Modelling Interval Data with Random Intercepts: A Beta Regression Approach for Clustered and Longitudinal Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Random Intercept Beta Regression Model
2.1. Beta Distribution
2.2. Random Intercept Model
2.3. Likelihood Inference
2.4. Estimating Procedure
3. Moments
4. Prediction of Random Effects
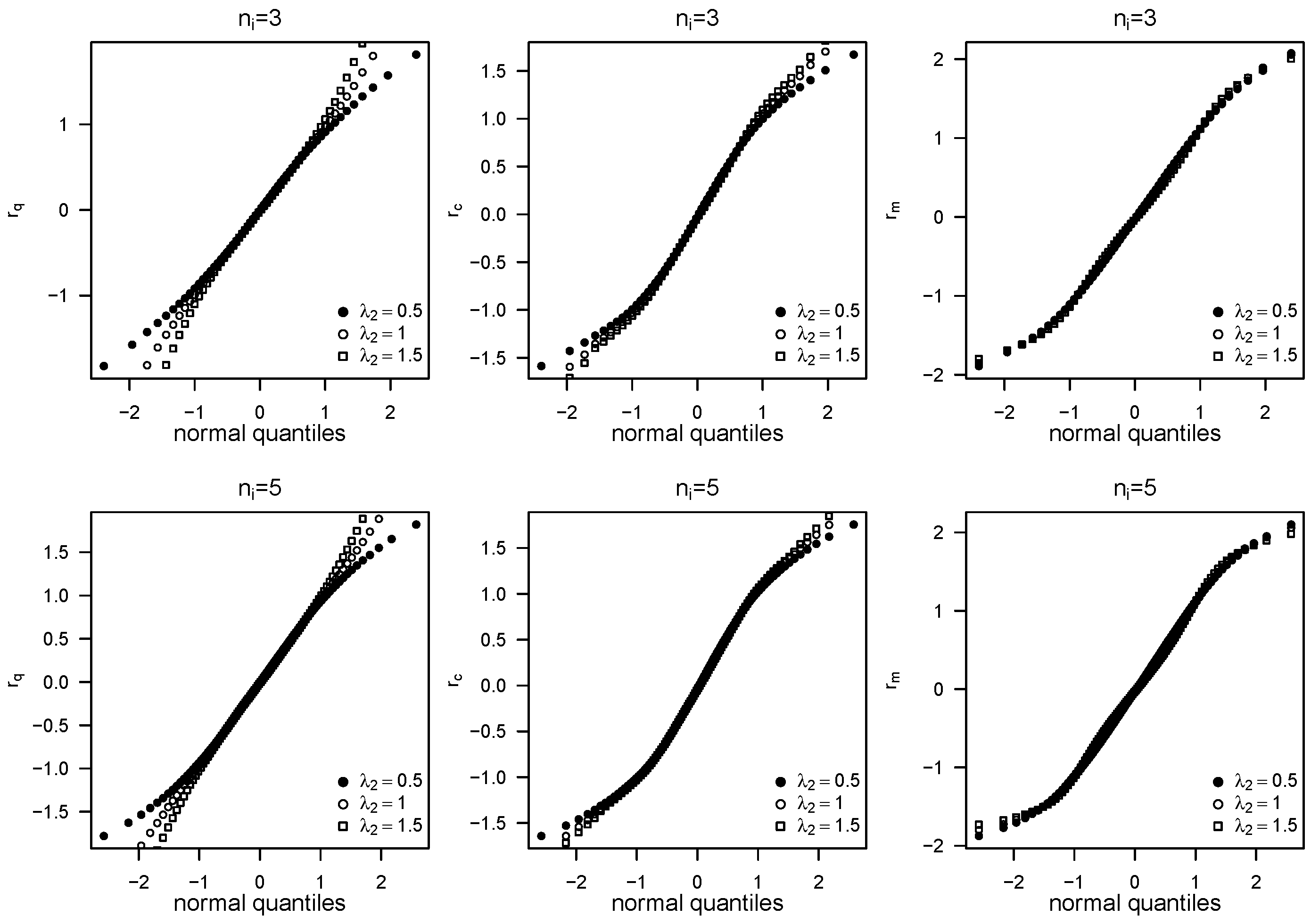
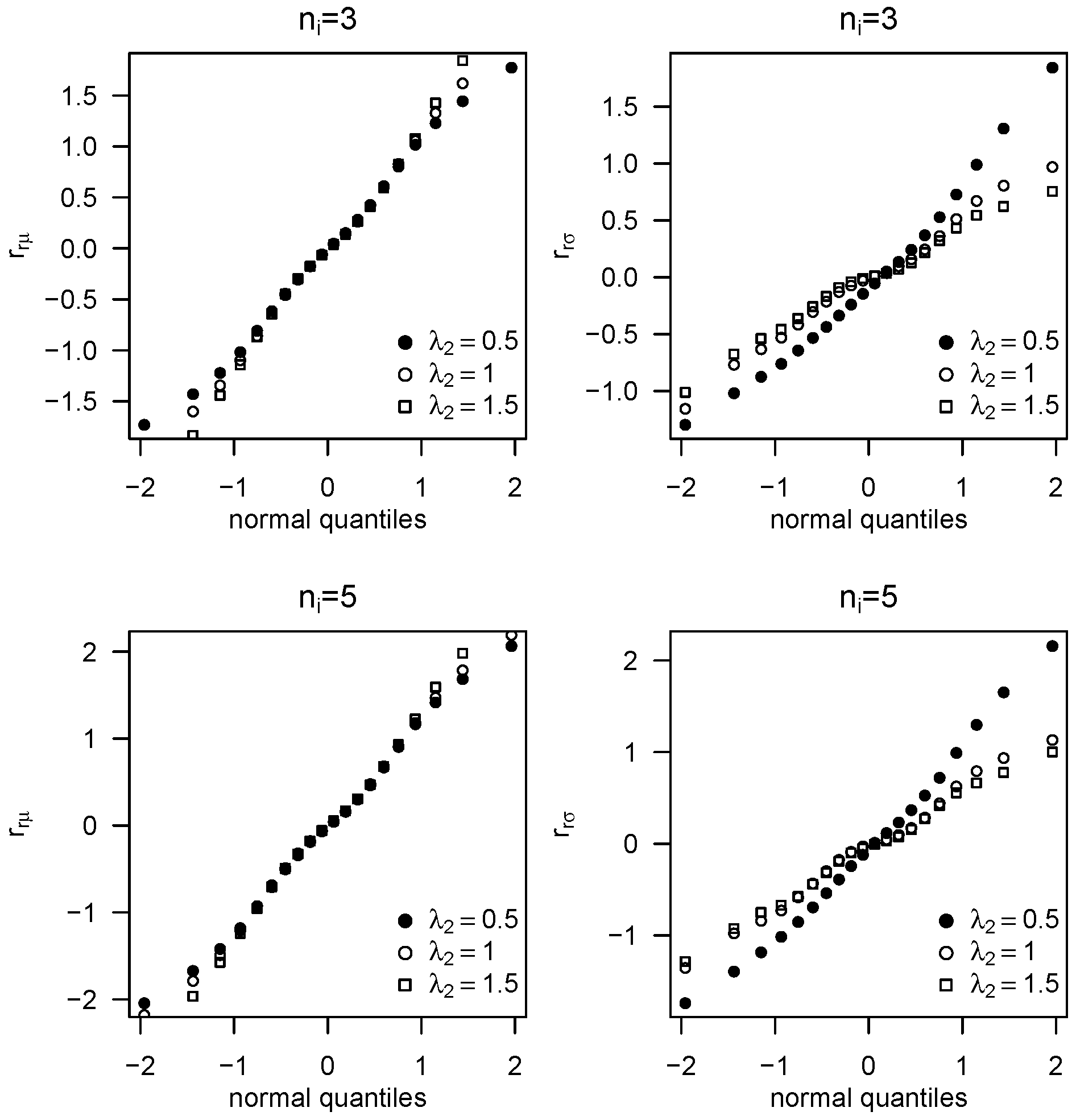
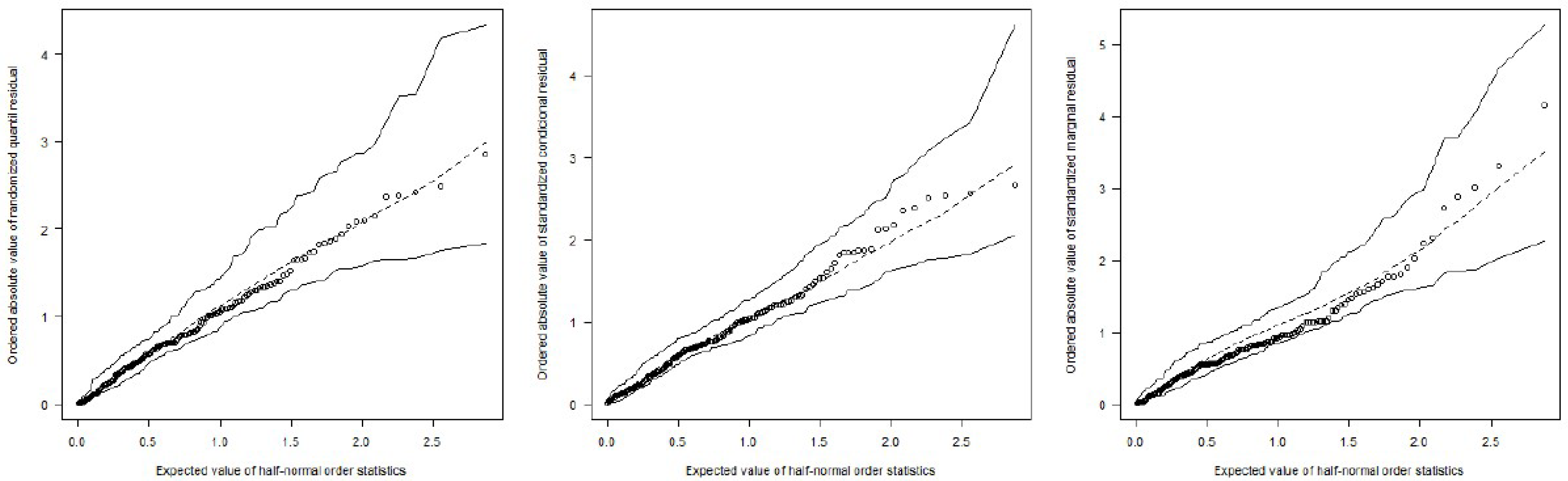
5. Residual Analysis
- Fit the beta random intercept model and generate a sample of n independent observations, treating the fitted model as the true model.
- Fit the beta random intercept model to the generated sample and compute the ordered absolute residuals.
- Repeat steps (1) and (2) k times.
- For each of the n positions, collect the k order statistics and compute their average, minimum, and maximum values.
- Plot these values together with the ordered residuals of the original sample against the half-normal scores , where i is the ith order statistic, , and n is the sample size.
6. Simulation Study
7. Application
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paolino, P. Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Models with Beta-Distributed Dependent Variables. Political Anal. 2001, 9, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieschnick, R.; McCullough, B. Regression analysis of variates observed on (0, 1): Percentages, proportions and fractions. Stat. Model. 2003, 3, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithson, M.; Verkuilen, J. A Better Lemon Squeezer? Maximum-Likelihood Regression with Beta-Distributed Dependent Variables. Psychol. Methods 2006, 11, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.; Cribari-Neto, F. Beta regression for modeling rates and proportions. J. Appl. Stat. 2004, 31, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venezuela, M. Equação de Estimação Generalizada e Influência Local para Modelos de Regressão Beta com Medidas Repetidas. Ph.D. Thesis, Instituto de Matemática e Estatística, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brasil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Simas, A.; Barreto-Souza, W.; Rocha, A. Improved estimators for a general class of beta regression models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2010, 54, 348–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Pinheiro, E. Improved likelihood inference in beta regression. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2011, 81, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cribari-Neto, F.; Souza, T. Testing inference in variable dispersion beta regressions. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2012, 82, 1827–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, R.; Stasinopoulos, D. Generalized additive models for location, scale and shape. Appl. Stat. 2005, 54, 507–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, P.; Månsson, K.; Kibria, B.G. A Liu estimator for the beta regression model and its application to chemical data. J. Chemom. 2020, 34, e3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonazel, M.R.; Dawoud, I.; Awwad, F.A.; Lukman, A.F. Dawoud–Kibria estimator for beta regression model: Simulation and application. Front. Appl. Math. Stat. 2022, 8, 775068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algamal, Z.Y.; Abonazel, M.R. Developing a Liu-type estimator in beta regression model. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2022, 34, e6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, R.; Marshall, L.; McGlynn, B. A beta regression model for improved solar radiation predictions. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 1923–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douma, J.C.; Weedon, J.T. Analysing continuous proportions in ecology and evolution: A practical introduction to beta and Dirichlet regression. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 1412–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissinger, E.; Khoo, C.; Richmond, I.; Faulkner, S.; Schneider, D. A case for beta regression in the natural sciences. Ecosphere 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonazel, M.R.; Said, H.A.; Tag-Eldin, E.; Abdel-Rahman, S.; Khattab, I.G. Using beta regression modeling in medical sciences: A comparative study. Commun. Math. Biol. Neurosci. 2023, 2023, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cribari-Neto, F. A beta regression analysis of COVID-19 mortality in Brazil. Infect. Dis. Model. 2023, 8, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; van Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.J.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.M. glmmTMB Balances Speed and Flexibility Among Packages for Zero-inflated Generalized Linear Mixed Modeling. R J. 2017, 9, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkuilen, J.; Smithson, M. Mixed and Mixture Regression Models for Continuous Bounded Responses Using the Beta Distribution. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 2012, 37, 82–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Nelder, J.; Pawitan, Y. Generalized Linear Models with Random Effects: Unified Analysis via H-Likelihood; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Orange, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Meyers, S.; Ambler, J.; Tan, M.; Werner, J.; Huang, S. Variation of perfluorproane disappearance after vitrectomy. Retina 1992, 12, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullagh, P.; Nelder, J. Generalized Linear Models, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L. Mixed Effects Models for Complex Data; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fahrmeir, L.; Tutz, G. Multivariate Statistical Modelling Based on Generalized Linear Models, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cribari-Neto, F.; Zeileis, A. Beta Regression in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 34, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzmaurice, G.; Davidian, M.; Verbeke, G.; Molenberghs, G. Longitudinal Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hilden-Minton, J. Multilevel Diagnostics for Mixed and Hierarchical Linear Models. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Verbeke, G.; Lesaffre, E. A linear mixed-effects model with heterogeneity in the random-effects population. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1996, 91, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D. Mixed-Effects Models in S ans S-PLUS; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nobre, J.; Singer, J. Residual Analysis for Linear Mixed Models. Biom. J. 2007, 49, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, P.; Smyth, G. Randomized Quantile Residuals. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1996, 5, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, A. Plots, Transformations and Regression: An Introduction to Graphical Methods of Diagnostic Regression Analysis; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Kutner, M.; Nachtsheim, C.; Neter, J.; Li, W. Applied Linear Statistical Models, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.G.; Wu, H. Backfitting and local likelihood methods for nonparametric mixed-effects models with longitudinal data. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2006, 136, 3760–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoyou, Q.; Zhongyi, Z. Robust estimation in partial linear mixed model for longitudinal data. Acta Math. Sci. 2008, 28, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Wang, Y.G. Quantile regression for longitudinal data with a working correlation model. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2012, 56, 2526–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. [Google Scholar]
