SARS-CoV-2, Endothelial Dysfunction, and the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS): A Potentially Dangerous Triad for the Development of Pre-Eclampsia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. SARS-CoV-2 and the Cardiovascular System: ED and RAS
3. Pre-Eclampsia: A COVID-19 Mimicry
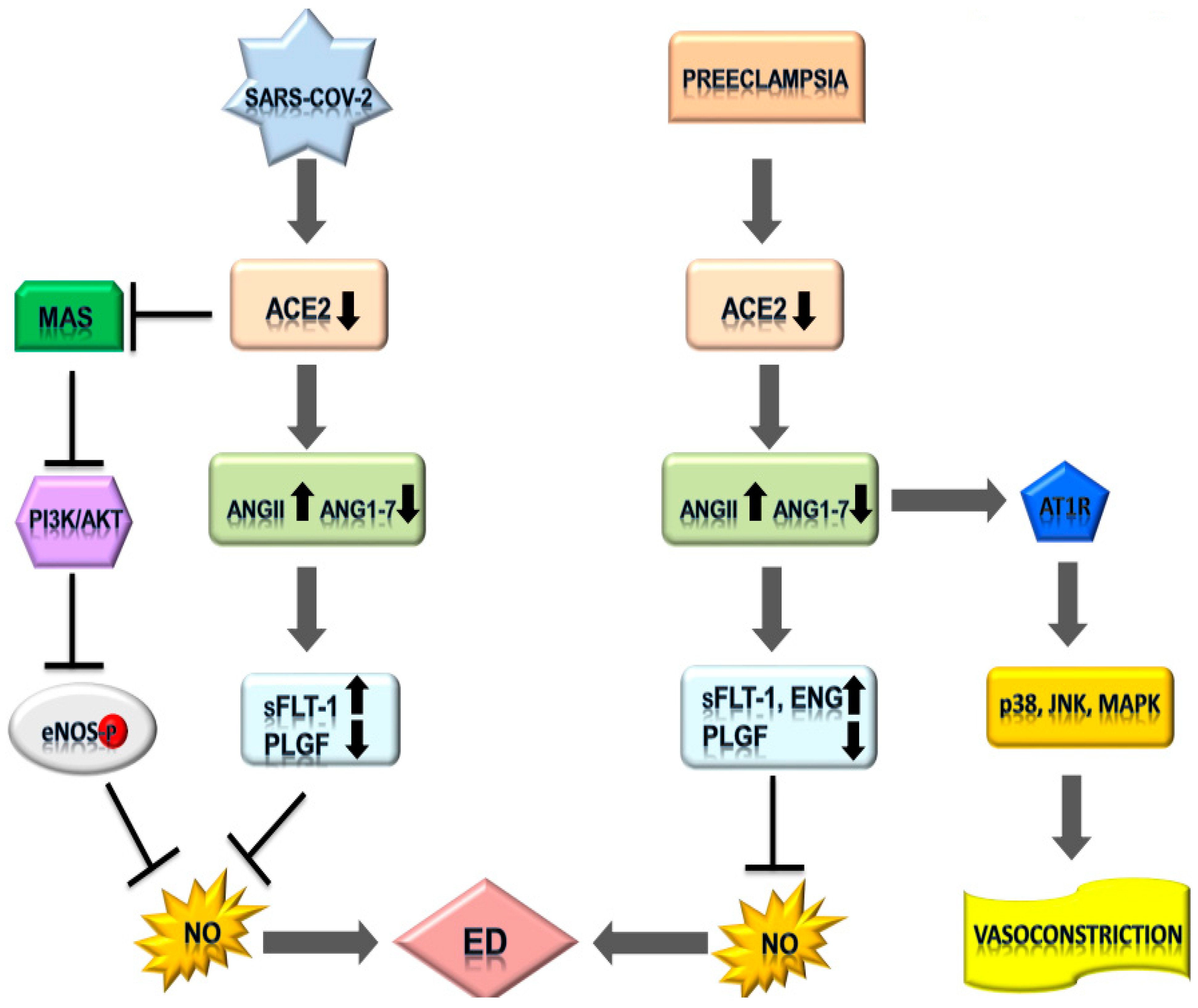
4. Integrating SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Pre-Eclampsia
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutard, B.; Valle, C.; de Lamballerie, X.; Canard, B.; Seidah, N.G.; Decroly, E. The spike glycoprotein of the new coronavirus 2019-nCoV contains a furin-like cleavage site absent in CoV of the same clade. Antivir. Res. 2020, 176, 104742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattinoni, L.; Coppola, S.; Cressoni, M.; Busana, M.; Rossi, S.; Chiumello, D. COVID-19 Does Not Lead to a “Typical” Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 1299–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikellis, C.; Thomas, M.C. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) Is a Key Modulator of the Renin Angiotensin System in Health and Disease. Int. J. Pept. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, S.A. The renin-angiotensin aldosterone system: Pathophysiological role and pharmacologic inhibition. J. Manag. Care Pharm. 2007, 13, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Ye, G.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11727–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdecchia, P.; Cavallini, C.; Spanevello, A.; Angeli, F. The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 76, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.Q. Organ-protective effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and its effect on the prognosis of COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.J.; Redman, C.W.; Roberts, J.M.; Moffett, A. Pre-eclampsia: Pathophysiology and clinical implications. BMJ 2019, 366, l2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Q.; Yang, K.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L.; Song, J. Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Tache, A.; Saint-Andre, J.P.; Milliez, J.; Sureau, C.; Corvol, P.; Menard, J. The renin-angiotensin system in pregnancy and parturition. Adv. Nephrol. Necker. Hosp. 1986, 15, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oelkers, W.K. Effects of estrogens and progestogens on the renin-aldosterone system and blood pressure. Steroids 1996, 61, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Wang, J.; Whitworth, J.A. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in pre-eclampsia. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 1997, 19, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, J.P.; Alexander, B.T.; Bennett, W.A.; Khalil, R.A. Pathophysiology of pregnancy-induced hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens 2001, 14, 178S–185S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.; Yellon, S.M.; Longo, L.D.; Mata-Greenwood, E. Placental gene expression in a rat ‘model’ of placental insufficiency. Placenta 2010, 31, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, G.; Neves, L.A.A.; Anton, L.; Corthorn, J.; Chacón, C.; Germain, A.M.; Merrill, D.C.; Ferrario, C.M.; Sarao, R.; Penninger, J.; et al. Distribution of angiotensin-(1-7) and ACE2 in human placentas of normal and pathological pregnancies. Placenta 2006, 27, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velloso, E.P.; Vieira, R.; Cabral, A.C.; Kalapothakis, E.; Santos, R.A. Reduced plasma levels of angiotensin-(1-7) and renin activity in preeclamptic patients are associated with the angiotensin I- converting enzyme deletion/deletion genotype. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2007, 40, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumbers, E.R.; Pringle, K.G. Roles of the circulating renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in human pregnancy. