Abstract
We evaluated the hospital evolution of hyponatremia and inflammation markers in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The hospital evolutions of a cohort of adult patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and hyponatremia were retrospectively analyzed. Data of the admission day, 2nd–3rd and 7th–10th day of hospitalization, and of the discharge day were collected. Comparative and multivariate analyzes were developed, and Hazzard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were calculated. Of the 172 hospitalized patients with COVID-19, 49 of them (28.5%) had hyponatremia, which were analyzed. A total of 32/49 (65.3%) patients were male, and 22/49 (44.9%) euvolemic. Mean age: 69.9 ± 14.7 years. All patients had high inflammatory markers at admission. Of the total patients with hyponatremia at admission, only 26.2% remained hyponatremic at the 7th–10th day of hospitalization. Improvement in serum sodium (SNa) coincided with improvement in inflammatory markers during hospitalization, in both euvolemic and hypovolemic hyponatremic patients. A higher serum creatinine at admission was independently associated with mortality (HR: 12.23, 95% CI: 2 to 25.6) in hyponatremic COVID-19 patients. In conclusion, both hypovolemic and euvolemic hyponatremia in COVID-19 patients occurred in an inflammation status, and improved as inflammation decreased.
1. Introduction
Hyponatremia, the most frequent electrolyte disorder, is observed in 19.7% of general hospitalized patients [1], and is associated with an increase in hospital mortality [1,2]. Hyponatremia is common in patients with pneumonia, where tends to be euvolemic, and caused by the syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH), being observed in approximately a third of hospitalized patients with pneumonia [3]. In this setting, one of the main causal mechanisms of hyponatremia is the inflammation, via cytokines [4,5].
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by SARS-CoV-2. Currently, it is known that COVID-19 can have two phases: a first, acute phase, and a second, chronic phase. The acute COVID-19 clinical spectrum varies from asymptomatic to severe clinical forms, the latter classically characterized by the presence of pneumonia associated with an acute respiratory failure and multiple organ failure [6]. Acute severe COVID-19 is also characterized by high levels of inflammatory cytokines [7,8,9], and is associated with a poor clinical prognosis and mortality. Unfortunately, to date, there is still not a completely effective and specific treatment of COVID-19 [10], and so the support treatment and controlling the factors related to a poor evolution are important.
COVID-19 patients commonly manifest hyponatremia at diagnosis, in a range from 9.9% to close to 50% [11,12,13,14,15]. Cumulative evidence demonstrates that hyponatremia is associated with a high risk of mortality and poor clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients [16]. However, the mechanisms behind hyponatremia etiopathogenesis in COVID-19 remain unclear. Although euvolemic forms, such as SIADH, have been proposed to be a frequent cause [17], both hypovolemic and hypervolemic forms could also occur [18]. Berni et al. showed an inverse relationship between levels of serum sodium (SNa) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in COVID-19 patients [19], proposing an inflammatory via implicated in the development of hyponatremia in these patients. In this line, Ayus et al. recently found that mild hyponatremia at admission is associated with elevated markers of systemic inflammation [15]. However, inflammatory mechanisms in the development of hyponatremia would be expected when the latter is induced by SIADH [5], but not when hypovolemic or hypervolemic, which are related to a decreased circulating effective volume. Whether an inflammatory status is also implicated in these latter types of hyponatremia has not been elucidated.
We aimed to investigate whether the inflammatory markers of hyponatremic hospitalized COVID-19 patients were related with the evolution of the SNa in the hospital stay, regardless the volemic status.
2. Methods
2.1. Design and Subjects
It is a retrospective study of a series of consecutive cases of adult patients with COVID-19 pneumonia who had hyponatremia at hospital admission and were followed during the hospitalization. Hyponatremia was defined as a SNa < 135 mmol/L after correction for glycemia [20]. COVID-19 pneumonia was confirmed by a positive reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test and clinical and/or radiological manifestations of pneumonia. All patients were admitted from 1 April to 30 April 2020, in three wards of different tertiary hospitals of Madrid, Spain, where the “COVID-19 teams”, including physicians of different medical specialties, attended COVID-19 patients during the first wave of the pandemic. Each of the authors of the current study was part of a COVID-19 team of their respective hospital ward during this period.
