Abstract
The world is currently experiencing a pandemic: a virus in the family Coronaviridae is causing serious respiratory infections in humans. The outbreak of novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) was declared a pandemic by the WHO on 11 March 2020. The outbreak began in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, and has since spread throughout the world. Despite measures taken by governments throughout the world to contain and control the spread, economic disruption at the global level is imminent and will affect all economic sectors, particularly the food sector. In a post-pandemic scenario, the use of new technologies will be decisive in a new model of food commercialization. The production and distribution of food will be configured to make supply chains optimal and safe systems. Against this background, the present study aims to explore and analyze the implications of the COVID-19 pandemic for global food security.
1. Introduction
This study aims to explore and analyze the implications of the COVID-19 pandemic in the context of food production and the profitability of multinational corporations.
The concept of food security and its counterpart food insecurity has evolved and generated a configuration of the global food system [1]. The dynamics of changes at a global level (e.g., population increase, connectivity, and industrialization) have permeated this concept by modifying the methods of producing, commercializing, and consuming [2]. In times of a pandemic, its re-valuation becomes necessary. An understanding of the interactions of the components of the global food system and its limitations will allow us to face the challenge of the health crisis caused by COVID-19 [3].
Amid the uncertainty posed by COVID-19, there is a certainty in which all analysts agree: the world will not be the same before and after the pandemic. Due to its disruptive impact and the context in which it is deployed, the virus will have serious repercussions on the global agri-food supply. The occurrence of worldwide pandemics has important antecedents [4,5,6]. Pandemic events have significance because economic development differs among countries, and such events have a greater effect on developing countries.
The study [4] posited that hotspots of emerging infectious diseases (EIDs) are more likely to appear in peripheral countries. In other words, for countries with little development (such as low infrastructure, little investment in research, poor health policies, and economic stagnation), the impact of EIDs can be significant [7].
However, this does not seem to be a constant, and the COVID-19 pandemic is affecting both developed and developing countries around the world with significant levels of loss of life and economic disruption.
EIDs are a growing threat to global health, the economy, and global food security [8]. The analysis of their trends suggests that their frequency and economic impact are increasing. The majority of EIDs (and almost all recent pandemics) originate from animals, mainly wildlife, and their emergence often involves dynamic interactions between wildlife populations and people in rapidly changing environments [6,9].
The need and expectation that control and prevention will involve coordinated actions across scientific, organizational, geographical, and political borders are greater today than at any other time [10]. It is now possible for a person to travel from one side of the globe to another in less time than it takes to develop symptoms of an infectious disease after exposure to a source of infection.
The experience of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV), the influenza pandemic of 2009, and the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV) demonstrate the need for coordinated international action to control outbreaks and emerging infections [5].
In this context, on 30 January 2020, the WHO declared the outbreak of COVID-19 in China a public health emergency of international importance [11]. The virus that causes COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, is the third coronavirus this century to produce severe pneumonia; the others are the severe acute respiratory syndrome virus (SARS-CoV: 8098 cases in 2003 and a lethality of 10%) and the Middle East respiratory syndrome virus (MERS-CoV: 2458 cases in 2012 and a lethality of 34%) [12].
The COVID-19 outbreak has already caused considerable human suffering and economic disruption [13]. In China, containment efforts have involved quarantines and generalized restrictions on labor mobility and travel, which have resulted in unplanned delays in restarting factories after the Lunar New Year holiday and in heavy cuts in many areas of the service sector [14].
2. Materials and Methods
To achieve the proposed objective, this study uses a qualitative approach. An extensive literature review was conducted on the following topics: COVID-19, pandemic, food security, global food system, and food implications in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Throughout March 2020, initiatives were followed to observe the behavior of the pandemic in an economic context, particularly in relation to the food system [14,15,16,17]. The methodological aspect of this study was based on [18]. The key words used in the review are connected by the effects of health measures implemented at the global level (confinement, border closure, voluntary isolation, and social distancing). These measures had a dominant effect on the first link of the food system, which is explained in detail in the following sections.
2.1. Literature Review
A systematic review of the literature was performed based on a keyword search of the ISI Web of Science (WoS) for journal articles with the following search terms: COVID-19*, pandemic*, global food system*, food security*, economics, and covid-19*. The search yielded 200 publications. For the systematic review, we used only journal articles and technical reports from international organizations and selected them according to the strategy outlined in Figure 1. We used the corresponding review and technical reports to locate findings related to this study.
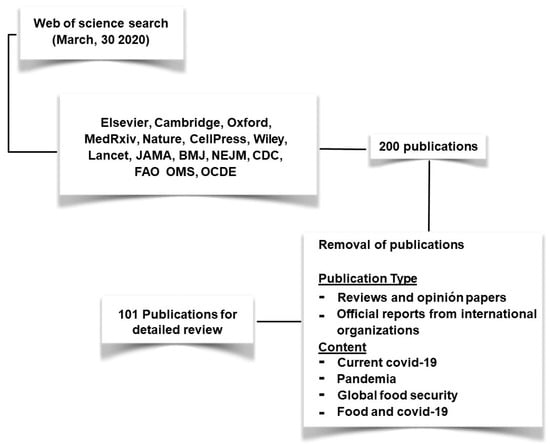
Figure 1.
Strategy used to identify the articles and reports relevant to the scope of this review.
Since the beginning of 2020, the COVID-19 theme has received the attention of the scientific community. Food systems have as well, although in a lesser proportion. The literature review was based on these two major themes; the search resulted in thousands of scientific contributions, for which it was necessary to refine the review, as explained above, establishing the connections between COVID-19 and the food systems, identifying economic implications at a global level of the pandemic. Under this logic, the search was reduced, and 200 publications were identified. Relevant information was obtained from more than 100 publications among scientific articles and reports from international organizations.
2.2. Categories and Criteria of the Systematic Review
Existing studies pertaining to COVID-19 were reviewed. Similarly, the origin and concept of the word “pandemic” were reviewed. A review of the global food system, its current status, and its importance was also conducted. Finally, the implications on the food system in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic were explored and analyzed. A review of the official reports of international organizations provided elements with which to evaluate the scope of the pandemic at a time when the disease has spread to more than 205 countries [14,15,16,17].
Although the analysis was descriptive, the findings of the review provided an approximation of the current state of the COVID-19 pandemic and how its spread is affecting the global food system and the main social actors in the food network (e.g., agricultural producers, sellers, and agricultural goods and services).
3. Theoretical-Conceptual
3.1. Pandemic
Etymologically, the word “pandemic” comes from the Greek expression pandêmonnosêma, translated as “disease of the whole town”. This word is not associated with the mortality of a disease but rather its propagation [19].
Historically, infectious diseases have constituted a serious threat to society; however, during much of the twentieth century, pandemics were considered extinct threats belonging to past centuries, since modern medicine had dealt with plague, smallpox, and other contagious catastrophes. However, current environmental changes have led to changes in the geographical distribution of microorganisms in general, causing numerous intermittent pandemics [20].
One of the most often remembered pandemics in the history of humanity is the plague, a disease caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, a microorganism carried by rats (Rattus rattus) that began to spread throughout the world when humans colonized the rodents’ territories, built cities, and then travelled to distant places. Humans did not make their trips alone; they were always accompanied by the black rat (R. rattus), an excellent swimmer that can climb aboard boats, allowing the plague to spread around the world [21,22].
