1. Introduction
Although palm oil waste products have been used for fuel production, they have previously been used entirely for biodiesel (fatty acid methyl ester (FAME)) or biogas [
1]. To our knowledge, this is the first time that thermal transformation of this waste material has been used to make a mixture of hydrocarbons in the diesel fuel, gas oil, or jet fuel boiling point range. Diesel fuel consists primarily of hydrocarbons in the 10–19 carbon chain range. It is typically about 64% aliphatic hydrocarbons, about 1–2% olefins, and up to 35% aromatic compounds. Kerosene consists mostly of alkanes with 10–16 carbon chains, as well as cycloalkanes and a small portion of aromatics. The process described in this paper is comparable to what has been done with brown grease, a major product of the sewage treatment industry. Unlike brown grease, whose product distribution is sensitive to the temperature profile, pre-purification, and other factors, the palm oil fats, oils, and greases (FOG) transform to a consistent mixture of hydrocarbons in a simple reactor heated to 325–350 °C. Hydrocarbon fuels are superior to biodiesel in some applications, and the two are often blended to obtain the optimal properties and cost.
Malaysia, being one of the world’s largest producers of palm oil and the world’s largest exporter of palm oil, produced 19.92 million tons in 2017, and occupied a total plantation land of 5.81 million hectares. This production resulted in total exports of oil palm products on a rising trend and hit 23.97 million tons in 2017 [
2]. The fresh fruit bunches (FFB) harvested from oil palm estates can be processed into a vast variety of useful products such as crude palm oil (CPO), palm kernel oil (PKO), and palm kernel cake (PKC). The yield of the CPO is further enhanced by the pressing of empty fruit bunches (EFB) which will also generate the pressed liquor as well as the press cake as the production line by-products. The CPO and PKO have commercial value and are collected. In contrast, the EFB pressed liquor does not have sufficient commercial value and is often dumped into collection ponds, where it causes severe pollution problems. Although the production of CPO and PKC has matured in the industry nowadays, there are still some wastes generated from the mills in common and left unsolved. The continuous generation of EFB pressed liquor during the production of CPO without proper treatment or disposal has caused serious problem to the mill operation. In addition, the untreated waste liquor also leaves heavy pollution to the surroundings and environment.
Brown grease, on the other hand, which usually contains 90% of saturated and unsaturated free fatty acid (FFA), can undergo pyrolysis to a kerosene-like mixture of hydrocarbons under relatively mild conditions without addition of an external catalyst [
3,
4]. The term brown grease refers to the greasy semi-solid material that collects in sewer systems and sewage treatment plants, which consists primarily of fatty acids and their calcium salts. The similarity in chemical composition suggests the possibility of some similarity in pyrolysis reactions between brown grease and palm oil waste products. Some studies discovered that the brown grease reaction appeared to be a simple metal catalyzed decarboxylation of a monocarboxylic acid [
5,
6,
7,
8]. Equilibration, hydrogen transfer, and coupling of alkyl radicals formed by decarboxylation could explain the chemistry behind the formation of alkane-alkene mixture. Further investigation showed that brown grease contains traces of many metals, particularly iron, and Fe (III) has been shown to promote some of the fatty acid reactions which ultimately produce hydrocarbons [
9]. The same study used model compounds palmitic acid, oleic acid, and a 1:1 mixture of the two. The latter generated similar but not identical results to the reaction of brown grease at the same temperatures. Optimal product formation requires good temperature control, and rapid spurts of endothermic reactions of fatty acids often make temperature control difficult [
10].
Palm oil and other feed stocks are suitable for conversion to conventional biodiesel, which consists of the methyl ester of fatty acids [
11,
12,
13]. One such industrial process uses a plug flow reactor with a solid acid catalyst [
14]. However, the low cost of petroleum diesel in Malaysia makes palm oil biodiesel non-cost competitive with petroleum diesel. Thus, this work uses free or ultra-low-cost waste byproducts to make this green diesel more cost competitive. Furthermore, palm oil-derived biodiesel can lead to pour point issues in colder temperatures, and thus is often blended with petroleum diesel [
15].
