Abstract
The biomechanical and optical properties of the cornea are responsible for its functional response, structural integrity and refractive function. Corneal viscoelasticity is the cornea’s ability to absorb transient increases in intraocular pressure (IOP) and constitutes a biomarker of glaucoma. The use of silicone hydrogel soft contact lenses (SiH-SCLs) can affect both corneal viscoelasticity and IOP. However, the behavior of the pure elastic and viscous components remains hidden within viscoelastic properties, and their influence and relationship with IOP in the biomechanical changes observed with short-term SiH-SCL use remains unknown. This study investigates the effects of silicone hydrogel soft contact lenses (SiH-SCLs) on corneal elasticity and viscosity and their influence on IOP over different lens wear periods: 10 or 20 consecutive days. Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA) measurements were combined with a biomechanical Standard Linear Solid Model (SLSM) to differentiate and calculate the elastic and viscous components of the cornea. The results showed that after 10 days of lens wear, elasticity and viscosity increased, with a significant reduction in IOP. After 20 days, elasticity and viscosity decreased, with a further reduction in IOP, reflecting a time-dependent effect of SiH-SCLs on corneal biomechanics. The study indicates the potential protective role of corneal viscosity against changes in IOP, which may be used for glaucoma treatment.
1. Introduction
The biomechanical and optical properties of the cornea play a fundamental role in maintaining corneal structure and shape, ocular integrity and refractive power [1]. These properties can be affected by various factors, such as intraocular pressure (IOP) [2], corneal hydration [3], and the microstructural organization of the stroma [4]. The use of soft contact lenses, and, in particular, silicone hydrogel contact lenses (SiH-CLs), has gained popularity due to their high oxygen permeability and wearing comfort. However, the impact of short-term SiH-CLs wear on corneal biomechanics and intraocular pressure remains a topic of interest. While some studies have reported that the use of SiH-CLs does not alter IOP measurements [5], other authors reported a significant influence of this type of CLs on IOP readings depending on the measurement technology [6]. Since accurate IOP measurement is essential for the diagnosis and treatment of ocular pathological conditions such as glaucoma [7], these alterations could have significant clinical implications.
In addition to its effect on IOP readings, contact lens wear has been associated with changes in corneal stiffness and thickness [8,9]. This is particularly relevant given that corneal biomechanics plays a key role in the distribution of mechanical stress along the corneal surface. Furthermore, soft contact lens wear has been shown to induce subclinical inflammatory response [10], alterations in endothelial cell morphology [11], endothelial polymegathism and pleomorfism [12] and epithelial thinning [13].
An emerging area of study is the potential applications of soft contact lenses in the treatment of glaucoma [14]. In this regard, we recently reported on the effects of short-term SiH-CL wear on corneal hysteresis and intraocular pressure [15]. While corneal hysteresis has been reported as a biomarker of glaucoma disease [16], the literature describing the effects of short-term SiH-CL wear is limited.
In glaucoma, IOP and corneal biomechanics are closely related. Recently, Xu et al. [17] reported that after IOP reduction in glaucoma treatment, a decrease in corneal stiffness is observed. In this sense, corneal hysteresis, defined as the viscous damping ability of the cornea to dissipate energy [18], is lower in patients with glaucoma compared to normal subjects [19].
However, corneal hysteresis assesses the viscoelastic property arising from the combination of elasticity and viscosity contributions that can show individual alterations while the viscoelasticity measure remains constant [20]. Recently, we reported a biomechanical model to calculate the pure elastic and viscous corneal properties and showed that corneal hysteresis is not sufficient to be employed as a risk factor of glaucoma disease, since the individual contributions of elasticity and viscosity can reverse its behavior as a function of a given IOP threshold [21]. Therefore, since these biomechanical properties change as a function of IOP, further research is needed to better understand their specific behavior in response to contact lens wear.
The working hypothesis is that SiH-CLs affect corneal biomechanics by altering corneal hydration, oxygenation and mechanical loading. SiH-CLs are capable of triggering alterations in epithelial and stromal hydration balance due to their oxygen and water permeability properties. These parameters influence collagen fiber spacing and orientation, which are major determinants of corneal stiffness and viscosity [3].
Therefore, the aim of this study was to analyze the effects of short-term SiH-CL use on the separate elastic and viscous components of corneal biomechanics and to explore their relationship with IOP over two wearing periods: after 10 and 20 days of daily wear in healthy young adults subjects.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
The investigation was designed as a prospective, longitudinal, experimental exploratory pilot study. In this work, control measurements are referred to as pre-lens wear, which is the baseline measurement, so prospective subjects were recruited and underwent baseline (pre-lens) measurements.
