From Data to Draught: Modelling and Predicting Mixed-Culture Beer Fermentation Dynamics Using Autoregressive Recurrent Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Training Data Characteristics
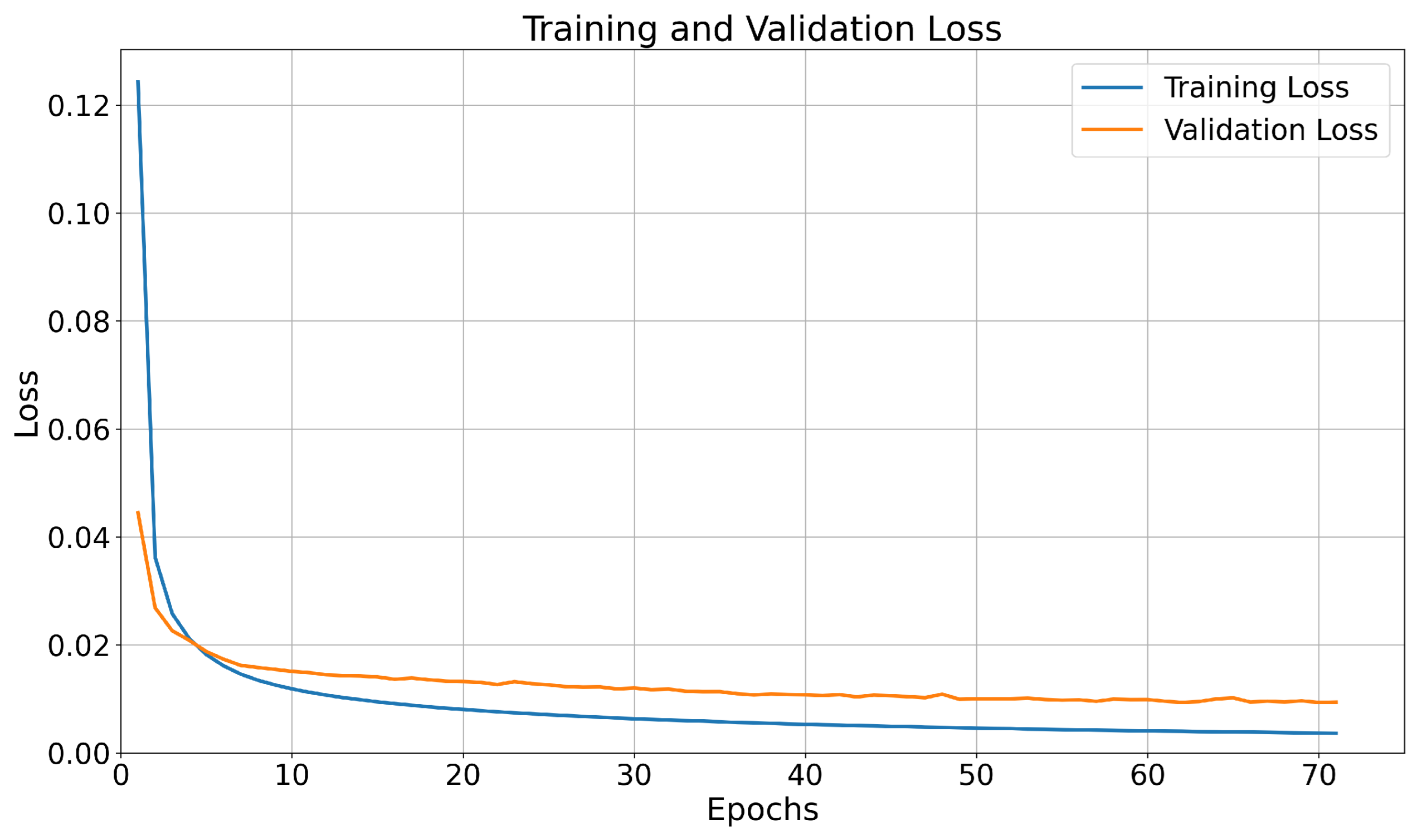
3.2. Hyperparameter Tuning
3.3. Residual Results for the AR-RNN Model
3.3.1. Monoculture Residuals
3.3.2. Mixed-Culture Residuals
3.4. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| AR-RNN | Autoregressive Recurrent Neural Network |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| LSTM | Long Short Term Memory |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
References
- Basso, R.F.; Alcarde, A.R.; Portugal, C.B. Could non-Saccharomyces yeasts contribute on innovative brewing fermentations? Food Res. Int. 2016, 86, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitaels, F.; Wieme, A.D.; Janssens, M.; Aerts, M.; Van Landschoot, A.; De Vuyst, L.; Vandamme, P. The microbial diversity of an industrially produced lambic beer shares members of a traditionally produced one and reveals a core microbiota for lambic beer fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2015, 49, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oevelen, D.; Spaepen, M.; Timmermans, P.; Verachtert, H. Microbiological Aspects of Spontaneous Wort Fermentation in the Production of Lambic and Gueuze. J. Inst. Brew. 1977, 83, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, J. Wild Brews: Beer Beyond the Influence of Brewer’s Yeast; Brewers Publications: Kent, OH, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tonsmeire, M. American Sour Beer: Innovative Techniques for Mixed Fermentations; Brewers Publications: Kent, OH, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shimotsu, S.; Asano, S.; Iijima, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yamagishi, H.; Aizawa, M. Investigation of beer-spoilage ability of Dekkera/Brettanomyces yeasts and development of multiplex PCR method for beer-spoilage yeasts. J. Inst. Brew. 2015, 121, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra Colomer, M.; Funch, B.; Forster, J. The raise of Brettanomyces yeast species for beer production. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 56, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roos, J.; De Vuyst, L. Microbial acidification, alcoholization, and aroma production during spontaneous lambic beer production. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dysvik, A.; La Rosa, S.L.; De Rouck, G.; Rukke, E.O.; Westereng, B.; Wicklund, T. Microbial Dynamics in Traditional and Modern Sour Beer Production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00566-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, H.; Iserentant, D.; Verachtert, H. Microbiological Aspects of a Mixed Yeast—Bacterial Fermentation in the Production of a Special Belgian Acidic Ale. J. Inst. Brew. 1997, 103, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.; Zainasheff, J. Yeast: The Practical Guide to Beer Fermentation; Brewers Publications: Kent, OH, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lodolo, E.J.; Kock, J.L.; Axcell, B.C.; Brooks, M. The yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae – Main Character Beer Brewing. FEMS Yeast Res. 2008, 8, 1018–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrés-Toro, B.; Girón-Sierra, J.M.; López-Orozco, J.A.; Fernández-Conde, C. Optimization of a Batch Fermentation Process by Genetic Algorithms. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1997, 30, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrés-Toro, B.; Girón-Sierra, J.; López-Orozco, J.; Fernández-Conde, C.; Peinado, J.; García-Ochoa, F. A kinetic model for beer production under industrial operational conditions. Math. Comput. Simul. 