The successful conversion of the EFB oil and grease into hydrocarbon fuel will be a breakthrough in the palm oil industry in Malaysia and the regional countries. This effort will not only help to decrease the waste generated from the mills significantly (which is causing serious environmental pollution nowadays), but will also provide an alternative fuel source to the mill owners as well as to the country. The subject of this investigation is to determine whether the lowest grade of palm oil and grease, produced from EFB pressed liquor, can be converted to a hydrocarbon fuel and thus diverted from acid waste ponds.
2. Materials and Methods
The oil and grease used in this study were obtained from the palm oil empty fruit bunches (EFB) pressed liquor, obtained from United Oil Palm Mill in Nibong Tebal, Malaysia. This crude material was separated by centrifugation into 4 distinct layers. The upper, least dense layer was crude palm oil (CPO), followed by a semi-solid layer of debris. The third layer was water, which was discarded. The lowest layer was a semi-solid sludge which contained crude grease. The EFB grease was obtained by hexane extraction of this bottom layer. EFB oil and EFB grease obtained averaged 30% and 20% of the total volume, respectively. The caloric value of the EFB oil and EFB grease was 2.5 and 2.7 kJ/g, respectively. The FFA content is variable with the source and age, but titration of the samples in this study showed the FFA content of the oil as 12.50%, and of the grease as 8.98%.
The reactor used for this study was a 3-neck flask fitted with a thermocouple probe connected to a temperature controller, and a distillation head and condenser. Unlike brown grease, which requires a pressure vessel for optimal reaction, this feed stock produces a satisfactory product at atmospheric pressure. The thermal reaction experiments were performed in 3 sets for each starting material and set of conditions: A control experiment with no added catalyst, ferric sulfate hydrate catalyst (Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), and molecular sieves catalyst (Aldrich, 3A, beads, 8–12 mesh size). The oil and EFB grease were dried by use of a toluene azeotropic distillation (75 mL toluene added per 100 g oil/grease), and the toluene-water azeotrope distilled until the temperature of the reaction flask reached 200 °C. Temperature control in the thermal reactions was maintained by a J-Kem model 310 temperature controller and thermocouple probe, connected to a heating mantle.
For each experiment, approximately 100 g of EFB oil was added to a 2-neck round bottom flask of 250 mL, and the mass of oil determined to the nearest 0.1 mg. For the EFB grease reactions, these reactions were scaled to between 20 and 50 g, due to the smaller quantities of grease available. For the catalyzed reactions, 0.25 g of ferric sulfate or molecular sieves was added, followed by 75 mL toluene. A Claisen adapter was fitted to the flask through which the thermocouple probe was inserted, and the other arm was fitted with a distillation head and condenser. Partial reflux was achieved by packing the Claisen adapter with ceramic pieces, thus preventing premature distillation of fatty acids and partly reacted starting materials. The water-toluene azeotrope with the excess toluene was removed by distillation. The flask was then heated to 350 °C for 48 h. At 12-h intervals two drops of the reaction flask contents were withdrawn for gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GCMS) analysis. Separate analysis of the distillate is necessary when the reaction is performed at atmospheric pressure, as the more volatile products distill out of the flask during the course of the reaction.
Gas chromatography analysis was performed on a Shimadzu model GCMS-QP2010 Plus with a mass sensitive detector. GCMS has been successfully used for quantitative determination of n-alkanes [
16]. The peak assignment was based on the mass spectra library, and the peak pattern confirmed by analogy to samples from brown grease pyrolysis, which generate many of the same compounds as the palm oil residue. The column was SLB-5MS with a total length of 30 m, a diameter of 0.25 mm, and 0.25 μm thickness. Samples were prepared with 2 drops of distillate or reaction flask contents in 1.5 mL dichloromethane in a 2 mL GC vial. A column temperature ramp profile of 50 °C for 3 min, 12 degrees/min to 250 °C for 5 min, 5 degrees/min to 300 °C for 4 min was used, with the injector temperature at 200 °C. The helium carrier gas had a column flow rate of 1.50 mL/min at a column pressure of 131.1 kPa. The total run time for each chromatogram was 39 min.
