Abstract
The present review focuses on steroid-induced adrenal insufficiency (SIAI) in children and discusses the latest findings by surveying recent studies. SIAI is a condition involving adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and cortisol suppression due to high doses or prolonged administration of glucocorticoids. While its chronic symptoms, such as fatigue and loss of appetite, are nonspecific, exposure to physical stressors, such as infection and surgery, increases the risk of adrenal crisis development accompanied by hypoglycemia, hypotension, or shock. The low-dose ACTH stimulation test is generally used for diagnosis, and the early morning serum cortisol level has also been shown to be useful in screening for the condition. Medical management includes gradually reducing the amount of steroid treatment, continuing administration of hydrocortisone corresponding to the physiological range, and increasing the dosage when physical stressors are present.
1. Mainstem Concepts of Adrenal Insufficiency
1.1. Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Adrenal Insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency (AI) is defined as the inability of the adrenal cortex to produce sufficient amounts of glucocorticoid hormone. It can also be associated with mineralocorticoid deficiency, depending on the pathophysiology of the disease [1]. Severe AI, or adrenal crisis, can be life-threatening because glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids play a central role in maintaining energy, salt, and fluid homeostasis [2]. AI is usually classified into the primary and secondary types, which are caused by adrenal diseases and hypothalamic/pituitary diseases, respectively. AI associated with hypothalamic dysfunction is sometimes called tertiary AI. The main causes of AI are described below (see Table 1).

Table 1.
Major causes of adrenal insufficiency.
Primary AI can be further divided into the congenital type, represented by congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), and the acquired type, represented by Addison’s disease [1]. One of the obvious differences in the clinical picture between primary, secondary, and tertiary AI is skin pigmentation, which is almost always present in primary AI (except in cases with a short duration) but is absent in secondary and tertiary AI [3]. Additionally, mineralocorticoid deficiency is generally associated with primary AI but not with secondary or tertiary AI because the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system is not impaired in the latter [4]. In exceptional cases of CAH due to 11 beta-hydroxylase deficiency and 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency, mineralocorticoid excess occurs concurrently with glucocorticoid deficiency [5].
Secondary and tertiary AI can be divided into congenital and acquired types as well. Various genetic etiologies involving not only central nervous system malformations, such as holoprosencephaly, but also combined pituitary hormone deficiencies and isolated ACTH deficiency, have been identified [6]. Besides the drug-induced etiologies described below, acquired secondary AI can be caused by a tumor (e.g., craniopharyngioma), trauma, surgery, inflammation, or infarction involving the pituitary gland. It should be noted that secondary and tertiary AI may be latent or their onset may often be slow; congenital AI may become apparent around puberty (especially in septo-optic dysplasia [7] or hypopituitarism associated with perinatal problems [8]), while acquired AI can occur months to years after intracranial radiation [9] or traumatic brain injury [10,11]. Severe hypoglycemia in the neonatal period is rather exceptional and can be seen in congenital isolated ACTH deficiency caused by a TBX19 gene mutation [12].
1.2. Iatrogenic Adrenal Insufficiency
Iatrogenic AI refers to primary, secondary, or tertiary hypoadrenocorticism associated with drug administration, surgery, or irradiation. This review focuses on the role of steroids, the most frequent etiology of tertiary AI [2], which induce iatrogenic adrenal insufficiency (steroid-induced iatrogenic adrenal insufficiency, or SIAI) when the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis is suppressed by high dosages or prolonged use of the drugs followed by abrupt discontinuation or rapid tapering. Patients with leukemia, asthma, collagen disease, or inflammatory bowel disease and those who have undergone transplant surgery [13] and have received long-term synthetic glucocorticoid treatment are especially at risk of SIAI development. There is currently insufficient evidence on the epidemiology, treatment strategy, and recovery process in SIAI; therefore, the optimal diagnostic criteria and management of the condition are still controversial. However, with the chief aim of preventing life-threatening adrenal crises [14], we discuss below the approaches available for managing patients treated with corticosteroids and summarize our tentative recommendations in Table 2. Other known causes of iatrogenic AI include drugs such as ketoconazole [15], mitotane [16], and etomidate [17], which inhibit the steroidogenesis pathway.

Table 2.
Summary and recommendations for SIAI management.
2. Case Presentations of SIAI
Significant lessons can be learned from actual cases, especially in pediatrics, where the clinical research is still insufficient. For this reason, we have presented three cases below that illustrate the typical presentation and course of SIAI. Based on the findings of a study of the response of healthy adults to the corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) stimulation test [18] and the criteria for the low-dose ACTH stimulation test described below, we used a peak serum cortisol concentration <18 μg/dL in the CRH stimulation test as the cutoff value for diagnosing SIAI.
