Abstract
In order to break the diffraction limit and improve the imaging resolution of optical microscope, in this article, we theoretically deduced the influence of phase difference on imaging resolution under coherent illumination. As the phase difference increased, the resolution improved gradually. Inspired by this conclusion, a super-resolution optical imaging system based on phase modulation was proposed and simulated. An optical mask was designed to generate additional phase difference for the adjacent area at the sample’s surface, and the influence of its structural parameters was analyzed numerically. The simulation results preliminarily confirm the feasibility of this scheme, laying the foundation for a more optimal and comprehensive super-resolution imaging scheme. Due to its advantages of high resolution, a wide field of view, and being compatible, this non-fluorescence super-resolution imaging scheme is worthy of further research and application.
1. Introduction
Lateral resolution is the most important performance parameter of optical microscopes. However, due to the diffraction limit, it is difficult for the resolution to overcome the half wavelength (~200 nm) order, which also limits the application of optical microscopy in various nano-imaging and nano-detection fields. To break through the diffraction limit, a variety of super-resolution imaging technologies for fluorescence and non-fluorescence microscopy have been developed. In the field of fluorescence microscopes, stimulated emission depletion microscopy [1,2] and stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy [3,4] have improved the imaging resolution to the nanometer level by controlling the luminescence of fluorescent molecules, which has greatly promoted the development of biomedical science. For non-fluorescence microscopy, many super-resolution imaging schemes, such as point spread function engineering [5,6], super oscillatory lenses [7,8], and microsphere-assisted nanoscopes [9,10,11], have been proposed to reduce the point spread function of the microscopic system based on light field modulation. Some others are based on the collection of evanescent waves in the near-field, such as near-field scanning optical microscopy [12] and optical super-lens [13]. There are also some other technologies based on spatial spectrum reconstruction and spatial frequency shift imaging, such as structured illumination microscopy [14,15] and near-field evanescent-wave illumination spatial-frequency-shift super-resolution microscopy [16,17,18,19]. Among the above super-resolution imaging technologies, each one has its own advantages, disadvantages, and fields of application, and there is no universal solution. Therefore, it is still urgent to explore new super-resolution imaging mechanisms and to make them more universal.
Compared to incoherent illumination, coherent illumination is rarely used in conventional optical microscopy. Firstly, interference is likely to occur during coherent illumination, which seriously affects the imaging quality. Secondly, under coherent illumination, its resolution is lower than that of incoherent illumination, according to Rayleigh criterion. However, as long as the phase and polarization of the incident light are fully modulated, sub-wavelength resolution can also be achieved under coherent illumination. In this article, we theoretically analyzed the influence of the phase difference between two coherent dipole sources on the imaging resolution of microscope, and proposed a new super-resolution imaging scheme based on this conclusion. Using our complete microscope imaging simulation model, we verified the effectiveness and feasibility of this super-resolution scheme, which can provide a new alternative for nano-imaging.
2. Theoretical Analysis and Simulation Model
2.1. Theoretical Analysis
According to Rayleigh criterion, when the central maximum of one diffraction spot coincides with the first-order dark stripe of the other diffraction spot in space, the two object points can be distinguished exactly. The above derivation process is based on the case that these two object points are considered to be two incoherent light sources. But if they are coherent, their diffraction spots at the image plane are also coherent, so the total intensity is the interference result of these two diffraction spots. Now, we will deduce the intensity distribution of diffraction spots at the image plane for two incoherent and coherent dipoles, respectively.
Assuming that the optical aperture of the imaging system is circular, according to the formula of Fraunhofer diffraction, the intensity of the diffraction spot of a dipole source at the image plane can be expressed as follows:
where I0 is the central intensity of the diffraction spot; J1 is a first class first order Bessel function; k is the wave vector of incident light, k = 2π/λ; a is the radius of optical aperture; ρ is the radial coordinate in object space; and z is the distance from the diffraction aperture to the image plane. To simplify this formula, we let x = kaρ/z, so that Δx = kaΔρ/z; then, the formula can be re-expressed as follows:
where x is a dimensionless quantity, which corresponds to each ρ value, one by one. Therefore, the intensity distribution at the image plane of two incoherent dipole sources separated by Δρ can be expressed as follows:
which is the direct sum of these two diffraction spots. However, if these two dipole sources are coherent, the light intensity distribution at the image plane is determined by the superposition of the amplitudes of two spots, as follows:
where the ϕ is the phase difference between these two dipole sources. If we set ϕ as 0, π/2, and π, respectively, and take Δx = 3.833, the light intensity distribution curves can be plotted for the above three cases, as shown in Figure 1a. When ϕ = 0, the light intensity is a single peak curve, so that these two dipole sources cannot be distinguished; when ϕ = π/2, the light intensity is a double-peak curve with a minimum value of 0.73, which means these two dipole sources can be marginally resolved according to the Rayleigh criterion; when ϕ = π, the light intensity plot is squeezed and the two peaks are more uplifted with a central value of 0, which means the resolution can be improved continuously. To explore the resolution limit in this case, we reduce Δx gradually, and plot the light intensity curves in Figure 1b. It can be seen that, as Δx decreases continuously, the light intensity distributions are always double-peak curves with center intensity of zero, but the intensity of two peaks will decrease gradually, and the center position of the peaks will move toward slowly. This means that, as long as the phase difference between the two dipole sources is π, no matter how close they are, they can be resolved. Therefore, the resolution limit can be determined by the signal-to-noise ratio of the actual imaging system.