The EFB oil thermal transformation experiments were done in three sets of two trials each. Set 1 was a control experiment with no added catalyst. Set 2 used 0.25 g ferric sulfate dihydrate per 100 g of oil, in analogy to the catalytic effect of that salt on the fatty acids of brown grease. Set 3 used 0.25 g molecular sieves per 100 g of oil. That material may act as a Lewis acid catalyst, as well as provide a solid surface where reaction can occur. Each reaction flask was heated to 350 °C with boiling chips and samples taken from the reaction flask at 12-h intervals for analysis. Distillate was collected in two fractions. The initial distillate was collected after 12 h, and referred to as distillate-12 in
Table 1 and Table 5. The final distillate was collected between 12 h and the final reaction time of 48 h, and is referred to as distillate-48. The percentage of water is the water removed by the initial azeotropic distillation, plus any additional water that separated from the distillates. The percentage of water, initial distillate, final distillate, and bottoms are shown in
Table 1, with about 8–12% of the original sample mass lost as gas.
3. Results and Discussion
Reaction times of 48 h were required for complete rection and distillation of the more volatile components of the product mixture. Comparing the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions in
Table 1, it is seen that with molecular sieves, the distillate yield is slightly higher with correspondingly less material in the bottoms after 48 h. This set also evolved slightly less water, possibly as a result of entrainment by the molecular sieves.
