Abstract
Resveratrol is a natural polyphenol with important anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties for treating cardiometabolic disorders. Therefore, the present meta-analysis aimed to review and investigate the oral resveratrol supplementation effects on metabolic syndrome (MetS) components. The bibliographic search was carried out in 2023 in the following databases: PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus. Studies that investigated the oral resveratrol effects on the MetS parameters were included. Statistical analyses were performed using RevMan Software V.5.3. The main findings showed that resveratrol significantly decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure while having no significant effects on waist circumference and high-density lipoprotein levels. In addition, glucose level was significantly decreased in the subgroup of studies reporting change from baseline means, although the overall effect was not statistically significant (p = 0.81), while triglyceride levels were increased after the treatment period. In conclusion, the present meta-analysis evidenced the potential therapeutic effect of resveratrol on improving some MetS features, especially regarding systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and glucose reduction; however, the results are still borderline and sometimes controversial, which might be justified by the methodological and statistical heterogeneity of the studies, with the latter varying from 17 to 57%.
1. Introduction
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is highly prevalent and considered a serious global health problem [1]. It comprises endocrine disturbances such as obesity, altered fasting glucose levels, dyslipidemia, and hypertension [2,3,4]. MetS is associated with an increased risk for atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) [5]. All these disturbances have serious impacts on individuals’ quality of life.
The literature has established different MetS diagnostic criteria and treatment strategies [3,6]. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), the first line of treatment for metabolic syndrome involves lifestyle changes such as weight loss, a healthy diet, and physical activity [3,7,8]. In some cases, a pharmacological intervention is indicated [9]; however, until now, there is no exclusive treatment for this syndrome. Novel treatments are under investigation, considering that preventive measures commonly fail and that current therapeutic options are insufficient [9].
Resveratrol (3,5,4-trihydroxystilbene) is a phytoalexin that is considered a natural polyphenol with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. This compound is found in different amounts in more than seventy plant species, as well as in beverages and foods—such as blackberries, peanuts, and grapes (and their derivatives, e.g., red wine) [10,11]. It is present in the isoforms cis and trans, with the latter being the most studied and filled with pharmacological properties [11], displaying several beneficial effects (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Resveratrol beneficial effects.
In animal models, resveratrol has been documented to exert favorable weight-reducing effects [12,13,14], such as total body fat and white adipose tissue reduction [12], in addition to regulating other signaling pathways [15]. Studies have proved that resveratrol’s anti-obesogenic properties are based on different mechanisms, including the inhibition of pre-adipocyte differentiation, adipocyte proliferation, lipogenesis, induction of adipocyte apoptosis, lipolysis, and fatty acid beta-oxidation (which leads to a decrease in the obesity-inflammatory profile), causing a decrease in the serum lipid levels and improvements in glucose homeostasis [13].
Furthermore, resveratrol can mimic calorie restriction effects [16]. Resveratrol supplementation effects on weight loss have been investigated in human studies, although the current results are still controversial. A study conducted by Faghihzadeh et al., where 500 mg of resveratrol was administered daily for 12 weeks in individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and overweight, reported improvements in body weight, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), and hepatic steatosis. Therefore, for the treatment of NAFLD, the results showed that 12 weeks of resveratrol supplementation, along with lifestyle changes, is superior to isolated lifestyle changes [17,18]. In contrast, high doses of resveratrol supplementation administered in men with obesity for 4 weeks did not affect resting energy expenditure, lipid oxidation rates, and visceral or ectopic lipid content [9,19,20].
It is well known that the abdominal circumference measurement is the main anthropometrical method that indirectly indicates visceral fat content. It is also known that central or abdominal obesity is the best predictor of adverse health effects compared to general obesity [21,22]. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial comprising 24 patients with MetS showed that resveratrol was capable of decreasing body weight, BMI, fat mass, waist circumference, the area under the curve of insulin, and total insulin secretion [23,24]. Batista-Jorge et al. also observed a significant decrease in visceral fat, which was assessed via WC and BMI in a similar study [25]. Experimental evidence has shown that resveratrol presents beneficial effects on cardiovascular diseases, including myocardial infarction, hypertensive cardiomyopathy, thrombosis, cardiac fibrosis, and atherosclerosis [15].
Resveratrol is metabolized by the intestinal microbiota modulating its composition. This polyphenol interaction with the host microbiome may strongly influence MetS treatment’s efficiency, increasing this compound’s availability, inducing the production of important metabolites, or even promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria [26,27,28,29]. Therefore, the resveratrol/microbiota interaction might be a key element in MetS treatment.
The scientific literature, however, presents conflicting evidence regarding the effects of oral resveratrol, which may be associated with the differences observed in this study’s design, population, resveratrol dosage, and intervention period. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis aiming to summarize the available evidence from clinical studies of resveratrol’s effects on the following MetS parameters in different population profiles: waist circumference, blood pressure, glucose fasting levels, triglycerides, and high-density lipoprotein.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
The present systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted and reported based on the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) [30]. The protocol for this systematic review and meta-analysis was registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO, number CRD42022327486).
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: this study was a clinical study performed with humans in diverse methodological designs, which was placebo-controlled, and that reported the mean and standard deviation or standard error of mean for the variables studied (waist circumference (WC), systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP and DBP, respectively), glucose, triglycerides (TGs), and high-density lipoprotein (HDL)) at baseline, at the end of intervention, and/or as a change from baseline. Studies in languages other than English and without full-text access were excluded. The PICOS strategy was used to improve this study’s selection, as follows: P—population: adults, I—intervention: resveratrol, C—comparison: placebo, O—outcome: metabolic syndrome parameters, S—study design: RCTs with diverse methodological designs.
2.3. Search Strategy
A systematic search for studies that examined oral resveratrol’s effects on metabolic syndrome parameters most commonly considered for diagnosis (waist circumference, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, glucose, triglycerides, and high-density lipoprotein) in the definitions of MetS by the World Health Organization, European Group for Study of Insulin Resistance, National Cholesterol Education Program—Adult Treatment Panel III, International Diabetes Federation, and American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, as summarized by Grundy et al. [6], was performed on November 2021. The databases used for the papers retrieval were PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science. The search was performed by using the following MeSH and text keywords: “Resveratrol” OR “Resveratrols” AND “waist-circumference” OR “waist circumferences” OR “WC” OR “triglyceride” OR “triacylglycerols” OR “TG” OR “High-density lipoprotein” OR “high-density lipoproteins” OR “HDL” OR “glucose” OR “blood pressure” OR “systolic blood pressure” OR “diastolic blood pressure” OR “SBP” OR “DBP”. The search for studies reporting resveratrol’s effects on individual metabolic parameters most commonly included in the metabolic syndrome definition in different populations was performed due to the scarcity of studies that investigated oral resveratrol’s effects on individuals diagnosed with this syndrome. The full search strategy is available in the Supplementary Materials. The first search was performed in 2019, followed by updates in 2021 and 2023, where limits of the publication year of studies were applied (only publications from 2019 to 2021 and from 2021 and 2023 were used, respectively).
2.4. Study Selection
Study selection was performed manually by two authors in two phases: (1) reading the title and abstract, and (2) reading the entire text. In the first phase, the studies were selected based on the identification of the MeSH terms used in the searches, and the presence of sufficient data in the title and abstract regarding the study population, intervention details, and outcome variables studied was scanned, with duplicates being excluded (by organizing the titles in alphabetic order). Then, the remaining studies were entirely read, with the details—including methodological design, population included, the mean (±SD or SEM), and the availability of results—being identified and extracted.
2.5. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
The following information was retrieved from each selected study: paper title, name of first author, year of publication, sample size, population characteristics (participants’ nationality and underlying diseases), intervention dose, type and duration, the mean (SD or SEM) for WC, TG, HDL, glucose, and blood pressure levels. This information was gathered on a Microsoft® Office Excel sheet and summarized in tables. The variables were reported in the following metric units (WC: cm, TG: mg/dL, HDL: mg/dL, glucose: mg/dL, and blood pressure: mmHg). To convert cholesterol, triglycerides, and glucose from mmol/L into mg/dL, the data were multiplied by 38.67, 88.57, or 18.0, respectively. The data were plotted as mean ± standard deviation, and, when necessary, the following formula was applied to convert the standard error of the mean into standard deviation: SD = SEM × sqrt (n), where n is the number of subjects.
The included studies’ quality of evidence was assessed following the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) for systematic reviews. The studies were classified by their quality of evidence: very low (the true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of the effect), low (the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect), moderate (the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different), and high (the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect). The following criteria were evaluated for all studies included: study design, risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision, and publication bias.
