficient separation of phenolic compounds from oil mixtures by imidazolium-based dicationic ionic liquids via forming deep eutectic solvents. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 10274–10282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Hou, Y.; Ren, S.; Yao, C.; Wu, W. Highly efficient extraction of phenolic compounds from oil mixtures by trimethylamine-based dicationic ionic liquids via forming deep eutectic solvents. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 171, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Hou, Y.; Ren, S.; Ji, Y.; Wu, W. Ternary phase behavior of phenol plus toluene plus zwitterionic alkaloids for separating phenols from oil mixtures via forming deep eutectic solvents. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 448, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Hou, Y.; Ren, S.; Wu, W.; Zhang, K.; Ji, Y.; Liu, H. Efficient separation of phenol from model oils using environmentally benign quaternary ammonium-based zwitterions via forming deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Hou, Y.; Ren, S.; Wu, W.; Ji, Y.; Liu, H. Sulfonate based zwitterions: A new class of extractants for separating phenols from oils with high efficiency via forming deep eutectic solvents. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 178, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Zhang, M.; Tan, T.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, H. Deep eutectic solvents as novel extraction media for phenolic compounds from model oil. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 11749–11752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Hou, Y.; Ren, S.; Yao, C.; Wu, W. Separation of phenolic compounds from oil mixtures using environmentally benign biological reagents based on Bronsted acid-Lewis base interaction. Fuel 2019, 239, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, T.; Li, C.; Zhuang, X.; Cao, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S. The new liquid-liquid extraction method for separation of phenolic compounds from coal tar. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, T.; Zhuang, X.; He, H.; Li, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S. Separation of phenolic compounds from coal tar via liquid liquid extraction using amide compounds. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 2573–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Xuan, X.; Wang, J. Efficient separation of phenolic compounds from model oil by the formation of choline derivative-based deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 163, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Feng, J.; Li, W.; Luo, Z. High-performance separation of phenolic compounds from coal-based liquid oil by deep eutectic solvents. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7777–7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.H.; Holbrey, J.D. Investigation of glycerol hydrogen-bonding networks in choline chloride/glycerol eutectic-forming liquids using neutron diffraction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 21782–21789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.H.; Byrne, E.L.; Pereira, T.; Holbrey, J.D. Enhanced extraction of phenol from model oils using ionic liquids elucidated with neutron diffraction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 10219–10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.H.; Holbrey, J.D. The solution structure of 1:2 phenol/N-methylpyridinium bis{(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl}imide liquid mixtures. J. Solution Chem. 2015, 44, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, H.; Ge, C.T.; Ren, N.N.; Ma, W.Y.; Lu, Y.Z.; Li, C.X. Complex extraction of phenol and cresol from model coal tar with polyols, ethanol amines, and ionic liquids thereof. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, M.A.; Bland, C.C.; Varma, K.S. A 11B NMR study of zwitterionic and cationic monoborate complexes with cationic 1,2-diol ligands. Polyhedron 2008, 27, 2226–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfurt, K.; Wandzik, I.; Walczak, K.; Matuszek, K.; Chrobok, A. Hydrogen-bond-rich ionic liquids as effective organocatalysts for Diels–Alder reactions. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3508–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnati, M.O.; Amigoni, S.; Taffin de Givenchy, E.P.; Darmanin, T.; Choulet, O.; Guittard, F. Glycerol carbonate as a versatile building block for tomorrow: Synthesis, reactivity, properties and applications. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 283–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Hou, Y.; Ren, S.; Tian, S.; Wu, W. Formation of deep eutectic solvents by phenols and choline chloride and their physical properties. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2013, 58, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Ye, F.; Song, N.; Xu, Y. Physicochemical properties of deep eutectic solvents formed by choline chloride and phenolic compounds at T = (293.15 to 333.15) K: The influence of electronic effect of substitution group. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 232, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Kong, J.; Ren, Y.; Ren, S.; Wu, W. Mass transfer dynamics in the separation of phenol from model oil with quaternary ammonium salts via forming deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.H.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Kong, J.; Hou, Y.C.; Wu, W.Z. Effect of water on the separation of phenol from model oil with choline chloride via forming deep eutectic solvent. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 137, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Type | Structure | References |
|---|---|---|
| Organic Salts and Ionic Liquids | ||
| Quaternary ammonium |  | Pang et al. [7], Guo et al. [8], Ji et al. [14] |
| Bifunctional ammonium |  | Pang et al. [7], Guo et al. [8], Meng et al. [31], Zhang et al. [26] |
| Aromatic ‘ionic liquid’ cations |  | Hou et al. [15], Turner and Holbrey [30], Sidek et al. [16] |
| Gemini dicationic salts |  | Ji et al. [17,18] |
| Zwitterions | ||
| Betaine |  | Yao et al. [19,20] |
| L-carnitine |  | Yao et al. [19,20] |
| Trialkylammonium-alkylsulfonate |  | Yao et al. [21] |
| L-lysine |  | Ji et al. [23] |
| Hydrogen bond acceptors | ||
| 1-Alkylimidazole |  | Jiao et al. [24] |
| Amides |  | Jiao et al. [25], Ji et al. [23] |
| Deep eutectic solvents | ||
| Choline/glycerol DES |  | Yi et al. [27] |
| Melting Point/C | Glass Transition Temperature/C | Decomposition Temperature (Td)/∘C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 206 | ||
| 0.33 | 202 | ||
| 0.50 | 196 | ||
| 0.67 | 205 | ||
| 0.75 | 140 | ||
| 1.00 | 105 |
| Salt | Hexane | Toluene | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 M | 0.1 M | 2 M | |
| [Me3NCH2CH(OH)CH2OH]Cl (1) | 87 | 2 | 92 |
| [Et3NCH2CH(OH)CH2OH]Cl (2) | 94 | 60 | 99 |
| [Bu3NCH2CH(OH)CH2OH]Cl (3) | 84 | ||
| [Me3NCH2CH2OH]Cl (ChCl) | 89 | 33 | 96 |
| [NMe4]Cl | 89 | 32 | |
| [NEt4]Cl | 100 | 95 | |
| [NPr4]Cl | 100 | 91 | |
| [NBu4]Cl | 100 | – | - |
| [PBu4]Cl | 99 | – |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Byrne, E.L.; Holbrey, J.D. Phenol Recovery from Aromatic Solvents by Formation of Eutectic Liquids with Trialkyl-2,3-dihydroxypropylammonium Chloride Salts. Sustain. Chem. 2020, 1, 49-61. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem1010004
Byrne EL, Holbrey JD. Phenol Recovery from Aromatic Solvents by Formation of Eutectic Liquids with Trialkyl-2,3-dihydroxypropylammonium Chloride Salts. Sustainable Chemistry. 2020; 1(1):49-61. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem1010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleByrne, Emily L., and John D. Holbrey. 2020. "Phenol Recovery from Aromatic Solvents by Formation of Eutectic Liquids with Trialkyl-2,3-dihydroxypropylammonium Chloride Salts" Sustainable Chemistry 1, no. 1: 49-61. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem1010004
APA StyleByrne, E. L., & Holbrey, J. D. (2020). Phenol Recovery from Aromatic Solvents by Formation of Eutectic Liquids with Trialkyl-2,3-dihydroxypropylammonium Chloride Salts. Sustainable Chemistry, 1(1), 49-61. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem1010004