Table 2,
Table 3 and
Table 4 show the percentage of hydrocarbons, fatty acids, ketones, and other compounds in the reaction flask (bottoms) and distillates at each sampling time. For each reaction set, analysis of the flask contents at 12 h showed the reaction to be more than 90% complete. However, significant amounts of fatty acids were found in the first distillate fraction. These were mostly C8–C10 fatty acids, although some C16 fatty acids were also found in the distillate. This indicates that fatty acid fragmentation reactions have occurred, similar to those in brown grease. It is not known whether these reactions occurred in the free fatty acid; in the triglycerides, followed by hydrolysis to the free fatty acid; or both. Also found in some of the distillate-12 fractions were siloxanes, apparently from thermal degradation of the silicone grease joint lubricant. In all 3 sets, the final distillate was more than 97% hydrocarbons. Both in the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions, the pyrolysis was essentially complete by 24 h, with little improvement at longer reaction times.
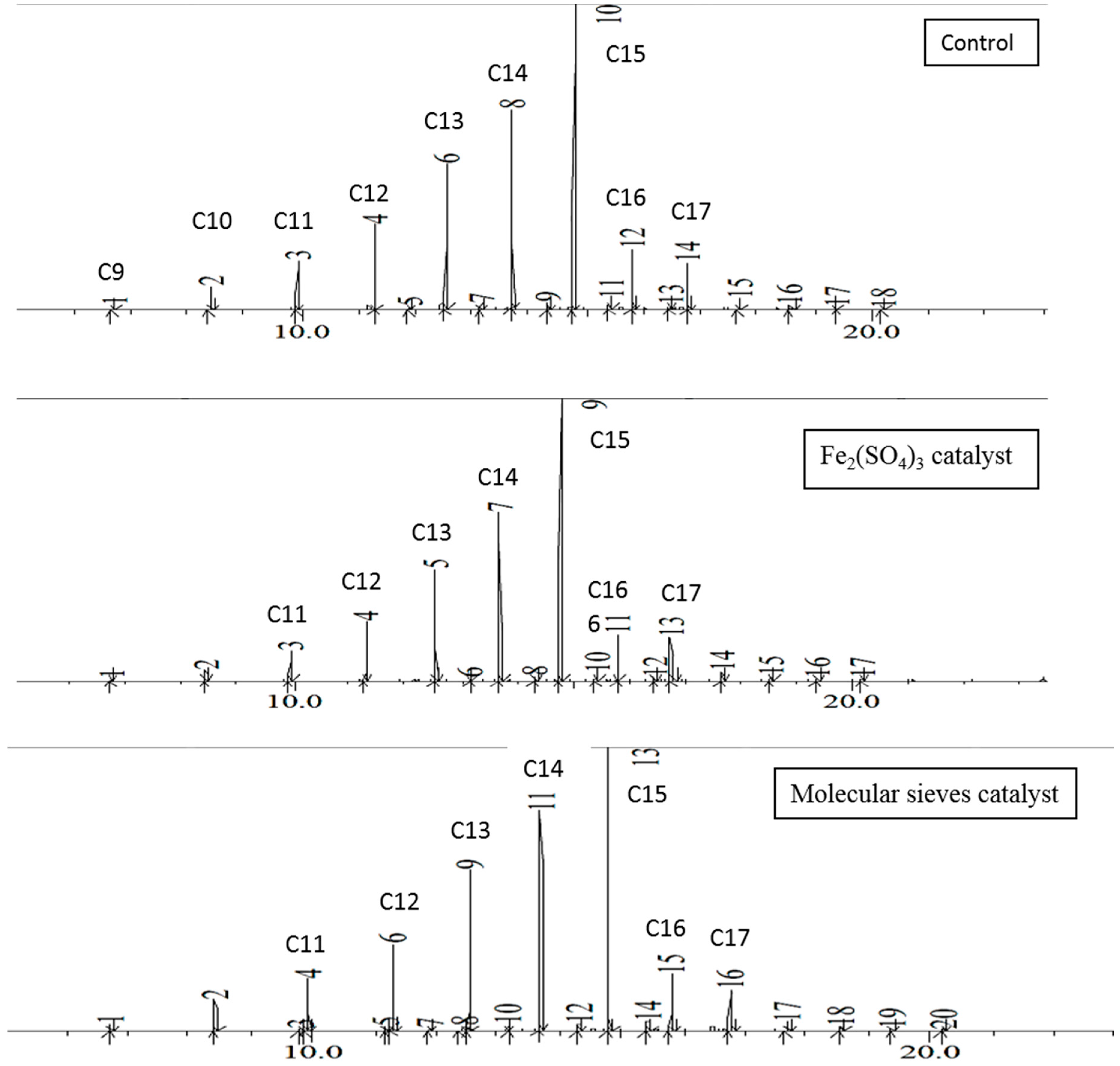
In each set of experiments the hydrocarbon distribution after 48 h was quite similar, as illustrated in
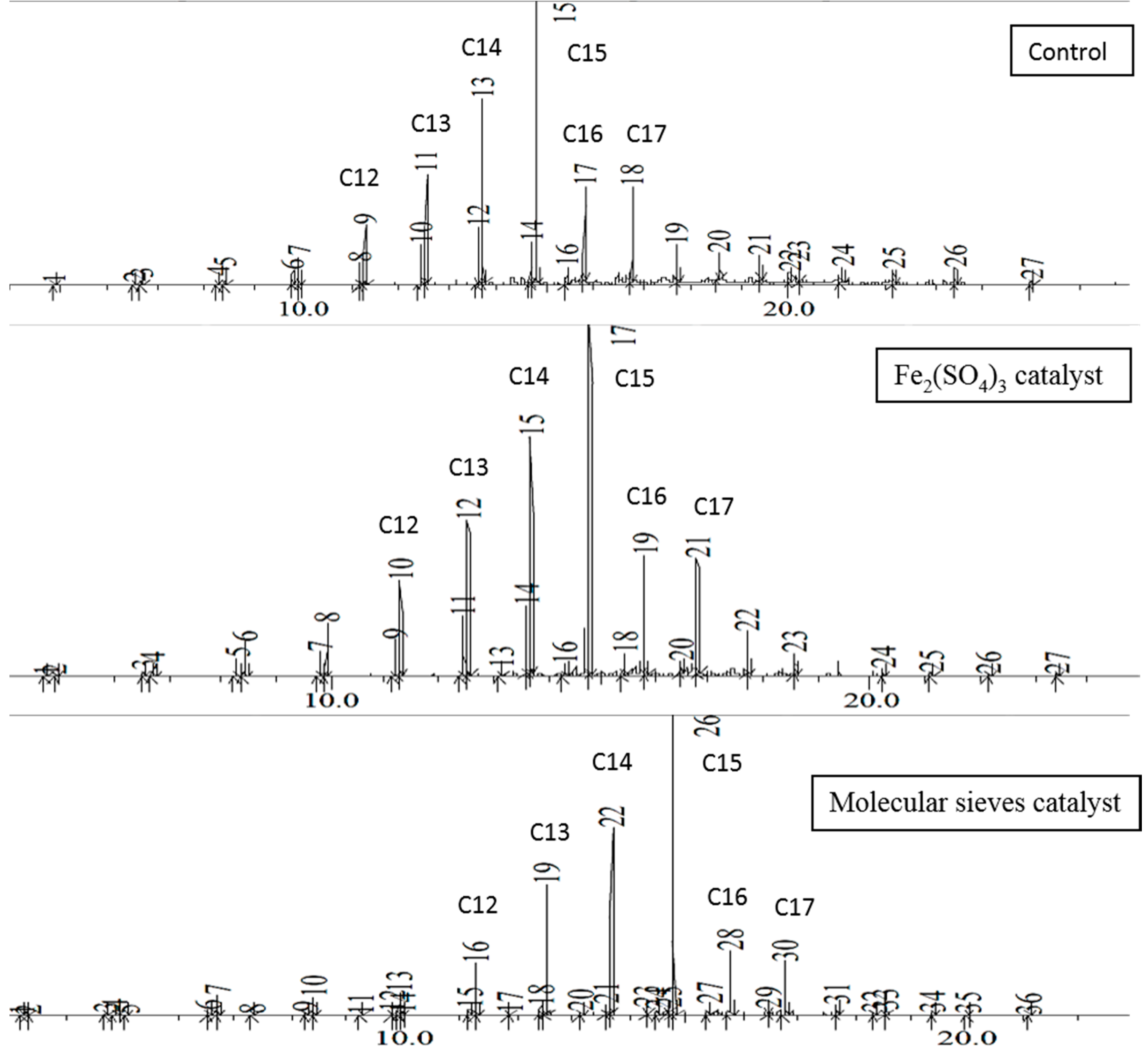
