Relationship between the Number of Deaths Due to Renal Failure and Air Temperature Parameters in Hokkaido and Okinawa Prefectures, Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Deaths Due to Renal Failure
2.3. Air Temperature Parameters
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Japan. Vital Statistics Overview. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/jinkou/suikei18/dl/2018gaiyou.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2020). (In Japanese)
- Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Japan. Cause of Death Ranking. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/jinkou/kakutei18/dl/10_h6.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2020). (In Japanese)
- The Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy. Available online: https://docs.jsdt.or.jp/overview/file/2018/pdf/01.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2020). (In Japanese).
- Vejakama, P.; Ingsathit, A.; McEvoy, M.; Attia, J.; Thakkinstian, A. Progression of chronic kidney disease: An illness-death model approach. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Malki, H.; Sadek, M.; Rashed, A.; Asim, M.; Fituri, O.; Abbass, M. Acute renal failure in the State of Qatar: Presentation and outcome. Transpl. Proc. 2009, 41, 1530–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dare, A.J.; Fu, S.H.; Patra, J.; Rodriguez, P.S.; Thakur, J.S.; Jha, P.; Million Death Study Collaborators. Renal failure deaths and their risk factors in India 2001-13: Nationally representative estimates from the Million Death Study. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e89–e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.; O’Keeffe, S.T.; Mulkerrin, E.C. Dehydration and renal failure in older persons during heatwaves-predictable, hard to identify but preventable? Age Ageing 2019, 48, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, D.; Young, O.; Holmes, J.; Allen, L.A.; Roberts, G.; Geen, J.; Williams, J.D.; Phillips, A.O.; Welsh AKI Steering Group. Seasonal pattern of incidence and outcome of Acute Kidney Injury: A national study of Welsh AKI electronic alerts. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2017, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obi, Y.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Streja, E.; Rhee, C.M.; Reddy, U.G.; Soohoo, M.; Wang, Y.; Ravel, V.; You, A.S.; Jing, J.; et al. Seasonal variations in transition, mortality and kidney transplantation among patients with end-stage renal disease in the USA. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2017, 32, ii99–ii105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwagami, M.; Moriya, H.; Doi, K.; Yasunaga, H.; Isshiki, R.; Sato, I.; Mochida, Y.; Ishioka, K.; Ohtake, T.; Hidaka, S.; et al. Seasonality of acute kidney injury incidence and mortality among hospitalized patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2018, 33, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iseki, K.; Morita, O.; Fukiyama, K. Seasonal variation in the incidence of end-stage renal disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 1996, 16, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, S.; Hamano, T.; Ogata, S.; Masakane, I. Seasonal variations in cause-specific mortality and transition to renal replacement therapy among patients with end-stage renal disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bando, M.; Miyatake, N.; Kataoka, H.; Kinoshita, H.; Tanaka, N.; Suzuki, H.; Katayama, A. Relationship between Air Temperature Parameters and the Number of Deaths Stratified by cause in Gifu Prefecture, Japan. Healthcare 2020, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geospatial Information Authority of Japan. Available online: https://www.gsi.go.jp/KOKUJYOHO/center.htm (accessed on 15 October 2020). (In Japanese)
- Statistics Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. 2015 National Census. Available online: https://www.stat.go.jp/data/kokusei/2015/kekka/kihon1/pdf/gaiyou1.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2020). (In Japanese)
- Hokkaido Official Homepage. Available online: http://www.pref.hokkaido.lg.jp/hf/sum/hoso/hotou/hotou01/nenpou.htm (accessed on 28 May 2020). (In Japanese).
- Okinawa Prefecture Official Homepage. Available online: https://www.pref.okinawa.jp/site/hoken/hokeniryo/toukei/vs/vs.html, (accessed on 27 May 2020). (In Japanese).