2.6. Publication Bias Assessment
A visual inspection of funnel plots was performed to detect publication bias according to the studies’ asymmetry.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using Review Manager software version 5.4.1 (Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, UK). A heterogeneity test (Higgins (I2) was performed to assess inconsistencies among studies. The random effect model was applied when the heterogeneity was above 50%, and the fixed effect model was applied otherwise. The statistical test applied was the mean difference for all variables. The studies’ weights were evaluated according to the inverse of the variance. Data are displayed as forest plots graphs for each of the metabolic syndrome variables analyzed as main outcomes (waist circumference, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, glucose, triglycerides, and high-density lipoprotein). To construct the forest plots, studies reporting post-intervention or change from baseline means were separated into subgroups for analyses. The significance level was set at 5% (p < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Eligibility Criteria and Search Strategy
The bibliographic search in the chosen databases (PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus) retrieved 8105 papers. In the next phase, 7494 were excluded after screening for titles and abstracts, 668 were excluded for duplicates. After this phase, 139 papers remained, from which 9 papers could not be retrieved due to restricted access, 130 were fully read, and 93 were excluded for several reasons. In total, 37 papers were included in this systematic review and meta-analysis. Figure 2 details the study selection update flow diagram, according to the PRISMA template [31].

Figure 2.
Flow diagram depicting criteria used in study selection.
3.2. Characteristics of the Selected Studies
Table 1 depicts the main characteristics of the studies included, comprising 1649 participants included in the present systematic review and meta-analysis. Among them, the earliest study was published in 2012, and the latest was published in 2023. The sample size of the included studies was considerably heterogeneous, with the number of participants varying from 5 to 65 (per group—placebo/intervention). Furthermore, the studies were performed with several different populations—which presented comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, overweight, obesity, schizophrenia, coronary heart disease, polycystic ovary syndrome, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and dyslipidemia—from different nationalities, including American countries (Brazil, The United States of America, and Mexico), European countries (Germany, Hungary, The Netherlands, Amsterdam, and Denmark), Asian (Iran and China), Singapore, and Australia.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the studies included in the present systematic review and meta-analysis (n = 37).
Regarding the oral resveratrol treatment characteristics of the studies included, resveratrol was applied in dosages ranging from 10 mg to 3000 mg/day, with 100 mg/day being the lowest effective dose of resveratrol capable of reducing at least one of the studied parameters when administered for 2 months. Another factor with great variability was the time of intervention, which varied from a single-dose treatment to 12 months of treatment. Most studies were conducted with adults, and one of the five metabolic syndrome variables was evaluated in each of the included studies. This study’s methodological heterogeneity, however, hindered the data analysis and the conclusions regarding resveratrol’s beneficial effects.