Participant subjects (see Section 2.2) were then split into two groups based on duration of wear: 10 or 20 consecutive days. Pre- and post-wear measurements from the same subjects were compared to identify intra-subject variation. No statistical calculation of sample size was performed, as it was exploratory in nature, and the intention was to identify initial trends and construct hypotheses for later powered studies.
2.2. Subjects
Thirty eyes of healthy young adults were recruited from students from the School of Optics and Optometry at the University of Zaragoza (Spain) who had not worn contact lenses before (see Table 1). In this study, “healthy” refers to individuals without general diseases.

Table 1.
Demographic information about the cohort of participants. M/F: male/female.
To be eligible, participants had to have myopia, hyperopia, or astigmatism. Those with a history of contact lens wear, corneal abnormalities, previous ocular surgery, dry eye syndrome, irregular astigmatism or those receiving systemic treatment known to affect the tear film stability and ocular surface were excluded.
Furthermore, those who experienced contact lens intolerance on the first day of wear were not included in the study. Table 1 summarizes the demographic information of the participant cohort.
Participants received detailed information about the purpose of the study, potential risks and possible adverse effects before providing written informed consent.
This study was evaluated by an independent ethics committee and adheres to the established principles and guidelines for the protection of human participants in biomedical research. The Ethical Committee of Research at the Health Sciences Institute of Aragon, Spain, approved the study under reference C.P.-C.I.PI20/377. All measurement procedures and data collection were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards established by the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.3. Contact Lenses Use
Silicone hydrogel soft contact lenses (SiH-SCLs) used in the study were Horizont Bio lenses provided by Tiedra Farmacéutica S.L. (Spain). They consist of a 55% water-content silicone hydrogel material with high oxygen permeability (Dk/t = 100) for providing sufficient corneal oxygenation upon extended wear during the day. The lenses were characterized by an elastic modulus of 0.6 Mpa and an aspheric optical design. The lenses were selected for mechanical characteristics and use for short-term wear studies (since they are monthly replacements), as well as for commercial availability and clinical use.
All the subjects used SiH-SCLs for 8 h a day for either 10 consecutive days (group I) or 20 consecutive days (group II), as shown in Table 1. The lens parameters of base curve, diameter and power were selected for each subject according to biometric data described in Section 2.4. Further details on product specifications are available from the manufacturer’s official website: https://optica.tiedra.net/ (accessed 9 May 2025).
2.4. Biometric and Biomechanical Assessment
Routinely, prior to biometry, the anterior pole of the eye is examined with a slit lamp to check the ocular surface before prescribing contact lenses.
The SiH-SCLs prescription required ocular parameters such as total diameter, base curve radius and ocular refraction. Ocular refraction was assessed with an open-view autorefractometer (Grand Seiko, WAM_5500, Grand-Seiko Co., Ltd., Nagano, Japan); corneal keratometry and central corneal thickness (CCT) were measured with a Dual Placido-Scheimpflug corneal analyzer (Galilei G2; Ziemer Ophthalmic Systems AG, Port, Switzerland); and intraocular pressure (IOP), elasticity and viscosity were determined using the Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA, Reichert Instruments, Depew, NY, USA) and a previously described methodology [21].
Although biometric measurements were used for contact lens fitting, biomechanical data were processed to obtain the intraocular pressure (IOP), corneal elasticity (E) and viscosity (ɳ). While IOP is directly provided by the ORA’s instrument, E and ɳ are computed by applying a previously reported Standard Linear Solid Model [21] to the ORA applanation/pressure curves (insets in Figure 1). The experimental protocol started with a pre-lens baseline dataset for both participant groups. Before starting SiH-SCLs wear, all participants were measured with the ORA device and then IOP, E and ɳ were established as a baseline. Immediately after the baseline measurements, subjects were instructed in the daily handling and manipulation of their contact lenses by a clinical optometrist, beginning the corresponding wearing period. Figure 1 schematizes the experimental procedure: after 10 and 20 days of respective SiH-SCL use, each subject’s cornea was analyzed with the ORA device immediately after the CL removal. Then, IOP, E and ɳ parameters were recalculated for each group.