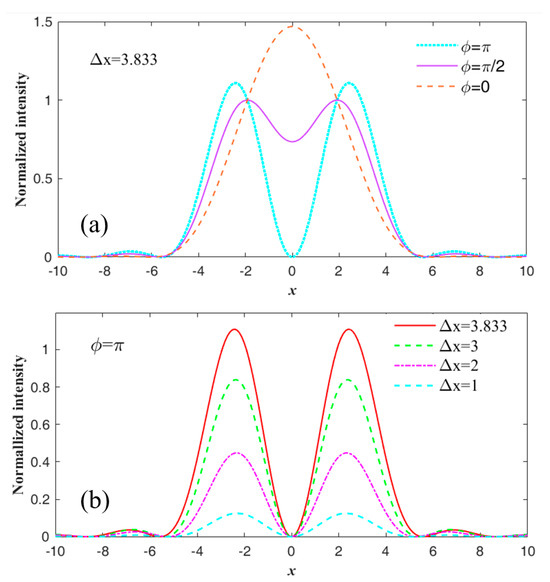
Figure 1.
Light intensity distribution of two coherent dipole sources’ diffraction spots at the image plane. (a) The separation of two dipoles remains constant, while their phase difference changes from 0, to π/2, and to π; (b) The phase difference between two dipoles remains π, while their separation decreases.
From the above calculation, the phase difference between two dipole sources greatly affects the resolution limit of microscopic system. However, for conventional imaging systems, the imaging target can be seen as a passive light source due to the reflection and scattering of the incident light. The phase of each object point depends on the optical path from the point to the light source. Therefore, the phase difference between two adjacent points depends on the spatial distance between them; that is, there is no sudden change in phase difference between them, so its resolution limit follows the Rayleigh criterion for incoherent illumination, as 0.61λ/NA, where the NA represents the numerical aperture of objective lens. To make use of the above conclusion, we propose a novel super-resolution imaging scheme for coherent illumination, in which the phase difference between two adjacent object points is modulated actively. Therefore, the originally indistinguishable two points can be resolved under this imaging system, thereby achieving super-resolution imaging. In the following sections, we will verify the above conclusion and prove the feasibility of this scheme.
2.2. Simulation Model
The imaging process of a microscope can be divided into three steps: firstly, the interaction between the illumination light and the imaging target, which forms a near-field light field around sample surface; secondly, the projection of the near-field light field from sample surface to the focal plane of objective lens; and, finally, the propagation of the light field at the focal plane to the image plane, passing through the lens group, and imaging at the image plane, as illustrated in Figure 2. The interaction between the incident light field and the nano-structures at sample surface can be simulated using the finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) algorithm; the far-field projection from the near-field monitor to the focal plane can be calculated by the angular spectrum theory; and, finally, the propagation from focal plane to image plane can be calculated using Chirp-Z transform.
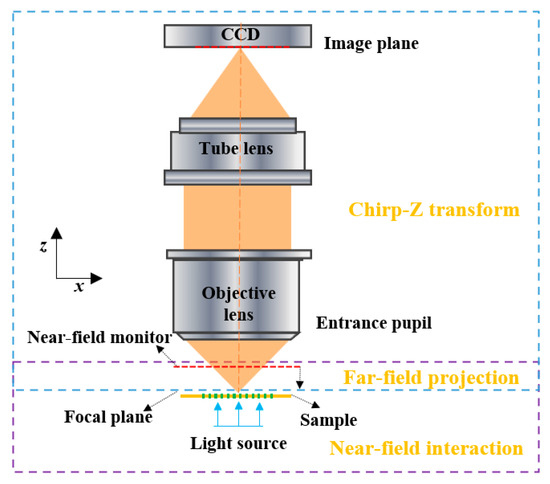
Figure 2.
