JC Polyomavirus and Transplantation: Implications for Virus Reactivation after Immunosuppression in Transplant Patients and the Occurrence of PML Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. JCPyV Biology
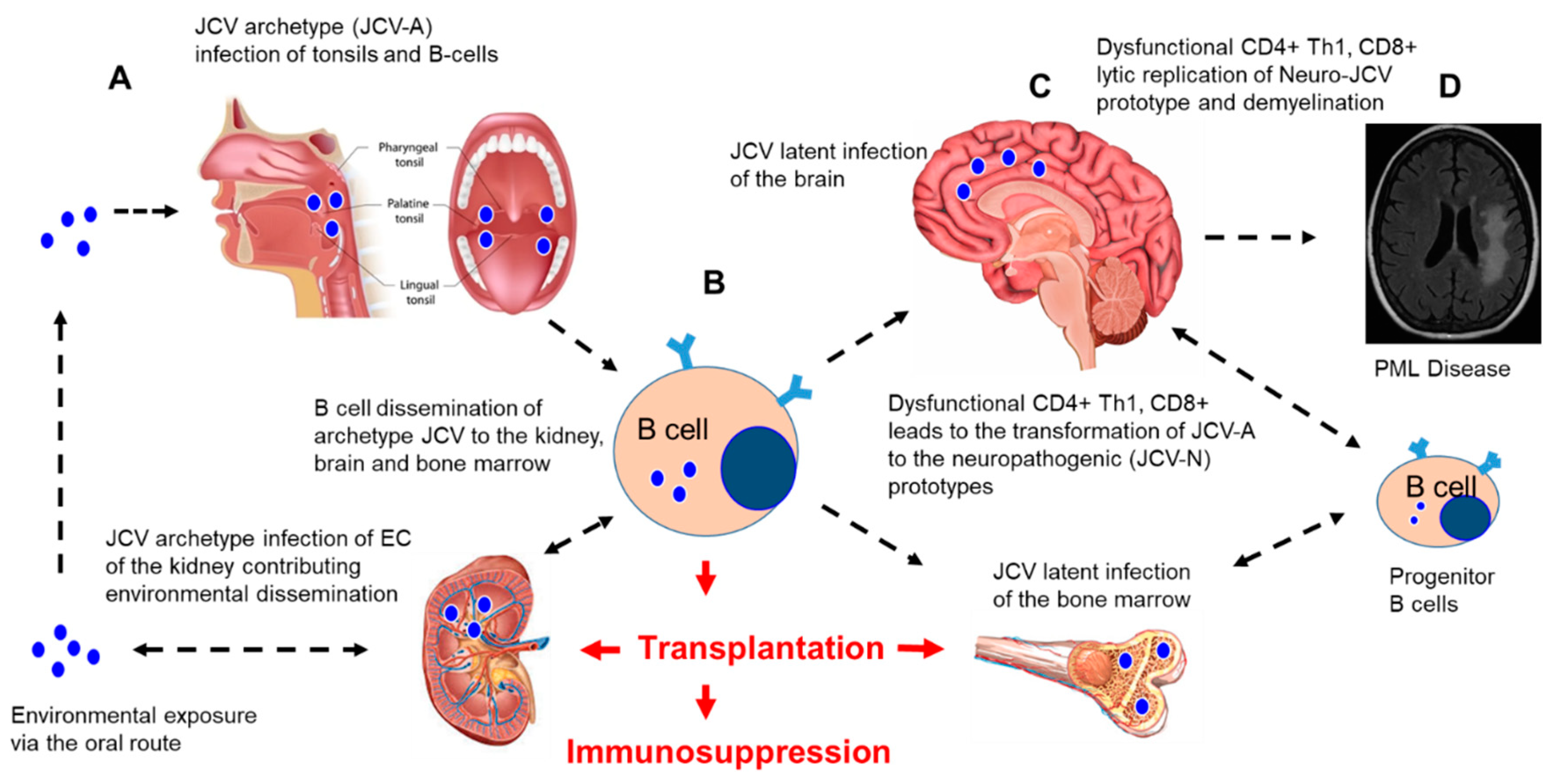
3. JCV Reactivation from Latency and CNS Dissemination after Immunosuppression
4. PML in Immunosuppressed Patients
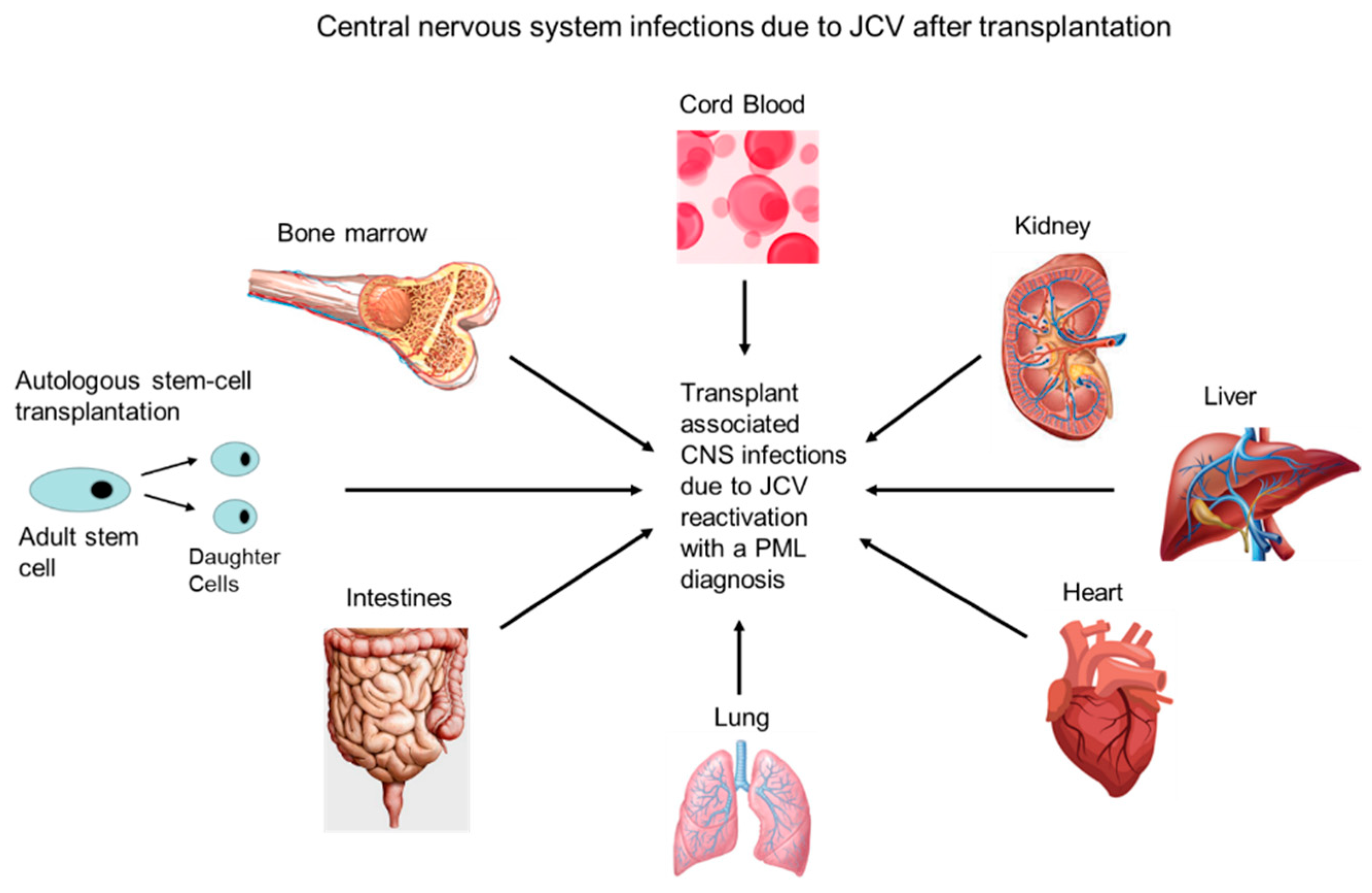
4.1. Transplant Patients
4.2. Patients Receiving Biologics
4.3. HIV Patients
5. Treatment Strategies for PML
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
Abbreviations
| ACR | Acute Cellular Rejection |
| AP-1 | Activator protein 1 |
| ART | Antiretroviral Therapy |
| ASCT | Autologous Stem Cell Transplant |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| BKV | BK polyomavirus |
| CCR5+ | Biomarker on CD4+ T-cells |
| C/EBPβ | CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta |
| CD4+ | Cluster of Differentiation 4 positive |
| CD8+ | Cluster of Differentiation 8 positive |
| CD20 | Cluster of Differentiation 20 positive |
| CD28-B7 | Cluster of Differentiation 28 and B7 positive |
| CSF | Cerebral Spinal Fluid |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CTLA4-Ig | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4-Immunoglobulin |
| CY-JCV | Archetype CY Strain of JCV |
| Egr-1 | Early Growth response protein 1 |
| EC | Endothelial cells |
| IL-2 | Interleukin-2 |
| IRIS | Immune Reconstitution inflammatory Syndrome |
| IVIG | Intravenous Immunoglobulin |
| JCV | JC polyomavirus |
| JCV PyVAN | JC polyomavirus associated nephropathy |
| MMF | Mycophenolate mofetil |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| NCRR | Non-Coding Regulatory Region |
| NF-kB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PML | Progressive multifocal Leukoencephalopathy |
| Tat | Trans-Activator of Transcription |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| T2-FLAIR | T2-weighted-Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery |
| VP1–3 | Viral Capsid Proteins 1–3 |
References
- Zurhein, G.; Chou, S.M. Particles resembling papova viruses in human cerebral demyelinating disease. Science 1965, 148, 1477–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padgett, B.L.; Walker, D.L.; ZuRhein, G.M.; Eckroade, R.J.; Dessel, B.H. Cultivation of papova-like virus from human brain with progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy. Lancet 1971, 7712, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, S.D.; Field, A.M.; Coleman, D.V.; Hulme, B. New human papovavirus (B.K.) isolated from urine after renal transplantation. Lancet 1971, 1, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, J.M.; Rao, S.; Wang, M.; Garcea, R.L. Seroepidemiology of human polyomaviruses. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, A.; Infanti, L.; Dumoulin, A.; Buser, A.; Samaridis, J.; Stebler, C.; Gosert, R.; Hirsch, H.H. Prevalence of polyomavirus BK and JC infection and replication in 400 healthy blood donors. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, E.O. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients on immunomodulatory therapies. Annu. Rev. Med. 2010, 61, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Walker, D.L. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurol. Clin. 1984, 2, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishido-Hara, Y.; Yazawa, T.; Nagane, M.; Higuchi, K.; Abe-Suzuki, S.; Kurata, M.; Kitagawa, M.; Kamma, H.; Uchihara, T. JC Virus Inclusions in Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy: Scaffolding Promyelocytic Leukemia Nuclear Bodies Grow With Cell Cycle Transition Through an S-to-G2–Like State in Enlarging Oligodendrocyte Nuclei. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenczy, M.W.; Marshall, L.J.; Nelson, C.D.; Atwood, W.J.; Nath, A.; Khalili, K.; Major, E.O. Molecular biology, epidemiology, and pathogenesis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, the JC virus-induced demyelinating disease of the human brain. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 3, 471–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Kardas, P.; Kranz, D.; Leboeuf, C. The human JC polyomavirus (JCPyV): Virological background and clinical implications. APMIS 2013, 8, 685–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, D.; Patera, A.C.; Nyberg, F.; Gerber, M.; Liu, M. Progressive Multifocal Leukeoncephalopathy Consortium. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: Current treatment options and future perspectives. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2015, 8, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astrom, K.E.; Mancall, E.L.; Richardson, E.P., Jr. Progressive multifocal leuko-encephalopathy; a hitherto unrecognized complication of chronic lymphatic leukemia and Hodgkin’s disease. Brain 1958, 8, 93–111. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, J.R. The clinical features of PML. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2011, 78 (Suppl. 2), S8–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padgett, B.L.; Walker, D.L. Virologic and serologic studies of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1983, 105, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.L.; Padgett, B.L. The epidemiology of human polyomaviruses. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1983, 105, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Bohra, C.; Sokol, L.; Dalia, S. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy and Monoclonal Antibodies: A Review. Cancer Control 2017, 4, 1073274817729901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, J.L.; Corral, I.; García, J.; Martinez-San Millán, J.; Navas, E.; Moreno, A.; Moreno, S. Continued declining incidence and improved survival of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in HIV/AIDS patients in the current era. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 2, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.R.; Pall, L.; Lanska, D.; Whiteman, M. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients with HIV infection. J. Neurovirol. 1998, 4, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, E.O.; Amemiya, K.; Tornatore, C.S.; Houff, S.A.; Berger, J.R. Pathogenesis and molecular biology of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, the JC virus-induced demyelinating disease of the human brain. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 5, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenbaum, L.; Khalili, K.; Major, E.; Khoury, G. Regulation of the host range of human papovavirus JCV. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 3695–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.K.; Gordon, J.; Berger, J.R.; Khalili, K. Animal Models for Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. J. Cell Physiol. 2015, 12, 2869–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, L. Polyomaviruses. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, K.D.; Garcea, R.L. Viral replication centers and the DNA damage response in JC virus-infected cells. Virology 2019, 528, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisque, R.J.; Bream, G.L.; Cannella, M.T. Human polyomavirus JC virus genome. J. Virol. 1984, 51, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Liz, G.; Del Valle, L.; Gentilella, A.; Croul, S.; Khalili, K. Detection of JC virus DNA fragments but not proteins in normal brain tissue. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.V.; Wolfendale, M.R.; Daniel, R.A.; Dhanjal, N.K.; Gardner, S.D.; Gibson, P.E.; Field, A.M. A prospective study of human polyomavirus infection in pregnancy. J. Infect. Dis. 1980, 142, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonsson, A.; Green, A.C.; Mallitt, K.A.; O’Rourke, P.K.; Pawlita, M.; Waterboer, T.; Neale, R.E. Prevalence and stability of antibodies to the BK and JC polyomaviruses: A long-term longitudinal study of Australians. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1849–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Kitamura, T.; Takasaka, T.; Tominaga, T.; Ishikawa, A.; Zheng, H.Y.; Yogo, Y. Detection of the archetypal regulatory region of JC virus from the tonsil tissue of patients with tonsillitis and tonsilar hypertrophy. J. Neurovirol. 2004, 10, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghi, L.; Randolph, A.E.; Chauhan, D.P.; Marra, G.; Major, E.O.; Neel, J.V.; Boland, C.R. JC virus DNA is present in the mucosa of the human colon and in colorectal cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7484–7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardiello, L.; Laghi, L.; Ramamirtham, P.; Chang, C.L.; Chang, D.K.; Randolph, A.E.; Boland, C.R. JC virus DNA sequences are frequently present in the human upper and lower gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, P.; Brennan, D.C. BK virus infection in transplant recipients: An overview and update. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 9, 2000–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, P.; Uhrmacher, J.; Pasculle, W.; Vats, A.; Shapiro, R.; Eghtsead, B.; Weck, K. A comparative study of BK and JC virus infections in organ transplant recipients. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 2, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, V.; Gutierrez, C.; Sola, E.; Garcia, I.; Burgos, D.; Cabello, M.; Leon, M.; Molina, M.G.; Hernandez, D. Does JC polyomavirus cause nephropathy in renal transplant patients? Transplant. Proc. 2010, 8, 2889–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegley, N.; Walavalkar, V.; Aujla, H.; Chen, L.X.; Huang, Y.; Lee, B.K.; Jen, K.Y. Clinicopathologic Characteristics of JC Virus Nephropathy in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, P.N.; Major, E.O. A classification scheme for human polyomavirus JCV variants based on the nucleotide sequence of the noncoding regulatory region. J. Neurovirol. 2001, 4, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz, R.B.; Thompson, H.C.; Mueller, J.F.; Cohen, J.A.; Dynan, W.S. Incidence of BK virus and JC virus viruria in human immunodeficiency virus-infected and -uninfected subjects. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 167, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.S.; Dezube, B.J.; Bhargava, P.; Autissier, P.; Wüthrich, C.; Miller, J.; Koralnik, I.J. Detection of JC virus DNA and proteins in the bone marrow of HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients: Implications for viral latency and neurotropic transformation. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapagain, M.L.; Nerurkar, V.R. Human polyomavirus JC [JCV] infection of human B lymphocytes: A possible mechanism for JCV transmigration across the blood–brain barrier. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbue, S.; Branchetti, E.; Boldorini, R.; Vago, L.; Zerbi, P.; Veggiani, C.; Tremolada, S.; Ferrante, P. Presence and expression of JCV early gene large T antigen in the brains of immunocompromised and immunocompetent individuals. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.R.; Houff, S.A.; Major, E.O. Monoclonal antibodies and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. mAbs 2009, 1, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ranganathan, P.N.; Khalili, K. The transcriptional enhancer element, kappa B, regulates promoter activity of the human neurotropic virus, JCV, in cells derived from the CNS. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayreddy, R.P.; Safak, M.; Razmara, M.; Zoltick, P.; Khalili, K. Transcription of the JC virus archetype late genome: Importance of the kappa B and the 23-base-pair motifs in late promoter activity in glial cells. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 2387–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safak, M.; Gallia, G.L.; Khalili, K.A. 23-bp sequence element from human neurotrophic JC virus is responsive to NF-kappa B subunits. Virology 1999, 262, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnoli, L.; Wollebo, H.S.; Deshmane, S.L.; Mukerjee, R.; Del Valle, L.; Safak, M.; White, M.K. Modulation of JC virus transcription by C/EBPb. Virus Res. 2009, 146, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnoli, L.; Sariyer, I.K.; Tung, J.; Feliciano, M.; Sawaya, B.E.; Del Valle, L.; Ferrante, P.; Khalili, K.; Safak, M.; White, M.K. Early growth response-1 protein is induced by JC virus infection and binds and regulates the JC virus promoter. Virology 2008, 375, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, H.; Rappaport, J.; Lashgari, M.; Amini, S.; Wong-Staal, F.; Khalili, K. Trans-activation of the JC virus late promoter by the tat protein of type 1 human immunodeficiency virus in glial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 3479–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, D.C.; Kinoshita, Y.; Khan, M.A.; Del Valle, L.; Khalili, K.; Rappaport, J.; Johnson, E.M. Internalization of exogenous human immunodeficiency virus-1 protein, Tat, by KG-1 oligodendroglioma cells followed by stimulation of DNA replication initiated at the JC virus origin. DNA Cell Biol. 2004, 23, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorries, K.; Vogel, E.; Gunther, S.; Czub, S. Infection of human polyomaviruses JC and BK in peripheral blood leukocytes from immunocompetent individuals. Virology 1994, 198, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Hotan, G.C.; Vogel, A.; Venna, N.; Mateen, F.J. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: A 25-year retrospective cohort study. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 6, e618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K.; Yamamoto, F.; Homma, S.; Okada, Y.; Nakamichi, K.; Saijo, M.; Tamaoka, A. Probable progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy-immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome with immunosuppressant dose reduction following lung transplantation: A case report and literature review. BMC Neurol. 2019, 1, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, K.M.; Storrar, N.; Johnson, P.; Fernandes, P.M. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) following autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 6, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippa, A.M.; Ocwieja, K.E.; Iglesias, J.; Fawaz, R.; Elisofon, S.; Lee, C.; Sharma, T.S. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy presenting with acute sensorineural hearing loss in an intestinal transplant recipient. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2020, 4, e13304. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadinejad, Z.; Talebi, F.; Ayoobi, Y.N.; Ghiasvand, F. A 41-year-old female with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy after liver transplant. J. Neurovirol. 2019, 4, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loyaga-Rendon, R.Y.; Taylor, D.O.; Koval, C.E. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a heart transplant recipient following rituximab therapy for antibody-mediated rejection. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 4, 1075–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowhurst, T.; Koszyca, B.; Holmes, M.; Holmes-Liew, C. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a lung transplant recipient presenting with memory impairment: Case report and literature review. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2020, 3, e13293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishida, S.; Tanaka, K. Mefloquine treatment in a patient suffering from progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy after umbilical cord blood transplant. Intern. Med. 2010, 22, 2509–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajaunie, R.; Mengelle, C.; Kamar, N.; Del Bello, A. Possible patient to patient transmission of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy among kidney-transplant patients. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 9, S1413-8670(20)30103-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, L.J.; Major, E.O. Molecular regulation of JC virus tropism: Insights into potential therapeutic targets for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010, 3, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.C.; Wu, M.Y.; Luh, H.T.; Lin, S.F.; Lin, C.M.; Tseng, Y.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Wu, M.S. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a renal transplant patient. J. Neurovirol. 2019, 4, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowder, C.D.; Gyure, K.A.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Werner, J.; Morales, R.E.; Hirsch, H.H.; Ramos, E. Successful outcome of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a renal transplant patient. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Delbue, S.; Mazziotti, R.; Valli, M.; Borghi, E.; Mancuso, R.; Calvo, M.G.; Ferrante, P. Presence, quantitation and characterization of JC virus in the urine of Italian immunocompetent subjects. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 4, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, T.; Yogo, Y.; Kunitake, T.; Suzuki, K.; Tajima, A.; Kawabe, K. Effect of immunosuppression on the urinary excretion of BK and JC polyomaviruses in renal allograft recipients. Int. J. Urol. 1994, 1, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateen, F.J.; Muralidharan, R.; Carone, M.; van de Beek, D.; Harrison, D.M.; Aksamit, A.J.; Gould, M.S.; Clifford, D.B. Nath A Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in transplant recipients. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 2, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shitrit, D.; Nirit, L.; Shiran, S.I.; Izbicki, G.; Sofer, D.; Eldad, M.; Kramer, M.R. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a lung transplant recipient. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2003, 8, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polman, C.H.; O’Connor, P.W.; Havrdova, E.; Hutchinson, M.; Kappos, L.; Miller, D.H.; Phillips, J.T.; Lublin, F.D.; Giovannoni, G.; Wajgt, A.; et al. AFFIRM Investigators. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of natalizumab for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 9, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, E.M.L.; Berger, J.R. Diagnosis and Treatment of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Associated with Multiple Sclerosis Therapies. Neurotherapeutics 2017, 4, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullien, D.; Prinz, J.C.; Langley, R.G.; Caro, I.; Dummer, W.; Joshi, A.; Dedrick, R.; Natta, P. T-cell modulation for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis with efalizumab (Raptiva): Mechanisms of action. Dermatology 2004, 4, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multani, A.; Ho, D.Y. JC Polyomavirus Infection Potentiated by Biologics. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 2, 359–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, B.O.; Garland, J.; Berger, J.; Kramer, J.; Sershon, L.; Olapo, T.; Sesing, J.; Dukic, M.; and Rehn, E. The effect of dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera™) on lymphocyte counts: A potential contributor to progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy risk. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2015, 4, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, A.; Waschbisch, A.; Kuhbandner, K.; Bayas, A.; Lee, D.; Duscha, A.; Haghikia, A.; Gold, R.; Ralf, A. The NRF2 pathway as potential biomarker for dimethyl fumarate treatment in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 6, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Mao, G.; Dowling, C.A.; Lundy, S.K.; Yang, D.M. Dimethyl Fumarate Selectively Reduces Memory T Cells and Shifts the Balance between Th1/Th17 and Th2 in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. J. Immunol. 2017, 8, 3069–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekeyser, M.; de Goër, M.G.; Hendel-Chavez, H.H.; Labeyrie, C.; Adams, D.; Nasser, G.A.; Gasnault, J.; Durrbach, A.; Taoufik, Y. Refractory T-Cell Anergy and Rapidly Fatal Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy After Prolonged CTLA4 Therapy. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, ofx100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartau, M.; Verkkoniemi-Ahola, A.; Paetau, A.; Palomäki, M.; Janes, R.; Ristola, M.; Lappalainen, M.; Anttila, V.J. The Incidence and Predisposing Factors of John Cunningham Virus-Induced Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in Southern Finland: A Population-Based Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 2, ofz024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, R.C.; Török, T.J.; Belay, E.D.; Janssen, R.S.; Schonberger, L.B. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in the United States, 1979–1994: Increased mortality associated with HIV infection. Neuroepidemiology 1998, 6, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, K.L.; Holman, R.C.; Hammett, T.A.; Belay, E.D.; Schonberger, L.B. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy deaths in the USA, 1979–2005. Neuroepidemiology 2010, 3, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, M.J.; Thurnher, M.M.; Clifford, D.B.; Nath, A.; Gonzalez, R.G.; Gupta, R.K.; Post, K.K. CNS-immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in the setting of HIV infection, part 1: Overview and discussion of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy-immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome and cryptococcal-immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 7, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Clifford, D.B.; Nath, A.; Cinque, P.; Brew, B.J.; Zivadinov, R.; Gorelik, L.; Zhao, Z.; Duda, P. A study of mefloquine treatment for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: Results and exploration of predictors of PML outcomes. J. Neurovirol. 