3.3. Quality of Evidence of the Included Studies
The quality of evidence of all included studies was evaluated based on the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE). Most of the studies displayed very low to moderate quality of evidence, with only three studies being classified as high and one as very high quality (Table 2), which emphasizes the need in the literature for more high-quality studies that evaluate resveratrol’s effects on metabolic parameters. The main limitations that contributed to the poor quality of evidence found in the evaluated studies are the inclusion of small convenient samples composed of specific groups of participants (e.g., individuals with specific comorbidities, gender-specific samples), the concomitant use of other medications/interventions (e.g., balanced energy diets, physical activity programs, use of anti-hypertensive and hypoglycemic agents, etc.), and no specification of resveratrol purity.

Table 2.
Summary of findings and quality of evidence assessment.
3.4. Meta-Analysis
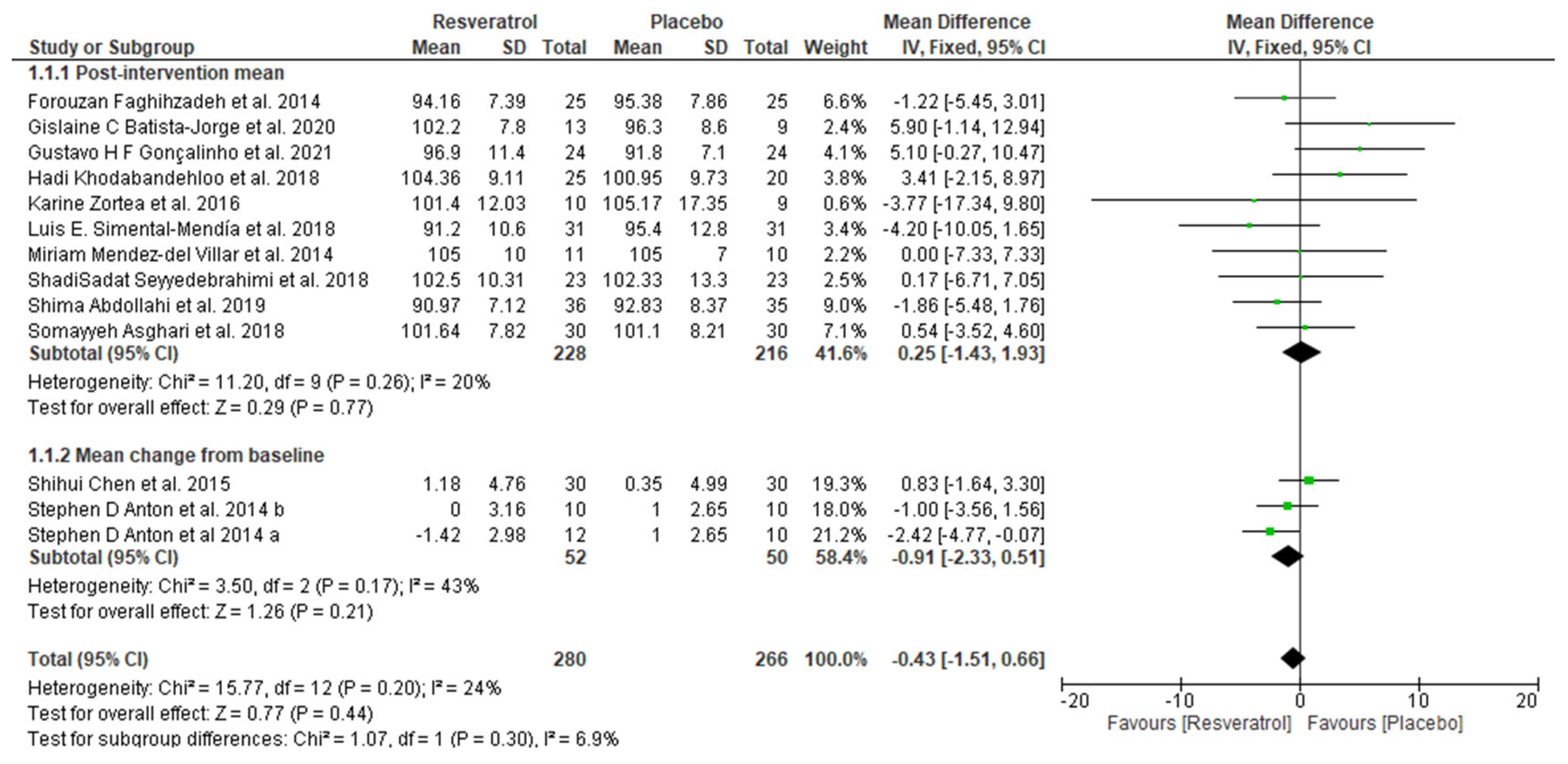
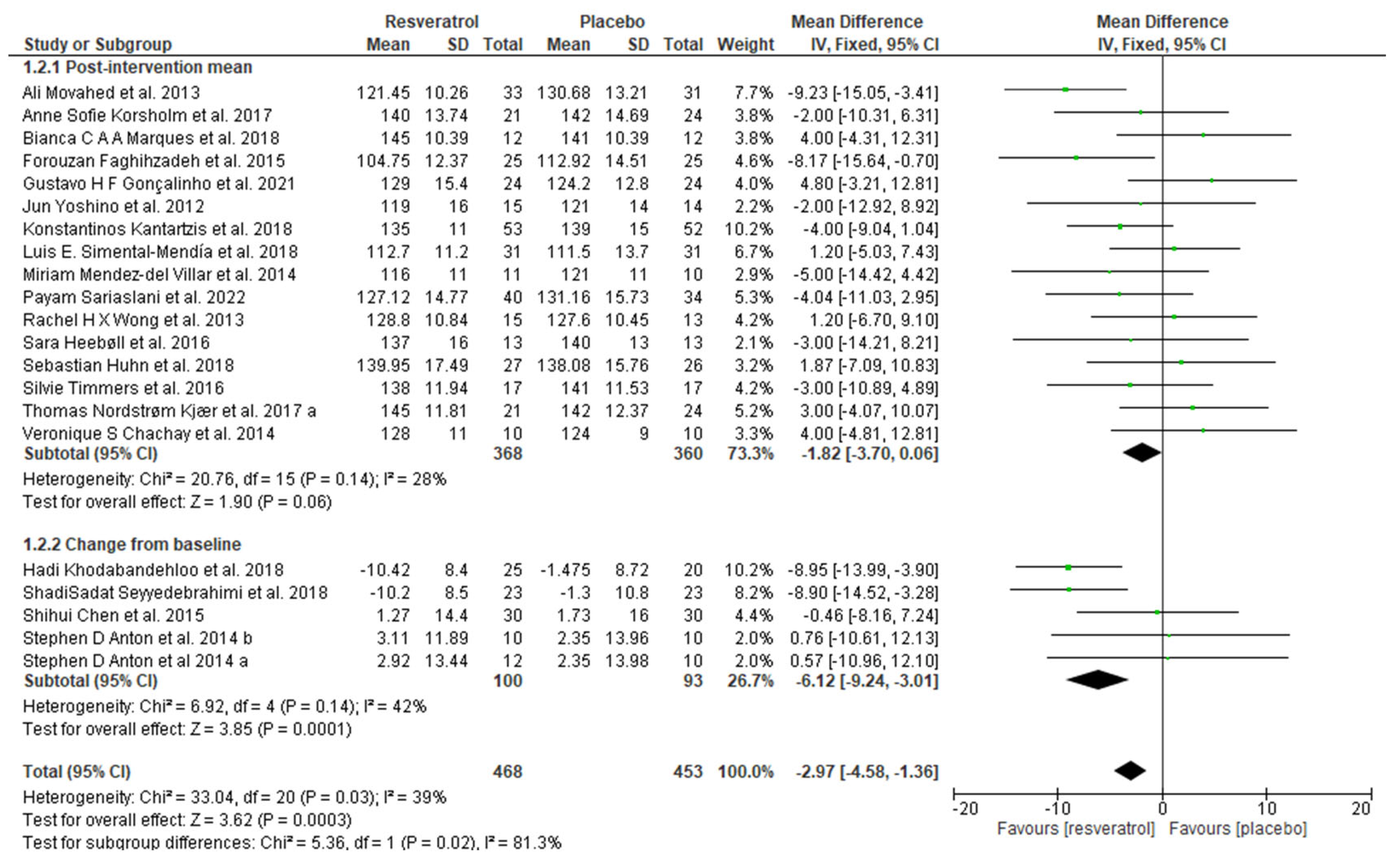
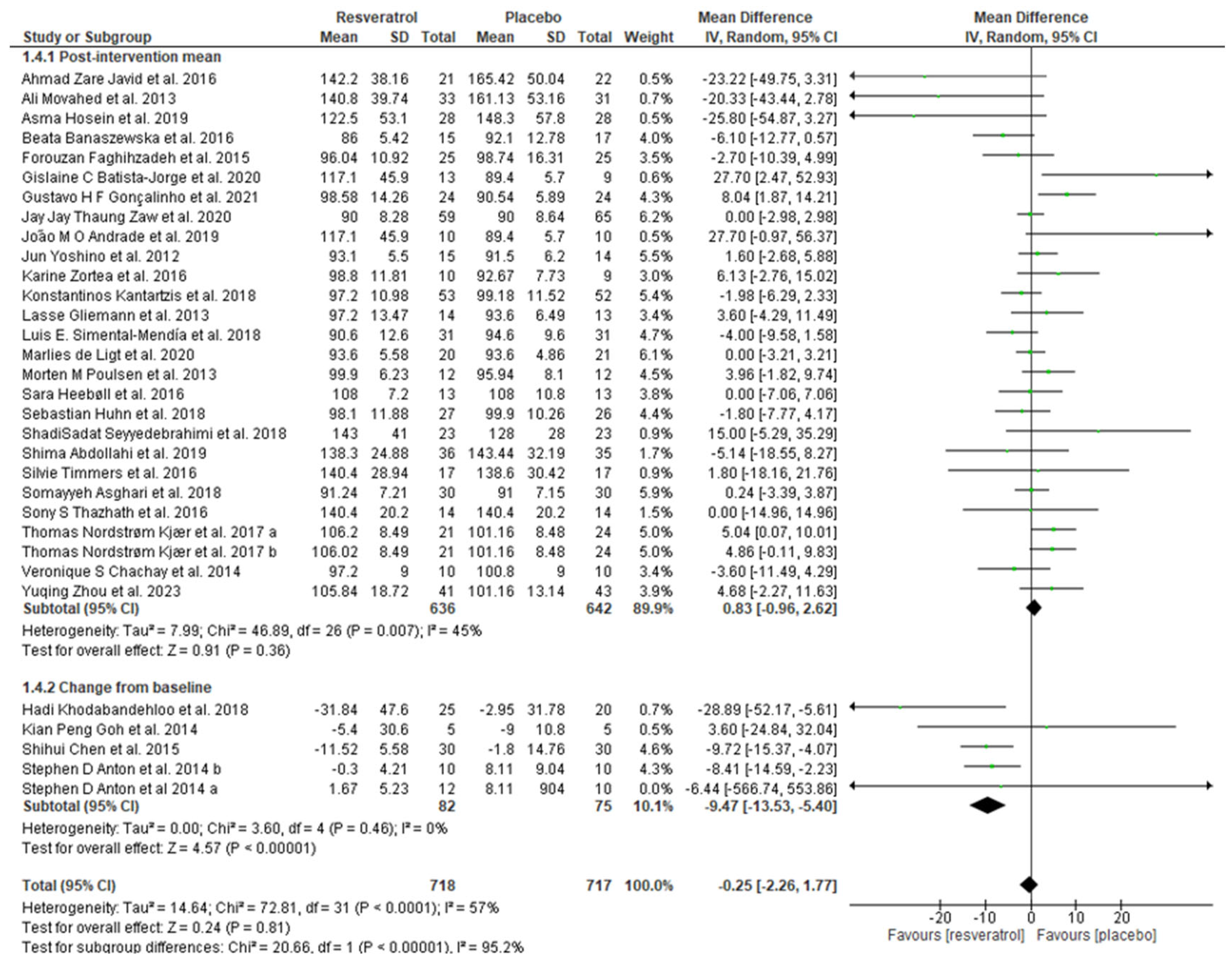
The effects of resveratrol on metabolic syndrome (waist circumference (WC), systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, glucose, TG, and HDL) were evaluated, and each parameter was individually analyzed in the present study. The pooled results showed that resveratrol had no significative effect on waist circumference (mean difference: −0.43; 95% confidence interval, −1.51, 0.66; p = 0.44; I2: 24%) (Figure 3) and that a significant decreased systolic blood pressure (mean difference: −2.97; 95% confidence interval, −4.58, −1.36; p = 0.0003; I2: 39%) (Figure 4) and diastolic blood pressure (mean difference: −1.22; 95% confidence interval, −2.28, −0.16; p = 0.02; I2: 43%) were observed (Figure 5). The overall effect of resveratrol on glucose levels was not statistically significant (mean difference: −0.25; 95% confidence interval, −2.26, 1.77; p = 0.81; I2: 57%); however, the analyses differed between subgroups (post-intervention mean subgroup: mean difference: 0.83; 95% confidence interval, −0.96, 2.62; p = 0.36; I2: 45%; change from baseline subgroup: mean difference: −9.47; 95% confidence interval, −13.53, −5.40; p < 0.00001; I2: 0%) (Figure 6). Surprisingly, resveratrol was associated with increased triglyceride levels (mean difference: 8.81; 95% confidence interval 1.98, 15.64; p = 0.01; I2: 29%), although the subgroup analyses were in disagreement (Figure 7). Finally, HDL levels seemed not to be affected by resveratrol (mean difference: −0.51; 95% confidence interval: −1.64, 0.62; p = 0.37; I2: 17%) (Figure 8).

Figure 3.
Forest plot depicting resveratrol versus placebo effects on waist circumference. Subgroup 1.1.1 summarizes the studies that provided post-intervention means [17,23,25,38,39,44,48,53,55,57]. Subgroup 1.1.2 summarizes the studies that provided a mean change from baseline [54,59].

Figure 4.
Forest plot depicting resveratrol versus placebo effects on systolic blood pressure. Subgroup 1.2.1 summarizes the studies that provided post-intervention means [19,23,33,34,36,38,42,46,48,50,51,52,56,60,61,63]. Subgroup 1.2.2 summarizes the studies that provided a mean change from baseline [39,53,54,59].
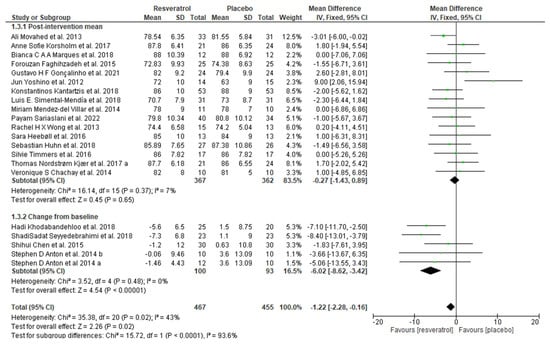
Figure 5.