Case 1: A 1-year-old, male patient was treated for Kawasaki disease with intravenous immunoglobulin 2 g/kg and methylprednisolone (mPSL) 30 mg/kg followed by oral aspirin and prednisolone (PSL). PSL was started at 2 mg/kg/day, then tapered, resulting in a total hydrocortisone (HDC) equivalent glucocorticoid dose of 5500 mg/m2 over three weeks. Thereafter, a physiological replacement dose of HDC (8 mg/m2/day) was started. A CRH stimulation test conducted one week after PSL discontinuation showed peak ACTH and cortisol levels of 52.9 pg/mL and 5.5 µg/dL, respectively. The normalization of his adrenal function was confirmed four months later by a CRH stimulation test, which showed peak ACTH and cortisol levels of 19.6 pg/mL and 55.5 µg/dL, respectively.
Case 2: A 13-year-old male patient was treated for ulcerative colitis with nutritional therapy, 5-aminosalicylic acid, and PSL. PSL was administered at an HDC equivalent dose of 2900 mg/m2 for six weeks and afterwards switched to a physiological replacement dose. HDC was increased to a stress dose of 100 mg/m2/day for a colectomy and colostomy performed three weeks and months later, respectively. A CRH stimulation study conducted eight months later demonstrated a peak ACTH level of 61.4 pg/mL and a cortisol level of 9.5 µg/dL 30 min after stimulation. Thereafter, daily HDC administration was discontinued, and no episodes of suspected SIAI have been observed to date. Nineteen months after the discontinuation of daily HDC, a CRH stimulation study showed recovery of the peak cortisol level to 17.4 µg/dL.
Case 3: A 5-year-old female patient was treated for acute tubulointerstitial nephritis with PSL 2 mg/kg/day initially, which was tapered by 0.5 mg/kg/day every two weeks to 0.25 mg/kg/day after two months of treatment. Three months after the start of treatment, when the cumulative dose of PSL was equivalent to HDC 8400 mg/m2, she was admitted to the hospital emergency department due to recurrent vomiting and diarrhea. SIAI was diagnosed based on the serum cortisol value, which was 2.9 µg/dL more than 12 h after the PSL administration on the previous evening despite the physical stress. After a PSL stress dose of 15 mg/m2 was administered on admission, her symptoms improved. Two days later, when the PSL dosage was reduced to 5 mg/m2, vomiting recurred. Thereafter, PSL was reintroduced and tapered again, and the patient was discharged with a prescription for PSL at the pre-hospitalization dosage.
3. Effect of Steroid Dosage and Administration Duration on SIAI
3.1. Dose Dependency
A systematic review of adult patients showed that higher steroid doses and longer durations of use were associated with an increased SIAI risk [13] although the evidence in pediatrics is currently insufficient to demonstrate a dose-dependent risk of SIAI [19,20]. The timing of administration may also affect the severity of SIAI, as high steroid doses at night are believed to inhibit the early morning ACTH surge [21].
Suppression of the HPA axis by exogenous glucocorticoids has been reported mainly in systemic and inhalation therapy and only rarely in topical applications [22,23] or intra-articular administration [13]. Studies of childhood asthma have suggested that patients using fluticasone ≧500 µg/day as a controller [24] or who received acute treatment with systemic steroids in the past [25] may be at higher risk of SIAI development. In a cohort study of children with asthma, the absolute risk of HPA suppression was 100% when using the beclomethasone dipropionate metered dose inhaler at a dose of 250–600 µg/m2/day for 6–42 months [26].
3.2. Dose Threshold for SIAI
There is no strict consensus on the cumulative steroid dose threshold for SIAI development. In the treatment of both adults [27] and children [28], even small doses and short-term administration of steroids can potentially cause SIAI. In adults, adrenal atrophy and functional decline are likely to occur after systemic administration of 30 mg or more of HDC equivalent steroids (>7.5 mg/day PSL or >0.75 mg/day dexamethasone) per day for three weeks or longer [4]. On the other hand, severe SIAI is reportedly unlikely to occur at a physiological replacement dose of glucocorticoids for up to two weeks of administration [29]. However, a prospective study of pediatric asthma showed that 11 patients receiving a PSL dosage of up to 2 mg/kg/day for five days, which is a shorter period of administration than in Case 1 above, showed statistically significant blunting of the peak cortisol response in an insulin tolerance test three days after discontinuation of the PSL therapy [30]. Further studies are needed to determine the cumulative steroid dose threshold for SIAI development.
3.3. Adverse Effects of Glucocorticoid Pulse Therapy
Glucocorticoid pulse therapy, which consists of a small number of intravenous, high-dose mPSL administrations, is reportedly associated with fewer adverse effects than daily oral steroid therapy at the equivalent dose for suppressing inflammation and the autoimmune response [31]. In a randomized controlled trial enrolling adults, no significant difference in systemic side effects was observed between an mPSL 30 mg single-dose group and the placebo group [32]. In an observational study of mPSL pulse therapy for pediatric Kawasaki disease, only transient bradycardia and hyperglycemia were observed [33]. However, a previous study reported that 22% of children with a rheumatic disease experienced unexpectedly diverse side effects of steroid pulse therapy, such as behavioral changes (10%), headache (5.2%), and abdominal complaints (4.7%) [34], underscoring the need for careful assessment of the safety of these treatments.