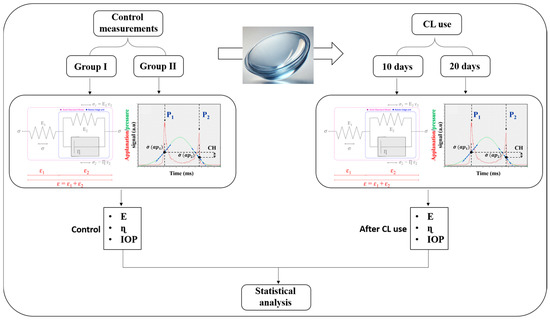
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the experimental protocol.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The analysis consisted of the Shapiro–Wilk test for data normality and, subsequently, a One-Way Repeated Measures Analysis of Variance (One-Way RM ANOVA) was performed to establish statistical differences between the study groups. Spearman’s correlations were also performed to determine or discard relationships between different biomechanical parameters. Graphical representations and statistical analyses were performed with Origin Lab scientific software 2024b (Origin Lab Corp., Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results
The 30 eyes analyzed corresponded to a young adult population with a mean age of 22.87 ± 4.14 years. The next subsections analyze the effect of SiH-SCL wear on corneal biomechanics in two temporal groups. Although not graphically indicated in the Results Section, no relationships were found between participants’ refractive error and corneal biomechanics (i.e., IOP, elasticity and viscosity).
3.1. Biomechanical Changes After 10 Days of SiH-SCL Use
Figure 2 shows box plots comparing the changes in elasticity (Figure 2a), viscosity (Figure 2b), intraocular pressure (Figure 2c) and central thickness (Figure 2d) induced by the use of SiH-SCLs over the shorter period of 10 days. Statistical analysis revealed that after 10 days of SiH-SCL use, corneal elasticity and viscosity changed (increased) significantly. Furthermore, IOP was significantly reduced. However, although a slight increase in central thickness (Figure 2d) was observed, this was not relevant.
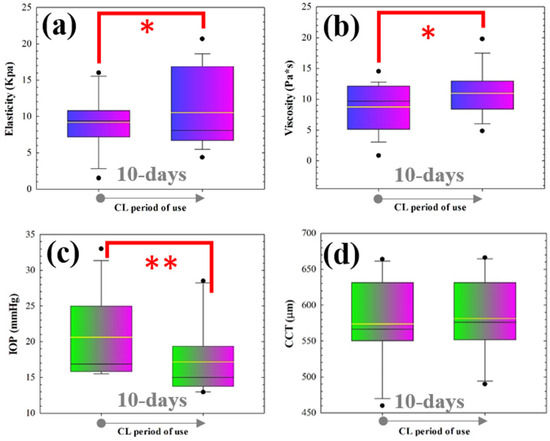
Figure 2.
Box diagrams of elasticity (a), viscosity (b), intraocular pressure (c) and central corneal thickness (d) comparing pre-lens wear measurements and those after the wearing period of 10 days. For each box, the median (central line inside each box), the Q1 and Q4 quartiles (lower and higher borders of each box, respectively) and maximum and minimum values (whiskers) are shown. (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.005).
Figure 3 shows the effect of SiH-SCLs use on the individual parameters E, ɳ and IOP. However, it is important to determine whether these variations in corneal biomechanics correlate with intraocular pressure. Figure 3 shows the correlations of E (Figure 3a) and ɳ (Figure 3b) with IOP, respectively. Spearman’s correlation coefficient revealed that IOP is influenced by variations in corneal elasticity and viscosity.
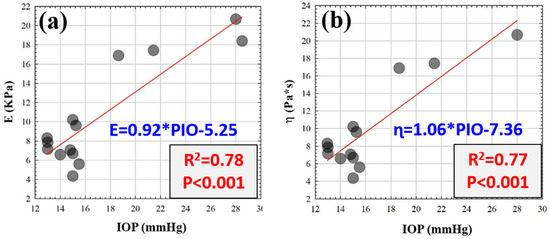
Figure 3.
Elasticity (a) and viscosity (b) as a function of the intraocular pressure (IOP). Red lines correspond to the linear fittings.
According to previous results, if, on the one hand, E and ɳ increase while IOP decreases after 10 days of SiH-SCL wear, and on the other hand, E and ɳ increase with IOP, there should be an inter-correlation between the three parameters, such that the joint increase in elasticity and viscosity results in a relaxation of IOP. This effect is illustrated in Figure 4. Contour plots plot viscosity versus the elasticity as a function of the IOP before (pre-lens wear measurements) (Figure 4a) and after using SiH-SCLs (Figure 4b) for 10 days.