Forest plot depicting resveratrol versus placebo effects on diastolic blood pressure. Subgroup 1.3.1 summarizes the studies that provided post-intervention means [19,23,33,34,36,38,42,46,48,50,51,52,56,60,61,63]. Subgroup 1.3.2 summarizes the studies that provided a mean change from baseline [39,53,54,59].

Figure 6.
Forest plot depicting resveratrol versus placebo effects on glucose levels. Subgroup 1.4.1 summarizes the studies that provided post-intervention means [9,19,25,32,33,35,37,38,40,41,42,44,46,47,48,49,51,52,53,55,56,57,58,60,61,62]. Subgroup 1.4.2 summarizes the studies that provided a mean change from baseline [39,45,54,59].

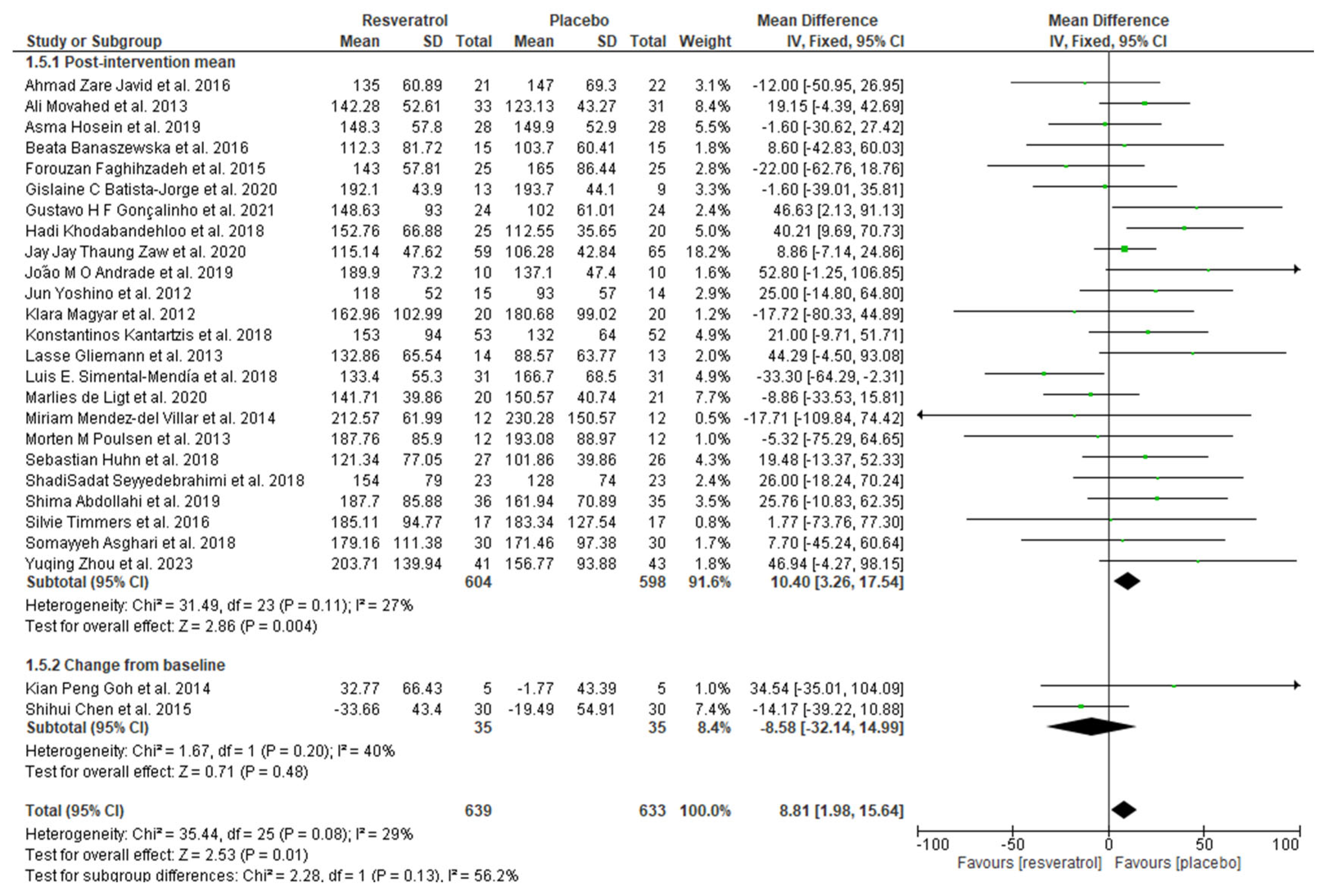
Figure 7.
Forest plot depicting resveratrol versus placebo effects on triglycerides levels. Subgroup 1.5.1 summarizes the studies that provided post-intervention means [9,19,23,25,32,33,35,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,46,47,48,49,52,53,55,56,57,62]. Subgroup 1.5.2 summarizes the studies that provided a mean change from baseline [45,54].

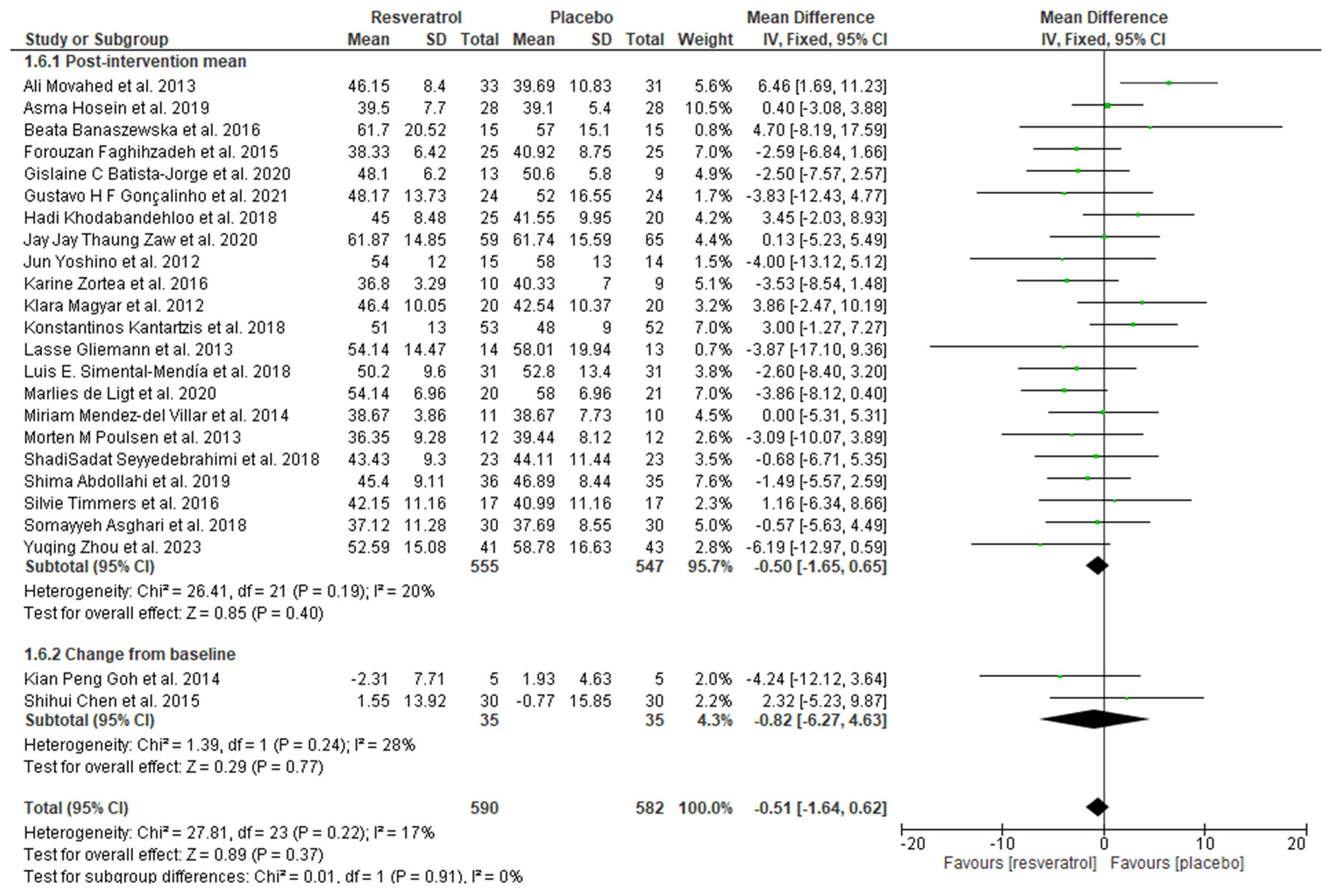
Figure 8.
