Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence and Overactive Bladder Among Female University Students in Kazakhstan
Abstract
1. Introduction
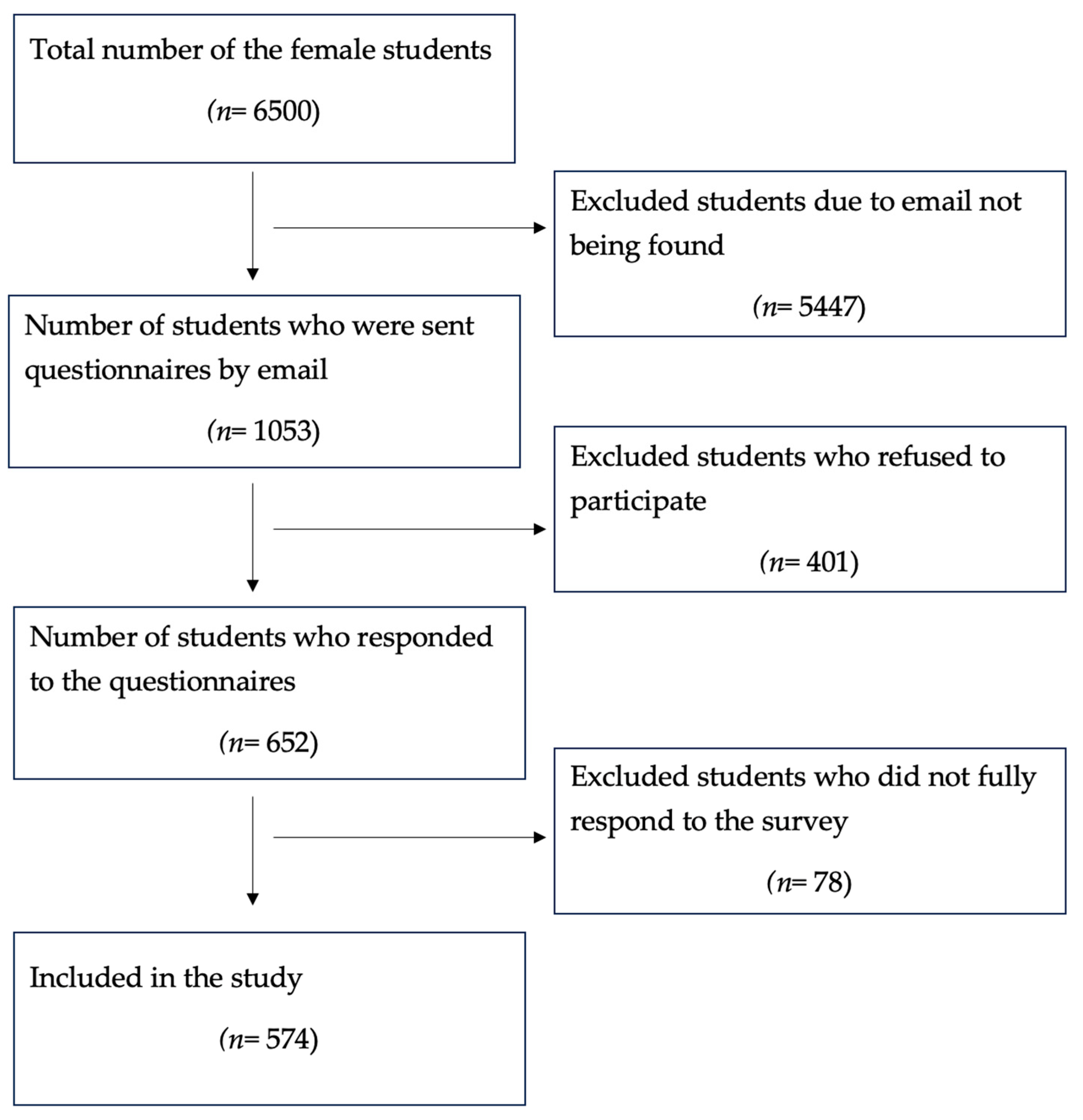
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Size
2.2. Questionnaire Format
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Prevalence of UI and Risk Factors
3.3. Prevalence of OAB and Risk Factors
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UI | Urinary Incontinence |
| OAB | Overactive Bladder |
| ICIQ-UI-SF | International Consultation on Urinary Incontinence Questionnaire Short Form |
| OAB-V8 | V8 Overactive Bladder Questionnaire |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
References
- Abrams, P.; Cardozo, L.; Fall, M.; Griffiths, D.; Rosier, P.; Ulmsten, U.; Van Kerrebroeck, P.; Victor, A.; Wein, A. Standardisation Sub-Committee of the International Continence Society. The standardisation of terminology in lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Urology 2003, 61, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, R.L. Female Urinary Incontinence and Sexuality. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2017, 43, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haylen, B.T.; de Ridder, D.; Freeman, R.M.; Swift, S.E.; Berghmans, B.; Lee, J.; Monga, A.; Petri, E.; Rizk, D.E.; Sand, P.K.; et al. An International Urogynecol.ogical Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female pelvic floor dysfunction. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2010, 29, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Brown, H.W.; Brubaker, L.; Cornu, J.N.; Daly, J.O.; Cartwright, R. Urinary Incontinence in Women. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mair, T. Urinary Incontinence and Urinary Tract Infections. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pr. 2022, 38, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunn, R.; Baessler, K.; Knüpfer, S.; Hampel, C. Urinary Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Women. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2023, 120, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodyńska, G.; Zalewski, M.; Rożek-Piechura, K. Urinary Incontinence in Postmenopausal Women—Causes, Symptoms, Treatment. Prz. Menopauzalny 2019, 18, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallock, J.L.; Handa, V.L. The Epidemiology of Pelvic Floor Disorders and Childbirth: An Update. Obs. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 43, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzal, Z.; Khatib, B.; Al-Quqa, B.; Abu-Taha, L.; Jaradat, A. The Prevalence and Risk Factors of Urinary Incontinence among Women with Type 2 Diabetes in the North West Bank: A Cross-Sectional Study. Lancet 2021, 398 (Suppl. 1), S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner-Hermanns, R.; Anding, R. Characteristic Features of Urinary Incontinence—Diagnostic Investigation in Geriatric Patients. Aktuelle Urol. 2016, 47, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.; Jeppson, P.C.; Dokmeci, F.; Marquini, G.V.; Sartori, M.G.F.; Moalli, P.; Malik, S.A. Management of Mixed Urinary Incontinence: IUGA Committee Opinion. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2024, 35, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leron, E.; Weintraub, A.Y.; Mastrolia, S.A.; Schwarzman, P. Overactive Bladder Syndrome: Evaluation and Management. Curr. Urol. 2018, 11, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temml, C.; Heidler, S.; Ponholzer, A.; Madersbacher, S. Prevalence of the Overactive Bladder Syndrome by Applying the International Continence Society Definition. Eur. Urol. 2005, 48, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogan, M.I.; Zachoval, R.; Ozyurt, C.; Schäfer, T.; Christensen, N. Epidemiology and Impact of Urinary Incontinence, Overactive Bladder, and Other Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Results of the EPIC Survey in Russia, Czech Republic, and Turkey. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2014, 30, 2119–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, E.; Tienforti, D.; D’Addessi, A.; Pinto, F.; Racioppi, M.; Totaro, A.; D’Agostino, D.; Marangi, F.; Bassi, P. Social, Economic, and Health Utility Considerations in the Treatment of Overactive Bladder. Open Access J. Urol. 2010, 2, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, M.; Williams, K.; Wells, M.; McGrother, C. Lifestyle Interventions for the Treatment of Urinary Incontinence in Adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD003505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, G. Management of Urinary Incontinence. Post. Reprod. Health 2020, 26, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, U.J.; Godecker, A.L.; Giles, D.L.; Brown, H.W. Updated Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence in Women: 2015-2018 National Population-Based Survey Data. Female Pelvic Med. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 28, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minassian, V.A.; Stewart, W.F.; Wood, G.C. Urinary Incontinence in Women: Variation in Prevalence Estimates and Risk Factors. Obs. Gynecol. 2008, 111, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, C.; Srivastava, K.; Ochuba, O.; Ruo, S.; Cureus, T.; Sandhu, J.K.; Waqar, A.; Jain, A.; Poudel, S. Stress Urinary Incontinence Among Young Nulliparous Female Athletes. Cureus 2021, 13, e17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayla, J.; Lamerton, M.A.; Gregore, I.M.; Wendy, J.B. Urinary Incontinence in Young Women: Risk Factors, Management Strategies, Help-Seeking Behavior, and Perceptions About Bladder Control. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2020, 39, 2284–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.; Cardozowan, L. Urinary Incontinence in the Young Woman: Treatment Plans and Options Available. Women’s Health 2014, 10, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitti, V.W. The Prelevalence of Urinary Incontinence. Rev. Urol. 2001, 3 (Suppl. 1), S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Russian Version of Questionnaires for Life Quality Assessment in Patients with Pelvic Organ Prolapse and Stress Urinary Incontinence. Experimental and Clinical Urology. Available online: https://ecuro.ru/en/article/russian-version-questionnaires-life-quality-assessment-patients-pelvic-organ-prolapse-and-st (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Klovning, A.; Avery, K.; Sandvik, H.; Hunskaar, S. Comparison of two questionnaires for assessing the severity of urinary incontinence: The ICIQ-UI SF versus the incontinence severity index. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2009, 28, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acquadro, C.; Kopp, Z.; Coyne, K.S.; Corcos, J.; Tubaro, A.; Choo, M.-S.; Oh, S.J. Translating Overactive Bladder Questionnaires in 14 Languages. Urology 2006, 67, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, C.; Papworth, E.; Pascoe, J.; Hashim, H. Update on the Management of Overactive Bladder. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2021, 13, 17562872211039034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunskaar, S.; Lose, G.; Sykes, D.; Voss, S. The Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence in Women in Four European Countries. BJU Int. 2004, 93, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Díaz, B.; Tirado-Morata, C.; Garrido-Elustondo, S. Prevalence of urinary incontinence in young and nulligravid women. Aten. Primaria 2025, 57, 103261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geirsson, G.; Hansen, B.; Hermannsdóttir, K. Prevalence of urinary incontinence among young female college students. Laeknabladid 2003, 89, 305–309. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, J.O.; Luz, S.T.D.; Brandão, S.; Da Luz, C.M.; Jorge, R.N.; Da Roza, T. Urinary Incontinence in Physically Active Young Women: Prevalence and Related Factors. Int. J. Sports Med. 2017, 38, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardino, M.; Di Martino, M.; Ricci, E.; Parazzini, F. Frequency and Determinants of Urinary Incontinence in Adolescent and Young Nulliparous Women. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Gynecol. 2015, 28, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Xue, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhuo, L.; Tu, S.; Palmer, M.H. Toileting Behaviors and Factors Associated with Urinary Incontinence in College-Aged Female Students in China. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2020, 31, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasu, A.F.G.; Cetin, C.; Pasin, Ö.; Karacabay, M.; Tanoglu, F.B.; Ilhan, G. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence and Anal Incontinence: An Internet-Based Cross-Sectional Study of Female Turkish University Students. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2023, 34, 2309–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ural, Ü.M.; Gücük, S.; Ekici, A.; Topçuoğlu, A. Urinary Incontinence in Female University Students. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2021, 32, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, N.; Mo, L.; Tian, X.; Liu, H.; Yu, B. Global Prevalence of Overactive Bladder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Bang, W.; Choi, H.G. Analysis of the prevalence of and factors associated with overactive bladder in adult Korean women. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuorouq, S.; Al-Zubi, M.; Al-Ali, A.M.; Aloqaily, L.H.; Talafha, M.A.; Migdadi, A.M.; Serhan, H.A. The Prevalence of Probable Overactive Bladder and Associated Risk Factors among Medical Students in Jordan: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Urol. 2024, 24, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Duan, Z. Joint Effect of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior with the Female Urinary Incontinence: An Analysis of NHANES 2011–2016. Urol. Int. 2024, 108, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvidman, L.; Foldspang, A.; Mommsen, S.; Nielsen, J.B. Postpartum urinary incontinence. Acta Obs. Gynecol. Scand. 2003, 82, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrat, L.; Haillot, O.; Bruyere, F.; Boutin, J.M.; Bertrand, P.; Lanson, Y. Prévalence et facteurs de risque de l’incontinence urinaire chez la femme jeune Prevalence and risk factors of urinary incontinence in young women. Prog. Urol. 2002, 12, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zizzi, P.T.; Trevisan, K.F.; Leister, N.; Cruz, C.D.; Riesco, M.L. Women’s pelvic floor muscle strength and urinary and anal incontinence after childbirth: A cross-sectional study. Rev. Esc. Enferm. USP 2017, 51, e03214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyne, K.S.; Sexton, C.C.; Thompson, C.L.; Milsom, I.; Irwin, D.; Kopp, Z.S.; Chapple, C.R.; Kaplan, S.; Tubaro, A.; Aiyer, L.P.; et al. The Prevalence of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in the USA, the UK and Sweden: Results from the Epidemiology of LUTS (EpiLUTS) Study. BJU Int. 2009, 104, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, X.; Dong, X.; Li, L. Associations Between Risk Factors and Overactive Bladder: A Meta-analysis. Female Pelvic Med. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 25, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.M.; Aznal, S.S.; Tham, S.W. Prevalence of Overactive Bladder Syndrome (OABS) Among Women with Gynaecological Problems and Its Risk Factors in a Tertiary Hospital, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia: Implication for Primary Healthcare Providers. Malays. Fam. Physician 2015, 10, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shawahna, R.; Hijaz, H.; Jallad, K.; Abushamma, M.; Sawafta, M. Prevalence of overactive bladder symptoms and their impact on health-related quality of life of medical and dentistry students: A multicenter cross-sectional study. BMC Urol. 2021, 21, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, K.S.; Sexton, C.C.; Clemens, J.Q.; Thompson, C.L.; Chen, C.I.; Bavendam, T.; Dmochowski, R. The impact of OAB on physical activity in the United States: Results from OAB-POLL. Urology 2013, 82, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Xu, B. The relationship between physical activity and overactive bladder among American adults: A cross-sectional study from NHANES 2007–2018. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 16280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | n = 574 | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| <19 | 126 | 22.0 |
| 19–23 | 280 | 48.8 |
| >23 | 168 | 29.2 |
| Educational program | ||
| Bachelor | 312 | 54.4 |
| Internship | 198 | 34.5 |
| Master | 10 | 1.7 |
| Residency | 42 | 7.3 |
| Doctoral | 12 | 2.1 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||
| <18.5 | 88 | 15.3 |
| 18.5–24.9 | 82 | 14.3 |
| >25 | 404 | 70.4 |
| History of childbirth | ||
| Yes | 88 | 15.3 |
| No | 486 | 84.7 |
| Chronic diseases | ||
| Yes | 148 | 25.8 |
| No | 426 | 74.2 |
| Smoking habit | ||
| Electronic cigarettes | 42 | 7.3 |
| Yes, less than 10 cigarettes a day | 10 | 1.7 |
| Yes, less than 20 cigarettes a day | 2 | 0.3 |
| No, I don’t smoke | 520 | 90.6 |
| Alcohol consumption | ||
| Yes | 48 | 8.4 |
| No | 526 | 91.6 |
| Physical exercise status | ||
| Twice a week | 134 | 23.3 |
| Every day | 48 | 8.4 |
| Irregularly | 326 | 56.8 |
| Never | 66 | 1.5 |
| Childhood enuresis | ||
| Yes | 96 | 16.7 |
| No | 478 | 83.3 |
| Daily fluid consumption | ||
| <1500 mL | 406 | 70.7 |
| 1500–3000 mL | 160 | 27.9 |
| >3000 mL | 8 | 1.4 |
| Characteristics | UI | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (%) | No (%) | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | <18.5 | 20 (12.7) | 68 (16.4) | 0.183 |
| 18.5–24.9 | 106 (67.0) | 298 (71.6) | ||
| >25 | 32 (20.3) | 50 (12.0) | ||
| History of childbirth | Yes | 38 (24.1) | 50 (12.0) | 0.012 |
| No | 120 (75.9) | 366 (88.0) | ||
| Chronic diseases | Yes | 44 (27.8) | 104 (25.0) | 0.622 |
| No | 114 (72.2) | 312 (75.0) | ||
| Smoking habit | Yes | 16 (10.1) | 38 (9.1) | 0.822 |
| No | 142 (89.9) | 378 (90.9) | ||
| Alcohol consumption | Yes | 16 (10.1) | 32 (7.7) | 0.483 |
| No | 142 (89.9) | 384 (92.3) | ||
| Physical exercise status | Twice a week | 42 (26.6) | 92 (22.1) | 0.027 |
| Every day | 16 (10.1) | 32 (7.7) | ||
| Irregularly | 70 (44.3) | 256 (61.5) | ||
| Never | 30 (19.0) | 36 (8.7) | ||
| Childhood enuresis | Yes | 24 (15.2) | 72 (17.3) | 0.668 |
| No | 134 (84.8) | 344 (82.7) | ||
| Daily fluid consumption | <1500 mL | 106 (67.1) | 300 (72.1) | 0.257 |
| 1500–3000 mL | 52 (32.9) | 108 (26.0) | ||
| >3000 mL | 0 (0.0) | 8 (1.9) | ||
| Variables | Unadjusted | Adjusted | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (CI 95%) | p-Value | OR (CI 95%) | p-Value | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 1.06 (0.99–1.14) | 0.069 | 1.06 (0.98–1.14) | 0.120 |
| To have a history of childbirth | 2.31 (1.19–4.50) | 0.013 | 2.30 (1.16–4.54) | 0.016 |
| To have chronic diseases | 1.15 (0.64–2.07) | 0.622 | 1.14 (0.61–2.13) | 0.661 |
