Visual Signal Recognition with ResNet50V2 for Autonomous ROV Navigation in Underwater Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Underwater Visual Signaling
2.2. Deep Neural Networks for Visual Recognition
2.3. Visual Dataset Construction and Augmentation
2.4. Embedded System Architecture
2.5. Depth Control System
2.6. Evaluation Metrics
3. Experimental Setup
3.1. Dataset Construction: Underwater Visual Signals Recognition Dataset (UVSRD)
3.2. AquaSignalNet Model Implementation
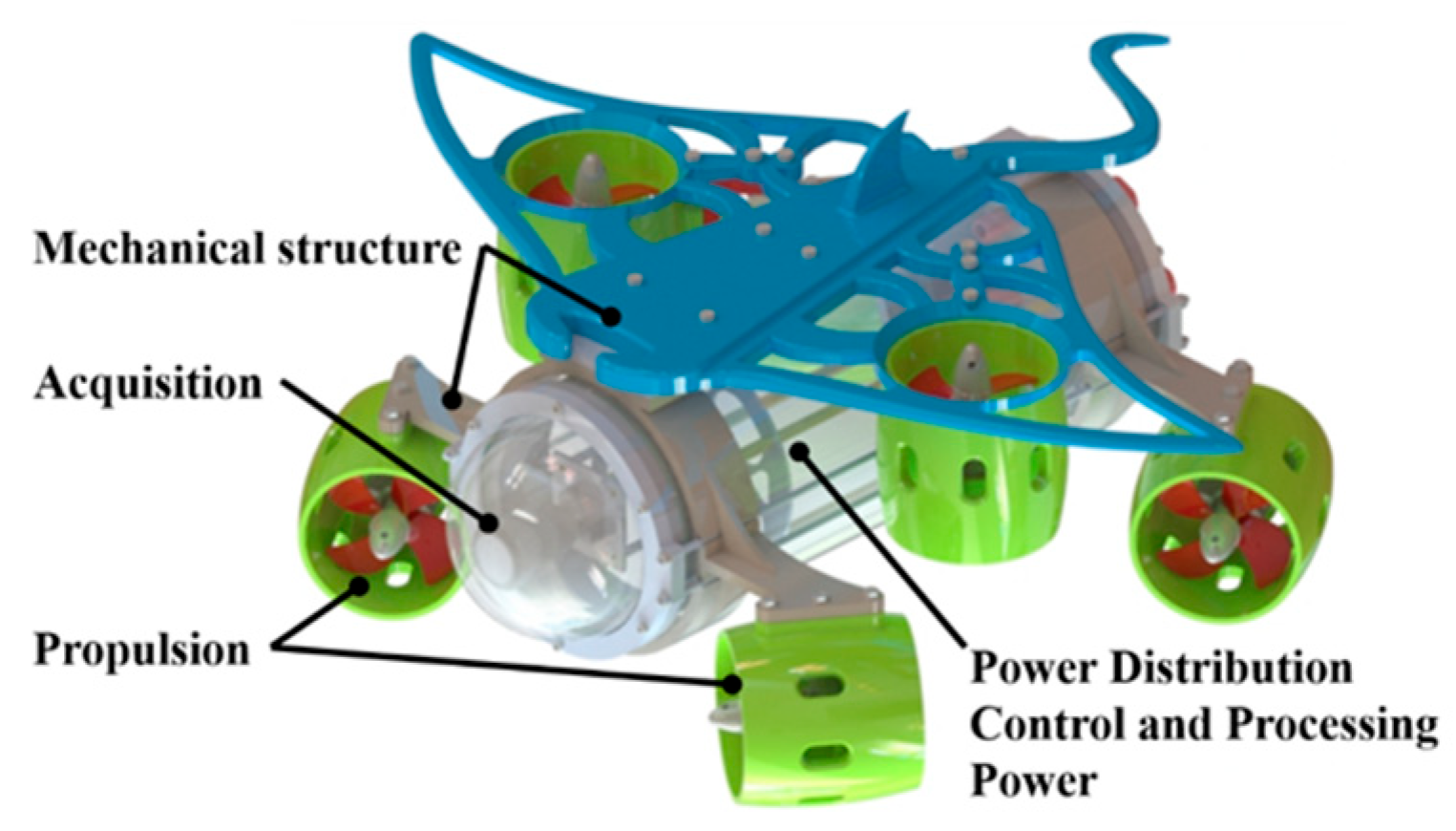
3.3. Embedded System Integration and Mechanical Design
3.4. Testing Environment and Validation Procedure
4. Results and Discussion
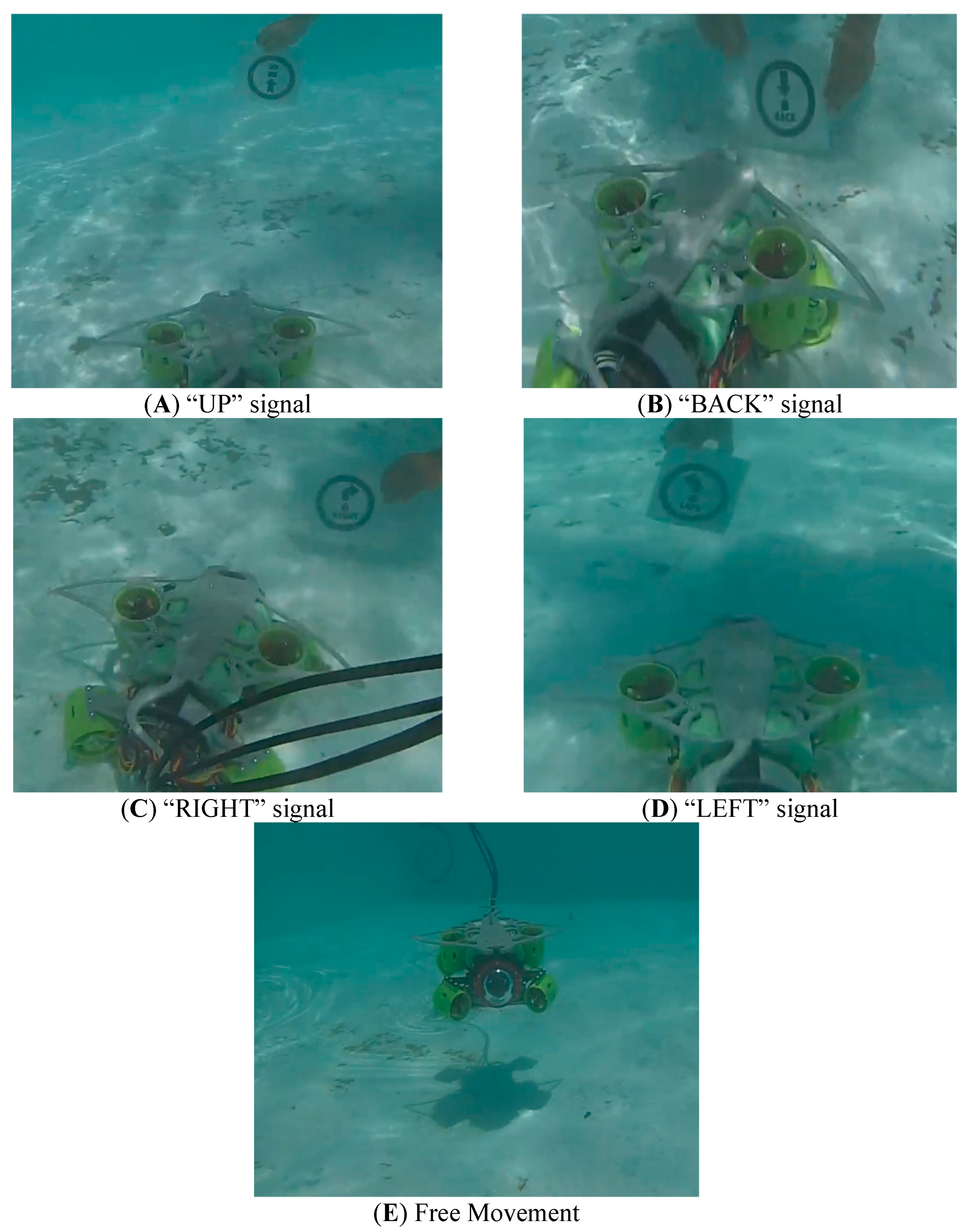
4.1. Trajectory 1
- LEFT → UP → RIGHT → 80 → 40 → RIGHT → 20 → UP → STOP
- The behavior associated with this trajectory is described below:
- LEFT—The ROV executed a 90° yaw rotation to the left using angle estimation from the MPU9250 sensor.
