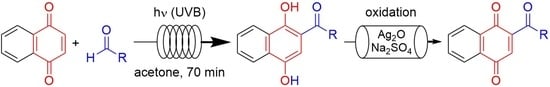
Photochemical Acylation of 1,4-Naphthoquinone with Aldehydes Under Continuous-Flow Conditions
Abstract
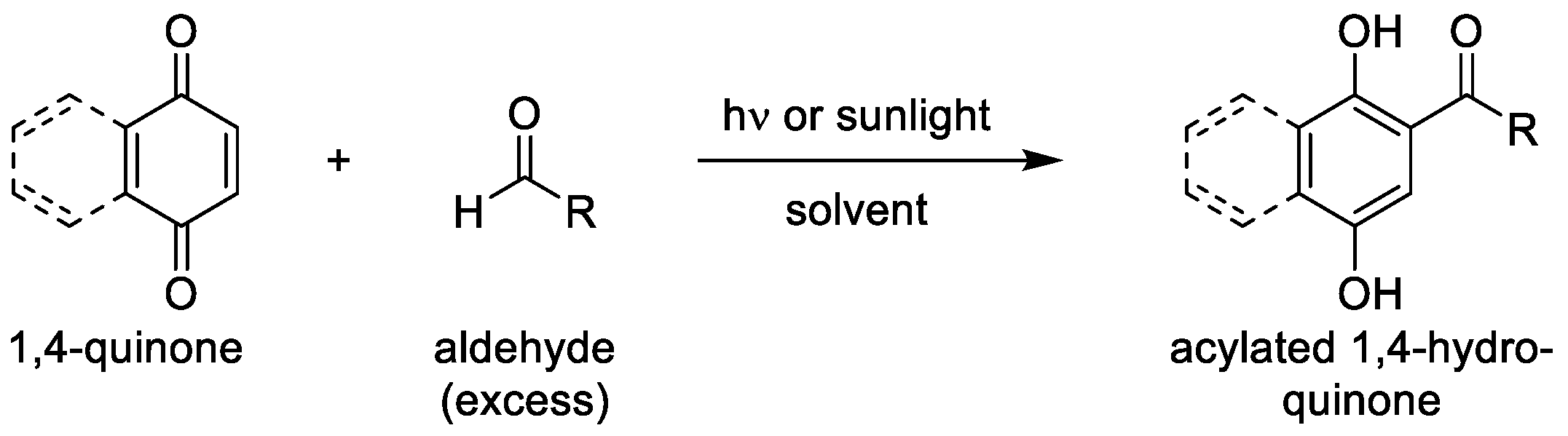
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Information
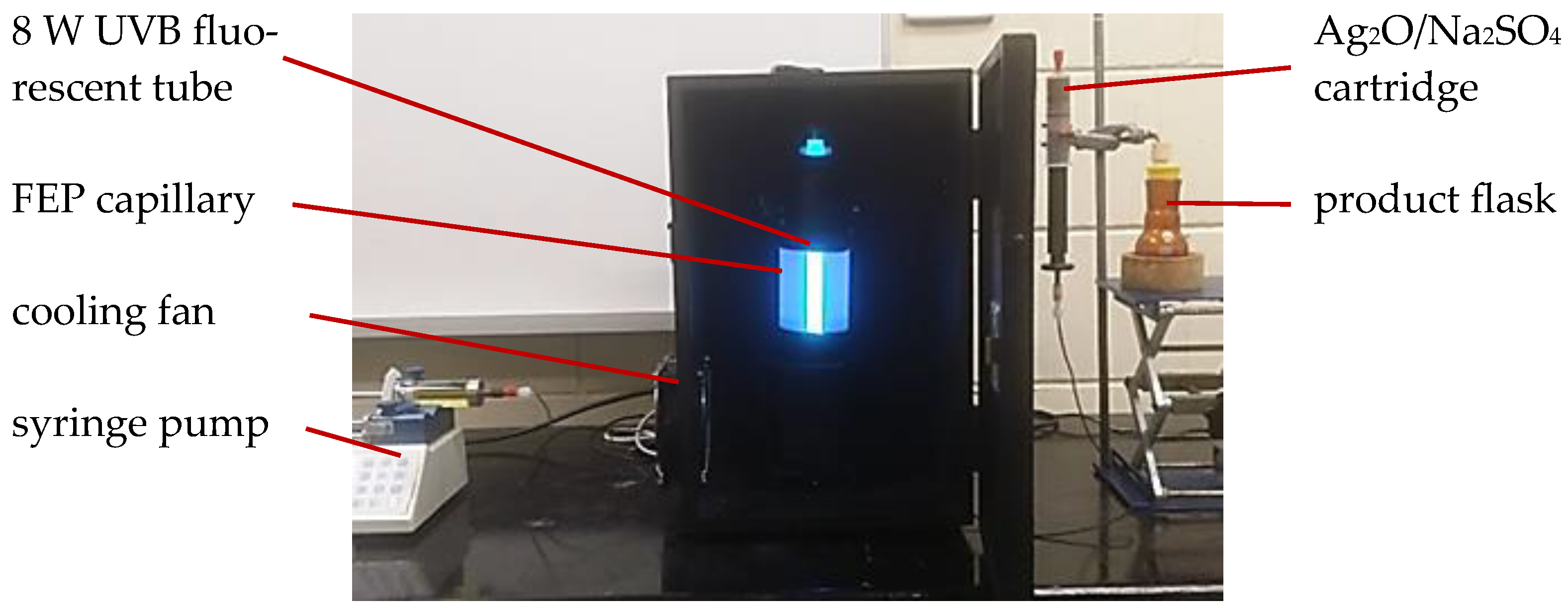
2.2. General Procedure for Photoacylations Under Continuous-Flow Conditions
2.3. General Procedure for Tandem Photoacylation–Oxidation Reactions
2.4. Spectroscopic Details
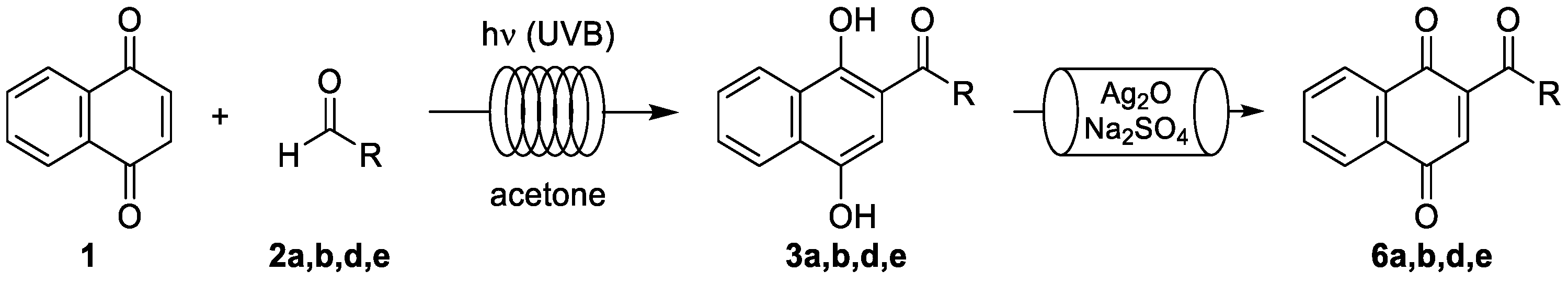
3. Results and Discussion
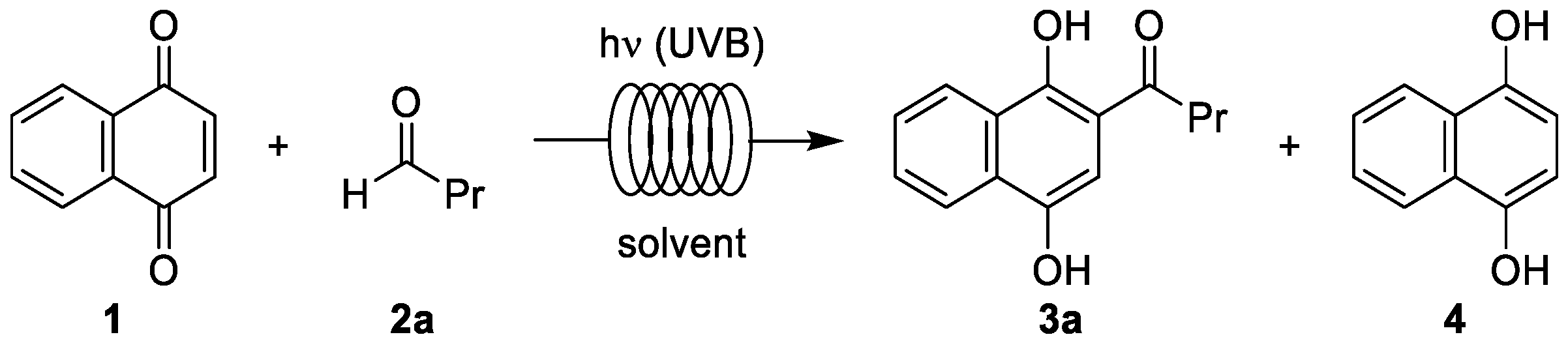
3.1. Photoacylations Under Continuous-Flow Conditions
3.1.1. In-House Capillary Reactor
3.1.2. Optimization Study
3.1.3. Photoacylations with Other Aldehydes
3.2. Tandem Photoacylation–Oxidation Reactions Under Continuous-Flow Conditions
3.2.1. In-House Tandem Capillary Reactor
3.2.2. Tandem Photoacylation–Oxidation Reactions with Selected Aldehydes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jha, R.K.; Kumar, S. Direct Functionalization of para-Quinones: A Historical Review and New Perspectives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 27, e202400535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mone, N.S.; Bhagwat, S.A.; Sharma, D.; Chaskar, M.; Patil, R.H.; Zamboni, P.; Nawani, N.N.; Satpute, S.K. Naphthoquinones and Their Derivatives: Emerging Trends in Combating Microbial Pathogens. Coatings 2021, 11, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, E.S.; Tajbakhsh, A.; Iranshahy, M.; Asili, J.; Kretschmer, N.; Shakeri, A.; Sahebkar, A. Naphthoquinone Derivatives Isolated from Plants: Recent Advances in Biological Activity. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 2019–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, L.I.; Leyva, E.; García de la Cruz, R.F. Naphthoquinones: More than Natural Pigments. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Farm. 2011, 42, 6–17. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.; Lee, G.; Cho, E.J. Visible Light Induced Reactions of Quinones. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2024, 45, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Suzuki, K. Photoredox Reactions of Quinones. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 15955–15964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lucas, N.C.; Ferreira, A.B.B.; Netto-Ferreira, J.C. Fotoquímica de Naftoquinonas. Rev. Virtual Quim. 2015, 7, 403–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, T. Photo and Radiation Chemistry of Quinones. In Proceedings of Indian National Science Academy A; Sapre, A.V., Mukherjee, T., Mittal, J.P., Eds.; Indian National Science Academy: New Delhi, India, 2000; Volume 66, pp. 239–265. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, K.; Osuka, A. Recent Advances in the Photochemistry of Quinones. In The Chemistry of Quinonoid Compounds; Patai, S., Rappaport, Z., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Volume 2, Part 1, Chapter 13; pp. 759–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, L.J.; Lewis, W.; Moody, C.J. Solar Photochemistry: Optimisation of the Photo Friedel–Crafts Acylation of Naphthoquinones. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2830–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benites, J.; Rios, D.; Díaz, P.; Valderrama, J.A. The Solar-chemical Photo-Friedel–Crafts Heteroacylation of 1,4-Quinones. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelgemöller, M.; Mattay, J. The “Photochemical Friedel-Crafts Acylation” of Quinones: From the Beginnings of Organic Photochemistry to Modern Solar Chemical Applications. In CRC Handbook of Organic Photochemistry and Photobiology, 2nd ed.; Horspool, W.M., Lenci, F., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; Chapter 88; pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benites, J.; Valderrama, J.A.; Contreras, Á.; Enríquez, C.; Pino-Rios, R.; Yáñez, O.; Calderon, P.B. Discovery of New 2-Phenylamino-3-acyl-1,4-naphthoquinones as Inhibitors of Cancer Cells Proliferation: Searching for Intra-Cellular Targets Playing a Role in Cancer Cells Survival. Molecules 2023, 28, 4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, G.; Benites, J.; Reyes, J.S.; Marcoleta, A.E.; Valderrama, J.A.; Lagos, R.; Monasterio, O. Inhibition of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis FtsZ Polymerization and Bacillus subtilis Growth by Dihydroxynaphtyl Aryl Ketones. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Idhayadhulla, A.; Lee, Y.R.; Wee, Y.-J.; Kim, S.H. Anti-tyrosinase, Antioxidant, and Antibacterial Activities of Novel 5-Hydroxy-4-acetyl-2,3-dihydronaphtho[1,2-b]furans. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 86, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedroza, D.A.; De Leon, F.; Varela-Ramirez, A.; Lema, C.; Aguilera, R.J.; Mito, S. The cytotoxic Effect of 2-Acylated-1,4-naphthohydroquinones on Leukemia/Lymphoma Cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Miyagi, Y. Photo-induced Condensation Reaction of p-Quinones with Aldehydes. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1974, 47, 1303–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albini, A. Norrish’ Type I and II Reactions and their Role in the Building of Photochemical Science. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2021, 20, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelgemöller, M.; Schiel, C.; Fröhlich, R.; Mattay, J. The “Photo-Friedel-Crafts Acylation” of 1,4-Naphthoquinones. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 2002, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, J.; van Vuuren, P.J.; Venter, D.P. Photodimerization. I. The syn and anti-Photodimers of 1,4-Naphthoquinone. J. Org. Chem. 1968, 33, 464–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protti, S.; Ravelli, D.; Fagnoni, M. Introduction to Photochemistry for the Synthetic Chemist. In Enabling Tools and Techniques for Organic Synthesis: A Practical Guide to Experimentation, Automation, and Computation; Newman, S.G., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Chapter 2; pp. 37–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, P.; Evans, R.C.; Burrows, H.D. The Photochemical Laboratory. In Applied Photochemistry; Evans, R.C., Douglas, P., Burrows, H.D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; Chapter 14; pp. 467–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochet, C.G. On the Sustainability of Photochemical Reactions. Chimia 2019, 73, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelli, D.; Protti, S.; Fagnoni, M.; Albini, A. Visible Light Photocatalysis. A Green Choice? Curr. Org. Chem. 2013, 17, 2366–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeberg, B.L.; Sagandira, M.B.; Sagandira, C.R.; Watts, P. Paradigm Shift in Medicinal Products Synthesis: Continuous Flow Technology. Tetrahedron 2024, 168, 134333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, A.I.; García-Lacuna, J.; Griffiths, O.M.; Ley, S.V.; Baumann, M. Continuous Flow Synthesis enabling Reaction Discovery. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 4618–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfano, A.I.; Pelliccia, S.; Rossino, G.; Chianese, O.; Summa, V.; Collina, S.; Brindisi, M. Continuous-Flow Technology for Chemical Rearrangements: A Powerful Tool to Generate Pharmaceutically Relevant Compounds. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, V.; Singh, P.P.; Sinha, S.; Singh, P.K.; Kumar, D. Continuous-Flow Photochemistry: The Synthesis of Marketed Pharmaceutical Compounds. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202405020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, T.; Kasakado, T.; Hyodo, M.; Ryu, I. Improved Efficiency of Photo-induced Synthetic Reactions Enabled by Advanced Photo Flow Technologies. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2022, 21, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politano, F.; Oksdath-Mansilla, G. Light on the Horizon: Current Research and Future Perspectives in Flow Photochemistry. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2018, 22, 1045–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, T.H. Flow Photochemistry as a Tool in Organic Synthesis. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 16952–16974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelgemöller, M.; Hoffmann, N.; Shvydkiv, O. From ‘Lab & Light on a Chip’ to Parallel Microflow Photochemistry. Austr. J. Chem. 2014, 67, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Roth, P. Flow photochemistry—From Microreactors to Large-scale Processing. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2023, 39, 100897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, M.A.; Guo, Z.; Junk, P.J.; Oelgemöller, M. [2+2]-Photocycloadditions of 1,4-Naphthoquinone Under Batch and Continuous-Flow Conditions. Molecules 2024, 29, 5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Rajesh, V.M.; Ravva, M.K.; Sen, S. Optimization of Blue LED Photo-Flow Synthesis in Continuous Flow Reactors Using Design of Experiments (DoE): Efficient Synthesis of Diverse Diaryl Ketones. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 501, 157657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, M.A.; Mumtaz, S.; Hunter, R.L.; Wall, D.; Belluau, V.; Robertson, M.J.; Oelgemöller, M. Continuous-Flow Photochemical Transformations of 1,4-Naphthoquinones and Phthalimides in a Concentrating Solar Trough Reactor. Austr. J. Chem. 2020, 73, 1149–1157, Erratum in Austr. J. Chem. 2020, 73, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marteaua, C.; Ruyffelaerea, F.; Aubrya, J.-M.; Penvernea, C.; Favier, D.; Nardello-Rataj, V. Oxidative Degradation of Fragrant Aldehydes. Autoxidation by Molecular Oxygen. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 2268–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, S.; Robertson, M.J.; Oelgemöller, M. Continuous Flow Photochemical and Thermal Multi-step Synthesis of Bioactive 3-Arylmethylene-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindolin-1-ones. Molecules 2019, 24, 4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helferich, B.; Klein, W. Zur Synthese von Disacchariden IV. Zwei Tetra-acetyl-β-d-glucosen. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1926, 450, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, G.A.; Kirihara, M. Quinone Photochemistry. A General Synthesis of Acylhydroquinones. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 3256–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.K.; Upadhyay, A.; Kanika Jain, S.; KA, N.; Kumar, S. Light-Driven Carbon−Carbon Coupling of α-sp3−CH of Aliphatic Alcohols with sp2−CH Bond of 1,4-Naphthoquinones. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 7605–7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hase, J.; Nishimura, T. Antibacterial Properties of Naphthoquinones. I. Syntheses and Antibacterial Properties of Acylnaphthoquinones. J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 1955, 75, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Muraoka, M.; Naruta, Y. Photo-oxygenation of Alkenoyl-1,4-quinones by Atmospheric Oxygen. Formation of Stable Cyclic Peroxides. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1980, 24, 1282–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batley, G.E. Use of Teflon Components in Photochemical Reactors. Anal. Chem. 1984, 56, 2261–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichs, F.; Murphy, B.; Nayrat, D.; Ahner, T.; Funke, M.; Ryan, M.; Lex, J.; Mattay, J.; Oelgemöller, M. An improved Procedure for the Photoacylation of 1,4-Naphthoquinone with Aliphatic Aldehydes. Synlett 2008, 20, 3137–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, A.; Monet, A.; Yaseen, M.; Hermanns, M.I.; Oelgemöller, M. Synthesis of Acylated Naphthohydroquinones through Photo-Friedel-Crafts Acylation and Evaluation of their Antibiotic Potential. Photochem 2024, 4, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sabio, J.C.; Hartman, R.L. When Solids Stop Flow Chemistry in Commercial Tubing. J. Flow Chem. 2015, 5, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernerova, M.; Hudlicky, T. On the Practical Limits of Determining Isolated Product Yields and Ratios of Stereoisomers: Reflections, Analysis, and Redemption. Synlett 2010, 18, 2701–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Venkataraman, B. Hydrogen Abstraction from Solvents by the Triplet State of p-Benzoquinone: A Time-resolved Electron Paramagnetic Resonance and Laser Flash Photolysis Study. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2005, 31, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givens, R.S.; Levi, N. The Photochemistry of Organic Acids, Esters, Anhydrides, Lactones and Imides. In The Chemistry of Acid Derivatives; Supplement, B., Patai, S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Part 1, Chapter 11; pp. 641–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, C.; Fischer, U.; Hungerbühler, K. What is a Green Solvent? A Comprehensive Framework for the Environmental Assessment of Solvents. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalti, M.; Credi, A.; Prodi, L.; Gandolfi, M.T. Handbook of Photochemistry, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bunce, N.J.; Ridley, J.E.; Zerner, M.C. On the Excited States of p-Quinones and an Interpretation of the Photocycloaddition of p-Quinones to Alkenes. Theor. Chim. Acta 1977, 45, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, G.A.; Liu, P. Benzophenone-Mediated Conjugate Additions of Aromatic Aldehydes to Quinones. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 7723–7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, C.A.; Sifniades, S. Isomerization as a Primary Process in the Photolysis of Crotonaldehyde. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1962, 84, 4606–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Fuse, S. Recent Advances in the Integrated Micro-flow Synthesis Containing Photochemical Reactions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruit, C.J.P. Carbonyl-substituted Naphthoquinones. Part I. Methyl Ketones Unsubstituted in the Side Chain. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 1947, 66, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derikvand, F.; Bigi, F.; Maggi, R.; Piscopo, C.G.; Sartori, G. Oxidation of Hydroquinones to Benzoquinones with Hydrogen Peroxide using Catalytic Amount of Silver Oxide under Batch and Continuous-flow Conditions. J. Catal. 2010, 271, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, K.; Baumann, M. Scalability of Photochemical Reactions in Continuous Flow Mode. J. Flow Chem. 2021, 11, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.; Josland, S.; Moore, J.; Guthrie, D.; Robertson, M.J.; Oelgemöller, M. Rapid Photochemical Reaction Studies under Continuous-flow Conditions in the Vapourtec UV-150 Reactor—A Technical Note. Curr. Org. Chem. 2018, 22, 2501–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Entry | Solvent | Residence Time (min) | Conversion (%) 1 | Yield of 3a (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | acetonitrile | 25 | 82 | 70 |
| 2 | acetonitrile | 50 | 87 | 78 |
| 3 | acetonitrile | 70 | 90 | 86 |
| 4 | acetonitrile | 100 | 92 | 90 |
| 5 | acetone | 70 | 96 | 88 |
| 6 | chloroform | 70 | 95 | 90 |
| 7 | tert-butyl alcohol | 70 | 92 (22 3) | 55 |
| 8 | ethyl acetate | 70 | 91 (16 3) | 53 |
| Entry | R | Yield of 3 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | C3H7 | 90 (a) 1 |
| 2 | C2H5 | 71 (b) 1 |
| 3 | C6H13 | 75 (c) 1 |
| 4 | C11H23 | 34 (d) 2/64 3 |
| 5 | E-CH3CH=CH | 72 (e) 1 |
| 6 | p-MeC6H4 | 66 (f) 2/12 (5) 2,4 |
| 7 | p-ClC6H4 | 80 (g) 1 |
| 8 | 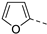 | 30 (h) 2 |
| Entry | R | Yield of 6 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | C3H7 | 94 (a) 1 |
| 2 | C2H5 | 76 (b) 1 |
| 3 | C11H23 | 15 (d) 1/61 2 |
| 4 | E-CH3CH=CH | 75 (e) 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yaseen, M.A.; Oelgemöller, M. Photochemical Acylation of 1,4-Naphthoquinone with Aldehydes Under Continuous-Flow Conditions. Organics 2025, 6, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6010009
Yaseen MA, Oelgemöller M. Photochemical Acylation of 1,4-Naphthoquinone with Aldehydes Under Continuous-Flow Conditions. Organics. 2025; 6(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleYaseen, Madyan A., and Michael Oelgemöller. 2025. "Photochemical Acylation of 1,4-Naphthoquinone with Aldehydes Under Continuous-Flow Conditions" Organics 6, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6010009
APA StyleYaseen, M. A., & Oelgemöller, M. (2025). Photochemical Acylation of 1,4-Naphthoquinone with Aldehydes Under Continuous-Flow Conditions. Organics, 6(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6010009