The study complied with accepted standards of good clinical practice of the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki, in accordance with the guidelines of the local Research Ethics Committee of the Hospital Clínico San Carlos.
Variables were collected from admission day, 2nd–3rd day of hospitalization, 7th–10th day of hospitalization, and from the day of discharge of the patients, when available. Collected variables were age, sex, SNa, serum potassium (SK), serum creatinine (SC), serum urea (SU), volemia, serum inflammatory markers (IM): D-dimer, fibrinogen, C-reactive protein, ferritin, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), IL-6; comorbidities: obesity, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/smoking habit, obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome, asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, any cancer, obstructive uropathy, and advanced/moderate chronic kidney disease (glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min); previous drug use; and the clinical outcomes: hospital death, admittance to the intensive care unit (ICU), and length of hospital stay (LOS). Treatment variables were not collected since an important heterogeneity and a lack of details of these variables were observed during the review of the clinical records.
All variables, including the volemic status of the patients, were collected in accordance as they appeared registered in the clinical record. If volemic status was not expressed in clinical records, we searched for symptoms/signs suggestive of hypovolemia, euvolemia, or hypervolemia as follows. Hypovolemia was considered when three or more of the following symptoms/signs were observed: thirst, orthostatic symptoms, blood pressure ≤ 90/60 mmHg, heart rate ≥ 90 bpm, urinary sodium ≤ 30 mmol/L [21,22], or an increase in SC accompanied the decrease in SNa [23]. The absence of the previous criterion was assumed as euvolemia if data of congestions or fluid overload were absent. Hypervolemia was considered present when explicit signs of hydric overload or edematous heart failure were registered in the clinical records.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
Univariate analysis for quantitative variables was developed with Mann–Whitney U or Kruskal–Wallis tests (when non-parametric) and T-student or ANOVA tests (when parametric). Univariate analysis for categorical variables was performed with chi-squared or Fisher tests. Correlation studies with Pearson and Spearman tests were executed for quantitative variables.
Multivariate analyses with logistic and Cox regressions including variables with a p value < 0.1 in the univariate analysis, and others of clinical relevance, were tested to evaluate the association of the variables with clinical outcomes, calculating odd ratio (OR) and Hazard ratio (HR), respectively. Multivariate analysis was developed with the forward steps Wald’s method. A two-tailed p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Ninety-five percent confidence intervals (95% CI) were calculated. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 25 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
3. Results
A total of 172 COVID-19 pneumonia patients were attended in the three wards by the respective COVID-19 teams in the period mentioned above. Of them, hyponatremia was observed in 49 (28.5%) patients at admission. All hyponatremic patients were admitted due to the presence of low respiratory tract symptoms with radiological or clinical data of pneumonia. Other specific symptoms such as gastrointestinal, neurological, or musculoskeletal symptoms were not registered. No patient was hypervolemic, whereas hypovolemia was found in 27/49 (55.1%) and euvolemia in 22/49 (44.9%) patients. The mean SNa of the entire cohort was 131.3 ± 2.4 mmol/L. The rate of patients with SNa < 130 mmol/L at admission was similar between hypovolemic and euvolemic (22.2 vs. 18.2%, p = 1). No patient had SNa < 125 mmol/L at admission.
The mean age of the entire hyponatremic cohort was 69.9 ± 14.7 years, and 32/49 (65.3%) were male. The patients’ general characteristics at admission grouped according to volemic status are described in Table 1. Thirty-four of the 49 patients (69.4%) were treated with systemic glucocorticoids during the first week of the hospitalization. In accordance with clinical records at admission, patients with euvolemic hyponatremia were treated with water restriction between up to 500 to 1000 mL per day, whereas hypovolemic received intravenous physiological isotonic saline (NaCl 0.9%). Time of water restriction or fluid therapy was not registered.