- UP—The ROV ascended vertically using the upper thrusters until the next signal was detected.
- RIGHT—Another 90° rotation was executed.
- 80/40/20—These numerical signals modulated the PWM duty cycle to adjust forward speed. Higher values produced stronger thrust.
- RIGHT—A third 90° yaw rotation aligned the ROV with the final segment of the trajectory.
- UP—The vehicle ascended again to reach the final navigation level.
- STOP—The ROV ceased all propulsion and maintained position.
4.2. Trajectory 2
- Perform precise horizontal orientation adjustments using yaw-based 90° turns.
- Regulate its propulsion speed using visual PWM percentage signals.
- Execute vertical ascents and descents in response to UP and DOWN commands.
- Respond to a long chain of commands while maintaining proper signal detection and control coordination.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, R.; Li, S.; Ji, G.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Pan, M. Survey on Deep Learning-Based Marine Object Detection. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thum, G.W.; Tang, S.H.; Ahmad, S.A.; Alrifaey, M. Toward a Highly Accurate Classification of Underwater Cable Images via Deep Convolutional Neural Network. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sabbagh, S.P.; Robles-Kelly, A. A Survey on Underwater Computer Vision. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, K.; Han, Z. Vision Technology in Underwater: Applications, Challenges and Perspectives. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Control and Robotics (ICCR), Guangzhou, China, 2–4 December 2022; pp. 369–378. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Tian, F.; Feng, Z.; Li, Y. MSF-ACA: Low-Light Image Enhancement Network Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Adaptive Contrast Adjustment. Sensors 2025, 25, 4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Pei, S.-C. Domain Adaptation for Underwater Image Enhancement via Content and Style Separation. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 90523–90534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, L.; Xu, M.; Yu, M.; Wang, K.; Lin, Y. Domain Adaptation for Underwater Image Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 1442–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Jiang, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, J. Towards domain adaptation underwater image enhancement and restoration. Multimed. Syst. 2024, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrunnisa; Leszczuk, M.; Juszka, D.; Zhang, Y. Improved Binary Classification of Underwater Images Using a Modified ResNet-18 Model. Electronics 2025, 14, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.; Yang, M.; Jeong, J. Hybrid-DC: A Hybrid Framework Using ResNet-50 and Vision Transformer for Steel Surface Defect Classification in the Rolling Process. Electronics 2024, 13, 4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Er, M.J. Review on deep learning techniques for marine object recognition: Architectures and algorithms. Control. Eng. Pr. 2022, 118, 104458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Srivastava, S.; Jayanth, J.P. A Survey of Deep Learning Techniques for Underwater Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 34, 6968–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birk, A. A Survey of Underwater Human-Robot Interaction (U-HRI). Curr. Robot. Rep. 2022, 3, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ríos, A.; Tabik, S.; Luengo, J.; Shihavuddin, A.; Herrera, F. Coral species identification with texture or structure images using a two-level classifier based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2019, 184, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, A.; Dubinsky, Z.; Iluz, D.; Netanyahu, N.S. Neural Network Recognition of Marine Benthos and Corals. Diversity 2020, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Bennamoun, M.; An, S.; Sohel, F.A.; Boussaid, F.; Hovey, R.; Kendrick, G.A.; Fisher, R.B. Deep Image Representations for Coral Image Classification. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2018, 44, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumini, A.; Nanni, L.; Maguolo, G. Deep learning for plankton and coral classification. Appl. Comput. Inform. 