Abstract
Urological complications (UC) following kidney transplantation (KT) are associated with increased morbidity. The aim of this study is to evaluate the risk factors for UC in the era of “extended criteria donors” (ECD) and their impact on patient and graft survivals. A retrospective monocentric study of all patients undergoing KT from 2010 to 2019 with a follow-up ≥30 days was performed. Out of 459 patients (males: 296 (64.5%); age: 57 (19–77) years) enrolled, 228 (49.7%) received ECD organs, moreover, 166 (67.2%) grafts had a cold ischemia time ≥10 h. UCs were reported in 32 (7%) patients. In 21 (65.6%) cases UC occurred within 3 months post-KT and 24 (5.2%) were associated with early urinary tract infection (UTI). The overall 5 year patient and graft survival rates were 96.5% and 90.6%, respectively. UC decreased graft survival (UC-group: 75.0% vs. noUC-group: 91.8%, p < 0.001), especially if associated with early UTI (UC-group: 71.4% vs. noUC-group: 77.8%, p < 0.001). At multivariate analysis, early UTI after KT (OR: 9.975, 95%-IC: 2.934–33.909, p < 0.001) and delayed graft function (DGF) (OR: 3.844, 95%-IC: 1.328–11.131, p: 0.013) were significant risk factors for UC, while ECD graft did not increase the risk of post-transplant UC. ECD grafts are not associated with UC. DGF and early UTI post-KT increase the risks of UC and reduce graft survival in the long-term. Therefore, aggressive management of early post-transplant UTI and strategies to reduce DGF incidence, such as machine preservation, are essential to prevent UC after KT.
1. Introduction
Surgical complication after kidney transplantation (KT) often lead to increased morbidity, length of hospitalization, incidence of re-admission, health costs, and in some cases, it might cause reduced long-term patient and graft survival [1,2,3]. The most frequent surgical problems following KT are urological complications (UC) [4]. Despite the reduced incidence of UC over recent decades—due to advances in surgical techniques and modern immunosuppression regimens—in the literature the UC rate is still reported to be up to 30% [5,6,7,8,9].
Meanwhile, the shortage of graft supply, the aging of deceased donor populations and the concomitant increased demand for KT candidates have driven increases in the use of renal grafts from “extended criteria donors” (ECD). Renal grafts from ECD nowadays represent 30% of organs used for KT [10]. Many studies reported that KT from ECD have a satisfactory short and long-term graft survival rate of approximately 85% at 5 years follow-up [11] when the donor is well selected and carefully matched with the recipient [12]. However, the use of ECD grafts has been associated with potential increased risks of surgical complications [9]. Thus, it is unclear as to the real effects of ECD on UC after KT. Several reports identified patient age, gender, diabetes, rejection, anatomical graft rejection and BK virus infection as risk factors of UC, but the majority of studies have not explored the combination of all these potential risk factors in the ECD setting [13,14,15].
The aim of the current study is to identify the risk factors for UC in the era of KT from ECD and to analyze their effects on patient and graft survivals.
2. Material and Methods
This is a retrospective monocentric study that enrolled all consecutive patients who underwent KT at the Transplant Center of the University of Rome Tor Vergata, Rome, Italy from January 2010 to December 2019, with at least 1 month of follow-up after transplantation. Only patients with a follow-up <1 month from KT were excluded. Recipient data at the time of transplantation (demographic characteristics, number of transplantations, single or dual transplantation, time on waiting list, cause of end stage renal disease (ESRD), pre-transplant urinary tract anomalies, pre-transplant cystography, and prostatic echography), donor and transplant variables (age, sex, cause of death, comorbidities, pre-implant renal biopsy score, cold ischemia time (CIT)) were analyzed. The study was approved by the local ethics committee board.
ECD was defined as donor age ≥ 60 years or donor age ≥ 50 years with at least two of the following donor variables: arterial hypertension on chronic medical treatment, death for cerebrovascular cause or pre-procurement creatinine serum level ≥ 1.5 mg/dL [16].
When performed, pre-implantation graft biopsy was assessed using the Italian necro-kidney score which is based on the percentage of sclerosed glomeruli (grade: 0–3), tubular atrophy (grade: 0–3), interstitial fibrosis (grade: 0–3) and atherosclerosis (grade: 0–3), giving a total score from 0 to 12 [17]. During the initial study period (2010–2012), kidneys with a score of 3 or lower were used as single transplants, while those with a score of 4 and 5 were used as dual transplantations, on the assumption that the sum of the viable nephrons in the two kidneys approached the number of one ideal kidney [18]. Since 2013, kidneys with a score of 4 were also allocated as a single transplantation; grafts with a score of 5 were allocated as single or dual transplants depending on the histological predominant component of the score.
Post-KT outcomes were evaluated with patient and graft survival, kidney function and incidence of UC at the last follow-up. Delayed graft function was defined as the need for dialysis during the first week post-KT [19,20]. UCs were classified by the type of complication, the median time of onset (early within 3 months, and late over 3 months) and the association with concurrent urinary tract infection (UTI); for each complication, the treatment chosen was collected.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) was diagnosed when a quantitative urine culture with a yield greater than 100,000 CFU/mL was present. Early UTI was defined when occurring within 3 months after transplantation, while late UTIs occurred after this time period. Simple UTI was determined as the presence of an infective pathogen susceptible to antibiotic therapy or patients with asymptomatic cystitis, while complicated UTI was defined as the presence of an infection which required longer antibiotic courses or pyelonephritis.