Table 1.
General characteristics of patients at admission.
3.1. Clinical Evolution of Hyponatremic Patients
Hyponatremia rate progressively decreased from admission to the discharge of the patients (Figure 1). At the 2nd–3rd day of hospitalization, 17 (34.7%) of the initial 49 patients remained hyponatremic. At the 7th–10th day, 11 (26.2%) of the 42 patients who were still hospitalized continued with hyponatremia. At the final follow-up, 37 patients were discharged, and, of them, 8 (21.6%) were hyponatremic. No significative differences between the rates of hypovolemic and euvolemic hyponatremia were encountered neither at the 2nd–3rd day of hospitalization, nor at discharge day. However, at the 7th–10th day of hospitalization, a higher rate of hyponatremic subjects were euvolemic: 72.7% vs. 27.3% (p = 0.043).
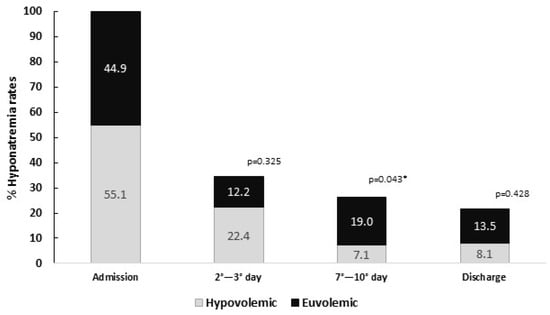
Figure 1.
Evolution of hyponatremia rates during hospitalization, grouped as hypovolemic and euvolemic. p value represents the statistical significance of the analysis of difference of ratios between hypovolemia and euvolemia. p-value indicates statistical differences between hypovolemic and euvolemic. * p < 0.05.
In accordance with the univariate analysis, patients with obesity had a higher risk of remaining hyponatremic at the 2nd–3rd day of hospitalization (OR 5.1, 95% CI: 1.02 to 25.54), whereas those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/smoking habit had a lower risk (OR 0.29, 95% CI: 0.18 to 0.46). With the exception of volemic status at admission, as shown in the previous paragraph, neither the comorbidities nor previous treatment at admission, nor the administration of glucocorticoids during hospitalization were associated with hyponatremia between the 7th and 10th day. Likewise, no difference of means or medians of IM was found between those who persisted hyponatremic on the 7th–10th day and those who did not.
At the end of follow-up, 37/49 (75.5%) patients were discharged, with 2 (4.1%) previously admitted to ICU, 5/49 (10.2%) remained hospitalized, and 7/49 (14.3%) died. Death occurred before the 7th day in all these patients. All patients who died were >70 years old, and three of them remained hyponatremic at their 2nd–3rd day of hospitalization.
No comorbidity or previous treatment at admission, neither sex, age, initial volemic status, IM at admission, hyponatremia at 2nd–3rd day, nor administration of glucocorticoids during hospitalization were statistically associated with death in the univariate analysis. In a multivariate analysis including age, sex, and the admission variables: SNa, D-Dimer, LDH, and C-reactive protein; a higher SNa level was found to be independently associated with a decrease in the risk of mortality, both in logistic regression (OR: 0.43, 95% CI: 0.20 to 0.93, p = 0.043) and Cox regression (HR: 0.53, 95% CI: 0.32 to 0.87, p = 0.013). However, when this Cox regression model is adjusted with admission SC, the SNa lost statistical significance. In this last model, SC was the unique variable associated with hospital death (HR: 12.23, 95% CI: 2 to 25.6, p = 0.003).
Of the total of survivors, the median LOS was 13.5 days [7.1–19.9]. A trend of a lower median LOS was found in hypovolemic compared to euvolemic patients (11 vs. 15 days, p = 0.546). However, in the entire cohort, neither an SNa < 130 mmol/L at admission, nor the persistence of hyponatremia at both 2nd–3rd and 7th–10th day of hospitalization were associated with a higher LOS.
