Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent (BOLD) MRI in Glomerular Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Primary Nephrotic Syndrome
3. Nephrotic Syndrome Secondary to Diabetes Mellitus
4. Nephritic Syndrome Secondary to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BOLD MRI | Blood oxygen level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| DN | Diabetic nephropathy |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| ISN/RPS | International Society of Nephrology/Renal Pathology Society |
| LN | Lupus nephritis |
| mGRE | Multiple gradient-recalled-echo |
| PNS | Primary nephrotic syndrome |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| TLCO | Twelve-layer concentric objects |
References
- Zech, P.; Colon, S.; Pointet, P.; Deteix, P.; Labeeuw, M.; Leitienne, P. The nephrotic syndrome in adults aged over 60: Etiology, evolution and treatment of 76 cases. Clin. Nephrol. 1982, 17, 232–236. [Google Scholar]
- Eckardt, K.-U.; Rosenberger, C.; Jürgensen, J.S.; Wiesener, M.S. Role of hypoxia in the pathogenesis of renal disease. Blood Purif. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Z.; Cai, J.; Tang, C.; Dong, Z. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in kidney injury and repair. Cells 2019, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhong, J.; Yang, H.C.; Fogo, A.B. Cross talk from tubules to glomeruli. Toxicol. Pathol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y. Application of BOLD-MRI in the classification of renal function in chronic kidney disease. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raichle, M.E. Behind the scenes of functional brain imaging: A historical and physiological perspective. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaudhary, U.J.; Duncan, J.S.; Lemieux, L. Mapping hemodynamic correlates of seizures using fMRI: A review. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruijm, M.; Mendichovszky, I.A.; Liss, P.; Van Der Niepen, P.; Textor, S.C.; Lerman, L.O.; Krediet, C.T.P.; Caroli, A.; Burnier, M.; Prasad, P.V. Renal blood oxygenation level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging to measure renal tissue oxygenation: A statement paper and systematic review. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.-P.; Halter, S.; Prasad, P. Blood oxygen level-dependent MR imaging of the kidneys. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pruijm, M.; Milani, B.; Burnier, M. Blood oxygenation level-dependent mri to assess renal oxygenation in renal diseases: Progresses and challenges. Front. Physiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, W. Noninvasive evaluation of renal oxygenation in primary nephrotic syndrome with blood oxygen level dependent magnetic resonance imaging: Initial experience. J. Int. Med. Res. 2015, 43, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brezis, M.; Agmon, Y.; Epstein, F.H. Determinants of intrarenal oxygenation I. Effects of diuretics. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Fluid Electrolyte Physiol. 1994, 267, F1059–F1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamali, A.; Sadowski, E.A.; Samaniego-Picota, M.; Fain, S.B.; Muehrer, R.J.; Alford, S.K.; Grist, T.M.; Becker, B.N. Noninvasive assessment of early kidney allograft dysfunction by blood oxygen level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging. Transplantation 2006, 82, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Kozawa, E.; Okada, H.; Inukai, K.; Watanabe, S.; Kikuta, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Takenaka, T.; Katayama, S.; Tanaka, J.; et al. Noninvasive evaluation of kidney hypoxia and fibrosis using magnetic resonance imaging. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satirapoj, B.; Adler, S.G. Comprehensive approach to diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 33, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, I.J. Current challenges in diabetic nephropathy: Early diagnosis and ways to improve outcomes. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 31, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caramori, M.L.; Fioretto, P.; Mauer, M. The need for early predictors of diabetic nephropathy risk is albumin excretion rate sufficient? Diabetes 2000, 49, 1399–1408. Available online: https://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/49/9/1399.short (accessed on 14 August 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gross, J.L.; de Azevedo, M.J.; Silveiro, S.P.; Canani, L.H.; Caramori, M.L.; Zelmanovitz, T. Diabetic nephropathy: Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.-Z.; Ye, Y.-J.; Cheng, Z.-Y.; Hu, J.-J.; Zhang, C.-B.; Qian, L.; Lu, X.-H.; Cai, X.-R.; Cai, X.-H. Non-invasive assessment of early stage diabetic nephropathy by DTI and BOLD MRI. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Kumar, R.; Banerjee, S.; Hsu, C. Blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) MRI of diabetic nephropathy: Preliminary experience. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 33, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.C.; Cai, Y.Z.; Tang, Z.G.; Zuo, P.L.; Liu, R.B.; Liu, F. Lipo-prostaglandin E1 improves renal hypoxia evaluated by BOLD-MRI in patients with diabetic kidney disease. Clin. Imaging 2018, 50, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruijm, M.; Hofmann, L.; Zanchi, A.; Maillard, M.; Forni, V.; Muller, M.-E.; Wuerzner, G.; Vogt, B.; Stuber, M.; Burnier, M. Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system and renal tissue oxygenation as measured with BOLD-MRI in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 99, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasitanon, N.; Magder, L.S.; Petri, M. Predictors of survival in systemic lupus erythematosus. Medicine 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, K.; Alemao, E.; Kawabata, H.; Hillson, J.L. Prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis in the United States: Analysis of commercial and public insurance billing data. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yan, F.; Chen, N. Diffusion weighted imaging and blood oxygen level-dependent MR imaging of kidneys in patients with lupus nephritis. J. Transl. Med. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapacchi, S.; Smith, R.X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, L.; Sigalov, V.; Krasileva, K.E.; Karpouzas, G.; Plotnik, A.; Sayre, J.; Hernandez, E.; et al. Towards the identification of multi-parametric quantitative MRI biomarkers in lupus nephritis. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 33, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.; Yan, T.; Li, N.; Jia, J.; Shang, W.; Wei, L.; Zheng, Z. Detection of renal hypoxia in lupus nephritis using blood oxygen level-dependent MR imaging: A multiple correspondence analysis. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017, 42, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Wu, L.-H.; Tan, Y.; Li, L.-H.; Wang, C.-L.; Wang, W.-K.; Qu, Z.; Chen, M.-H.; Gao, J.-J.; Li, Z.-Y.; et al. Tubulointerstitial lesions of patients with lupus nephritis classified by the 2003 International Society of Nephrology and Renal Pathology Society system. Kidney Int. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, P.V.; Thacker, J.; Li, L.-P.; Haque, M.; Li, W.; Koenigs, H.; Zhou, Y.; Sprague, S.M. Multi-Parametric evaluation of chronic kidney disease by MRI: A preliminary cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bane, O.; Mendichovszky, I.A.; Milani, B.; Dekkers, I.A.; Deux, J.