A Systematic Review of the Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Adults with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
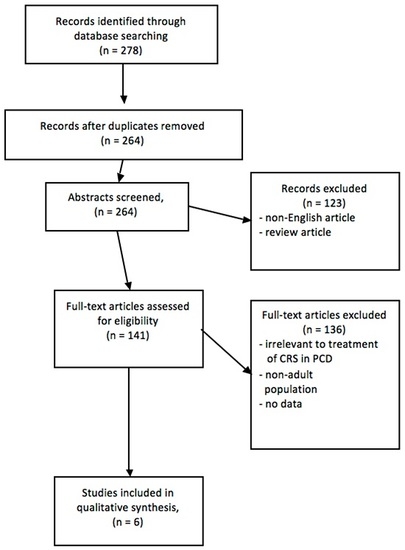
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Afzelius, B.A. A human syndrome caused by immotile cilia. Science 1976, 193, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, M.R.; Daniels, L.A.; Davis, S.D.; Zariwala, M.A.; Leigh, M.W. Primary ciliary dyskinesia. Recent advances in diagnostics, genetics, and characterization of clinical disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartagener, M. Zur pathogenese der bronkiectasien. Bronkiectasien bei situs viscerum inversus. Beitr Klin Tuberk Spezif Tuberk. 1933, 83, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgersen, J. Transposition of viscera, bronchiectasis and nasal polyps; a genetical analysis and a contribution to the problem of constitution. Acta Radiol. 1947, 28, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuhara, K.; Kawamoto, S.; Wakabayashi, T.; Belsky, J.L. Situs inversus totalis and Kartagener’s syndrome in a Japanese population. Chest 1972, 61, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.J.; Zariwala, M.A.; Ferkol, T.; Davis, S.D.; Sagel, S.D.; Dell, S.D.; Rosenfeld, M.; Olivier, K.N.; Milla, C.; Daniel, S.J.; et al. Diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of primary ciliary dyskinesia: PCD foundation consensus recommendations based on state of the art review. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2016, 51, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, J.U.; Schafer, K.; Omran, H.; Olbrich, H.; Wallmeier, J.; Blum, A.; Hormann, K.; Stuck, B.A. ENT manifestations in patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia: Prevalence and significance of otorhinolaryngologic co-morbidities. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 268, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, R. Managing upper respiratory tract complications of primary ciliary dyskinesia in children. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 12, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, M.R.; Zariwala, M.; Leigh, M. Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Clin. Chest Med. 2016, 37, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mener, D.J.; Lin, S.Y.; Ishman, S.L.; Boss, E.F. Treatment and outcomes of chronic rhinosinusitis in children with primary ciliary dyskinesia: Where is the evidence? A qualitative systematic review. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013, 3, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howick, J.; Chalmers, I.; Glasziou, P.; Greenhalgh, T.; Heneghan, C.; Liberati, A.; Moschetti, I.; Phillips, B.; Thornton, H. The Oxford Levels of Evidence. 2; Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alanin, M.C.; Aanaes, K.; Høiby, N.; Pressler, T.; Skov, M.; Nielsen, K.G.; Johansen, H.K.; von Buchwald, C. Sinus surgery can improve quality of life, lung infections, and lung function in patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanin, M.C.; Johansen, H.K.; Aanaes, K.; Høiby, N.; Pressler, T.; Skov, M.; Nielsen, K.G.; von Buchwald, C. Simultaneous sinus and lung infections in patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2015, 135, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kido, T.; Yatera, K.; Yamasaki, K.; Nagata, S.; Choujin, Y.; Yamaga, C.; Hara, K.; Ishimoto, H.; Hisaoka, M.; Mukae, H. Two Cases of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia with Different Responses to Macrolide Treatment. Intern. Med. 2012, 51, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mygind, N.; Pedersen, M. Nose-, sinus- and ear-symptoms in 27 patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia. Eur. J. Respir. Dis. 1983, 64, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka, D.; Sakamoto, N.; Ishimatsu, Y.; Kakugawa, T.; Ishii, H.; Mukae, H.; Kadota, J.; Kohno, S. Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia that Responded to Long-Term, Low-Dose Clarithromycin. Intern. Med. 2010, 49, 1437–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilos, D. Chronic rhinosinusitis in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 4, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, D.; di Cicco, M.; Giunta, A.; Amabile, G. Nasal polyposis in cystic fibrosis treated by beclomethasone dipropionate. Acta Univ. Carol. Med. 1990, 36, 220–221. [Google Scholar]