2.1. Surgical Technique
According to the center’s practice, KT was placed in the right or left iliac fossa. After the preparation of the retroperitoneal fossa, the iliac arteries and veins were exposed and lymphatic vessels ligated. The renal graft was anastomosed to the external or common iliac vessels. All ureterocystostomies were performed by the Lich–Gregoir technique with a double-J ureteral stent insertion [21]. In case of double KT, ureters were anastomosed individually to the bladder. One peri-renal drain was routinely positioned.
2.2. Post-Operative Care
Routine renal graft doppler-ultrasound (US) was performed on post-operative day (POD) 1. Foley catheters were regularly removed on POD 3 and abdominal drains on POD 4, unless sustained output of the drain was present (>100 mL/day). Usually, the double-J ureteral stent was removed after 6 weeks from KT by cystoscopy.
Depending on panel reactive antibody (PRA), a post-operative immunosuppressive regimen was based on induction with basiliximab (20 mg intraoperatively and on POD 4) or antithymocyte globulin (3–4 doses of 1.5 mg/kg) and maintenance therapy with tacrolimus once daily (0.1 mg/kg/day), mychophenolate mofetil (500–1500 mg/day) or sodium (360–1080 md/day), and steroids (20 mg/day tapered to 5 mg/day within 3 months). Tacrolimus trough level aimed to achieve 7–9 ng/mL within the first months after KT, 6–8 ng/mL within 6 months after KT, and 5–6 ng/mL thereafter.
2.3. Urinary Complications and Their Management
UC included ureteral stricture, urinary leak, symptomatic vescico-ureteral reflux (VUR) and urinary retention.
Ureteral stricture was defined as ureteral luminal narrowing or obstruction, and its diagnosis was made through a combination of dilated pyelocaliceal cavities of the renal graft and an alteration of its function (Figure 1A).
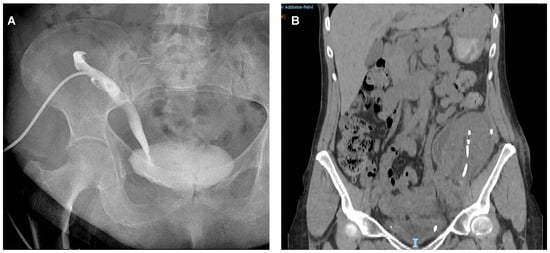
Figure 1.
Images of urinary complications. (A) Urinary stricture: plain X-ray demonstrating the ureteral stricture of transplanted kidney by percutaneous pyelography in a kidney transplant recipient with urinary stricture. (B) Urinary leak: Computer Tomography scan demonstrating the peri-renal collection in a kidney transplant recipients with urinary fistula.
In case of suspect of ureteral stricture, a nephrostomy tube was placed and an anterograde pyelography was performed. As primary treatment, a minimally invasive approach was chosen by anterograde ureteral stent placement with or without balloon dilatation. As second-choice treatment, open surgical procedure was adopted performing a re-anastomosis of the ureterocystostomy or uretero-ureterostomy with a double-J ureteral stent insertion.
Urinary fistula was suspected in the presence of urine leakage in the drainage or if a fluid collection was opacified at late excretory phase imaging (Figure 1B). To confirm diagnosis, when the graft function allowed, a computed tomography (CT) urogram was performed or, when it was technically feasible, an anterograde pyelography trough nephrostomy was carried out. The treatment for the urinary leak was based on the fistula output: initially the Foley catheter was positioned; subsequently, in case of reduction in the leak output, the Foley catheter was maintained for 1–2 weeks. Thus, if the leak output was sustained (>200 mL/day) and not resolved, a surgical approach was adopted by the reimplantation of the graft’s ureter on the bladder or, if not possible, to the native ureter, using a double-J ureteral stent.
Symptomatic VUR was defined as recurrent UTI associated with VUR into the kidney graft, diagnosed by voiding cystourethrogram, and in males it was commonly associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia [22]. Symptomatic VUR was managed by endoscopic treatment and, if that failed, by surgical reimplantation.
Urinary retention was defined as a post-void residual urine more than 200 mL at US and was treated by Foley catheter insertion for 7 days. In case of benign prostate hyperplasia, a photoselective Greenlight Laser vaporization of the prostate (PVP) was performed electively.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
We prospectively collected data on a consecutive database. All statistical tests were run using IBM SPSS 26.0 Software (IBM, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) for Windows. Continuous variables were reported as median with range or mean ± standard deviation. Categorical variables were described as numbers and percentages. Normal distribution continuous data were analysed by a parametric test (Student’s t-test). The Mann–Whitney U test and Fisher’s exact test were used for univariate analysis, and Cox multiple regression analysis for multivariate analysis.
