Modern Control Techniques and Operational Challenges in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PMSM Types and Applications with Recent Technologies in Constructions
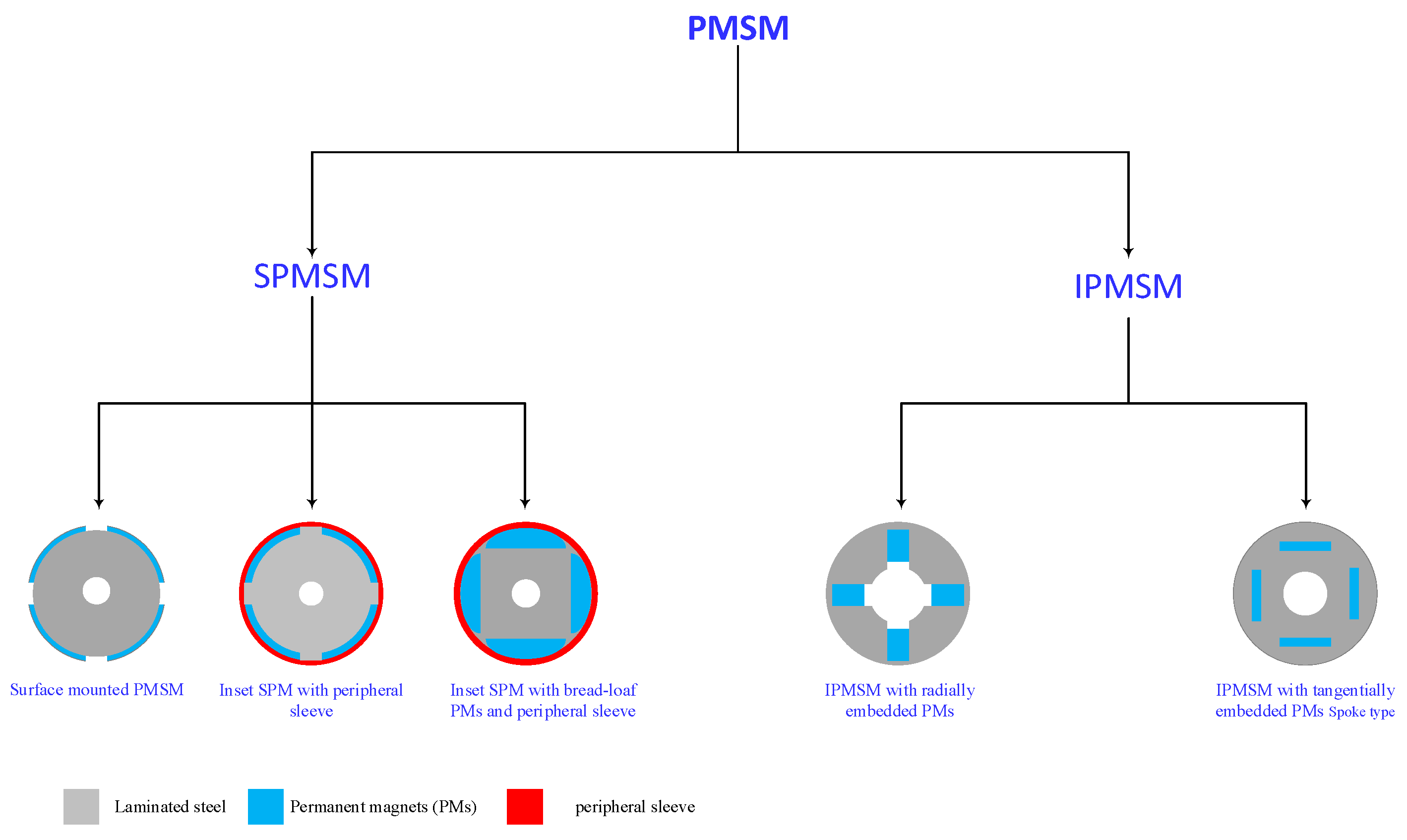
2.1. PMSM Types and Applications
2.2. PMSM Recent Technology Construction Design
3. PMSM Operation and Control
3.1. Mathematical Model of PMSMs
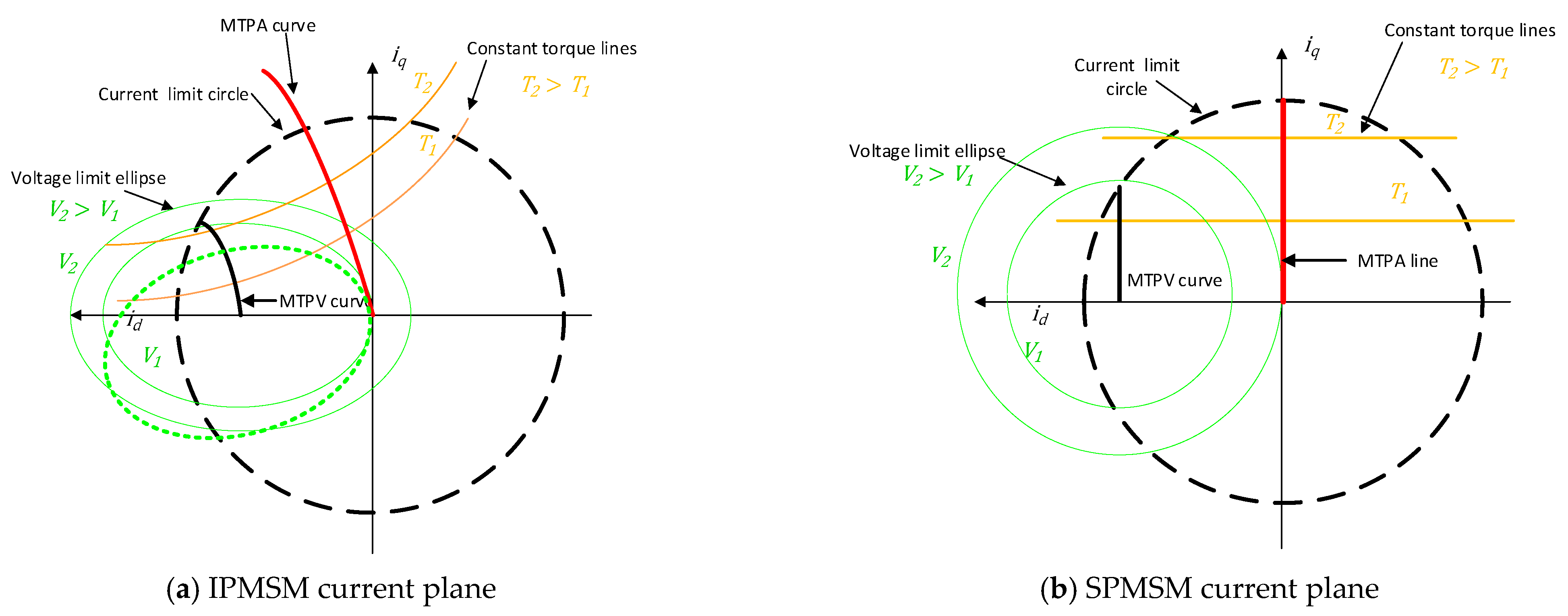
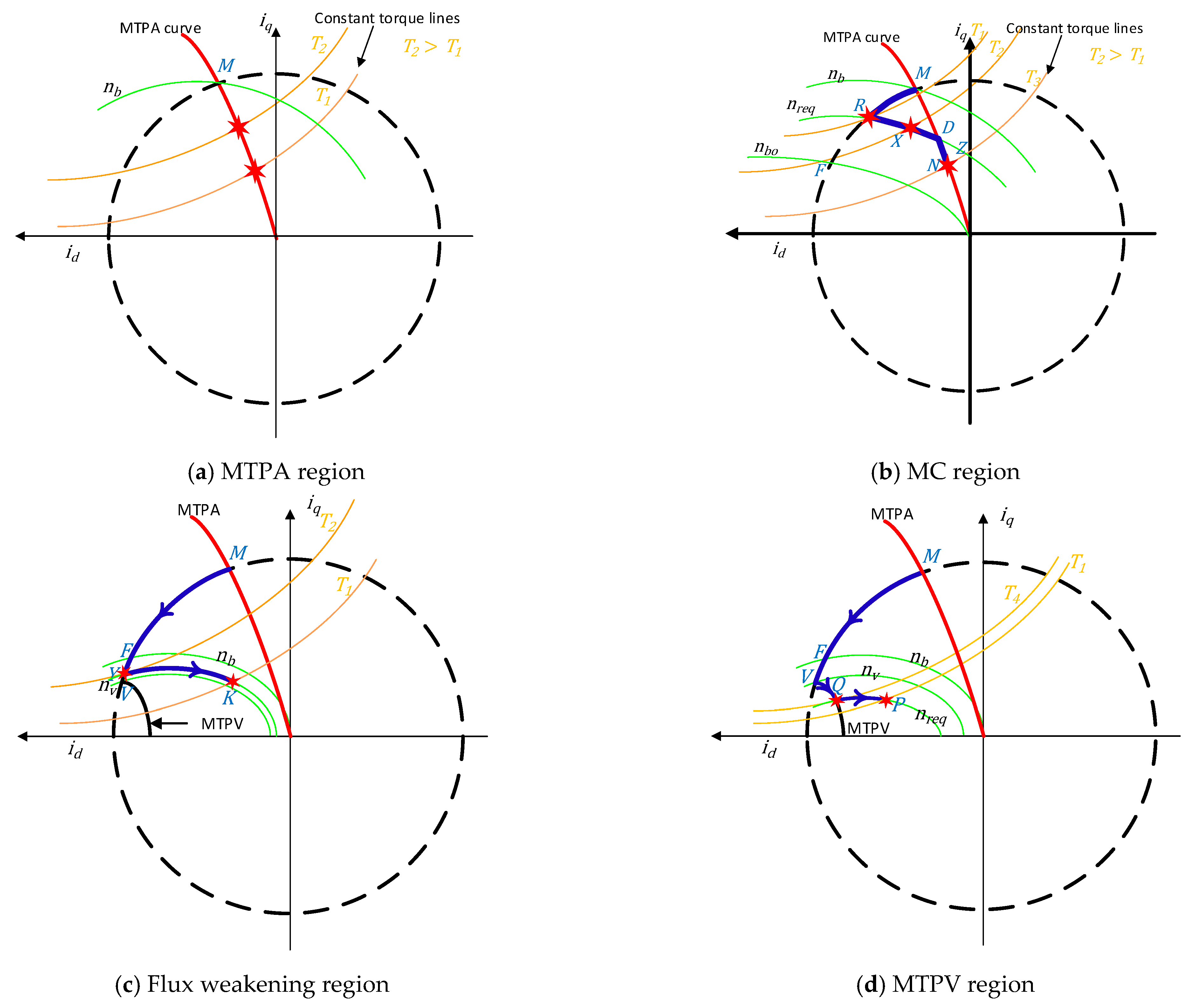
3.2. PMSM Operation Regions
3.3. General Control Methods for PMSMs in Solving PMSM Issues
3.3.1. Vector Control
3.3.2. Scalar Control
3.3.3. Flux-Weakening Control Methods
- (a)
- Feed forward method
- (b)
- Feedback technique
- (c)
- Hybrid technique
3.3.4. Control and Converter Considerations
3.3.5. Single-Loop Control Structure for PMSM Speed and Current Regulation
4. Maximum Torque per Ampere Control Methods
4.1. Machine-Parameter-Dependent MTPA Techniques
4.1.1. Premeasurements Assisted Methods
4.1.2. Approaches Based on Parameter Estimates and Approximated Functions
4.1.3. Parameter-Adaption-Based Methods
4.2. Machine-Parameter-Independent MTPA Techniques
4.2.1. Extremum Searching Based
4.2.2. Power-Measurement-Based Methods
4.2.3. Artificial-Intelligence-Assisted Methods
5. Sensorless Control Methods
5.1. Open Loop Methods
5.2. Closed Loop Methods
5.3. Saliency and Signal Injection (Non-Ideal Property)-Based Method
6. Parameter Identification Control Methods
6.1. Offline Parameter Estimation Techniques
6.2. Online Parameter Estimation Techniques
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poorfakhraei, A.; Narimani, M.; Emadi, A. A review of modulation and control techniques for multilevel inverters in traction applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 24187–24204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Park, H.; Kim, C.; Lee, H. A Review of State-of-the-art Techniques for PMSM Parameter Identification. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2020, 15, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaq, M.S.; Jung, J.-W. A comprehensive review of state-of-the-art parameter estimation techniques for permanent magnet synchronous motors in wide speed range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 4747–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Shi, P. A Review of Position Sensorless Compound Control for PMSM Drives. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Tiwari, A. Various techniques of sensorless speed control of PMSM: A review. In Proceedings of the 2017 Second International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Technologies (ICECCT), Coimbatore, India, 22–24 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, H.; Honda, Y.; Kiriyama, H.; Morimoto, S.; Takeda, Y. The performance comparison of SPMSM, IPMSM and SynRM in use as air-conditioning compressor. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 1999 IEEE Industry Applications Conference. Thirty-Forth IAS Annual Meeting (Cat. No. 99CH36370), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 3–7 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar, V.K.A.; Umashankar, S.; Paramasivam, S.; Hanigovszki, N. A comprehensive review on energy efficiency enhancement initiatives in centrifugal pumping system. Appl. Energy 2016, 181, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, A.M.; Yeoh, S.S.; Bozhko, S.; Guo, F.; Gerada, C.; Galea, M. Discrete flux weakening controller design for future aircraft electric starter/generator system operating in high-speed range. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Workshop on Electrical Machines Design, Control and Diagnosis (WEMDCD), Modena, Italy, 8–9 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Belhadj, J.; Roboam, X. Investigation of different methods to control a small variable-speed wind turbine with PMSM drives. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2007, 129, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyed, A.; Aouiti, A.; Bacha, F. Study and Analysis of the Indirect Matrix Converter for Wind Energy System based on FOC-SVM and MPC Control Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT), Rome, Italy, 3–6 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nouraldin, N.A.; Chebaani, M.; Számel, L.; Abdelwahab, S.A.M.; Abdellatif, W.S. Experimental investigation of predictive control for PMSM-based wind turbine generation system. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2024, 119, 109554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Zhu, Z.-Q.; Odavic, M.; Li, Y. A novel zero-sequence model-based sensorless method for open-winding PMSM with common DC bus. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6777–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Dutta, R.; Chu, G.; Xiao, D.; Thippiripati, V.K.; Rahman, M.F. Open-winding permanent magnet synchronous generator for renewable energy—A review. Energies 2023, 16, 5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shneen, S.W.; Mao, C.; Wang, D. Advanced optimal PSO, Fuzzy and PI controller with PMSM and WTGS at 5Hz side of generation and 50 Hz Side of Grid. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. (IJPEDS) 2016, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, P.; Rajan, R.; Shanmugam, L.; Joo, Y.H. Adaptive fractional fuzzy integral sliding mode control for PMSM model. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 27, 1674–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azom, M.A.; Khan, M.Y. Recent developments in control and simulation of permanent magnet synchronous motor systems. Control Syst. Optim. Lett. 2025, 3, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagati, A.; Pellegrino, G.; Guglielmi, P. Comparison between SPM and IPM motor drives for EV application. In Proceedings of the XIX International Conference on Electrical Machines—ICEM 2010, Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino, G.; Vagati, A.; Guglielmi, P.; Boazzo, B. Performance comparison between surface-mounted and interior PM motor drives for electric vehicle application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 59, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.B.; El-Refaie, A.M.; Huh, K.-K.; Tangudu, J.K.; Jahns, T.M. Comparison of interior and surface PM machines equipped with fractional-slot concentrated windings for hybrid traction applications. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2012, 27, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, X.; Atallah, K. Design optimization of a surface-mounted permanent-magnet motor with concentrated windings for electric vehicle applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 62, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You-Young, C.; Ki-Doek, L.; Ik-Sang, J.; Mi-Jung, K.; Sang-Hwan, H.; Ju, L.; Kwang-Cheol, K. Research on the Output Characteristics of IPMSM according to the Pole-Slot Combinations. Energy Procedia 2012, 14, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasolo, A.; Alberti, L.; Bianchi, N. Performance comparison between switching-flux and IPM machines with rare-earth and ferrite PMs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3708–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Huang, Y.; Jin, L.; Lin, H. Comparative study of surface-mounted and interior permanent-magnet motors for high-speed applications. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 5200304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thampi, P.; Kiran, C. A review on controlling techniques for permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) and current state of the art in the research area. Appl. Electron. 2019, 7, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thike, R.; Pillay, P. Mathematical model of an interior PMSM with aligned magnet and reluctance torques. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 6, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacik, M.; Rafajdus, P.; Kocan, S. Comparison of various PMSM rotor topologies for high-speed drives in automotive applications. Transp. Res. Procedia 2021, 55, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madichetty, S.; Mishra, S.; Basu, M. New trends in electric motors and selection for electric vehicle propulsion systems. IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2021, 11, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, N.; Carlet, P.G.; Cinti, L.; Ortombina, L. A Review about Flux-Weakening Operating Limits and Control Techniques for Synchronous Motor Drives. Energies 2022, 15, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Du, C. Performance comparison and optimization of a PMSM based on hybrid-type permanent magnet with two kinds of rotor topology. Energies 2024, 17, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaibu, I.; Wei, E.H.T.; Kannan, R.; Samaila, Y.A. Advancements in axial flux permanent magnet machines utilizing coreless technology: A systematic review. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 103091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Cai, W.; Shao, B. Study on flow field of oil-cooling permanent magnet synchronous motor with hairpin winding using porous medium model. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2024, 18, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wu, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y. Research on Rotor Loss and Rotor Structure Optimization of Rare Earth Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors in the Weak Field Area. Energies 2023, 16, 7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemsen, J.; Nowak, N.; Eckstein, L. Production cost modeling for permanent magnet synchronous machines for electric vehicles. Automot. Engine Technol. 