Environmental Assessment of a Constructed Wetland with Ornamental Vegetation for Wastewater Treatment: A Sustainable Option for Neighborhoods (The Case of Veracruz, Mexico)
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1:
- Based on the physical conditions of plants, we expect that the growth and removal of pollutants in CWs with Canna hybrids will be higher than in CWs with Zingiber spectabile or Alpinia purpurata.
- 2:
- The removal of pollutants will be higher in systems with plants than in systems without vegetation (control).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Operation of Horizontal Flow Constructed Wetlands
2.2. Pollutant Measurements
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Climate Characteristics in the Study Area
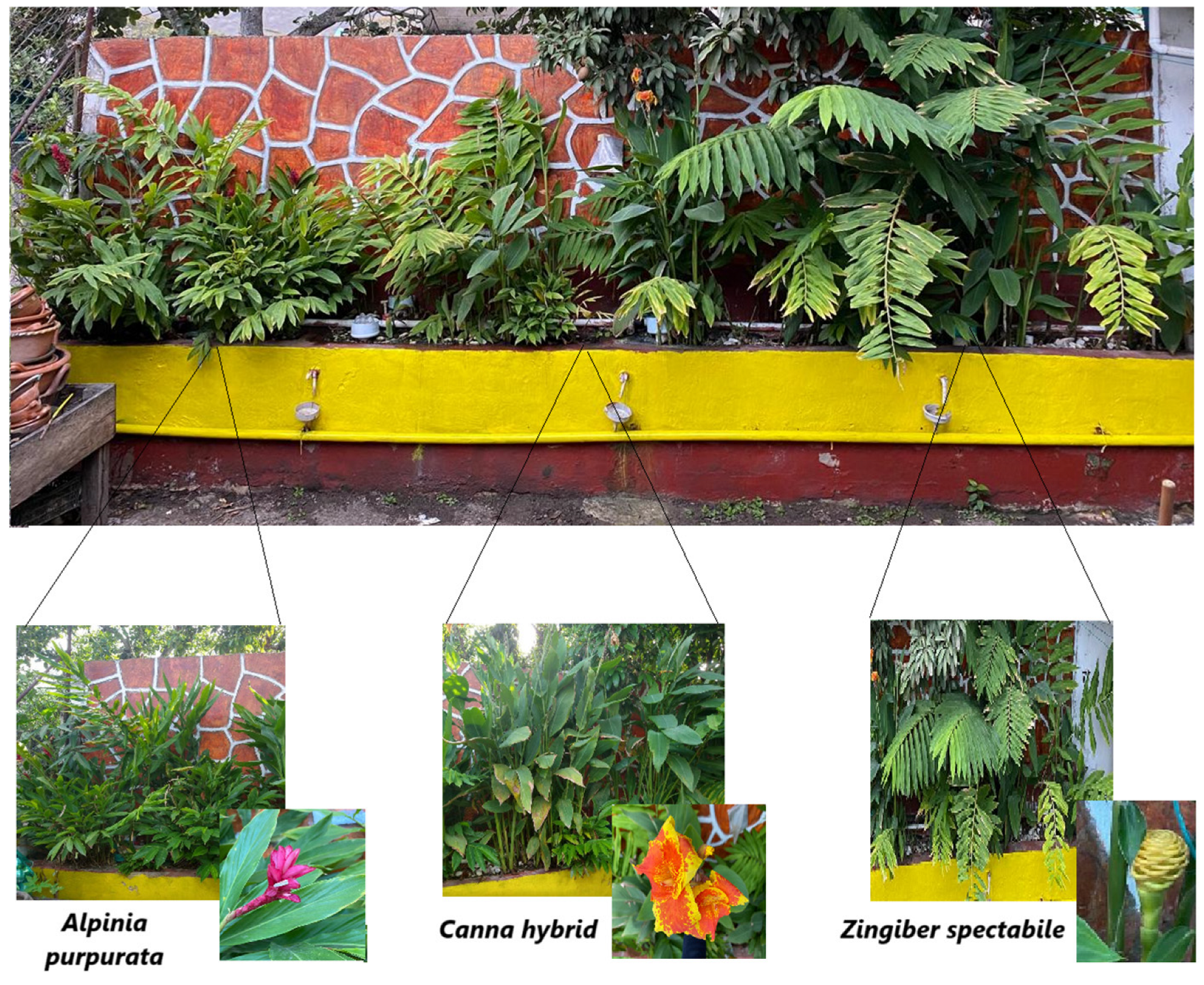
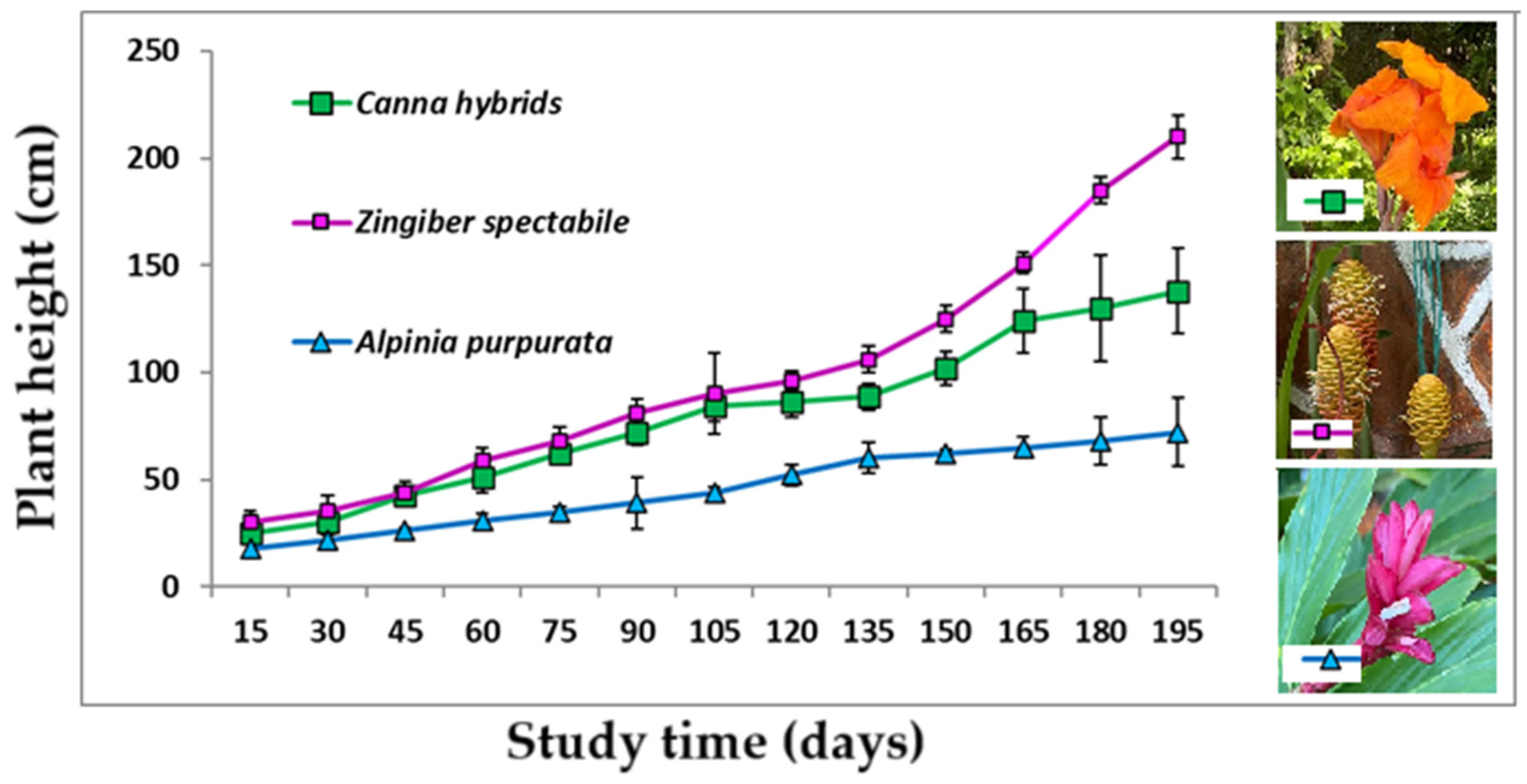
3.2. Growth of Wetland Vegetation
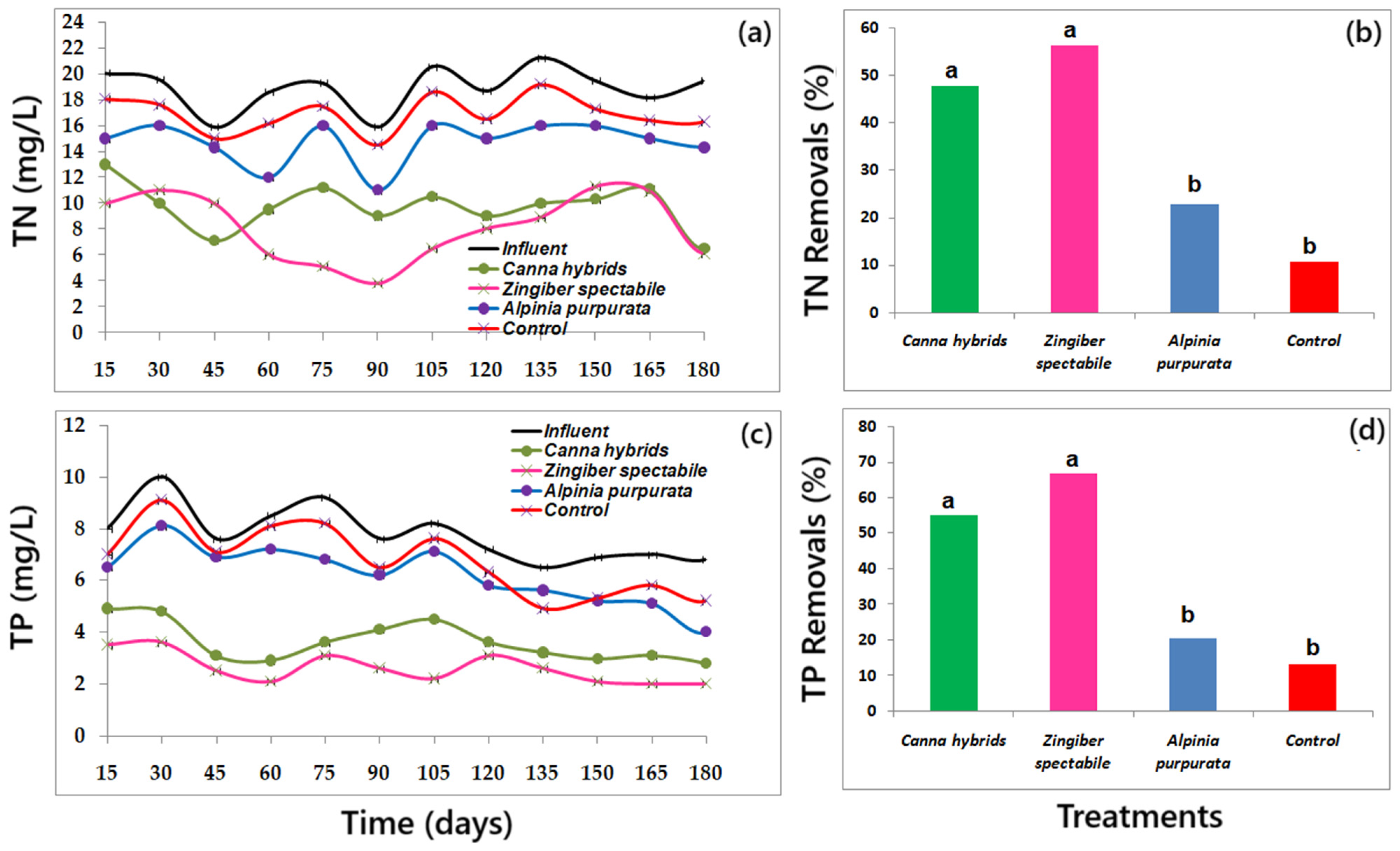
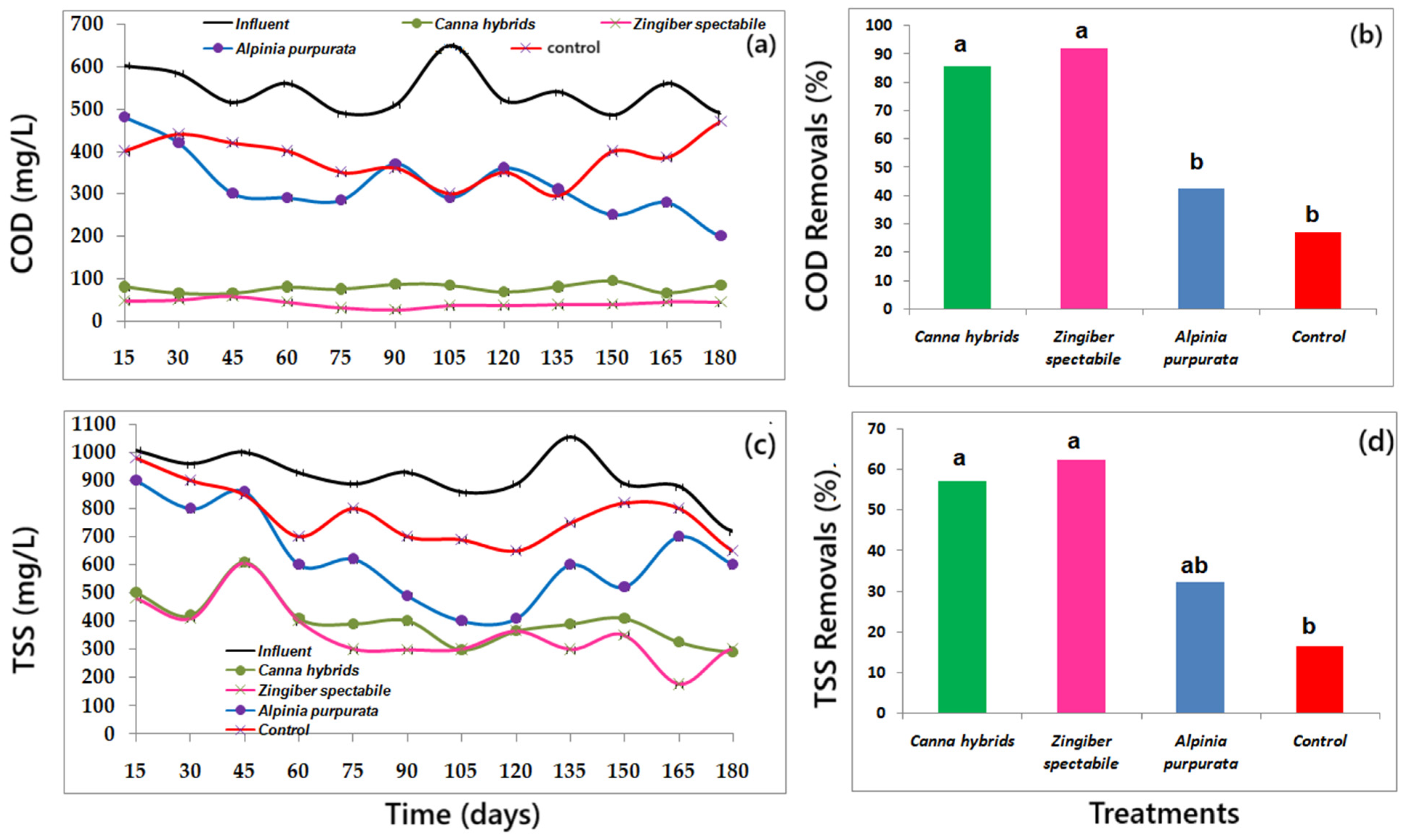
3.3. Concentrations and Removal of Pollutants
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hernández, M.E. Humedales ornamentales con participación comunitaria para el saneamiento de aguas municipales en México. Rinderesu 2016, 1, 1–12. Available online: http://rinderesu.com/index.php/rinderesu/article/view/16/32 (accessed on 15 November 2024). (In Spanish).