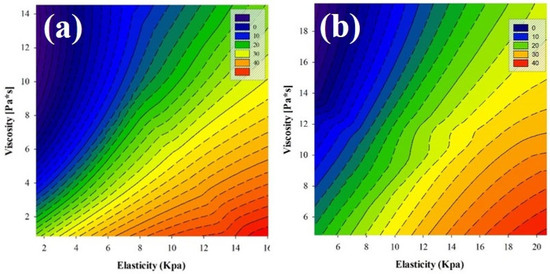
Figure 4.
Contour plots of viscosity versus the elasticity as a function of the IOP before (pre-lens wear) (a) and after using SiH-SCLs (b) for 10 days. The dashed lines represent the isobars for intraocular pressure. The colorbar is shown in mmHg units.
Multiple linear regression was performed on the data shown in Figure 4b. The analysis revealed that IOP could be predicted from a linear combination of E and
for both the baseline measurements (pre-lens wear) (R2 = 0.98, p < 0.001, Equation (1)) and group I (R2 = 0.92, p < 0.0001, Equation (2)).
These multiple regression analyses revealed that E and ɳ increase together to preserve the IOP.
3.2. Biomechanical Changes After 20 Days of CL Use
Figure 5 shows the reversal of the biomechanical parameters after 20 days of CL wear compared to Group I. As shown in the box plots, corneal elasticity (Figure 5a) and viscosity (Figure 5b) are significantly reduced after CL wear. Furthermore, the significant change (decrease) in IOP (Figure 5c) was more accused than in group I. Regarding the central thickness (CCT, Figure 5d), a more pronounced edematization is observed than in group I, but again without statistical significance.
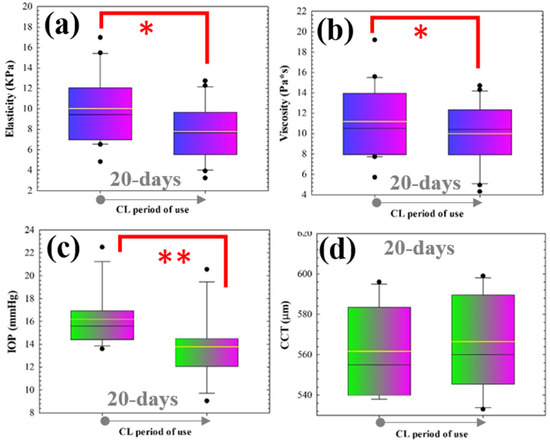
Figure 5.
Box diagrams of elasticity (a), viscosity (b), intraocular pressure (c) and central corneal thickness (d) comparing baseline (pre-lens wear) measurements and those after the wearing period of 20 days. For each box, the median (central line inside each box), the Q1 and Q4 quartiles (lower and higher borders of each box, respectively) and maximum and minimum values (whiskers) are shown. (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.005).
Similarly to group I, elasticity and IOP showed a positive correlation, as shown in Figure 6a. However, after 20 days of wear, corneal viscosity became independent of the intraocular pressure (Figure 6b). That is, any influence of corneal biomechanics in IOP is due to purely elastic corneal fluctuations.
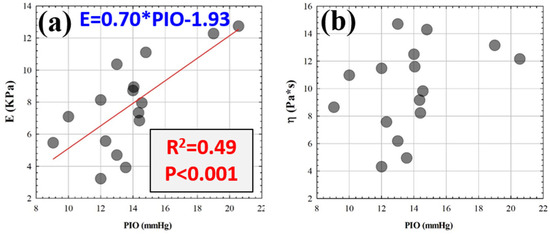
Figure 6.
Elasticity (a) and viscosity (b) as a function of the intraocular pressure (IOP) after 20 days of CLs wear. The red line corresponds to the best linear fitting.
4. Discussion
This work expands on a previously published study on corneal biomechanical alterations due to short-term wear of silicone hydrogel soft contact lenses [15]. That study revealed how IOP is significantly reduced while corneal hysteresis, a measure of viscoelasticity provided by the ORA device, increases.
Although CH has been reported as a biomarker of glaucoma disease [16], it reflects the cornea’s ability to absorb or dissipate energy and does not discriminate between constituent elementary biomechanical properties, such as purely elastic and viscous components.
Recently, a biomechanical Standard Linear Solid Model [21] was developed for application to ORA measures and, subsequently, to calculate the E and ɳ components separately. This model allowed us to complete a more comprehensive study of the effects on the elastic and viscous properties of the cornea, which could be masked in a global assessment of viscoelasticity.