- Broström, G.; Holmberg, H. glmmML: Generalized Linear Models with Clustering; R Package Version 0.82-1; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2011; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=glmmML (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Wissel, J. A New Biased Estimator for Multivariate Regression Models with Highly Collinear Variables. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut für Mathematik, Universität Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Song, P.X.K.; Tan, M. Marginal models for longitudinal continuous proportional data. Biometrics 2000, 56, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Qiu, Z.; Tan, M. Modelling Heterogeneous Dispersion in Marginal Models for Longitudinal Proportional Data. Biom. J. 2004, 46, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| N | N | ||||||||
| 20 | 3 | 2.897 | 3.188 | 2.296 | 20 | 3 | 3.577 | 3.619 | 3.506 |
| 5 | 1.388 | 1.499 | 1.497 | 5 | 1.811 | 1.822 | 1.868 | ||
| 8 | 0.918 | 0.995 | 1.116 | 8 | 1.279 | 1.369 | 1.543 | ||
| 12 | 0.706 | 0.807 | 0.950 | 12 | 1.075 | 1.191 | 1.458 | ||
| 40 | 3 | 1.250 | 1.462 | 1.472 | 40 | 3 | 1.645 | 1.737 | 1.789 |
| 5 | 0.781 | 0.860 | 0.954 | 5 | 1.031 | 1.157 | 1.301 | ||
| 8 | 0.572 | 0.638 | 0.782 | 8 | 0.857 | 1.000 | 1.189 | ||
| 12 | 0.435 | 0.558 | 0.745 | 12 | 0.771 | 0.928 | 1.181 | ||
| 60 | 3 | 0.937 | 1.014 | 1.062 | 60 | 3 | 1.134 | 1.244 | 1.364 |
| 5 | 0.590 | 0.663 | 0.756 | 5 | 0.816 | 0.903 | 1.092 | ||
| 8 | 0.430 | 0.518 | 0.658 | 8 | 0.693 | 0.816 | 1.061 | ||
| 12 | 0.347 | 0.443 | 0.656 | 12 | 0.646 | 0.805 | 1.050 | ||
| 100 | 3 | 0.638 | 0.688 | 0.727 | 100 | 3 | 0.777 | 0.859 | 1.005 |
| 5 | 0.432 | 0.459 | 0.570 | 5 | 0.593 | 0.692 | 0.909 | ||
| 8 | 0.315 | 0.387 | 0.540 | 8 | 0.556 | 0.677 | 0.901 | ||
| 12 | 0.257 | 0.356 | 0.537 | 12 | 0.553 | 0.675 | 0.895 | ||
| 150 | 3 | 0.476 | 0.528 | 0.566 | 150 | 3 | 0.599 | 0.682 | 0.963 |
| 5 | 0.339 | 0.368 | 0.466 | 5 | 0.491 | 0.641 | 0.861 | ||
| 8 | 0.252 | 0.314 | 0.478 | 8 | 0.490 | 0.590 | 0.822 | ||
| 12 | 0.210 | 0.295 | 0.407 | 12 | 0.454 | 0.573 | 0.792 | ||
| N | N | ||||||||
| 20 | 3 | 0.997 | 0.849 | 0.903 | 20 | 3 | 0.700 | 0.957 | 0.970 |
| 5 | 1.000 | 0.958 | 0.975 | 5 | 0.875 | 0.985 | 0.943 | ||
| 8 | 1.000 | 0.990 | 0.978 | 8 | 0.996 | 0.979 | 0.893 | ||
