Abstract
Climate-smart agriculture (CSA) has emerged as a critical strategy to address the intertwined challenges of climate change, food insecurity, and environmental degradation, particularly among smallholder farmers in Southern Africa. This study reviews the existing literature on the adoption and scaling of CSA innovations among smallholder farmers in South Africa, focusing specifically on the roles played by institutional mechanisms, policy frameworks, and market dynamics. The findings reveal that while CSA interventions—such as conservation agriculture, drought-tolerant crop varieties, and precision irrigation—have demonstrated positive outcomes in enhancing productivity, food and nutritional security, and climate resilience, adoption remains uneven and limited. Key barriers include insecure land tenure, insufficient extension and climate information services, limited access to credit and inputs, and fragmented institutional support. The analysis highlights the importance of secure land rights, functional farmer cooperatives, effective NGO involvement, and inclusive governance structures in facilitating CSA adoption. Further, the review critiques the implementation gaps in South Africa’s climate and agricultural policy landscape, despite the existence of comprehensive strategies like the National Climate Change Response Policy and the Agricultural Policy Action Plan. This study concludes that scaling CSA among smallholder farmers requires a holistic, multi-level approach that strengthens institutional coordination, ensures policy coherence, improves market access, and empowers local actors. Targeted financial incentives, capacity-building programs, and value chain integration are essential to transform CSA from a conceptual framework into a practical, scalable solution for sustainable agricultural development in South Africa.
1. Introduction
Climate change significantly diminishes agricultural productivity and exacerbates crop production volatility, thereby disrupting the global food supply and intensifying food and nutrition security [1]. Specifically, climate change adversely impacts food production by inducing water scarcity, escalating pest infestations, and accelerating soil degradation, which collectively contribute to substantial crop yield reductions and pose critical threats to global food security [2,3,4]. The United Nations projects that the global population will reach 9.7 billion by 2050, necessitating a 70% increase in food-calorie production to meet the rising demand [5]. Achieving this target amidst escalating climate-related stresses calls for a fundamental transformation of agricultural systems—one that not only enhances productivity but also mitigates environmental degradation and promotes long-term sustainability [6,7].
Agriculture is uniquely positioned within the climate discourse as both acutely vulnerable to climate change impacts and a substantial contributor to global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions [8]. The sector accounts for roughly 14.5% of total GHG emissions, primarily through methane emissions from enteric fermentation in livestock, nitrous oxide emissions from the application of nitrogen-based fertilizers, and methane emissions from manure management practices [9]. However, agriculture also holds significant potential as a climate mitigation pathway through carbon sequestration in soils, the establishment of agroforestry systems, and enhanced biomass management, which can effectively reduce atmospheric CO₂ concentrations [10,11].
Addressing the intricate relationship between the vulnerability of the agricultural sector and its contribution to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions requires the adoption of evidence-based, sustainable interventions that harmonize productivity objectives with the principles of environmental sustainability. Within this framework, climate-smart agriculture (CSA) has emerged as a holistic and integrative approach that concurrently seeks to enhance agricultural productivity, build resilience to climate variability and change, and mitigate GHG emissions [12].
Climate-smart agriculture comprises a diverse array of innovations aimed at enhancing agricultural resilience and sustainability in the face of climate change. These innovations include climate-resilient crop varieties, precision irrigation systems, conservation agriculture techniques, and data-driven farming technologies [13,14]. Despite their significant potential, the widespread adoption of CSA—particularly among smallholder farmers, is contingent upon supportive institutional mechanisms, enabling policy frameworks, and favorable market conditions [15].
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) [16] emphasizes the critical role of coherent policies in promoting CSA. These policies must facilitate knowledge dissemination, build the capacity of farmers, and provide financial incentives to encourage uptake. Institutional support structures—including government departments, research institutions, international agencies, and non-governmental organizations—serve as critical actors in driving the dissemination and scaling of CSA innovations. Additionally, localized entities such as agricultural extension services and farmer cooperatives are instrumental in bridging the gap between innovation development and practical implementation by facilitating knowledge transfer at the community level [12].
National and regional policy frameworks significantly influence the rate and extent of CSA adoption by shaping funding priorities, fostering innovation, and improving market accessibility [17]. Furthermore, market dynamics—such as access to affordable credit, the development of climate-resilient value chains, and the establishment of equitable pricing mechanisms—serve as critical enablers for smallholder farmers to incorporate CSA practices into their production systems. Vermeulen et al. [18] highlight the effectiveness of market-based mechanisms, including sustainability certification programs and climate finance initiatives, in accelerating CSA adoption across various regions.
Globally, several countries and regions have implemented innovative CSA strategies. The European Union (EU), for example, has integrated strong climate objectives into its agricultural agenda through the Farm to Fork Strategy, a central pillar of the European Green Deal [19,20]. This initiative aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote organic and sustainable farming systems, and incentivize environmentally friendly practices via eco-schemes under the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) [21,22,23]. In contrast, South Africa’s CSA-related policies remain less institutionalized and are constrained by limited large-scale financing mechanisms [6]. Nonetheless, both the EU and South Africa share common objectives, particularly in striving to build sustainable food systems. South Africa places a comparatively stronger focus on smallholder development and equity. In Latin America, Civil Society Organizations (CSOs) have played a critical role in addressing knowledge and financing barriers by improving smallholders’ access to CSA-supportive technologies and resources [24]. Meanwhile, China’s ecological agriculture policy forms part of its broader environmental modernization and rural revitalization strategy. This state-driven model emphasizes reduced chemical use, land restoration, and the integration of advanced technologies such as drones and big data analytics [25]. Although South Africa operates under a more decentralized framework, it could adapt elements of China’s approach to enhance land restoration efforts and adopt smart agricultural technologies.
India’s National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) exemplifies a smallholder-centric, climate-resilient framework. The NMSA emphasizes dryland farming, agroecological practices, and community-based interventions such as Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) [26]. Notably, India has made significant investments in digital climate advisory services to support informed decision-making at the grassroots level [27]. South Africa, which also prioritizes smallholder development, could benefit from India’s experience with decentralized implementation and grassroots institutional engagement.
Across Africa, CSA is frequently integrated into broader agricultural development strategies. Continental initiatives like the Adaptation of African Agriculture (AAA) and the Comprehensive Africa Agriculture Development Programme (CAADP) aim to strengthen institutional capacities and harmonize policies to support CSA implementation [28,29]. At the national level, countries such as Ghana and Malawi have made notable progress. Ghana has launched training programs that have significantly increased the awareness and adoption of CSA practices [30,31], while Malawi has implemented integrated soil fertility management (ISFM) initiatives that combine crop rotation with legume inoculation to enhance soil health [32].
In South Africa, CSA-specific policies are currently being developed under the guidance of the Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (DAFF) [33]. Nonetheless, several existing initiatives provide indirect support for CSA. The Land Care Programme (LCP), a public–private partnership, promotes land restoration and conservation agriculture across all nine provinces, while also contributing to food security and job creation. Additionally, the Policy on Agriculture and Sustainable Development (ASD) and the National Agricultural Research and Development Strategy (NARDS) aim to align sustainable environmental management with economic growth and innovation [33]. While South Africa shares many of the strategic goals pursued by other countries, such as enhancing climate resilience, supporting smallholder livelihoods, and ensuring food security—it continues to face challenges related to financing, technological integration, and coordinated implementation [34]. Comparative international experiences suggest that South Africa could enhance its CSA efforts by adopting a hybrid approach that combines coherent policy design, targeted farmer incentives, digital technologies, and inclusive market structures to achieve scalable and sustainable agricultural transformation.
Recent empirical studies have demonstrated the impact of CSA adoption in South Africa. For instance, Kativhu et al. [35] found that the adoption of drip irrigation in the Nwanedi irrigation scheme significantly improved water use efficiency and crop yields. Omotoso and Omotayo [36] reported that CSA adoption among rural maize farmers led to a 27% increase in household dietary diversity and a 23% reduction in food insecurity. Similarly, Omotoso et al. [37] observed higher productivity and improved food security outcomes among CSA adopters in the North West Province. Abegunde et al. [38] documented the positive effects of CSA on food security in the King Cetshwayo District, while Ighodaro et al. [39] found income gains from soil conservation in Qamata irrigation. Khumalo et al. [40] showed that CSA practices enhanced food and nutrition security among urban crop farmers in eThekwini Municipality.
While these findings highlight CSA’s transformative potential, large-scale adoption remains limited, especially among resource-constrained smallholder farmers [41,42,43]. Emerging literature attributes the low adoption rates to several constraints, including limited empirical success stories, dependence on external donor funding, weak institutional frameworks, and the lack of coherent and long-term policy support [44,45,46]. As emphasized by Steenwerth et al. [47], scaling CSA successfully requires an integrated approach that aligns scientific innovation, policy interventions, and local socioeconomic realities.
This study, therefore, aims to contribute to the growing body of knowledge on CSA adoption by identifying the institutional mechanisms, policy frameworks, and market dynamics that influence its uptake among smallholder farmers in South Africa. Strengthening these enabling factors is essential to scaling CSA innovations. Targeted efforts to improve access to inputs, technologies, advisory services, financial resources, and market linkages can catalyze adoption and ensure CSA becomes an integral part of climate-resilient development pathways. Therefore, the specific objectives of this study are to (i) investigate the contribution of CSA to smallholder farmers’ resilience in South Africa; (ii) assess the adoption of CSA practices by smallholder farmers in South Africa; and (iii) examine how institutional mechanisms, policy instruments, and market structures influence the adoption and scaling of CSA technologies in the country.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design and Approach
This study adopts a qualitative, interpretive, and integrative general narrative review methodology. The review specifically investigates the adoption and scaling of climate-smart agriculture innovations among smallholder farmers in South Africa, emphasizing the roles played by institutional mechanisms, policy frameworks, and market dynamics. The objective of this review is to synthesize the existing knowledge comprehensively, identify prevailing research gaps, and critically analyze the interplay between these determinants and CSA adoption at the smallholder level. A narrative review approach is particularly suitable for integrating diverse bodies of literature, thereby facilitating a holistic and nuanced understanding of complex, interconnected themes prevalent within multidisciplinary fields such as climate-smart agriculture.
2.2. Literature Search Strategy
A narrative and purposive search strategy was employed to gather a comprehensive body of literature relevant to the research focus. The search prioritized scholarly publications, policy reports, and grey literature that address the adoption and scaling of CSA practices within the South African smallholder farming context. The literature was sourced from multiple academic databases and institutional repositories, including Google Scholar Scopus, Web of Science, South African government departments (e.g., Department of Agriculture, Land Reform and Rural Development; Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries), International Organizations (e.g., FAO, World Bank), and NGOs. A targeted keyword search was conducted using combinations of terms such as “Climate-Smart Agriculture” AND “Smallholder farmers” AND “South Africa” AND “CSA adoption” AND “Institutional mechanisms” OR “policy framework” OR “market dynamics”. The temporal scope broadly includes works published from 2005 to 2025, capturing the emergence and evolution of CSA in the national discourse, though earlier foundational documents were also consulted when relevant. The selection of literature was based on predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria (outlined in Table 1). This ensured that the review focused on literature that directly addressed the CSA adoption landscape in South Africa.

Table 1.
Criteria for literature selection for review.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Contribution of Climate-Smart Agriculture to Smallholder Farmers in South Africa
Climate-smart agriculture is crucial in enhancing South African smallholder farmers’ sustainability, resilience, and productivity. Given the region’s vulnerability to climate change, characterized by erratic rainfall, increased temperature, and prolonged drought, CSA is viewed as a viable approach to mitigate risks and improve food security [48]. Numerous studies have examined the benefits of CSA for smallholder agricultural systems. For instance, Nhamo et al. [49] reported that the adoption of climate-smart irrigation technologies (CSITs) by smallholder farmers significantly enhanced agricultural productivity, thereby improving livelihoods, food security, and nutritional outcomes. Similarly, Omotoso et al. [37] examined CSA interventions in the North West Province of South Africa. They found that the use of drought-tolerant maize varieties, mulching, cover cropping, and zero tillage resulted in higher productivity and improved household food and nutrition security. In the Mooifontein district of Northern Cape Province, Mathew et al. [50] emphasized the critical role of appropriate CSA practices in sustaining rural livelihoods. Abegunde et al. [38] demonstrated that CSA adaptation positively influenced household food security among small-scale farmers in the King Cetshwayo District of KwaZulu-Natal Province. Makamane et al. [51] explored the determinants of CSA adoption in the Mangaung Municipality, Free State Province, and found that it led to notable improvements in crop productivity. Further supporting evidence is provided by Msweli et al. [52], who investigated the socioeconomic drivers of CSA acceptance in the Nkomazi Local Municipality of Mpumalanga Province. Their study found that CSA adoption contributed to increased crop yields, improved food access, and enhanced household income. Likewise, Ighodaro [39] showed that older farmers and those with better awareness of CSA practices were more likely to adopt such strategies, thereby achieving higher overall income levels in the Qamata irrigation scheme.
