Monitoring Water Balance to Predict Hospitalization in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Study Subjects
2.3. BIA
2.4. Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Correlation Analysis
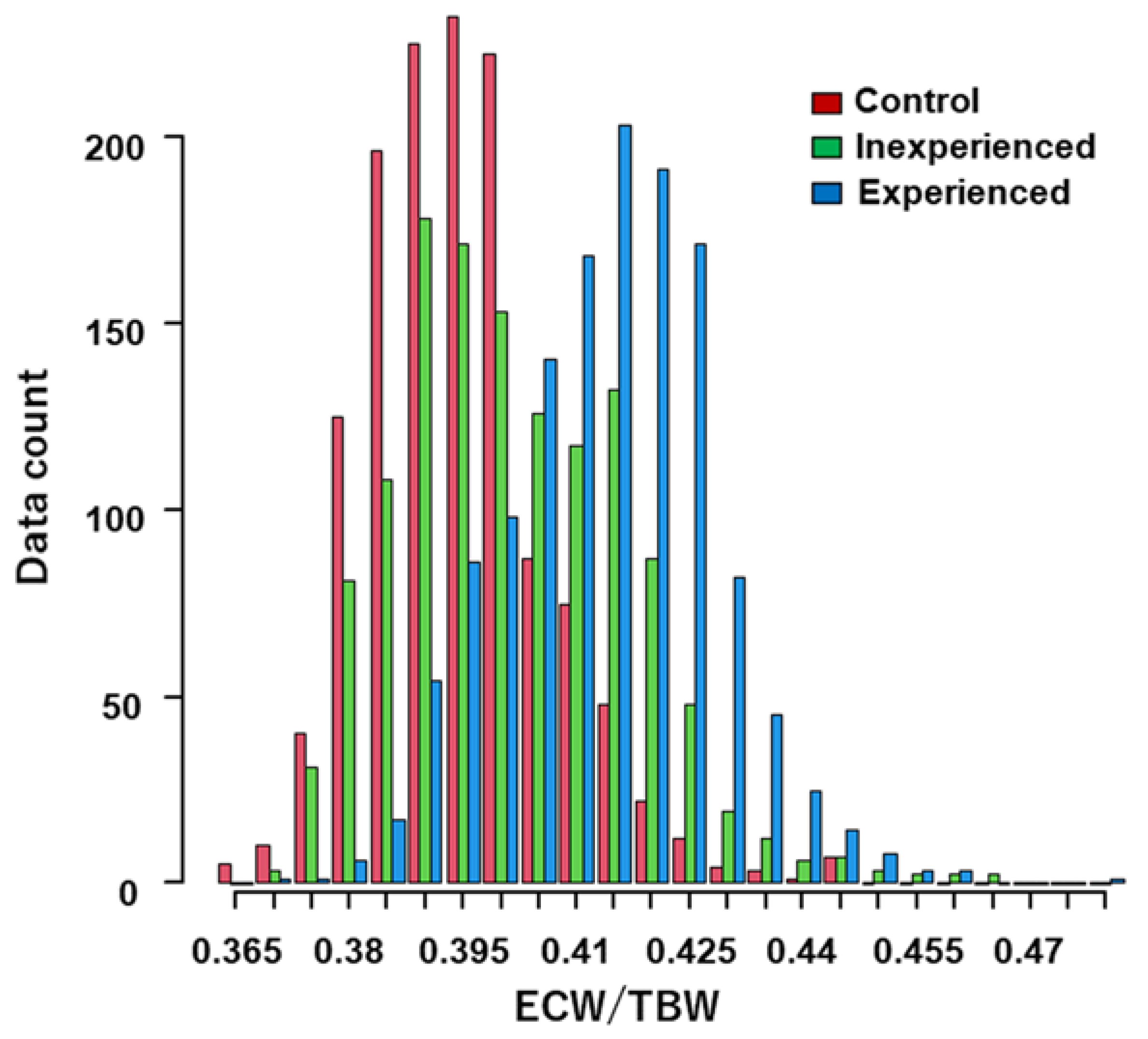
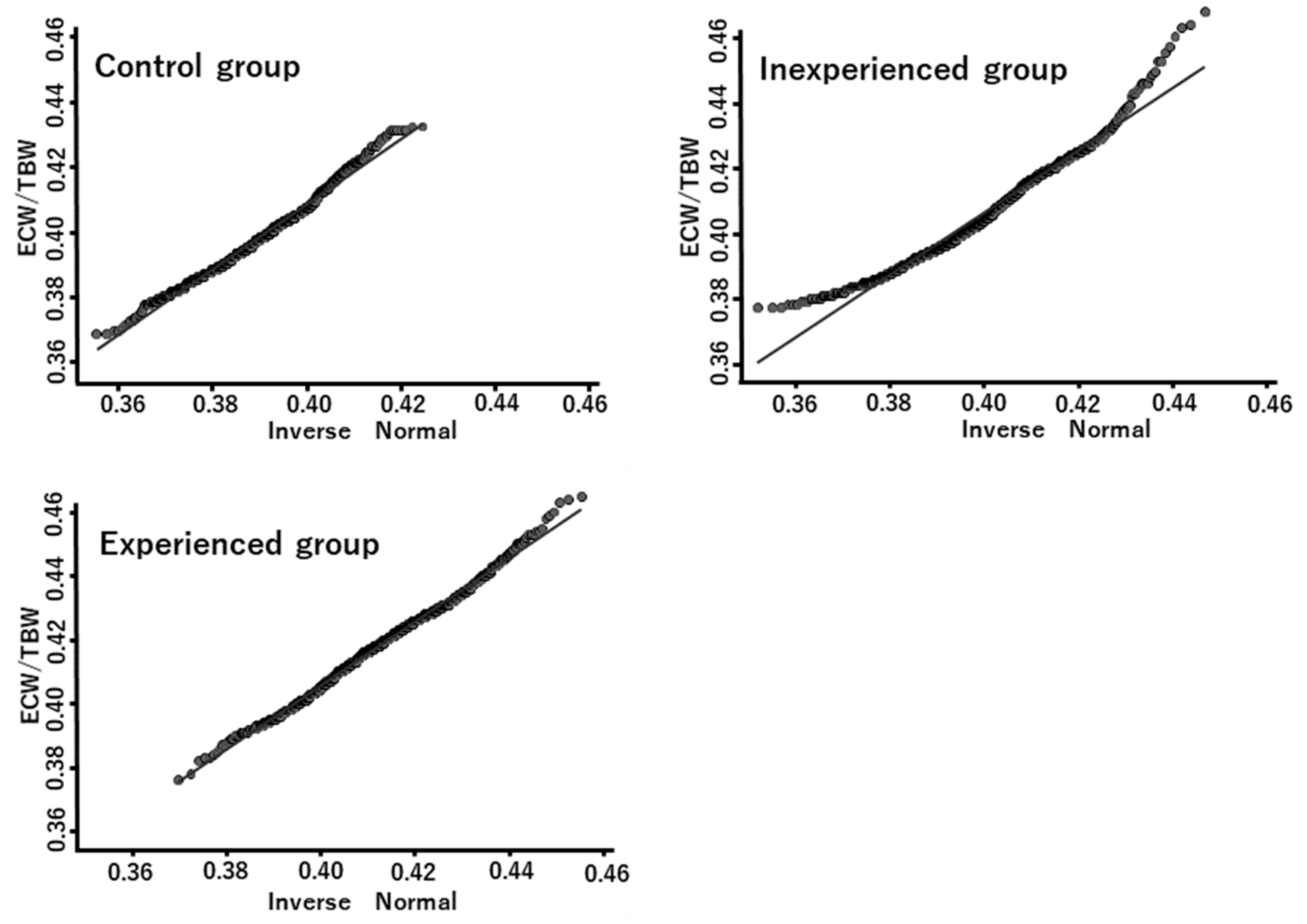
3.3. Distributions of the ECW/TBW Ratio
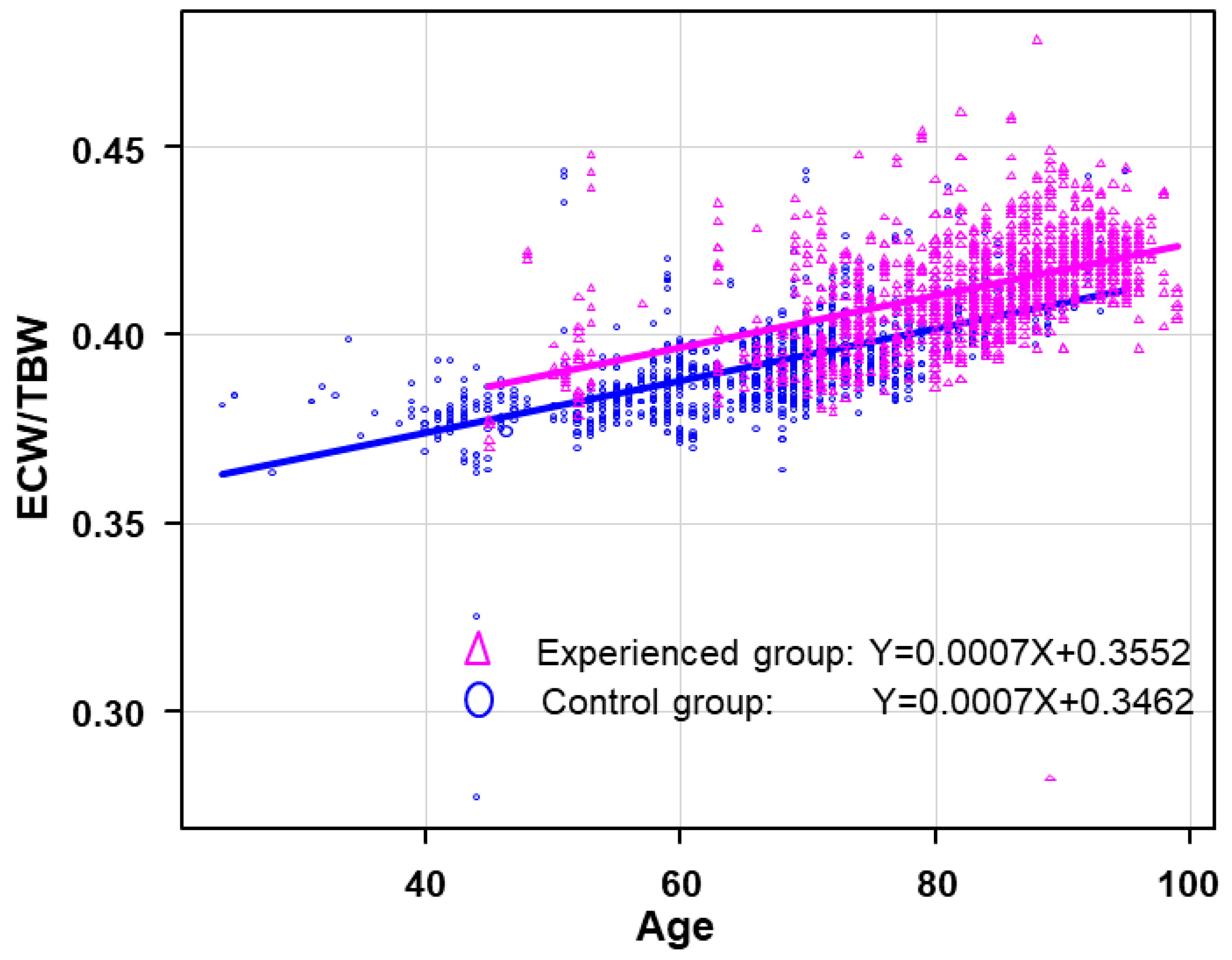
3.4. Regression Analysis and ANCOVA
4. Discussion
4.1. Statistical Aspects
4.2. Clinical Utility of Water Balance Monitoring
4.3. Comparison with Other Assessment Methods
4.4. ECW/TBW Ratio
4.5. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shiba, N.; Watanabe, J.; Shinozaki, T.; Koseki, Y.; Sakuma, M.; Kagaya, Y.; Shirato, K. Analysis of Chronic Heart Failure Registry in the Tohoku District-Third Year Follow-up-. Circ. J. 2004, 68, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchihashi-Makaya, M.; Hamaguchi, S.; Kinugawa, S.; Yokota, T.; Goto, D.; Yokoshiki, H.; Kato, N.; Takeshita, A.; Tsutsui, H. Characteristics and Outcomes of Hospitalized Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Vs Preserved Ejection Fraction. Report from the Japanese Cardiac Registry of Heart Failure in Cardiology (Jcare-Card). Circ. J. 2009, 73, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.S.; Stevenson, L.W. Rehospitalization for Heart Failure. Circulation 2012, 126, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.S.; Chen, J.; Lin, Z.; Bueno, H.; Curtis, J.P.; Keenan, P.S.; Normand, S.-L.T.; Schreiner, G.; Spertus, J.A.; Vidán, M.T.; et al. Recent National Trends in Readmission Rates After Heart Failure Hospitalization. Circ. Hear. Fail. 2010, 3, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.; Tu, J.V.; Wijeysundera, H.C.; Austin, P.C.; Wang, X.; Levy, D.; Lee, D.S. Lifetime Analysis of Hospitalizations and Survival of Patients Newly Admitted With Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2012, 5, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukoyama, M.; Nakao, K.; Saito, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Hosoda, K.; Suga, S.; Shirakami, G.; Jougasaki, M.; Imura, H. Increased Human Brain Natriuretic Peptide in Congestive Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisel, A.S.; Krishnaswamy, P.; Nowak, R.M.; McCord, J.; Hollander, J.E.; Duc, P.; Omland, T.; Storrow, A.B.; Abraham, W.T.; Wu, A.H.; et