Figure 1. The first major chromatogram peak corresponds to decane, although traces of lighter hydrocarbons may be present. The percentage of each component increases with the length of the carbon chain and peaks at pentadecane, then rapidly decreases at longer chain lengths. Essentially no hydrocarbons of greater than C25 are present. The 48-h distillates follow the same trend, as shown in
Figure 2. This palm oil thermal reaction shows one significant advantage over brown grease in that very little ketone byproduct is formed. In contrast, brown grease forms significant amounts of palmitone, depending on the exact reaction conditions, as well as other lower molar mass ketones resulting from thermal degradation of palmitone.
From the results presented in
Table 2,
Table 3 and
Table 4 as well as chromatograms shown in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2, it was observed that both ferric sulfate and molecular sieves utilized have slight influence on the products distribution on the chromatograms. The major peaks are still similar to the control set, ranging between hydrocarbons from C11 to C17. The role of ferric sulfate and molecular sieves are Lewis acids in the thermal transformation of the EFB oil. The percentage of the predominant product, pentadecane, was estimated from the peak heights and peak areas. In the EFB oil flask contents, it ranged from 30–45%. The control and molecular sieves samples were each about 30% pentadecane, while the higher amount was found with the ferric sulfate-catalyzed reaction. Less pentadecane was found in the distillates, as it is less volatile than the lower molar mass components.