3.2. Inflammation Status
All patients in both volemic groups had at least one IM in high levels at admission. In detail: all patients had LDH levels ≥ 150 UI/L, 89.5% had ferritin ≥ 250 ng/mL, 71.4% had C-reactive protein ≥ 5 mg/L, 74.4% had D-dimer ≥ 500 ng/mL, and 91.2% had fibrinogen ≥ 450 mg/dL. Only in 14/49 patients was IL-6 measured at admission, and in 64.3% of them it was ≥ 10 pg/mL. No differences of the medians of the IM at admission were found between hypovolemic and euvolemic (Table 2). We did not find significative correlations between IM levels and SNa at admission when all patients were analyzed together. However, SNa from hypovolemic patients was correlated with their fibrinogen levels at admission (r: −0.529, p = 0.035).

Table 2.
Comparison of the inflammatory markers between hypovolemic and euvolemic at admission and at the 7th–10th hospitalization day.
We observed that C-reactive protein, LDH, and fibrinogen levels statistically decreased from admission to the 7th–10th day of hospitalization in the entire cohort (Table 3). Parallelly, an increase in SNa levels, as well as a reduction in the hyponatremia rate, was also observed at the same time. However, we did not find correlations between values of SNa and each IM at the 7th–10th day of hospitalization, neither when patients were analyzed in the global cohort nor when were analyzed according to their initial volemic status.

Table 3.
Evolution of the inflammatory markers and serum sodium in the global cohort of patients from admission to the 7th–10th hospitalization day.
Although IM levels had a trend to be higher in hypovolemic than euvolemic patients at the 7th–10th day of hospitalization, no statistical differences were found (Table 2). Furthermore, in the 11 patients who remained hyponatremic at the 7th–10th day of hospitalization, no correlation was found between IM levels and SNa.
4. Discussion
The results of the current study suggest that the evolution of both hypovolemic and euvolemic hyponatremia during the hospitalization of the patients with COVID-19 pneumonia coincides with their inflammatory status. In fact, the decrement in IM levels during hospitalization is accompanied by an increment in SNa values and a reduction in the rate of hyponatremia at the same time. The fact that SNa is not correlated with any IM supports the idea that SNa values would not depend on a single specific inflammatory marker, but on the inflammatory state itself as a whole. Therefore, our findings permit us to hypothesize that the presence of hyponatremia in COVID-19 patients, either hypovolemic or euvolemic, could depend on the inflammation generated in these patients.
As in other type of pneumonias [24,25], hyponatremia is also a risk factor for a poor hospital prognosis in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia [11,12,16,19,26]. In fact, a lower SNa at admission is related with a higher risk for mortality [12]. Our current study found similar results. Although most of the patients in our cohort have mild hyponatremia, with no patient with SNa below 125 mmol/L, we observed that per each increment in mmol/L of SNa at admission, the risk of mortality was significantly reduced in one of our models of multivariable analysis. However, the specific mechanisms behind the impact of low SNa levels, or of hyponatremia at admission or during the hospitalization, on the risk of mortality, have not been totally elucidated.