3.4. Factors Associated with SIAI Development
A study enrolling adults with various, underlying diseases demonstrated that possible predictors of adrenal suppression may include central obesity, nausea/vomiting, fatigue, low serum cholesterol, low serum sodium, and chronic kidney disease [35]. A pediatric study reported that responsiveness of the HPA axis to stress was more pronounced in female children than in male children [36], and another study of severely ill children reported that patients in an adrenal suppression group were older than subjects in the control group [37]. In addition, concurrent administration of other drugs may synergistically augment the potency of steroids and the severity of HPA axis suppression. For example, drugs that inhibit CYP3A4, such as ritonavir, suppress inhaled fluticasone clearance [38]. Drugs with an affinity for glucocorticoid receptors, such as progesterone derivatives, which are given to oncology patients in high doses, have also been linked to SIAI [39].
4. Clinical Manifestations of SIAI
4.1. Chronic Symptoms
Patients may present with chronic symptoms while recovering from HPA suppression. The common symptoms are weakness, fatigue, anorexia, and weight loss [40]. Frequent gastrointestinal complaints include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain, which are probably related to decreased bowel motility. These symptoms are more likely to occur with greater HPA suppression [1] and soon after stopping steroids [41]. In addition, adrenal insufficiency inevitably leads to a deficiency of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), a substrate for peripheral sex hormone biosynthesis, which can lead to androgen deficiency in women. Its clinical manifestations include loss of axillary and pubic hair, dry skin, and decreased libido [42].
4.2. Symptoms as Side Effects of Glucocorticoids
Awareness of a variety of side effects of glucocorticoids is necessary when assessing SIAI. Particularly serious effects include immunosuppression, impaired growth, osteoporosis, and somewhat less frequently, but importantly, cataract formation and pancreatitis [43]. Medical Cushing’s syndrome, i.e., central obesity, muscle atrophy, and hypertension, can also occur in infants [44]. Nonspecific symptoms include mood disorders, abdominal symptoms, and dizziness [34], which can be difficult to differentiate from the symptoms of SIAI.
4.3. Acute Symptoms in the Presence of Stressors
It is even more important to note that physical stressors, such as severe infection or surgery, can trigger acute symptoms. Nonspecific symptoms, such as vomiting and diarrhea seen in Case 3, are common [40]. Laboratory findings are often normal [35,45]. Hyponatremia can develop as a result of increased vasopressin secretion and water retention [46]. The most severe and acute form is adrenal crisis, which consists of tachycardia, hypoglycemia, hypotension, dehydration, and acute abdominal pain [40,47]. Although the incidence of adrenal crisis is unknown, a questionnaire study of physicians across the UK revealed that adrenal crisis associated with inhaled corticosteroids (ICSs) occurred in 28 children, one of whom died from the condition. The mean patient age, duration of ICS treatment, and dosage of fluticasone, which was administered to 94% of the patients, was 6.4 years, 1.7 years, and 980 µg/day (range of 500–2000 µg/day), respectively [48]. At the time of the study, only 16% of all asthma patients were reportedly using fluticasone in the UK, indicating the gravity of the risk of adrenal crisis associated with fluticasone use [24].
5. Diagnostic Approaches to SIAI
5.1. Variation in Diagnostic Approaches
The symptoms of SIAI are nonspecific, and the diagnostic criteria are basically based on dynamic testing rather than the symptoms. The insulin tolerance test (ITT) has traditionally been the gold standard for HPA axis assessment in adults [49], but this can be replaced by the safer, cheaper, and faster Synacthen test (SST) [50,51]. In pediatric medicine, the test most commonly used to diagnose secondary adrenal insufficiency is the low-dose ACTH stimulation test [52] because it is easy to administer, physiologically sound, safe, and reasonably sensitive. The glucagon [53] and CRH [14,54] stimulation tests (used in Cases 1–3 above) are also administered. Furthermore, early morning cortisol levels can also be used in screening [55,56] and assessment [57] of HPA function.
5.2. Low-Dose ACTH Stimulation Test
Low-dose ACTH stimulation testing is performed by administering 1 μg/1.73 m2 intravenous cosyntropin and assessing the subsequent increase in the serum cortisol level. A serum cortisol level of 16–20 μg/dL 30 min after cosyntropin administration is generally used as the threshold level although this may vary somewhat among assays [58,59,60,61]. Additional cortisol draws at 15 and 60 min may reduce the risk of false positive results [62]. We suggest performing this test at the initial evaluation 1 to 6 months after the end of the pharmacological dosing (depending on the duration of the steroid therapy), then every 3 to 6 months as needed in combination with early morning serum cortisol level testing, although the evidence and guideline recommendations supporting this approach are still inadequate. Once the values normalize, HDC maintenance therapy can be safely discontinued [41].