al. Rapid Measurement of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in the Emergency Diagnosis of Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Hamm, C. Role of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide (Bnp) and Nt-Probnp in Clinical Routine. Heart 2006, 92, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, P.A.; Castelli, W.P.; McNamara, P.M.; Kannel, W.B. The Natural History of Congestive Heart Failure: The Framingham Study. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrinello, G.; Greene, S.J.; Torres, D.; Alderman, M.; Bonventre, J.V.; Di Pasquale, P.; Gargani, L.; Nohria, A.; Fonarow, G.C.; Vaduganathan, M.; et al. Water and sodium in heart failure: A spotlight on congestion. Heart Fail. Rev. 2015, 20, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; De Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Gómez, J.M.; Heitmann, B.L.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. Pichard, and Espen Working Group Composition of the. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis—Part I: Review of Principles and Methods. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; De Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Gómez, J.M.; Heitmann, B.L.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.-C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis—Part II: Utilization in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1430–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dylke, E.S.; Ward, L.C. Three Decades of Bioelectrical Impedance Spectroscopy in Lymphedema Assessment: An Historical Perspective. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2021, 19, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, Y.; Jaffrin, M.Y.; Morel, H. Body fluid volumes measurements by impedance: A review of bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) and bioimpedance analysis (BIA) methods. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Moonen, H.P.F.X.; Van Zanten, A.R.H. Bioelectric impedance analysis for body composition measurement and other potential clinical applications in critical illness. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2021, 27, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, K.; Chertow, G.M.; Gonzalez, J.; Lazarus, J.M.; Wilmore, D.W. Multifrequency bioelectrical impedance estimates the distribution of body water. J. Appl. Physiol. 