According to [22,23], determining factors in the proliferation of diseases include economic development and land use, changes in agricultural practices, intensive agriculture, deforestation, and environmental exploitation and degradation, all of which have facilitated the translocation of pathogenic microorganisms.
With the currently available scientific means and the technological capacity, it was possible to identify and characterize COVID-19 in a few short few weeks, making its containment and control possible [24,25]. However, the future of the planet is uncertain: the planet’s resiliency is weakening due to the unlimited exploitation of natural resources as food systems transform [18,26].
Climate change, the expanding agricultural frontier, the intensification of agricultural activity, and the colonization of new rural territories are displacing animals and microorganisms that in many cases are unknown to science. The likelihood that new pathogens will emerge is growing [10].
3.2. COVID-19: A Pandemic
The outbreak of COVID-19 was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) on 11 March 2020. In December 2019, the WHO reported a cluster of pneumonia-like cases of a novel coronavirus zoonosis in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China, and these have spread throughout the world since then [15]. The outbreak was due to a new or novel coronavirus, which would later be called Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) [27,28,29,30]. Human coronaviruses are an extensive family of respiratory viruses that cause various conditions and diseases in humans, such as the common cold, SARS, and MERS [31]. SARS-CoV is one of 36 coronaviruses of the family Coronaviridae within the order Nidovirales. It is known that coronaviruses cause respiratory or intestinal infections in humans and other animals. SARS-CoV has a higher degree of stability in the environment than other known human coronaviruses. It can survive for at least 2 to 3 days on dry surfaces at room temperature and 2 to 4 days in faeces [9].
The epidemiology of COVID-19, the original source of the outbreak, and the involvement of animals as reservoirs of infection or intermediate hosts are being investigated [32,33,34,35,36]. The epidemiological link of the initial human cases in the 2003 pandemic with wild game animals suggested that SARS-CoV is of zoonotic origin [37]. The isolation of SARS-CoV-type viruses in civets (Paguma larvata) and, subsequently, bats (Rhinolophus spp.) further supported this assertion [38,39].
A seroprevalence rate of approximately 80% was found in civets in animal markets in Guangzhou [40]. However, person-to-person transmission has been the main mode of spread of the epidemic and has occurred in health centers, workplaces, homes, and public transit [9].
According to [9], the medical and scientific community has made great progress in the understanding of SARS-CoV in a short time, as demonstrated by the availability of more than 6000 publications online.
Despite these achievements, there are still gaps related to the understanding of the molecular basis of the virus’s physical stability and transmissibility, the molecular and immunological basis of the pathogenesis of the disease in humans, tests for the early detection of SARS cases, and an effective vaccine. Coronaviruses can undergo genetic recombination [41], which can lead to new genotypes and outbreaks. The presence of a large reserve of viruses similar to SARS-CoV in bats (Rhinolophus spp.) and civets (P. larvata), along with the custom of eating exotic mammals in Southern China, is a time bomb. The possibility of the resurgence of SARS and other new animal or laboratory viruses and, therefore, the need for preparation should not be ignored [42].
The previous approach coincides with the current situation of COVID-19, which has shown an aggressive capacity to spread. The situation currently facing Southeast Asian countries and Europe is worrisome; as of 20 September 2020, the WHO [15] had reported 30,675,675 confirmed cases and more than 954,417 deaths. Among the recommendations to contain and mitigate the virus is social distancing, in which people should stay at home to avoid contact with people who have the disease [43]. The data provided by the WHO [15] are worrying, if we consider that the recommended containment measures (for example, social distancing, border closure, and confinement) can cause a slowdown in the global agri-food system. These measures can contribute to the transformation of the food system by influencing the way food is produced, distributed, and consumed in developing countries [2].
These measures recommended by the WHO [15] affect small producers in all countries (developed and non-developed). According to [44], for small-scale farmers globally, production is differential, and they must meet a constant demand for food all year round. Agricultural production is partly for self-consumption and partly for the market, but the current conditions imposed by climate change are changing production patterns. In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, these changes will be more profound, affecting the food supply of national economies. Although the resilience of family farming is high, external support will be needed in the form of public policies to guarantee food supplies during the COVID-19 pandemic.
3.3. Global Food Security
By food security, we mean the availability, access, utilization, and stability of food at all times for all people. This food must be sufficient, safe, and nutritious to allow the person to have a healthy life [45,46].
In food systems, different elements can be identified that interact with each other. Within these systems, the processes are complex, generating products oriented towards adaptation and transformation. An important element is health [16,47]. It is pertinent to remember that a food system operates as a socio-ecological system. Its components, as they interact, are learning, generating processes of adaptation and transformation throughout the system. An important part of these interactions is the health component, which, in a crisis situation, affects the entire system.
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, the world showed a robust and efficient food supply chain. For example, the EU food and drink industry employs 4.72 million people and generates a turnover of EUR 1.2 trillion and EUR 236 billion in value added, making it the largest manufacturing industry in the EU. The EU is the largest exporter of food and drink products in the world, with extra-EU exports reaching EUR 110 billion and a trade surplus of EUR 36 billion [48].
Five months after the declaration of pandemic COVID-19 by the WHO [15], the measures taken around the world are unprecedented [49]. According to [50], one of the major issues that COVID-19 has revealed is the food insecurity faced by a large part of the population. Social measures such as school meals and family/grandparent support, to a great extent, have been stopped because of the lockdown. Induced unemployment contributed to food insecurity for low-income households.
This is a clear example of how the COVID-19 pandemic is contributing to food insecurity. Food insecurity is a global problem affecting the entire planet, in particular, countries with agricultural systems sensitive to climate change [51,52]. The lack of food, particularly quality food, not only contributes to malnutrition of the population, but on a wider scale is also the main slowing element of rural territories, leading to hunger, poverty, and unemployment [51].
The world population has steadily increased, and currently, the majority lives in urban areas. Technology has evolved at a rapid speed, while the economy has become increasingly interconnected and globalized. All this has led to significant changes in the way food is produced, distributed, and consumed worldwide [53].
The base of a local food system is small producers; if this component is affected, the entire system will be affected, affecting national and global levels. It is important that in times of crisis, small producers develop adaptation strategies that allow continuity to local food systems.
The COVID-19 pandemic affects the functional structure of small-scale agricultural producers due to the implementation of countries’ sanitary measures to control the pandemic (e.g., confinement, social distancing, and closure of local and national borders) that interrupt spatial mobility, social networks, and production and marketing processes. This phenomenon has cascading implications; food-exporting countries are affected by the interruption in the food supply of their national economies and these subsequently cannot comply with exports.
At the local level, food chains have been affected by the slowdown in the food supply, resulting in the recovery of knowledge of local processes. Many communities are custodians of ancestral food systems that have been progressively replaced due to the globalization of trade. With the advance of the COVID-19 pandemic, these communities have felt the need for this local knowledge in order to produce their own food. This phenomenon has been observed in Africa [52], Asia [53], and Latin America [51]. It is important to highlight that communities, despite health restrictions, have used social networks at the local level, knowledge transfer, the exchange of genetic material, and reciprocal work. These aspects promoted by social networks have allowed for a small amount of production for self-consumption. However, the reality of small farmers in developed countries is not the same. Globalization has been a destabilizing element in their communities, and the pandemic has caused the loss of their jobs. The food supply has been interrupted by the lack of economic income, and responses have consisted of the storage of food products and their rationed use. Social networks are also present, with a focus on collaborative networks.