Forest plot depicting resveratrol versus placebo effects on high-density lipoprotein levels. Subgroup 1.6.1 summarizes the studies that provided post-intervention means [9,19,23,25,33,35,37,38,39,40,42,43,44,46,47,48,49,53,55,56,57,62]. Subgroup 1.6.2 summarizes the studies that provided a mean change from baseline [45,54].
3.5. Publication Bias Assessment
The assessment of publication bias was performed via the visual evaluation of the funnel plots generated in the meta-analysis. It was possible to observe a significant asymmetry for the studies included in all variables analyses (Supplementary Materials), indicating the potential influence of publication bias.
4. Discussion
The present systematic review and meta-analysis summarizes the evidence obtained from 37 scientific studies investigating the effects of resveratrol on MetS parameters (waist circumference, blood pressure, glucose, triglycerides, and high-density lipoprotein). The main findings showed that resveratrol supplementation significantly decreased systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Moreover, resveratrol significantly decreased glucose levels from baseline. Finally, triglyceride levels seemed to be increased via resveratrol supplementation. The other studied parameters were not significantly changed.
The overall results of the present meta-analysis indicate that resveratrol supplementation may significantly decrease systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. By analyzing the studies included in the meta-analysis, it was possible to observe that resveratrol’s blood pressure-lowering effects were observed in studies mainly reporting dosages starting at 300 mg/day for at least 3 months and higher dosages (600–1000 mg/day) for 2 to 3 months. In contrast, dosages as low as 75 mg/day for 45 days or 3 months had no significant effects on systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Sariaslani et al. carried out a double-blind clinical trial, which evaluated resveratrol’s effect following an acute ischemic stroke. The patients were randomly allocated to receive resveratrol (500 mg/day) for 30 consecutive days or a placebo, but no significant effects were observed on their results with regard to systolic or diastolic blood pressure [63].
Corroborating our findings, animal studies suggested that a higher resveratrol dosage may significantly reduce arterial pressure in different hypertension models [64]. Interestingly, Zivarpour P et al. [15] showed that low doses of resveratrol (20–25 mg/day) may reduce or regulate diastolic arterial pressure in patients with cardiovascular diseases. The administration of a minimum dosage of 10 mg/kg of resveratrol may be necessary for a significant reduction in arterial pressure in the majority of animal models. In contrast, other studies with dosages lower than 2.5 mg/kg reported no significant effects of resveratrol on this parameter [65,66].
It is possible to suggest a few effects and mechanisms by which resveratrol may act on blood pressure control. The scientific literature already showed that resveratrol has a calorie restriction-like effect on the metabolic profile, being beneficial regarding the blood pressure levels of individuals with obesity [67]. Animal studies establish that resveratrol may restore the mesenteric and cardiac eNOS activity and reduce thiobarbituric acid-reactive substance (TBARS) levels, which are oxidative species [68]; however, it may still modulate the production of ET-1, Ang II, and NO, preventing an increase in systolic blood pressure levels in nephrectomized rat models [69].
Regarding the evaluation of resveratrol on glucose levels, conflicting findings were observed. In the subgroup of studies that reported a change from baseline, resveratrol supplementation significantly decreased glucose levels. In the other group of studies (those reporting post-intervention means), no differences were found. One of the studies included, which was performed by Movahed et al., carried out testing on individuals with T2D, reporting that a dosage of 1000 mg/day of resveratrol supplementation for 45 days was capable of significantly reducing fasting glucose levels and systolic blood pressure [33]. In fact, in a meta-analysis performed by Gu et al., resveratrol reduced fasting glucose levels in individuals with T2D [70].
Interestingly, in the present study with six studied variables, glucose was reduced in a greater number of the reported researches, including Movahed et al.’s study with 1000 mg/day/45 days) (p = 0.0001) [33]; Abdollahi et al.’s study with 1000 mg/day/8 weeks [55]; Anton et al.’s study with 300 mg/day and 1000 mg/day/3 months) (p = 0.023 and p = 0.008, respectively) [59]; Khodabandehloo et al.’s study with 800 mg/day/2 months (p = 0.048) [39]; and Chen et al.’s study with 600 mg/day/3 months (p = 0.001) [54]. It is noteworthy that the lowest effective dose of resveratrol for glucose reduction was verified by Stephen D. Anton et al., with 300 mg/day for 3 months [59]. It is known that the reduction in blood glucose levels is important for diabetes treatment. Diabetes is one of the most important causes of cardiovascular diseases, mainly due its effect on cardiac remodeling that induces cardiac fibrosis, which is characterized by the accumulation of proteins in the extracellular matrix of the myocardium [15].
In this perspective, several studies, clinical and experimental, were performed to evaluate resveratrol’s effects in hyperglycemic conditions observed in patients with T2D. Evidence supports a consistent reduction in glucose following treatment with this compound [71]. Interestingly, a meta-analysis performed by Hausenblas et al. reported that supplementation with resveratrol significantly reduced the HbA1c values in individuals with T2D, but not in fasting glucose levels [72]. In contrast, Faghihzadeh et al. reported that supplementation with 500 mg of resveratrol for 3 months had no beneficial effect on fasting glycemia and insulin resistance markers in individuals with NAFLD [19,73].
It is hypothesized, based on the inconsistent and controversial findings regarding resveratrol’s effects on glucose metabolism, that individuals without diabetes have normal basal levels of glucose and insulin, and that resveratrol consumption may not affect the physiological glucose and insulin regulation in these individuals. In individuals with diabetes, on the other hand, animal and human studies have evidenced that resveratrol is a potential agent in the reduction in glucose levels [74,75]. It is worth mentioning that although insulin resistance is considered a key aspect of MetS, its difficult assessment hinders its measurement in clinical and scientific settings. Thus, it not considered as a criterion for some definitions of this syndrome [6], nor is it included as an outcome in all studies performed in the metabolic field.
It is known that obesity is associated with several metabolic consequences that increase morbidity and mortality risks [76,77], especially abdominal obesity (android or central obesity), which is assessed by waist circumference and associated with increased cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes risks [78]. WC is recognized as a predictor of CVD risk as it reflects visceral adiposity deposition [79,80]. Increased food intake and decreased physical activity explain most of cases of obesity. Furthermore, other factors including genetics, medical conditions, sleep disturbances, and the use of a few medications may predispose individuals to weight gain [81,82]. Diet changes (low-calorie foods rich in fiber, such as fruits and vegetables) and physical activity (150 to 250 min of moderate to intense physical activity per week) represent the first step in obesity control and are good options to be included in a health-oriented routine [25].
However, obesity treatment and prevention are difficult tasks to achieve as preventive measures usually fail and therapeutic options are insufficient. Therefore, new treatment approaches are being investigated, raising the need for the study of nutraceutical therapeutic alternatives. In the present study, resveratrol supplementation did not decrease WC. However, several pre-clinical trials offer substantial evidence to support the concept that resveratrol may neutralize the negative effects of obesity [83], which was not corroborated by the clinical trials performed in the context of obesity and its inflammatory-associated state included in the present meta-analysis, reporting inconsistent results [17]. Mendez et al., in a study included in the present meta-analysis, months reported statistically significant reductions in WC when administering a resveratrol dose of 1500 mg/day for 3 (p = 0.004) [23].
The results found in the present meta-analysis are different from those reported by Sahebkar et al. [84] regarding resveratrol’s effects on lipid fractions. We showed that resveratrol did not affect the circulating levels of HDL-c, while TG seemed to have increased, although it was a small increase that might not have clinical importance. However, this finding is conflicting as in the one in the subgroup of studies reporting a change from baseline, in which no differences were found. TG may have increased in the former subgroup because of the individuals’ life habits and not the use of resveratrol per se. It is known that the current therapeutic approaches to modify triglycerides are limited, making the management of lifestyle habits the most important principle adopted [85].
The study performed by Kjæ et al. (included in our analysis), which investigated resveratrol’s effects on all parameters of MetS in middle-aged men, reported no beneficial clinical effects, as determined by a series of defined outcomes. High doses of resveratrol (1000 mg/day) were associated with increased levels of fructosamine, total cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol [60]. However, the literature reports several studies performed in animals and humans signaling that the long-term oral use of resveratrol supplementation has a protective effect for individuals at a high risk of developing cardiovascular diseases [86,87,88]. Studies performed by our group highlighted resveratrol’s beneficial effects on several metabolic parameters [25,41,89,90]. In this context, the absence of statistically significant differences regarding resveratrol’s effects on a few parameters might be related to the fact that the studies included here were performed with normocholesterolemic individuals or due to the short durations of the treatments.
Zhou et al. investigated if resveratrol was able to improve the profile of serum lipids and other metabolic markers in a dose–response manner in individuals with dyslipidemia. In their study, individuals received resveratrol (600 mg/day) or a placebo for approximately 2 months. Clinical trials, however, show inconclusive findings regarding this compound’s effect on dyslipidemia, which might be attributed to the heterogeneity of dosages among studies. Zhou et al. failed to show the beneficial effects of resveratrol on the lipid profile. However, this polyphenol antilipidemic effect must be questioned with caution as more studies are needed [62].