2023, 8, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomše, T.; Kubelka, P.; Moreno López, R.; Fleissner, P.; Grau, L.; Zaplotnik, M.; Burkhardt, C. Magnetic Performance and Anticorrosion Coating Stability of Thermally Demagnetized Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnets for Reuse Applications. Materials 2024, 17, 5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Y.; Zheng, P.; Yin, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, C. Open-circuit fault-tolerant control of five-phase PM machine based on reconfiguring maximum round magnetomotive force. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yi, J.; Lyu, Z.; Hu, S. Fault-tolerant operation for five-phase permanent magnet synchronous machine drives with five-phase six-leg inverter. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2024, 18, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zheng, H.; Kaku, C. Design of Fault-Tolerant Control Strategy for Dual-Winding Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor in Vehicles; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, P.; Lu, L.; Wang, Z. Optimization-based maximum-torque fault-tolerant control of dual three-phase PMSM drives under open-phase fault. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 38, 3653–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wang, X.; Jin, L.; Mao, Y.; Bao, Q.; Wang, Z. Fault-tolerant optimization control of open-winding dual three-phase PMSM drives in full operation range. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 40, 3385–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.S.; Lee, D.-C. Optimized Maximum Torque and Minimum Loss Fault-Tolerant Control Schemes for Dual Three-Phase PMSM. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–20 March 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, S.M.; Mendes, A.M.S. Fault-tolerant predictive current control of six-phase PMSMs with minimal reconfiguration requirements. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 11, 2084–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Hua, W. Generalized fault-tolerant model predictive control of five-phase PMSM drives under single/two open-switch faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 7569–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Li, B.; Sun, X.; Jiang, F. Optimized fault-tolerant control of dual three-phase PMSM under open-switch faults. Energies 2024, 17, 5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, R.; Kugi, A.; Kemmetmüller, W. Optimal torque control with radial force compensation for multiphase PMSMs under an open-circuit fault. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2023, 56, 4412–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, R.; Deutschmann-Olek, A.; Kugi, A.; Kemmetmüller, W. Optimal fault-tolerant control with radial force compensation for multiple open-circuit faults in multiphase PMSMs-A comparison of n-phase and multiple three-phase systems. Control Eng. Pract. 2024, 147, 105924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Lu, Y.; Lai, C.; Feng, G. Single Open-Phase Fault Tolerant Control of Salient Dual Three-Phase PMSMs With Maximized Torque to Total Loss Ratio Considering Peak Phase Current Limit. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 6852–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, F.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, L. Direct voltage vector control for field weakening operation of PM machines. In Proceedings of the 2010 Power and Energy Conference at Illinois (PECI), Urbana, IL, USA, 12–13 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.; Zhu, L.; Xu, L. Maximum Torque per Volt operation and stability improvement of PMSM in deep flux-weakening Region. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Raleigh, NC, USA, 15–20 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Qian, Y.; Asgarpoor, S.; Sharif, H. Simulation study on on-line MTPA/MTPV trajectory tracking in PMSMs with power management. Electr. Power Components Syst. 2020, 48, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Espinar, C.; Heredero-Peris, D.; Gross, G.; Llonch-Masachs, M.; Montesinos-Miracle, D. Maximum torque per voltage flux-weakening strategy with speed limiter for PMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 9254–9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Nalakath, S.; Tarvirdilu-Asl, R.; Sun, Y.; Wiseman, J.; Emadi, A. Online optimal tracking method for interior permanent magnet machines with improved MTPA and MTPV in whole speed and torque ranges. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 9753–9769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, C.; Bisceglie, G.; Torreggiani, A.; Davoli, M.; Macrelli, E.; Bellini, A.; Frigieri, M. Effects of the Magnetic Model of Interior Permanent Magnet Machine on MTPA, Flux Weakening and MTPV Evaluation. Machines 2023, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kang, J.; Degano, M.; Galassini, A.; Gerada, C. An accurate wide-speed range control method of IPMSM considering resistive voltage drop and magnetic saturation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 2630–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.K.; Laursen, M.; Hansen, S. Voltage vector based control for PMSM in industry applications. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Bari, Italy, 4–7 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bida, V.M.; Samokhvalov, D.V.; Al-Mahturi, F.S. PMSM vector control techniques—A survey. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EIConRus), Moscow, Russia, 29 January–1 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Korkmaz, F.; Topaloğlu, İ.; Cakir, M.F.; Gürbüz, R. Comparative performance evaluation of FOC and DTC controlled PMSM drives. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Power Engineering, Energy and Electrical Drives, Istanbul, Turkey, 13–17 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Geweth, D.; Zanelli, A.; Frison, G.; Vollmer, U.; Diehl, M. Field oriented economic model predictive control for permanent magnet synchronous motors. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 9093–9099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrami, M.; Jamshidpour, E.; Pierfederici, S.; Frick, V. Comparison of Flatness-based Control and Field-Oriented Control for PMSMs in Automotive Water Pump Application. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2023 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC/I&CPS Europe), Madrid, Spain, 6–9 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Goutham, P.; Chandrakala, K.V.; Saravanan, S.; Shankar, A. Sliding Mode-Based Field-Oriented Control Using SVPWM for the Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. In Proceedings of the 2024 Second International Conference on Emerging Trends in Information Technology and Engineering (ICETITE), Vellore, India, 22–23 February 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mocanu, R.; Onea, A. Passivity Based Torque Control of PMSM used in electrical vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2015 19th International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC), Cheile Gradistei, Romania, 14–16 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ouhrouche, M.; Errouissi, R.; Trzynadlowski, A.M.; Tehrani, K.A.; Benzaioua, A. A novel predictive direct torque controller for induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 5221–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Caporal, R.; Leal-López, M.E.; de Jesús Rangel-Magdaleno, J.; Sandre-Hernández, O.; Cruz-Vega, I. Direct torque control of a PMSM-drive for electric vehicle applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Electronics, Communications and Computers (CONIELECOMP), Cholula, Mexico, 21–23 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ghamri, A.; Boumaaraf, R.; Benchouia, M.T.; Mesloub, H.; Goléa, A.; Goléa, N. Comparative study of ANN DTC and conventional DTC controlled PMSM motor. Math. Comput. Simul. 2020, 167, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, A.; Prabhakaran, K.; Nagamani, C. Four quardrant operation of direct torque controlled PMSM drive using speed loop PDFF controller. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Power, Instrumentation, Control and Computing (PICC), Thrissur, India, 18–20 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanayem, H.; Alathamneh, M.; Nelms, R.J. Decoupled Speed and Flux Control of Three-Phase PMSM Based on the Proportional-Resonant Control Method. Energies 2023, 16, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gu, W.; Lu, K.; Wu, Z. Vector control of asymmetric dual three-phase PMSM in full modulation range. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 104479–104493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, X. Virtual voltage vector based model predictive control for a nine-phase open-end winding PMSM with a common DC bus. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 5386–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhier, Y.; Abdelyazid, A.; Oubelaid, A.; Khosravi, N.; Bajaj, M.; Vishnuram, P.; Zaitsev, I. Experimental analysis of passivity-based control theory for permanent magnet synchronous motor drive fed by grid power. IET Control. Theory Appl. 2024, 18, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colby, R.S.; Novotny, D. An efficiency-optimizing permanent-magnet synchronous motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1988, 24, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, P.C.; Blaabjerg, F.; Pedersen, J.K.; Thogersen, P. A sensorless, stable V/f control method for permanent-magnet synchronous motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sue, S.