Complications of Short-Course Oral Corticosteroids for Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis during Long-Term Follow-Up
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Patients
2.2. Study Protocol
2.3. Outcome Measures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bachert, C.; Zhang, N.; Hellings, P.W.; Bousquet, J. Endotype-driven care pathways in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleimer, R.P. Immunopathogenesis of Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyposis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2017, 12, 331–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, T.; Kusunoki, T.; Yao, T.; Kawano, K.; Kojima, Y.; Miyahara, K.; Onoda, J.; Yokoi, H.; Ikeda, K. Role of interleukin-17A in the eosinophil accumulation and mucosal remodeling in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps associated with asthma. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2009, 151, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Shiozawa, A.; Ono, N.; Kusunoki, T.; Hirotsu, M.; Homma, H.; Saitoh, T.; Murata, J. Subclassification of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp based on eosinophil and neutrophil. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zele, T.; Claeys, S.; Gevaert, P.; Van Maele, G.; Holtappels, G.; Van Cauwenberge, P.; Bachert, C. Differentiation of chronic sinus disease by measurement of inflammatory mediators. Allergy 2006, 61, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mygind, N.; Lildholdt, T. Nasal polyps treatment: Medical management. Allergy Asthma Proc. 1996, 17, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badia, L.; Lund, V. Topical corticosteroids in nasal polyposis. Drugs 2001, 61, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Mullol, J.; Bachert, C.; Alobid, I.; Baroody, F.; Cohen, N.; Cervin, A.; Douglas, R.; Gevaert, P.; et al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology 2012, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stjarne, P.; Olsson, P.; Alenius, M. Use of mometasone furoate to prevent polyp relapse after endoscopic sinus surgery. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2009, 135, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingsor, G.; Kramer, J.; Olsholt, R.; Soderstrom, T. Flunisolide nasal spray 0.025% in the prophylactic treatment of nasal polyposis after polypectomy. A randomized, double blind, parallel, placebo controlled study. Rhinology 1985, 23, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hissaria, P.; Smith, W.; Wormald, P.J.; Taylor, J.; Vadas, M.; Gillis, D.; Kette, F. Short course of systemic corticosteroids in sinonasal polyposis: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial with evaluation of outcome measures. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, L.J.; Lewis, S.A.; Wong, C.A.; Cooper, S.; Oborne, J.; Cawte, S.A.; Harrison, T.; Green, D.J.; Pringle, M.; Hubbard, R.; et al. The impact of oral corticosteroid use on bone mineral density and vertebral fracture. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zele, T.; Gevaert, P.; Holtappels, G.; Beule, A.; Wormald, P.J.; Mayr, S.; Hens, G.; Hellings, P.; Ebbens, F.A.; Fokkens, W.; et al. Oral steroids and doxycycline: Two different approaches to treat nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirtsreesakul, V.; Wongsritrang, K.; Ruttanaphol, S. Clinical efficacy of a short course of systemic steroids in nasal polyposis. Rhinology 2011, 49, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vaidyanathan, S.; Barnes, M.; Williamson, P.; Hopkinson, P.; Donnan, P.T.; Lipworth, B. Treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis with oral steroids followed by topical steroids: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 154, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poetker, D.M. Oral corticosteroids in the management of chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps: Risks and benefits. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2015, 29, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfils, P.; Halimi, P.; Malinvaud, D. Adrenal suppression and osteoporosis after treatment of nasal polyposis. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006, 126, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, K.; Seth, R.; Abelson, A.; Betra, P.S. Prevalence of metabolic bone disease among chronic rhinosinusitis patients treated with oral glucorticoids. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2010, 24, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapucu, B.; Cekin, E.; Erkul, B.E.; Cincik, H.; Gungor, A.; Berber, U. The effects of systemic, topical, and intralesional steroid treatments on apoptosis level of nasal polyps. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 147, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broersen, L.H.A.; Pereira, A.M.; Jorgensen, J.O.L.; Dekkers, O.M. Adrenal insufficiency in corticosteroids use: Systemic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullol, J.; Obando, A.; Pujols, L.; Alobid, I. Corticosteroid treatment in chronic rhinosinusitis: The possibilities and the limits. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2009, 29, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokunaga, T.; Sakashita, M.; Haruna, T.; Asaka, D.; Takeno, S.; Ikeda, H.; Nakayama, T.; Seki, N.; Ito, S.; Murata, J.; et al. Novel scoring system and algorithm for classifying chronic rhinosinusitis: The JESREC Study. Allergy 2015, 70, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Kondo, Y.; Sunose, H.; Hirano, K.; Oshima, T.; Shimomura, A.; Suzuki, H.; Takasaka, T. Subjective and objective evaluation in endoscopic sinus surgery. Am. J. Rhinol. 1996, 10, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seino, Y.; Nanjo, K.; Tajima, N.; Kadowaki, T.; Kashiwagi, A.; Araki, E.; Ito, C.; Inagaki, N.; Iwamoto, Y.; Kasuga, M. Report of the committee on the classification and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Investig. 2010, 1, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, D.G. Practical Statistics for Medical Research; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1996; pp. 299–303. [Google Scholar]
- Delaunay, F.; Khan, A.; Cintra, A.; Davani, B.; Ling, Z.C.; Andersson, A.; Ostenson, C.G.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Efendic, S.; Okret, S. Pancreatic beta cells are important targets for the diabetogenic effects of glucocorticoids. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2094–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imatoh, T.; Sai, K.; Hori, K.; Segawa, K.; Kawakami, J.; Kimura, M.; Saito, Y. Development of a novel algorithm for detecting glucocorticoid-induced diabetes mellitus using a medical information database. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 42, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arlt, W.; Allolio, B. Adrenal insufficiency. Lancet 2003, 361, 1881–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinoff, A.D.; Hollister, J.R. Steroid induced fractures and bone loss in patients with asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 309, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