One study [54] exemplified the importance of small agricultural producers in the dynamics of the local food system. The analysis contained information from 5159 households located across 15 countries in Africa, Asia, and Central America.
The family agricultural unit is strategic in food production in many countries of the world. According to [55], there are at least 570 million small-scale farms (two hectares of land) that are managed by individuals or families with a worldwide production that exceeds 80%, in terms of value. The agricultural production of these family units is the basis of local and strategic food systems in the reconfiguration of the global food system.
According to [54], smallholder farmers are already undertaking adaptive farm-level changes. It is important to understand how these types of adaptive behavior affect their welfare. Policymakers and development practitioners can use this information to target interventions to given contexts, and to assess whether policies aimed at incentivizing farmers to undertake adaptive activities are able to mitigate the anticipated losses arising from changing climatic and economic conditions.
Approximately 2 billion people worldwide suffer from moderate or severe food insecurity. The lack of regular access to nutritious and sufficient food increases the risk of malnutrition and poor health. Although it is concentrated in low- and middle-income countries, moderate or severe food insecurity also affects 8% of the population in North America and Europe. On each of these continents, the prevalence rate is slightly higher among women than among men [53]. Figure 2 shows the prevalence of severe food insecurity in the global population (%).
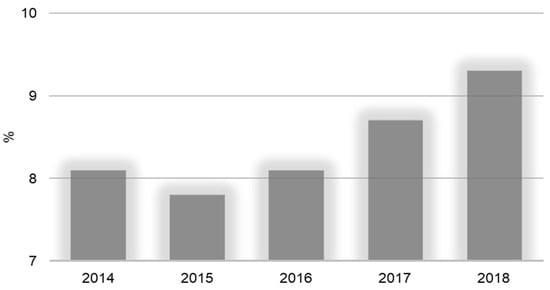
Figure 2.
Prevalence of severe food insecurity in the global population (%) (annual value). Source: [56].
The member states of the United Nations recognized the importance of addressing food issues beyond hunger when they established universal and ambitious goals in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The goal of zero hunger is not only to end hunger but also to ensure access to quality food for all people [57]. Hunger has been increasing in many countries whose economy has entered a phase of slowdown or contraction. Between 2011 and 2017, this increase coincided with an episode of slowing or weakening of the economy in 65 of 77 countries. These economic shocks influence food crises. In 2018, economic shocks were notable in 33 of the 53 countries that suffered food crises and affected more than 96 million people [53].
According to official data, the majority of the countries in which an increase in undernourishment occurred as the economy was entering a deceleration phase were found in Africa (32). Several were in Asia (17), followed by Latin America and the Caribbean (11), Oceania (3), and Eastern Europe (2). Most of them (44 out of 65) were middle-income countries; 19 (of the 65) were low-income, and 17 were in Africa (the other two were Tajikistan and Yemen) [53,58].
Faced with the discouraging panorama described above, several authors have proposed different strategies to mitigate food insecurity throughout the world. These strategies range from increases in production, food access, and respect for biodiversity to the consideration of local alternatives [51,57,59,60,61,62,63]. In this logic, [64] gave a broader perspective that encompasses availability, access, utilization, and stability.
3.3.1. Availability
Buying and selling are strategic elements in the diversity, quality, and availability of food. The logic of capital has a positive effect on competition by triggering a dynamism not only in supply, but also in productivity and R&D. By availability, we mean the supply of food products. This differs from stability because the supply is not interrupted.
- The impact on food availability
Given the effects of a pandemic, the following scenarios may occur: the dynamics of food-producing countries are assured of domestic consumption in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, but these dynamics may be affected by the needs of global trade causing disruptions in national economies. On the other hand, countries with a dependent food structure may experience a scenario of food insecurity, and, in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, this scenario may become even more acute.
The health measures associated with the COVID-19 pandemic have a direct effect on the availability of food in a national economy. In this context, reduced spatial mobility and border restrictions affect food availability. For national economies with a dependent food structure, these constraints arising from the COVID-19 pandemic may result in a disruption of the food chain, an example being the African Sahel region [65].
3.3.2. Access
The accessibility factor in a country is associated with price dynamics; constraints on food supply affect food prices, and households are restricted in their ability to access food in quantity and quality.
- The impact on food access
Given the effects of a pandemic, the following scenarios may occur: food-producing countries may face a scenario of uncertainty; health measures resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic are causing a reduction in food supply and affecting prices.
The instability in the food supply has major implications for a national economy. In food-producing countries, the instability of the food supply affects other sectors of society such as employment. In this sector, small agricultural producers may see their income affected due to spatial mobility restrictions. Households with low economic incomes may not be able to feed themselves with food of an adequate quality, and their health could be affected due to an inability to acquire enough food [65].
3.3.3. Utilization
The diversity that a food system offers to a national economy results in a robust food system because society can use varieties of food and generate healthy diets that subsequently strengthen the immune system, an important aspect in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The impact on food utilization
Given the effects of a pandemic, the following scenarios may occur: a greater reliance on imported foods has been associated with the increased consumption of cheaper and more readily available high-calorie/low-nutritional-value foods. Prioritization of commodity exports can divert land and resources from traditional indigenous foods that are often superior from a nutrition point of view [65].
People in food crises often have higher rates of underlying health conditions, including non-communicable diseases and malnutrition (acute, chronic and micronutrient deficiencies), which weaken the immune system and increase the risk of people developing severe COVID-19 symptoms [65].
3.3.4. Stability
Imports reduce the seasonal effect on food availability and consumer prices. Imports mitigate local production risks. Global markets are less prone to policy- or weather-related shocks.
- The impact on food stability
Given the effects of a pandemic, the following scenarios may occur: for net food-importing countries, relying primarily on global markets for food supplies and open trade policies reduces the policy space to deal with shocks. Net food-importing countries may be vulnerable to changes in trade policy by exporters, such as export bans. Sectors at earlier stages of development may become more susceptible to price shocks and/or import surges.
Growing fear in global markets could result in a severe decline in international financing and portfolio outflows from food-insecure countries. As these countries often have limited fiscal and external buffers, this trend could pose a significant risk to their governments’ ability to fight the pandemic and maintain existing support to vulnerable households [65].
3.4. Global Food Security in the Context of the COVID-19 Pandemic
In this section, I would like to start with a question: is the increased appearance of viruses closely related to food production and the profitability of multinational corporations? This approach is currently the subject of intense debate [66].
The novel coronavirus (COVID-19) emerged in the city of Wuhan, China. This country is the main agri-food power on the planet. These facts affect the long-term plan established by the Chinese government and its opening-up strategy. According to official data, since 1978, China has carried out a reform policy and a step-by-step opening-up process that has accelerated the pace of agricultural reform and development. In particular, in recent years, the Chinese government has prioritized agricultural work, rural areas, and farmers by adopting a series of public policies [67,68].