- Marín-Muñiz, J.L. Humedales construidos en México para el tratamiento de aguas residuales, producción de plantas ornamentales y reúso del agua. Agroproductividad 2017, 10, 90–95. Available online: https://revista-agroproductividad.org/index.php/agroproductividad/article/view/1028 (accessed on 11 December 2024). (In Spanish).
- Kadlec, R.H.; Knight, R.L. Treatment Wetlands; Lewis Publishers: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsch, W.J.; Gosselink, J.; Anderson, C.; Fennessy, S. Wetlands, 6th ed.; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vymazal, J. The historical development of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Land 2022, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguín, E.J.; Sánchez-Galván, G.; González-Portela, R.E.; López-Vela, M. Constructed wetland mesocosms for the treatment of diluted sugarcane molasses stillage from ethanol production using Pontederia sagittata. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3659–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, G.; Hormozábal, S. Humedales Construidos. Diseño y Operación. Concepción, Chile. 2018. Available online: https://ciudadesverdes.com/download/humedales-construidos-diseno-y-operacion/ (accessed on 2 January 2025). (In Spanish).
- Marín-Muñiz, J.L.; Sandoval, L.C.; López-Méndez, M.C.; Sandoval-Herazo, M.; Meléndez-Armenta, R.A.; González-Moreno, R.; Zamora, S. Treatment wetlands in Mexico for control of wastewater contaminants: A review of experiences during the last twenty-two years. Processes 2023, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Plants used in constructed wetlands with horizontal subsurface flow: A review. Hydrobiologia 2011, 20, 133–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, L.; Zamora-Castro, S.A.; Vidal-Álvarez, M.; Marín-Muñiz, J.L. Role of wetland plants and use of ornamental flowering plants in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: A review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ávila, F.; Avilés-Añazco, A.; Cabello-Torres, R.; Guanuchi-Quito, A.; Cadme-Galabay, M.; Gutiérrez-Ortega, H.; Alvarez-Ochoa, R.; Zhindón-Arévalo, C. Application of ornamental plants in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: A scientometric analysis. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 7, 100307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Muniz, J.L.; Hernández, M.E.; Zamora Castro, S. Ornamental plant growth in different culture conditions and fluoride and chloride removals with constructed wetlands. Hydrology 2024, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nani, G.; Sandoval-Herazo, M.; Martínez-Reséndiz, G.; Marín-Pena, O.; Zurita, F.; Sandoval, L.C. Influence of bed depth on the development of tropical ornamental plants in subsurface flow treatment wetlands for municipal wastewater treatment: A pilot-scale case. Plants 2024, 13, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita, F.; Sandoval, L.C. La tecnología de los humedales construidos para el tratamiento de aguas residuales. Terys 2024, 3, 6–10. Available online: https://aldeser.org/journals/index.php/TERYS/article/view/186 (accessed on 1 January 2025). (In Spanish). [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Álvarez, M. Tratamiento de aguas residuales en México: Problemáticas de salud pública y oportunidad de uso de ecotecnologías sustentables. Rinderesu 2018, 3, 41–58. Available online: http://rinderesu.com/index.php/rinderesu/article/view/32 (accessed on 5 January 2025). (In Spanish).