-M.; Hung, T.-W.; Liaw, J.-H.; Li, Y.-F.; Sun, C.-Y. A new MTPA control strategy for sensorless V/f controlled PMSM drives. In Proceedings of the 2011 6th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Beijing, China, 21–23 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, S.H.; Corzine, K.A.; Huang, J. Efficiency optimization of a sensorless V/f control method for PMSM. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Sensorless Control for Electrical Drives (SLED 2012), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 21–22 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, F.; Ahir, J.; Patel, P. Control Theory For Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor—A Review. Asian J. Converg. Technol. (AJCT) 2019, V. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, J.-I.; Nomura, N.; Ohsawa, H. A comparison between V/f control and position-sensorless vector control for the permanent magnet synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the Power Conversion Conference-Osaka 2002 (Cat. No. 02TH8579), Osaka, Japan, 2–5 April 2002. [Google Scholar]
- OS, S.B.; Khalid, M.; Binojkumar, A. Evaluation of Single Current Regulator Based Field Weakening Strategy For PMSM Drives and Experimental Validation using HIL. In Proceedings of the 2022 Second International Conference on Next Generation Intelligent Systems (ICNGIS), Kottayam, India, 29–31 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Koraqi, L.; Koteich, M. Torque Maximization Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Using a Two-Stage Virtual Signal Injection. In Proceedings of the 2022 XIV International Symposium on Industrial Electronics and Applications (INDEL), Banja Luka, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 9–11 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tursini, M.; Chiricozzi, E.; Petrella, R. Feedforward flux-weakening control of surface-mounted permanent-magnet synchronous motors accounting for resistive voltage drop. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 57, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, G.; Armando, E.; Guglielmi, P. Direct flux field-oriented control of IPM drives with variable DC link in the field-weakening region. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahns, T.M.; Kliman, G.B.; Neumann, T.W. Interior permanent-magnet synchronous motors for adjustable-speed drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1986, 22, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Rahman, M.A. High-speed control of IPMSM drives using improved fuzzy logic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macminn, S.R.; Jahns, T.M. Control techniques for improved high-speed performance of interior PM synchronous motor drives. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 1988 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2–7 October 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Jahns, T.M. Flux-weakening regime operation of an interior permanent magnet synchronous motor drive. In Proceedings of the 1986 Annual Meeting Industry Applications Society, Denver, CO, USA, 28 September–3 October 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.-H.; Kim, J.-M.; Sul, S.-K. A new robust SPMSM control to parameter variations in flux weakening region. In Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE IECON. 22nd International Conference on Industrial Electronics, Control, and Instrumentation, Taipei, Taiwan, 5–10 August 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-M.; Sul, S.-K. Speed control of interior permanent magnet synchronous motor drive for the flux weakening operation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1997, 33, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, B.-H.; Patel, N.; Schulz, S.; Sul, S.-K. New field weakening technique for high saliency interior permanent magnet motor. In Proceedings of the 38th IAS Annual Meeting on Conference Record of the Industry Applications Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 12–16 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lenke, R.U.; De Doncker, R.W.; Kwak, M.-S.; Kwon, T.-S.; Sul, S.-K. Field weakening control of interior permanent magnet machine using improved current interpolation technique. In Proceedings of the 2006 37th IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 18 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, T.-S.; Sul, S.-K. Novel antiwindup of a current regulator of a surface-mounted permanent-magnet motor for flux-weakening control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 42, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sue, S.-M.; Pan, C.-T. Voltage-constraint-tracking-based field-weakening control of IPM synchronous motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olarescu, N.; Weinmann, M.; Zeh, S.; Musuroi, S. Novel flux weakening control algorithm for PMSMS. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Power Engineering, Energy and Electrical Drives, Lisbon, Portugal, 18–20 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dolecek, R.; Simanek, J.; Novak, J.; Cerny, O. Dynamics of a feedback optimal-current-vector flux-weakening strategy for traction permanent-magnet synchronous motors. In Proceedings of the 2009 8th International Symposium on Advanced Electromechanical Motion Systems & Electric Drives Joint Symposium, Lille, France, 1–3 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Tesch, T.R. Torque feedforward control technique for permanent-magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Kar, N.C. A review of flux-weakening control in permanent magnet synchronous machines. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Lille, France, 1–3 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Azizi, A.; Akhbari, M.; Danyali, S.; Tohidinejad, Z.; Shirkhani, M. A review on topology and control strategies of high-power inverters in large-scale photovoltaic power plants. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, T.A.; Shalaby, M.; Wahab, N.I.A.; Zaynal, H.I.; Hassan, M.K.; Al-Sowayan, S.; Alawad, M.A. Recent Advancements in Multilevel Inverters: Topologies, Modulation Techniques, and Emerging Applications. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.-A.; Hieu, L.; Pham, V.-T.; Ngo, V.-Q. Enhanced model predictive current framework for a PMSM powered by three-level NPC inverters with DC-link voltage self-balancing mechanisms. Results Eng. 2025, 27, 105918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, Y. A low-complexity double vector model predictive current control for permanent magnet synchronous motors. Energies 2023, 17, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.M.; Otten, D.M.; Lang, J.H.; Kirtley, J.L.; Perreault, D.J. Comparison of inverter topologies for high-speed motor drive applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 7404–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, M. Review of Key Technologies of the High-Speed Permanent Magnet Motor Drive. Energies 2024, 17, 5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellmann, C.; Khaleel, A.R.; Brinkmann, T.; Wahl, A.; Monissen, C.; Eisenbarth, M.; Andert, J. Electric machine co-optimization for EV drive technology development: Integrating Bayesian optimization and nonlinear model predictive control. eTransportation 2025, 23, 100392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Yu, J.; Zhao, L. Combined speed and current terminal sliding mode control with nonlinear disturbance observer for PMSM drive. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 29594–29601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y. Speed-current single-loop control with overcurrent protection for PMSM based on time-varying nonlinear disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Yu, H. Time-varying disturbance observer based improved sliding mode single-loop control of PMSM drives with a hybrid reaching law. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 2539–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X. An improved super-twisting sliding mode single-loop control with current-constraint for PMSM based on two-time scale disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 10, 5389–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dai, B.; Guo, Z.; Yang, J. Single-Loop Current-Constrained Speed Regulation for PMSM via a Switching Controller. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 11, 5974–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Single-loop robust model predictive speed regulation of PMSM based on exogenous signal preview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 12719–12729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ren, W.; Sun, X.-M. Extended-state-observer-based nonlinear control for PMSM servo systems with current constraints and voltage saturations. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 10, 2713–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, M.; Xie, E. Non-cascade structure equivalent SMC for PMSM driving based on improved ESO. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 40, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, S. Critical Current-Constrained Continuous Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Control for PMSM Based on Control Barrier Function. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 15093–15103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, G.; Sayeef, S.; Rahman, M.J. Low-speed and standstill operation of a sensorless direct torque and flux controlled IPM synchronous motor drive. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M. A Reference Value Calculation Scheme for Torque and Flux and an Anti-Windup Implementation of Torque Controller for Direct Torque Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEJ Trans. Ind. Appl. 2010, 130, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M. Control method suitable for direct-torque-control-based motor drive system satisfying voltage and current limitations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Sozer, Y.; Hamdan, M. Maximum torque per ampere control for buried magnet PMSM based on DC-link power measurement. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Inoue, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M. Maximum torque per ampere control of a direct torque-controlled PMSM in a stator flux linkage synchronous frame. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 2360–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Wang, X.; Gao, H.; Liu, J. Sliding mode based speed regulating of PMSM MTPA control system for electrical vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electronic & Mechanical Engineering and Information Technology, Harbin, China, 12–14 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhou, M.; You, X. Parameters compensation of permanent magnet synchronous motor in flux-weakening region for rail transit. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 12509–12521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Miao, Y.; Bilgin, B.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B.; Emadi, A. Speed range extended maximum torque per ampere control for PM drives considering inverter and motor nonlinearities. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 7151–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Egashira, J.; Kaneko, K. High efficiency control of IPMSM for electric motorcycles. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 6th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, Wuhan, China, 17–20 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-S.; Lee, Y.; Sul, S.-K.; Yu, J.; Oh, J. Online MTPA control of IPMSM based on robust numerical optimization technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 3736–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.-T.; Sue, S.-M. A linear maximum torque per ampere control for IPMSM drives over full-speed range. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2005, 20, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, Z.; Huang, K.; Gao, J. Maximum torque per ampere and flux-weakening control for PMSM based on curve fitting. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Lille, France, 1–3 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Luo, X.; Ma, X. Realization of maximum torque per ampere control for IPMSM based on inductance segmentation. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 66088–66094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. A universal maximum torque per ampere method for permanent magnet synchronous machines. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Harbin, China, 11–14 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, H. MTPA control of PMSM system considering saturation and cross-coupling. In Proceedings of the 2012 15th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Sapporo, Japan, 21–24 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Y.; Ge, H.; Preindl, M.; Ye, J.; Cheng, B.; Emadi, A. MTPA fitting and torque estimation technique based on a new flux-linkage model for interior-permanent-magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 5451–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Inoue, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M. Mathematical model for MTPA control of permanent-magnet synchronous motor in stator flux linkage synchronous frame. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3620–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Xu, J.; Huang, Y.; Jatskevich, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X. Parameter-Estimation-Based Adaptive MTPA Control for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT), Paris, France, 23–26 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, Q.K.; Petrich, M.; Roth-Stielow, J. Implementation of the MTPA and MTPV control with online parameter identification for a high speed IPMSM used as traction drive. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Power Electronics Conference (IPEC-Hiroshima 2014-ECCE ASIA), Hiroshima, Japan, 18–21 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Sanada, M. Experimental Evaluation of the Online MTPA Angle Search Method Based on Flux-linkage Plane Estimation for IPMSMs. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2024, 13, 23009975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Migita, H. MTPA Control of IPMSM with Online Parameter Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2019 21st European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’19 ECCE Europe), Genova, Italy, 3–5 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara, A.; Inoue, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M. Direct calculation method of reference flux linkage for maximum torque per ampere control in DTC-based IPMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, P.; Toliyat, H.A.; Goodarzi, A. Robust maximum torque per ampere (MTPA) control of PM-assisted SynRM for traction applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2007, 56, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phowanna, P.; Boonto, S.; Konghirun, M. Online parameter identification method for IPMSM drive with MTPA. In Proceedings of the 2015 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Pattaya, Thailand, 25–28 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Khazaee, A.; Yazdani, A.; Makhdoumi, A.; Atashin, S.A.; Wu, B. Loss Minimization Algorithm for Surface-Mounted PMSM Using Ripple-Based Extremum Seeking. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 15325–15335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, J. A novel MTPA control for IPMSMs based on extremum seeking control. In Proceedings of the 2015 34th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Hangzhou, China, 28–30 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, M.; Zeng, F.; Yu, Y. An improved MTPA control based on amplitude-adjustable square wave injection. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, Y. Maximum torque per ampere (MTPA) control for IPMSM drives using signal injection and an MTPA control law. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 5588–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yoon, Y.-D.; Sul, S.-K.; Ide, K. Maximum torque per ampere (MTPA) control of an IPM machine based on signal injection considering inductance saturation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 28, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, R.; Carraro, M.; Zigliotto, M. Maximum-torque-per-ampere operation of anisotropic synchronous permanent-magnet motors based on extremum seeking control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 61, 5086–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yoon, Y.-D.; Sul, S.-K.; Ide, K.; Tomita, K. Parameter independent maximum torque per ampere (MTPA) control of IPM machine based on signal injection. In Proceedings of the 2010 Twenty-Fifth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Palm Springs, CA, USA, 21–25 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, F.; Liu, J.; Mai, Z.; Li, C. Maximum torque per ampere control for IPMSM traction system based on current angle signal injection method. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2020, 15, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.-J.; Liu, Y.-T.; Yu, W.-A. Power perturbation based MTPA with an online tuning speed controller for an IPMSM drive system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 3677–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognani, S.; Sgarbossa, L.; Zordan, M. Self-tuning of MTPA current vector generation scheme in IPM synchronous motor drives. In Proceedings of the 2007 European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Aalborg, Denmark, 2–5 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bedetti, N.; Calligaro, S.; Olsen, C.; Petrella, R. Automatic MTPA tracking in IPMSM drives: Loop dynamics, design, and auto-tuning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 4547–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, J.; Chen, X. Maximum torque per ampere (MTPA) control for interior permanent magnet synchronous machine drives based on virtual signal injection. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 30, 5036–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, J. Extension of virtual-signal-injection-based MTPA control for interior permanent-magnet synchronous machine drives into the field-weakening region. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6809–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, J.; Koc, M. On accuracy of virtual signal injection based MTPA operation of interior permanent magnet synchronous machine drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 7405–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, J.; Koc, M.; Chen, X. Self-learning MTPA control of interior permanent-magnet synchronous machine drives based on virtual signal injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 3062–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Online MTPA control for salient-pole PMSMs using square-wave current injection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 18–22 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Koç, M.; Wang, J. MTPA control of IPMSM drives based on virtual signal injection considering machine parameter variations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 6089–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.; Pinhal, D.B.; Reiland, N.; Gerling, D. Improved online maximum-torque-per-ampere algorithm for speed controlled interior permanent magnet synchronous machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 3398–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Niu, F.; Fang, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhang, H. An accurate virtual signal injection control of MTPA for an IPMSM with fast dynamic response. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 7916–7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Virtual square-wave current injection based maximum torque per ampere control for interior permanent-magnet synchronous machines. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Dearborn, MI, USA, 27–29 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, M.H.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Extremum seeking-based optimum reference flux searching for direct torque control of interior permanent magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2019, 6, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahami, F.; Nademi, H.; Rezaei, M. A high-performance vector-controlled PMSM drive with maximum torque per ampere operation. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE 2nd International Power and Energy Conference, Johor Bahru, Malaysia, 1–3 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, M.A. Speed and Position Sensorless Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives; Memorial University of Newfoundland: St. John’s, NL, Canada, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Benjak, O.; Gerling, D. Review of position estimation methods for IPMSM drives without a position sensor part I: Nonadaptive methods. In Proceedings of the XIX International Conference on Electrical Machines—ICEM 2010, Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, C.; Zhang, Z.; Qiao, W. A review on position/speed sensorless control for permanent-magnet synchronous machine-based wind energy conversion systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2013, 1, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, S.; Tiwari, A. PMSM drives and its application: An overview. Recent Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. (Former. Recent Pat. Electr. Electron. Eng.) 2023, 16, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.B.; Ehsani, M. A novel position sensor elimination technique for the interior permanent-magnet synchronous motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1992, 28, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, J.W.; Giaouris, D. Controlled AC electrical drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongdong, L.; Hao, Z. Sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motor—A survey. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Harbin, China, 3–5 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, H.-C.; Yang, S.-M. Phase inductance and rotor position estimation for sensorless permanent magnet synchronous machine drives at standstill. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 32897–32907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Kim, G.; Gu, B.-G. Sensorless PMSM Drive Inductance Estimation Based on a Data-Driven Approach. Electronics 2021, 10, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Yao, X. A modified flux sliding-mode observer for the sensorless control of PMSMs with online stator resistance and inductance estimation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 8652–8662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, M.; Bose, B.K. Rotor position estimation scheme of a permanent magnet synchronous machine for high performance variable speed drive. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 1992 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Houston, TX, USA, 4–9 October 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Yang, L.; Ma, X. Sensorless control of PMSM using generalized extended state observer and adaptive resistance estimation. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 2062–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Sensorless back EMF based control of synchronous PM and reluctance motor drives—A review. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 10290–10305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, Y. Back EMF-based dynamic position estimation in the whole speed range for precision sensorless control of PMLSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 19, 6525–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, J.; Ye, M.; Chen, J.; Kong, W.; Kang, M.; Yu, M. An EMF observer for PMSM sensorless drives adaptive to stator resistance and rotor flux linkage. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2018, 7, 1899–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Feng, J. Sensorless control of salient PMSM with EKF of speed and rotor position. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Wuhan, China, 17–20 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vaclavek, P.; Blaha, P. PMSM position estimation algorithm design based on the estimate stability analysis. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 15–18 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nicola, M.; Nicola, C.-I. Sensorless control of PMSM using fractional order SMC and extended Kalman observer. In Proceedings of the 2021 18th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD), Monastir, Tunisia, 22–25 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tondpoor, K.; Saghaiannezhad, S.M.; Rashidi, A. Sensorless control of pmsm using simplified model based on extended kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 2020 11th Power Electronics, Drive Systems, and Technologies Conference (PEDSTC), Tehran, Iran, 4–6 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dilys, J.; Stankevič, V.; Łuksza, K. Implementation of extended Kalman filter with optimized execution time for sensorless control of a PMSM using ARM cortex-M3 microcontroller. Energies 2021, 14, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermayr, P.; Alberti, L.; Bolognani, S.; Abl, R. Implementation and experimental validation of ultrahigh-speed pmsm sensorless control by means of extended kalman filter. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 10, 3337–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, D. Study of position sensorless control of PMSM based on MRAS. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, Churchill, VIC, Australia, 10–13 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakaran, K.; Karthikeyan, A. Electromagnetic torque-based model reference adaptive system speed estimator for sensorless surface mount permanent magnet synchronous motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 5936–5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.A.A.; Sreejeth, M.; Bhattacharya, A. Sensorless control of PMSM using Direct and Model References Adaptive system estimation techniques and observing the effect of using PI Fuzzy logic controller in MRAS Model. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference for Innovation in Technology (INOCON), Bangaluru, India, 6–8 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, A.; Luo, X.; Tang, Q.; Li, Z. Multi-sliding mode current disturbance suppression scheme based model reference adaptive system for sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motor. ISA Trans. 2023, 137, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Khalil, A.G.; Eltamaly, A.M.; Alsaud, M.S.; Sayed, K.; Alghamdi, A.S. Sensorless control for PMSM using model reference adaptive system. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2021, 31, e12733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Dong, D. Dynamic performance enhancement method based on improved model reference adaptive system for SPMSM sensorless drives. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 135012–135023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Fan, L.; Zhang, Z. Sensorless PMSM control with sliding mode observer based on sigmoid function. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2021, 16, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Lai, C.; Iyer, K.L.V. A review of sliding mode observer based sensorless control methods for PMSM drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 11352–11367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Elbuluk, M. A sliding mode observer for sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motors. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2001 IEEE Industry Applications Conference. 