| To have smoking habit | 1.12 (0.47–2.67) | 0.797 | 0.98 (0.35–2.75) | 0.977 |
| Physical exercise status | ||||
| Every day | 1.09 (0.40–2.95) | 0.858 | 1.07 (0.38–3.05) | 0.887 |
| Twice a week | 1.27 (0.70–2.31) | 0.425 | 1.33 (0.71–2.52) | 0.368 |
| Irregularly | 0.59 (0.31–1.13) | 0.115 | 0.58 (0.30–1.15) | 0.122 |
| Never (reference category) | ||||
| To have a childhood enuresis | 0.85 (0.42–1.74) | 0.668 | 0.73 (0.33–1.59) | 0.432 |
| Daily fluid consumption | ||||
| <1500 mL | 0.73 (0.41–1.28) | 0.281 | 0.72 (0.39–1.31) | 0.292 |
| 1500–3000 mL | 1.39 (0.79–2.45) | 0.242 | 1.40 (0.77–2.55) | 0.267 |
| >3000 mL (reference category) | ||||
| Characteristics | OAB | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (%) | No (%) | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | <18.5 | 84 (16.3) | 4 (6.9) | 0.144 |
| 18.5–24.9 | 354 (68.6) | 50 (86.2) | ||
| >25 | 78 (15.1) | 4 (6.9) | ||
| History of childbirth | Yes | 66 (12.8) | 22 (37.9) | 0.001 |
| No | 450 (87.2) | 36 (62.1) | ||
| Chronic diseases | Yes | 120 (23.3) | 28 (48.3) | 0.006 |
| No | 396 (76.7) | 30 (51.7) | ||
| Smoking habit | Yes | 46 (8.9) | 8 (13.8) | 0.333 |
| No | 470 (91.1) | 50 (86.2) | ||
| Alcohol consumption | Yes | 42 (8.1) | 6 (10.3) | 0.721 |
| No | 474 (91.9) | 52 (89.7) | ||
| Physical exercise status | Twice a week | 128 (24.8) | 6 (10.3) | 0.021 |
| Every day | 44 (8.5) | 4 (6.9) | ||
| Irregularly | 294 (57.0) | 32 (55.2) | ||
| Never | 50 (9.7) | 16 (27.6) | ||
| Childhood enuresis | Yes | 80 (15.5) | 16 (27.6) | 0.115 |
| No | 436 (84.5) | 42 (72.4) | ||
| Daily fluid consumption | <1500 mL | 362 (70.2) | 44 (75.9) | 0.694 |
| 1500–3000 mL | 146 (28.3) | 14 (24.1) | ||
| >3000 mL | 8 (1.6) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Variables | Unadjusted | Adjusted | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (CI 95%) | p-Value | OR (CI 95%) | p-Value | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 1.03 (0.96–1.11) | 0.385 | 1.02 (0.94–1.10) | 0.603 |
| To have a history of childbirth | 4.14 (2.29–7.48) | <0.001 | 3.36 (1.76–6.42) | <0.001 |
| To have chronic diseases | 3.13 (1.80–5.46) | <0.001 | 2.74 (1.51–4.96) | 0.001 |
| To have smoking habit | 1.72 (0.76–3.86) | 0.188 | 1.84 (0.62–5.49) | 0.269 |
| To have a childhood enuresis | 2.02 (1.08–3.78) | 0.026 | 1.50 (0.74–3.02) | 0.256 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharapatov, Y.; Nurberdiev, A.; Keulimzhayev, N.; Botabayeva, A.; Toleubayev, M.; Dmitriyeva, M.; Zhankina, R. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence and Overactive Bladder Among Female University Students in Kazakhstan. Epidemiologia 2025, 6, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia6030038
Sharapatov Y, Nurberdiev A, Keulimzhayev N, Botabayeva A, Toleubayev M, Dmitriyeva M, Zhankina R. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence and Overactive Bladder Among Female University Students in Kazakhstan. Epidemiologia. 2025; 6(3):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia6030038
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharapatov, Yerzhan, Aluadin Nurberdiev, Nurbol Keulimzhayev, Aigul Botabayeva, Medet Toleubayev, Mariya Dmitriyeva, and Rano Zhankina. 2025. "Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence and Overactive Bladder Among Female University Students in Kazakhstan" Epidemiologia 6, no. 3: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia6030038
APA StyleSharapatov, Y., Nurberdiev, A., Keulimzhayev, N., Botabayeva, A., Toleubayev, M., Dmitriyeva, M., & Zhankina, R. (2025). Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence and Overactive Bladder Among Female University Students in Kazakhstan. Epidemiologia, 6(3), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia6030038