In the EFB oil distillates at 48 h, the product distribution in chromatograms are mainly C12 to C17, with more minor peaks compared to that of EFB oil in
Figure 1. Ferric sulfate is able to catalyze FAME formation from FFA and methanol via inter-esterification reaction [
17]. Hence in this reaction, it is believed to catalyze the formation of hydrocarbons, with additional minor products such as FFA and ketones. For the molecular sieves, it was observed to speed up the reaction with similar product distribution. However, there are more minor products formed alongside with the major hydrocarbon, which might be some alkenes other than FFA and ketones. This work will need further investigation in the future.
The same experiments were repeated with EFB grease, and the yields of each component are reported in
Table 5. The water contents and 12-h distillate yields were comparable to the EFB oil thermal transformation. In contrast, less 48-h distillate was obtained from the grease and slightly more of the original mass was lost as gas.
Table 6,
Table 7 and
Table 8 show the percentage of hydrocarbons, fatty acids, ketones, and other compounds in the reaction flask and distillates at each sampling time. Once again, the pyrolysis reactions were essentially complete after 12 h both with and without catalysts. The 12-h distillate contained significant amounts of fatty acids, which were largely C8–C10 acids, again indicating the thermal degradation of longer chain fatty acids.
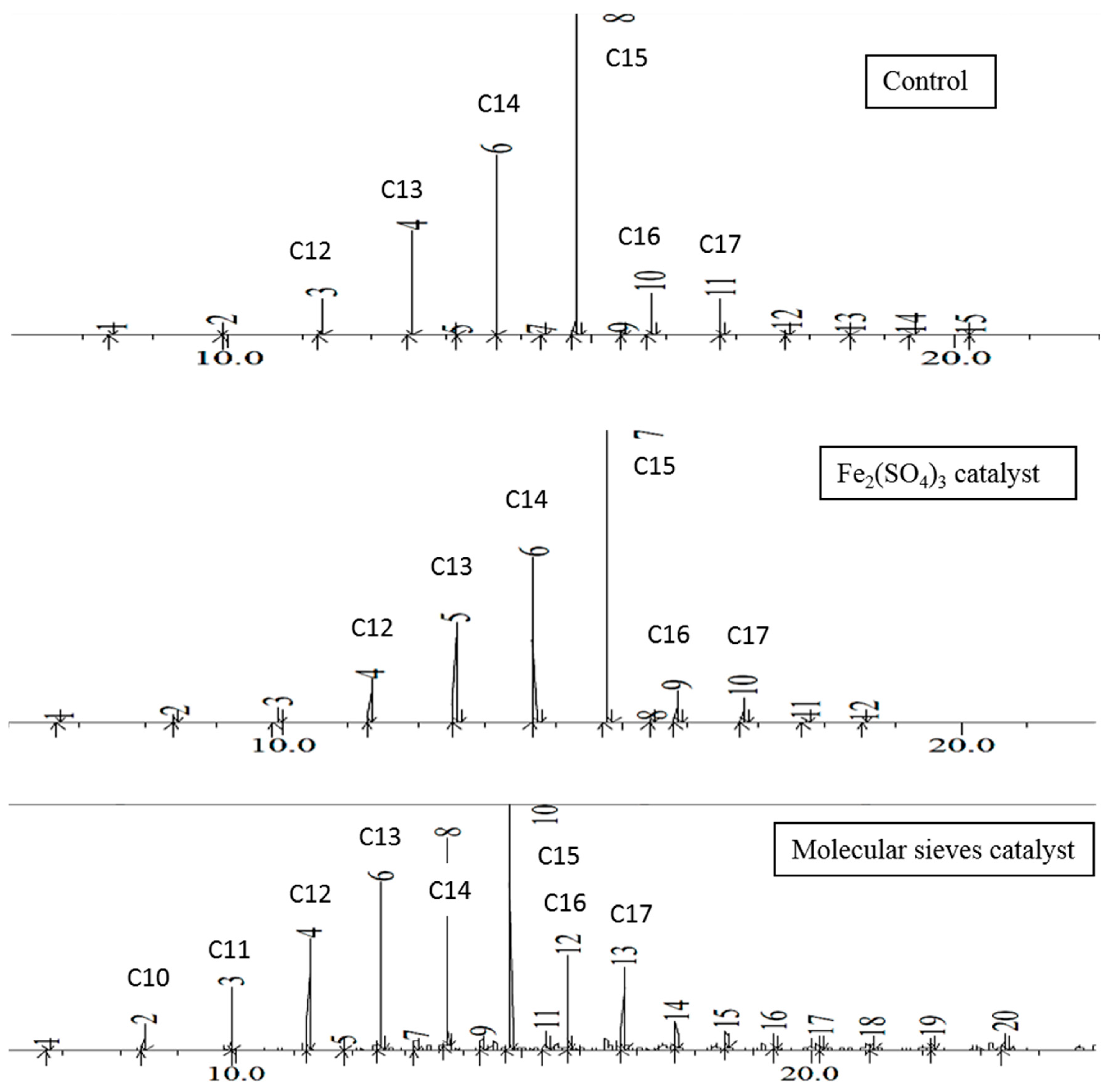
Examination of the chromatograms for the EFB grease thermal transformation shows a similar pattern to the EFB oil, as hydrocarbon contents increase from decane to pentadecane, and then drop sharply. This is illustrated in