1995, 79, 1316–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, K.; Shin, S.; Shon, C.; Choi, S.; Wilmore, D.W. Evaluation of segmental bioelectrical impedance analysis for measuring muscle distribution. J. ICHPER SD-ASIA 1997, 1, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sartorio, A.; Malavolti, M.; Agosti, F.; Marinone, P.G.; Caiti, O.; Battistini, N.; Bedogni, G. Body water distribution in severe obesity and its assessment from eight-polar bioelectrical impedance analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 59, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, G.; Malavolti, M.; Severi, S.; Poli, M.; Mussi1, C.; Fantuzzi1, A.L.; Battistini, N. Accuracy of an eight-point tac-tile-electrodeimpedance method in the assessment of total bodywater. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 56, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Inai, K.; Shimizu, M.; Sugiyama, H.; Nakanishi, T. Bioelectrical impedance analysis in the management of heart failure in adult patients with congenital heart disease. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2019, 14, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Pierson, R.N., Jr.; Heymsfield, S.B. The Five-Level Model: A New Approach to Organizing Body-Composition Research. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 56, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, A.; Sayed, R.H.; Fan, S. Is Extracellular Volume Expansion of Peritoneal Dialysis Patients Associated with Greater Urine Output? Blood Purif. 2011, 32, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohria, A.; Tsang, S.W.; Fang, J.C.; Lewis, E.F.; A Jarcho, J.; Mudge, G.H.; Stevenson, L.W. Clinical assessment identifies hemodynamic profiles that predict outcomes in patients admitted with heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conraads, V.M.; Bosmans, J.M.; Vrints, C.J. Chronic heart failure: An example of a systemic chronic inflammatory disease resulting in cachexia. Int. J. Cardiol. 2002, 85, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.A.; Altman, D.G. Basic statistical reporting for articles published in Biomedical Journals: The “Statistical Analyses and Methods in the Published Literature” or the SAMPL Guidelines. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2015, 52, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanapholsart, J.; Khan, E.; Lee, G.A. A Current Review of the Uses of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis and Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis in Acute and Chronic Heart Failure Patients: An Under-valued Resource? Res. Nurs. 2023, 25, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ieso, F.; Mutke, M.R.; Brasier, N.K.; Raichle, C.J.; Keller, B.; Sucker, C.; Abdelhamid, K.; Bloch, T.; Reissenberger, P.; Schönenberg, L.; et al. Body composition analysis in patients with acute heart failure: The Scale Heart Failure trial. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 4593–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayne, K.J.; Shemilt, R.; Keane, D.F.; Lees, J.S.; Mark, P.B.; Herrington, W.G. Bioimpedance Indices of Fluid Overload and Cardiorenal Outcomes in Heart Failure and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Card. Fail. 2022, 28, 1628–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Lee, S.-E.; Cho, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kang, H.-J.; Oh, B.-H.; Lee, H.-Y. Body fluid status assessment by bio-impedance analysis in patients presenting to the emergency department with dyspnea. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, T.; Yasumura, K.; Nishida, H.; Inoue, H.; Furukawa, T.; Shinouchi, K.; Miura, H.; Miyazaki, K.; Hamano, G.; Koide, M.; et al. Quantitative Assessment of Fluid Accumulation Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Patients With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. Circ. J. 2015, 79, 2616–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webel, A.R.; Frazier, S.K.; Moser, D.K.; Lennie, T.A. Daily Variability in Dyspnea, Edema and Body Weight in Heart Failure Patients. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2007, 6, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voors, A.A.; Kremer, D.; Geven, C.; Maaten, J.M.T.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Pickkers, P.; Metra, M.; Mebazaa, A.; Düngen, H.D.; et al. Adrenomedullin in Heart Failure: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Application. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, S.I.; Wang, Y.; Concato, J.; Gill, T.M.; Krumholz, H.M. Patterns of Weight Change Preceding Hospitalization for Heart Failure. Circulation 2007, 116, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Goode, K.M.; Cuddihy, P.E.; Cleland, J.G.; TEN-HMS Investigators. Predicting hospitalization due to worsening heart failure using daily weight measurement: Analysis of the Trans-European Network-Home-Care Management System (TEN-HMS) study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2009, 11, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vader, J.M.; Drazner, M.H. Clinical Assessment of Heart Failure: Utility of Symptoms, Signs, and Daily Weights. Heart Fail. Clin. 2009, 5, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancy, C.W.; Jessup, M.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Drazner, M.H.; Fonarow, G.C.; Geraci, S.A.; Horwich, T.; Januzzi, J.L.; et al. 2013 Accf/Aha Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, e147–e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosy, A.P.; Pang, P.S.; Khan, S.; Konstam, M.A.; Fonarow, G.C.; Traver, B.; Maggioni, A.P.; Cook, T.; Swedberg, K.; Burnett, J.C.; et al. Clinical course and predictive value of congestion during hospitalization in patients admitted for worsening signs and symptoms of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: Findings from the EVEREST trial. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchihashi, M.; Tsutsui, H.; Kodama, K.; Kasagi, F.; Setoguchi, S.; Mohr, M.; Kubota, T.; Takeshita, A. Medical and socioenvironmental predictors of hospital readmission in patients with congestive heart failure. Am. Heart J. 2001, 142, 20A–26A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Female + Male | Female | Male | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of outpatients | 756 | 370 (48.9%) | 386 (51.1%) |
| Data count | 3922 | 1865 (47.6%) | 2057 (52.4%) |
| Number of examinations | 6.8 ± 8.42 | 7.4 ± 10.02 | 6.3 ± 6.62 |
| Age | 74.8 ± 12.83 | 77.3 ± 12.29 | 72.5 ± 12.88 |
| Height (cm) | 156.84 ± 10.49 | 148.97 ± 7.28 | 163.97 ± 7.41 |
| weight (kg) | 59.68 ± 15.36 | 52.67 ± 13.66 | 66.00 ± 13.88 |
| BFM (Body Fat Mass) | 19.19 ± 8.87 | 19.09 ± 9.47 | 19.29 ± 8.28 |
| SLM (Soft Lean Mass) | 38.29 ± 11.68 | 31.56 ± 5.82 | 44.17 ± 7.76 |
| FFM (Fat Free Mass) | 40.49 ± 9.90 | 33.58 ± 6.06 | 46.71 ± 8.14 |
| BMI (Body Mass Index) | 24.16 ± 8.35 | 23.59 ± 5.21 | 24.46 ± 4.41 |