Regionally, the implementation of small-scale irrigation as a CSA measure in the Chiyanya Triangle of Southern Africa significantly elevated household income levels [53]. This improvement was attributed to expanded production capacity through the intensification and diversification of farming activities. Small-scale irrigation enabled farmers to sustain crop cultivation during dry periods and extend growing seasons to include off-season production. Branca et al. [54] conducted an economic assessment of CSA practices, revealing that transitions from conventional to CSA approaches yielded higher economic returns, particularly in semi-arid regions. Their findings underscored the cost-effectiveness of land management practices, crop residue incorporation, cover cropping, and the inclusion of legumes. Similarly, Ma and Rahut [1] explored the factors influencing CSA adoption and estimated the impacts of CSA adoption on farm production, income, and well-being. The findings of their study revealed that the adoption of CSA positively impacted crop yields, farm income, and economic diversification. Their study further highlighted that the integration of CSA technologies into traditional systems not only enhances economic outcomes but also promotes environmental sustainability and health benefits.
The threat of climate change, exacerbated by greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, presents a critical challenge for the agricultural sector. Carbon credits have emerged as a strategic mechanism for mitigating these emissions while enhancing productivity [55]. Recognizing this, the 2023 Climate Change Conference (COP28) identified carbon credits as a key tool in emission reduction strategies. Hayo and Hasegawa [55] applied stochastic frontier analysis to panel data (1991–2020) to evaluate the effectiveness of CSA in reducing agricultural GHG emissions in South Africa. Their analysis supported the hypothesis that incentivizing CSA through mechanisms such as carbon credits can simultaneously reduce emissions and enhance productivity.
The contributions of CSA to South Africa’s smallholder farming systems are both substantial and transformative. The adoption of CSA practices has been associated with increased resilience, enhanced productivity, and improved food and nutrition security. Nevertheless, several challenges continue to hinder the widespread adoption of CSA. A primary barrier is the limited access to financial resources and support services necessary for adopting and maintaining improved practices [56]. Smallholder farmers often struggle to access essential inputs such as credit and financial capital, limiting their capacity to fully implement CSA interventions [57,58]. An important consideration is how CSA can be made more accessible and tailored to meet the specific needs of smallholder farmers. Additional barriers include inadequate technical knowledge among farmers, extension agents, and development practitioners [59]. Successful CSA implementation requires specialized skills, consistent management, and the ability to navigate trade-offs—factors that must be systematically assessed [56]. Moreover, farmers’ willingness and readiness to invest in new technologies are critical determinants of adoption. For example, conservation agriculture, a fundamental CSA practice, relies on minimal soil disturbance techniques that demand advanced knowledge and costly equipment [60]. Likewise, the shift from synthetic fertilizers to organic manure introduces trade-offs such as greater land requirements, reduced livestock feed availability, and the need for specialized manure management practices [61]. Mwongera et al. [61] noted that smallholder farmers tend to prioritize short-term productivity gains over long-term technical benefits, a trend that must be accounted for in CSA design and promotion. Figure 1 presents the benefits of CSA to smallholder farmers documented by different studies.
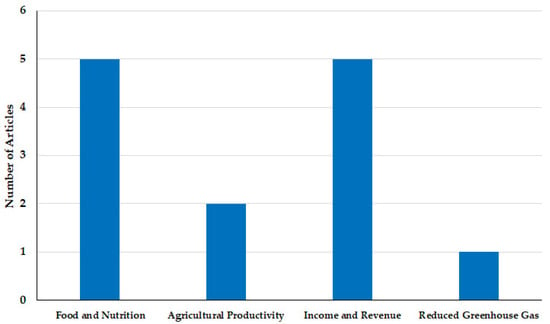
Figure 1.
Benefits of Climate-Smart Agricultural practices to smallholder farmers in South Africa.
3.2. Adoption of Climate-Smart Agriculture by South African Smallholder Farmers
Climate-smart agriculture (CSA) has gained prominence as a strategic framework for addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by climate change within the agricultural sector. CSA aims to sustainably increase agricultural productivity, enhance the resilience of farming systems to climate variability and extremes (adaptation), reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (mitigation), and contribute to broader goals of food security and rural development [33]. Empirical studies demonstrate that CSA interventions—such as agroforestry, conservation agriculture, and the use of climate-resilient crop varieties—offer substantial benefits to smallholder farmers by improving yields and reducing vulnerability to climate-related risks [62,63,64]. Despite the documented benefits, the adoption of CSA among smallholder farmers in South Africa remains uneven and highly context-dependent. Adoption patterns are shaped by disparities in resource access, institutional support, and knowledge dissemination [12]. This heterogeneity underscores the need for targeted and context-specific CSA promotion strategies that account for smallholder farming systems’ socioeconomic and agroecological diversity [65].
Smallholder agriculture in South Africa is characterized by a high degree of structural variation at both the micro and macro levels. Factors such as land access, market integration, household resource base, and exposure to climate risks significantly influence farmers’ capacity and willingness to adopt CSA practices [66]. Over the past thirty years, research has largely focused on developing low-cost agricultural technologies tailored for small-scale farming in Sub-Saharan Africa [59]. However, attention is increasingly shifting toward scaling climate-resilient innovations—such as crop diversification, cereal–legume intercropping, stress-tolerant crop varieties, and agroecological practices like agroforestry and conservation agriculture—in response to emerging threats, including land degradation, declining yields, and increased climate-induced risks [53,56]. Although these CSA practices have demonstrated success in boosting productivity, improving livelihoods, and enhancing ecosystem services, their widespread adoption remains limited [67,68,69]. Studies on peri-urban farming systems reveal that low CSA uptake is often linked to dissemination strategies that overlook the heterogeneity of smallholder farmers [70,71]. A prevailing limitation in current adoption efforts is the misconception that smallholder farmers constitute a uniform group. This oversimplified view neglects the complex socioeconomic realities and diverse constraints that shape adoption behavior [71].
International development agencies such as the World Bank, Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), and International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) emphasize the importance of resource access, capacity-building, and knowledge transfer in facilitating CSA adoption [72]. To be effective, CSA policies and technologies must be adapted to the localized needs of smallholder farmers and designed to address existing disparities in knowledge, resources, and institutional support.
Recognizing the heterogeneity of small-scale farming systems is critical for identifying the opportunities and constraints related to CSA adoption [41]. A more effective approach to CSA promotion involves integrating socioeconomic assessments with adaptive strategies that target specific farmer profiles [56,73,74]. One promising strategy is the stratification of farming households into relatively homogeneous groups based on factors such as livelihood strategies, resource endowment, production goals, and location-specific constraints. This allows for the development of farm typologies, which serve as powerful tools for designing CSA interventions [63]. Research shows that farm typologies improve the relevance and effectiveness of CSA implementation by providing insight into adoption dynamics and identifying key enabling and limiting factors [75,76]. For instance, early adopters of CSA often possess relatively greater financial capital, education levels, access to information, or openness to innovation [56]. Understanding these adoption drivers is crucial for the design of scalable and inclusive CSA initiatives. A wide range of studies have explored the socioeconomic, technical, and institutional determinants of CSA adoption. Among these, resource constraints such as limited access to credit, farm inputs, land, and reliable information have consistently emerged as major barriers [58,76]. Farmer characteristics such as gender, age, education, household size, farming experience, farm income, and location have also been shown to significantly influence CSA uptake [52,77,78,79]. For example, Obi and Maya [80] found that factors such as the farmer’s primary occupation, type of farming system, group membership, and household demographics are critical in shaping CSA adoption decisions. From a technical perspective, limited awareness, inadequate training, and insufficient knowledge of CSA practices have been identified as key constraints [81,82]. These findings underscore the urgent need for expanded outreach and knowledge-sharing platforms to support farmers’ understanding of CSA practices. In the Mpumalanga province, Thabane et al. [83] reported that education, household size, farm experience, and soil fertility positively influenced CSA adoption. They emphasized that increasing farmer education and providing targeted training on climate adaptation strategies are essential for effective implementation.
Similarly, Makamane et al. [51] and Slayi et al. [84] highlighted the lack of financial support, insufficient access to credit, and high costs of inputs as major barriers. These constraints limit smallholders’ ability to transition to CSA practices, especially where upfront investments are required. Slayi et al. [84] further recommended integrating indigenous knowledge with modern technologies to facilitate the adoption and design of localized capacity-building programs to foster pro-environmental behavior. Senyolo et al. [57] explored the adoption of drought-tolerant seed varieties as a CSA measure and found that the adoption was shaped by a combination of drivers and barriers, including insufficient training, lack of weather information, gender dynamics, marital status, and limited access to financial services. Broader institutional challenges—such as poor access to markets, inadequate extension services, and weak governance structures—have also been identified as significant impediments to CSA uptake, with adverse implications for rural food security and productivity [85,86]. As illustrated in Figure 2, socioeconomic and institutional factors are the most frequently cited determinants of CSA adoption. This suggests that external enablers, including socioeconomic factors, financial incentives, and institutional capacity, play a more decisive role in facilitating CSA uptake than technical feasibility alone. Policymakers should therefore prioritize strengthening institutional frameworks and enhancing economic incentives to support the widespread adoption and scaling of CSA. While numerous studies have examined socioeconomic, technical, and institutional determinants of CSA adoption among smallholder farmers in South Africa, there remains a significant gap in the research regarding other potential barriers. Specifically, the literature has not adequately explored factors related to natural conditions, policy frameworks, and environmental constraints. Addressing these overlooked dimensions is crucial for a more comprehensive understanding of the challenges impeding CSA adoption and scaling in this region.
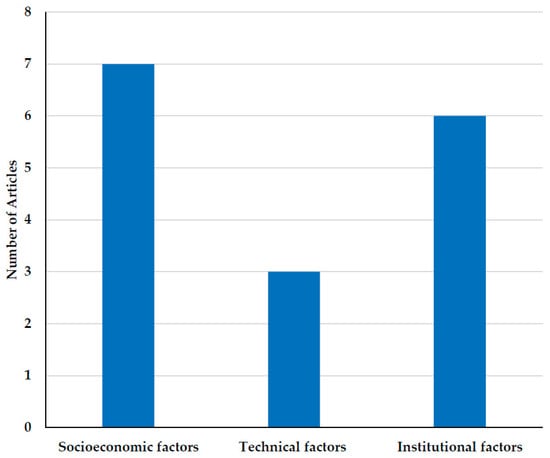
Figure 2.
Factors influencing the adoption of CSA among smallholder farmers in South Africa.
3.3. Influence of Institutional Mechanisms on the Adoption and Scaling of CSA Practices
Institutional mechanisms encompass formal and informal structures that are socially constructed to regulate norms, guide individual behavior, and shape interactions within society [87]. Informal institutions refer to unwritten cultural norms, and traditional practices that function independently of codified legal frameworks. In contrast, formal institutions are composed of officially documented laws, regulations, and public policies enacted through governmental authority [88]. Both institutional forms play a critical role in influencing behavioral change and decision-making processes and are therefore central to the adoption and scaling of climate-smart agriculture interventions. Key institutional actors with the capacity to influence CSA uptake include public, private, and civic institutions [87]. Private institutions consist of non-governmental organizations (NGOs), charitable organizations, and private sector actors such as agro-dealers supplying seeds, fertilizers, and agrochemicals, as well as companies offering agricultural insurance and financial services. Public institutions include government departments responsible for agricultural extension, research, and rural finance. Meanwhile, civic institutions comprise farmer-based organizations, cooperatives, savings and loan associations, and various civil society groups that provide platforms for collective action and resource sharing.
Institutional factors, such as property rights and financial policies, are fundamentally linked to farmers’ access to essential resources, thereby exerting a significant influence on the adoption of improved agricultural practices [89,90,91]. Existing research highlights the critical role of institutional arrangements in facilitating the dissemination and uptake of climate-smart agricultural practices, while also identifying key institutional determinants that influence adoption dynamics [89,92]. These determinants include land tenure security, provision of services, access to resources, farmers’ organizations and cooperatives, and support from non-governmental organizations (Figure 3).
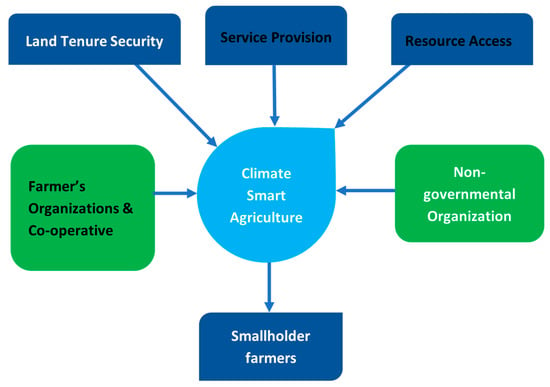
Figure 3.