5.3. Early Morning Serum Cortisol Level
While random cortisol testing might be helpful in an emergency setting, as seen in Case 3, serum cortisol levels at 8 a.m. to 9 a.m. are often used when screening for SIAI. Previous studies have proposed an early morning cortisol level cutoff value of 8.5–10.3 µg/dL in adults [55,57]. A reference value of plasma cortisol, which is equivalent to that of serum cortisol [63,64,65], ≤3 μg/dL (83 nmol/L), may indicate SIAI, while a value >19 μg/dL (525 nmol/L) can be used to exclude SIAI [66]. A cohort study suggested a serum cortisol level of 5 µg/dL at 9 a.m. in children as a cutoff value for SIAI screening following steroid administration for Kawasaki disease [67].
6. Recovery Course in SIAI
6.1. Long-Term Administration
In an observational study of the natural history of SIAI in adults, both ACTH and cortisol secretion were initially suppressed. Then, ACTH secretion quickly increased before dropping to the normal range while cortisol secretion increased in response to the ACTH increase and normalized over several months [68]. Figure 1 shows a schema of ACTH and cortisol levels in SIAI following glucocorticoid therapy. SIAI due to steroid treatment for chronic diseases tends to show slower recovery. Studies reviewing adult cases of leukemia, hemangioma, and asthma reported that six to 12 months were required for recovery from SIAI [69], while a study of glomerular disease reported that 8.7 ± 4.6 months (mean ± SD) [56] were required. A pediatric study reported that recovery after treatment for acute lymphocytic leukemia took an average of 8.5 months (95% confidence interval: 6.3–10.7 months) [70], and another study reported that 11% of patients still had adrenal suppression 20 months after treatment for a rheumatic disease [71]. In line with the results of these studies, the patient in Case 2 did not show adequate cortisol secretion in the CRH stimulation test as late as eight months after the cessation of a six-week PSL treatment regimen.
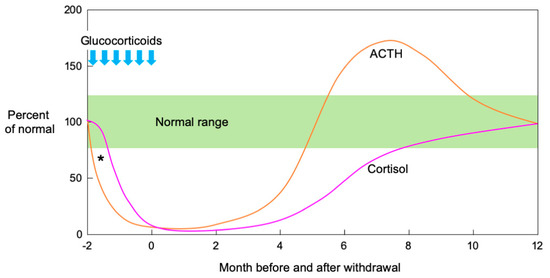
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of ACTH and cortisol levels after pharmacological glucocorticoid therapy. Both ACTH and cortisol secretion are initially suppressed when high-dose or long-term glucocorticoid administration is followed by abrupt cessation or rapid tapering. Theoretically, ACTH precedes cortisol in the suppression phase after pharmacological glucocorticoid therapy (*). In the recovery phase, ACTH secretion increases rapidly, then decreases to the normal range while cortisol secretion increases in response to increased ACTH and normalizes over several months. (Modified from [73] Kim E. Barrett, et al. The Adrenal Medulla & Adrenal Cortex. Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 24th Ed. 2012, Chapter 20).
6.2. Short-Term Administration
If the dosages are small or the treatment short-term, recovery tends to be faster. The above literature review found that adrenal function recovered rapidly when steroids were administered for less than 14 days [69]. In an interventional study where a high-dose, short-term glucocorticoid (HDC 25 mg twice daily for five days) was administered to healthy adult subjects, the peak cortisol response to the ITT significantly decreased two days after PSL discontinuation but nearly returned to pretreatment levels five days after the intervention [72]. An observational study of childhood asthma found that adrenal function normalized in all 11 patients ten days after the completion of short-term PSL treatment [30], and another study of PSL treatment for Kawasaki disease in children reported recovery in more than half the patients within two months [67].
7. Practical Management of SIAI
7.1. Tapering from the Therapeutic to Physiological Replacement Dose
Weeks or months may be required to taper steroids until normal adrenal function is restored, and measures should be taken to prevent adrenal crisis during episodes of stress. In adults, the PSL dosage may be reduced from the pharmacological to the physiological level for several weeks. For example, depending on the patient’s condition, PSL may be reduced by 1 mg per day every two to four weeks [21]. Alternatively, HDC may be reduced weekly by 2.5 mg/day and maintained at 10 mg/day, which corresponds to endogenous cortisol synthesis as measured by isotope dilution [74].
In children, dose tapering to levels equivalent to the physiological dose (6–8 mg/m2/day of HDC [75,76,77]) is believed to be important to prevent symptoms of SIAI, although it has not been shown to restore adrenal cortical function [78]. Despite the lack of a consensus on how HDC should be prescribed, oral HDC administration once a day may be feasible and can improve compliance. Another option is to divide the total daily dose into four doses, two on waking, one at noon, and one in the evening, which may be acceptable to some patients [41].
7.2. Stress Doses
When the patient is under stress, the rescue method should be chosen according to the degree of the stress and the symptoms. Expert opinion [1,2] on steroid dosages for adults during stress was shown to be valid by a clinical study enrolling adults [79]. The stress dose for children is estimated by converting the adult dose into HDC per body surface area. For moderate physical stressors, such as infection associated with high fever (>38.5 °C), minor trauma, or dental treatment, three-fold the maintenance dosage or 50 mg/m2/day of HDC is administered orally in three to four divided doses [40,80]. If vomiting, lethargy, or other reasons make oral intake difficult, 50 mg/m2 HDC may first be injected intravenously. If an intravenous line cannot be placed, an intramuscular injection may be used [80]. In both adult and pediatric patients who are under severe stress, such as that caused by sepsis or major surgery, intravenous HDC 100 mg/m2/day administered continuously or every six hours in divided doses is recommended until recovery is achieved [40,47,80,81,82].