-F.; Eckerbom, P.; Grenier, N.; Hall, M.E.; Inoue, T.; Laustsen, C.; et al. Consensus-based technical recommendations for clinical translation of renal BOLD MRI. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalid, M.U.; Shah, A.; Seghouane, A.K. Adaptive 2DCCA based approach for improving spatial specificity of activation detection in functional MRI. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Digital Image Computing Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Fremantle, WA, Australia, 3–5 December 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.C.W.; Faull, O.K.; Pattinson, K.T.S.; Jenkinson, M. Physiological noise in brainstem fMRI. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, F.; Liao, Y.; Cui, K.; Tao, Y. Noninvasive evaluation of renal oxygenation in children with chronic kidney disease using blood-oxygen-level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr. Radiol. 2020, 50, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin-Long, P.; Jing-Xia, X.; Jian-Yu, L.; Song, W.; Xin-Kui, T. A preliminary study of blood-oxygen-level-dependent MRI in patients with chronic kidney disease. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, B.; Ansaloni, A.; Sousa-Guimaraes, S.; Vakilzadeh, N.; Piskunowicz, M.; Vogt, B.; Stuber, M.; Burnier, M.; Pruijm, M. Reduction of cortical oxygenation in chronic kidney disease: Evidence obtained with a new analysis method of blood oxygenation level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2017, 32, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
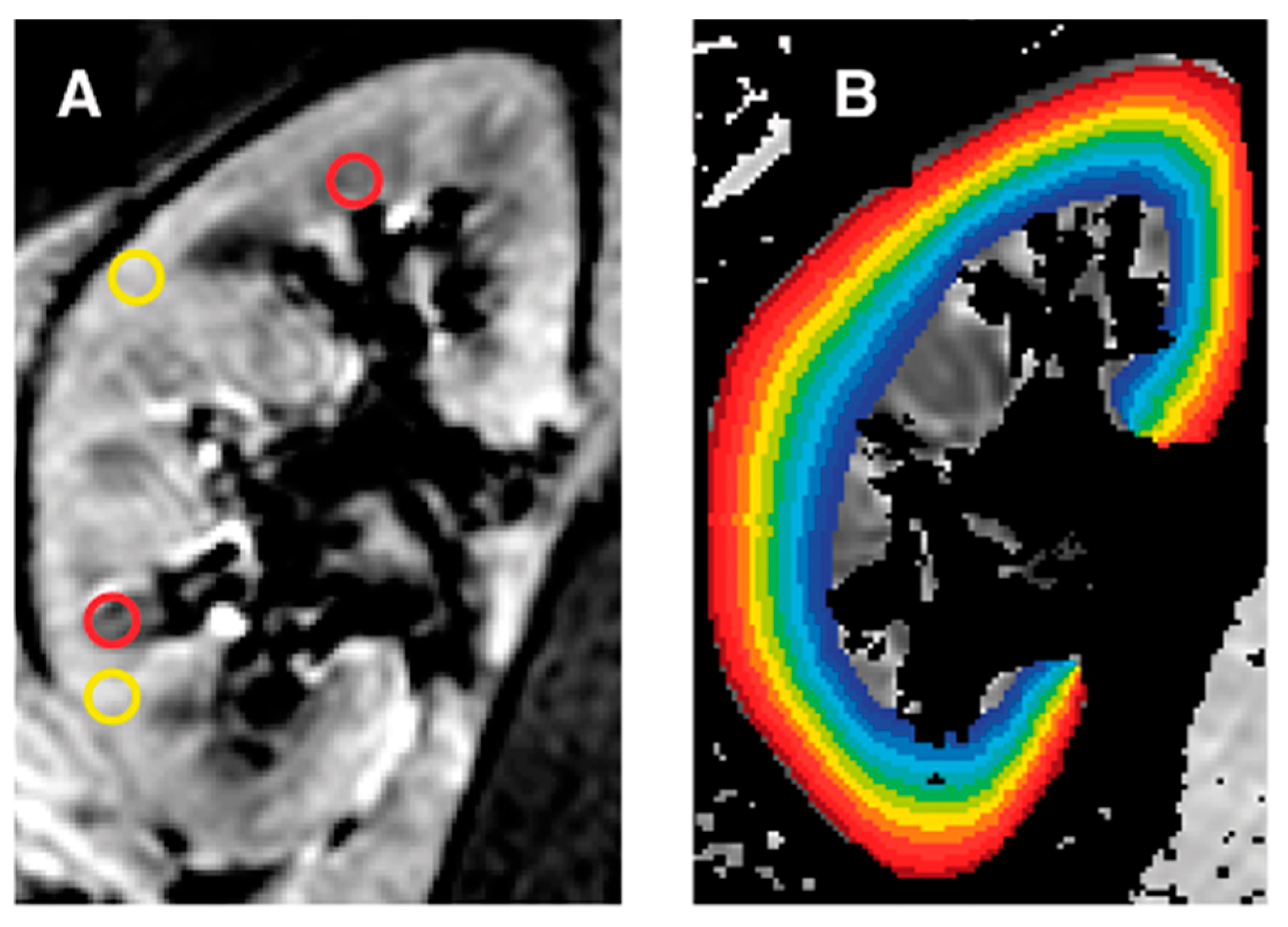
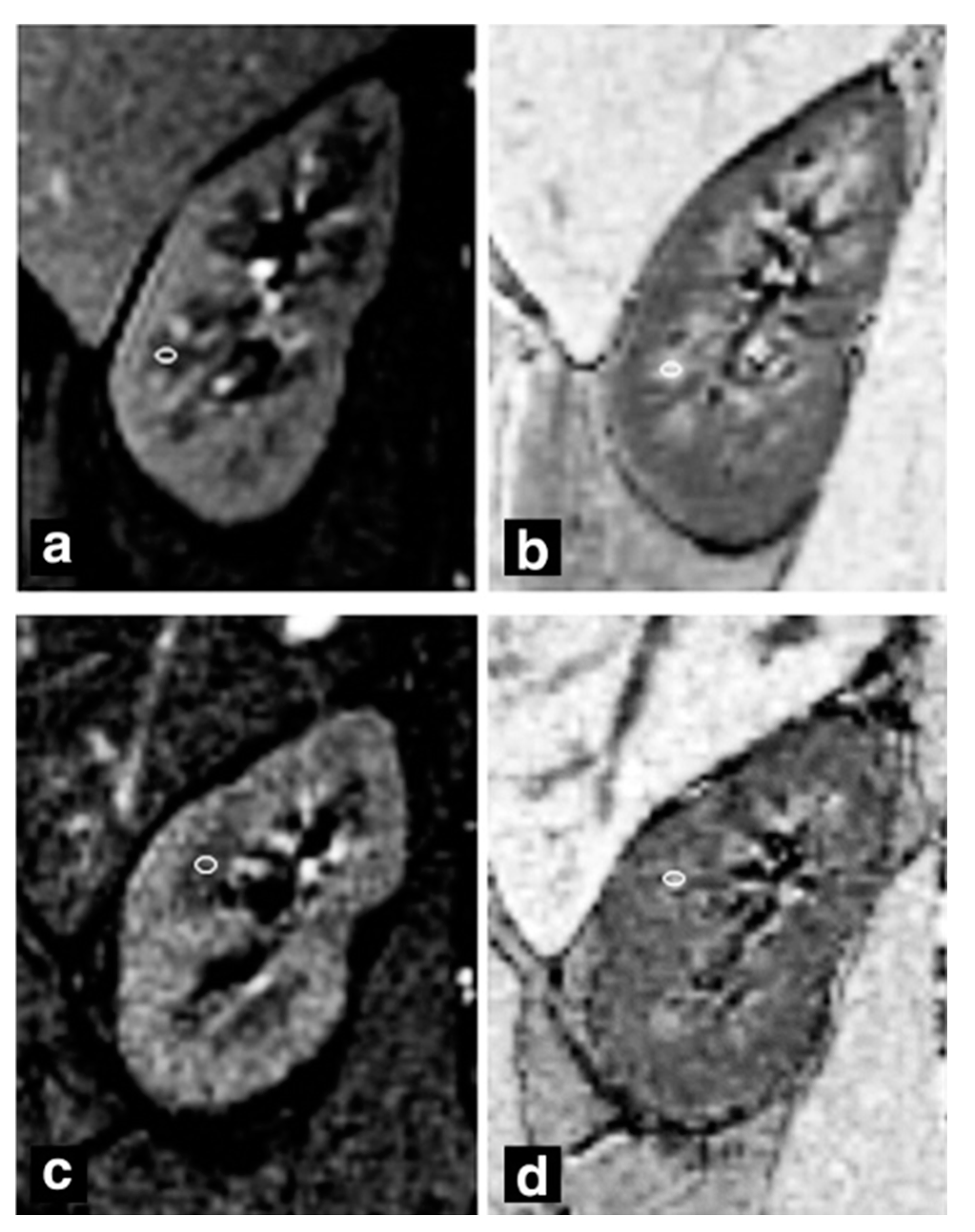

| Author | Year | Design | Population | TR (ms)/ TE (ms) | Disease Stage | eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) (Patients, Volunteers) | cR2* (sec−1) (Patients, Volunteers) | mR2 * (sec−1) (Patients, Volunteers) | Statistical Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al. [5] | 2018 | Prospective case-control | 9 MG patients, 27 healthy volunteers | 100/1.76–18.68 | -- | --, 110.8 ± 11.2 | -- | -- | Pearson correlation, ANOVA |
| Zhang et al. [11] | 2015 | Prospective case-control | 20 PNS patients, 18 healthy volunteers | 150/1.6–77.5 | -- | -- | 20.4 ± 3.9, 19.7 ± 0.7 | 24.0 ± 5.9, 36.5 ± 1.3 | Spearman’s correlation coefficient, t-test |