Influence of institutional mechanisms on the adoption of CSA practices among smallholder farmers in South Africa.
3.3.1. Land Tenure System
Land tenure security refers to the legal certainty and institutional recognition of land rights, enabling individuals or communities to use, manage, and transfer land without the fear of arbitrary dispossession or eviction [93]. Secure land tenure forms a foundational precondition for sustainable agricultural investment, particularly in practices associated with climate-smart agriculture, such as agroforestry, conservation agriculture, and soil fertility enhancement [94]. Conversely, insecure tenure discourages long-term planning and discourages resource-intensive agricultural practices, due to the persistent risk of land expropriation and a lack of ownership guarantees [95].
In South Africa, land tenure arrangements are historically rooted in colonial dispossession, apartheid-era land policies, and post-apartheid reforms intended to redress systemic inequalities [96]. The national land tenure system can be broadly classified into three categories: freehold (private ownership), leasehold (state-owned land), and communal tenure (customary land managed under traditional authority structures) [97]. Among smallholder farmers, particularly those residing on communal or state-held lands, tenure insecurity remains widespread. This uncertainty undermines their ability to make long-term investments in CSA technologies, which require substantial time, financial input, and resource security [98]. Empirical evidence demonstrates that secure tenure significantly increases farmers’ willingness to invest in CSA interventions, including agroforestry, terracing, and water harvesting [98,99]. These practices typically yield benefits over an extended timeframe, reinforcing the importance of tenure security for their uptake. Studies have shown that farmers with formally recognized land rights are more likely to adopt conservation agriculture and agroecological innovations due to the limited risk of land loss [99]. Smallholder farmers with documented ownership or long-term use rights on privately held land display a greater propensity to invest in CSA practices than those farming under customary arrangements, where land rights are often ambiguous and controlled by traditional leaders [100].
Moreover, secure tenure plays a significant role in enhancing access to agricultural finance. Since most financial institutions require land titles as collateral for credit provision, farmers operating under communal tenure systems without legally recognized land documentation often find themselves excluded from formal financial markets. This exclusion hinders their capacity to acquire CSA-related inputs such as drought-tolerant seed varieties, drip irrigation systems, and organic soil amendments [101,102]. A compelling illustration of these dynamics can be found in the Eastern Cape Province. This region is characterized by extensive communal landholdings governed by traditional authorities, where smallholder farmers face significant challenges related to unclear land rights [103]. Mtero et al. [104] found that tenure insecurity discouraged farmers from investing in CSA interventions such as agroforestry and soil conservation, primarily due to fears of dispossession and unresolved land disputes. The study further revealed that financial institutions were generally unwilling to extend credit to these farmers, citing the absence of formal land titles. In contrast, farmers who had secured long-term lease agreements with the state exhibited a higher adoption rate of CSA practices, particularly in climate-resilient crop cultivation and efficient irrigation systems. Similarly, Serote et al. [58] identified insecure tenure systems as a major barrier to the uptake of climate-smart irrigation technologies in the Limpopo Province. Mdoda and Gidi [105] further reported that land ownership positively influenced agricultural productivity in the Eastern Cape, where smallholders with legally owned small plots outperformed those cultivating larger, rented parcels. Studies by Msweli et al. [52] and Serote et al. [77] also affirm that access to privately owned land significantly influences CSA adoption among South African smallholders.
Given these insights, policy interventions to enhance land tenure security are essential for scaling CSA practices. Although South Africa’s land reform initiatives aim to address historical injustices, their implementation has been uneven, leading to persistent tenure insecurity among smallholder farmers [98]. Strengthening land tenure systems to support CSA adoption should begin with accelerating the formalization of land rights, especially in communal and redistributed areas. This process should be grounded in participatory land registration and titling initiatives that involve local communities in mapping, verification, and certification activities [96]. Additionally, capacity-building programs should be established to raise awareness among farmers regarding their land rights, legal redress options, and the socioeconomic and ecological benefits of CSA adoption. Empowering farmers with this knowledge can enhance their decision-making capacity and foster more sustainable land-use practices [101]. Recognizing that tenure insecurity frequently limits access to conventional finance, both government and private sector actors should explore alternative financing models that do not rely exclusively on land-based collateral. These could include group lending schemes, peer guarantees, and socially collateralized financial instruments tailored to smallholder contexts [98]. Furthermore, it is critical to institutionalize inclusive and participatory land-use planning processes, involving stakeholders across all levels—including smallholder farmers, traditional leaders, and local government bodies—to ensure that land tenure arrangements align with national CSA objectives. Such collaborative governance frameworks are essential for reconciling competing land claims and promoting sustainable land management [97].
3.3.2. Service Provision
The adoption and scaling of climate-smart agriculture among smallholder farmers are influenced by multiple factors, including access to reliable agricultural extension services and climate information services. Extension services serve as a crucial interface between research institutions and farmers, ensuring that innovative CSA practices are effectively communicated and implemented. In South Africa, extension services are delivered by both public and private institutions, often in collaboration with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and development agencies [33]. Climate information systems on the other hand, provide smallholder farmers with forecasts and advisories that inform agricultural practices, thereby enhancing resilience and productivity [106]. The provision of services by both extension and climate information services helps to facilitate the adoption of CSA practices by providing smallholder farmers with the necessary knowledge, technical skills, and climate-related insights required to implement sustainable agricultural practices [106]. However, in South Africa, disparities in access to these services, particularly among smallholder farmers in rural areas, present challenges to CSA uptake and scalability. For instance, Bontsa et al. [107] revealed that while 80% of smallholder farmers in the Raymond Mhlaba district municipality found extension advisory services helpful, the quality of climate change-related extension services was perceived as poor. Factors such as age, marital status, employment status, knowledge about climate change, and access to extension services significantly affected these perceptions. The study concluded that socioeconomic factors influenced the perceived quality of extension services and recommended enhancing accessibility and training to improve service delivery [107]. A study conducted by Kubanza and Oladele [81] in the Ngaka district municipality of North West Province, South Africa, found that 30% of community members, 70% of farmers, 50% of NGO representatives, and 60% of government participants lacked awareness or a clear understanding of climate-smart agriculture practices. Furthermore, the study identified a widespread lack of awareness and knowledge regarding CSA policies among all participant groups, highlighting a substantial gap in information dissemination and education on sustainable agricultural practices. The findings underscore the urgent need for targeted awareness and educational programs to enhance the adoption and implementation of CSA in the region. Serote et al. [58] explored the barriers to the adoption of climate-smart irrigation technology (CSIT) in the Limpopo province; their study revealed that insufficient communication channels, a lack of financial availability, and insufficient training were the main barriers to the implementation of CSIT. Their study suggests the need for policy and decision-makers to improve communication channels for disseminating agro-meteorological information to the intended beneficiaries. Mnkeni et al. [33] highlight that government support for small-scale farmers remains limited, with a relatively minor overall impact. The study further revealed that empirical data from Statistics South Africa indicate that between 2014 and 2017, only approximately 2% of small-scale farmers received extension support annually, underscoring the inadequate reach and accessibility of agricultural advisory services for this farming sector. Senyolo et al.’s [57] study on the adoption of drought-tolerant seed varieties (DTSVs) by smallholder farmers in the Limpopo province found that the adoption of DSTVs was influenced by training, demonstration, knowledge, and benefits related to DTSVs and weather information. The study proposed that access to sufficient training, climate information services, and credit support should be enhanced to improve the effective adoption of DTSVs among smallholder farmers. A similar study by Chitakira and Ngcobo [70] also revealed that despite the lack of knowledge of CSA practices by smallholder farmers in the Gauteng province of South Africa, farmers were able to take up some adaptation mechanisms acquired from Indigenous knowledge systems, some of which include mulching, cover cropping, crop rotation, and improved crop varieties. The study recommended one-on-one extension programs to raise awareness of climate-smart agriculture technologies appropriate to the unique conditions of the farmers. Tall et al. [106] identified knowledge and skill gaps as factors influencing the adoption of cattle feedlots as a CSA practice. The study proposed interventions to promote the adoption of cattle feedlot practice. These interventions include providing capacity-building programs on feedlot management and climate-smart practices, disseminating information on feedlot benefits and best practices, developing necessary infrastructure, and creating a supportive policy environment.
Research by Thamaga-Chitja and Morojeje [108] highlights that knowledge gaps are a significant barrier to CSA adoption in South Africa. They found that farmers with access to effective extension services were more likely to adopt improved agricultural practices, including CSA techniques, as they had a better understanding of how these practices could improve yields and sustainability in the context of climate variability. Mmbengwa et al. [109] pointed out that farmers who had regular access to extension services were more likely to integrate CSA innovations into their farming systems. A study by Hansen et al. [110] highlighted that timely access to climate information enhances the effectiveness of CSA interventions by facilitating the alignment of agricultural activities with climatic patterns.
By providing data on weather trends and soil moisture levels, CIS helps optimize the timing and efficiency of agricultural inputs. This supports sustainable productivity through CSA practices such as precision agriculture, intercropping, and conservation tillage, which require precise information for successful implementation. Archer et al. [111] observed that CIS improved smallholder farmers’ abilities to adopt adaptive planting strategies, ultimately boosting yields and resource use efficiency. These practices are essential for scaling CSA because they help conserve resources, reduce costs, and improve the long-term viability of farming under changing climate conditions. Despite the benefits of extension and climate information services (CIS), Mnkeni et al. [33] highlight that inadequate infrastructure, limited financial resources, and insufficient training of extension personnel hinder their effective delivery. Addressing these challenges necessitates strengthening institutional capacity and formulating policies that ensure equitable access to extension services and CIS, particularly for marginalized groups such as women and youth. Additionally, leveraging digital platforms and mobile technologies can enhance the dissemination of climate information and agricultural advisories, thereby reaching a wider audience [33]. Furthermore, actively involving farmers in the development and dissemination of CSA practices is crucial to ensuring that solutions are context-specific and effectively address local agricultural challenges [33].
3.3.3. Access to Resources
The availability of financial services, credit, and agricultural inputs significantly influences CSA adoption and scaling. These resources provide smallholder farmers with the necessary capital to invest in climate-resilient technologies and practices. Makamane et al. [51] found that access to credit significantly enhances the likelihood of smallholder farmers adopting climate-smart agriculture technologies. Specifically, their study indicated that a 1% increase in credit access raises the probability of CSA adoption by 63%, thereby improving household welfare. Smallholder farmers, constrained by limited capital and resources, rely heavily on financial institutions to overcome initial investment barriers associated with adopting new agricultural technologies. Financial institutions, both formal and informal, have been identified as critical stakeholders in facilitating the uptake of CSA by providing credit schemes, insurance products, and financial literacy programs [112]. The extent and nature of financial inclusion significantly influence farmers’ ability to access and utilize climate-resilient inputs such as drought-resistant seeds, organic fertilizers, irrigation equipment, and agroforestry seedlings [112]. In South Africa, the smallholder agricultural sector is marked by systemic inequalities, with limited access to formal financial services disproportionately affecting historically marginalized rural populations [108].
Recent research emphasizes the critical role of microfinance institutions (MFIs) and cooperative banks in addressing the financial needs of smallholder farmers, particularly in facilitating the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices [113]. Traditional banks often perceive small-scale agriculture as high-risk, resulting in a financing gap that MFIs and cooperative banks seek to bridge. These institutions have introduced innovative financial mechanisms, such as weather-indexed insurance and group lending schemes, to mitigate individual financial risks associated with CSA adoption [114]. For example, the Climate-Smart Lending Platform integrates climate risk assessments into lending decisions, thereby enhancing smallholder farmers’ access to credit and promoting the uptake of sustainable agricultural practices [115]. Similarly, the Land Bank of South Africa has developed specialized credit products to support smallholder farmers in transitioning to sustainable agriculture [116]. Through its Emerging Farmer Support Program, the bank offers low-interest loans to facilitate investments in climate-smart irrigation systems and soil conservation measures [116]. Zeleke et al. [117] showed that farmers with access to insurance were more likely to invest in CSA practices such as water-efficient irrigation systems and drought-tolerant crops. Similarly, Mullins et al. [118] found that access to insurance reduced farmers’ financial vulnerability, making them more open to experimenting with climate-smart technologies that might otherwise be perceived as risky. Despite these advancements, several barriers continue to constrain the widespread adoption of CSA technologies. Inadequate financial infrastructure limits the accessibility of these innovative financial products, particularly in remote farming communities [109]. Moreover, high interest rates on some microfinance products deter farmers from seeking necessary credit, while the limited scalability and outreach capacity of MFIs restrict their ability to serve a broader segment of the smallholder farming population [109]. Also, Elum et al. [119] found that smallholder farmers showed limited interest in adopting insurance as a risk management tool, primarily due to the limited availability of suitable insurance products. Overcoming these challenges requires strengthening financial infrastructure, developing affordable credit products, and expanding the operational reach of MFIs to effectively support smallholder farmers in transitioning to climate-resilient agricultural systems [109].