Commonly, it has been discussed whether hyponatremia, especially when mild, is a direct cause of increased mortality risk, or whether it is only another “indicator” of a worse clinical situation. Based on our results, we hypothesize that the latter could be the most probable situation. On the one hand, we observed a parallel significative decrement in the rate of hyponatremia as IM levels were decreasing. This suggests that an inflammatory status could predispose a patient to the development of hyponatremia and that the presence of hyponatremia could reflect the degree of the inflammation. Thus, when inflammation decreases, a recovery in the water/sodium balance is expected, as occurred in our cohort. Inflammatory pathways via different cytokines, such as tumoral necrosis factor-α, IL-1, or IL6, are involved in a non-osmotic release of arginine vasopressin [4]. In fact, it has been reported that the risk of hyponatremia is higher in the setting of acute inflammatory situations, especially when patients are receiving hypotonic fluids [27,28]. Beukhof et al., in a case-–control study of patients with hyponatremia, observed that those who developed hyponatremia had a coincident increase in C-reactive protein levels [28]. Likewise, IL-6 is strongly correlated with arginine vasopressin concentrations in blood, and directly related with the development of SIADH, both in children [29] and adults [30,31]. This does not seem to be the exception in COVID-19. Berni et al. [19] found an inverse moderate correlation between IL-6 levels and SNa in 29 COVID-19 patients. They also observed a significative increment in SNa when hyponatremic patients with elevated IL-6 levels were treated with tocilizumab (humanized monoclonal antibody against the IL-6 receptor). Furthermore, Ayus et al. recently found in a prospective study that hyponatremic COVID-19 patients had higher levels of IM (D-dimer, C-reactive protein, and ferritin) than eunatremic patients [15]. All this evidence, in accordance with our results, strongly supports our hypothesis. Thus, hyponatremia would depend on the inflammatory involvement affecting respiratory function. In fact, higher respiratory rates [11,12] and lower oxygen levels [11] are reported as more frequent in hyponatremic than eunatremic COVID-19 patients. On the other hand, those patients who remained hyponatremic during hospitalization in our study were not at a high risk of death. These patients have a mild hyponatremia. This finding contrasts with the idea that a mild hyponatremia induces direct damage and, therefore, increases the mortality risk. In fact, of the seven patients who died, only three were hyponatremic at 2nd–3rd day pf hospitalization, and all of them died before the first week of hospitalization. This suggests that their clinical severity was principally caused by COVID-19 itself, rather than hyponatremia. Therefore, we suspect that hyponatremia, at least when mild, is a sign suggestive of severity and a predictor of mortality in COVID-19 patients, rather than a direct cause of them.
However, we cannot deny that even mild hyponatremia could impair the metabolic cellular response to inflammation in different tissues, and, therefore, perpetuate the damage already stablished by the inflammation itself. Thus, the role of hyponatremia seems to be more complex. In fact, in the HOPE-COVID-19 study [12], with a predominantly mild hyponatremic cohort, hyponatremia was also associated with a higher risk of sepsis. Furthermore, in that study, the combination of sepsis with hyponatremia increased the mortality risk of these patients [12]. Sepsis, in its inflammatory state, can cause Na+ and Ca++ channel dysfunction [32]. Hyponatremia itself can also alter the normal function of Na+ and Ca++ channels [33,34]. Thus, a combination of both factors could harm the mechanisms of voltage-dependent cellular conduction and, therefore, impair several cellular functions, which can lead to organ/tissue dysfunction (e.g., in the kidney [35]) and, consequently, induce multi-organ failure. In fact, we observed that the increase in SC levels is a predominant risk factor for mortality in our cohort of hyponatremic patients, with similar results reported in many previous studies of COVID-19 patients. Therefore, we encourage physicians to properly correct hyponatremia in all clinical situations, even when mild, in order to avoid this cellular dysregulation.
One would expected that SIADH, an euvolemic hyponatremia, is the main cause of hyponatremia in COVID-19 patients, as some authors have proposed [17]. However, we found a similar rate of hypovolemic and euvolemic hyponatremia in our cohort. Unfortunately, our study lacks the power to determine specific etiologies of hyponatremia, since neither adrenal axis nor the withdrawal of SIADH-related drugs, urine ions studies, and data of clinical losses of volemia were fully evaluated and registered in the clinical records of our cohort. Nevertheless, the fact that the IM levels were similar between hypovolemic and euvolemic patients, both at admission and at 7th–10th day of hospitalization, indicates that in both types of hyponatremia, the inflammatory status plays a similar role. Therefore, although other factors may be involved in the development of hyponatremia depending on whether it is hypovolemic or euvolemic, it is a fact that the inflammatory status of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia favors its presence.