7.3. Patient Education
It is important that patients understand how to manage their condition, including knowing how much hydrocortisone to take or inject outside the hospital during episodes of stress. Patients are encouraged to wear a tag or a pin containing medical information, such as measures required in an emergency, hospital contact information, etc., which can enable others to provide assistance when needed [2,40,41,82,83].
8. Further Considerations Regarding SIAI
8.1. Pathophysiological and Pharmacological Research
Despite the availability of hydrocortisone replacement therapy and the asymptomatic clinical course in most cases, it is essential to recognize that any patient with SIAI who has been receiving prolonged glucocorticoid therapy may experience reduced quality of life and have a risk of experiencing adrenal crisis [84,85].
New oral hydrocortisone drugs that allow sustained absorption through delayed or biphasic release are being developed as a promising method of mimicking the physiological cortisol profile [86,87]. Additionally, a deeper understanding of steroid activity pathways and how these change in different target tissues may enable the development of tissue-specific glucocorticoid analogs, such as those that can suppress inflammation without causing osteopenia or other symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome [88,89,90,91].
8.2. Clinical and Epidemiological Research
The methods of diagnosing adrenal insufficiency and the administration of physiological and stress doses addressed in this review are all based on various studies of patients with different backgrounds. In particular, the criteria for continuing/discontinuing physiological and stress doses need to be discussed in terms of the treatment target. For example, our interpretation of dynamic test results will differ depending on whether the goal is to prevent chronic and acute symptoms or adrenal crisis. Furthermore, adrenal crisis is difficult to define in clinical studies because its physical and laboratory findings are nonspecific, and endocrinological testing is often difficult in the acute phase. Further research is warranted to optimize practical management of the disease, and clinical studies enrolling an adequate number of cases with a sufficient follow-up period are needed to standardize the diagnostic criteria and treatment methods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A. and Y.H.; writing—original draft preparation, S.A.; writing—review and editing, Y.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
No honorarium, grant or other form of funding was given to anyone to produce the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank James Robert Valera for his assistance with editing this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Oelkers, W. Adrenal insufficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charmandari, E.; Nicolaides, N.C.; Chrousos, G.P. Adrenal insufficiency. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2014, 383, 2152–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, R.K.; Argese, N.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Stewart, P.M. Central hypoadrenalism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 4027–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.S.; Stewart, P.M. Corticosteroid insufficiency in acutely ill patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Sanchez, C.E.; Gomez-Sanchez, E.P.; Yamakita, N. Endocrine causes of hypertension. Semin. Nephrol. 1995, 15, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patti, G.; Guzzeti, C.; Di Iorgi, N.; Maria Allegri, A.E.; Napoli, F.; Loche, S.; Maghnie, M. Central adrenal insufficiency in children and adolescents. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 32, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cemeroglu, A.P.; Coulas, T.; Kleis, L. Spectrum of clinical presentations and endocrinological findings of patients with septo-optic dysplasia: A retrospective study. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 28, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, J.; Hasegawa, Y.; Ohnami, N.; Onigata, K.; Kinoshita, E.; Nishi, Y.; Tachibana, K.; Hasegawa, T. Development of growth hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiencies in patients with prenatal or perinatal-onset hypothalamic hypopituitarism having invisible or thin pituitary stalk on magnetic resonance imaging. Endocr. J. 2001, 48, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberfield, S.E.; Chin, D.; Uli, N.; David, R.; Sklar, C. Endocrine late effects of childhood cancers. J. Pediatr. 1997, 131, S37–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenga, S.; Campenni, A.; Ruggeri, R.M.; Trimarchi, F. Clinical review 113: Hypopituitarism secondary to head trauma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einaudi, S.; Bondone, C. The effects of head trauma on hypothalamic-pituitary function in children and adolescents. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2007, 19, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Sun, G.; Tang, Z.; Hou, X. Congenital Isolated ACTH Deficiency Caused by TBX19 Gene Mutation: A Family Report. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broersen, L.H.; Pereira, A.M.; Jorgensen, J.O.; Dekkers, O.M. Adrenal Insufficiency in Corticosteroids Use: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaghecke, R.; Kornely, E.; Santen, R.T.; Ridderskamp, P. The effect of long-term glucocorticoid therapy on pituitary-adrenal responses to exogenous corticotropin-releasing hormone. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loose, D.S.; Kan, P.B.; Hirst, M.A.; Marcus, R.A.; Feldman, D. Ketoconazole blocks adrenal steroidogenesis by inhibiting cytochrome P450-dependent enzymes. J. Clin. Investig. 1983, 71, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimondo, G.; Puglisi, S.; Zaggia, B.; Basile, V.; Saba, L.; Perotti, P.; De Francia, S.; Volante, M.; Zatelli, M.C.; Cannavo, S.; et al. Effects of mitotane on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in patients with adrenocortical carcinoma. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 177, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majesko, A.; Darby, J.M. Etomidate and adrenal insufficiency: The controversy continues. Crit. Care 2010, 14, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCherney, G.S.; DeBold, C.R.; Jackson, R.V.; Sheldon, W.R., Jr.; Island, D.P.; Orth, D.N. Diurnal variation in the response of plasma adrenocorticotropin and cortisol to intravenous ovine corticotropin-releasing hormone. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1985, 61, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensen, N.; Gemke, R.J.; van Dalen, E.C.; Rotteveel, J.; Kaspers, G.J. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression after treatment with glucocorticoid therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD008727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollner, E.W. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression in asthmatic children on inhaled corticosteroids (Part 2)—the risk as determined by gold standard adrenal function tests: A systematic review. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 18, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell-Price, J.D.C.; Auchus, R.J. The Adrenal Cortex. Williams Textb. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 1792. [Google Scholar]
- Bulus, A.D.; Andiran, N.; Kocak, M. Cushing’s syndrome: Hidden risk in usage of topical corticosteroids. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 27, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood Heickman, L.K.; Davallow Ghajar, L.; Conaway, M.; Rogol, A.D. Evaluation of Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Suppression following Cutaneous Use of Topical Corticosteroids in Children: A Meta-Analysis. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2018, 89, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmet, A.; Kim, H.; Spier, S. Adrenal suppression: A practical guide to the screening and management of this under-recognized complication of inhaled corticosteroid therapy. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2011, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolan, L.M.; Kesarwala, H.H.; Holroyde, J.C.; Fischer, T.J. Short-term, high-dose, systemic steroids in children with asthma: The effect on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1987, 80, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, R.; Senior, B.; Morris, M.; Binkiewicz, A. Adrenal effects of beclomethasone inhalation therapy in asthmatic children. J. Pediatr. 1982, 100, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, R.M.; Hunter, A.L.; Ray, D.W.; Dixon, W.G. Systemic glucocorticoid therapy and adrenal insufficiency in adults: A systematic review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2016, 46, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljebab, F.; Choonara, I.; Conroy, S. Systematic review of the toxicity of short-course oral corticosteroids in children. Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 101, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, R.J.; Vigersky, R.A.; Oliff, A.I.; Echelberger, C.K.; Bruton, J.; Poplack, D.G. Adrenal suppression after short-term corticosteroid therapy. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 1979, 1, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zora, J.A.; Zimmerman, D.; Carey, T.L.; O’Connell, E.J.; Yunginger, J.W. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression after short-term, high-dose glucocorticoid therapy in children with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1986, 77, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Bagga, A. Pulse steroid therapy. Indian J. Pediatr. 2008, 75, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, E.; Stubbs, S.S.; Seckman, C.E.; Hearron, M.S. Effects of a single large intravenous dose of methylprednisolone sodium succinate. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1970, 11, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, M.; Ohki, H.; Yoshiba, S.; Ueda, H.; Sugaya, A.; Satoh, M.; Yamagishi, H. Adverse effects of methylprednisolone pulse therapy in refractory Kawasaki disease. Arch. Dis. Child. 2005, 90, 1096–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Klein-Gitelman, M.S.; Pachman, L.M. Intravenous corticosteroids: Adverse reactions are more variable than expected in children. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 25, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Manosroi, W.; Phimphilai, M.; Khorana, J.; Atthakomol, P.; Pipanmekaporn, T. Predictive Factors of Adrenal Insufficiency in Outpatients with Indeterminate Serum Cortisol Levels: A Retrospective Study. Med. Kaunas 2020, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollanders, J.J.; van der Voorn, B.; Rotteveel, J.; Finken, M.J.J. Is HPA axis reactivity in childhood gender-specific? A systematic review. Biol. Sex. Differ. 2017, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, K.; Ward, R.E.; Lawson, M.L.; Gaboury, I.; Hutchison, J.S.; Hebert, P.C.; Canadian Critical Care Trials, G. A prospective multicenter study of adrenal function in critically ill children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foisy, M.M.; Yakiwchuk, E.M.; Chiu, I.; Singh, A.E. Adrenal suppression and Cushing’s syndrome secondary to an interaction between ritonavir and fluticasone: A review of the literature. HIV Med. 2008, 9, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schacke, H.; Schottelius, A.; Docke, W.D.; Strehlke, P.; Jaroch, S.; Schmees, N.; Rehwinkel, H.; Hennekes, H.; Asadullah, K. Dissociation of transactivation from transrepression by a selective glucocorticoid receptor agonist leads to separation of therapeutic effects from side effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornstein, S.R.; Allolio, B.; Arlt, W.; Barthel, A.; Don-Wauchope, A.; Hammer, G.D.; Husebye, E.S.; Merke, D.P.; Murad, M.H.; Stratakis, C.A.; et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary Adrenal Insufficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 364–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, A.; Willenberg, H.S.; Gruber, M.; Bornstein, S.R. Adrenal Insufficiency. Endocrinol. Adult Pediatr. 2016, 102, 2704. [Google Scholar]