Also, the high cost and limited accessibility of essential agricultural inputs, such as improved seed varieties, fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation equipment, significantly exacerbate the vulnerability of smallholder farmers to climate-related shocks. These constraints hinder their capacity to effectively adopt and implement CSA practices [120]. Addressing these challenges requires targeted policy interventions such as subsidies, input vouchers, and comprehensive extension services that go beyond mere financial support to ensure holistic and sustainable adoption. Government-led initiatives, notably, the Comprehensive Agricultural Support Programme (CASP) and Ilima/Letsema have been established to improve access to agricultural inputs among smallholder farmers. While these programs are commendable in their objectives, their impact has often been limited by persistent challenges, including inefficient implementation, corruption, and weak monitoring and evaluation systems [121]. These shortcomings limit their potential to contribute meaningfully to the broader CSA agenda. To promote the widespread adoption and sustained scaling of CSA practices, it is essential to restructure existing financial instruments and input delivery systems in alignment with the strategic priorities of climate-resilient agriculture. This calls for the reinforcement of institutional frameworks, as well as the cultivation of robust public–private partnerships. Such multi-stakeholder collaboration can play a vital role in improving input affordability, enhancing access to financial services, and supporting inclusive agricultural innovation [113]. Ultimately, these efforts are critical for building resilient farming systems and securing sustainable livelihoods for South Africa’s smallholder farmers.
3.3.4. Farmers’ Organization and Cooperatives
Farmers’ organizations, including cooperatives, associations, and informal groups, are essential for knowledge dissemination, input provision, and collective bargaining power [113]. One of the most immediate advantages of farmers’ organizations is their role in facilitating knowledge exchange and collective learning. The adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices often necessitates new knowledge regarding optimal planting techniques in conservation agriculture, the management of tree seedlings in agroforestry, or the operation of drip irrigation systems [122]. Farmer cooperatives and organized groups significantly enhance the dissemination of such knowledge among their members [80]. When farmers participate in collective groups, they engage in discussions about successful and unsuccessful techniques on their farms, thereby reducing uncertainty around novel agricultural practices. Empirical studies substantiate this observation. In the Eastern Cape, participation in farmers’ associations has significantly influenced the selection and implementation of CSA practices [80]. Farmer interactions—both among themselves and with extension officers in group settings—play a crucial role in shaping adaptation decisions [80]. This peer-to-peer learning and group deliberation facilitate transitions from non-adaptation to the adoption of practices such as crop diversification and the use of improved seed varieties [80]. Evidence further indicates that the presence of active farmer groups correlates with a heightened awareness of CSA. For instance, in Limpopo province, Machete et al. [123] reported that farmers involved in organized study groups exhibited superior knowledge of conservation agriculture principles compared to their counterparts in similar villages lacking such groups. These learning platforms not only enhance technical understanding but also support iterative experimentation and adaptive decision-making. Farmers’ organizations also function as key intermediaries between smallholder farmers and public agricultural extension systems. Given the persistent human resource constraints within South Africa’s extension services, working with organized groups has become an operational necessity to maximize outreach and efficiency [124]. Government extension officers and NGOs frequently engage with cooperatives and associations to deliver CSA-related training and workshops. Notably, smallholders affiliated with such organizations are more likely to receive regular, high-quality extension support, which, in turn, increases their likelihood of adopting CSA practices [124]. In uMkhanyakude, KwaZulu-Natal, a quantitative study found that access to extension services was one of the most significant determinants of CSA adoption, and this effect was magnified when delivered through organized farmer groups [125].
Beyond knowledge facilitation, resource constraints remain a fundamental barrier to CSA uptake among smallholders. Many farmers lack the financial capital to invest in improved seeds, seedlings, fertilizers, or CSA-related equipment [33]. In this context, farmer cooperatives serve as important mechanisms for pooling resources and improving access to agricultural inputs and financial services [126]. Group-based procurement strategies reduce transaction costs and increase affordability through bulk purchasing. Studies indicate that smallholders affiliated with cooperatives have a 14% higher likelihood of using fertilizers, due to improved affordability and logistical coordination [126,127]. This increased access allows for more optimal and timely input use, thereby improving productivity and resilience outcomes. Importantly, farmers’ organizations also enhance market access—an essential enabler of CSA adoption. By facilitating collective marketing, aggregating produce for bulk sales, and negotiating better prices, these organizations help reduce post-harvest losses and strengthen the economic viability of climate-resilient practices [128]. In the Eastern Cape, several cooperatives have established vegetable packing sheds, thereby securing reliable market outlets for members [129]. The assurance of market access encourages farmers to invest in sustainable technologies such as hybrid seeds, protective mulching, and diversified cropping systems [128].
Despite these significant contributions, not all farmers’ organizations operate effectively. Several smallholder cooperatives in South Africa face internal and external challenges that constrain their performance. These include weak institutional structures, limited financial and technical support, sociocultural constraints, and governance issues such as elite capture or limited participation by marginalized groups [130]. Addressing these barriers requires strengthening governance and accountability mechanisms within cooperatives, increasing government and donor support, and promoting public–private partnerships. Additionally, gender-sensitive policies and inclusive membership strategies must be promoted to ensure that women and marginalized groups have equitable access to the benefits of farmer organizations [33]. Furthermore, supporting cooperatives to meet certification standards and access climate-resilient markets can amplify their development impact and sustainability [124].
3.3.5. Support from Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs)
The role of non-governmental organizations in promoting climate-smart agriculture in South Africa is multifaceted, involving activities such as providing technical assistance, capacity-building, and facilitating access to resources for CSA adoption [131]. NGOs have been identified as critical stakeholders, often bridging the gap between government policy and the practical needs of smallholder farmers, who are often more vulnerable to climate change due to their limited adaptive capacity [91].
A significant body of literature highlights the instrumental role of NGOs in facilitating knowledge transfer and enhancing farmers’ technical capacity for CSA adoption [119,132,133]. According to Musara et al. [133], NGOs enhance smallholders’ understanding of CSA principles through structured educational activities such as on-farm demonstrations, workshops, and farmer field schools. These initiatives have been directly linked to increased uptake of sustainable agricultural practices, including conservation agriculture, agroforestry, and the cultivation of drought-tolerant crop varieties.
Limited access to quality inputs and financial resources is a common barrier to smallholder farmers’ adoption of CSA practices. NGOs have increasingly facilitated access to climate-resilient seeds, organic fertilizers, and other inputs necessary for CSA [134]. Some organizations also provide financial support in the form of grants or low-interest loans, helping farmers invest in sustainable practices without assuming high financial risks [135]. For instance, the African Climate Change Resilience Alliance (ACCRA) has collaborated with microfinance institutions to extend affordable micro-loans to smallholder farmers, enabling investment in climate-adaptive farming practices without imposing excessive financial risk [135]. Beyond technical and financial support, NGOs also foster collective action and social learning through the promotion of cooperative models and community-based knowledge exchange platforms. Kansiime and Mastenbroek [136] emphasize the importance of social networks in enhancing the diffusion of CSA practices, noting that NGOs frequently promote participatory approaches that allow farmers to share experiences, challenges, and success stories. These collaborative environments not only reduce information asymmetries but also build trust and reinforce local ownership of CSA initiatives. NGOs also play a crucial advocacy role by engaging in policy dialogue to ensure that agricultural and climate policies reflect the realities and priorities of smallholder farmers. Agyekum et al. [137] highlight that NGOs frequently act as intermediaries between grassroots farming communities and policymakers, advocating for policy reforms that facilitate smallholder adaptation and the mainstreaming of CSA within national agricultural development strategies. By representing the voices of marginalized farming populations, NGOs contribute to a more inclusive and responsive policy environment.
Although NGOs generally play a positive role in promoting climate-smart agriculture, their effectiveness is often contingent upon various mediating factors, including local socioeconomic conditions, institutional capacity, and the degree of stakeholder coordination. Studies by Mutenje et al. [138] and Lipper et al. [43] point out that many NGO interventions are implemented as fragmented, short-term projects that lack continuity. Such fragmentation undermines the long-term sustainability and scalability of CSA outcomes, often leading to inconsistent implementation and a loss of trust among farming communities. To maximize the transformative potential of NGOs in the CSA landscape, a more integrated, collaborative, and long-term approach is required. Strategic partnerships involving NGOs, government institutions, and private sector actors can create synergies that enhance coordination, resource mobilization, and policy coherence [139]. de Aragão Fernandes et al. [140] emphasize that the long-term impact of NGO interventions hinges on sustained funding and adaptive policy environments. Inconsistent funding cycles not only limit program scalability but also risk the premature termination of promising initiatives, which can erode farmer confidence and reduce willingness to invest in CSA technologies over time.
3.4. Impact of Policy Initiatives on the Adoption and Scaling of CSA Practices
A policy framework refers to a structured and coherent set of legislative instruments, regulatory guidelines, and strategic directives developed and implemented by national governments, regional entities, and international organizations to support the adoption and scaling of climate-smart agriculture [141]. In the context of South Africa, where smallholder farmers are particularly susceptible to the adverse effects of climate variability and extreme weather events, the establishment of an enabling policy environment is critical for fostering the widespread adoption of CSA technologies. These frameworks play a vital role in determining access to key resources, institutional and technical support, financial incentives, and information dissemination channels—all of which directly influence the uptake of CSA innovations [142].
A central policy instrument in this regard is South Africa’s National Climate Change Response Policy (NCCRP), promulgated in 2012, which provides a comprehensive blueprint for national climate action [143]. The NCCRP identifies agriculture as a priority sector exposed to climate-related risks, necessitating both adaptive and mitigation strategies. It aligns CSA objectives with broader national development goals by promoting sustainable land-use practices, climate-resilient agricultural systems, and the enhancement of early warning and climate information systems to improve adaptive capacity [33,143].
Complementing the NCCRP is the Agricultural Policy Action Plan (APAP), launched in 2014 by the Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (DAFF). APAP adopts a value chain-oriented strategy aimed at promoting inclusive economic development and ecological resilience in the agricultural sector [144]. It seeks to integrate smallholder and emerging farmers into commercial value chains by incentivizing the adoption of CSA practices that align with market quality and environmental standards [33,144]. Through the promotion of agroecological principles, conservation agriculture, and enhanced extension services, APAP has contributed to heightened awareness and capacity-building for CSA among smallholder farmers. Notable implementations include the Eastern Cape Conservation Agriculture Programme and the Land Care Programme, both of which emphasize minimum tillage, cover cropping, and crop rotation. These techniques have yielded demonstrable benefits, including improved soil health, enhanced productivity, and increased resilience to climate-related shocks among participating smallholders [144]. These initiatives highlight the strategic value of targeted policy frameworks in fostering the scaling of CSA innovations within vulnerable farming systems. Additional complementary policies include the Policy on Agriculture and Sustainable Development, which aims to harmonize the three pillars of sustainable development—social equity (people), environmental stewardship (land), and economic prosperity. This policy seeks to promote responsible agricultural development to ensure intergenerational equity and sustainability [33]. Furthermore, the National Agricultural Research and Development Strategy provides direction for the generation, adaptation, and application of agricultural knowledge and innovations to support sustainable development. Its overarching goal is to enhance the contribution of research towards achieving 6% economic growth through increased productivity, competitiveness, food security, and poverty reduction [33]. Despite the existence of these comprehensive policy frameworks, the implementation of CSA policies at the local level has been uneven and, in many cases, insufficient. Empirical evidence underscores a persistent gap between policy formulation and execution, often attributed to limited institutional capacity, inadequate financial and human resources, and fragmented coordination across governance levels [145,146]. These challenges are further exacerbated by the disjunction between national CSA objectives and localized development priorities, which impedes the alignment of CSA strategies with the actual needs and constraints of smallholder farmers.
3.4.1. Subsidy and Incentives
Subsidies and incentives are policy tools aimed at mitigating key barriers to the adoption of agricultural innovations, particularly among smallholder farmers. These barriers include high initial investment costs, limited technical knowledge, and risk aversion [147]. Support mechanisms such as input subsidies, financial grants, tax incentives, and capacity-building programs have been instrumental in promoting the implementation of CSA technologies. Van Niekerk et al. [148] argue that financial mechanisms such as input subsidies and fiscal incentives significantly encourage farmers to adopt CSA technologies like drought-resistant crops and conservation agriculture. Similarly, a study by Chivenge et al. [149] indicated that targeted subsidies are essential for overcoming initial cost barriers, which are substantial deterrents to adopting innovative agricultural practices among smallholders.