1998, 48, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, D.W.K.; Chua, J.Y.; Liu, S.Q. Impact of simultaneous fermentation with Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Torulaspora delbrueckii on volatile and non-volatile constituents in beer. LWT 2018, 91, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dysvik, A.; La Rosa, S.L.; Liland, K.H.; Myhrer, K.S.; Østlie, H.M.; De Rouck, G.; Rukke, E.O.; Westereng, B.; Wicklund, T. Co-fermentation Involving Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Lactobacillus Species Tolerant to Brewing-Related Stress Factors for Controlled and Rapid Production of Sour Beer. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhonsale, S.; Mores, W.; Van Impe, J. Dynamic Optimisation of Beer Fermentation under Parametric Uncertainty. Fermentation 2021, 7, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepworth, N.; Brown, A.K.; Hammond, J.R.M.; Boyd, J.W.R.; Varley, J. The Use of Laboratory-Scale Fermentations as a Tool for Modelling Beer Fermentations. Food Bioprod. Process. 2003, 81, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, M. A New Look at Models of the Combined Effect of Temperature, pH, Water Activity, or Other Factors on Microbial Growth Rate. Food Eng. Rev. 2022, 14, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerolla, R.; Mehshan K M, M.; Roy, N.; Harsha, N.S.; Pavan Ganesh, M.P.; Besta, C.S. Beer fermentation modeling for optimum flavor and performance. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, G.; Hawkins, C. The Real-Time Optimisation of an Industrial Fermentation Process. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2004, 37, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trelea, I.C.; Titica, M.; Landaud, S.; Latrille, E.; Corrieu, G.; Cheruy, A. Predictive modelling of brewing fermentation: From knowledge-based to black-box models. Math. Comput. Simul. 2001, 56, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhou, Z.K.; Zhang, G.X. Ant colony system algorithm for the optimization of beer fermentation control. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2004, 5, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monerawela, C.; Bond, U. The hybrid genomes of Saccharomyces pastorianus: A current perspective. Yeast 2018, 35, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, W.Y.; Teo, K.T.K.; Tan, M.K.; Tham, H.J. Fermentation Process Control and Optimization. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2022, 45, 1731–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondakci, T. Recent Applications of Advanced Control Techniques in Food Industry. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 522–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, N.; Bai, G.Y.; Fu, Y.J.; Yan, L.Q. Fault Diagnosis Model of Beer Fermentation Process Based on Multiway Kernel Principal Component Analysis. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 644–650, 2556–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Rehman, K.U.; Wang, B.; Shahzad, M. Modern Soft-Sensing Modeling Methods for Fermentation Processes. Sensors 2020, 20, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, S.; Amigo, J.M.; Lyndgaard, C.B.; Foschino, R.; Casiraghi, E. Beer fermentation: Monitoring of process parameters by FT-NIR and multivariate data analysis. Food Chem. 2014, 155, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Nguang, S.K.; Chen, X.D.; Li, X.M. Modelling and optimization of fed-batch fermentation processes using dynamic neural networks and genetic algorithms. Biochem. Eng. J. 2004, 22, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, C.; Quain, D. Brewing Yeast and Fermentation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, B.R.; Lawrence, S.J.; Leclaire, J.P.R.; Powell, C.D.; Smart, K.A. Yeast responses to stresses associated with industrial brewery handling. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 31, 535–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginovart, M.; López, D.; Giró, A.; Silbert, M. Flocculation in brewing yeasts: A computer simulation study. Biosystems 2006, 83, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallone, B.; Steensels, J.; Prahl, T.; Soriaga, L.; Saels, V.; Herrera-Malaver, B.; Merlevede, A.; Roncoroni, M.; Voordeckers, K.; Miraglia, L.; et al. Domestication and Divergence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Beer Yeasts. Cell 2016, 166, 1397–1410.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Bamforth, C.W. The Microbiology of Malting and Brewing. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2013, 77, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parapouli, M.; Vasileiadis, A.; Afendra, A.S.; Hatziloukas, E. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its industrial applications. AIMS Microbiol. 2020, 6, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, E.; Wang, B.; Bellora, N.; Peris, D.; Hulfachor, A.B.; Koshalek, J.A.; Adams, M.; Libkind, D.; Hittinger, C.T. The Genome Sequence of Saccharomyces eubayanus and the Domestication of Lager-Brewing Yeasts. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2818–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libkind, D.; Hittinger, C.T.; Valério, E.; Gonçalves, C.; Dover, J.; Johnston, M.; Gonçalves, P.; Sampaio, J.P. Microbe domestication and the identification of the wild genetic stock of lager-brewing yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14539–14544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monerawela, C.; Bond, U. Brewing up a storm: The genomes of lager yeasts and how they evolved. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]























| Sensor | Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Specific Gravity Sensor | ±0.2 °P |
| pH Sensor | ±0.1 °P |
| Fluid Temperature Sensor | ±1 °P |
| Hyperparameter | Tuned Value |
|---|---|
| LSTM Units Layer 1 | 27 |
| LSTM Units Layer 2 | 127 |
| Dense Units | 197 |
| Batch Size | 110 |
| Epochs | 71 |
| Learning Rate | 0.000251355666177083 |
| Dropout Rate | 0.2529847965068651 |
| L2 Regularisation | 0.000022464551680532603 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Brien, A.; Zhang, H.; Allwood, D.M.; Rawsthorne, A. From Data to Draught: Modelling and Predicting Mixed-Culture Beer Fermentation Dynamics Using Autoregressive Recurrent Neural Networks. Modelling 2024, 5, 201-222. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling5010011
O’Brien A, Zhang H, Allwood DM, Rawsthorne A. From Data to Draught: Modelling and Predicting Mixed-Culture Beer Fermentation Dynamics Using Autoregressive Recurrent Neural Networks. Modelling. 2024; 5(1):201-222. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling5010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Brien, Alexander, Hongwei Zhang, Daniel M. Allwood, and Andy Rawsthorne. 2024. "From Data to Draught: Modelling and Predicting Mixed-Culture Beer Fermentation Dynamics Using Autoregressive Recurrent Neural Networks" Modelling 5, no. 1: 201-222. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling5010011
APA StyleO’Brien, A., Zhang, H., Allwood, D. M., & Rawsthorne, A. (2024). From Data to Draught: Modelling and Predicting Mixed-Culture Beer Fermentation Dynamics Using Autoregressive Recurrent Neural Networks. Modelling, 5(1), 201-222. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling5010011