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 306, R91–R101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumbers, E.R.; Delforce, S.J.; Arthurs, A.L.; Pringle, K.G. Causes and Consequences of the Dysregulated Maternal Renin-Angiotensin System in Preeclampsia. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, B.E.; Goldenberg, N.M.; Lee, W.L. Do viral infections mimic bacterial sepsis? The role of microvascular permeability: A review of mechanisms and methods. Antivir. Res. 2012, 93, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pober, J.S.; Merola, J.; Liu, R.; Manes, T.D. Antigen Presentation by Vascular Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, V.L.; Henault, L.; Lichtman, A.H. Endothelial antigen presentation: Stimulation of previously activated but not naive TCR-transgenic mouse T cells. Cell Immunol. 1998, 189, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijaro, J.R.; Walsh, K.B.; Cahalan, S.; Fremgen, D.M.; Roberts, E.; Scott, F.; Martinborough, E.; Peach, R.; Oldstone, M.B.; Rosen, H. Endothelial cells are central orchestrators of cytokine amplification during influenza virus infection. Cell 2011, 146, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klok, F.A.; Kruip, M.J.H.A.; Van der Meer, N.J.M.; Arbous, M.S.; Gommers, D.A.M.P.J.; Kant, K.M.; Kaptein, F.H.J.; van Paassen, J.; Stals, M.A.M.; Huisman, M.V.; et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demelo-Rodríguez, P.; Cervilla-Muñoz, E.; Ordieres-Ortega, L.; Parra-Virto, A.; Toledano-Macías, M.; Toledo-Samaniego, N.; García-García, A.; García-Fernández-Bravo, I.; Ji, Z.; de-Miguel-Diez, J.; et al. Incidence of asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and elevated D-dimer levels. Thromb. Res. 2020, 192, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Flammer, A.J.; Steiger, P.; Haberecker, M.; Andermatt, R.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Mehra, M.R.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Ruschitzka, F.; Moch, H. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 395, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamming, I.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M.L.C.; Lely, A.T.; Navis, G.V.; van Goor, H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, X.; Chen, M.; Feng, Y.; Xiong, C. The ACE2 expression in human heart indicates new potential mechanism of heart injury among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteil, V.; Kwon, H.; Prado, P.; Hagelkrüys, A.; Wimmer, R.A.; Stahl, M.; Leopoldi, A.; Garreta, E.; Del Pozo, C.H.; Prosper, F.; et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Engineered Human Tissues Using Clinical-Grade Soluble Human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigrist, C.J.; Bridge, A.; Le Mercier, P. A potential role for integrins in host cell entry by SARS-CoV-2. Antivir. Res. 2020, 177, 104759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulous, F.E.; Petrich, B.G. Integrin-dependent regulation of the endothelial barrier. Tissue Barriers 2019, 7, 1685844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardini, V.; Carrer, A.; Casati, M.; Contro, E.; Vergani, P.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C. Increased sFLT-1/PlGF ratio in COVID-19: A novel link to angiotensin II-mediated endothelial dysfunction. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, E188–E191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinski, H.J.; Gudermann, T.; Breit, A. Pharmacology and signaling of MAS-related G protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 570–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmanan, A.P.; Thandavarayan, R.A.; Watanabe, K.; Sari, F.R.; Meilei, H.; Giridharan, V.V.; Sukumaran, V.; Soetikno, V.; Arumugam, S.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Modulation of AT-1R/MAPK cascade by an olmesartan treatment attenuates diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2012, 348, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, L.; Brosnihan, K.B. Systemic and uteroplacental renin--angiotensin system in normal and pre-eclamptic pregnancies. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 2, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Magee, L.A.; Kenny, L.C.; Karumanchi, S.A.; McCarthy, F.P.; Saito, S.; Hall, D.R.; Warren, C.E.; Adoyi, G.; Ishaku, S. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: ISSHP Classification, Diagnosis, and Management Recommendations for International Practice. Hypertension 2018, 72, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, D.; Peterson, E. A critical review of early-onset and late-onset preeclampsia. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2011, 66, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibai, B.M. Maternal and uteroplacental hemodynamics for the classification and prediction of preeclampsia. Hypertension 2008, 52, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paauw, N.D.; Lely, A.T. Cardiovascular Sequels During and After Preeclampsia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1065, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananth, C.V.; Keyes, K.M.; Wapner, R.J. Pre-eclampsia rates in the United States, 1980–2010: Age-period-cohort analysis. BMJ 2013, 347, f6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonney, V. “Pre-eclampsia” at the Twenty-fourth Week; Acute Toxaemia; Caesarean Section. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1914, 7, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thilaganathan, B.; Kalafat, E. Cardiovascular System in Preeclampsia and Beyond. Hypertension 2019, 73, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thilaganathan, B. Pre-eclampsia and the cardiovascular-placental axis. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 51, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenney, B., Jr. The toxemias of pregnancy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1947, 238, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.J.; Woods, A.W.; Jauniaux, E.; Kingdom, J.C. Rheological and physiological consequences of conversion of the maternal spiral arteries for uteroplacental blood flow during human pregnancy. Placenta 2009, 30, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.Y.; Barrett, C.J.; Guild, S.J.; Chamley, L.W. Necrotic trophoblast debris increases blood pressure during pregnancy. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2013, 97, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, M.L.; Sivanathan, J.; Laoreti, A.; Thilaganathan, B.; Khalil, A. Placental histopathology associated with pre-eclampsia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 50, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonk, K.; Visser, W.; Van Den Meiracker, A.H.; Danser, A.H. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in pre-eclampsia: The delicate balance between good and bad. Clin. Sci. 2014, 126, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Jauniaux, E.; Cooper, D.; Harrington, K. Pulse wave analysis in normal pregnancy: A prospective longitudinal study. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeldt, D.S.; Yi, F.X.; Bird, I.M. eNOS activation and NO function: Pregnancy adaptive programming of capacitative entry responses alters nitric oxide (NO) output in vascular endothelium--new insights into eNOS regulation through adaptive cell signaling. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 210, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Graaf, A.M.; Toering, T.J.; Faas, M.M.; Lely, A.T. From preeclampsia to renal disease: A role of angiogenic factors and the renin-angiotensin aldosterone system? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27 (Suppl. 