- Allolio, B.; Arlt, W. DHEA treatment: Myth or reality? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 13, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimsza, M.E. Complications of corticosteroid therapy. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1978, 132, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, R.R.; Maresh, A. Iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome and adrenal insufficiency in infants on intranasal dexamethasone drops for nasal obstruction—Case series and literature review. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 105, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, K.; Izawa, M.; Higuchi, A.; Kotoh, S.; Hasegawa, Y. Stress doses of glucocorticoids cannot prevent progression of all adrenal crises. Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2009, 18, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelkers, W. Hyponatremia and inappropriate secretion of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) in patients with hypopituitarism. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 321, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.J.; Shah, R. Disorders of the Adrenal Gland. Netter Pediatr. 2011, 70, 864. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, G.R.; Acerini, C.L.; Ross-Russell, R.; Zahra, S.; Warner, J.T.; McCance, D. Survey of adrenal crisis associated with inhaled corticosteroids in the United Kingdom. Arch. Dis. Child. 2002, 87, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, I.; Cunningham, S.; Lindsay, J. The diagnosis and investigation of adrenal insufficiency in adults. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 46, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, J.; Kehlet, H. Re-evaluation of the clinical value of the 30 min ACTH test in assessing the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical function. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 1987, 26, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.M.; Corrie, J.; Seckl, J.R.; Edwards, C.R.; Padfield, P.L. A rational approach for assessing the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 1988, 1, 1208–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.C. Adrenocortical Insufficiency. Nelson Textb. Pediatr. 2020, 593, 4264. [Google Scholar]
- Claahsen-van der Grinten, H.L.; Otten, B.J. Adrenal function: A gold standard test for adrenal insufficiency in children? Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 605–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazlauskaite, R.; Maghnie, M. Pitfalls in the diagnosis of central adrenal insufficiency in children. Endocr. Dev. 2010, 17, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Villarreal, J.; Perez-Arredondo, L.A.; Rodriguez-Gutierrez, R.; Gonzalez-Colmenero, A.D.; Solis, R.C.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, J.G.; Mancillas-Adame, L.G. Serum Morning Cortisol as a Screening Test for Adrenal Insufficiency. Endocr. Pract. 2020, 26, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karangizi, A.H.K.; Al-Shaghana, M.; Logan, S.; Criseno, S.; Webster, R.; Boelaert, K.; Hewins, P.; Harper, L. Glucocorticoid induced adrenal insufficiency is common in steroid treated glomerular diseases—proposed strategy for screening and management. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, I.L.; Lahner, H.; Mann, K.; Petersenn, S. Diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency: Evaluation of the corticotropin-releasing hormone test and Basal serum cortisol in comparison to the insulin tolerance test in patients with hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4193–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, S.A.; Henry, R. Pediatric Adrenal Insufficiency: Diagnosis, Management, and New Therapies. Int. J. Pediatr. 2018, 2018, 1739831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina, N.S.; Al Nofal, A.; Bancos, I.; Javed, A.; Benkhadra, K.; Kapoor, E.; Lteif, A.N.; Natt, N.; Murad, M.H. ACTH Stimulation Tests for the Diagnosis of Adrenal Insufficiency: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazlauskaite, R.; Evans, A.T.; Villabona, C.V.; Abdu, T.A.; Ambrosi, B.; Atkinson, A.B.; Choi, C.H.; Clayton, R.N.; Courtney, C.H.; Gonc, E.N.; et al. Corticotropin tests for hypothalamic-pituitary- adrenal insufficiency: A metaanalysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4245–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorin, R.I.; Qualls, C.R.; Crapo, L.M. Diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, H.; Barrowman, N.; Webster, R.; Ahmet, A. Evaluating the Low-Dose ACTH Stimulation Test in Children: Ideal Times for Cortisol Measurement. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 4587–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SRL Inc. Serum Cortisol. Available online: http://test-guide.srl.info/hachioji/test/detail/004100902 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- SRL Inc. Plasma Cortisol. Available online: http://test-guide.srl.info/hachioji/test/detail/004100906 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Siskos, A.P.; Jain, P.; Romisch-Margl, W.; Bennett, M.; Achaintre, D.; Asad, Y.; Marney, L.; Richardson, L.; Koulman, A.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Interlaboratory Reproducibility of a Targeted Metabolomics Platform for Analysis of Human Serum and Plasma. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinspoon, S.K.; Biller, B.M. Clinical review 62: Laboratory assessment of adrenal insufficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1994, 79, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Miyagawa, N.; Kikunaga, K.; Miura, M.; Hasegawa, Y. Single serum cortisol values at 09:00 h can be indices of adrenocortical function in children with Kawasaki disease treated with intravenous immunoglobulin plus prednisolone. Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2015, 24, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, A.L.; Ney, R.L.; Nicholson, W.E.; Island, D.P.; Liddle, G.W. Natural History of Pituitary-Adrenal Recovery Following Long-Term Suppression with Corticosteroids. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1965, 25, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, A.K.; Younes, N.K. Recovery of steroid induced adrenal insufficiency. Transl. Pediatr. 2017, 6, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, T.R.; Juul, A.; Lausten-Thomsen, U.; Lausen, B.; Hjalgrim, H.; Kvist, T.K.; Andersen, E.W.; Schmiegelow, K. Duration of adrenal insufficiency during treatment for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2011, 33, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, B.M.; Bolt, I.B.; Sauvain, M.J.; Fluck, C.E. Adrenal insufficiency after glucocorticoid withdrawal in children with rheumatic diseases. Acta Paediatr. 2010, 99, 1889–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streck, W.F.; Lockwood, D.H. Pituitary adrenal recovery following short-term suppression with corticosteroids. Am. J. Med. 1979, 66, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.B.; Susan, M.B.; Scott, B.; Heddwen, L.B. The Adrenal Medulla & Adrenal Cortex. In Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 24th ed.; McGraw Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Chapter 20. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, N.V.; Loughlin, T.; Yergey, A.L.; Zawadzki, J.K.; Booth, J.D.; Winterer, J.C.; Loriaux, D.L. Daily cortisol production rate in man determined by stable isotope dilution/mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1991, 72, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, B.L.; Esteban, N.V.; Yergey, A.L.; Winterer, J.C.; Loriaux, D.L.; Cassorla, F. Cortisol production rate in childhood and adolescence. J. Pediatr. 1990, 117, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, N.V.; Yergey, A.L. Cortisol production rates measured by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Steroids 1990, 55, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrigan, J.R.; Veldhuis, J.D.; Leyo, S.A.; Iranmanesh, A.; Rogol, A.D. Estimation of daily cortisol production and clearance rates in normal pubertal males by deconvolution analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 76, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmet, A.; Brienza, V.; Tran, A.; Lemieux, J.; Aglipay, M.; Barrowman, N.; Duffy, C.; Roth, J.; Jurencak, R. Frequency and Duration of Adrenal Suppression Following Glucocorticoid Therapy in Children With Rheumatic Diseases. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2017, 69, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prete, A.; Taylor, A.E.; Bancos, I.; Smith, D.J.; Foster, M.A.; Kohler, S.; Fazal-Sanderson, V.; Komninos, J.; O’Neil, D.M.; Vassiliadi, D.A.; et al. Prevention of Adrenal Crisis: Cortisol Responses to Major Stress Compared to Stress Dose Hydrocortisone Delivery. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mass Screening, C.; Japanese Society for Pediatric, E.; Japanese Society for Mass, S.; Ishii, T.; Anzo, M.; Adachi, M.; Onigata, K.; Kusuda, S.; Nagasaki, K.; Harada, S.; et al. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of 21-hydroxylase deficiency (2014 revision). Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2015, 24, 77–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, D.I.; Palmert, M.R.; Kemp, S.F.; Lawson Wilkins, D.; Therapeutics, C. Adrenal insufficiency: Still a cause of morbidity and death in childhood. Pediatrics 2007, 119, e484–e494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, T.; Barker, P.; Daniel, S.; Fletcher, S.; Wass, J.A.H.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Misra, U.; Dattani, M.; Arlt, W.; Vercueil, A. Guidelines for the management of glucocorticoids during the peri-operative period for patients with adrenal insufficiency: Guidelines from the Association of Anaesthetists, the Royal College of Physicians and the Society for Endocrinology UK. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wass, J.A.; Arlt, W. How to avoid precipitating an acute adrenal crisis. BMJ 2012, 345, e6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, A.; Johannsson, G.; Quinkler, M.; Zelissen, P. Therapy of endocrine disease: Perspectives on the management of adrenal insufficiency: Clinical insights from across Europe. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 169, R165–R175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinkler, M.; Hahner, S.; Johannsson, G.; Stewart, P.M. Saving lives of patients with adrenal insufficiency: A pan-European initiative? Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2014, 80, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannsson, G.; Nilsson, A.G.; Bergthorsdottir, R.; Burman, P.; Dahlqvist, P.; Ekman, B.; Engstrom, B.E.; Olsson, T.; Ragnarsson, O.; Ryberg, M.; et al. Improved cortisol exposure-time profile and outcome in patients with adrenal insufficiency: A prospective randomized trial of a novel hydrocortisone dual-release formulation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitaker, M.; Debono, M.; Huatan, H.; Merke, D.; Arlt, W.; Ross, R.J. An oral multiparticulate, modified-release, hydrocortisone replacement therapy that provides physiological cortisol exposure. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2014, 80, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, K.L.; Cidlowski, J.A. Tissue-specific glucocorticoid action: A family affair. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 19, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhder, F.; Reichardt, H.M. Novel Drug Delivery Systems Tailored for Improved Administration of Glucocorticoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, S.; Souffriau, J.; Libert, C. A General Introduction to Glucocorticoid Biology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whirledge, S.; DeFranco, D.B. Glucocorticoid Signaling in Health and Disease: Insights From Tissue-Specific GR Knockout Mice. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).