| ECW/TBW | 0.4014 ± 0.0161 | 0.4050 ± 0.0147 | 0.3981 ± 0.0165 |
| Chronic heart failure | 481 | 234 | 247 |
| Renal failure | 14 | 4 | 10 |
| Chronic renal failure | 93 | 38 | 55 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 380 | 168 | 212 |
| Dyslipidemia | 65 | 31 | 34 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 203 | 101 | 102 |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 311 | 160 | 151 |
| Experienced | Inexperienced | Control | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of outpatients | 257 (34.1%) | 224 (29.6%) | 275 (36.3%) |
| Data count | 1318 (33.6%) | 1288 (32.8%) | 1316 (33.6%) |
| Number of examinations | 4.6 ± 10.93 | 4.2 ± 8.68 | 4.7 ± 3.55 |
| Age | 82.9 ± 10.00 | 74.2 ± 11.90 | 67.4 ± 11.47 |
| Height (cm) | 153.16 ± 10.58 | 157.19 ± 9.74 | 160.17 ± 9.93 |
| Weight (kg) | 52.39 ± 15.78 | 63.25 ± 14.789 | 63.48 ± 12.66 |
| BFM (Body Fat Mass) | 16.04 ± 9.36 | 21.38 ± 8.38 | 20.20 ± 7.90 |
| SLM (Soft Lean Mass) | 34.19 ± 8.93 | 39.55 ± 9.08 | 41.15 ± 14.82 |
| FFM (Fat Free Mass) | 36.35 ± 9.30 | 41.87 ± 9.50 | 43.28 ± 9.51 |
| BMI (Body Mass Index) | 22.07 ± 4.99 | 25.44 ± 4.71 | 24.99 ± 12.42 |
| ECW/TBW | 0.4121 ± 0.0141 | 0.3996 ± 0.0150 | 0.3924 ± 0.0123 |
| Chronic heart failure | 257 | 224 | 0 |
| Renal failure | 9 | 1 | 4 |
| Chronic renal failure | 60 | 23 | 10 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 104 | 113 | 163 |
| Dyslipidemia | 10 | 19 | 36 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 52 | 77 | 74 |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 78 | 117 | 116 |
| Wei | BFM | SLM | FFM | BMI | E/T | Gen | Age | CHF | RF | CRF | DM | DL | HL | HS | HH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height | 0.63 * | 0.16 * | 0.85 * | 0.85 * | 0.16 * | −0.41 * | 0.71 * | −0.52 * | −0.23 * | −0.10 * | −0.07 * | 0.23 * | 0.06 * | -0.02 | 0.12 * | −0.24 * |
| Wei | ― | 0.80 * | 0.84 * | 0.84 * | 0.86 * | −0.48 * | 0.44 * | −0.61 * | −0.16 * | −0.18 * | −0.12 * | 0.27 * | 0.08 * | 0.11 * | 0.29 * | −0.34 * |
| BFM | ― | 0.35 * | 0.35 * | 0.92 * | −0.35 * | 0.01 | −0.38 * | −0.08 * | −0.17 * | −0.15 * | 0.18 * | 0.06 * | 0.14 * | 0.29 * | −0.26 * | |
| SLM | ― | 0.99 * | 0.51 * | −0.43 * | 0.67 * | −0.61 * | −0.19 * | −0.13 * | −0.07 * | 0.26 * | 0.07 * | 0.04 * | 0.19 * | −0.30 * | ||