In summary, given the still-controversial and borderline findings regarding resveratrol’s effects, determining an ideal dosage of this compound for human usage is still a challenge. However, based on the studies included in the present review, the consumption of 300 mg/day of resveratrol seems to be an appropriate dose. Despite this, further studies are necessary. The study performed by Simental-Mendía et al., for example, used a lower effective dose (100 mg/day) of resveratrol in a short-term treatment (2 months) and evaluated WC, HDL-c, and TG, with the latter being the only one that was significantly reduced (p = 0.04) [48]. Mohaved et al., on the other hand, administered a higher dose (1000 mg/day) during a shorter intervention period (45 days) and reported significant reductions in glucose (p = 0.001) and blood pressure (p = 0.000) levels and increased HDL-c levels (p = 0.001), in addition to a borderline reduction in TG levels (p = 0.051) [33].
A few limitations of the present meta-analysis must be disclosed. First, potential basal differences in the diets of the intervention and placebo groups might have existed and interfered with the results. The short period of the interventions reported in most of the studies, participants coming from different health backgrounds, and the different dosages of resveratrol are among the discrepancies observed among the analyzed studies, which might explain the controversies that we observed. The period of the interventions must be highlighted, with the length of studies differing from a single-dose administration to a long-term 12-month treatment. From all the papers included, most reported treatment periods administered were up to 4 months, which is a limiting factor as metabolic responses usually require a minimum of a 12-week treatment period to be initiated. Another potential limitation of the results is resveratrol bioavailability [91], which varied with respect to the formulation chosen between the studies. A few trials used formulations with pure trans-resveratrol, while others used extracts in combination with trans-resveratrol.
Additionally, several studies did not provide the necessary data for the performance of the meta-analysis (mean and standard deviation/error), hindering their inclusion criteria. Sample size was also considered a limitation, as the number of participants varied from 5 to 65 per group (placebo vs. intervention). The studies included different populations (from several nationalities) with specific comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, overweight, obesity, and even schizophrenia. In this context, the methodological, clinical, and statistical heterogeneity (with the latter varying from 17 to 57%) observed among the studies, in addition to their general low quality of evidence, may have had an important effect on the results observed in the present meta-analysis.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the present systematic review and meta-analysis evidenced the potential therapeutic effect of resveratrol under some aspects of metabolic syndrome, especially regarding reductions in systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and glucose levels. However, the results are still borderline and somewhat controversial, which might be justified by the large heterogeneity and low quality of the studies retrieved from the literature. In this sense, the need for additional studies that would further investigate resveratrol’s effects on metabolic parameters is urgent, especially due to the vast literature that is already published regarding this compound’s effects on experimental studies with animal models, showing that resveratrol may have the potential of being more widely used in clinical practice if more robust evidence would be available.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/endocrines5020016/s1, Figure S1: Funnel plots for assessment of publication bias.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.C.B.-J., D.F.L. and R.S.M.-J.; methodology, G.C.B.-J., A.S.B.-J., D.F.L., D.E.S., A.H.J. and R.S.M.-J.; formal analysis, A.S.B.-J. and D.F.L.; data curation, G.C.B.-J., D.E.S. and A.H.J.; writing—original draft preparation, G.C.B.-J. and D.F.L.; writing—review and editing, G.C.B.-J., D.F.L., R.S.M.-J. and S.H.S.S.; supervision, R.S.M.-J. and S.H.S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially funded by grants from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG—Brazil), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq—Brazil), and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES—Brazil).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, C.; Williams, K.; Hunt, K.J.; Haffner, S.M. The National Cholesterol Education Program—Adult Treatment Panel III, International Diabetes Federation, and World Health Organization Definitions of the Metabolic Syndrome as Predictors of Incident Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Joo, M.; Hong, H.; Kang, H. Eating Speed, Physical Activity, and Cardiorespiratory Fitness Are Independent Predictors of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean University Students. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-González, J.G.; Violante-Cumpa, J.R.; Zambrano-Lucio, M.; Burciaga-Jimenez, E.; Castillo-Morales, P.L.; Garcia-Campa, M.; Solis, R.C.; González-Colmenero, A.D.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, R. HOMA-IR as a Predictor of Health Outcomes in Patients with Metabolic Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2022, 29, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safaei, M.; Sundararajan, E.A.; Driss, M.; Boulila, W.; Shapi’i, A. A Systematic Literature Review on Obesity: Understanding the Causes & Consequences of Obesity and Reviewing Various Machine Learning Approaches Used to Predict Obesity. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of the Metabolic Syndrome: An American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005, 112, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catelli De Carvalho, M.H. I Diretriz Brasileira de Diagnóstico e Tratamento Da Síndrome Metabólica. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2005, 84 (Suppl. S1), 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liese, A.D.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Haffner, S.M. Development of the Multiple Metabolic Syndrome: An Epidemiologic Perspective. Epidemiol. Rev. 1998, 20, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, M.M.; Vestergaard, P.F.; Clasen, B.F.; Radko, Y.; Christensen, L.P.; Stødkilde-Jørgensen, H.; Møller, N.; Jessen, N.; Pedersen, S.B.; Jørgensen, J.O.L. High-Dose Resveratrol Supplementation in Obese Men an Investigator- Initiated, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of Substrate Metabolism, Insulin Sensitivity, and Body Composition. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Gál, R.; Halmosi, R.; Gallyas, F.; Tschida, M.; Mutirangura, P.; Tóth, K.; Alexy, T.; et al. Resveratrol and beyond: The Effect of Natural Polyphenols on the Cardiovascular System: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramzadeh, A.; Bolandnazar, K.; Meshkani, R. Resveratrol as a Potential Protective Compound against Skeletal Muscle Insulin Resistance. Heliyon 2023, 9, 2405–8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberdi, G.; Rodríguez, V.M.; Miranda, J.; Macarulla, M.T.; Arias, N.; Andrés-Lacueva, C.; Portillo, M.P. Changes in White Adipose Tissue Metabolism Induced by Resveratrol in Rats. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Chen, L.; Mo, H.; Shastri, A.; Su, R.; Bapat, P.; Kwun, I.; Shen, C.-L. Novel Insights of Dietary Polyphenols and Obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calmasini, F.B.; Silva, F.H.; Alexandre, E.C.; Antunes, E. Efficacy of Resveratrol in Male Urogenital Tract Dysfunctions: An Evaluation of Pre-Clinical Data. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2023, 36, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivarpour, P.; Reiner, Ž.; Hallajzadeh, J.; Mirsafaei, L. Resveratrol and Cardiac Fibrosis Prevention and Treatment. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2022, 23, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barger, J.L.; Kayo, T.; Vann, J.M.; Arias, E.B.; Wang, J.; Hacker, T.A.; Wang, Y.; Raederstorff, D.; Morrow, J.D.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; et al. A Low Dose of Dietary Resveratrol Partially Mimics Caloric Restriction and Retards Aging Parameters in Mice. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihzadeh, F.; Adibi, P.; Rafiei, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Resveratrol Supplementation Improves Inflammatory Biomarkers in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yi, D.; Qiu, F.; Wu, L.; Tang, Y.; Wang, N. Mediterranean Diet Affects the Metabolic Outcome of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1225946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faghihzadeh, F.; Adibi, P.; Hekmatdoost, A. The Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, I.F.; Miranda, R.G.; Dorta, D.J.; Rolo, A.P.; Palmeira, C.M. Targeting Oxidative Stress with Polyphenols to Fight Liver Diseases. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.Y.; Huxley, R.R.; Wildman, R.P.; Woodward, M. Indices of Abdominal Obesity Are Better Discriminators of Cardiovascular Risk Factors than BMI: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi Dezfouli, R.; Mohammadian Khonsari, N.; Hosseinpour, A.; Asadi, S.; Ejtahed, H.S.; Qorbani, M. Waist to Height Ratio as a Simple Tool for Predicting Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2023, 47, 1286–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Del Villar, M.; González-Ortiz, M.; Martínez-Abundis, E.; Pérez-Rubio, K.G.; Lizárraga-Valdez, R. Effect of Resveratrol Administration on Metabolic Syndrome, Insulin Sensitivity, and Insulin Secretion. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2014, 12, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Martínez, B.I.; Ruiz-Ramos, M.