2020, 19, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khai, T.H.; Abdullah, S.N.H.S.; Hasan, M.K.; Tarmizi, A. Underwater Fish Detection and Counting Using Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network. Water 2022, 14, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, D. Underwater sea cucumber identification via deep residual networks. Inf. Process. Agric. 2019, 6, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, M.; Goel, N. FishResNet: Automatic Fish Classification Approach in Underwater Scenario. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Li, T.; Zhou, L.; Jin, S.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, W. DAMNet: Dual Attention Mechanism Deep Neural Network for Underwater Biological Image Classification. IEEE Access 2022, 11, 6000–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.; Mladenović, S.; Gotovac, S.; Zaharija, G. Deep-Feature-Based Approach to Marine Debris Classification. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymak, P.; Piskur, P.; Naus, K. The Effectiveness of Using a Pretrained Deep Learning Neural Networks for Object Classification in Underwater Video. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Barajas, S.; Sanz, P.J.; Marín-Prades, R.; Gómez-Espinosa, A.; González-García, J.; Echagüe, J. Inspection Operations and Hole Detection in Fish Net Cages through a Hybrid Underwater Intervention System Using Deep Learning Techniques. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvasić, I.; Antillon, D.O.; Nađ, Đ.; Walker, C.; Anderson, I.; Mišković, N. Diver-robot communication dataset for underwater hand gesture recognition. Comput. Netw. 2024, 245, 110392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nađ, Đ.; Walker, C.; Kvasić, I.; Antillon, D.O.; Mišković, N.; Anderson, I.; Lončar, I. Towards Advancing Diver-Robot Interaction Capabilities. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martija, M.A.M.; Dumbrique, J.I.S.; Naval, P.C., Jr. Underwater Gesture Recognition Using Classical Computer Vision and Deep Learning Techniques. J. Image Graph. 2020, 8, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalvedhekar, S.; Nahar, S.; Maskare, S.; Mahajan, K.; Bagade, A. Inter-pretable Underwater Diver Gesture Recognition. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, K.; Yuan, F. Underwater Accompanying Robot Based on SSDLite Gesture Recognition. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saquín, H. Underwater Visual Signals Recognition Dataset UVSRD. Available online: https://ieee-dataport.org/documents/underwater-visual-signals-recognition-dataset-uvsrd (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Plotnikov, V.A.; Akhtyamov, T.R.; Serebenny, V.V. Diver Gestures Recognition in Underwater Human-Robot Interaction Using Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 6th International Youth Conference on Radio Electronics, Electrical and Power Engineering (REEPE), Moscow, Russia, 29 February–2 March 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chiarella, D.; Bibuli, M.; Bruzzone, G.; Caccia, M.; Ranieri, A.; Zereik, E.; Marconi, L.; Cutugno, P. A Novel Gesture-Based Language for Underwater Human–Robot Interaction. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Ma, L.; Cui, Z.; Yu, Y. Computer vision-based hand gesture recognition for human-robot interaction: A review. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 10, 1581–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Sattar, J. Visual Diver Recognition for Underwater Human-Robot Collaboration. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 6839–6845. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Wei, F. An Underwater Human–Robot Interaction Using a Visual–Textual Model for Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. Sensors 2022, 23, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Identity Mappings in Deep Residual Networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision-ECCV 2016-14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 630–645. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A.; Liu, W.; et al. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; pp. 4278–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boom, B.J.; Huang, P.X.; He, J.; Fisher, R.B. Supporting ground-truth annotation of image datasets using clustering. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Tsukuba, Japan, 11–15 November 2012; pp. 1542–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Anantharajah, K.; Ge, Z.; McCool, C.; Denman, S.; Fookes, C.; Corke, P.; Sridharan, S. Local inter-session variability modelling for object classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Steamboat Springs, CO, USA, 24–26 March 2014; pp. 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, T.P.; Albu, A.B. L2UWE: A Framework for the Efficient Enhancement of Low-Light Underwater Images Using Local Contrast and Multi-Scale Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 2286–2295. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Fan, X.; Zhu, M.; Hou, M.; Luo, Z. Real-World Underwater Enhancement: Challenges, Benchmarks, and Solutions Under Natural Light. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 4861–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, C.; Ren, W.; Cong, R.; Hou, J.; Kwong, S.; Tao, D. An Underwater Image Enhancement Benchmark Dataset and Beyond. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 4376–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Luo, P.; Sattar, J. Simultaneous Enhancement and Super-Resolution of Underwater Imagery for Improved Visual Perception. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems 2020, Corvalis, OR, USA, 12–16 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, J.; Xia, Y.; Sattar, J. Fast Underwater Image Enhancement for Improved Visual Perception. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Saquín, C.H.; Barriga-Rodríguez, L.; Baldenegro-Pérez, L.A.; Ronquillo-Lomeli, G.; Rodríguez-Olivares, N.A. Novel Neural Networks for Camera Calibration in Underwater Environments. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 181767–181786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, F.; Qi, Z.; Duan, K.; Xi, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xiong, H.; He, Q. A Comprehensive Survey on Transfer Learning. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 43–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Agency for Marine Earth Science and Technology, Deep-Sea Debris Database. Available online: http://www.godac.jamstec.go.jp/catalog/dsdebris/metadataList?lang=en (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Jung, J.; Choi, H.-T.; Lee, Y. Persistent Localization of Autonomous Underwater Vehicles Using Visual Perception of Artificial Landmarks. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Background Type | Water With Blue Dye | Clean Water | Water With Green Dye |
|---|---|---|---|
| White |  |  |  |
| Pool tile mosaic |  |  |  |
| Simulated seabed |  |  |  |
| Classes |  | ||
| Class | Precision (%) |
|---|---|
| STOP | 90 |
| FRONT | 89 |
| BACK | 88 |
| LEFT | 88 |
| RIGHT | 90 |
| UP | 90 |
| DOWN | 87 |
| 20 | 89 |
| 40 | 91 |
| 60 | 90 |
| 80 | 89 |
| 100 | 90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Saquín, C.H.; Gómez-Hernández, A.; Salgado-Jiménez, T.; Fernández, J.M.B.; Barriga-Rodríguez, L.; Gómez-Espinosa, A. Visual Signal Recognition with ResNet50V2 for Autonomous ROV Navigation in Underwater Environments. Automation 2025, 6, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation6040051
Sánchez-Saquín CH, Gómez-Hernández A, Salgado-Jiménez T, Fernández JMB, Barriga-Rodríguez L, Gómez-Espinosa A. Visual Signal Recognition with ResNet50V2 for Autonomous ROV Navigation in Underwater Environments. Automation. 2025; 6(4):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation6040051
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Saquín, Cristian H., Alejandro Gómez-Hernández, Tomás Salgado-Jiménez, Juan M. Barrera Fernández, Leonardo Barriga-Rodríguez, and Alfonso Gómez-Espinosa. 2025. "Visual Signal Recognition with ResNet50V2 for Autonomous ROV Navigation in Underwater Environments" Automation 6, no. 4: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation6040051
APA StyleSánchez-Saquín, C. H., Gómez-Hernández, A., Salgado-Jiménez, T., Fernández, J. M. B., Barriga-Rodríguez, L., & Gómez-Espinosa, A. (2025). Visual Signal Recognition with ResNet50V2 for Autonomous ROV Navigation in Underwater Environments. Automation, 6(4), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation6040051