In the South African context, the government has instituted several strategic agricultural support programs aimed at improving the productivity, sustainability, and climate resilience of smallholder farming systems. Prominent among these are the Comprehensive Agricultural Support Programme (CASP) and the Ilima/Letsema Programme, both of which provide financial and technical assistance for infrastructure development, equipment access, and the dissemination of sustainable farming practices [150]. Empirical evidence highlights the positive impact of these programs. For example, Phatudi-Mphahlele [151] reported that CASP significantly improved rural livelihoods and increased smallholder incomes in Gauteng Province. In a related study, Shiba [152] demonstrated that CASP beneficiaries in Mpumalanga Province experienced a 10% increase in maize yields relative to non-beneficiaries. Furthermore, Sikwela [153] found that participation in agricultural support programs was strongly correlated with improvements in household income and welfare, thereby facilitating the adoption and scaling of CSA interventions. An additional initiative, the Land Care Programme, targets land and soil degradation through community-based natural resource management strategies [144]. A key feature of this program is the LandCare Conditional Grant, which is allocated to provinces that have identified critical land and water degradation challenges [144]. The program seeks to simultaneously address environmental degradation and improve agricultural productivity through localized support interventions. In line with this program are the Payments for Ecosystem Services (PES) schemes, which provide financial compensation to farmers for adopting land management practices that generate measurable ecological benefits, such as carbon sequestration, biodiversity conservation, and watershed protection [33]. By monetizing these ecosystem services, PES mechanisms create an alternative and complementary income stream for smallholder farmers implementing climate-smart agriculture practices [33]. Although comprehensive, formalized PES programs specifically focused on cover cropping or agroforestry are not yet widespread in South Africa, the foundational principles of PES are increasingly being mainstreamed into broader environmental and agricultural policy frameworks [144]. These evolving initiatives aim to cultivate an enabling policy and institutional environment in which farmers are economically incentivized to adopt sustainable practices that yield both agronomic and ecological co-benefits.
Given the demonstrated benefits of these programs, several challenges constrain the full potential of subsidies and incentives in catalyzing CSA adoption. One of the most pressing issues is the inadequate inclusion of marginalized groups, especially women and youth, who frequently face systemic exclusion from agricultural support schemes [154]. Furthermore, many subsidy programs are short-lived and lack the continuity necessary to support the sustained adoption of CSA practices [155]. A further limitation is the insufficient alignment of current support initiatives with CSA-specific objectives, resulting in a diluted policy impact and reduced contributions to long-term climate resilience [156]. Muller and Shackleton [157] argue that the efficacy of subsidies is heavily dependent on precise targeting and efficient program administration; their study documents cases where poor implementation undermined both farmer participation and the scalability of CSA technologies. To strengthen the contribution of subsidies and incentives to the widespread adoption of CSA, it is imperative that national policy frameworks explicitly prioritize CSA interventions within their funding criteria [158]. Additionally, governments should foster an enabling environment for private sector engagement in CSA-related services, including weather-indexed insurance, carbon finance initiatives, and climate advisory systems [33]. Expanding subsidy coverage to include digital information platforms, climate-smart training modules, and localized extension services can further support smallholders in building resilient farming systems [33]. Integrated, well-targeted, and sustained subsidy mechanisms are therefore essential for achieving transformative climate resilience in smallholder agriculture [159].
3.4.2. Effectiveness of Policies
The implementation of agricultural policies in South Africa has consistently faced significant structural, institutional, and socio-political constraints, severely limiting their transformative potential, particularly for smallholder farmers and land reform beneficiaries [158]. These constraints span across coordination inefficiencies, inadequate funding, policy inconsistencies, tenure insecurity, capacity limitations, and insufficient stakeholder participation. A critical barrier to effective policy implementation is the fragmented institutional landscape [158]. Agricultural development responsibilities are dispersed across various spheres of government, including the Department of Agriculture, Land Reform and Rural Development (DALRRD), provincial departments, and local municipalities. This fragmentation leads to overlapping mandates, the duplication of interventions, and the inefficient use of resources [160]. Moreover, insufficient communication and weak accountability mechanisms exacerbate this institutional discord, diminishing the effectiveness of agricultural support services [161]. Despite aspirational goals articulated in national agricultural strategies, their practical implementation is often undermined by inadequate financial resources and poor fiscal governance. Key government support programs such as the Comprehensive Agricultural Support Programme (CASP) and Ilima/Letsema have faced scrutiny for failing to deliver their objectives effectively due to underfunding, bureaucratic inefficiencies, and financial mismanagement [162,163]. As a result, allocated resources frequently fail to reach the targeted beneficiaries—particularly smallholder farmers—thereby undermining trust in public agricultural initiatives and perpetuating structural exclusion within the sector. Moreover, internal contradictions within South Africa’s agricultural policy framework further complicate implementation efforts. While policy advocates for the adoption of agroecological and climate-smart agriculture practices, government subsidies continue to support mechanization and input-intensive conventional farming methods. These subsidies are often misaligned with the core principles of conservation agriculture (CA), such as minimal soil disturbance, intercropping, and biodiversity enhancement [164]. This policy incoherence underscores a fundamental lack of integrated planning and reveals the absence of a coherent, unified vision for sustainable agricultural transformation in the country [155]. Land tenure insecurity poses yet another significant constraint, particularly in communal areas and redistributed lands. Many smallholder farmers operate without formalized land rights, which restricts their access to credit, inhibits long-term investment, and limits eligibility for public support programs [165]. The absence of secure tenure also acts as a deterrent to adopting CSA practices, many of which require sustained investment in land management, soil fertility, and ecosystem services [113].
The effectiveness of policy implementation is further weakened by a shortage of skilled human capital and inadequate extension services. Many extension officers lack the necessary training in contemporary climate-resilient and sustainable agricultural techniques, limiting their ability to provide effective support to smallholder farmers [33]. This gap is especially pronounced in rural and historically marginalized areas, such as the former homelands, where logistical and infrastructural barriers continue to impede the delivery of agricultural services [144,166]. An additional systemic weakness arises from the predominantly top-down approach to policy formulation and planning. Smallholder farmers and local institutions are rarely afforded meaningful participation in the design and development of agricultural policies. This exclusion often results in the creation of strategies that are poorly aligned with local realities, overlook community-specific constraints, and fail to incorporate indigenous knowledge systems [167]. Consequently, policy legitimacy and effectiveness are compromised, limiting the potential for transformative and inclusive agricultural development [168].
Addressing the persistent issue of institutional fragmentation in South Africa’s agricultural sector, it is imperative to establish a coherent and integrated framework that facilitates the effective coordination of policy initiatives across all levels of government and among key stakeholders. This could be operationalized through the creation of a centralized institutional body or an intergovernmental task force mandated to oversee, align, and integrate agricultural development interventions [161]. Strengthening intergovernmental communication channels and accountability mechanisms would further mitigate redundancies, enhance policy coherence, and promote the efficient allocation and utilization of resources [161]. Moreover, the adoption of a more integrated and decentralized governance model would enable local governments to develop and implement context-specific agricultural strategies tailored to the distinct socioeconomic and agroecological conditions of their regions. Such a governance approach would not only increase institutional responsiveness but also improve the relevance and effectiveness of agricultural interventions, particularly in meeting the needs of smallholder farmers [160].
3.5. Impact of Market Dynamics on the Adoption and Scaling of Climate-Smart Agriculture
Market access is a significant determinant in farmers’ adaptation strategies to climate change. A study conducted by Mayiza et al. [125] in the uMkhanyakude district of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, revealed that market access positively influences the adoption of various climate change adaptation strategies, including mixed farming and adjusting planting dates. Farmers with better market access are more likely to invest in CSA practices, anticipating higher returns from improved market opportunities. Christian [169] demonstrated a significant positive relationship between market access and the adoption of smart irrigation technologies among smallholder farmers in the Eastern Cape Province. This finding aligns with broader evidence presented by AGRA [170], which emphasizes that the effective adoption and scaling of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) among smallholder farmers is highly dependent on improved access to both local and international markets. Proximity to markets has been shown to positively influence the adoption of input-intensive CSA practices, such as the application of inorganic fertilizers, due to the enhanced economic viability and access to agricultural inputs. In contrast, farmers situated in geographically remote or poorly connected areas, where market access is constrained, are more likely to adopt low-cost, resource-conserving practices such as composting and soil conservation techniques [170]. This pattern highlights the dual role of market access, not only as a facilitator of economic returns but also as a determinant of the type and intensity of CSA practices employed. Consequently, inadequate market accessibility may restrict the profitability and scalability of capital-intensive or mechanized CSA interventions, thereby limiting broader transformation toward climate-resilient agricultural systems.
Elum et al. [119] reinforce the observed linkage between market access and climate resilience by highlighting that limited access to formal markets substantially constrains the adaptive capacity of smallholder farmers in South Africa. This constraint undermines their ability to transition toward more resilient farming systems in response to climate variability. In KwaZulu-Natal, Hitayezu et al. [171] found that only a small proportion of smallholder farmers were engaged in market-oriented agricultural production, such as sugarcane farming. The study attributed this limited participation to insufficient access to both public and private infrastructure, identifying it as a major barrier to integration into broader market economies. The lack of connectivity and infrastructure not only restricts market participation but also diminishes farmers’ ability to absorb and recover from climate-related shocks, thereby weakening the overall objectives of CSA. Similarly, Corfee-Morlot et al. [172] emphasized that inadequate transportation, poor road infrastructure, limited communication channels, and the absence of storage facilities collectively constrain smallholder farmers’ capacity to engage in functional markets. These deficiencies restrict farmers’ competitiveness, limit opportunities to diversify livelihoods, and ultimately hinder their resilience in the face of environmental stressors. Enhancing market access through deliberate and well-targeted interventions is therefore critical for fostering the adoption of CSA practices. Strategic investments such as rural road construction, the promotion of farmer cooperatives, and the strengthening of group marketing initiatives can play a significant role in reducing transaction costs, improving economies of scale, and facilitating the uptake of CSA-related technologies, including climate-smart mechanization [33].
Livingston et al. [173] further note that the geographical isolation of many rural farming communities exacerbates market access challenges by introducing logistical barriers that impede economic engagement. Addressing these spatial and infrastructural constraints requires a comprehensive rural development agenda underpinned by proactive public investment and policy realignment. Godfray et al. [174] argue that overcoming persistent market failures in the agricultural sector necessitates increased governmental commitment to the provision of critical public goods. Priority areas include the development of road, rail, and port infrastructure; irrigation facilities to enable year-round production; storage and agro-processing infrastructure; strengthened research and extension systems; and the establishment of reliable market information systems. Moreover, institutional reforms are essential to improve market efficiency and inclusivity, thereby ensuring that smallholder farmers are effectively integrated into climate-resilient value chains and can benefit equitably from CSA interventions.
Value Chain Development
Value chain development refers to the strategic strengthening and coordination of the various stages involved in agricultural production, processing, distribution, and marketing. This integrated approach enhances the agricultural sector’s overall efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness [33]. Importantly, it also facilitates improved access to markets, resources, and support services for smallholder farmers, thereby positioning them to effectively respond to evolving agricultural challenges, including climate change.
In the South African context, integrating smallholder farmers into structured and efficient agricultural value chains has been increasingly recognized as a critical strategy for advancing the adoption and scaling of climate-smart agriculture practices [16,54]. According to Branca et al. [54], approximately 13% of planned agricultural investments globally are dedicated to value chain interventions across various crop and livestock systems. These investments aim to enhance market connectivity, improve income stability, and foster the uptake of sustainable agricultural practices among smallholder producers.
The Department of Environment, Forestry, and Fisheries (DEFF) has further emphasized the necessity of creating enabling environments through coherent policy frameworks and institutional support mechanisms to facilitate effective value chain development in support of CSA objectives [33]. Such enabling conditions are vital for improving the infrastructure, services, and market linkages that underpin sustainable agricultural transformation [175].
A key component of value chain development is access to financial services, particularly credit. Access to credit empowers smallholder farmers to invest in CSA technologies, such as drought-resistant seed varieties, soil conservation measures, and efficient irrigation systems. Several studies have underscored the significant role of credit access in accelerating the adoption of CSA practices. For example, Zurihun [176] and Mwadzingeni et al. [177] demonstrated that farmers with reliable access to financial capital are more likely to invest in climate-resilient technologies. Similarly, Slayi et al. [84] observed that limited access to credit constrains smallholders’ ability to adopt CSA, while those with better financial access show higher rates of investment in climate-adaptive strategies.
Moreover, the availability of targeted credit products has been positively associated with improved value chain sustainability. Jones and Christian [178] found that credit access not only enhances farmers’ participation in agricultural value chains but also contributes to the long-term sustainability of these chains through the promotion of environmentally sound practices. Access to finance, therefore, plays a dual role in supporting both individual farmer investment capacity and the broader functionality of sustainable value chains.
The synergistic interplay between robust value chain development and improved credit access establishes a favorable environment conducive to the adoption and scaling of CSA practices. Integration into efficient value chains coupled with financial empowerment through accessible credit enables smallholder farmers to leverage CSA technologies more effectively. Supporting this, a systematic review by Finizola et al. [175] concluded that increased farm-generated income and credit accessibility substantially elevate CSA adoption rates. Thus, strategic interventions aimed at enhancing these specific factors are likely to result in notable improvements in CSA adoption among smallholder farmers.