To assess the influence of UC on patients and graft survival we used the Kaplan–Meyer method, and the groups with and without UCs were compared with log–rank tests. A p-value of <0.05 was considered to be significant.
3. Results
3.1. Study Population and Transplant Characteristics
Out of 498 KTs performed during the study period, 459 (92.2%) patients were enrolled, while 39 (7.8%) KT recipients were excluded because of follow-up <1 month or lost to follow-up.
Two-hundred and ninety-six (64.5%) patients were male and the median age at the time of KT was 57 (19–77) years. Indications for KT included 143 (31.2%) glomerulonephritis, 91 (19.8%) autosomal dominant polycystic kidney diseases, 79 (17.2%) unknown ESRD, 46 (10.0%) hypertensive nephropathies, 20 (4.4%) diabetic nephropathies, 31 (6.8%) pyelonephritis, 12 (2.6%) congenital malformations of the urinary tract and 37 (8.1%) other causes.
The majority (n = 445, 96.9%) of grafts were from deceased donors after brain death, while 14 (3.1%) were derived from living-related donors. The median donor age was 56 (11–81) years and 228 (49.7%) were ECD.
A single KT was performed in 438 (95.4%) cases, while a double KT in 21 (4.6%) patients. Before implantation, graft biopsy was obtained in 222 (44.6%) cases, and of those, 85 (38.3%) kidneys had a histological score > 3. The median CIT was 11 h (0.5–29) and 166 (67.2%) grafts had a CIT ≥ 10 h. Characteristics of recipients, donors, and transplants are detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of recipients, donors and transplants.
3.2. Transplant Outcomes and Urological Complications
Post-operative outcomes are detailed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Transplant outcome and post-operative urinary complications.
Post-transplant delayed graft function (DGF) was found in 165 (36.0%) cases. Twenty-four (5.2%) KT recipients developed early post-transplant UTI, of which 15 (62.5%) were simple UTI and nine (37.5%) developed complicated UTI. Regarding the adopted induction therapy, we did not find any difference in UTI incidence among patients receiving basiliximab or antithymocite globulin (22/438 vs. 2/21, respectively, p = 0.3015). After a median follow-up of 61 (1–120) months, the median serum creatinine and urea values were 1.61 (0.5–13.5) mg/dL and 65 (15–50) mg/dL, respectively.
Occurrence of UC was reported in 32 (7%) cases including 20 (62.5%) ureteral stenosis, 7 (21.9%) urinary leaks and 5 (15.6%) urinary retentions. Of those, 21 (65.6%) UC occurred early (within 3 months) and 11 (34.4%) late after KT. Symptomatic VUR was observed after 4 months from KT in one patient who had early post-operative urinary retention. Of the seven patients with urinary leaks, five (71.4%) experienced DGF, four (57.1%) were associated with early UTI, four (57.1%) received an ECD graft and two (28.5%) were transplanted with a CIT ≥ 10 h. UCs were treated by percutaneous nephrostomy and ureteral stenting in 17 (53.1%) cases, surgical intervention in five (15.6%) cases (three revisions of the ureteral anastomosis, two PVP), cystostomy and ureteral stenting in three (9.4%) cases, Foley catheter insertion in five (15.6%) cases, and nephrostomy in two (6.2%) patients.
Among nine patients with early complicated UTI, seven (77.8%) patients were transplanted with ECD grafts and developed DGF, and six (66.7%) recipients presented post-operative UC.
Overall, the 5 year patient survival was 96.5% and the 5 year graft survival was 90.6%. KT recipients who developed UC showed a 5 year patient survival compared to those without UC (96.5% vs. 96.9%, p: 0.939), while the 5 year graft survival rate significantly reduced (91.8% vs. 75.0%, p < 0.0001) (Figure 2).
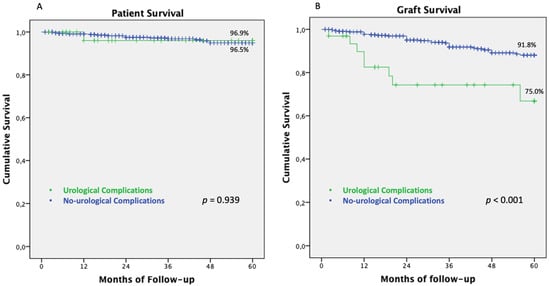
Figure 2.
Patient and graft-survivals of KT recipients with and without UC. (A) Five-years patient survival in KT recipients with and without post-operative urinary complications. (B) 5 year graft survival in KT recipients with and without post-operative urinary complications. Abbreviations. KT: Kidney transplantation; UC: Urological complications.
Early UCs after KT were associated with slightly inferior 5 year graft outcomes (66.7%) compared to late UCs (90.9%, p: 0.078) (Figure 3A). According to the type of UC, the 5 year graft survival was 80.0% for urinary retention, 75% for urinary stenosis and 71.4% for urinary leak (p: 0.002) (Figure 3B).