Currently, China is the leading producer of grains, cotton, fruits, vegetables, meat, poultry, eggs, and fish products worldwide and has successfully solved the problem of feeding its own population, which represents 21 percent of the world’s total population [68]. Along these lines, China continues to deepen supply-side structural reform in agriculture to develop the sector [69]. The goal is to increase the production of high-quality products based on green and innovative production practices, projecting the incorporation of new industries and new types of businesses [70,71].
This partly underpins Wallace’s description [66] of how capital logic directs China’s efforts towards change because it has implications for the expansion of China’s agricultural border and its industrial openness policy towards multinational food corporations. In the context of the emergence of COVID-19, this strategy remains interesting because the expansion of the agricultural frontier implies new functions for soil that was not previously used for cultivation, particularly under conditions of intensive agriculture, according to the logic of capital.
An advancing agricultural frontier involves the agricultural colonization of new territories and the possible loss of biodiversity as a result [72,73]. The sale of wild animals in Chinese markets provides a clear picture of the impact of these policies as implemented by the Chinese government, which likely triggered the COVID-19 crisis in Wuhan [74].
Although China represents only a portion of global food production, the effects of COVID-19 have led to a series of containment measures, with collateral effects in the world. An example is the changes in the dynamics of the consumption of goods in the United Kingdom that is affecting the supply and prices [75].
These measures, such as social distancing, can negatively impact the work of small farmers due to restrictions of spatial mobility that aim to reduce exposure to sources of infection. However, this lack of mobility can reduce agri-food inventories globally and generate shortages in several crops.
Furthermore, this strategy of social distancing may negatively impact the population [76], since in the context of a pandemic, the availability, accessibility, utilization, and stability of food could be interrupted [75,77,78].
The populations of countries that experience economic slowdown are more affected by collateral effects of measures to control the pandemic [79]. Countries in which poverty and hunger coexist are highly susceptible to food insecurity, which will lead to a decline in health and will lower the population’s resilience in a pandemic such as COVID-19 because people’s immune systems will be weakened by poor quality diets and insufficient food.
According to [17], the economic consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic are political issues of leadership and coordination. The loss of consumer and investor confidence are the most immediate effects of the pandemic, but the deflation of asset prices, weak aggregate demand, the increase in debt, and the worsening income inequality pose greater policy challenges.
An effective response to the economic consequences of COVID-19 will require not only active and specific macroeconomic measures but also a series of corrective policies and institutional reforms to build robust, sustained, equitable, and climate-friendly growth [17,80]. According to data from the OECD [14] this year, the world’s economy will grow at a rate lower than 2.5%. The estimates made by [17] are slightly more daunting. Figure 3 shows the growth of world GDP.
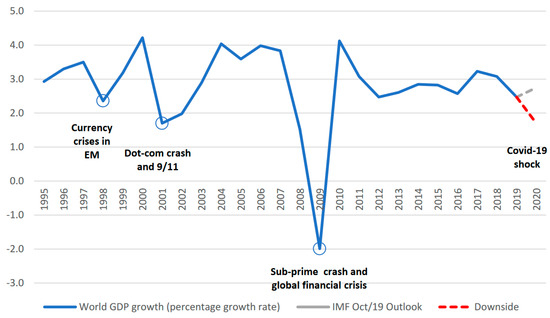
Figure 3.
World GDP growth 1995–2020. Source: [17].
A fall of one percentage point in global economic growth costs approximately 900 billion dollars in lost revenue. Most forecasts have eliminated a trillion dollars of global income for this year, and if growth falls to 1.7%, the cost of COVID-19 could reach 2 trillion dollars [17].
According to [81], a global economic slowdown of one percentage point could increase food insecurity by 2%, or by about 14 million people worldwide, mainly affecting rural territories in developing countries.
The simulated poverty impact is sensitive to assumptions made about the duration of the pandemic and transmission mechanisms. In these estimates, we assume the slowdown is caused by a temporary paralysis of domestic economic activity in many countries. Impacts could be higher if the slowdown involved the disruption of trade channels [14].
Figure 4 shows how the forecasts in cereal production have had a downward trend since 2018. In a scenario of contraction of world trade flow due to the spread of COVID-19, the downward trend would increase considerably.
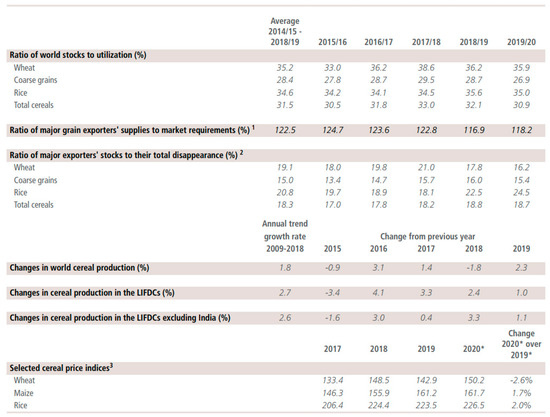
Figure 4.
Global cereal supply and demand indicators. Source: [82]. Note: Utilization is defined as the sum of food use, feed, and other uses. Cereals refer to wheat, coarse grains, and rice; grains refer to wheat and coarse grains (barley, maize, millet, sorghum, and cereals NES). 1 Major wheat exporters include Argentina, Australia, Canada, the European Union, Kazakhstan, the Russian Federation, Ukraine, and the United States of America; major coarse grains exporters include Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, the European Union, the Russian Federation, Ukraine, and the United States of America; major rice exporters include India, Pakistan, Thailand, the United States of America, and Vietnam. 2 Disappearance is defined as domestic utilization plus exports for any given season. 3 Price indices: The Wheat Price Index has been constructed based on the International Grains Council Wheat Price Index, rebased to 2002-2004 = 100; for maize, the U.S. maize No.2 Yellow (delivered U.S. Gulf ports) with base 2002-2004 = 100; for rice, the FAO Rice Price Index, 2002-2004 = 100, is based on 16 rice export quotations. * January–February average.
Based on previous projections, if the spread of COVID-19 continues, the economic consequences for the global food system this year could reach 0.3 trillion dollars, encompassing losses due to the deceleration of the global agri-food trade flow (e.g., maritime, air, ground transport, agricultural goods and services, and income reduction for small agricultural producers) [17].
The slowdown in the global flow of agri-food trade in a post-pandemic scenario poses a threat before and after the world health crisis [83]. The reconfiguration of global marketing models will be inevitable, and the restriction of spatial mobility will modify international food trade, defining new technologies and new rules for food supply.
4. Results and Discussion
The analysis of the literature review and the information provided by international organizations supports a slowdown in the global food system. UNCTAD and FAO pointed out that these changes will deepen as the COVID-19 pandemic advances [17,82]. Months before the COVID-19 pandemic, the global food system showed signs of a contraction in global cereal production (wheat, rice, and coarse grains), as shown in Figure 4. This progressive drop in production because of the COVID-19 pandemic was subsequently endorsed by the FAO [56]. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the global food system was further deepened by the global economic effects that affected various sectors (maritime, air, land, tourism, and trade) [17,82]. The global agri-food system is affected by the mobility of each national economy, which, in order to preserve national food sovereignty, has implemented public policies to guarantee food supply in its territories; countries that depend on imports already have restrictions on their food inventories, with risks to their food security [56,84].