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Santiago-Osorio, E.; Mendoza-Núñez, V.M. Effect of Resveratrol on Markers of Oxidative Stress and Sirtuin 1 in Elderly Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista-Jorge, G.C.; Barcala-Jorge, A.S.; Silveira, M.F.; Lelis, D.F.; Andrade, J.M.O.; de Paula, A.M.B.; Guimarães, A.L.S.; Santos, S.H.S. Oral Resveratrol Supplementation Improves Metabolic Syndrome Features in Obese Patients Submitted to a Lifestyle-Changing Program. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.M.; Eckardt, P.; Aleman, J.O.; Rosa, J.C.d.; Liang, Y.; Iizumi, T.; Etheve, S.; Blaser, M.J.; Breslow, J.L.; Holt, P.R. The Effects of Trans-Resveratrol on Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Microbiota in Men with the Metabolic Syndrome: A Pilot Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2019, 4, 122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mendes, K.L.; Lelis, D.d.F.; Souza, L.A.A.; Ronize Viviane Jorge Brito, M.C.A.; Nobre, S.A.M.; Guimarães, A.L.S.; Paula, A.M.B.d.; Lima, J.P.d.; Hilzendeger, A.M.; Santos, S.H.S. Lactococcus Lactis and Resveratrol Decrease Body Weight and Increase Benefic Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Mice. Protein Pept. Lett. 2020, 28, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, J.K.; Raederstorff, D.; Weber, P.; Steinert, R.E. Cardiovascular and Antiobesity Effects of Resveratrol Mediated through the Gut Microbiota. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Raka, F.; Heirali, A.A.; Shao, W.; Liu, D.; Gu, J.; Feng, J.N.; Mineo, C.; Shaul, P.W.; Qian, X.; et al. Resveratrol Intervention Attenuates Chylomicron Secretion via Repressing Intestinal FXR-Induced Expression of Scavenger Receptor SR-B1. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rethlefsen, M.L.; Kirtley, S.; Waffenschmidt, S.; Ayala, A.P.; Moher, D.; Page, M.J.; Koffel, J.B. PRISMA-S: An Extension to the PRISMA Statement for Reporting Literature Searches in Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javid, A.Z.; Hormoznejad, R.; Yousefimanes, H.A.; Zakerkish, M.; Haghighi, M.H.; Ravanbakhsh, M. The Impact of Resveratrol Supplementation on Blood Glucose, Insulin, Insulin Resistance, Triglyceride and Periodontal Markers in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Chronic Periodontitis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, C183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahed, A.; Nabipour, I.; Lieben Louis, X.; Thandapilly, S.J.; Yu, L.; Kalantarhormozi, M.; Rekabpour, S.J.; Netticadan, T. Antihyperglycemic Effects of Short Term Resveratrol Supplementation in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 851267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korsholm, A.S.; Kjær, T.N.; Ornstrup, M.J.; Pedersen, S.B. Comprehensive Metabolomic Analysis in Blood, Urine, Fat, and Muscle in Men with Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial on the Effects of Resveratrol after Four Months’ Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseini, A.; Namazi, G.; Farrokhian, A.; Reiner, Ž.; Aghadavod, E.; Bahmani, F.; Asemi, Z. The Effects of Resveratrol on Metabolic Status in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Coronary Heart Disease. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6042–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, B.C.A.A.; Trindade, M.; Aquino, J.C.F.; Cunha, A.R.; Gismondi, R.O.; Neves, M.F.; Oigman, W. Beneficial Effects of Acute Trans-Resveratrol Supplementation in Treated Hypertensive Patients with Endothelial Dysfunction. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2018, 40, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaszewska, B.; Wrotyńska-Barczyńska, J.; Spaczynski, R.Z.; Pawelczyk, L.; Duleba, A.J. Effects of Resveratrol on Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 4322–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalinho, G.H.F.; Roggerio, A.; Goes, M.F.d.S.; Avakian, S.D.; Leal, D.P.; Strunz, C.M.C.; Mansur, A.d.P. Comparison of Resveratrol Supplementation and Energy Restriction Effects on Sympathetic Nervous System Activity and Vascular Reactivity: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Molecules 2021, 26, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodabandehloo, H.; Seyyedebrahimi, S.S.; Esfahani, E.N.; Razi, F.; Meshkani, R. Resveratrol Supplementation Decreases Blood Glucose without Changing the Circulating CD14 + CD16 + Monocytes and Inflammatory Cytokines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutr. Res. 2018, 54, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaw, J.J.T.; Howe, P.R.C.; Wong, R.H.X. Sustained Cerebrovascular and Cognitive Benefits of Resveratrol in Postmenopausal Women. Nutrients 2020, 12, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.M.O.; Barcala-Jorge, A.S.; Batista-Jorge, G.C.; Paraíso, A.F.; Freitas, K.M.d.; Lelis, D.d.F.; Guimarães, A.L.S.; de Paula, A.M.B.; Santos, S.H.S. Effect of Resveratrol on Expression of Genes Involved Thermogenesis in Mice and Humans. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, J.; Conte, C.; Fontana, L.; Mittendorfer, B.; Imai, S.; Schechtman, K.B.; Gu, C.; Kunz, I.; Fanelli, F.R.; Patterson, B.W.; et al. Resveratrol Supplementation Does Not Improve Metabolic Function in Nonobese Women with Normal Glucose Tolerance. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magyar, K.; Halmosi, R.; Palfi, A.; Feher, G.; Czopf, L.; Fulop, A.; Battyany, I.; Sumegi, B.; Toth, K.; Szabados, E. Cardioprotection by Resveratrol: A Human Clinical Trial in Patients with Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2012, 50, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zortea, K.; Franco, V.C.; Francesconi, L.P.; Cereser, K.M.M.; Lobato, M.I.R.; Belmonte-De-Abreu, P.S. Resveratrol Supplementation in Schizophrenia Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial Evaluating Serum Glucose and Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Nutrients 2016, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, K.P.; Lee, H.Y.; Lau, D.P.; Supaat, W.; Chan, Y.H.; Koh, A.F.Y. Effects of Resveratrol in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Skeletal Muscle SIRT1 Expression and Energy Expenditure. Int. J. Sport. Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2014, 24, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantartzis, K.; Fritsche, L.; Bombrich, M.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Staiger, H.; Kunz, I.; Schoop, R.; Lehn-Stefan, A.; Heni, M.; et al. Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation on Liver Fat Content in Overweight and Insulin-Resistant Subjects: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1793–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliemann, L.; Schmidt, J.F.; Olesen, J.; Biensø, R.S.; Peronard, S.L.; Grandjean, S.U.; Mortensen, S.P.; Nyberg, M.; Bangsbo, J.; Pilegaard, H.; et al. Resveratrol Blunts the Positive Effects of Exercise Training on Cardiovascular Health in Aged Men. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 5047–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Effect of Resveratrol Supplementation on Lipid Profile in Subjects with Dyslipidemia: A Randomized Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrition 2019, 58, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ligt, M.; Bergman, M.; Fuentes, R.M.; Essers, H.; Moonen-Kornips, E.; Havekes, B.; Schrauwen-Hinderling, V.B.; Schrauwen, P. No Effect of Resveratrol Supplementation after 6 Months on Insulin Sensitivity in Overweight Adults: A Randomized Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.H.X.; Berry, N.M.; Coates, A.M.; Buckley, J.D.; Bryan, J.; Kunz, I.; Howe, P.R.C. Chronic Resveratrol Consumption Improves Brachial Flow-Mediated Dilatation in Healthy Obese Adults. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heebøll, S.; Kreuzfeldt, M.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.; Kjær Poulsen, M.; Stødkilde-Jørgensen, H.; Møller, H.J.; Jessen, N.; Thorsen, K.; Kristina Hellberg, Y.; Bønløkke Pedersen, S.; et al. Placebo-Controlled, Randomised Clinical Trial: High-Dose Resveratrol Treatment for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huhn, S.; Beyer, F.; Zhang, R.; Lampe, L.; Grothe, J.; Kratzsch, J.; Willenberg, A.; Breitfeld, J.; Kovacs, P.; Stumvoll, M.; et al. Effects of Resveratrol on Memory Performance, Hippocampus Connectivity and Microstructure in Older Adults—A Randomized Controlled Trial. Neuroimage 2018, 174, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyyedebrahimi, S.S.; Khodabandehloo, H.; Nasli Esfahani, E.; Meshkani, R. The Effects of Resveratrol on Markers of Oxidative Stress in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Ran, L.; Wan, J.; Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; Shu, F.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Resveratrol Improves Insulin Resistance, Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahi, S.; Salehi-Abargouei, A.; Toupchian, O.; Sheikhha, M.H.; Fallahzadeh, H.; Rahmanian, M.; Tabatabaie, M.; Mozaffari-Khosravi, H. The Effect of Resveratrol Supplementation on Cardio-Metabolic Risk Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 3153–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmers, S.; De Ligt, M.; Phielix, E.; Van De Weijer, T.; Hansen, J.; Moonen-Kornips, E.; Schaart, G.; Kunz, I.; Hesselink, M.K.C.; Schrauwen-Hinderling, V.B.; et al. Resveratrol as Add-on Therapy in Subjects with Well-Controlled Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghari, S.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Somi, M.H.; Ghavami, S.M.; Rafraf, M. Comparison of Calorie-Restricted Diet and Resveratrol Supplementation on Anthropometric Indices, Metabolic Parameters, and Serum Sirtuin-1 Levels in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2018, 37, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thazhath, S.S.; Wu, T.; Bound, M.J.; Checklin, H.L.; Standfield, S.