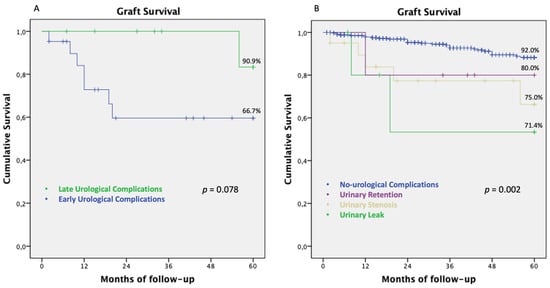
Figure 3.
Graft survival in patients with UC, according to the timing of occurrence after transplantation and type of complications. (A) Five year graft survival of patients with urinary complications according to the time of complication occurrence after transplantation (early: (≤3 months) vs. late (>3 months)). (B) Five year graft survival for each type of UC. Abbreviations. UC: Urological complications; KT: kidney transplantation.
Moreover, if UCs were associated with an early UTI after KT, renal graft showed inferior graft survival rates compared to UCs without UTI (71.4% vs. 77.8%, p < 0.0001), as shown in Figure 4.
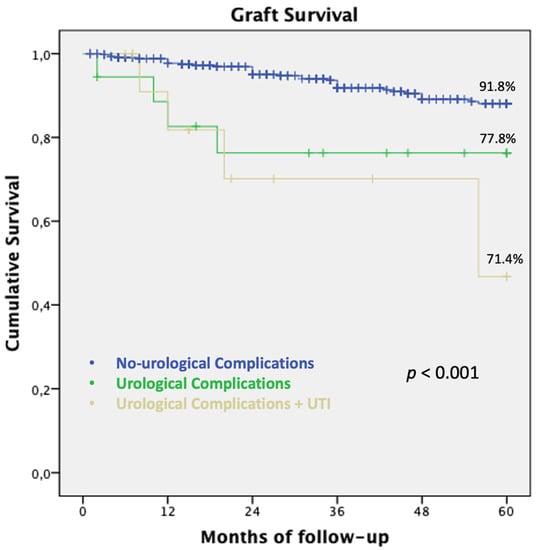
Figure 4.
Graft survival in patients developing UC with and without early UTI. Five year graft survival in patients with UCs associated with early UTI after KT: renal graft showed inferior outcome compared to UC without UTI. Abbreviations. UC: Urological complications; KT: kidney transplantation; UTI: Urinary tract infection.
3.3. Predictive Factors for UC after KT
In order to identify risk factors for UC, patients who experienced UC (n = 32) were compared with those who did not experience UC (n = 427).
At univariate analysis, KT recipients with UCs were older (60 (40–76) years vs. 56 (19–77) years, p: 0.010) at the time of transplantation and had a higher frequency of pre-transplant pathological cystography (15 (46.9% vs. 107 (25.1%), p: 0.012) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Characteristic of recipients with and without urological complications.
At transplantation, the UC group was transplanted with older donors (61 (15–88) years for the UC group and 55 (11–88) years for the non-UC group, p: 0.016) and mainly with kidney grafts from ECD (22 (68.8%) for the UC group and 206 (48.2%) for the non-UC group, p: 0.028). Post-operatively, patients who developed UC had a higher incidence of DGF (22 (68.7%) vs. 143 (33.5%), p: 0.001) and of early UTI (seven (21.9%) vs. 17 (4.0%), p: 0.0006), especially complicated UTI, compared to KT recipients without UC.
In the multivariate Cox-regression analysis, early UTI after KT (OR: 9.975, 95%-IC: 2.934–33.909, p < 0.001) and DGF (OR: 3.844, 95%-IC: 1.328–11.131, p:0.013) were found to be significant risk factors for UC, while ECD graft did not increase the risk of post-KT UC (Table 4).

Table 4.
Cox-multivariate model evaluating risk factors for urinary complications after KT.
Moreover, grafts from ECD did not increase the risk of patient and graft failure at 5 years post follow-up (Figure S1).
In the sub-group analysis of patients with congenital urinary tract anomalies (n = 12), KT recipients were significantly younger compared to the general population (43 (28–66) years vs. 57 (19–99) years, respectively, p: 0.025) and only two (16.7%) patients received an ECD graft (2/12 in congenital urinary tract anomalies sub-group vs. 226/447 in the general population, p: 0.036). This match was related to the younger age of the recipients. Post-operatively, none of the KT recipients with congenital urinary tract anomalies developed post-transplant UC and only one patient developed early UTI related to Escherichia coli.
4. Discussion
UC remains the most frequent surgical adverse event after KT and the majority of instances occur in the early period after transplantation [4,15,23]. In the literature, multiple risk factors for UC after KT have been identified, including recipient gender, recipient and donor age, diabetes, DGF, rejection, BK virus, anatomical vascular and ureter variations [2,13,14,15,24,25,26,27].
So far, a few studies have explored the relationship between ECD and UC after KT, but these have yielded contrasting results [9,12,28,29,30,31,32,33]. Several authors reported that ECDs are associated with increased surgical complications [30,31,32,33], while others did not find significant differences [9,12,28,29]. Thus, in the current era of organ shortages and the aging of the general population, the use of ECD—defined as donors aged 60 years or older and 50–59 year old deceased donors with comorbidities [16]—seems unavoidable for KT.