The results of this pilot study indicate that the use of soft silicone hydrogel contact lenses (SiH-SCLs) has a considerable effect on corneal elastic and viscous properties and intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements. Specifically, at 10 days of wear, both corneal viscosity and elasticity were highly significantly increased, while IOP was highly significantly reduced. However, at 20 days of wear, there was a decrease in corneal viscosity and elasticity, with a larger reduction in IOP.
These findings describe the temporal dependence of the SiH-SCL effect on corneal biomechanics and intraocular pressure. Previous studies have proven that soft contact lenses can temporarily change corneal curvature and induce warpage [22,23].
Another relevant finding is that the use of SiH-SCLs induces progressive and reversible changes in corneal biomechanics. In this regard, the modulation of corneal viscoelasticity has been investigated in both short- and long-term soft contact lens wear [15,24].
These results are consistent with previous studies indicating that contact lens wear can induce transient changes in corneal stress distribution [25]. However, we believe this is the first study to show the influence of soft contact lens use on the elastic and viscous properties of the cornea separately, and their relationship with IOP over short periods of wear.
The positive correlation observed between corneal elasticity and IOP in both groups aligns with studies that have highlighted the influence of corneal stiffness on intraocular pressure dynamics [17,26].
In our study, we observed two distinct phases: first, after 10 days, both elasticity and viscosity increased significantly and correlated with a decrease in IOP. That is, while IOP increases with elasticity, the viscous component appears to play a compensatory role for the increase in IOP, even reducing it in the early stages of SiH-CL use.
On the other hand, the second phase was observed during the longer period of use, where both elasticity and viscosity decreased with intraocular pressure. However, after 20 days of use, corneal viscosity no longer correlated with IOP, while the reduction in IOP linearly correlated with a decrease in pure elastic corneal property. Therefore, the viscous component seems to play a protective role against increased IOP.
Regarding the corneal pachymetry, mild edema was observed in both study groups (more pronounced in group II), but this increase was not statistically significant in either group. Therefore, the observed biomechanical changes are not influenced by an inflammatory process associated with corneal edema.
Finally, our study included subjects with myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism. Attempts have been made to correlate the refractive error with the elastic and viscous corneal properties, but the results have been negative.
Some of the methodological limitations of the study need to be mentioned. The Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA), used widely and clinically tested, could still be under the influence of the status of corneal thickness, hydration, or positional measurement and hence subject to variance. Secondly, biomechanical interpretation by Standard Linear Solid Model (SLSM), although convenient to separate the viscous from elastic contributions, is based on simplifying hypotheses related to the material behavior of the cornea. Real corneal tissue additionally possesses anisotropy and nonlinear viscoelasticity unaccounted for by this theory. Despite such shortcomings, the technique is a convenient, non-invasive assessment of biomechanical properties of clinical value. Therefore, interpretations must be considered preliminary given the study’s pilot nature and limitations.
5. Conclusions
This study describes corneal biomechanical changes in a time-dependent manner observed after short-term SiH-SCL wear in a pilot experimental study. Increased elasticity and viscosity of the cornea shortly after 10 days of wear and decreased parameters after 20 days were observed. Concurrently, IOP decreased significantly and correlated with corneal elasticity.