| 12 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.969 | 12 | 0.992 | 0.942 | 0.817 | ||
| 40 | 3 | 0.870 | 0.960 | 0.977 | 40 | 3 | 0.869 | 0.983 | 0.950 |
| 5 | 0.992 | 0.999 | 0.988 | 5 | 0.981 | 0.968 | 0.867 | ||
| 8 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.970 | 8 | 0.993 | 0.940 | 0.779 | ||
| 12 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.951 | 12 | 0.967 | 0.883 | 0.648 | ||
| 60 | 3 | 0.953 | 0.986 | 0.988 | 60 | 3 | 0.940 | 0.979 | 0.913 |
| 5 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 0.987 | 5 | 0.992 | 0.960 | 0.846 | ||
| 8 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.962 | 8 | 0.985 | 0.917 | 0.686 | ||
| 12 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.923 | 12 | 0.964 | 0.842 | 0.524 | ||
| 100 | 3 | 0.994 | 0.999 | 0.985 | 100 | 3 | 0.987 | 0.973 | 0.855 |
| 5 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.974 | 5 | 0.989 | 0.929 | 0.724 | ||
| 8 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 0.937 | 8 | 0.962 | 0.866 | 0.511 | ||
| 12 | 1.000 | 0.997 | 0.860 | 12 | 0.935 | 0.742 | 0.348 | ||
| 150 | 3 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.991 | 150 | 3 | 0.996 | 0.959 | 0.785 |
| 5 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.962 | 5 | 0.986 | 0.894 | 0.610 | ||
| 8 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 0.909 | 8 | 0.964 | 0.814 | 0.398 | ||
| 12 | 1.000 | 0.994 | 0.814 | 12 | 0.917 | 0.647 | 0.229 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Usuga-Manco, O.; Hernández-Barajas, F.; Giampaoli, V. Modelling Interval Data with Random Intercepts: A Beta Regression Approach for Clustered and Longitudinal Structures. Modelling 2025, 6, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6040128
Usuga-Manco O, Hernández-Barajas F, Giampaoli V. Modelling Interval Data with Random Intercepts: A Beta Regression Approach for Clustered and Longitudinal Structures. Modelling. 2025; 6(4):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6040128
Chicago/Turabian StyleUsuga-Manco, Olga, Freddy Hernández-Barajas, and Viviana Giampaoli. 2025. "Modelling Interval Data with Random Intercepts: A Beta Regression Approach for Clustered and Longitudinal Structures" Modelling 6, no. 4: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6040128
APA StyleUsuga-Manco, O., Hernández-Barajas, F., & Giampaoli, V. (2025). Modelling Interval Data with Random Intercepts: A Beta Regression Approach for Clustered and Longitudinal Structures. Modelling, 6(4), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6040128