- Statistics Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. Government Statistics Portal Site. Available online: https://www.e-stat.go.jp (accessed on 23 August 2020). (In Japanese)
- Japan Meteorological Agency. Available online: https://www.data.jma.go.jp/obd/stats/etrn/index.php (accessed on 23 August 2020). (In Japanese)
- Okayama, Y. Water balance in the elderly in summer and winter. Jpn. J. Biometeor. 1998, 35, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, S.H.; Cheng, L.T.; Zheng, D.X.; Wang, T. Seasonal changes in blood pressure in chronic kidney disease patients. Clin. Nephrol. 2010, 73, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, C.; Miyatake, N.; Hishii, S.; Suzuki, H.; Katayama, A. Seasonal changes in continuous sedentary behavior in community-dwelling Japanese adults: A pilot study. Medicines 2020, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Hokkaido | Okinawa | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Minimum | Maximum | Minimum | Maximum | |||
| Number of months | 108 | 108 | |||||
| Number of deaths due to renal failure (total) | 2.28 ± 0.30 | 1.66 | 3.04 | 1.17 ± 0.31 | 0.50 | 2.00 | <0.01 |
| Number of deaths due to renal failure (men) | 1.09 ± 0.19 | 0.78 | 1.66 | 0.51 ± 0.20 | 0.14 | 1.04 | <0.01 |
| Number of deaths due to renal failure (women) | 1.19 ± 0.18 | 0.81 | 1.70 | 0.71 ± 0.24 | 0.27 | 1.73 | <0.01 |
| Mean air temperature (°C) | 9.47 ± 9.27 | −4.70 | 24.80 | 23.31 ± 4.49 | 14.90 | 29.80 | <0.01 |
| Mean of the highest air temperature (°C) | 13.37 ± 9.86 | −2.00 | 29.10 | 26.02 ± 4.57 | 17.00 | 32.90 | <0.01 |
| Mean of the lowest air temperature (°C) | 6.00 ± 9.19 | −8.00 | 21.30 | 21.11 ± 4.62 | 12.70 | 27.60 | <0.01 |
| The highest air temperature (°C) | 20.60 ± 9.76 | 1.80 | 34.50 | 29.36 ± 3.44 | 22.60 | 34.80 | <0.01 |
| The lowest air temperature (°C) | 0.77 ± 9.40 | −14.30 | 16.90 | 17.45 ± 5.43 | 6.10 | 25.70 | <0.01 |
| Hokkaido | Okinawa | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Men | Women | Total | Men | Women | |||||||
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| Mean air temperature (°C) | −0.51 | <0.01 | −0.39 | <0.01 | −0.44 | <0.01 | −0.20 | 0.04 | −0.20 | 0.04 | −0.17 | 0.08 |
| Mean of the highest air temperature (°C) | −0.51 | <0.01 | −0.39 | <0.01 | −0.44 | <0.01 | −0.19 | 0.04 | −0.20 | 0.04 | −0.16 | 0.10 |
| Mean of the lowest air temperature (°C) | −0.50 | <0.01 | −0.39 | <0.01 | −0.43 | <0.01 | −0.21 | 0.03 | −0.21 | 0.03 | −0.17 | 0.08 |
| The highest air temperature (°C) | −0.52 | <0.01 | −0.41 | <0.01 | −0.44 | <0.01 | −0.22 | 0.02 | −0.21 | 0.03 | −0.16 | 0.09 |
| The lowest air temperature (°C) | −0.49 | <0.01 | −0.36 | <0.01 | −0.44 | <0.01 | −0.19 | 0.05 | −0.18 | 0.06 | −0.17 | 0.09 |