- Lomeli, J.S.; Zamora-Castro, S.A.; Zamora-Lobato, T.; Sandoval-Herazo, E.J.; Adame-Garcia, J.; Zurita, F.; Monroy-Pineda, M.C.; Aguilar-Cortes, G.; Rivera, S.; Sandoval-Herazo, M. Performance of large-scale ornamental wetlands for municipal wastewater treatment: A case study in a polluted estuary in the Gulf of Mexico. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Mendoza, A.S.; Bello-Mendoza, R.; Herrera-López, D.; Mejía-González, G.; Calixto-Romo, A. Performance of constructed wetlands with ornamental plants in the treatment of domestic wastewater under the tropical climate of South Mexico. Water Pract. Technol. 2015, 10, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Marín-Muñiz, J.L.; García-González, M.; Ruelas-Monjardín, L.; Moreno-Casasola, P. Influence of different porous media and ornamental vegetation on wastewater pollutant removal in vertical subsurface flow wetland microcosms. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, V.; Casas-Ledón, Y.; Neumann, P.; Vidal, G. Environmental performance of constructed wetland planted with monocultures and polycultures for wastewater treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 193, 107015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Muñiz, J.L.; Hernández, M.E.; Gallegos-Pérez, M.P.; Amaya-Tejeda, S.I. Plant growth and pollutant removal from wastewater in domiciliary constructed wetland microcosms with monoculture and polyculture of tropical ornamental plants. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 147, 105658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita-Martínez, F.; Castellanos-Hernández, O.A.; Rodríguez-Sahagún, A. El tratamiento de las aguas residuales municipales en las comunidades rurales de México. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agric. 2011, 1, 139–150. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=263120987011 (accessed on 20 June 2024). (In Spanish).
- Lara-Acosta, M.; Lango-Reynoso, F.; Castañeda-Chávez, M. Use of tropical macrophytes in wastewater treatment. Agroproductividad 2022, 15, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Domínguez, M.; Konnerup, D.; Brix, H.; Arias, C. Constructed wetlands in Latin America and the Caribbean: A review of experiences during the last decade. Water 2020, 12, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maucieri, C.; Salvato, M.; Borin, M. Vegetation contribution on phosphorus removal in constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 152, 105853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, H.A.; Barceló-Quintal, I.; Moeller, G.E. Pollutant removal in a multistage municipal wastewater treatment system comprised of constructed wetlands and a maturation pond, in a temperate climate. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akratos, C.S.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Effect of temperature, HRT, vegetation and porous media on removal efficiency of pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Ghosal, P.S.; Majumder, A.A. Review on performance of constructed wetlands in tropical and cold climate: Insights of mechanism, role of influencing factors, and system modification in low temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 755, 142540. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969720360691 (accessed on 26 December 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyás, T.; Álvarez-Contreras, L.; Marín-Muñiz, J.L.; Celis-Pérez, M.; Zamora-Castro, S.; Landa, M. Condiciones ambientales para el óptimo desarrollo de plantas ornamentales y fitorremediadoras. J. Basic Sci. 2022, 8, 96–103. Available online: http://revistas.ujat.mx/index.php/jobs (accessed on 5 June 2024). (In Spanish).
- Pérez-Flores, J.; Mejía-Muñoz, J.M.; López-Quiroga, A.; Calderón-Bolaina, V.; Saldaña-Hernández, M.I.; Peña-Gutiérrez, A.M. Production of Red and Pink Ginger [Alpinia purpurata (Viell.) K. Schum] in three municipalities of Tabasco, Mexico. Acta Agrícola Pecu. 2017, 3, 98–109. Available online: https://aap.uaem.mx/index.php/aap/article/view/45 (accessed on 5 June 2024). [CrossRef]
- Björn, L.O.; Middleton, B.A.; Germ, M.; Gaberšcik, A. Ventilation systems in wetland plant species. Diversity 2022, 14, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karungamye, P.N. Potential of Canna indica in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: A Review. Conservation 2022, 2, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, K.; Alves, R.; Campos, P.; Menezes, M.E.; Alexandre, C. Aspects of the reproductive biology of Zingiber spectabile (Zingiberaceae). Rev. Ceres Viçosa 2021, 68, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, E.; Hernández-Vásquez, L.A.; Alvarado-Lassman, A.; Sánchez-Valera, O.V.; Hernández-Salina, G. Zingiber spectabile en humedales artificiales para el tratamiento de aguas residuales y su uso en la agricultura. Cienc. Tecnol. Agrop. Mex. 2022, 10, 84–92. Available online: https://www.somecta.org.mx/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/11-Spectabili-tratamiento-agua.pdf (accessed on 6 December 2024). (In Spanish).