The global slowdown scenario proposed by [81] indicates that the world in the coming months may face a situation of global food insecurity affecting all countries equally. A post-pandemic COVID-19 scenario will require coordinated action at the global level. FAO has taken the first step by suggesting the implementation of regional policies for most of the countries that have vulnerable food systems, considering the technical needs and climate change that shape food production [85].
As a viable option to face a scenario of food shortage in most importing countries, these countries must develop policies that allow for a use of their natural resources with sustainability criteria. The literature review indicates that most of these countries are biodiverse and possess a cultural richness that can allow for the tracing of ancestral knowledge in the food context.
Megadiverse countries [86] and culturally diverse countries [87] will have the opportunity to design and implement public policies that lead to the coordination of a regional food system that ensures food sovereignty [51]. Local institutions with experiences of resilience (among poor and indigenous populations) will have a greater capacity to construct strategies for securing the food supply [51,57]. These countries contain 70% of the world’s biodiversity in only 10% of the Earth’s surface. These countries are Bolivia, Brazil, China, Colombia, Costa Rica, Democratic Republic of Congo, Ecuador, India, Indonesia, Kenya, Madagascar, Malaysia, Mexico, Peru, Philippines, South Africa, and Venezuela [86].
On the other hand, exporting countries and their governments face the dilemma of either attending to human life or helping the economic sectors [88]. A relevant element in the analysis is that the global agri-food system must guarantee the supply of food to the world’s population. The countries that depend on food imports during the COVID-19 pandemic are vulnerable because of the decline in agri-food trade flows [82,89]. With the recommendation of social distancing and other health measures [43], developing countries are seeing their food inventories decline and their economies suffer from unemployment and reductions in household income.
In the context of social distancing, family farms throughout the world must face the challenge of sustaining social networks (e.g., the purchase of goods and services and the sale of agricultural products) that will allow them to develop their agricultural practice without problems if they want to continue producing [44,90]. The internal resource mobilization of each country will be tested; even if production continues, the mobilization of different agricultural items and the supply of resources and food products will slow [91]. According to FAO, more than 40 countries, most of which are in Africa, are experiencing an internal crisis of resource mobilization at critical levels, and food insecurity is increasing due to the impact of climate change on food systems [82].
Not only African countries are suffering the immediate effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Fifteen countries in the Eastern European region have implemented restrictive policies on the export of food products. The direct implication of this measure is that, if a trading partner suddenly restricts food exports to a given country, the short-term impact on domestic food availability results in shortages [92,93].
In Latin America, the COVID-19 pandemic has affected international trade, causing a drop of more than −15 percent, this trade shock in Latin America has had negative implications for food prices. The food prices in the months of February and March of 2020 increased 0.76% [94,95].
In the Southeast Asian and Pacific region, poverty will increase by 11 million people; the effect in rural areas in terms of food availability, access, utilization, and stability will be greater [96]. The cases of several Asian countries (Vietnam, Malaysia, and Singapore) show how the policy of export restrictions is generating a food inventory crisis in these countries [97].
Rural territories are an important part of the food system. The changes (restrictions on spatial mobility, low economic incomes, and low food production) that small agricultural producers are suffering are affecting food supply chains. These social actors are the basis of the food system. If they are affected, the food system will cascade. Both exporting and importing countries must implement policies to assist smallholder farmers to maintain the base of the food system in each of the functioning national economies. FAO has argued that, in a continuing scenario of the COVID-19 pandemic, these actors are important for the strategic food system, even if we also consider a post-pandemic scenario [94,95].
In summary, net exporting countries are facing the challenge of the COVID-19 pandemic by identifying a strategic decline in the supply of food exports due to rising world food prices, which in turn has negative effects on the trade policies of the national economies of partners (net importing countries). The direct price effect of export restrictions can be particularly costly for many poor countries that depend on imported food. The changing dynamics that the COVID-19 pandemic is imposing globally could affect eating habits and consumer behavior. Exporting countries will see their exports reduced and importing countries will see their inventories affected, but in turn local food systems that have been forgotten will be promoted, generating new trade opportunities.
4.1. Post-Pandemic Scenario COVID-19 in the Global Agri-Food System
The COVID-19 pandemic is occurring in a highly developed capitalist context. It is known that the capitalist system presents at least three general tendencies: expansion of the social division of labor, the depth of social differentiation and inequity, and the development of productive forces [98]. The deepening and expansion of these three trends, 250 years after the birth of modern capitalism, can be easily visualized in global production chains. If we pay attention to the pandemic, those trends are expressed in multiple ways directly connected to the disease. They are manifested in the unlimited and globalized expansion of production and the market, which manages to erase the natural barriers that epidemics once contained [83].
The global food supply chain is linked to the transport network at a global level. If this network slows down, the food supply will be affected [99]. This is precisely what is happening with the COVID-19 pandemic. According to [100], the aviation industry is in a state of shock. This constitutes an obstacle to the food supply chain and its growth in the short term.
Global food supply chains five months after the detection of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, began to suffer the effects of strategies to contain the COVID-19 pandemic. Space mobility restrictions are reconfiguring production processes globally. The use of information technology is intensifying, projecting the phenomenon of telework as one of the most suitable options for the global food system to remain active and functioning.
However, this new form of food marketing may be sustainable if food production is relevant within the global agri-food system. Otherwise, in the short term, it will affect small- and medium-sized farms. We are witnessing this crisis affect small agricultural producers. The developed countries have a protective structure for family agriculture, but it does not work the same way for the undeveloped countries, whose public policies scarcely support agricultural practice at the family level. FAO has identified this problem, but it is up to governments, in times of the COVID-19 pandemic, to establish a support structure for small-scale agricultural producers. It is necessary to include within the support structure the creation and strengthening of information technologies. An example is the situation of small agricultural producers in Africa, Asia, and Latin America, which have social networks but only at the local level, the contact with other regions being limited, which guarantees the dynamism of agricultural practices (for example, agricultural goods and services, the purchase and sale of food products, and technical assistance services).
According to [83], it is estimated that, on the capitalist periphery, there are 85 million workers directly employed in more than 3500 export processing zones located in 130 countries. The movement of capital, goods, and labor forces brings countless unintended results, including the repercussions of the health crisis.
4.2. Agricultural Globalization and Pandemic
First steps have been taken to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic [82], which translates into active communication in each of the offices where the agency has representation, achieving flexible contractual agreements to take advantage of logistics channels for delivery, so as to help and minimize exposure of staff and beneficiaries. The advance procurement of inputs (such as seeds and tools) and pre-positioning is being worked on. Input packages are being developed to meet long-term needs, and storage and logistics capabilities are increasing.
However, a few months after the pandemic, the relationship between health and economy covered news and public policy: should the population be isolated to avoid contagion at the cost of ruining the economy? Or should the economy be retained and the weakest members of the population sacrificed? [83].
As neither of these two alternatives is viable in its most radical form in a globalized world, the production, transport, and essential distribution of goods continue to work in combination with different modes of confinement [83].