4. Conclusions
The adoption and scaling of climate-smart agriculture practices among smallholder farmers in South Africa have demonstrated considerable potential in enhancing agricultural productivity, sustainability, resilience, and food security. Empirical evidence highlights that CSA innovations such as climate-resilient crop varieties, precision irrigation, conservation agriculture, and data-driven farming technologies significantly contribute to productivity improvements, income stability, and reduced vulnerability to climate-related risks. However, despite these benefits, widespread adoption remains limited, impeded by socioeconomic, institutional, technical, and policy-related constraints. Institutional mechanisms, including secure land tenure, effective extension services, robust financial support, and well-structured farmer organizations, are crucial determinants influencing the adoption and scaling of CSA practices. Secure land tenure encourages long-term investments necessary for adopting sustainable practices, while extension services and climate information systems are essential for disseminating CSA knowledge and technologies effectively. Financial institutions, especially those providing tailored credit schemes and insurance products, substantially facilitate the uptake of CSA by mitigating risks and overcoming financial barriers. Farmer organizations and cooperatives further strengthen collective learning, resource pooling, and market bargaining power, playing a vital role in scaling CSA interventions.
Policy frameworks, notably South Africa’s National Climate Change Response Policy and Agricultural Policy Action Plan, provide essential guidelines and financial incentives, promoting climate-resilient agricultural practices. However, implementation gaps due to fragmented institutional frameworks, inadequate funding, weak coordination, tenure insecurity, and insufficient stakeholder engagement significantly constrain policy effectiveness. These gaps highlight the need for integrated and coherent policy approaches that enhance coordination, align interventions with localized farmer needs, and ensure sustained financial and institutional support.
Market dynamics including access to markets, credit, and integrated value chains are critical to making CSA economically viable for smallholders. Improved infrastructure, market linkages, and financial services not only enhance farmer participation in climate-resilient value chains but also incentivize the adoption of sustainable practices. Current constraints in rural infrastructure and credit availability limit CSA’s scalability and must be addressed through targeted investments and public–private partnerships.
Finally, the adoption and scaling of CSA innovations in South Africa hinge on an enabling environment that combines institutional coordination, policy coherence, market integration, and farmer empowerment. Addressing the barriers identified in this review demands a holistic, inclusive, and multi-stakeholder approach that strengthens farmer capacities, aligns institutional efforts, and embeds CSA into broader rural development strategies. By fostering such synergies, South Africa can unlock the full potential of CSA in advancing sustainable agriculture and building climate-resilient livelihoods for its smallholder farmers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.F.O. and M.C.; methodology, M.F.O.; investigation, M.F.O.; resources, M.C.; writing—original draft preparation, M.F.O.; writing—review and editing, M.F.O. and M.C.; visualization, M.F.O.; supervision, M.C.; project administration, M.F.O.; funding acquisition, M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the University of South Africa and the Department of Environmental Science, University of South Africa for funding this research project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ma, W.; Rahut, D.B. Climate-smart agriculture: Adoption, impacts, and implications for sustainable development. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2024, 29, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.K. Impact of climate change on agriculture production and its sustainable solutions. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 2, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizinga, A.; Rurinda, J.; Mubiru, D.N. Climate-smart agriculture adoption and smallholder farmers’ resilience to climate variability in Uganda. J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 160, 319–332. [Google Scholar]
- Mirón, I.J.; Linares, C.; Díaz, J. The influence of climate change on food production and food safety. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations. Economic and social council: Population, food security, nutrition and sustainable development. In Oxford Handbook of United Nations; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Climate-Smart Agriculture Case Studies 2021—Projects from Around the World; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, B.; Qi, A.; Fitt, B.D. Control of crop diseases through integrated crop management to deliver climate-smart farming systems for low- and high-input crop production. Plant Pathol. 2022, 71, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Chhogyel, N.; Gopalakrishnan, T.; Hasan, K.; Jayasinghe, S.L.; Kariyawasam, C.S.; Kogo, B.K.; Ratnayake, S. Climate change and future of agri-food production. In Future Foods; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 49–79. [Google Scholar]
- Malaka, S.F. Estimation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Agriculture in the Eastern Free State, South Africa. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Köninger, J.; Lugato, E.; Panagos, P.; Kochupillai, M.; Orgiazzi, A.; Briones, M.J. Manure management and soil biodiversity: Towards more sustainable food systems in the EU. Agric. Syst. 2021, 194, 103251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschuuren, J. Achieving Agricultural Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions in the EU Post-2030: What Options Do We Have? Rev. Eur. Comp. Int. Environ. Law 2022, 31, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipper, L.; Thornton, P.; Campbell, B.M.; Baedeker, T.; Braimoh, A.; Bwalya, M.; Caron, P.; Cattaneo, A.; Garrity, D.; Henry, K.; et al. Climate-smart agriculture for food security. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The Future of Food and Agriculture—Trends and Challenges; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, P.K.; Whitbread, A.; Baedeker, T.; Cairns, J.; Claessens, L.; Baethgen, W.; Bunn, C.; Friedmann, M.; Giller, K.E.; Herrero, M.; et al. A framework for priority-setting in climate-smart agriculture research. Agric. Syst. 2018, 167, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollni, M.; Andersson, C. Spatial patterns of organic agriculture adoption: Evidence from Honduras. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 97, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Climate-Smart Agriculture Sourcebook; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Scaling Up Climate-Smart Agriculture; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, S.J.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Campbell, B.M.; Thornton, P.K. Options for Support to Agriculture and Food Security under Climate Change. Environ. Sci. Policy 2012, 15, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongeneel, R.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A. Implementing the EU eco-scheme in the Netherlands: A results-based points system approach. EuroChoices 2023, 22, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanarella, L.; Panagos, P. The Relevance of Sustainable Soil Management within the European Green Deal. Land Use Policy 2021, 100, 104950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseler, J. The EU’s Farm-to-Fork Strategy: An Assessment from the Perspective of Agricultural Economics. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 2022, 44, 1826–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruysschaert, D.; Carter, N.H.; Martínez, S. The role of digital agriculture in enhancing environmental sustainability and food security in Europe. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112147. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T. Civil society organizations for sustainable agriculture: Negotiating power relations for pro-poor development in India. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2016, 40, 381–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Pan, X.; Zhang, X. China’s policies on climate change adaptation in agriculture: Progress and gaps. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2020, 11, 208–217. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, India. National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA). Available online: https://agricoop.nic.in (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Ghosh, N.; Ghosh, M.; Baig, K. Sustainable agriculture in India: A strategy for climate adaptation and mitigation. Clim. Dev. 2019, 11, 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Cuadros-Casanova, I.; Cristiano, A.; Biancolini, D.; Cimatti, M.; Sessa, A.A.; Mendez Angarita, V.Y.; Dragonetti, C.; Pacifici, M.; Rondinini, C.; Di Marco, M. Opportunities and Challenges for Common Agricultural Policy Reform to Support the European Green Deal. Conserv. Biol. 2023, 37, e14052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NEPAD. Comprehensive Africa Agriculture Development Programme (CAADP); NEPAD: Midrand, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- African Union. Comprehensive Africa Agriculture Development Programme (CAADP); African Union Commission: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria, A.; Azumah, S.B.; Appiah-Twumasi, M.; Dagunga, G. Adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices among farm households in Ghana: The role of farmer participation in training programmes. Technol. Soc. 2020, 63, 101338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martey, E.; Etwire, P.M.; Mockshell, J. Climate-smart cowpea adoption and welfare effects of comprehensive agricultural training programs. Technol. Soc. 2021, 64, 101468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roobroek, D.; Van Asten, P.; Jama, B.; Harawa, R.; Vanlauwe, B. Integrated Soil Fertility Management: Contributions Framework and Practices to Climate-Smart Agriculture; CGIAR: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015; Available online: https://cgspace.cgiar.org (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Mnkeni, P.N.S.; Mutengwa, C.S.; Aliber, M.; Ngarava, S. Actionable Guidelines for the Implementation of Climate-Smart Agriculture in South Africa. In Volume 3: Enabling Environments; Department of Environment, Forestry and Fisheries: Pretoria, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sango, I.; Obi, A. Climate change adaptation strategies for smallholder farmers in Sub-Saharan Africa. Afr. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2020, 15, 234–250. [Google Scholar]
- Kativhu, S.; Mwale, M.M.; Zuwarimwe, J. Agricultural resilience under increasing water security threats: Insights for smallholder farming in Limpopo Province, South Africa. Water Pract. Technol. 2020, 15, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotoso, A.B.; Omotayo, A.O. Impact of behavioural intention to adopt climate-smart agricultural practices on the food and nutrition security of farming households: A microeconomic level evidence. Clim. Change 2024, 177, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotoso, A.B.; Letsoalo, S.S.; Daud, S.A.; Tshwene, C.; Omotayo, A.O. Climate-smart agricultural practices, productivity, and food-nutrition security in rural South Africa: A dataset of smallholder maize farmers. Data Brief. 2024, 55, 110725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abegunde, V.O.; Sibanda, M.; Obi, A. Effect of climate-smart agriculture on household food security in small-scale production systems: A micro-level analysis from South Africa. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2022, 8, 2086343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, I.; Mushunje, A.; Lewu, B.; Omoruyi, B.E. Climate-smart agriculture and smallholder farmers income: The case of soil conservation practice adoption at Qamata irrigation scheme South Africa. J. Hum. Ecol. 2020, 69, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumalo, N.Z.; Sibanda, M.; Mdoda, L. The effect of heterogeneous adoption of climate-smart agriculture practices on household food and nutrition security of small-scale urban crop farmers in eThekwini Municipality. PLoS Clim. 2025, 4, e0000551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.M.; Thornton, P.; Zougmoré, R.; Van Asten, P.; Lipper, L. Sustainable Intensification: What Is Its Role in Climate-Smart Agriculture? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 8, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermann, O.; Thornton, P.; Förch, W. Reaching More Farmers—Innovative Approaches to Scaling Up Climate-Smart Agriculture; CCAFS Working Paper 2015; CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015; p. 135. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10568/68403 (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Lipper, L.; McCarthy, N.; Zilberman, D.; Asfaw, S.; Branca, G. Climate-Smart Agriculture: Building Resilience to Climate Change; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; p. 630. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, P.K.; Jarvis, A.; Campbell, B.M.; Zou more, R.B.; Khatri-Chhetri, A.; Vermeulen, S.J.; Yen, B.T. The Climate-Smart Village Approach. Ecol. Soc. 2018, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Linn, J.F. Scaling Up: A Framework and Lessons for Development Effectiveness from Literature and Practice; Wolfensohn Center for Development Working Paper No. 5; Brookings Institution: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ajayi, T.; Fatunbi, O.; Akinbamijo, Y. Strategies for Scaling Agricultural Technologies in Africa; Forum for Agricultural Research in Africa (FARA): Accra, Ghana, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Steenwerth, K.L.; Hodson, A.K.; Bloom, A.J.; Carter, M.R.; Cattaneo, A.; Chartres, C.J.; Hatfield, J.L.; Henry, K.; Hopmans, J.W.; Horwath, W.R.; et al. Climate-Smart Agriculture Global Research Agenda: Scientific Basis for Action. Agric. Food Secur. 2014, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpandeli, S.; Naidoo, D.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Nhemachena, C.; Nhamo, L.; Liphadzi, S.; Modi, A.T. Climate Change Adaptation through the Water-Energy-Food Nexus in Southern Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhamo, L.; Mpandeli, S.; Liphadzi, S.; Hlophe-Ginindza, S.; Kapari, M.; Molwantwa, J.; Mabhaudhi, T. Advances in Water Research: Enhancing Sustainable Water Use in Irrigated Agriculture in South Africa. In Progress in Sustainable Development; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 233–248. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, J.A.; Wentink, G.J.; Kruger, L. Climate-Smart Agriculture for Sustainable Agricultural Sectors: The Case of Mooifontein. Jàmbá J. Disaster Risk Stud. 2018, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makamane, A.; Van Niekerk, J.; Loki, O.; Mdoda, L. Determinants of Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA) Technologies Adoption by Smallholder Food Crop Farmers in Mangaung Metropolitan Municipality, Free State. S. Afr. J. Agric. Ext. 2023, 51, 52–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msweli, N.S.; Agholor, I.A.; Sithole, M.Z.; Morepje, M.T.; Thabane, V.N.; Mgwenya, L.I. The Determinants and Acceptance of Climate Smart Agriculture Practices in South Africa. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2024, 24, 24591–24610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mango, N.; Zamasiya, B.; Makate, C.; Nyikahadzoi, K.; Siziba, S. Factors Influencing Household Food Security among Smallholder Farmers in the Mudzi District of Zimbabwe. Dev. S. Afr. 2014, 31, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, G.; Arslan, A.; Paolantonio, A.; Grewer, U.; Cattaneo, A.; Cavatassi, R.; Vetter, S. Assessing the Economic and Mitigation Benefits of Climate-Smart Agriculture and Its Implications for Political Economy: A Case Study in Southern Africa. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 125161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayo, L.; Hasegawa, H. Enhancing Emission Reductions in South African Agriculture: The Crucial Role of Carbon Credits in Incentivizing Climate-Smart Farming Practices. Sustain. Futures 2024, 8, 100260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, U.; Gebremedhin, Z.; Brychkova, G.; Spillane, C. Smallholder Farmers and Climate-Smart Agriculture: Technology and Labour-Productivity Constraints Amongst Women Smallholders in Malawi. Gend. Technol. Dev. 2016, 20, 117–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senyolo, M.P.; Long, T.B.; Blok, V.; Omta, S.W.F.; van der Velde, G. Smallholder Adoption of Technology: Evidence from the Context of Climate Smart Agriculture in South Africa. J. Dev. Agric. Econ. 2021, 13, 156–173. [Google Scholar]
