Structural, Electronic, and Optical Properties of p-Type Semiconductors Cu2O and ZnRh2O4: A Self-Consistent Hybrid Functional Investigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Properties
3.2. Electronic and Optical Properties
4. Summary and Outlook
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DFT | Density functional theory |
| GGA | Generalised gradient approximation |
| TCO | Transparent conducting oxide |
References
- Hosono, H. Recent progress in transparent oxide semiconductors: Materials and device application. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, D. Electronic and optical properties of spinel zinc ferrite: ab initio hybrid functional calculations. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2018, 30, 095502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fritsch, D.; Ederer, C. Epitaxial strain effects in the spinel ferrites CoFe2O4 and NiFe2O4 from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 104117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fritsch, D.; Ederer, C. Effect of epitaxial strain on the cation distribution in spinel ferrites CoFe2O4 and NiFe2O4: A density functional theory study. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 081916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caffrey, N.; Fritsch, D.; Archer, T.; Sanvito, S.; Ederer, C. Spin-filtering efficiency of ferrimagnetic spinels CoFe2O4 and NiFe2O4. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 024419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamiya, T.; Narushima, S.; Mizoguchi, H.; Shimizu, K.; Ueda, K.; Ohta, H.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Electrical properties and structure of p-type amorphous oxide semiconductor xZnO·Rh2O3. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narushima, S.; Mizoguchi, H.; Shimizu, K.; Ueda, K.; Ohta, H.; Hirano, M.; Kamiya, T.; Hosono, H. A p-type amorphous oxide semiconductor and room temperature fabrication of amorphous oxide p-n heterojunction diodes. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, A.R.; Perry, N.H.; Mason, T.O.; Tang, Y.; Grayson, M.; Paudel, T.R.; Lany, S.; Zunger, A. Band or polaron: The hole conduction mechanism in the p-type spinel Rh2ZnO4. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 95, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, D.O.; Watson, G.W. Band gap anomalies of the ZnM2IIIO4 (MIII = Co, Rh, Ir) spinels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, M.N.; Dixit, H.; Saniz, R.; Lamoena, D.; Partoens, B. The origin of p-type conductivity in ZnM2O4 (M = Co, Rh, Ir) spinels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 16, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsch, D.; Schorr, S. Climbing Jacob’s ladder: A density functional theory case study for Ag2ZnSnSe4 and Cu2ZnSnSe4. J. Phys. Energy 2021, 3, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skone, J.H.; Govoni, M.; Galli, G. Self-consistent hybrid functional for condensed systems. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 89, 195112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fritsch, D.; Morgan, B.J.; Walsh, A. Self-consistent hybrid functional calculations: Implications for structural, electronic, and optical properties of oxide semiconductors. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fritsch, D. Self-consistent Hybrid Functionals: What We have Learned So Far. In Theory and Simulation in Physics for Materials Applications: Cutting-Edge Techniques in Theoretical and Computational Materials Science; Levchenko, E.V., Dappe, Y.L., Ori, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, The Netherlands, 2020; p. 79. [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch, D. Amorphous Sn-Ti oxides: A combined molecular dynamics and density functional theory study. Phys. Status Solidi A 2018, 215, 1800071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahila, M.J.; Lebens-Higgins, Z.W.; Butler, K.T.; Fritsch, D.; Treharne, R.E.; Palgrave, R.G.; Woicik, J.C.; Morgan, B.J.; Walsh, A.; Piper, L.F.J. Accelerated optimization of transparent, amorphous zinc-tin-oxide thin films for optoelectronic applications. APL Mater. 2019, 7, 022509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ruzsinszky, A.; Perdew, J. Strongly constrained and appropriately normed semilocal density functional. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 036402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Remsing, R.C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ruzsinszky, A.; Peng, H.; Yang, Z.; Paul, A.; Waghmare, U.; Wu, X.; et al. Accurate first-principles structures and energies of diversely bonded systems from an efficient density functional. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular-dynamics simulation of the liquid-metal–amorphous-semiconductor transition in germanium. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 14251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comp. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöchl, P.E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murnaghan, F.D. Finite deformations of elastic solids. Am. J. Math. 1937, 59, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murnaghan, F.D. The compressibility of media under extreme pressure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1944, 30, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fritsch, D.; Ederer, C. Strain effects in spinel ferrite thin films from first principles calculations. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 292, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirfel, A.; Eichhorn, K. Accurate structure analysis with synchrotron radiation. The electron density in Al2O3 and Cu2O. Acta Cryst. A 1990, 46, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.K.; Polity, A.; Reppin, D.; Becker, M.; Hering, P.; Kramm, B.; Klar, P.J.; Sander, T.; Reindl, C.; Heiliger, C.; et al. The physics of copper oxide (Cu2O). In Oxide Semiconductors, Semiconductors and Semimetals; Svensson, B.G., Pearton, S.J., Jagadish, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 88, p. 201. [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg, J.; Hanson, R.C. The elastic constants