- de Campos, S.X.; Soto, M. The Use of Constructed wetlands to treat effluents for water reuse. Environments 2024, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, F.; Rizzo, A.; Regelsberger, M. The role of constructed wetlands in a new circular economy, resource oriented, and ecosystem services paradigm. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 216, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waly, M.M.; Mickovski, S.B.; Thomson, C.; Amadi, K. Impact of implementing constructed wetlands on supporting the sustainable development goals. Land 2022, 11, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Crespo, C.; Oliver, N.; Gil-Martínez, E.; Año, M.; Fernández-Alba, S.; Benedito, V.; Montoya, T.; Martín, M. Integrating circular economy and biodiversity in upgrading full-scale constructed wetlands (LIFE Renaturwat). Ecol. Eng. 2024, 204, 107263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, A.M.N.; Alfarra, A.; Sorlini, S. Constructed Wetlands as a Solution for Sustainable Sanitation: A comprehensive review on integrating climate change resilience and circular economy. Water 2022, 14, 3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Rodrigues, S.; Magalhaes, M.; Rodriguez, K.; Pereira, L.; Marinho, G. A state-of-the-art review (2019-2023) on constructed wetlands for greywater treatment and reuse. Environ. Chall. 2024, 16, 100973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Echeverría, E.; Sandoval, L.C.; Zurita, F.; Betanzo-Torres, E.; Sandoval-Herazo, M. Development of Heliconia latispatha in constructed wetlands, for the treatment of swine/domestic wastewater in tropical climates, with PET as a substitute for the filter medium. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quím 2022, 21, IA2811. Available online: https://rmiq.org/iqfvp/Numbers/V21/No2/IA2811.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2024). (In Spanish). [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamora-Castro, S.A.; González-Moreno, H.R.; Hernández-Orduña, M.G.; Zitácuaro-Contreras, I.; Marín-Muñiz, J.L. Environmental Assessment of a Constructed Wetland with Ornamental Vegetation for Wastewater Treatment: A Sustainable Option for Neighborhoods (The Case of Veracruz, Mexico). World 2025, 6, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/world6020050
Zamora-Castro SA, González-Moreno HR, Hernández-Orduña MG, Zitácuaro-Contreras I, Marín-Muñiz JL. Environmental Assessment of a Constructed Wetland with Ornamental Vegetation for Wastewater Treatment: A Sustainable Option for Neighborhoods (The Case of Veracruz, Mexico). World. 2025; 6(2):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/world6020050
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamora-Castro, Sergio Aurelio, Humberto Raymundo González-Moreno, María Graciela Hernández-Orduña, Irma Zitácuaro-Contreras, and José Luis Marín-Muñiz. 2025. "Environmental Assessment of a Constructed Wetland with Ornamental Vegetation for Wastewater Treatment: A Sustainable Option for Neighborhoods (The Case of Veracruz, Mexico)" World 6, no. 2: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/world6020050
APA StyleZamora-Castro, S. A., González-Moreno, H. R., Hernández-Orduña, M. G., Zitácuaro-Contreras, I., & Marín-Muñiz, J. L. (2025). Environmental Assessment of a Constructed Wetland with Ornamental Vegetation for Wastewater Treatment: A Sustainable Option for Neighborhoods (The Case of Veracruz, Mexico). World, 6(2), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/world6020050