- Serote, B.; Mokgehle, S.; Senyolo, G.; du Plooy, C.; Hlophe-Ginindza, S.; Mpandeli, S.; Araya, H. Exploring the Barriers to the Adoption of Climate-Smart Irrigation Technologies for Sustainable Crop Productivity by Smallholder Farmers: Evidence from South Africa. Agriculture 2023, 13, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaafsma, M.; Utila, H.; Hirons, M.A. Understanding Trade-Offs in Upscaling and Integrating Climate-Smart Agriculture and Sustainable River Basin Management in Malawi. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 80, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye-Smith, C. Farming’s Climate-Smart Future: Placing Agriculture at the Heart of Climate-Change Policy; CTA Policy Pointer: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mwongera, C.; Shikuku, K.M.; Twyman, J.; Läderach, P.; Ampaire, E.; Van Asten, P.; Winowiecki, L.A. Climate-smart agriculture rapid appraisal (CSA-RA): A tool for prioritizing context-specific climate-smart agriculture technologies. Agric. Syst. 2017, 151, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunduka, R.W.; Mateva, K.I.; Magorokosho, C.; Manjeru, P. Impact of adoption of drought-tolerant maize varieties on total maize production in southeastern Zimbabwe. Clim. Dev. 2019, 11, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makate, C.; Makate, M.; Mango, N. Sustainable agriculture practices and livelihoods in pro-poor smallholder farming systems in Southern Africa. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2017, 9, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michler, J.D.; Baylis, K.; Arends-Kuenning, M.; Mazvimavi, K. Conservation agriculture and climate resilience. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2019, 93, 148–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makate, M.; Nelson, N.; Makate, C. Farm household typology and adoption of climate-smart agriculture practices in smallholder farming systems of Southern Africa. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2018, 10, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegunde, V.O.; Sibanda, M.; Obi, A. Determinants of the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices by small-scale farming households in King Cetshwayo District Municipality, South Africa. Sustainability 2020, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassie, M.; Jaleta, M.; Shiferaw, B.; Mmbando, F.; Mekuria, M. Adoption of interrelated sustainable agricultural practices in smallholder systems: Evidence from rural Tanzania. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2013, 80, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollni, M.; Lee, D.R.; Thies, J.E. Conservation agriculture, organic marketing, and collective action in the Honduran hillsides. Agric. Econ. 2010, 41, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklewold, H.; Kassie, M.; Shiferaw, B.; Köhlin, G. Cropping system diversification, conservation tillage and modern seed adoption in Ethiopia: Impacts on household income, agrochemical use and demand for labour. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 93, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitakira, M.; Ngcobo, N.Z. Uptake of climate-smart agriculture in peri-urban areas of South Africa’s economic hub requires up-scaling. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 706738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giller, K.E.; Tittonell, P.; Rufino, M.C.; Van Wijk, M.T.; Zingore, S.; Mapfumo, P.; Vanlauwe, B. Communicating complexity: Integrated assessment of trade-offs concerning soil fertility management within African farming systems to support innovation and development. Agric. Syst. 2011, 104, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank; FAO; IFAD. Gender in Climate-Smart Agriculture; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Huyer, S.; Twyman, J.; Koningstein, M.; Ashby, J.; Vermeulen, S. Supporting Women Farmers in a Changing Climate: Five Policy Lessons; CCAFS Policy Brief No. 10; CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Twyman, J.; Bernier, Q.; Muriel, J.; Paz, L.P.; Ortega, L.A.; Koningstein, M. Ensuring Climate-Smart Agriculture is Gender-Smart: A Participatory Method for Local Adaptation Planning with a Gender Focus; Poster; CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS) and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT): Cali, Colombia, 2015; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10568/65655 (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Kuivanen, K.S.; Michalscheck, M.; Descheemaeker, K.; Adjei-Nsiah, S.; Mellon-Bedi, S.; Groot, J.C.; Alvarez, S. A comparison of statistical and participatory clustering of smallholder farming systems—A case study in Northern Ghana. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 45, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikowo, R.; Zingore, S.; Snapp, S.; Johnston, A. Farm typologies, soil fertility variability and nutrient management in smallholder farming in Sub-Saharan Africa. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2014, 100, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serote, B.; Mokgehle, S.; Du Plooy, C.; Mpandeli, S.; Nhamo, L.; Senyolo, G. Factors influencing the adoption of climate-smart irrigation technologies for sustainable crop productivity by smallholder farmers in arid areas of South Africa. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myeni, L.; Moeletsi, M.E. Assessing the adoption of improved seeds as a coping strategy to climate variability under smallholder farming conditions in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2023, 119, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mthethwa, K.N.; Ngidi, M.S.C.; Ojo, T.O.; Hlatshwayo, S.I. The determinants of adoption and intensity of climate-smart agricultural practices among smallholder maize farmers. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, A.; Maya, O. Innovative climate-smart agriculture (CSA) practices in the smallholder farming system of South Africa. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubanza, N.S.; Oladele, O.J. Climate Smart Agricultural Policy in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Case Study of Ngaka Modiri Molema District Municipality of North West Province, South Africa. Local Environ. 2024, 29, 1579–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myeni, L.; Moeletsi, M.E. Factors Determining the Adoption of Strategies Used by Smallholder Farmers to Cope with Climate Variability in the Eastern Free State, South Africa. Agriculture 2020, 10, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabane, V.N.; Agholor, I.A.; Sithole, M.Z.; Morepje, M.T.; Msweli, N.S.; Mgwenya, L.I. Socio-Demographic Determinants of Climate-Smart Agriculture Adoption among Smallholder Crop Producers in Bushbuckridge, Mpumalanga Province of South Africa. Climate 2024, 12, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slayi, M.; Zhou, L.; Jaja, I.F. Constraints Inhibiting Farmers’ Adoption of Cattle Feedlots as a Climate-Smart Practice in Rural Communities of the Eastern Cape, South Africa: An In-Depth Examination. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, G. What Makes Climate Change Adaptation Effective? A Systematic Review of the Literature. Glob. Environ. Change 2020, 62, 102071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, T.O.; Adetoro, A.A.; Ogundeji, A.A.; Belle, J.A. Quantifying the Determinants of Climate Change Adaptation Strategies and Farmers’ Access to Credit in South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A. Local Institutions and Adaptation to Climate Change. In Social Dimensions of Climate Change: Equity and Vulnerability in a Warming World; Mearns, R., Norton, A., Eds.; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, L.; Weldon, S.L. Climate Change Policy and Informal Institutions; Purdue University Policy Brief; Purdue University: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yegbemey, R.N.; Yabi, J.A.; Tovignan, S.D.; Gantoli, G.; Kokoye, S.E.H. Farmers’ Decisions to Adapt to Climate Change under Various Property Rights: A Case Study of Maize Farming in Northern Benin (West Africa). Land Use Policy 2013, 34, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitko, N.J.; Scognamillo, A.; Malevolti, G. Does Receiving Food Aid Influence the Adoption of Climate-Adaptive Agricultural Practices? Evidence from Ethiopia and Malawi. Food Policy 2021, 102, 102041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waaswa, A.; Oywaya Nkurumwa, A.; Mwangi Kibe, A.; Ngeno Kipkemoi, J. Climate-smart agriculture and potato production in Kenya: Review of the determinants of practice. Clim. Dev. 2022, 14, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, R.; Khatri-Chhetri, A.; Chhetri, N. Institutional innovations for climate-smart agriculture: Assessment of climate-smart village approach in Nepal. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 734319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, F. Land tenure and agricultural productivity in Africa: A comparative analysis of the economics literature and recent policy strategies and reforms. World Dev. 2009, 37, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinzen-Dick, R.; Quisumbing, A.; Doss, C.; Theis, S. Women’s land rights as a pathway to poverty reduction: Framework and review of available evidence. Agric. Syst. 2019, 172, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, G.; Feeny, D. Land tenure and property rights: Theory and implications for development policy. World Bank Econ. Rev. 1991, 5, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mfune, W. Land Reform in South Africa: The Issues and Challenges—Ideology, Politics and Post-Settlement Support Services. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, R. Land grabbing in Southern Africa: The many faces of the investor rush. Rev. Afr. Political Econ. 2011, 38, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiff, E. ‘Willing buyer, willing seller’: South Africa’s failed experiment in market-led agrarian reform. In Market-Led Agrarian Reform; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2013; pp. 161–182. [Google Scholar]
- Chavula, P.; Turyasingura, B. Land tenurial system influence among smallholder farmers’ climate smart agriculture technologies adoption, Sub-Sahara Africa: A review paper. Int. J. Food Sci. Agric. 2022, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, B.; Scoones, I. Contested paradigms of ‘viability’ in redistributive land reform: Perspectives from southern Africa. J. Peasant Stud. 2010, 37, 31–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pienaar, L.; Traub, L. Understanding the Smallholder Farmer in South Africa: Towards a Sustainable Livelihoods Classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Agricultural Economists (ICAE), Milan, Italy, 9–14 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lahiff, E. Land Reform and Sustainable Livelihoods in South Africa’s Eastern Cape Province; Sustainable Livelihoods in Southern Africa Programme, University of Sussex: Brighton, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cousins, B. Smallholder irrigation schemes, agrarian reform and ‘accumulation from above and from below’ in South Africa. J. Agrar. Change 2013, 13, 116–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtero, F.; Palmer, R.; Hara, M. Land tenure insecurity and its implications for rural livelihoods: A case study of communal landholders in the Eastern Cape. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2020, 116, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mdoda, L.; Gidi, L.S. Impact of land ownership in enhancing agricultural productivity in rural areas of Eastern Cape Province. S. Afr. J. Agric. Ext. 2023, 51, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tall, A.; Hansen, J.; Jay, A.; Campbell, B.; Kinyangi, J.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Zougmoré, R.B. Scaling Up Climate Services for Farmers: Mission Possible. In Learning from Good Practice in Africa and South Asia; CCAFS Report No. 13; CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014; p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- Bontsa, N.V.; Gwala, L.; Ngarava, S.; Mdiya, L.; Zhou, L. Quality of climate change extension services provided to smallholder farmers in Raymond Mhlaba Local Municipality, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Agric. Ext. 2023, 51, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamaga-Chitja, J.M.; Morojele, P. The context of smallholder farming in South Africa: Towards a livelihood asset-building framework. J. Hum. Ecol. 2014, 45, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mmbengwa, V.; Rambau, M.K.; Groenewald, I.B. Smallholder agriculture development in South Africa: Opportunities, constraints, and challenges. Agric. Food Secur. 2020, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J.W.; Hellin, J.; Rosenstock, T.; Fisher, E.; Cairns, J.; Stirling, C.; Campbell, B.M. Climate risk management and climate-smart agriculture: Innovations and insights from the CGIAR research program on climate change, agriculture and food security. Clim. Risk Manag. 2019, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, E.R.M.; Landman, W.A.; Tadross, M.A.; Malherbe, J.; Weepener, H.; Maluleke, P.; Marumbwa, F.M. Understanding the evolution of the 2014–2016 summer rainfall seasons in southern Africa: Key lessons. Clim. Risk Manag. 2017, 16, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanzo, J.; Haddad, L.; Schneider, K.R.; Béné, C.; Covic, N.M.; Guarin, A.; Moncayo, J.R. Rigorous monitoring is necessary to guide food system transformation in the countdown to the 2030 global goals. Food Policy 2021, 104, 102163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncube, B. Constraints to smallholder agricultural production in the Western Cape, South Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth 2018, 106, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungai, E.M.; Ndiritu, S.W.; Da Silva, I. Unlocking climate finance potential for climate adaptation: Case of climate-smart agricultural financing in sub-Saharan Africa. In African Handbook of Climate Change Adaptation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 2063–2083. [Google Scholar]