Figure 3. In the control and ferric sulfate experiments, few if any hydrocarbons longer than C20 were observed in the flask at 48 h. With molecular sieves, hydrocarbon chains up to C25 were observed in small quantities. With the EFB grease, the reaction flask contained about 44% pentadecane with the control and ferric sulfate experiments, and about 25% with molecular sieves. Once again, the distillate contained a higher portion of the more volatile components. Although these heavy hydrocarbons can be used as fuel oils, they are less valuable than the lighter hydrocarbons, and thus, the use of molecular sieves is disadvantageous for this thermal transformation.
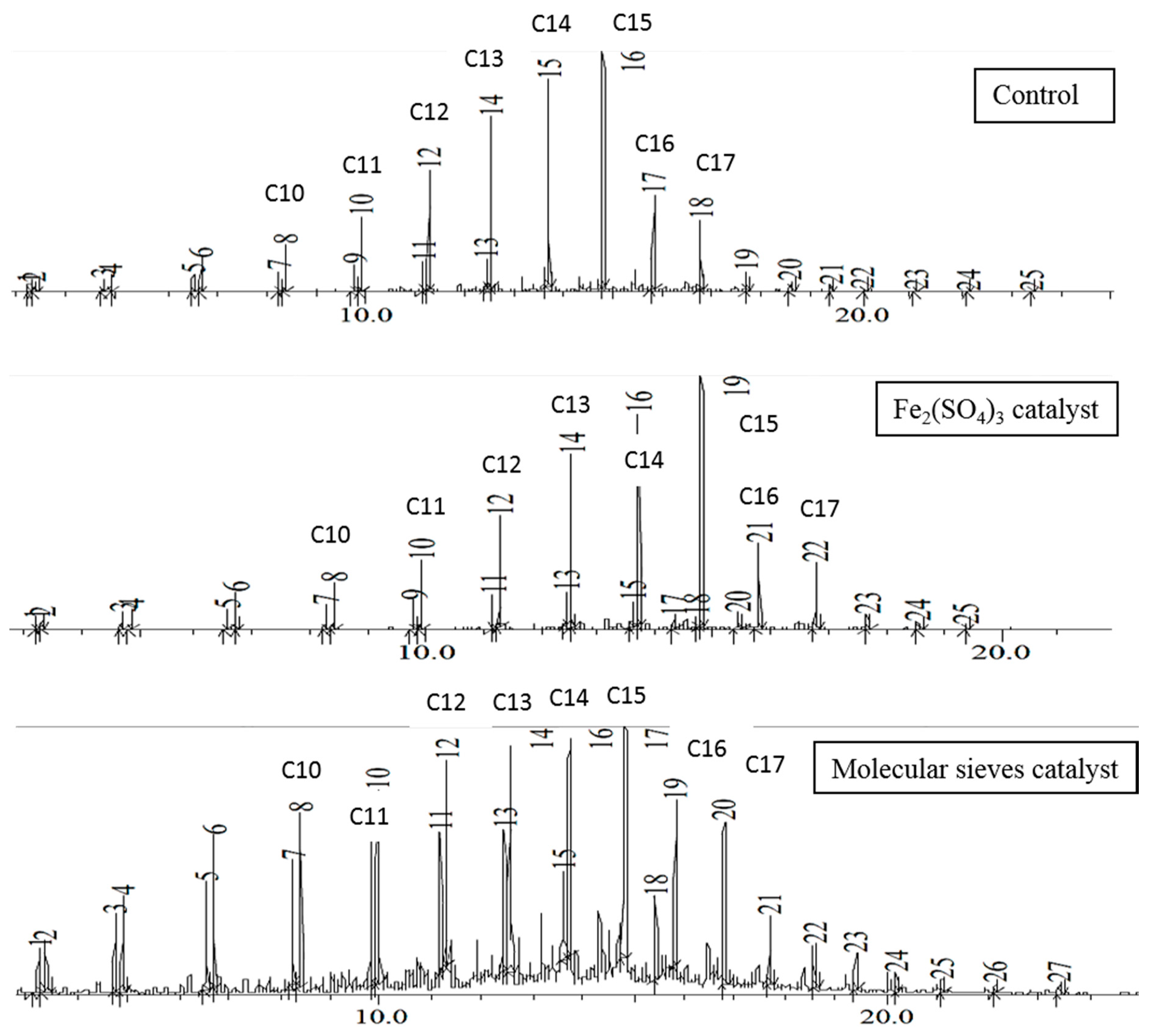
Figure 4 shows the chromatograms of the EFB grease 48-h distillate. In the control and ferric sulfate catalyzed reactions, the product distribution in the distillate was similar to that of EFB oil, except there was a slightly wider range of products on either side of the C15 peak, and some lower molar mass alkenes were present. With molecular sieves, the chromatograms were quite similar to those obtained from brown grease reaction, with hydrocarbons being formed from C7 to at least C25, and large quantities of alkenes from C7 to about C14. Use of molecular sieves did increase the alkene content of the distillate compared to the control. This was also observed in brown grease transformation under gradual temperature ramp conditions, although other heating profiles resulted in different distributions of hydrocarbon products.
4. Conclusions
FOG from EFB pressed liquor are a potential source of hydrocarbons in the kerosene and diesel fuel range. EFB oil and EFB grease undergo thermal transformation reactions, as described below, proceeded with better temperature control, as the set temperature of 350 °C was maintained within ±10 °C. This may be the