The health system at a global level has entered a crisis, particularly in those industrialized countries such as Italy, Spain, the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, and the Netherlands, and this represents an economic obstacle for the agricultural marketing system to continue operating in optimal conditions. The immediate consequences will be a poor food supply. This last point coincides with the positions of [17,82].
The impact of disruption due to the pandemic will generate global uncertainty once the health crisis is mitigated. Unemployment and hunger will remain. A new theory of food marketing should be established on the basis of information technology, and teleworking and logistics structures need to adapt to the new conditions of the world market.
Without even observing a slowdown in the health crisis, the case of India is evident. This country is experiencing an interruption in its food supply chain. This interruption is characterized by a shortage of labor and a decrease in demand [101].
The food supply chain includes all the steps needed to produce and move foods from field to fork. These steps consist of agricultural production, storage and distribution, processing and packaging, and retail and marketing, among others. Farmers, processors, wholesalers, transporters, and retailers are some of the people involved in food supply chains [102].
The steps in the food supply chain are all connected. Changes to one step affect other steps along the chain. In this sense, the variation in food prices in recent months has marked a negative effect of the COVID-19 pandemic. The FAO food price index shows a decline that began in April and has been on a downward trend since then [82].
An international indicator of the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic can also be seen in China’s export balance, which has been reduced by more than 40 percent, generating a slowdown in the annual growth rate. This can be seen not only in China but also in countries that sell to China [103].
The precariousness of the global aeronautical system is also a problem. We believe that the status of the global food system may be negative [99,100]. The design of pandemic containment strategies is important and must consider the food supply of vulnerable people. However, there is a global lack of public policies aimed at family agriculture in non-developed countries that would allow for the continuity of family agriculture in times of the COVID-19 pandemic.
To avoid the negative effects of the pandemic, most exporting countries are beginning to design containment policies, such as the application of new non-tariff measures (e.g., sanitary or phytosanitary measures), new economic incentives for farmers and workers in the agri-food system, the mandatory implementation of biosafety measures for workers in the agri-food systems, the provision of information technologies to farmers and workers in the agri-food systems to improve production and marketing processes, and the facilitation of the movement of agricultural food products and of access by small-scale producers to the market. Figure 5 shows the dynamics of the world population and the impact that the COVID-19 pandemic has had through the global sanitary measures that have been implemented for its containment and control—measures that are influencing global food security.
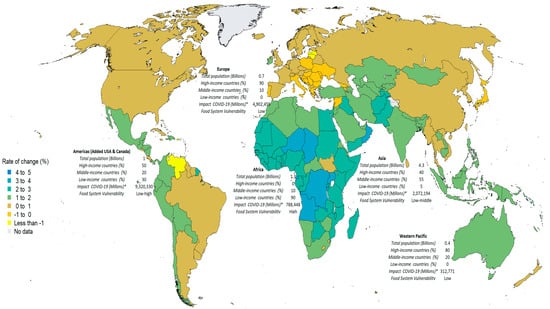
Figure 5.
Average annual rate of population change (%), 2015–2020, and vulnerability of food security in agreement with the advance of the pandemic COVID-19 by WHO regions (June 2020). Source: Own elaboration with data from [15,53,56,104]. * confirmed cases.
5. Conclusions
Food security in a country depends on four elements: availability, access, utilization, and stability. National economies play an important role in sustaining these elements. However, many times, economic variables do not work in favor of a given country’s national economy due to the country’s level of development.
The changes projected by international organizations in the level of GDP are relevant and point to considering an economic slowdown for developing countries with implications for their agri-food systems. However, the aggressive spread of COVID-19 is severely affecting developed countries, where an agri-food slowdown scenario is possible.
Central, technologically superior countries with robust economies can assure a continuous supply of food to their population. Meanwhile, technologically inferior and peripheral countries with weak economies cannot assure their population a continuous supply of food. By this logic, the global agricultural food chain plays an important role in providing food to both peripheral and central countries with marked differences in their economies, but these conditions can be reversed. In a post-pandemic scenario, the use of new technologies will be decisive in a new model of food commercialization. The ways of producing food and distributing it will be configured to make supply chains optimal and safe systems.
However, in a pandemic context, this scenario can change; the majority of megadiverse and culturally diverse countries are peripheral countries with the capacity to build regional food systems. The results of the presented analysis are preliminary and will depend on the duration of the COVID-19 pandemic and its mortality rate.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
References
- Maxwell, S. Food security: A post-modern perspective. Food Policy 1996, 21, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, S.; Slater, R. Food Policy Old and New. Dev. Policy Rev. 2003, 21, 531–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinstrup-Andersen, P. Food security: Definition and measurement. Food Secur. 2009, 1, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Patel, N.; Levy, M.; Storeygard, A.; Balk, D.; Gittleman, J.L.; Daszak, P. Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2008, 451, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, J.; Lockhart, C.; Pongolini, S.; Karesh, W.B.; Baylis, M.; Goldberg, T.; Slingenbergh, J.; Gale, P.; Venturini, T.; Catchpole, M.; et al. Drivers for emerging issues in animal and plant health. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 0512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.; Murray, K.A.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.; Morse, S.S.; Rondinini, C.; Moreno, D.M.; Breit, N.; Olival, K.J.; Shí, Z. Global hotspots and correlates of emerging zoonotic diseases. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morens, D.M.; Folkers, G.K.; Fauci, A.S. The challenge of emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2004, 430, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauci, A.S. Infectious Diseases: Consideraciones for the 21st Century. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, V.C.C.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Yuen, K.-Y. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus as an Agent of Emerging and Reemerging Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 660–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daszak, P. Emerging Infectious Diseases of Wildlife—Threats to Biodiversity and Human Health. Science 2000, 287, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, C.; Alsafi, Z.; O’Neill, N.; Khan, M.; Kerwan, A.; Al-Jabir, A.; Iosifidis, C.; Agha, R. World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Int. J. Surg. 2020, 76, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Otero, D.; Díaz-Pérez, D.; De-La-Rosa-Carrillo, D.; Bello-Dronda, S. ¿Preparados para el nuevo coronavirus? Arch. Bronconeumol. 2020, 56, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, I.; Maity, P. COVID-19 outbreak: Migration, effects on society, global environment and prevention. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Coronavirus: The World Economy at Risk. OECD Interim Economic Outlook, March Paris: Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico (OECD). Available online: https://www.oecd.org/economic-outlook/ (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- WHO. Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Situation. Available online: https://experience.arcgis.com/experience/685d0ace521648f8a5beeeee1b9125cd (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- FAO. Developing Sustainable Food Value Chain. Guiding Principles; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- UNCTAD. Coronavirus (COVID-19): News, Analysis, and Resources. Trade and Development Report (9 March 2020). Available online: https://unctad.org/en/PublicationsLibrary/gds_tdr2019_update_coronavirus.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2020).