of cuprous oxide. Phys. Status Solidi B 1970, 42, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manghnani, M.H.; Brower, W.S.; Parker, H.S. Anomalous elastic behavior in Cu2O under pressure. Phys. Status Solidi A 1974, 25, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uihlein, C.; Fröhlich, D.; Kenklies, R. Investigation of exciton fine structure in Cu2O. Phys. Rev. B 1981, 23, 2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, M.; Rijnders, G.; Blank, D.H.A. ZnIr2O4, a p-type transparent oxide semiconductor in the class of spinel zinc-d6-transition metal oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 021903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, H.; Hirano, M.; Fujitsu, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Ueda, K.; Hosono, H. ZnRh2O4: A p-type semiconducting oxide with a valence band composed of a low spin state of Rh3+ in a 4d6 configuration. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahila, M.J.; Lebens-Higgins, Z.W.; Jackson, A.J.; Scanlon, D.O.; Lee, T.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.H.L.; Piper, L.F.J. Band edge evolution of transparent ZnM2IIIO4 (MIII = Co, Rh, Ir) spinels. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 100, 085126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
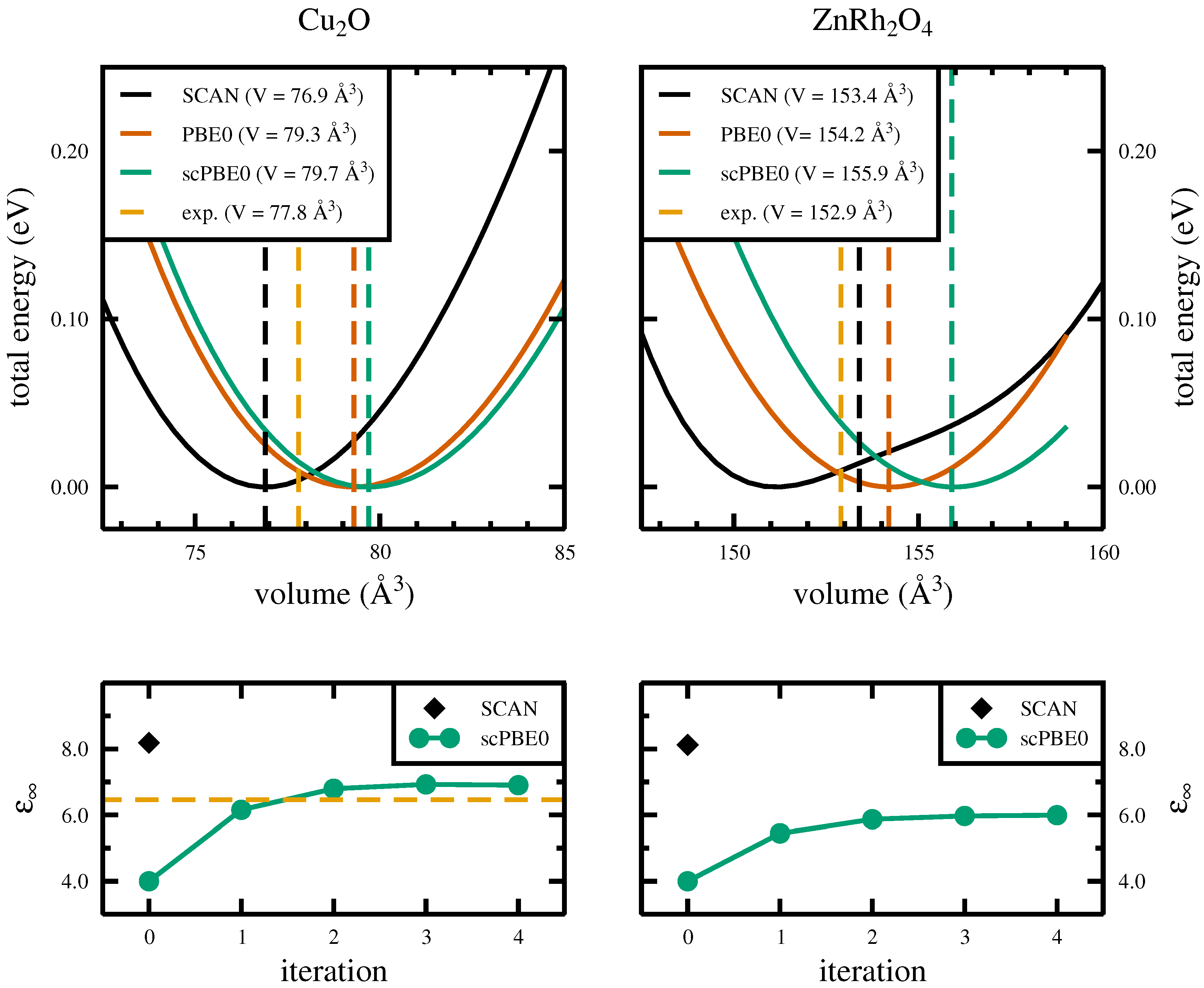

| CuO | SCAN | PBE0 | scPBE0 | Exp. |
| a [Å] | 4.252 | 4.296 | 4.303 | 4.2685 [27], 4.2696 [28] |
| [GPa] | 122.0 | 110.8 | 109.8 | 110.6 [29], 111.96 [30] |
| 4.9 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.46 [30] | |
| 8.186 | 6.153 | 6.922 | 6.46 [28] | |
| 0.122 | 0.250 | 0.147 | 0.15 [28] | |
| [eV] | 0.559 | 2.685 | 1.703 | 2.1720 [31] |
| ZnRhO | SCAN | PBE0 | scPBE0 | Exp. |
| a [Å] | 8.498 | 8.513 | 8.544 | 8.489 [32] |
| u | 0.260 | 0.261 | 0.261 | − |
| [GPa] | 196.9 | 205.4 | 198.3 | − |
| 6.9 | 3.6 | 3.6 | − | |
| 8.125 | 5.445 | 5.990 | − | |
| 0.123 | 0.250 | 0.168 | − | |
| [eV] | 0.989 | 3.666 | 2.707 | 2.1 [33], 2.74 [32] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fritsch, D. Structural, Electronic, and Optical Properties of p-Type Semiconductors Cu2O and ZnRh2O4: A Self-Consistent Hybrid Functional Investigation. Electron. Mater. 2021, 2, 504-510. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat2040035
Fritsch D. Structural, Electronic, and Optical Properties of p-Type Semiconductors Cu2O and ZnRh2O4: A Self-Consistent Hybrid Functional Investigation. Electronic Materials. 2021; 2(4):504-510. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat2040035
Chicago/Turabian StyleFritsch, Daniel. 2021. "Structural, Electronic, and Optical Properties of p-Type Semiconductors Cu2O and ZnRh2O4: A Self-Consistent Hybrid Functional Investigation" Electronic Materials 2, no. 4: 504-510. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat2040035
APA StyleFritsch, D. (2021). Structural, Electronic, and Optical Properties of p-Type Semiconductors Cu2O and ZnRh2O4: A Self-Consistent Hybrid Functional Investigation. Electronic Materials, 2(4), 504-510. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat2040035