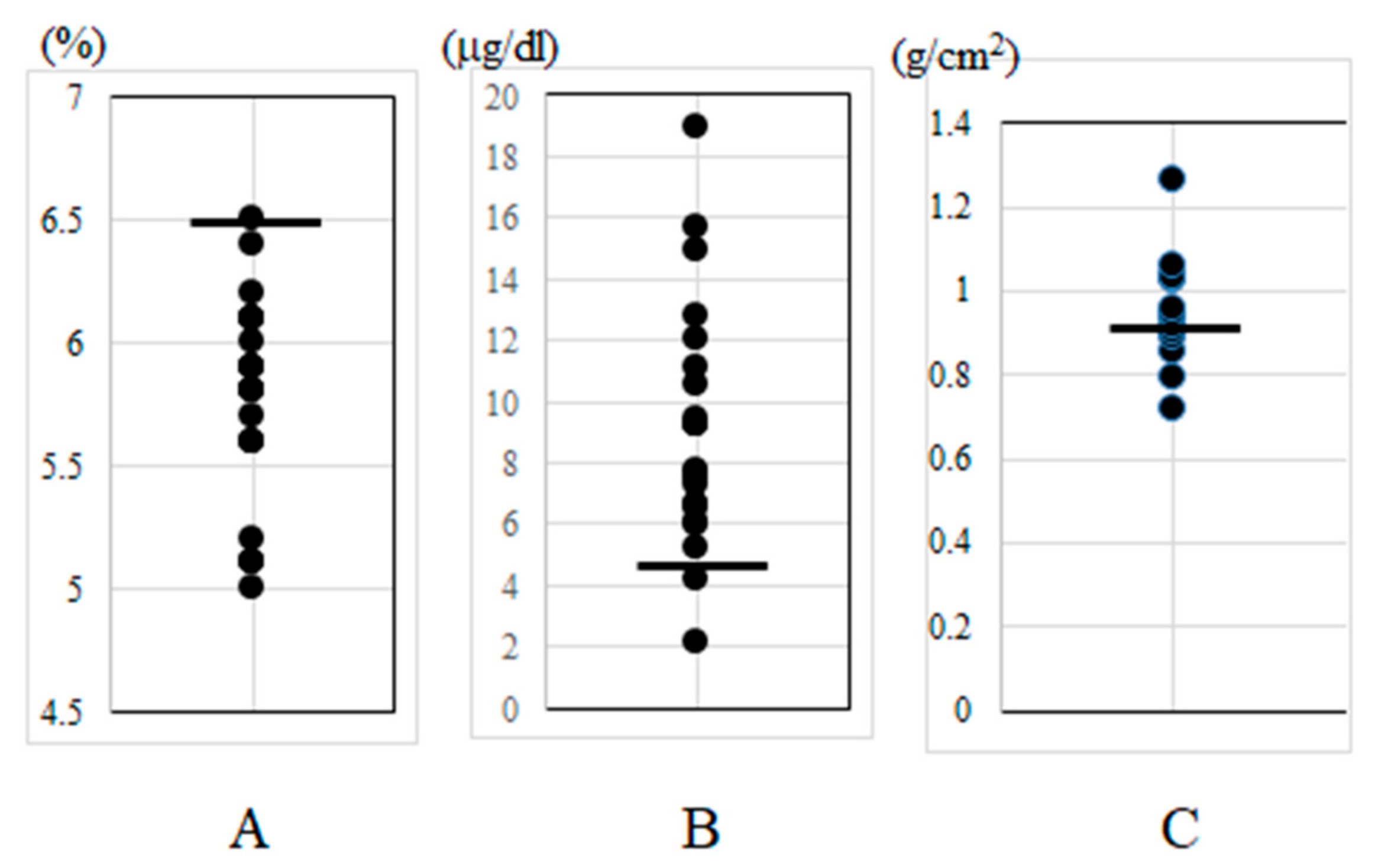
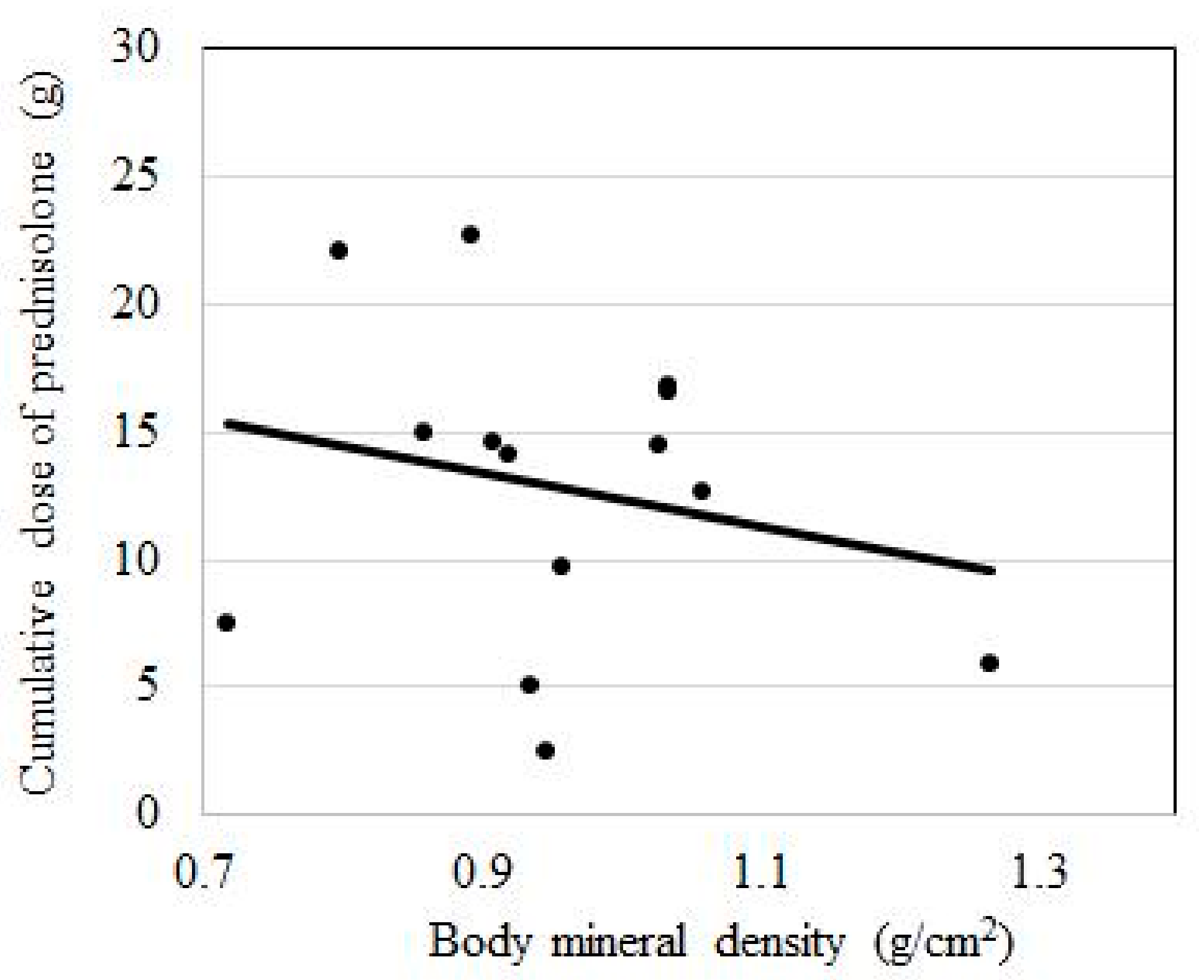
| Baseline Demographics and Clinical Information | |
|---|---|
| Male, no. (%) | 26 (60) |
| Age, mean (min., max.) | 51 (22, 73) |
| Serum eosinophil (%), mean (min., max.) | 8.7 (0.3, 19.1) |
| Total IgE (IU/ml), mean (min., max.) | 387 (18, 2288) |
| History of bronchial asthma, no. (%) | 18 (42) |
| History of allergic rhinitis, no. (%) | 10 (23) |
| History of eosinophilic otitis media, no. (%) | 3 (0.7) |
| n | Osteoroporosis(+) | Osteoroporosis(−) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 15 | 53.0 (11.5) | 50.2 (11.5) |
| Sex, women versus men | 15 | 3 vs 2 | 3 vs 7 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2, mean (SD) | 15 | 0.79 (0.08) | 1.01 (0.1) |
| Peripheral blood eosinophils, /μL, mean (SD) | 15 | 726 (430) | 942 (370) |
| Cumulative PSL dose, g, mean (SD) | 15 | 14.2 (7.6) | 11.2 (4.9) |
| Duration of PSL, mth, mean (SD) | 15 | 67.6 (36.1) | 55.0 (24.3) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Motegi, R.; Ito, S.; Homma, H.; Ono, N.; Okada, H.; Kidokoro, Y.; Shiozawa, A.; Ikeda, K. Complications of Short-Course Oral Corticosteroids for Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis during Long-Term Follow-Up. Sinusitis 2018, 3, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis3020005
Motegi R, Ito S, Homma H, Ono N, Okada H, Kidokoro Y, Shiozawa A, Ikeda K. Complications of Short-Course Oral Corticosteroids for Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis during Long-Term Follow-Up. Sinusitis. 2018; 3(2):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis3020005
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotegi, Remi, Shin Ito, Hirotomo Homma, Noritsugu Ono, Hiroko Okada, Yoshinobu Kidokoro, Akihito Shiozawa, and Katsuhisa Ikeda. 2018. "Complications of Short-Course Oral Corticosteroids for Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis during Long-Term Follow-Up" Sinusitis 3, no. 2: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis3020005
APA StyleMotegi, R., Ito, S., Homma, H., Ono, N., Okada, H., Kidokoro, Y., Shiozawa, A., & Ikeda, K. (2018). Complications of Short-Course Oral Corticosteroids for Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis during Long-Term Follow-Up. Sinusitis, 3(2), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis3020005