- Meyer, M.A. The role of resilience in food system studies in low- and middle-income countries. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 24, 100356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Rutherford, S.; Mao, A.; Chu, C. The Pandemic and its Impacts. Health Cult. Soc. 2017, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, G.; Sánchez, D.; Sosa, C.A. Pandemia: Influenza Humana A H1N1: Lo Que Hay Que Saber Sobre Ella; Editorial Alfil: Mexico City, Mexico, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Márquez, M. Zoonosis, epizootias, epidemias y antropozoonosis. Prod. Anim. 2014, 113, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Uribe-Corrales, N. Algunas pandemias en la humanidad. Una mirada a sus determinantes. Rev. CES Salud Pública 2015, 6, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Omran, A.R. The Epidemiologic Transition: A Theory of the Epidemiology of Population Change. Milbank Q. 2005, 83, 731–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Z.; He, Y.; Qi, Y.; Chen, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, F.; Lai, K.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; et al. A new and rapid approach for detecting COVID-19 based on S1 protein fragments. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kache, T.; Mrowka, R. How Simulations May Help Us to Understand the Dynamics of COVID-19 Spread—Visualizing Non-Intuitive Behaviours of a Pandemic (pansim.uni-jena.de). Acta Physiol. 2020, 229, e13520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seekell, D.A.; Carr, J.; Dell’Angelo, J.; D’Odorico, P.; Fader, M.; Gephart, J.A.; Kummu, M.; Magliocca, N.; Porkka, M.; Puma, M.J.; et al. Resilience in the global food system. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruickshank, M.; Shaban, R.Z. COVID-19: Lessons to be learnt from a once-in-a-century global pandemic. J. Clin. Nurs. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shí, Z. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralph, R.; Jocelyne, L.J.; Zeng, T.; Francis, M.; Xue, B.; Roux, M.; Ostadgavahi, A.T.; Rubino, S.; Dawe, N.J.; Al-Ahdal, M.N.; et al. 2019-nCoV (Wuhan virus), a novel Coronavirus: Human-to-human transmission, travel-related cases, and vaccine readiness. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2020, 14, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, M.N.; Geraghty, E.M. Geographical tracking and mapping of coronavirus disease COVID-19/severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) epidemic and associated events around the world: How 21st century GIS technologies are supporting the global fight against outbreaks and epidemics. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2020, 19, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, D.S.C. Epidemic and Emerging Coronaviruses (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome). Clin. Chest Med. 2017, 38, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M. Why we should care about bats. Curr. Boil. 2019, 29, R1163–R1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan-Tian, C.; Yu-Ting, L.; Li-Ying, G.; Xiang-Guo, L.; Lu-Shan, W.; Jian-Wei, J.; Jia-Bao, L.; Jing, M.; Zhai-Yi, Z.; Li, W.; et al. Traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of coronavirus disease 2019: A review. Tradit. Med. Res. 2020, 5, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Robson, B. Computers and viral diseases. Preliminary bioinformatics studies on the design of a synthetic vaccine and a preventative peptidomimetic antagonist against the SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV, COVID-19) coronavirus. Comput. Boil. Med. 2020, 119, 103670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Lin, Q.; Jin, S.; You, L. Coronavirus 2019-nCoV: A brief perspective from the front line. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. Unveiling the Origin and Transmission of 2019-nCoV. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, N.S.; Zheng, B.J.; Li, Y.M.; Poon, Z.H.; Xie, K.H.; Chan, L.P.H.; Tan, S.Y.; Chang, Q.; Xie, J.P.; Liu, X.Q.; et al. Epidemiology and cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong, People’s Republic of China, in February, 2003. Lancet 2003, 362, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Zheng, B.J.; He, Y.Q.; Liu, X.L.; Zhuang, Z.X.; Cheung, C.L.; Luo, S.W.; Li, P.H.; Zhang, L.J.; Butt, K.M.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Viruses Related to the SARS Coronavirus from Animals in Southern China. Science 2003, 302, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Li, K.S.M.; Huang, Y.; Tsoi, H.-W.; Wong, B.H.L.; Wong, S.S.Y.; Leung, S.Y.; Chan, K.-H.; Yuen, K.-Y. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in Chinese horseshoe bats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14040–14045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Crameri, G.; Kong, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Yu, M.; Xiang, H.; Xia, X.; Liu, S.; Ren, T.; et al. Antibodies to SARS Coronavirus in Civets. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 2244–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Huang, Y.; Tsoi, H.-W.; Chan, K.-H.; Yuen, K.-Y. Comparative Analysis of 22 Coronavirus HKU1 Genomes Reveals a Novel Genotype and Evidence of Natural Recombination in Coronavirus HKU1. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7136–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. New Virus, New Challenge. Innovation 2020, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, R.A. COVID-19 and rationally layered social distancing. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2020, 74, e13501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, K.; Giroux, S.; Blekking, J.P.; Baylis, K.; Evans, T.P. Smallholder food storage dynamics and resilience. Food Secur. 2019, 12, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Food Summit. Rome Declaration on World Food Security and the World Food Summit Plan of Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ericksen, P. Conceptualizing food systems for global environmental change research. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2008, 18, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, J.S.I. A food systems approach to researching food security and its interactions with global environmental change. Food Secur. 2011, 3, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Data & Trends EU Food & Drink Industry. Available online: https://www.fooddrinkeurope.eu/publication/data-trends-of-the-european-food-and-drink-industry-2019/ (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- Pantano, E.; Pizzi, G.; Scarpi, D.; Dennis, C. Competing during a pandemic? Retailers’ ups and downs during the COVID-19 outbreak. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 116, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakalis, S.; Valdramidis, V.P.; Argyropoulos, D.; Ahrné, L.; Chen, J.; Cullen, P.; Cummins, E.; Datta, A.K.; Emmanouilidis, C.; Foster, T.; et al. How COVID-19 changed our food systems and food security paradigms. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2020, 3, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugo-Morin, D.R. Indigenous communities and their food systems: A contribution to the current debate. J. Ethn. Foods 2020, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, K.; Zerriffi, H.; Le Billon, P. Land scarcity, resettlement and food security: Assessing the effect of voluntary resettlement on diet quality in Malawi. Food Secur. 2020, 12, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; FIDA; OMS; PMA; UNICEF. El Estado de la Seguridad Alimentaria y la Nutrición en el Mundo Protegerse Frente a la Desaceleración y el Debilitamiento de la Economía. Informe Técnico; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, K.; Wichmann, B.; Luckert, M.K.; Laderach, P. Impacts of smallholder agricultural adaptation on food security: Evidence from Africa, Asia, and Central America. Food Secur. 2019, 12, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture 2014. Innovation in Family Farming; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- FAOSTAT. Datos Sobre Alimentación y Agricultura. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/es/#data/FS/visualize (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Torres, G. Seguridad y soberanía alimentaria. Ética y alternativas locales. In Inseguridad Alimentaria y Políticas de Alivio a la Pobreza: Una Visión Multidisciplinaria; Rubio, B., Pasquier, A., Eds.; UNAM: Mexico City, Mexico, 2019; pp. 69–93. [Google Scholar]
- Burkitbayeva, S.; Swinnen, J.; Warrinnier, N. Food, and nutrition security in Eurasia: Evolution, shocks, and policies. Russ. J. Econ. 2020, 6, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, K.; Place, F. Global food systems: Can foresight learn from hindsight? Glob. Food Secur. 2019, 20, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, T.S.; Snapp, S.; Place, F.; Sitko, N.J. Sustainable agricultural intensification in an era of rural transformation in Africa. Glob. Food Secur. 2019, 20, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W.; Rockström, J.; Loken, B.; Springmann, M.; Lang, T.; Vermeulen, S.; Garnett, T.; Tilman, D.; Declerck, F.; Wood, A.; et al. Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT–Lancet Commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems. Lancet 2019, 393, 447–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bilali, H. Transition heuristic frameworks in research on agro-food sustainability transitions. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2018, 22, 1693–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.M.; Drimie, S.; Maciejewski, K.; Tonissen, P.B.; Biggs, R.O. Food System Transformation: Integrating a Political–Economy and Social–Ecological Approach to Regime Shifts. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO; IFAD; WFP. The State of Food Insecurity in the World Meeting the 2015 International Hunger Targets: Taking Stock of Uneven Progress; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Global Report on Food Crises. Global Network Against Food Crises and Food Security Information Network. Available online: https://www.wfp.org/publications/2020-global-report-food-crises (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Wallace, R. Big Farms Make Big Flu: Dispatches on Infectious Disease, Agribusiness, and the Nature of Science; Monthly Review Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, H.; Remais, J.V.; Fung, M.-C.; Xu, L.; Sun, S.S. Food supply and food safety issues in China. Lancet 2013, 381, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- About MOA-Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. 2020. Available online: http://english.agri.gov.cn/aboutmoa/message (accessed on 18 March 2020).