- Cimmino, M.; Nardone, M.; Cavaliere, M.; Plantulli, A.; Sepe, A.; Esposito, V.; Mazzarella, G.; Raia, V. Dornase alfa as postoperative therapy in cystic fibrosis sinonasal disease. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 131, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virgin, F.; Rowe, S.; Wade, M.; Gaggar, A.; Leon, K.J.; Young, K.R.; Woodworth, B.A. Extensive surgical and comprehensive postoperative medical management for cystic fibrosis chronic rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2012, 26, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, R.B.; King, V.V. Management of sinusitis in cystic fibrosis by endoscopic surgery and serial antimicrobial lavage: Reduction in recurrence requiring surgery. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1995, 121, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gremmo, M.L.; Guenza, M.C. Positive expiratory pressure in the physiotherapeutic management of primary ciliary dyskinesia in paediatric age. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 1999, 54, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Madsen, A.; Green, K.; Buchvald, F.; Hanel, B.; Nielsen, K.G. Aerobic fitness in children and young adults with primary ciliary dyskinesia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Morris, P.S.; Chang, A.B. Influenza vaccine for children and adults with bronchiectasis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, 3, CD006218. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C.; Singleton, R.J.; Morris, P.S.; Chang, A.B. Pneumococcal vaccines for children and adults with bronchiectasis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, 2, CD006316. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, J.S.; Behan, L.; Dunn Galvin, A.; Alpern, A.; Morris, A.M.; Carroll, M.P.; Knowles, M.R.; Leigh, M.W.; Quittner, A.L. A quality-of-life measure for adults with primary ciliary dyskinesia: QOL-PCD. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, D.S.; Greene, B.A. A treatment for primary ciliary dyskinesia: Efficacy of functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Laryngoscope 1993, 103, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BESTCILIA. Available online: http://bestcilia.eu (accessed on 16 January 2017).
| Population | Adult (>18 Years Old) Men and Women |
|---|---|
| Intervention | Treatment of sinusitis in primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) |
| Control | No comparison group |
| Outcome | Results of treatment i.e., improvement or worsening of symptoms |
| Study Design | Case Report, Case Series, Cross-Sectional, Retrospective Cohort, Prospective Single-Arm Trial |
| Study | N | Setting | Level of Evidence | Intervention | Outcome Assessment | Results | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alanin et al., 2016 | 24 | Denmark | 3 | Endoscopic Sinus Surgery | SNOT-22, spirometry, precipitins, BMI, infection status of upper and lower airways | Improvement in CRS-related symptoms, reduced lung infection | Small, lacks control group |
| Alanin et al., 2015 | 8 | Denmark | 3 | Endoscopic sinus surgery | Number of precipitins against Pseudomonas pre- and post-operatively | Reduced precipitins in ¾ patients after surgery | Small number of adults, pre and post-operative testing not performed in all patients |
| Kido et al., 2012 | 2 | Japan | 4 | Long-term macrolide therapy | Chest CT findings, FEV1, physical symptoms | Improvement of outcome assessments in one case, decline in the other | Small case series |
| Mygind et al., 1983 | 27 | Denmark | 4 | Antibiotics, nasal saline, sinus surgery, PE tube insertion | Physical symptoms | Improvement of sinonasal symptoms with antibiotics, nasal saline, and sinus surgery (Caldwell-Luc) | Case series, subjective outcome measures |
| Sommer et al., 2010 | 44 | Germany | 3 | Antibiotic treatment, sinus surgery, tympanostomy tube placement | Questionnaire of treatment history in adults with PCD | 19% needed antibiotics up to 10 times, 24% up to 30 times and 32% more than 30 times. 69% of patients underwent sinus surgery | Lack of age-specific data, non-validated questionnaire |
| Yoshioka et al., 2010 | 1 | Japan | 5 | Long-term clarithromycin | Physical symptoms, pulmonary function, arterial blood gases, chest CT findings | Improvement in all outcome assessments | Single case report, subjective outcome measures |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brunner, J.P.; Riley, C.A.; McCoul, E.D. A Systematic Review of the Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Adults with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Sinusitis 2017, 2, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis2010001
Brunner JP, Riley CA, McCoul ED. A Systematic Review of the Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Adults with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Sinusitis. 2017; 2(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis2010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrunner, Jacob P., Charles A. Riley, and Edward D. McCoul. 2017. "A Systematic Review of the Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Adults with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia" Sinusitis 2, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis2010001
APA StyleBrunner, J. P., Riley, C. A., & McCoul, E. D. (2017). A Systematic Review of the Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Adults with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Sinusitis, 2(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis2010001