result of the higher triglyceride content of palm oils and greases, or the lack of some brown grease impurities which can interfere with radical chain reactions. The similarity between this raw material and brown grease results in similarities in the product distribution. Like brown grease, the transformation takes place without addition of an external catalyst. However, EFB pressed liquor is superior to brown grease in that far smaller quantities of palmitone and other high molar mass ketones are formed, unless brown grease impurities are removed in a separate processing step. Furthermore, optimal reaction of brown grease requires a pressure reactor, while this feedstock gives a satisfactory product at atmospheric pressure. The EFB oil reaction flask contents consisted primarily of alkanes in the diesel fuel and kerosene range (10–19 carbon chains) in the control and ferric sulfate experiments, and a slightly broader range with molecular sieves. The distillate was similar, but with some small alkene peaks adjacent to the n-alkanes, and small amounts of FFA. Results were similar with the EFB grease, with the flask contents entirely within the kerosene range of hydrocarbons for the control and ferric sulfate reactions. Like the EFB oil, addition of molecular sieves broadened the range of hydrocarbons and produced a slightly higher percentage of alkenes and FFA.
Diesel engines can run on a wide variety of fuels, including aliphatic hydrocarbons, aliphatic and aromatic blends, fatty acid methyl esters (biodiesel), or blends of these. A major limitation is solidification in cold climates of fuels with long chains or polar molecules, such as biodiesel. By proper modulation of the chain length and blending, this waste and other materials can add significantly to the available fuel supply.