3), iii51–iii57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herse, F.; Dechend, R.; Harsem, N.K.; Wallukat, G.; Janke, J.; Qadri, F.; Hering, L.; Muller, D.N.; Luft, F.C.; Staff, A.C. Dysregulation of the circulating and tissue-based renin-angiotensin system in preeclampsia. Hypertension 2007, 49, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, D.C.; Karoly, M.; Chen, K.; Ferrario, C.M.; Brosnihan, K.B. Angiotensin-(1-7) in normal and preeclamptic pregnancy. Endocrine 2002, 18, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shams, M.; Zhu, J.; Khalig, A.; Wilkes, M.; Whittle, M.; Barnes, N.; Ahmed, A. Cellular localization of AT1 receptor mRNA and protein in normal placenta and its reduced expression in intrauterine growth restriction. Angiotensin II stimulates the release of vasorelaxants. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ansari, R.; Yu, Z.; Shah, D. Definitive molecular evidence of renin-angiotensin system in human uterine decidual cells. Hypertension 2000, 36, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Liu, T.; Jiang, F.; Liu, C.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z. microRNA-155 regulates angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression in umbilical vein endothelial cells from severely pre-eclamptic pregnant women. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 27, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Diao, Z.; Su, L.; Sun, H.; Li, R.; Cui, H.; Hu, Y. MicroRNA-155 contributes to preeclampsia by down-regulating CYR61. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 202, 466.e1–466.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, F.D.; Ferreira, A.J.; Sinisterra, R.D.; Jacoby, B.A.; Sousa, F.B.; Caliari, M.V.; Silva, G.A.; Melo, M.B.; Nadu, A.P.; Souza, L.E.; et al. An oral formulation of angiotensin-(1-7) produces cardioprotective effects in infarcted and isoproterenol-treated rats. Hypertension 2011, 57, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todros, T.; Masturzo, B.; De Francia, S. COVID-19 infection: ACE2, pregnancy and preeclampsia. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 253, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Penninger, J.M.; Li, Y.; Zhong, N.; Slutsky, A.S. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: Molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, A.; Yagil, Y.; Bursztyn, M.; Barkalifa, R.; Scharf, S.; Yagil, C. ACE2 expression and activity are enhanced during pregnancy. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 295, R1953–R1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.Y.; Romero, R.; Mor, G. New insights into the relationship between viral infection and pregnancy complications. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2014, 71, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfo, A.; Giuffrida, D.; Nuzzo, A.M.; Pierobon, D.; Cardaropoli, S.; Piccoli, E.; Giovarelli, M.; Todros, T. Pro-inflammatory profile of preeclamptic placental mesenchymal stromal cells: New insights into the etiopathogenesis of preeclampsia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.M.; Ahmed, O.A.; Shaltout, A.S. COVID-19 and maternal pre-eclampsia: A synopsis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2020, 92, e12918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.F.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashraath, P.; Wong, J.L.J.; Lim, M.X.K.; Lim, L.M.; Li, S.; Biswas, A.; Choolani, M.; Mattar, C.; Su, L.L. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 222, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, L.; Amiri, M.; Pouy, S. Risks of Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in Pregnancy; a Narrative Review. Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2020, 8, e34. [Google Scholar]
- Alserehi, H.; Wali, G.; Alshukairi, A.; Alraddadi, B. Impact of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) on pregnancy and perinatal outcome. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, M.; Cagino, K.; Matthews, K.C.; Friedlander, R.L.; Glynn, S.M.; Kubiak, J.M.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhao, Z.; Baergen, R.N.; DiPace, J.I.; et al. Pregnancy and postpartum outcomes in a universally tested population for SARS-CoV-2 in New York City: A prospective cohort study. BJOG An Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2020, 127, 1548–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govender, R.; Moodley, J.; Naicker, T. The COVID-19 Pandemic: An Appraisal of its Impact on Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection and Pre-Eclampsia. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2021, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, K.G.; Tadros, M.A.; Callister, R.J.; Lumbers, E.R. The expression and localization of the human placental prorenin/renin-angiotensin system throughout pregnancy: Roles in trophoblast invasion and angiogenesis? Placenta 2011, 32, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.Y.; Guild, S.J.; Barrett, C.J.; Chen, Q.; McCowan, L.; Jordan, V.; Chamley, L.W. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and interleukin-10 levels are altered in preeclampsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2013, 70, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludag, S.Z.; Gokmen Karasu, A.F.; Kutuk, M.S.; Takmaz, T. Incidence and outcomes of eclampsia: A single-center 30-year study. Hypertens Pregnancy 2019, 38, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, M.; Garcia-Ruiz, I.; Maiz, N.; Rodo, C.; Garcia-Manau, P.; Serrano, B.; Lopez-Martinez, R.M.; Balcells, J.; Fernandez-Hidalgo, N.; Carreras, E.; et al. Pre-eclampsia-like syndrome induced by severe COVID-19: A prospective observational study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2020, 127, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosier, H.; Farhadian, S.F.; Morotti, R.A.; Deshmukh, U.; Lu-Culligan, A.; Campbell, K.H.; Yasumoto, Y.; Vogels, C.B.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Vijayakumar, P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection of the placenta. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 4947–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanes, E.D.; Mithal, L.B.; Otero, S.; Azad, H.A.; Miller, E.S.; Goldstein, J.A. Placental Pathology in COVID-19. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloise, E.; Zhang, J.; Nakpu, J.; Hamada, H.; Dunk, C.E.; Li, S.; Imperio, G.E.; Nadeem, L.; Kibschull, M.; Lye, P.; et al. Expression of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 cell entry genes, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane protease serine 2, in the placenta across gestation and at the maternal-fetal interface in pregnancies complicated by preterm birth or preeclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 224, 298.e1–298.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.A.; Stovall, K.; Joyner, J.; Valdés, G.; Gallagher, P.E.; Ferrario, C.M.; Merrill, D.C.; Brosnihan, K.B. ACE2 and ANG-(1-7) in the rat uterus during early and late gestation. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R151–R161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, C.; Li, X. The SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 expression of maternal-fetal interface and fetal organs by single-cell transcriptome study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pique-Regi, R.; Romero, R.; Tarca, A.L.; Luca, F.; Xu, Y.; Alazizi, A.; Leng, Y.; Hsu, C.D.; Gomez-Lopez, N. Does the human placenta express the canonical cell entry mediators for SARS-CoV-2? Elife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, D.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ding, C.; Poon, L.C.; Wang, H.; Yang, H. Single-cell RNA expression profiling of SARS-CoV-2-related ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in human trophectoderm and placenta. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 57, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenizia, C.; Biasin, M.; Cetin, I.; Vergani, P.; Mileto, D.; Spinillo, A.; Gismondo, M.R.; Perotti, F.; Callegari, C.; Mancon, A.; et al. Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 vertical transmission during pregnancy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, L.; Wang, D.; Guo, M.; Jiang, A.; Guo, D.; Hu, W.; Yang, J.; Tang, Z.; et al. Transcriptomic characteristics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in COVID-19 patients. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2020, 9, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojkova, D.; Klann, K.; Koch, B.; Widera, M.; Krause, D.; Ciesek, S.; Cinatl, J.; Münch, C. Proteomics of SARS-CoV-2-infected host cells reveals therapy targets. Nature 2020, 583, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaport, N.; Twik, M.; Plaschkes, I.; Nudel, R.; Iny Stein, T.; Levitt, J.; Gershoni, M.; Morrey, C.P.; Safran, M.; Lancet, D. MalaCards: An amalgamated human disease compendium with diverse clinical and genetic annotation and structured search. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D877–D887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Melo, D.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Liu, W.C.; Uhl, S.; Hoagland, D.; Møller, R.; Jordan, T.X.; Oishi, K.; Panis, M.; Sachs, D.; et al. Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19. Cell 2020, 181, 1036–1045.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Dijke, P.; Goumans, M.J.; Pardali, E. Endoglin in angiogenesis and vascular diseases. Angiogenesis 2008, 11, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vivo, A.; Baviera, G.; Giordano, D.; Todarello, G.; Corrado, F.; D’anna, R. Endoglin, PlGF and sFlt-1 as markers for predicting pre-eclampsia. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2008, 87, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beys-da-Silva, W.O.; da Rosa, R.L.; Santi, L.; Tureta, E.F.; Terraciano, P.B.; Guimarães, J.A.; Passos, E.P.; Berger, M. The risk of COVID-19 for pregnant women: Evidences of molecular alterations associated with preeclampsia in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 165999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigat, B.; Hubert, C.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Cambien, F.; Corvol, P.; Soubrier, F. An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene accounting for half the variance of serum enzyme levels. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 1343–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uma, R.; Forsyth, S.J.; Struthers, A.D.; Fraser, C.G.; Godfrey, V.; Murphy, D.J. Polymorphisms of the angiotensin converting enzyme gene in early-onset and late-onset pre-eclampsia. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010, 23, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Ariumi, Y.; Nishida, N.; Yamamoto, R.; Bauer, G.; Gojobori, T.; Shimotohno, K.; Mizokami, M. SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 mortalities strongly correlate with ACE1 I/D genotype. Gene 2020, 758, 144944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Illi, B.; Vasapollo, B.; Valensise, H.; Totta, P. SARS-CoV-2, Endothelial Dysfunction, and the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS): A Potentially Dangerous Triad for the Development of Pre-Eclampsia. Reprod. Med. 2021, 2, 95-106. https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed2020010
Illi B, Vasapollo B, Valensise H, Totta P. SARS-CoV-2, Endothelial Dysfunction, and the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS): A Potentially Dangerous Triad for the Development of Pre-Eclampsia. Reproductive Medicine. 2021; 2(2):95-106. https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed2020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlli, Barbara, Barbara Vasapollo, Herbert Valensise, and Pierangela Totta. 2021. "SARS-CoV-2, Endothelial Dysfunction, and the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS): A Potentially Dangerous Triad for the Development of Pre-Eclampsia" Reproductive Medicine 2, no. 2: 95-106. https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed2020010
APA StyleIlli, B., Vasapollo, B., Valensise, H., & Totta, P. (2021). SARS-CoV-2, Endothelial Dysfunction, and the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS): A Potentially Dangerous Triad for the Development of Pre-Eclampsia. Reproductive Medicine, 2(2), 95-106. https://doi.org/10.3390/reprodmed2020010