In this setting, since the ureter is still a common source of complications after KT, we designed a retrospective study to evaluate the risk factors for UC in the era of ECD grafts and the impact of UC on patient and graft survival at long-term.
In our analysis, UC occurred in 7% of cases after KT, mainly represented by urinary strictures. The UC rate of our population is in line with these reported by other recent studies [2,34]. Arpali E et al. in 2018 described that UCs were observed in 9.3% of 2274 patients undergoing KT [2]. Moreover, in 2019 a national registry study from the Netherlands reported that, among 3329 KT recipients, UCs were developed in 208 (6.2%) of patients within 3 months after surgery [34]. Compared to an older cohort [24,25,35,36], the reduced incidence of UC observed in the last decade could be related to many factors, but advances in surgical techniques have most probably had a major effect. In particular, a recent review on surgical options for ureter reconstruction in KT showed that the routine adoption of Lich–Gregoire anastomosis with a double-J ureteral stent, which is frequently used in many centers, was significantly associated with reduced incidence of UC and improved KT outcomes [36]. As for center practice, in our experience all ureteroneocystostomies have been performed according to the Lich–Gregoire technique with double-J ureteral stent insertion, which was usually removed 4–6 weeks after KT.
In our study population, half of KT recipients were transplanted with ECD organs, thus, the use of such “marginal” grafts did not increase the risk of UC. Our results are in contrast with those reported by Barba J et al. [9], who showed that ECD grafts are associated with a higher incidence of UC. However, in this study when the analysis was adjusted for recipient age, the risk was no-different between non-extended and extended criteria donors. The absence of correlation between post-transplant UC and ECD grafts in our analysis, supports the notion that the use of ECD kidneys is an acceptable alternative to remaining on dialysis for older patients or patients for whom a non-extended criteria kidney is unavailable. This attitude of exploiting marginal grafts is evident when assessing the current organ allocation policies adopted worldwide, where ECD grafts represent a significant source of organs. In 2019, in North America, around 24% of potential donors were ECD, while in Europe up to 30% of potential donors were ECD [10]. In Italy, during 2019 the majority (84%) of KTs were performed from deceased donors with a median deceased donor age of 59 years [37]. Moreover, in the near future, the numbers of potential ECD donors are expected to increase [38]: recent data from the World Population Prospects predicts that, by 2050, a quarter or more of the population will be aged 60 and above [39].
Among risk factors for UC after KT, in our series, transplant-related factors such as donor age and prolonged CIT did not influence the occurrence of UC at the multivariate analysis. Only post-transplant related complications, namely DGF (p = 0.013) and early UTI (p < 0.001), were identified as predictive factors of UC, increasing the risk of developing post-operative urinary problems.
In our cohort, the incidence of DGF within the first week after KT was about 36%. It is questionable if this rate could be related to the fact that half of recipients were transplanted with ECD grafts. In the USA, the overall DGF rate is about 30.8% in KT from deceased donors [40], but this increases up to 45–55.1% in marginal donors [41]. The association between DGF and UC has been described in the literature, [42,43,44] but its mechanism is still debated [45]. Potential explanations for this association could include a common physiopathological pathway during KT related to ischemia-reperfusion injury [35]. In KT, the ischemia-reperfusion damage—especially for prolonged ischemia times [46]—could, on the one hand, cause DGF, while on the other hand cause edema of the ureteral wall, remodeling of the muscular layer and fibrosis, contributing to the development of ureteral stricture, which are the most common UCs after KT [35]. In this setting, the adoption of machine preservation—as a hypothermic machine perfusion—could not only reduce the incidence of DGF, but also of UC with consequent improved graft survival, especially in ECD [47,48]. However, in the current study, none of the used grafts had been preserved with machine perfusion, therefore, further trials should focus on the correlation of ECD grafts (treated with machine preservation) and UC.
The occurrence of early UTI after KT, especially in the case of complicated UTI, was also associated with the development of UC in our analysis. In the early post-transplant period, various factors might predispose an individual to UTI, including urinary catheterization, urinary tract obstruction (intrinsic and extrinsic), urinary tract reflux, the presence of a double-J stent and immunosuppression. All of these factors could lead to a continuous inflammatory state within the urinary tract, resulting in anastomotic fistula or fibrosis and stenosis in the long-term [49]. Of course, UC itself could cause UTI as well, therefore, observed correlations are frequently difficult to interpret. Thus, the occurrence of early UTIs has not been explored in previous studies on UC [15,23,24,25,36] and further data are needed. Regarding the type of immunosuppression, we did not find any difference in UTI incidence among patients receiving basiliximab or antithymocite globulin as induction therapy; thus, the paucity of patients receiving antithymocite globulin in the current study requires further investigation of its possible association with post-transplant UTI.
Despite the fact that all UCs in our cohort were resolved by radiological interventional or surgical treatments, the development of UC was associated with impaired graft survival at the 5 year follow-up stage (91.8% vs. 75.0%, p < 0.0001). In the literature, the effect of UCs on graft outcomes is controversial: some analyses affirmed that UCs do not influence long-term graft survival [49], while others observed an impairment of graft survival in KT recipients with UC [50,51]. Interestingly, UC occurring within 3 months from KT had a slightly worse impact on graft survival (66.7%) compared to those that developed later (90.9%). Moreover, when UCs were associated with early UTIs, graft outcomes were further impaired, reducing the graft survival rate to 71.4% at the 5 year follow-up stage.