36th IAS Annual Meeting (Cat. No. 01CH37248), Chicago, IL, USA, 30 September–4 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Salvatore, L.; Cupertino, F.; Cascella, G.L. A new approach to sensorless vector control of SPMSM with adaptive sliding-mode observer. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), L’Aquila, Italy, 8–11 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chretien, L.; Husain, I. Position sensorless control of non-salient pmsm from very low speed to high speed for low cost applications. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Industry Applications Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–27 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Lee, J. Design of iterative sliding mode observer for sensorless PMSM control. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2012, 21, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Hu, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, L. An improved delay-suppressed sliding-mode observer for sensorless vector-controlled PMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 5913–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Lu, K.; Dwivedi, S.K.; Rosholm, J.R.; Blaabjerg, F. Minimum-voltage vector injection method for sensorless control of PMSM for low-speed operations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-H.; Sul, S.-K.; Ha, J.-I.; Ide, K.; Sawamura, M. Sensorless drive of surface-mounted permanent-magnet motor by high-frequency signal injection based on magnetic saliency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-H.; Ha, J.-I.; Ohto, M.; Ide, K.; Sul, S.-K. Analysis of permanent-magnet machine for sensorless control based on high-frequency signal injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2004, 40, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigosa, D.; gu Kang, Y.; Martínez, M.; Fernández, D.; Guerrero, J.M.; Briz, F. SPMSMs sensorless torque estimation using high-frequency signal injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 2700–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, M.; Gao, H. Position sensorless control system of SPMSM based on high frequency signal injection method with passive controller. Int. J. Electr. Hybrid Veh. 2022, 14, 112–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, C.; Duan, W.; Jiang, J. Research on sensorless control system of low speed and high power PMSM based on improved high frequency signal injection. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, G.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Q.; Ding, D.; Li, B.; Wang, G.; Xu, D. High-frequency injection angle self-adjustment based online position error suppression method for sensorless PMSM drives. EEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 38, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskola, M.; Tuusa, H. Sensorless control of salient pole PMSM using a low-frequency signal injection. In Proceedings of the 2005 European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Dresden, Germany, 11–14 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, G.; Wang, G.; Yu, Y. A review of sensorless control methods for AC motor drives. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2018, 2, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. Research Review on Sensorless Measurement Technology of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Int. J. Mech. Electr. Eng. 2024, 2, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Chen, C. Review of sensorless control techniques for PMSM drives. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2019, 14, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrodl, M.; Lambeck, M. Statistic properties of the INFORM method for highly dynamic sensorless control of PM motors down to standstill. In Proceedings of the IECON’03. 29th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37468), Roanoke, VA, USA, 2–6 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Ni, R.; Jiang, T.; Gu, S. Position Sensorless Control of PMSMs Using Improved INFORM Method with a Single Current Sensor at Low Speed. In Proceedings of the 2021 24th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Gyeongju, Republic of Korea, 31 October–3 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, X.M. Sensorless Control and Fast on-Line Parameter Estimation of IPMSM Based on Current Derivative Measurements; UNSW Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, M.X.; Le, K.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Rahman, F. Sensorless control and on-line estimation of inductances of IPMSMs using current derivatives. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Hanoi, Vietnam, 14–17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Isidori, A.; Astolfi, A. Disturbance attenuation and H/sub infinity/-control via measurement feedback in nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1992, 37, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Schaft, A. L 2-gain analysis of nonlinear systems and nonlinear state feedback H∞ control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1992, 37, 770–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, I.U.; Bentsman, J.; Orlov, Y.; Aguilar, L.T. Generic Nonsmooth H∞ Output Synthesis: Application to a Coal-Fired Boiler/Turbine Unit With Actuator Dead Zone. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2015, 23, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Villalobos, R.; Aguilar, L.T.; Coria, L.N. Sensorless H∞ speed-tracking synthesis for surface-mount permanent magnet synchronous motor. ISA Trans. 2017, 67, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellschopp, F.; Arjona, M. DC decay test for estimating d-axis synchronous machine parameters: A two-transfer-function approach. IEE Proc.-Electr. Power Appl. 2006, 153, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, J.N.H.; Hernandez, O.S.; Caporal, R.M.; Magdaleno, J.d.J.R.; Barreto, H.P. Parameter identification of a permanent magnet synchronous machine based on current decay test and particle swarm optimization. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2013, 11, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horning, S.; Keyhani, A.; Kamwa, I. On-line evaluation of a round rotor synchronous machine parameter set estimated from standstill time-domain data. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1997, 12, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Radun, A. A new method to measure the switched reluctance motor’s flux. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 42, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilthau, A.; Pacas, J. Parameter-measurement and control of the synchronous reluctance machine including cross saturation. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2001 IEEE Industry Applications Conference. 36th IAS Annual Meeting (Cat. No. 01CH37248), Chicago, IL, USA, 30 September–4 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sellschopp, F.S. A tool for extracting synchronous machines parameters from the dc flux decay test. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2005, 31, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasni, M.; Touhami, O.; Ibtiouen, R.; Fadel, M.; Caux, S. Synchronous machine parameter identification by various excitation signals. Electr. Eng. 2008, 90, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.; Reece, A.; Macdonald, D. The DC decay test for determining synchronous machine parameters: Measurement and simulation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1989, 4, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumageanian, A.; Keyhani, A. Identification of synchronous machine linear parameters from standstill step voltage input data. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1995, 10, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Murthy, S.S.; Singh, B. An improved method for the determination of saturation characteristics of switched reluctance motors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1999, 48, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamwa, I.; Viarouge, P.; Dickinson, E. Identification of generalised models of synchronous machines from time-domain tests. IEE Proc. C (Gener. Transm. Distrib.) 1991, 138, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasni, M.; Touhami, O.; Ibtiouen, R.; Fadel, M.; Caux, S. Estimation of synchronous machine parameters by standstill tests. Math. Comput. Simul. 2010, 81, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boje, E.; Balda, J.; Harley, R.; Beck, R. Time-domain identification of synchronous machine parameters from simple standstill tests. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1990, 5, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groza, V. Experimental determination of synchronous machine reactances from DC decay at standstill. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2003, 52, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicol, L.; Tu Xuan, M.; Wetter, R.; Simond, J.-J.; Viorel, I. On the Identification of the Synchronous Machine Parameters Using Standstill DC Decay Test. In Proceedings of the 2006 ICEM (International Conference on Electrical Machines), Chania, Crete, Greece, 2–5 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sandre-Hernandez, O.; Morales-Caporal, R.; Rangel-Magdaleno, J.; Peregrina-Barreto, H.; Hernandez-Perez, J.N. Parameter identification of PMSMs using experimental measurements and a PSO algorithm. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 2146–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldea, I. Reluctance Synchronous Machines and Drives; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996; Volume 38. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Qu, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, W. Review of off-line synchronous inductance measurement method for permanent magnet synchronous machines. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference and Expo Transportation Electrification Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Beijing, China, 31 August–3 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Qu, R.; Liu, Y. An improved AC standstill method for inductance measurement of interior permanent magnet synchronous motors. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Busan, Republic of Korea, 26–29 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Balda, J.; Fairbairn, R.; Harley, R.; Rodgerson, J.; Eitelberg, E. Measurement of synchronous machine parameters by a modified frequency response method-Part II: Measured results. IEEE Power Eng. Rev. 1987, EC-2, 4652–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touhami, O.; Guesbaoni, H.; Iung, C. Synchronous machine parameter identification by a multitime scale technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1994, 30, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavagnino, A.; Lazzari, M.; Profumo, F.; Tenconi, A. Axial flux interior PM synchronous motor: Parameters identification and steady-state performance measurements. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 1999 IEEE Industry Applications Conference. Thirty-Forth IAS Annual Meeting (Cat. No. 99CH36370), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 3–7 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Dedene, N.; Pintelon, R.; Lataire, P. Estimation of a global synchronous machine model using a multiple-input multiple-output estimator. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2003, 18, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senjyu, T.; Urasakt, N.; Simabukuro, T.; Uezato, K. Modelling and parameter measurement of salient-pole permanent magnet synchronous motors including stator iron loss. Math. Comput. Model. Dyn. Syst. 1998, 4, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.; Rahman, M. A comparative analysis of two test methods of measuring d- and q-axes inductances of interior permanent-magnet machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 3712–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandoorn, T.L.; Frederik, M.; Vyncke, T.J.; Melkebeek, J.A.; Lataire, P. Generation of multisinusoidal test signals for the identification of synchronous-machine parameters by using a voltage-source inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 57, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Kwon, S.-O.; Lee, J.-J.; Hong, J.-P. An improved AC standstill method for testing inductances of interior PM synchronous motor considering cross-magnetizing effect. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, San Jose, CA, USA, 20–24 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chiba, A.; Nakamura, F.; Fukao, T.; Rahman, M.A. Inductances of cageless reluctance-synchronous machines having nonsinusoidal space distributions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1991, 27, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K.M.; Hiti, S. Identification of machine parameters of a synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nee, H.-P.; Lefevre, L.; Thelin, P.; Soulard, J. Determination of d and q reactances of permanent-magnet synchronous motors without measurements of the rotor position. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2000, 36, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Lee, W.; Kwon, S.-O.; Hong, J.-P. Experimental estimation of inductance for interior permanent magnet synchronous machine considering temperature distribution. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 2990–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaible, U.; Szabados, B. Dynamic motor parameter identification for high speed flux weakening operation of brushless permanent magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1999, 14, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumberger, B.; Kreca, B.; Hribernik, B. Determination of parameters of synchronous motor with permanent magnets from measurement of load conditions. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1999, 14, 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumberger, B.; Stumberger, G.; Dolinar, D.; Hamler, A.; Trlep, M. Evaluation of saturation and cross-magnetization effects in interior permanent-magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, G.-H.; Hong, J.-P.; Hur, J. Determination of parameters considering magnetic nonlinearity in an interior permanent magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 1303–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meessen, K.J.; Thelin, P.; Soulard, J.; Lomonova, E.A. Inductance calculations of permanent-magnet synchronous machines including flux change and self-and cross-saturations. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 2324–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseghi, B.; Takorabet, N.; Meibody-Tabar, F. Fault analysis and parameter identification of permanent-magnet motors by the finite-element method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 3290–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-H.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, K.-D.; Lee, J.-J.; Han, J.-H.; Jeong, T.-C.; Cho, S.-Y.; Lee, J. Inductance calculation in IPMSM considering magnetic saturation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 50, 4001304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Howe, D. Calculation of d-and q-axis inductances of PM brushless ac machines accounting for skew. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 3940–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Bernal, F.; Garcia-Cerrada, A.; Faure, R. Determination of parameters in interior permanent-magnet synchronous motors with iron losses without torque measurement. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2001, 37, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Qu, L.; Zhan, H.; Xu, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, G.; Xu, D. Self-commissioning of permanent magnet synchronous machine drives at standstill considering inverter nonlinearities. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 6615–6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadokoro, D.; Morimoto, S.; Inoue, Y.; Sanada, M. Method for auto-tuning of current and speed controller in IPMSM drive system based on parameter identification. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Power Electronics Conference (IPEC-Hiroshima 2014-ECCE ASIA), Hiroshima, Japan, 18–21 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M.; Takeda, Y. Mechanical sensorless drives of IPMSM with online parameter identification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 42, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimi, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Matsui, K. Parameter identification for IPMSM position sensorless control based on unknown input observer. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Symposium on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ISIEA), Penang, Malaysia, 3–5 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa, S.; Tomita, M.; Doki, S.; Okuma, S. Sensorless control of permanent-magnet synchronous motors using online parameter identification based on system identification theory. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M. Performance improvement of sensorless IPMSM drives in a low-speed region using online parameter identification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2010, 47, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Yamada, K.; Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M. Effectiveness of voltage error compensation and parameter identification for model-based sensorless control of IPMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, S.; Tomita, M.; Doki, S.; Okuma, S. Sensorless control of synchronous reluctance motors based on extended EMF models considering magnetic saturation with online parameter identification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 42, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijie, L.; Dongliang, L.; Qiuxuan, W.; Lili, C.; Xiaodan, Z. A novel deadbeat-direct torque and flux control of IPMSM with parameter identification. In Proceedings of the 2016 18th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’16 ECCE Europe), Karlsruhe, Germany, 5–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Underwood, S.J.; Husain, I. Online parameter estimation and adaptive control of permanent-magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 57, 2435–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Lee, H.-W.; Kim, K.-S.; Bae, J.-N.; Im, J.-B.; Kim, C.-J.; Lee, J. Torque ripple improvement for interior permanent magnet synchronous motor considering parameters with magnetic saturation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 4720–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Parspour, N.; Vollmer, U. Torque ripple minimization using online estimation of the stator resistances with consideration of magnetic saturation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 61, 5105–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.; Wilson, W. Synchronous machine parameter identification: A time domain approach. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1988, 3, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouni, E.; Tnani, S.; Champenois, G. Synchronous generator modelling and parameters estimation using least squares method. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2008, 16, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Gupta, R.; Bansal, A.K. Identification and control of PMSM using artificial neural network. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Vigo, Spain, 4–7 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Z.-Q.; Zhang, J. Online multiparameter estimation of nonsalient-pole PM synchronous machines with temperature variation tracking. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 58, 1776–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, H.-W.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, K.-B. On-line parameter estimation of interior permanent magnet synchronous motor using an extended Kalman filter. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2014, 9, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, Z.-Q. Online estimation of the rotor flux linkage and voltage-source inverter nonlinearity in permanent magnet synchronous machine drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, Z.-Q.; Stone, D.A. Parameter estimation for condition monitoring of PMSM stator winding and rotor permanent magnets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 5902–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, A.; Zhang, J. Online estimating voltage source inverter nonlinearity for PMSM by Adaline neural network. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Fifth International Conference on Bio-Inspired Computing: Theories and Applications (BIC-TA), Changsha, China, 23–26 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.; Hoque, M. On-line adaptive artificial neural network based vector control of permanent magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1998, 13, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Husain, I.; Elbuluk, M. Torque ripple minimization with on-line parameter estimation using neural networks in permanent magnet synchronous motors. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of 1998 IEEE Industry Applications Conference. Thirty-Third IAS Annual Meeting (Cat. No. 98CH36242), St. Louis, MI, USA, 12–15 October 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gatto, G.; Marongiu, I.; Serpi, A. Discrete-time parameter identification of a surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 60, 4869–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piippo, A.; Hinkkanen, M.; Luomi, J. Adaptation of motor parameters in sensorless PMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boileau, T.; Leboeuf, N.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B.; Meibody-Tabar, F. Online identification of PMSM parameters: Parameter identifiability and estimator comparative study. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1944–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Sun, L. On-line parameter identification for vector controlled PMSM drives using adaptive algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Harbin, China, 3–5 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, K.; Huang, L.; Li, Y. Online identification of permanent magnet flux based on extended Kalman filter for IPMSM drive with position sensorless control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 59, 4169–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamida, M.A.; De Leon, J.; Glumineau, A.; Boisliveau, R. An adaptive interconnected observer for sensorless control of PM synchronous motors with online parameter identification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 60, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Y.-R.; Lee, T. Adaptive self-tuning MTPA vector controller for IPMSM drive system. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2006, 21, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, Z.-Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J. Influence of nonideal voltage measurement on parameter estimation in permanent-magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 59, 2438–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Matsui, K. Position sensorless control for interior permanent magnet synchronous motor using adaptive flux observer with inductance identification. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2009, 3, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boileau, T.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B.; Meibody-Tabar, F. On-line identification of PMSM parameters: Model-reference vs EKF. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 5–9 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi, K.; MatSui, N.; Hori, Y. Estimation, identification, and sensorless control in motion control system. Proc. IEEE 1994, 82, 1253–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cartes, D. Synchronisation based adaptive parameter identification for permanent magnet synchronous motors. IET Control. Theory Appl. 2007, 1, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthi, V.D.; Kumar, J. Model reference adaptive control based parameters estimation of permanent magnet synchronous motor drive. J. Electr. Eng. 2013, 2, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Song, W.; Gang, Y.; Zhi-Jian, Q.; Shuang-shuang, S.; Chao, C. Identification of PMSM based on EKF and elman neural network. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Automation and Logistics, Shenyang, China, 5–7 August 2009. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Bolognani, S.; Tubiana, L.; Zigliotto, M. Extended Kalman filter tuning in sensorless PMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwasilu, F.; Jung, J.-W. Enhanced fault-tolerant control of interior PMSMs based on an adaptive EKF for EV traction applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 5746–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaouadi, R.; Mohan, N.; Norum, L. Design and implementation of an extended Kalman filter for the state estimation of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1991, 6, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaq, M.S.; Mwasilu, F.; Kim, J.; Choi, H.H.; Jung, J.-W. Online parameter identification for model-based sensorless control of interior permanent magnet synchronous machine. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 4631–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, D.Q.; Rafaq, M.S.; Choi, H.H.; Jung, J.-W. Online parameter estimation technique for adaptive control applications of interior PM synchronous motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 63, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
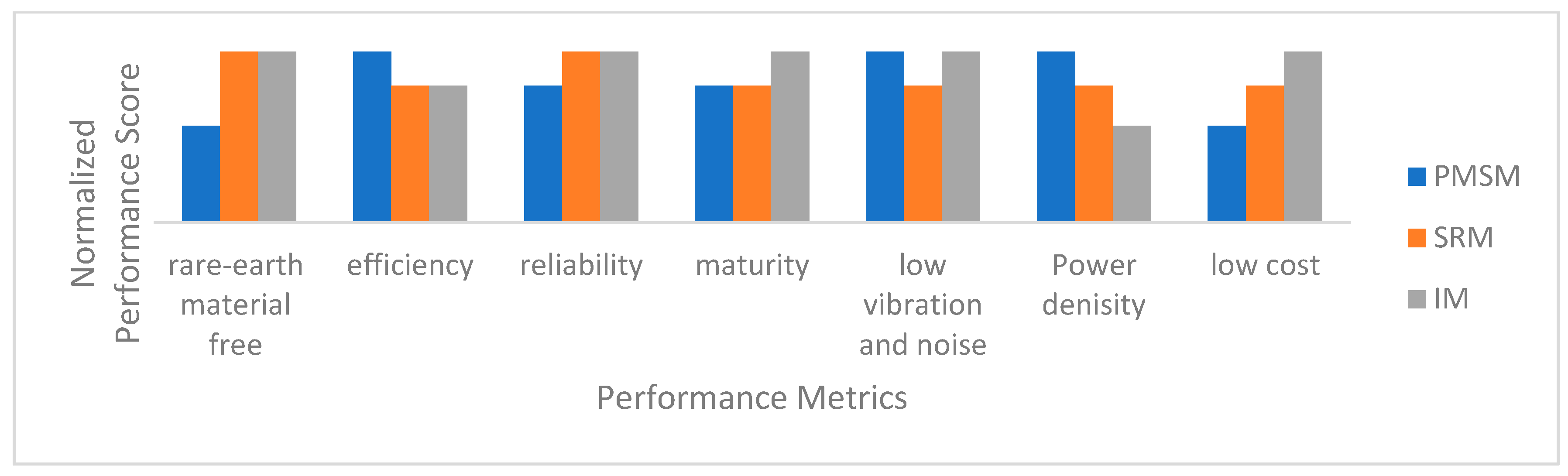

| PMSM Type | IPMSM | SPMSM | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design | Require peripheral sleeve | Need a peripheral sleeve in order to protect PMs from centrifugal forces. Because of this, manufacturing SPM rotors is more difficult than IPMs. | [26] |
| Losses | More core losses | Reduced core losses as a result of the rotor steel’s greater separation from the air gap and SPMs’ reduced magnetic flux leaking. | |
| Volume of PM material | More PM material volume is needed | Compared to IPMs, less PM material is used. | |
| Cost | Is superior in costs | High cost. | [23] |
| Robustness | Less robust | SPM is more robust. | |
| Efficiency | Less efficiency | Higher overall efficiency and cooler. | |
| Cooling | Less in cooling | Cooler. | |
| Speed range | If the machine’s saliency is maximized, IPM has an excellent overload capacity over the whole speed range | The SPM motor is unable to surpass the continuous power rating, regardless of the applied current overload. | [18] |
| Joule losses vs. speed | Requires a suitable number of stator slots and rotor segments to keep the harmonic losses in control, which can increase the fabrication cost, and has larger Joule losses at low speed because of end connections | Extra-Joule losses for deexciting the PM flux at high speeds and PM losses that necessitate segmentation in both directions (axial and circumferential) have an impact on the SPM motor. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elkholy, M.M.; Algendy, M.M.; El-Hay, E.A. Modern Control Techniques and Operational Challenges in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: A Comprehensive Review. Automation 2025, 6, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation6040049
Elkholy MM, Algendy MM, El-Hay EA. Modern Control Techniques and Operational Challenges in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: A Comprehensive Review. Automation. 2025; 6(4):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation6040049
Chicago/Turabian StyleElkholy, Mahmoud M., Mohamed M. Algendy, and Enas A. El-Hay. 2025. "Modern Control Techniques and Operational Challenges in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: A Comprehensive Review" Automation 6, no. 4: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation6040049
APA StyleElkholy, M. M., Algendy, M. M., & El-Hay, E. A. (2025). Modern Control Techniques and Operational Challenges in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: A Comprehensive Review. Automation, 6(4), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation6040049