2013, 4, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Ammassari, A.; Pezzotti, P.; Cinque, P.; Gasnault, J.; Berenguer, J.; Di Giambenedetto, S.; Cingolani, A.; Taoufik, Y.; Miralles, P.; et al. Gesida 9/99, IRINA, ACTG 363 Study Groups. Cidofovir in addition to antiretroviral treatment is not effective for AIDS-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: A multicohort analysis. AIDS 2008, 14, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.D.; Dafni, U.; Simpson, D.; Clifford, D.; Wetherill, P.E.; Cohen, B.; McArthur, J.; Hollander, H.; Yainnoutsos, C.; Major, E.; et al. Failure of cytarabine in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. AIDS Clinical Trials Group 243 Team. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 19, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindå, H.; von Heijne, A. Presymptomatic diagnosis with MRI and adequate treatment ameliorate the outcome after natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Front. Neurol. 2013, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.R.; Levy, R.M.; Flomenhoft, D.; Dobbs, M. Predictive factors for prolonged survival in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann. Neurol. 1998, 3, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Pasquier, R.A.; Kuroda, M.J.; Schmitz, J.E.; Zheng, Y.; Martin, K.; Peyerl, F.W.; Lifton, M.; Gorgone, D.; Autissier, D.; Letvin, N.L.; et al. Low frequency of cytotoxic T lymphocytes against the novel HLA-A*0201-restricted JC virus epitope VP1 (p36) in patients with proven or possible progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J. Virol. 2003, 22, 11918–11926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balduzzi, A.; Lucchini, G.; Hirsch, H.H.; Basso, S.; Cioni, M.; Rovelli, A.; Zincone, A.; Grimaldi, M.; Corti, P.; Bonanomi, S.; et al. Polyomavirus JC-targeted T-cell therapy for progressive multiple leukoencephalopathy in a hematopoietic cell transplantation recipient. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011, 7, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomini, P.S.; Rozenberg, A.; Metz, I.; Araujo, D.; Arbour, N.; Bar-Or, A. Maraviroc in Multiple Sclerosis–Associated PML–IRIS (MIMSAPI) Group. Maraviroc and JC virus-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 5, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortese, I.; Muranski, P.; Enose-Akahata, Y.; Ha, S.K.; Smith, B.; Monaco, M.; Ryschkewitsch, C.; O’Major, E.; Ohayon, J.; Schindler, M.K.; et al. Pembrolizumab Treatment for Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 17, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavazzi, E.; White, M.K.; Khalili, K. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: Clinical and molecular aspects. Rev. Med. Virol. 2012, 1, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hildreth, J.E.K.; Alcendor, D.J. JC Polyomavirus and Transplantation: Implications for Virus Reactivation after Immunosuppression in Transplant Patients and the Occurrence of PML Disease. Transplantology 2021, 2, 37-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology2010004
Hildreth JEK, Alcendor DJ. JC Polyomavirus and Transplantation: Implications for Virus Reactivation after Immunosuppression in Transplant Patients and the Occurrence of PML Disease. Transplantology. 2021; 2(1):37-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology2010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleHildreth, James E. K., and Donald J. Alcendor. 2021. "JC Polyomavirus and Transplantation: Implications for Virus Reactivation after Immunosuppression in Transplant Patients and the Occurrence of PML Disease" Transplantology 2, no. 1: 37-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology2010004
APA StyleHildreth, J. E. K., & Alcendor, D. J. (2021). JC Polyomavirus and Transplantation: Implications for Virus Reactivation after Immunosuppression in Transplant Patients and the Occurrence of PML Disease. Transplantology, 2(1), 37-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology2010004