Among UCs, KT recipients developing urinary fistula had inferior graft outcomes compared to those experiencing urinary strictures or retention. This could be related on the one hand to the fact that all patients with urinary leakage presented at least one other risk factor for graft impairment, such as CIT ≥ 10 h, ECD grafts or associated UTI. On the other hand, 16.7% of patients with urinary leak required a surgical re-intervention in a short-time period after transplantation, which might have harmed graft outcomes. However, the current study is limited by its retrospective monocentric design, and the lack of data such as duration of hospitalization and re-admission rate caused by UC. Therefore, larger multicenter prospective studies are needed to confirm our results and to explore possible morbidity related to the development of UC.
5. Conclusions
UCs are still a significant cause of morbidity after KT and can lead to impairment of graft survival, especially if occurring within 3 months after transplantation and associated with early UTI. The use of ECD grafts do not impact on UC after KT, but the development of DGF might increase the risk of UC. Therefore, further studies should explore if the minimization of ischemia-reperfusion injury and DGF by machine perfusion preservation could reduce the incidence of UC in KT.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2673-3943/2/1/3/s1, Figure S1 Five-years patient and graft survivals after KT in “Extended Criteria Donor” grafts and standards grafts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.A., G.I.; methodology, R.A., G.I., T.M.M.; formal analysis, R.A., M.P., F.V., L.T.; investigation, R.A., M.P., F.V.; resources, M.P., F.V., A.M., A.A.; data curation, R.A., M.P., F.V., A.M., A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A., M.P.; writing—review and editing, T.M.M., R.C., G.I.; visualization, R.A., M.P.; supervision, G.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Local Institutional Ethical Committee borad (University of Rome Tor Vergata).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lempinen, M.; Stenman, J.; Kyllönen, L.; Salmela, K. Surgical complications following 1670 consecutive adult renal transplantations: A single center study. Scand. J. Surg. 2015, 104, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpali, E.; Marka, N.; Martinez, E.; Redfield, R.R.; Leverson, G.E.; Kaufman, D.B.; Odorico, J.S.; Sollinger, H.W. Impact of ureteral stricture and treatment choice on long-term graft survival in kidney transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Kantas, A.; Ramcke, K.; Drabik, A.I.; Nashan, B. Surgical complications after kidney transplantation: Different impacts of immunosuppression, graft function, patient variables, and surgical performance. Clin. Transplant. 2015, 29, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englesbe, M.J.; Dubay, D.A.; Gillespie, B.W.; Moyer, A.S.; Pelletier, S.J.; Sung, R.S.; Magee, J.C.; Punch, J.D.; Campbell, D.A., Jr.; Merion, R.M. Risk Factors for Urinary Complications After Renal Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 1536–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, M.T.; Velidedeoglu, E.; Bloom, R.D.; Grossman, R.A.; Markmann, J.W.; Naji, A.; Frank, A.M.; Kass, A.B.; Nathan, H.M.; Hasz, R.D.; et al. Expanded-Criteria Donor Kidneys: A Single-Center Clinical and Short-Term Financial Analysis—Cause for Concern in Retransplantation. Transplantation 2004, 78, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, P.; Impedovo, S.V.; Palazzo, S.; Ditonno, P.; Ricapito, V.; Saracino, G.A.; Lucarelli, G.; Tedeschi, M.; Bettocchi, C.; Battaglia, M. Ureteral strictures after kidney transplantation: Risk factors. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. 2012, 84, 287–290. [Google Scholar]
- Slagt, I.K.B.; Ijzermans, J.N.M.; Visser, L.J.; Weimar, W.; Roodnat, J.I.; Terkivatan, T. Independent Risk Factors for Urological Complications after Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahnemai-Azar, A.A.; Gilchrist, B.F.; Kayler, L.K. Independent risk factors for early urologic complications after kidney transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2015, 29, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, J.; Zudaire, J.J.B.; García, J.E.R.; Rosell, D.; Berian, J.M.; Pascual, I. Complications of kidney transplantation with grafts from expanded criteria donors. World J. Urol. 2013, 31, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, O.; Kamar, N.; Vernerey, D.; Viglietti, D.; Martinez, F.; Duong-Van-Huyen, J.-P.; Eladari, D.; Empana, J.