| Hokkaido | Okinawa | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Men | Women | Total | Men | Women | ||||
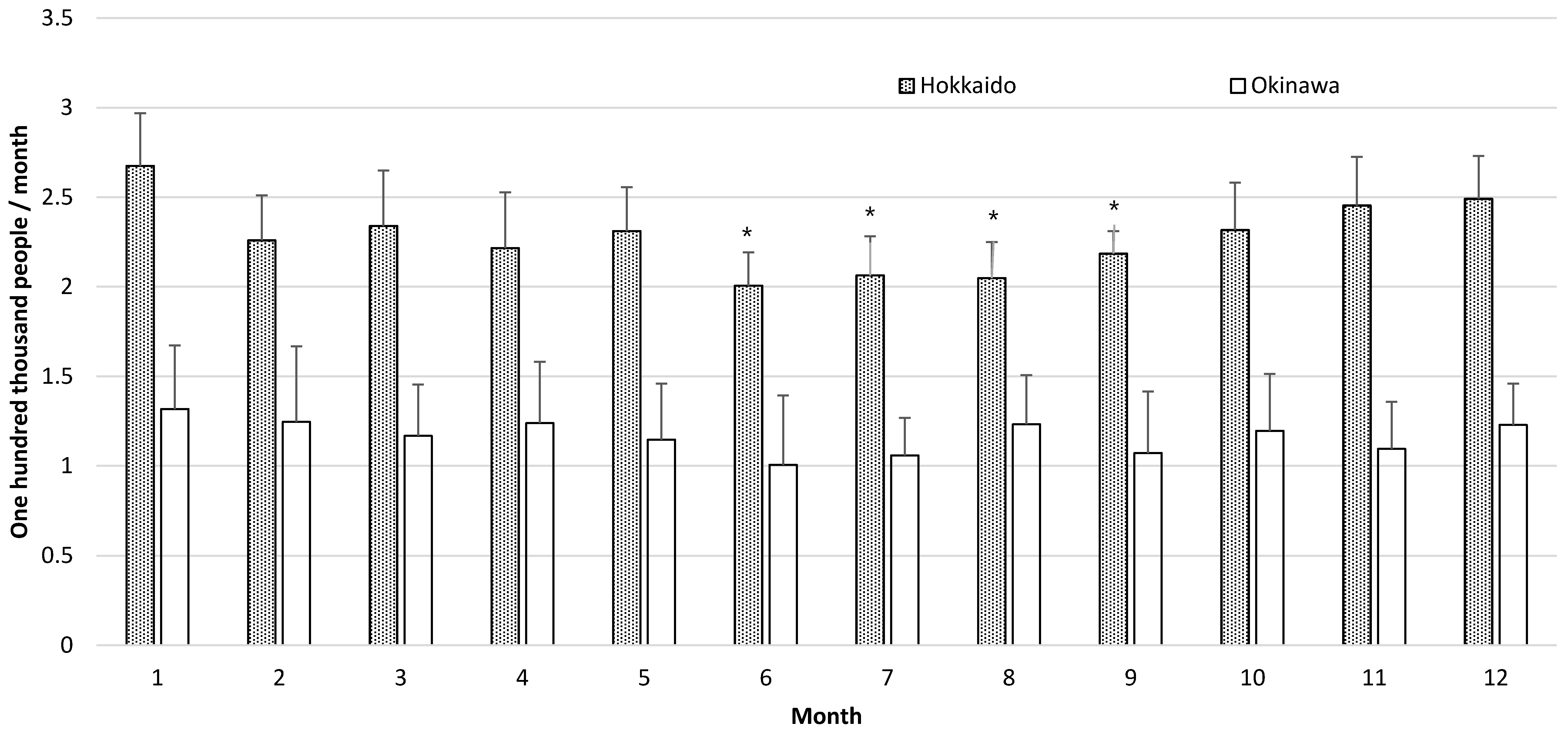
| January | 2.67 ± 0.29 | 1.31 ± 0.24 | 1.36 ± 0.14 | 1.32 ± 0.36 | 0.59 ± 0.21 | 0.77 ± 0.23 | |||
| February | 2.26 ± 0.25 | 1.05 ± 0.13 | 1.21 ± 0.19 | 1.25 ± 0.42 | 0.58 ± 0.26 | 0.73 ± 0.26 | |||
| March | 2.34 ± 0.31 | 1.12 ± 0.19 | 1.22 ± 0.18 | 1.17 ± 0.29 | 0.50 ± 0.18 | 0.76 ± 0.41 | |||
| April | 2.22 ± 0.31 | 1.00 ± 0.14 | 1.21 ± 0.25 | 1.24 ± 0.34 | 0.54 ± 0.22 | 0.74 ± 0.19 | |||
| May | 2.31 ± 0.25 | 1.11 ± 0.18 | 1.20 ± 0.13 | 1.15 ± 0.31 | 0.54 ± 0.16 | 0.68 ± 0.33 | |||
| June | 2.01 ± 0.19 | a | 0.96 ± 0.12 | a | 1.05 ± 0.14 | a | 1.01 ± 0.39 | 0.35 ± 0.23 | 0.69 ± 0.20 |
| July | 2.06 ± 0.22 | a | 1.03 ± 0.16 | 1.04 ± 0.09 | a | 1.06 ± 0.21 | 0.51 ± 0.17 | 0.58 ± 0.17 | |
| August | 2.05 ± 0.20 | a | 0.97 ± 0.18 | 1.08 ± 0.10 | a | 1.23 ± 0.28 | 0.53 ± 0.16 | 0.76 ± 0.21 | |
| September | 2.18 ± 0.13 | a | 0.97 ± 0.12 | a | 1.22 ± 0.17 | 1.07 ± 0.34 | 0.48 ± 0.26 | 0.62 ± 0.14 | |
| November | 2.45 ± 0.27 | 1.18 ± 0.21 | 1.27 ± 0.12 | 1.10 ± 0.26 | 0.47 ± 0.13 | 0.70 ± 0.15 | |||
| December | 2.49 ± 0.24 | 1.19 ± 0.14 | 1.30 ± 0.14 | 1.23 ± 0.23 | 0.57 ± 0.18 | 0.77 ± 0.28 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mori, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Miyatake, N.; Bando, M.; Kinoshita, H.; Tanaka, N.; Okada, S. Relationship between the Number of Deaths Due to Renal Failure and Air Temperature Parameters in Hokkaido and Okinawa Prefectures, Japan. Epidemiologia 2021, 2, 68-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia2010006
Mori Y, Suzuki H, Miyatake N, Bando M, Kinoshita H, Tanaka N, Okada S. Relationship between the Number of Deaths Due to Renal Failure and Air Temperature Parameters in Hokkaido and Okinawa Prefectures, Japan. Epidemiologia. 2021; 2(1):68-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia2010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleMori, Yoshiro, Hiromi Suzuki, Nobuyuki Miyatake, Masaki Bando, Hiroshi Kinoshita, Naoko Tanaka, and Setsuo Okada. 2021. "Relationship between the Number of Deaths Due to Renal Failure and Air Temperature Parameters in Hokkaido and Okinawa Prefectures, Japan" Epidemiologia 2, no. 1: 68-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia2010006
APA StyleMori, Y., Suzuki, H., Miyatake, N., Bando, M., Kinoshita, H., Tanaka, N., & Okada, S. (2021). Relationship between the Number of Deaths Due to Renal Failure and Air Temperature Parameters in Hokkaido and Okinawa Prefectures, Japan. Epidemiologia, 2(1), 68-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia2010006