| FFM | ― | 0.50 * | −0.43 * | 0.67 * | −0.61 * | −0.18 * | −0.12 * | −0.06 * | 0.26 * | 0.07 * | 0.04 * | 0.18 * | −0.30 * | |||
| BMI | ― | −0.34 * | 0.09 * | −0.43 * | −0.08 * | −0.18 * | −0.12 * | 0.20 * | 0.06 * | 0.15 * | 0.29 * | −0.30 * | ||||
| E/T | ― | −0.21 * | 0.71 * | 0.39 * | 0.09 * | 0.37 * | −0.31 * | −0.13 * | −0.18 * | −0.29 * | 0.44 * | |||||
| Gen | ― | −0.19 * | −0.01 | −0.08 * | 0.03 * | 0.15 * | 0.01 | −0.03 | 0.01 | −0.06 * | ||||||
| Age | ― | 0.41 * | 0.17 * | 0.23 * | −0.30 * | −0.08 * | −0.10 * | −0.22 * | 0.44 * | |||||||
| CHF | ― | 0.09 * | 0.29 * | −0.26 * | −0.20 * | 0.00 | −0.11 * | 0.34 * | ||||||||
| RF | ― | 0.19 * | 0.08 * | −0.06 * | 0.10 * | −0.04 * | 0.18 * | |||||||||
| CRF | ― | −0.11 * | −0.07 * | −0.06 * | −0.19 * | 0.27 * | ||||||||||
| DM | ― | 0.09 * | 0.17 * | 0.19 * | −0.20 * | |||||||||||
| DL | ― | −0.16 * | −0.01 | −0.11 * | ||||||||||||
| HL | ― | 0.17 * | −0.15 * | |||||||||||||
| HS | ― | −0.21 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hirose, K.; Otsuka, K.; Shiozawa, S.; Hirose, G.; Shino, M.; Hokari, T.; Kohno, S.; Nakayama, K. Monitoring Water Balance to Predict Hospitalization in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: A Retrospective Study. Hearts 2023, 4, 48-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/hearts4030006
Hirose K, Otsuka K, Shiozawa S, Hirose G, Shino M, Hokari T, Kohno S, Nakayama K. Monitoring Water Balance to Predict Hospitalization in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: A Retrospective Study. Hearts. 2023; 4(3):48-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/hearts4030006
Chicago/Turabian StyleHirose, Kenichi, Keita Otsuka, Shinichiro Shiozawa, Go Hirose, Miwa Shino, Takeo Hokari, Satoru Kohno, and Kohzo Nakayama. 2023. "Monitoring Water Balance to Predict Hospitalization in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: A Retrospective Study" Hearts 4, no. 3: 48-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/hearts4030006
APA StyleHirose, K., Otsuka, K., Shiozawa, S., Hirose, G., Shino, M., Hokari, T., Kohno, S., & Nakayama, K. (2023). Monitoring Water Balance to Predict Hospitalization in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: A Retrospective Study. Hearts, 4(3), 48-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/hearts4030006