-P.; Rabant, M.; Verine, J.; et al. Long term outcomes of transplantation using kidneys from expanded criteria donors: Prospective, population based cohort study. BMJ 2015, 351, h3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kwon, K.H.; Kim, M.H.; Jun, K.W.; Hwang, J.K.; Kim, S.D.; Park, S.C.; Kim, J.; Yun, S.S.; et al. Kidney Transplantation Using Expanded-Criteria Deceased Donors: A Comparison with Ideal Deceased Donors and Non–Expanded-Criteria Deceased Donors. Transplant. Proc. 2018, 50, 3222–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratta, R.; Rohr, M.S.; Sundberg, A.K.; Armstrong, G.; Hairston, G.; Hartmann, E.; Farney, A.C.; Roskopf, J.; Iskandar, S.S.; Adams, P.L. Increased Kidney Transplantation Utilizing Expanded Criteria Deceased Organ Donors with Results Comparable to Standard Criteria Donor Transplant. Ann. Surg. 2004, 239, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, H.; Wilms, H.; Kirste, G. Incidence, diagnosis, and treatment of ureteric stenosis in 1298 renal transplant patients. Transpl. Int. 1994, 7, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselmo, A.; Iaria, G.; Materazzo, M.; Sforza, D.; Parente, A.; Campisi, A.; Cacciatore, C.; Calafiore, E.; Pisani, G.; Tisone, G. Native Nephrectomy in Patients With Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Evaluated for Kidney Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2019, 51, 2914–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoskes, D.A.; Hanbury, D.; Cranston, D.; Morris, P.J. Urological Complications in 1000 Consecutive Renal Transplant Recipients. J. Urol. 1995, 153, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port, F.K.; Bragg-Gresham, J.L.; Metzger, R.A.; Dykstra, D.M.; Gillespie, B.W.; Young, E.W.; Delmonico, F.L.; Wynn, J.J.; Merion, R.M.; Wolfe, R.A.; et al. Donor characteristics associated with reduced graft survival: An approach to expanding the pool of kidney donors1. Transplant. 2002, 74, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpinski, J.; Lajoie, G.; Cattran, D.; Fenton, S.; Zaltzman, J.; Cardella, C.; Cole, E. Outcome of kidney transplantation from high-risk donors is determined by both structure and function. Transplantation 1999, 67, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remuzzi, G.; Cravedi, P.; Perna, A.; Dimitrov, B.D.; Turturro, M.; Locatelli, G.; Rigotti, P.; Baldan, N.; Beatini, M.; Valente, U.; et al. Long-Term Outcome of Renal Transplantation from Older Donors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, A.O.; Wolfe, R.A.; Held, P.J.; Port, F.K.; Schmouder, R.L. Delayed Graft Function: Risk Factors and Implications for Renal Allograft Survival1. Transplantation 1997, 63, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siedlecki, A.; Irish, W.; Brennan, D.C. Delayed Graft Function in the Kidney Transplant. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 2279–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lich, R., Jr.; Howerton, L.W.; Davis, L.A. Childhood urosepsis. J. Ky. Med Assoc. 1961, 59, 1177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lebowitz, R.L.; Olbing, H.; Parkkulainen, K.V.; Smellie, J.M.; Tamminen-Möbius, T.E. International system of radiographic grading of vesicoureteric reflux. International Reflux Study in Children. Pediatr. Radiol. 1985, 15, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Roijen, J.H.; Kirkels, W.J.; Zietse, R.; Roodnat, J.I.; Weimar, W.; Ijzermans, J.N.M. Long-term graft survival after urological complications of 695 kidney transplantations. J. Urol. 2001, 165 Pt 1, 1884–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, V.; Minnee, R.C.; Bemelman, F.; Pant, K.V.D.-V.D.; Pes, P.L.; Idu, M. Ureteral Reconstruction after Renal Transplantation: Clinical Outcome and Risk Factors. Urol. Int. 2012, 88, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, A.; Adorno, D.; Poggi, E.; Borrelli, L.; Buonomo, O.; Pisani, F.; Valeri, M.; Torlone, N.; Camplone, C.; Monaco, P.; et al. Flow cytometry crossmatch: A sensitive technique for assessment of acute rejection in renal transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 1998, 30, 1769–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, H.; Tautenhahn, H.-M.; Schmelzle, M.; Krenzien, F.; Schoenberg, M.B.; Morgul, M.; Uhlmann, D.; Wiltberger, G.; Rasche, M.; Bachmann, A.; et al. Management of Urologic Complications in Renal Transplantation: A Single-Center Experience. Transplant. Proc. 2014, 46, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.; Parada, B.; Cunha, M.; Mota, A.; Furtado, A. Ureteral complications: Analysis of risk factors in 1000 renal transplants. Transplant. Proc. 2003, 35, 1087–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagala, P.; Kwiatkowski, A.; Wszoła, M.; Czerwinski, J.; Cybula, K.; Trzebicki, J.; Chmura, A. Complications of Transplantation of Kidneys From Expanded-Criteria Donors. Transplant. Proc. 2009, 41, 2970–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, M.; Ditonno, P.; Selvaggio, O.; Peschechera, R.; Ricapito, V.; Deceglie, G.; Schena, A.; Stallone, G.; Schena, F.; Falagario, M.; et al. Medical and surgical complications after kidney transplantation from “suboptimal donors”: One centre’s experience. Transplant. Proc. 2004, 36, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, P.R.; Alexander, J.W.; First, M.R.; Peddi, V.R.; Munda, R.; Cavallo, T. Immediate Allograft Dysfunction Due to Atheroembolic Disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 37, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, L.E.; Kraus, E.; Magnuson, T.; Bender, J.S. Transplantation of kidneys from expanded criteria donors. Surgery 1996, 119, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessing, M.; Budde, K.; Fritsche, L.; Slowinski, T.; Tuerk, I.; Schoenberger, B.; Neumayer, H.