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K. Administration of Resveratrol for 5 Wk Has No Effect on Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Secretion, Gastric Emptying, or Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, S.D.; Embry, C.; Marsiske, M.; Lu, X.; Doss, H.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Manini, T.M. Safety and Metabolic Outcomes of Resveratrol Supplementation in Older Adults: Results of a Twelve-Week, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 57, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjær, T.N.; Ornstrup, M.J.; Poulsen, M.M.; Stødkilde-Jørgensen, H.; Jessen, N.; Jørgensen, J.O.L.; Richelsen, B.; Pedersen, S.B. No Beneficial Effects of Resveratrol on the Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 1642–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chachay, V.S.; Macdonald, G.A.; Martin, J.H.; Whitehead, J.P.; O’Moore-Sullivan, T.M.; Lee, P.; Franklin, M.; Klein, K.; Taylor, P.J.; Ferguson, M.; et al. Resveratrol Does Not Benefit Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 2092–2103.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Pan, Z.; Jin, Y.; Li, Q.; Pang, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ling, W. A Randomized Trial on Resveratrol Supplement Affecting Lipid Profile and Other Metabolic Markers in Subjects with Dyslipidemia. Nutrients 2023, 15, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariaslani, P.; Asgharzadeh, S.; Mohammadi, H.; Ghanbari, A.; Hezarkhani, L.; Shahbazi, F.; Mirzaeei, S. Does Resveratrol Enhance Recovery from Acute Ischemic Stroke? A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Rep. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jojima, K.; Tanaka, A.; Node, K. Resveratrol Supplementation: A Therapeutic Potential for Cardiac Remodeling in Hypertensive Heart Disease. Hypertens. Res. 2023, 46, 1596–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rush, J.W.E.; Quadrilatero, J.; Levy, A.S.; Ford, R.J. Chronic Resveratrol Enhances Endothelium-Dependent Relaxation but Does Not Alter ENOS Levels in Aorta of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 232, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kawai, Y.; Yamori, Y. Protective Effect of Resveratrol on Oxidative Damage in Male and Female Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2001, 28, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmers, S.; Konings, E.; Bilet, L.; Houtkooper, R.H.; van de Weijer, T.; Goossens, G.H.; Hoeks, J.; van der Krieken, S.; Ryu, D.; Kersten, S.; et al. Calorie Restriction-like Effects of 30 Days of Resveratrol Supplementation on Energy Metabolism and Metabolic Profile in Obese Humans. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miatello, R.; Vázquez, M.; Renna, N.; Cruzado, M.; Zumino, A.P.; Risler, N. Chronic Administration of Resveratrol Prevents Biochemical Cardiovascular Changes in Fructose-Fed Rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2005, 18, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Mao, W.; Wang, W.; Cui, W.; Zhang, X.; Jia, X.; et al. Effects of Trans-Resveratrol on Hypertension-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy Using the Partially Nephrectomized Rat Model. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2005, 32, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Geng, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Song, G. Effects of Resveratrol on Metabolic Indicators in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 9734738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, C.; Qiu, S.; Yuan, X.; Li, L. Effects of Resveratrol on Glucose Control and Insulin Sensitivity in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausenblas, H.A.; Schoulda, J.A.; Smoliga, J.M. Resveratrol Treatment as an Adjunct to Pharmacological Management in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus--Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihzadeh, F.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Adibi, P. Resveratrol and Liver: A Systematic Review. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2015, 20, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamardl, H.A.M.A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Merzeban, D.H.; Elamir, A.M.; Golam, R.M.; Elsayed, A.M. Resveratrol and Dulaglutide Ameliorate Adiposity and Liver Dysfunction in Rats with Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome: Role of SIRT-1/Adipokines/PPARγ and IGF-1. Daru 2023, 31, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reda, D.; Elshopakey, G.E.; Mahgoub, H.A.; Risha, E.F.; Khan, A.A.; Rajab, B.S.; El-Boshy, M.E.; Abdelhamid, F.M. Effects of Resveratrol Against Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Rats: Role of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 3362005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, E.; Cho, N.-J.; Kang, H.; Kim, S.H.; Park, H.K.; Kwon, S.H. Computed Tomography Evaluation of Skeletal Muscle Quality and Quantity in People with Morbid Obesity with and without Metabolic Abnormality. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0296073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wharton, S.; Lau, D.C.W.; Vallis, M.; Sharma, A.M.; Biertho, L.; Campbell-Scherer, D.; Adamo, K.; Alberga, A.; Bell, R.; Boulé, N.; et al. Obesity in Adults: A Clinical Practice Guideline. CMAJ 2020, 192, E875–E891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiklund, P.; Toss, F.; Weinehall, L.; Hallmans, G.; Franks, P.W.; Nordstrom, A.; Nordstrom, P. Abdominal and Gynoid Fat Mass Are Associated with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Men and Women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4360–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedhoseinpour, A.; Barzin, M.; Mahdavi, M.; Valizadeh, M.; Azizi, F.; Ghareh, S.; Hosseinpanah, F. BMI Category-Specific Waist Circumference Thresholds Based on Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes and All-Cause Mortality: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study (TLGS). BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva de Lima Loureiro, N.I.; Lameira Maciel Amaral, T.I.; de Araújo Amaral, C., III; Torres Rego Monteiro, G.I.; Teixeira Leite de Vasconcellos, M.V.; Junior Sordi Bortolini, M.V.; Lameira Maciel Amaral, T. Relationship between Anthropometric Indicators and Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease in Adults and Older Adults of Rio Branco, Acre. Rev. Saude Publica 2020, 54, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.; Duncan, M.J.; Patte, K.A.; Roy, B.D.; Ditor, D.S.; Klentrou, P. Changes in Body Mass, Physical Activity, and Dietary Intake during the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdowns in Canadian University Students. Biology 2023, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.; Christensen, S.M.; Richardson, L.; Ingersoll, A.B.; Burridge, K.; Golden, A.; Karjoo, S.; Cortez, D.; Shelver, M.; Bays, H.E. Nutrition and Physical Activity: An Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) Clinical Practice Statement 2022. Obes. Pillars 2022, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, M.M.; Fjeldborg, K.; Ornstrup, M.J.; Kjaer, T.; Nohr, M.K.; Pedersen, S.B. Resveratrol and Inflammation: Challenges in Translating Pre-Clinical Findings to Improved Patient Outcomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahebkar, A. Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation on Plasma Lipids: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catapano, A.L.; Graham, I.; De Backer, G.; Wiklund, O.; Chapman, M.J.; Drexel, H.; Hoes, A.W.; Jennings, C.S.; Landmesser, U.; ESC Scientific Document Group; et al. 2016 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 2999–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomé-Carneiro, J.; Gonzálvez, M.; Larrosa, M.; García-Almagro, F.J.; Avilés-Plaza, F.; Parra, S.; Yáñez-Gascón, M.J.; Ruiz-Ros, J.A.; García-Conesa, M.T.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; et al. Consumption of a Grape Extract Supplement Containing Resveratrol Decreases Oxidized LDL and ApoB in Patients Undergoing Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Triple-Blind, 6-Month Follow-up, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Trial. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighatdoost, F.; Hariri, M. Effect of Resveratrol on Lipid Profile: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Randomized Clinical Trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 129, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-Ros, R.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Arós, F.; Fitó, M.; Lapetra, J.; Estruch, R.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; et al. High Urinary Levels of Resveratrol Metabolites Are Associated with a Reduction in the Prevalence of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in High-Risk Patients. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 65, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, K.L.; Pinho, L.d.; João Marcus Oliveira Andrade, A.F.P.; Lula, J.F.; Macedo, S.M.; Feltenberger, J.D.; Guimarães, A.L.S.; Paula, A.M.B.d.; Santos, S.H.S. Distinct Metabolic Effects of Resveratrol on Lipogenesis Markers in Mice Adipose Tissue Treated with High-Polyunsaturated Fat and High-Protein Diets. Life Sci. 2016, 153, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.M.O.; Paraíso, A.F.; Oliveira, M.V.M.d.; Martins, A.M.E.; Neto, J.F.; Guimarães, A.L.S.; Paula, A.M.d.; Qureshi, M.; Santos, S.H.S. Resveratrol Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis in High-Fat Fed Mice by Decreasing Lipogenesis and Inflammation. Nutrition 2014, 30, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitaglione, P.; Sforza, S.; Galaverna, G.; Ghidini, C.; Caporaso, N.; Vescovi, P.P.; Fogliano, V.; Marchelli, R. Bioavailability of Trans-Resveratrol from Red Wine in Humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).