| Feng et al. [19] | 2020 | Retrospective case-control | 30 DN patients, 15 healthy volunteers | 150/3.4–27.8 | NAU, MAU | 97.9 ± 8.8, 103.7 ± 11.9 a | 17.0 ± 1.9, 16.7 ± 1.6 a,b | 28.1 ± 3.8, 28.9 ± 3.8 a,b | Pearson correlation, ANOVA |
| Wang et al. [20] | 2011 | Prospective non-randomized trial | 20 DN patients, 7 healthy volunteers | 65/7–53 | Mild, moderate-severe | -- | 13.8 ± 2.4, 19.3 ± 1.2 | 11.1 ± 0.9, 11.5 ± 0.7 | Multiple logistic regression, t-test |
| Li et al. [21] | 2018 | Prospective case-control | 16 DN patients | 90/3.29–40.22 | Class II–IV | 28.4 ± 25.1, -- | 23.3 ± 6.5, -b | 29.4 ± 6.7, --b | t-test, ANOVA |
| Pruijm et al. [22] | 2013 | Prospective randomized two-way crossover study | 12 DN patients | 68/6–52.2 | -- | 62.0 ± 22.0, -- | 17.9 ± 1.5, -- | 28.7 ± 1.3, -- | Spearman’s rank test, ANOVA |
| Li et al. [25] | 2014 | Retrospective case-control | 65 LN patients, 16 healthy volunteers | 110/2.2–27.5 | Class I–V | -- | 11.0 ± 1.6, 12.6 ± 1.4 | 14.1 ± 3.4, 18.1 ± 2.5 | Pearson correlation, t-test |
| Rapacchi et al. [26] | 2015 | Retrospective case-control | 10 LN patients, 10 healthy volunteers | 187/2.2–43.7 | Class III–V | 104.7 ± 38.3, 88.3 ± 13.1 | -- | -- | Stepwise logistic regression, unpaired t-test |
| Shi et al. [27] | 2017 | Retrospective case-control | 23 LN patients, 10 healthy volunteers | 100/2.4–29 | Class III–V | 102.7 ± 24.8, 112.2 ± 18.8 | -- | -- | Multiple correspondence, ANOVA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nemirovsky, D.R.; Gupta, P.; Hu, S.; Wong, R.; Thakor, A.S. Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent (BOLD) MRI in Glomerular Disease. Transplantology 2021, 2, 109-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology2020011
Nemirovsky DR, Gupta P, Hu S, Wong R, Thakor AS. Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent (BOLD) MRI in Glomerular Disease. Transplantology. 2021; 2(2):109-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology2020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleNemirovsky, Daniel R., Puneet Gupta, Sophia Hu, Raymond Wong, and Avnesh S. Thakor. 2021. "Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent (BOLD) MRI in Glomerular Disease" Transplantology 2, no. 2: 109-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology2020011
APA StyleNemirovsky, D. R., Gupta, P., Hu, S., Wong, R., & Thakor, A. S. (2021). Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent (BOLD) MRI in Glomerular Disease. Transplantology, 2(2), 109-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology2020011