These preliminary results may be of clinical interest to contact lens wearers in the evaluation of IOP, particularly in glaucoma treatment. The time-dependent change in corneal biomechanical values shows that lens wear duration needs to be considered in clinical tonometry interpretations. These findings support the need for larger, controlled studies to validate their clinical relevance.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated in this study are shown in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to warmly thank the company “TIEDRA FARMACEUTICA S.L”. (Spain) for the donation of all contact lenses required in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ávila, F.J.; Marcellán, M.C.; Remón, L. On the Relationship between Corneal Biomechanics, Macrostructure, and Optical Properties. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, R.; Zamani, M.H.; Eslami, Y.; Fakhraei, G.; Tabatabaei, M.; Esfandiari, A.R. Comparing Corneal Biomechanics and Intraocular Pressure between Healthy Individuals and Glaucoma Subtypes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 82, 104677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theo, G.; Seiler, P.; Shao, P.; Engler, M.; Beck, E.; Kochevar, I.E.; Yun, S.H. Corneal Hydration and the Relation to the Biomechanical Properties. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 4333. [Google Scholar]
- Studer, H.; Larrea, X.; Riedwyl, H.; Büchler, P. Biomechanical Model of Human Cornea Based on Stromal Microstructure. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; De Wit, D.; Saleh, G. Applanation Tonometry in Silicone Hydrogel Contact Lens Wearers. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fırat, P.; Cankaya, C.; Doganay, S.; Cavdar, M.; Duman, S.; Ozsoy, E.; Koc, B. The Influence of Soft Contact Lenses on the Intraocular Pressure Measurement. Eye 2012, 26, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, F.; Lira, M. Intraocular Pressure Measurement: A Review. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2022, 67, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Pflugfelder, S.C. The Effects of Long-Term Contact Lens Wear on Corneal Thickness, Curvature, and Surface Regularity. Ophthalmology 2000, 107, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyman, A.; Ghoreishi, M.; Hashemi-Estabragh, S.S.; Mirmohammadkhani, M.; Mohammadinia, M.; Pourazizi, M. Corneal Biomechanical Properties after Soft Contact Lens Wear Measured on a Dynamic Scheimpflug Analyzer: A Before and After Study. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2021, 44, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliman, N.H.; Morgan, P.B.; MacDonald, A.S.; Maldonado-Codina, C. Subclinical Inflammation of the Ocular Surface in Soft Contact Lens Wear. Cornea 2020, 39, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd-Ali, B.; Chen, L.Y. The Morphology of Corneal Endothelial Cells in Long-Term Soft Contact Lens Wearers in Kuala Lumpur. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2021, 44, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutwaly, R.F., Sr. Corneal Endothelial Polymegathism and Pleomorphism Induced by Daily-Wear Soft Contact Lenses. Cureus 2024, 16, e74187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdolalizadeh, P.; Karimi, M.; Latifi, G.; Nouri, L.; Hashemian, M.N.; Hashemian, H.; Mehrpour, M.; Alipour, F. Role of Different Types of Contact Lenses in Epithelial Thickness. Eye Contact Lens 2022, 48, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.J.; Meyer, D.; Park, W.; Lee, S.A.; Dai, Y.; Kim, B.; Moon, H.; Shah, J.V.; et al. Smart Soft Contact Lenses for Continuous 24-Hour Monitoring of Intraocular Pressure in Glaucoma Care. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcellán, M.C.; Remón, L.; Ávila, F.J. Corneal Hysteresis and Intraocular Pressure Are Altered in Silicone-Hydrogel Soft Contact Lenses Wearers. Int. Ophthalmol. 2022, 42, 2801–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimprich, L.; Diedrich, J.; Bleeker, A.; Schweitzer, J.A. Corneal Hysteresis as a Biomarker of Glaucoma: Current Insights. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Fan, Y.; Chong, I.T.; Yu, K.; et al. The Impact of Intraocular Pressure Changes on Corneal Biomechanics in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2025, 269, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deol, M.; Taylor, D.A.; Radcliffe, N.M. Corneal hysteresis and its relevance to glaucoma. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2015, 26, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sit, A.J.; Chen, T.C.; Takusagawa, H.L.; Rosdahl, J.A.; Hoguet, A.; Chopra, V.; Richter, G.M.; Ou, Y.; Kim, S.J.; WuDunn, D. Corneal Hysteresis for the Diagnosis of Glaucoma and Assessment of Progression Risk: A Report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology 2023, 130, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, D.H.; Roberts, C.J.; Litsky, A.S.; Weber, P.A. A Viscoelastic Biomechanical Model of the Cornea Describing the Effect of Viscosity and Elasticity on Hysteresis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 3919–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, F.J.; del Barco, Ó.; Marcellán, M.C.; Remón, L. A Comprehensive Study on Elasticity and Viscosity in Biomechanics and Optical Properties of the Living Human Cornea. Photonics 2024, 11, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çavdarlı, C.; Topçu-Yılmaz, P. Does Long-Term Soft Contact Lens Wear Affect Corneal and Anterior Chamber Parameters? Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 48, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayess, Y.; Arej, N.; Abdel Massih, Y.; Antoun, J.; Waked, N. Influence of Soft Contact Lens Material on Corneal Warpage: Prevalence and Time to Resolution. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 53, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radaie-Moghadam, S.; Hashemi, H.; Jafarzadehpur, E.; Yekta, A.A.; Khabazkhoob, M. Corneal Biomechanical Changes Following Toric Soft Contact Lens Wear. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2016, 11, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramasubramanian, D.; Hernández-Verdejo, J.L.; López-Alonso, J.M. Influence of Contact Lens Parameters on Cornea: Biomechanical Analysis. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, X. Corneal Stiffness Affects IOP Elevation During Rapid Volume Change in the Eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 2224–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).