It is of note that the most of our cohort was above 70 years old and male, and these findings are statistically different between hypovolemic and euvolemic patients. An older age has been related to higher necessity for hospital admission in COVID-19. It is known that elderly patients have a higher risk of developing dysnatremia than younger patients [36]. In the elderly, the renal capacity to excrete free water is decreased as AVP production is increased [37]. This factor, in a specific context of inflammation, facilitates the apparition of hyponatremia in elderly people, explaining why, in our study, patients with euvolemic hyponatremia were older than hypovolemic patients. Likewise, male sex has been associated with hyponatremia in COVID-19 [12,13,14], although its mechanism has not been elucidated. A previous study showed that hospitalized hyponatremic male patients had higher lethality than female patients in general clinical settings [38]. One probable explanation given by the authors is the fact that male people tend to be more comorbid. In the case of COVID-19, it is known that the male sex has a higher risk of mortality. Therefore, in accordance with our findings and hypothesis, hyponatremia, as a severity marker, should be more frequently observed in male people. However, it is interesting the fact that, in our cohort, the male sex was more frequent in hypovolemic patients, but not in euvolemic hyponatremia. Our study lacks the power to elucidate this finding. However, sex differences in Na+ cellular transport are reported [39], which could be a basis for a probable explanation. Further investigations are necessary in order to clear this relationship.
A weakness of the study is the size of the series. Another is the lack of more detailed information of hospital treatments of the patients. However, at that moment of the pandemic, different protocols were used in different hospitals, so these data would have been heterogeneous and biased. Nevertheless, the current data are enough to permit the main objective to be evaluated. Unfortunately, IL-6 was not measured in all patients, which decreased the statistical potency to assay this variable. Furthermore, the fact that 34/49 patients (69.4%) were treated with systemic glucocorticoids during the first week of the hospitalization could have induced a lower value than expected and, therefore, explain the lack of relationship between IM and SNa levels.
Likewise, no hypervolemic hyponatremia is encountered in our registry, therefore, it is still unknown whether hypervolemic hyponatremia has the same inflammatory characteristics as hypovolemic or euvolemic hyponatremia. The main strength is that this study highlights the role of hyponatremia as a clinical marker of severity and inflammation in COVID-19 patients, which could help physicians stratify patient risk in order to make clinical decisions. It is likely that this same interpretation could be made in other types of pneumonia-related hyponatremia.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, in our hyponatremic COVID-19 cohort, the resolution of admission hyponatremia during the hospitalization coincided with the improvement of IM levels. This evolution was similar in both hypovolemic and euvolemic hyponatremia. Therefore, the implication of the inflammatory status on the development of COVID-19-related hyponatremia is proposed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.G.R.-S.; methodology, J.G.R.-S. and J.C.-S.; investigation, J.G.R.-S., P.C.-D. and J.C.-S.; data curation, J.G.R.-S.; writing—original draft preparation, J.G.R.-S.; writing—review and editing, J.G.R.-S., P.C.-D. and J.C.-S.; supervision, J.C.-S.; resources: J.G.R.-S., P.C.-D. and J.C.-S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Waikar, S.S.; Mount, D.B.; Curhan, G.C. Mortality after Hospitalization with Mild, Moderate, and Severe Hyponatremia. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wald, R. Impact of Hospital-Associated Hyponatremia on Selected Outcomes. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuesta, M.; Slattery, D.; Goulden, E.L.; Gupta, S.; Tatro, E.; Sherlock, M.; Tormey, W.; O’Neill, S.; Thompson, C.J. Hyponatraemia in patients with community-acquired pneumonia; prevalence and aetiology, and natural history of SIAD. Clin. Endocrinol. 2019, 90, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swart, R.M.; Hoorn, E.J.; Betjes, M.G.; Zietse, R. Hyponatremia and inflammation: The emerging role of interleukin-6 in osmoregulation. Nephron. Physiol. 2011, 118, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastorakos, G.; Weber, J.S.; Magiakou, M.A.; Gunn, H.; Chrousos, G.P. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activation and stimulation of systemic vasopressin secretion by recombinant interleukin-6 in humans: Potential implications for the syndrome of inappropriate vasopressin secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1994, 79, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascella, M.; Rajnik, M.; Aleem, A.; Dulebohn, S.C.; Di Napoli, R. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19); StatPearls: Tampa, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Liang, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Tong, Q.; Yi, J.; Zhao, L.; et al. Longitudinal characteristics of lymphocyte responses and cytokine profiles in the peripheral blood of SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. EBioMedicine 2020, 55, 102763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satış, H.; Özger, H.S.; Aysert Yıldız, P.; Hızel, K.; Gulbahar, Ö.; Erbaş, G.; Aygencel, G.; Guzel Tunccan, O.; Öztürk, M.A.; Dizbay, M.; et al. Prognostic value of interleukin-18 and its association with other inflammatory markers and disease severity in COVID-19. Cytokine 2021, 137, 155302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, B.; Qu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, J.; Feng, Y.; Men, D.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.; et al. Detectable Serum Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Viral Load (RNAemia) Is Closely Correlated With Drastically Elevated Interleukin 6 Level in Critically Ill Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1937–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şimşek-Yavuz, S.; Komsuoğlu Çelikyurt, F.I. An update of anti-viral treatment of COVID-19. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 51, 3372–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atila, C.; Sailer, C.O.; Bassetti, S.; Tschudin-Sutter, S.; Bingisser, R.; Siegemund, M.; Osswald, S.; Rentsch, K.; Rueegg, M.; Schaerli, S.; et al. Prevalence and outcome of dysnatremia in patients with COVID-19 compared to controls. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 184, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Sánchez, J.G.; Núñez-Gil, I.J.; Cuesta, M.; Rubio, M.A.; Maroun-Eid, C.; Arroyo-Espliguero, R.; Romero, R.; Becerra-Muñoz, V.M.; Uribarri, A.; Feltes, G.; et al. Prognostic Impact of Hyponatremia and Hypernatremia in COVID-19 Pneumonia. A HOPE-COVID-19 (Health Outcome Predictive Evaluation for COVID-19) Registry Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 599255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Lv, X.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Cai, F.; Liu, D.; Yue, J.; et al. Disorders of sodium balance and its clinical implications in COVID-19 patients: A multicenter retrospective study. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontera, J.A.; Valdes, E.; Huang, J.; Lewis, A.; Lord, A.S.; Zhou, T.; Kahn, D.E.; Melmed, K.; Czeisler, B.M.; Yaghi, S.; et al. Prevalence and Impact of Hyponatremia in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in New York City. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, e1211–e1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayus, J.C.; Negri, A.L.; Moritz, M.L.; Lee, K.M.; Caputo, D.; Borda, M.E.; Go, A.S.; Eghi, C. Hyponatremia, Inflammation at Admission, and Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 748364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, M.R.; Pranata, R.; Wibowo, A.; Irvan; Sihite, T.A.; Martha, J.W. The Prognostic Value of Hyponatremia for Predicting Poor Outcome in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 666949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, G.; Ilie, M.; Bungau, S.; Stoian, A.M.P.; Bacalbasa, N.; Diaconu, C.C. Is There a Relationship between COVID-19 and Hyponatremia? Medicina 2021, 57, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez Martinez, A.; Barajas Galindo, D.; Ruiz Sanchez, J. Management of hyponatraemia and hypernatraemia during the Covid-19 pandemic: A consensus statement of the Spanish Society for Endocrinology (Acqua Neuroendocrinology Group). Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berni, A.; Malandrino, D.; Parenti, G.; Maggi, M.; Poggesi, L.; Peri, A. Hyponatremia, IL-6, and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection: May all fit together? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 43, 1137–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, T.A.; Abbott, R.D.; Barrett, E.J. Hyponatremia: Evaluating the correction factor for hyperglycemia. Am. J. Med. 1999, 106, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoorn, E.J.; Zietse, R. Diagnosis and treatment of hyponatremia: Compilation of the guidelines. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.-M.; Kluge, R.; Schrier, R.W.; Anderson, R.J. Clinical assessment of extracellular fluid volume in hyponatremia. Am. J. Med. 1987, 83, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Sánchez, J.G.; Cuesta, M.; Gómez-Hoyos, E.; Cárdenas-Salas, J.; Rubio-Herrera, M.Á.; Martínez-González, E.; De Miguel Novoa, P.; Ternero-Vega, J.E.; Calle-Pascual, A.L.; Runkle, I. Changes in Serum Creatinine Levels Can Help Distinguish Hypovolemic from Euvolemic Hyponatremia. Medicina 2022, 58, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.; Schefold, J.C.; Guignard, V.; Exadaktylos, A.K.; Pfortmueller, C.A. Hyponatraemia is independently associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with pneumonia. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 54, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, V.; Niederman, M.S.; Masani, N.; Fishbane, S. Hyponatremia in Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Am. J. Nephrol. 2007, 27, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, H.; Letellier, T.; Karakachoff, M.; Desvaux, G.; Caillon, H.; Papuchon, E.; Bentoumi-Loaec, M.; Benaouicha, N.; Canet, E.; Chapelet, G.; et al. Hyponatremia is associated with poor outcome in COVID-19. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira da Cunha, D.; Pontes Monteiro, J.; Modesto dos Santos, V.; Araújo Oliveira, F.; Freire de Carvalho da Cunha, S. Hyponatremia in Acute-Phase Response Syndrome Patients in General Surgical Wards. Am. J. Nephrol. 2000, 20, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beukhof, C.M.; Hoorn, E.J.; Lindemans, J.; Zietse, R. Novel risk factors for hospital-acquired hyponatraemia: A matched case?control study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2007, 66, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gionis, D.; Ilias, I.; Moustaki, M.; Mantzos, E.; Papadatos, I.; Koutras, D.A.; Mastorakos, G. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis and Interleukin-6 Activity in Children with Head Trauma and Syndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Antidiuretic Hormone. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 16, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Matoba, H.; Kuga, Y.; Ozawa, S.; Kubota, K.; Yoshida, S. Hyponatremia in a Patient with Chronic Inflammatory Disease. Intern. Med. 1998, 37, 792–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ota, K.; Kumon, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Unexpected impaired consciousness in RA: A rare complication of SIADH induced by increased IL-6. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2004, 22, 134. [Google Scholar]
- Rossignol, B.; Gueret, G.; Pennec, J.-P.; Morel, J.; Giroux-Metges, M.A.; Talarmin, H.; Arvieux, C.C. Effects of chronic sepsis on the voltage-gated sodium channel in isolated rat muscle fibers*. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, M.; Karabagli, H.; Yanardag, S.B. Can Hypo/Hypernatremic Conditions be a Factor for Na Ion Channel Kinetics: Model Study. Turk. Neurosurg. 2018, 28, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squecco, R.; Luciani, P.; Idrizaj, E.; Deledda, C.; Benvenuti, S.; Giuliani, C.; Fibbi, B.; Peri, A.; Francini, F. Hyponatraemia alters the biophysical properties of neuronal cells independently of osmolarity: A study on Ni2+-sensitive current involvement. Exp. Physiol. 2016, 101, 1086–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, A.B.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Ortiz, A. TWEAK, a multifunctional cytokine in kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, R.C. Age and gender as risk factors for hyponatremia and hypernatremia. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 337, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowen, L.E.; Hodak, S.P.; Verbalis, J.G. Age-associated abnormalities of water homeostasis. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 42, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheimer, B.; Skov, J.; Falhammar, H.; Calissendorff, J.; Lindh, J.D.; Nathanson, D. Sex-specific risks of death in patients hospitalized for hyponatremia: A population-based study. Endocrine 2019, 66, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grikiniene, J.; Volbekas, V.; Stakisaitis, D. Gender differences of sodium metabolism and hyponatremia as an adverse drug effect. Medicina 2004, 40, 935–942. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).