- Zhan, S.; Zhang, H.; He, D. China’s flexible overseas food strategy: Food trade and agricultural investment between Southeast Asia and China in 1990–2015. Globalizations 2018, 15, 702–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man-Hung, T.C. The Belt and Road Initiative—The New Silk Road: A Research Agenda. J. Contemp. East Asia Stud. 2018, 7, 104–123. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. China Focus: China to Deepen Reform in Agricultural Sector. 2020. Available online: http://english.agri.gov.cn/news/dqnf/201702/t20170206_247179.htm (accessed on 18 March 2020).
- Cohen, D.J. The Beginnings of Agriculture in China: A multiregional view. Curr. Anthr. 2011, 52, S273–S293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massé, F.; Margulies, J.D. The geopolitical ecology of conservation: The emergence of illegal wildlife trade as national security interest and the re-shaping of US foreign conservation assistance. World Dev. 2020, 132, 104958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, A.T.; Cheung, S.; Yip, P.K. Wildlife markets in South China. Hum. Wildl. Interact. 2014, 8, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Blundell, R.; Griffith, R.; Levell, P.; O’Connell, M. Could COVID-19 Infect the Consumer Price Index? Fisc. Stud. 2020, 41, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, J. Experts examine MH consequences of social distancing. Ment. Health Wkly. 2020, 30, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nicola, M.; Alsafi, Z.; Sohrabi, C.; Kerwan, A.; Al-Jabir, A.; Iosifidis, C.; Agha, M.; Agha, R. The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19): A review. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 78, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napier, A.D. Rethinking vulnerability through Covid-19. Anthr. Today 2020, 36, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramíreuz, E.E.R.; Grin, E.J.; Sanabria-Pulido, P.; Cravacuore, D.; Orellana, A. The Transaction Costs of the Governments’ Response to the COVID-19 Emergency in Latin America. Public Adm. Rev. 2020, 80, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Kinnunen, P.; Lehikoinen, E.; Porkka, M.; Queiroz, C.; Röös, E.; Troell, M.; Weil, C. Interplay of trade and food system resilience: Gains on supply diversity over time at the cost of trade independency. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 24, 100360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debucquet, D.L.; Martin, W. Implications of the global growth slowdown for rural poverty. Agric. Econ. 2018, 49, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Crop Prospects and Food Situation—Quarterly Global Report No. 1, March 2020; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foladori, G.; De Zacatecas, U.A.; Wise, R.D. Para comprender el impacto disruptivo de la COVID-19, un análisis desde la crítica de la economía política. Migr. Desarro. 2020, 18, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnick, D. Political economy of food system reform. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukase, E.; Martin, W. Economic growth, convergence, and world food demand and supply. World Dev. 2020, 132, 104954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittermeier, R.; Gil, P.; Goettsch-Mittermeier, C. Megadiversity: Earth’s Biologically Wealthiest Nations; Cemex, Prado Norte: Mexico City, Mexico, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lugo-Morin, D.R. Resiliencia institucional y desarrollo comunitario: Hacia la promoción de los territorios culturalmente superiores. In Sociedad Global, Crisis Ambiental y Sistemas Socio-Ecológicos; Fausto Quintana Solórzano Coord; Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2019; pp. 158–173. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosio, G.; Juselius, M. Dealing with the Costs of the COVID-19 Pandemic What Are the Fiscal Options? 2020. BoF Economics Review, No. 2/2020, Bankof Finland, Helsinki. Available online: http://nbn-resolving.de/urn:nbn:fi:bof-202004092069 (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Ataguba, J.E. COVID-19 Pandemic, a War to be Won: Understanding its Economic Implications for Africa. Appl. Health Econ. Health Policy 2020, 18, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedberg, R.C.; Zimmerer, K.S. What’s the market got to do with it? Social-ecological embeddedness and environmental practices in a local food system initiative. Geoforum 2020, 110, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Zhang, L.; Marley, G.; Tang, W. Differentiating COVID-19 Response Strategies. Innovation 2020, 1, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, R.; Martin, W.; Laborde, D. As COVID-19 spreads, no Major Concern for Global Food Security Yet. Available online: https://www.ifpri.org/blog/covid-19-spreads-no-major-concern-global-food-security-yet (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- FAO. Vulnerabilidad a Las Disrupciones Del Comercio de Alimentos Por COVID-19; FAO: Santiago, Chile, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. COVID-19 and Rural Poverty: Supporting and Protecting the Rural Poor in Times of Pandemic; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. COVID-19: Inflación en Los Precios Reales de Los Alimentos; FAO: Santiago, Chile, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. World Bank East Asia and Pacific Economic Update, April 2020: East Asia and Pacific in the Time of COVID-19; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- IPES-FOOD. COVID-19 and the Crisis in Food Systems: Symptoms, Causes, and Potential Solutions. Available online: http://www.ipes-food.org/_img/upload/files/COVID-19_CommuniqueEN%283%29.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Rubin, I.I. Essays on Marx’s Theory of Value; Black and Red: Detroit, MI, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Mahutga, M.C.; Ma, X.; Smith, D.A.; Timberlake, M. Economic Globalisation and the Structure of the World City System: The Case of Airline Passenger Data. Urban Stud. 2010, 47, 1925–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieralski, J.B. COVID-19 and airline employment: Insights from historical uncertainty shocks to the industry. Transp. Res. Interdiscip. Perspect. 2020, 5, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhishek, V.B.; Puneet, G.; Manu, K.; Avinash, K.; Ritesh, K.; Abhishek, S.; Shilp, V. India’s Food System in the Time of COVID-19. Econ. Polit. Wkly. 2020, 55, 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, K.; Hawkes, C.; Wells, R. What is the food system? A Food policy perspective. In Rethinking Food Policy: A Fresh Approach to Policy and Practice; Centre for Food Policy: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fugazza, M. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Commodities Exports to China. In UNCTAD Research Paper; UNCTAD: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- World Population Prospects. Population Dynamics. Special Aggregates: Economic and Trading Groups; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).