-H.; Loening, S.A. “Old-for-Old” Cadaveric Renal Transplantation: Surgical Findings, Perioperative Complications and Outcome. Eur. Urol. 2003, 44, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentas, W.; Jones, J.; Karaoguz, A.; Tilp, U.; Probst, M.; Scheuermann, E.; Hauser, I.A.; Jonas, D.; Gossmann, J. Renal transplantation in the elderly: Surgical complications and outcome with special emphasis on the Eurotransplant Senior Programme. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 2043–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruintjes, M.H.; D’Ancona, F.C.; Zhu, X.; Hoitsma, A.J.; Warlé, M.C. An Update on Early Urological Complications in Kidney Transplantation: A National Cohort Study. Ann. Transplant. 2019, 24, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessede, T.; Hammoudi, Y.; Bedretdinova, D.; Parier, B.; François, H.; Durrbach, A.; Benoit, G. Preoperative Risk Factors Associated With Urinary Complications After Kidney Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2017, 49, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedersdorff, F.; Weinberger, S.; Biernath, N.; Plage, H.; Cash, H.; El-Bandar, N. The Ureter in the Kidney Transplant Setting: Ureteroneocystostomy Surgical Options, Double-J Stent Considerations and Management of Related Complications. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2020, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REPORT ANNUALE 2019 Rete Nazionale Trapianti. Available online: http://www.trapianti.salute.gov.it/trapianti/archivioDatiCnt.jsp (accessed on 8 December 2020).
- Noble, J.; Jouve, T.; Malvezzi, P.; Süsal, C.; Rostaing, L. Transplantation of Marginal Organs: Immunological Aspects and Therapeutic Perspectives in Kidney Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 10, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Available online: https://population.un.org/wpp (accessed on 8 December 2020).
- Wang, C.J.; Wetmore, J.B.; Israni, A.K. Old versus new: Progress in reaching the goals of the new kidney allocation system. Hum. Immunol. 2017, 78, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zens, T.J.; Danobeitia, J.S.; Leverson, G.; Chlebeck, P.J.; Zitur, L.J.; Redfield, R.R.; D’Alessandro, A.M.; Odorico, S.; Kaufman, D.B.; Fernandez, L.A. The impact of kidney donor profile index on delayed graft function and transplant outcomes: A single-center analysis. Clin. Transplant. 2018, 32, e13190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karam, G.; Hetet, J.-F.; Maillet, F.; Rigaud, J.; Hourmant, M.; Soulillou, J.-P.; Giral, M. Late Ureteral Stenosis Following Renal Transplantation: Risk Factors and Impact on Patient and Graft Survival. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 6, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, I.; Bertocchi, M.; Rossi, A.M.; Gasloli, G.; Santori, G.; Barabani, C.; Fregatti, P.; Valente, U. Late Ureteral Stenosis After Kidney Transplantation: A Single-Center Experience. Transplant. Proc. 2010, 42, 1174–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayetano-Alcaraz, A.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, J.S.; Vilatobá-Chapa, M.; Alberú-Gómez, J.; Gabilondo-Pliego, B.; Rodríguez-Covarrubias, F.; Morales-Buenrostro, L.E.; Mendez-Probst, C.E. Is delayed graft function associated with ureteral stenosis in the kidney transplant recipient? A case-control study. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2019, 13, E361–E365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponticelli, C. Ischaemia-reperfusion injury: A major protagonist in kidney transplantation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannon, R.B. Delayed Graft Function: The AKI of Kidney Transplantation. Nephron 2018, 140, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moers, C.; Smits, J.M.; Maathuis, M.-H.J.; Treckmann, J.; Van Gelder, F.; Napieralski, B.P.; Van Kasterop-Kutz, M.; Van Der Heide, J.J.H.; Squifflet, J.-P.; Van Heurn, E.; et al. Machine Perfusion or Cold Storage in Deceased-Donor Kidney Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adani, G.L.; Pravisani, R.; Tulissi, P.; Isola, M.; Calini, G.; Terrosu, G.; Boscutti, G.; Avital, I.; Ekser, B.; Baccarani, U. Hypothermic machine perfusion can safely prolong cold ischemia time in deceased donor kidney transplantation. A retrospective analysis on postoperative morbidity and graft function. Artif. Organs 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsit, M.-O.; Kleinclauss, F.; Richard, V.; Thuret, R. Complications chirurgicales de la transplantation rénale [Surgical complications of renal transplantation]. Progrès Urol. 2016, 26, 1066–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollyer, I.; Ison, M.G. The challenge of urinary tract infections in renal transplant recipients. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2018, 20, e12828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisserand, B.; Doré, B.; Touchard, G.; Bridoux, F.; Irani, J. Impact à long terme des complications chirurgicales sur la survie du transplant rénal [Long-term outcome of renal transplantation: Impact of surgical complications on graft survival]. Progrès Urol. 2013, 23, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).