- Ngara, T. Weather index-based insurance as a CSA strategy. In Climate-Smart Agriculture Manual for Agriculture Education in Zimbabwe; Ngara, T., Ed.; Climate Technology Centre and Network: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Land Bank. Emerging Farmers Support Programme; Land Bank: Centurion, South Africa, 2021; Available online: www.landbank.co.za (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Zeleke, T.; Beyene, F.; Deressa, T.; Yousuf, J.; Kebede, T. Smallholder farmers’ perception of climate change and choice of adaptation strategies in East Hararghe Zone, Eastern Ethiopia. Int. J. Clim. Change Strat. Manag. 2022, 15, 515–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, J.; Zivin, J.G.; Cattaneo, A.; Paolantonio, A.; Cavatassi, R. The adoption of climate-smart agriculture: The role of information and insurance under climate change. In Climate Smart Agriculture: Building Resilience to Climate Change; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 353–383. [Google Scholar]
- Elum, Z.A.; Modise, D.M.; Marr, A. Farmer’s perception of climate change and responsive strategies in three selected provinces of South Africa. Clim. Risk Manag. 2017, 16, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegunde, V.O.; Sibanda, M.; Obi, A. The dynamics of climate change adaptation in Sub-Saharan Africa: A review of climate-smart agriculture among small-scale farmers. Climate 2019, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.; Cousins, B. Commercial Farming and Agribusiness in South Africa and Their Changing Roles in Africa’s Agro-Food System. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rural Transformations and Food Systems: The BRICS and Agrarian Change in the Global South, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 20–21 April 2015; BRICS Initiative for Critical Agrarian Studies (BICAS): Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kahsay, G.A.; Endalew, Y.G. The Role of Cooperatives in Promoting Climate-Smart Agriculture: Panel Evidence from Ethiopia. Agric. Econ. 2025, e70011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machete, K.C.; Senyolo, M.P.; Gidi, L.S. Adaptation through climate-smart agriculture: Examining the socioeconomic factors influencing the willingness to adopt climate-smart agriculture among smallholder maize farmers in the Limpopo Province, South Africa. Climate 2024, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zantsi, S. Why do agricultural co-operatives fail to attract youth and create rural employment? Evidence from a case study of Zanokhanyo in Butterworth, Eastern Cape. S. Afr. J. Agric. Ext. 2021, 49, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziya, M.; Nkonki-Mandleni, B.; Van Niekerk, J.A. Smallholder Farmers’ Choice of Climate Change Adaptation Strategies in the uMkhanyakude District in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Agric. Ext. 2024, 52, 97–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makate, C. Effective scaling of climate-smart agriculture innovations in African smallholder agriculture: A review of approaches, policy and institutional strategy needs. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 96, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinyolo, S.; Mudhara, M. Farmer groups and inorganic fertiliser use among smallholders in rural South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2018, 114, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cele, T.; Mudhara, M. Impact of Market Participation on Household Food Security among Smallholder Irrigators in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Agriculture 2022, 12, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (DAFF). A Framework for the Development of Smallholder Farmers through Cooperatives; DAFF: Pretoria, South Africa, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ortmann, G.F.; King, R.P. Agricultural cooperatives I: History, theory and problems. Agrekon 2007, 46, 40–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senyolo, M.P.; Long, T.B.; Blok, V.; Omta, O. How the characteristics of innovations impact their adoption: An exploration of climate-smart agricultural innovations in South Africa. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3825–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoma, H.; Angelsen, A.; Jayne, T.S.; Chapoto, A. Understanding adoption and impacts of conservation agriculture in eastern and southern Africa: A review. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 671690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musara, J.P.; Tibugari, H.; Moyo, B.; Mutizira, C. Crop-livestock integration practices, knowledge, and attitudes among smallholder farmers: Hedging against climate change-induced shocks in semi-arid Zimbabwe. Open Life Sci. 2021, 16, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, J.P.; Sapkota, T.B.; Rahut, D.B.; Krupnik, T.J.; Shahrin, S.; Jat, M.L.; Stirling, C.M. Major climate risks and adaptation strategies of smallholder farmers in coastal Bangladesh. Environ. Manag. 2020, 66, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretty, J. The sustainable intensification of agriculture. Resour. Mag. 2019, 26, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kansiime, M.K.; Mastenbroek, A. Enhancing resilience of smallholder farmers through agroecological practices: The case of push-pull technology in Uganda. Agric. Syst. 2016, 150, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyekum, T.P.; Antwi-Agyei, P.; Dougill, A.J.; Stringer, L.C. Benefits and barriers to the adoption of climate-smart agriculture practices in West Africa: A systematic review. Clim. Resil. Sustain. 2024, 3, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutenje, M.J.; Farnworth, C.R.; Stirling, C.; Thierfelder, C.; Mupangwa, W.; Nyagumbo, I. A cost-benefit analysis of climate-smart agriculture options in Southern Africa: Balancing gender and technology. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 163, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynberg, R. African Perspectives on Agroecology: Why Farmer-Led Seed and Knowledge Systems Matter; Practical Action Publishing: Rugby, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- de Aragão Fernandes, P.; Gwebu, L.; Johansson, L.; Meattle, C.; Radmore, J.V.; Solomon, C. South African Climate Finance Landscape 2023; Presidential Climate Commission: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2023; Available online: https://www.climatepolicyinitiative.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/The-South-African-Climate-Finance-Landscape-2023.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Howlett, M.; Mnkeni, R.M.; Perl, A. Studying Public Policy: Policy Cycles and Policy Subsystems; Oxford University Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1995; Volume 163. [Google Scholar]
- Sabatier, P.A.; Weible, C. (Eds.) Theories of the Policy Process; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- DEA. National Climate Change Response Policy (NCCRP); Department of Environmental Affairs: Pretoria, South Africa, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- DAFF. Agricultural Policy Action Plan (APAP) 2015–2019; Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries: Pretoria, South Africa, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zembe, A.; Nemakonde, L.D.; Chipangura, P. A policy coherence framework for food security, climate change adaptation and disaster risk reduction in South Africa. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2023, 95, 103877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakweya, R.B. Challenges and prospects of adopting climate-smart agricultural practices and technologies: Implications for food security. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoma, H.; Mulenga, B.P.; Jayne, T.S. What Explains Minimal Usage of Minimum Tillage Practices in Zambia? Evidence from District-Representative Data. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257285286_What_Explains_Minimal_Usage_of_Minimum_Tillage_Practices_in_Zambia_Evidence_from_District-_Representative_Data (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Van Niekerk, W.; Le Roux, A.; Pieterse, P.J. Climate-smart agriculture in South Africa: Identifying effective policy interventions. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2020, 116, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chivenge, P.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Modi, A.T.; Mafongoya, P. The potential role of neglected and underutilised crop species as future crops under water scarce conditions in Sub-Saharan Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 5685–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliber, M.; Hall, R. Support for smallholder farmers in South Africa: Challenges of scale and strategy. Dev. S. Afr. 2012, 29, 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phatudi-Mphahlele, M.D. Analysis of Socio-Economic Impact of Comprehensive Agricultural Support Programme on Agrarian Reform Farmers of Sedibeng District Municipality in Gauteng Province South Africa. Master’s Thesis, University of South Africa, Pretoria, South Africa, 2016. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10500/23488 (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Shiba, W.T. An impact analysis of Comprehensive Agricultural Support Programme (CASP) on maize production smallholder farmers in Mpumalanga, South Africa. J. Agric. Rural Res. 2017, 1, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Sikwela, M.M. The Impact of Farmer Support Programmes on Market Access of Smallholder Farmers in the Eastern Cape and KwaZulu-Natal Provinces, South Africa. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Fort Hare, Alice, South Africa, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cousins, B. ‘Through a Glass, Darkly’: Towards Agrarian Reform in South Africa. In Land Divided, Land Restored: Land Reform in South Africa for the 21st Century; Cousins, B., Walker, C., Eds.; Jacana Media: Auckland Park, South Africa, 2015; pp. 250–269. Available online: https://www.kzndard.gov.za/images/Documents/RURAL_DEVELOPMENT/KZN_DARD_Colloquium/PLENERY_1/Prof.-Ben-Cousins-PLAAS---Through-a-glass-darkly_Towards-Agrarian-Reform-in-South-Africa.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (DAFF). National Policy on Comprehensive Producer Development Support. Draft Policy Put Out for Public Consultation; 2018. Available online: https://www.daff.gov.za/docs/media/Draft%205%20ver%203%20Policy%20on%20CPDS_30May2018_accepted%20chchan.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Maponya, P.; Mpandeli, S. Climate change and agricultural production in South Africa: Impacts and adaptation options. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, C.; Shackleton, S.E. Perceptions of climate change and barriers to adaptation amongst commonage and commercial livestock farmers in the semi-arid Eastern Cape Karoo. Afr. J. Range Forage Sci. 2014, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnkeni, P.; Mutengwa, C. A Comprehensive Scoping and Assessment Study of Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA) Policies in South Africa; FANRPAN: Pretoria, South Africa, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Financing Climate-Smart Agriculture. 2021. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/climate-smart-agriculture (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Aliber, M.; Hall, R. The Case for Re-Strategising Spending Priorities to Support Small-Scale Farmers in South Africa; Working Paper No. 17; Institute for Poverty, Land and Agrarian Studies (PLAAS), University of the Western Cape: Cape Town, South Africa, 2010; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10566/4475 (accessed on 19 March 2025).
- Cousins, B. Land Reform in South Africa Is Sinking. Can It Be Saved? Nelson Mandela Foundation: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2016; pp. 1–23. Available online: https://www.nelsonmandela.org/uploads/files/Land__law_and_leadership_-_paper_2.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- National Treasury. Budget Review 2020; National Treasury: Pretoria, South Africa, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (DAFF). Strategic Plan for the Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries 2015/16–2019/20. 2016. Available online: https://cer.org.za/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/DAFF-15-16-19-20.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Thierfelder, C.; Rusinamhodzi, L.; Ngwira, A.R.; Mupangwa, W.; Nyagumbo, I.; Kassie, G.T.; Cairns, J.E. Conservation agriculture in Southern Africa: Advances in knowledge. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2015, 30, 328–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, B.; Walker, C. (Eds.) Land Divided, Land Restored: Land Reform in South Africa for the 21st Century; Jacana: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liebenberg, F. Agricultural Advisory Services in South Africa; Working Paper 241722; Department of Agricultural Economics, Extension and Rural Development, University of Pretoria: Pretoria, South Africa, 2015; Available online: https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/record/241722/files/agric_advisory_services.zp64017.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2025).
- Aliber, M.; Cousins, B. Livelihoods after land reform in South Africa. J. Agrar. Change 2013, 13, 140–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R. Land Reform for What? Land Use, Production and Livelihoods. In Another Countryside? Policy Options for Land and Agrarian Reform in South Africa; Hall, R., Ed.; Institute for Poverty, Land and Agrarian Studies (PLAAS), University of the Western Cape: Cape Town, South Africa, 2009; pp. 23–61. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/68338041/Land_reform_for_what (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Christian, M. Analysis of the Impact of Smallholder Irrigation Schemes on the Choice of Rural Livelihood Strategy and Household Food Security in Eastern Cape. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Fort Hare, Alice, South Africa, 2017. Available online: https://ouci.dntb.gov.ua/en/works/4wJyqBB7/ (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- AGRA. Africa Agriculture Status Report 2018. Nairobi, Kenya. 2018. Available online: https://agra.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/AASR-2018.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Hitayezu, P.; Zegeye, E.W.; Ortmann, G.F. Some aspects of agricultural vulnerability to climate change in the KwaZulu-Natal Midlands, South Africa: A systematic review. J. Hum. Ecol. 2014, 48, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corfee-Morlot, J.; Marchal, V.; Kauffmann, C.; Kennedy, C.; Stewart, F.; Kaminker, C.; Ang, G. Towards a Green Investment Policy Framework: The Case of Low-Carbon, Climate-Resilient Infrastructure; OECD Environment Working Papers No. 48; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, G.; Schonberger, S.; Delaney, S. Sub-Saharan Africa: The State of Smallholders in Agriculture. In Proceedings of the IFAD Conference on New Directions for Smallholder Agriculture, Rome, Italy, 24–25 January 2011; International Fund for Agricultural Development: Rome, Italy, 2011. Available online: https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/livingston-38764320/38764320 (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finizola e Silva, M.; Van Schoubroeck, S.; Cools, J.; Van Passel, S. A systematic review identifying the drivers and barriers to the adoption of climate-smart agriculture by smallholder farmers in Africa. Front. Environ. Econ. 2024, 3, 1356335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerihun, M.F. Institutional analysis of adoption of agroforestry practices in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. S. Afr. J. Environ. Educ. 2020, 36, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwadzingeni, L.; Mugandani, R.; Mafongoya, P. Localized institutional actors and smallholder irrigation scheme performance in Limpopo province of South Africa. Agriculture 2020, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, N.; Christian, M. Transforming South African agriculture: The role of credit in supporting value chain sustainability. Agriculture 2025, 15, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).