Simulation model for a microscopic imaging system. The incident light interacts with the nano-structures on the sample’s surface and forms a near-field light field containing evanescent waves, which could be projected to the focal plane of objective lens and collected by the CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera at image plane.
In order to verify the correctness of the above imaging model, firstly, two polarized dipoles along x direction with the wavelength of 500 nm are used to demonstrate the imaging resolution of the microscope. The two dipoles are located at the focal plane of the objective lens and separated by a distance d along x direction, and they have the same wavelength, phase, polarization, and intensity, as shown in Figure 3a. Here, an objective lens with the highest numerical aperture (NA = 0.9) is selected, whose resolution is closest to the ideal diffraction limit. When d = 500 nm, they are clearly distinguishable, and the imaging results are shown in Figure 3b; when d = 450 nm, the two diffraction spots overlap slightly in space, but they are still distinguishable, as shown in Figure 3c; when d = 400 nm, the two diffraction spots at the image plane have overlapped completely, and they are no longer distinguishable, as illustrated in Figure 3d. This yellow-blue pseudo color figure shows the normalized light intensity distribution on the image plane. The closer to yellow, the greater light intensity, and the closer to blue, the smaller light intensity. The following simulated imaging results are the same, so we have omitted their respective scales and labels. Obviously, the minimum resolvable distance for this objective lens is around 450 nm, which is consistent with the diffraction limit of coherent illumination.
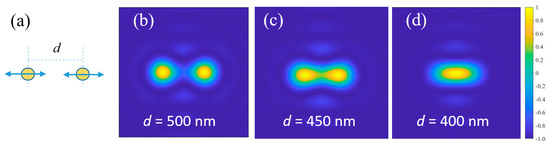
Figure 3.
Image results of two coherent dipole sources with same amplitude and same phase, but different separations. (a) Schematic diagram of two dipoles; (b) the two dipoles are distinguishable when the separation is 500 nm; (c) the two dipoles are marginally resolved when the separation d = 450 nm; (d) the two dipoles are indistinguishable when d = 400 nm.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Optical Phase on the Diffraction Limit
Firstly, we analyze the influence of phase on the resolution limit with the above simulation model and same parameters. When the two x dipoles are separated by 400 nm and set with the same optical phase, they are indistinguishable, as shown in Figure 4a; if other parameters remain unchanged and only the phase difference between the two dipoles is set to π/3 radians, the two diffraction spots on the image plane can be barely distinguished, as shown in Figure 4b; if the phase difference is set to 2π/3, these two spots can be clearly resolved, as shown in Figure 4c; and, when the phase difference is set to π, the two spots are completely divided with zero light intensity at the center point of these two, which means the best resolvable effect, as shown in Figure 4d. The same results are found using theoretical calculations; the imaging resolution gradually improves as the phase difference between two dipoles increases, and reaches the best resolution when the phase difference reaches π.
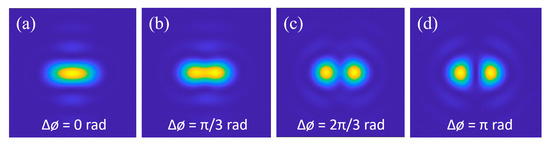
Figure 4.
Image results of two dipole sources with different phase differences, (a) 0, (b) π/3, (c) 2π/3, and (d) π, respectively, which indicates the resolution improvement with phase modulation.
The above results indicate that the light phase is very important and sensitive to the resolution limit of a microscope under coherent illumination. Therefore, in order to apply this conclusion for resolution improvement, the key is to find a feasible method to modulate the phase of each point at imaging target actively.
3.2. Super-Resolution Imaging System Based on Phase Modulation
To realize the accurate modulation of light phase for each point on a sample’s surface, an optical mask with nano-structures is applied. The schematic diagram of this super-resolution microscopic imaging system is illustrated in Figure 5, which has an additional optical mask when compared to a conventional microscope. The function of this optical mask is to provide a particular optical path difference for adjacent object points, thereby generating an additional phase difference between adjacent object points. The optical mask consists of a transparent substrate and nano-structures. The thickness h of the nano-structures is determined by the incident wavelength λ and the refractive index n of the nano-structures, namely h = λ/2(n − 1), which could ensure that the adjacent two object points have a particular phase difference of π.
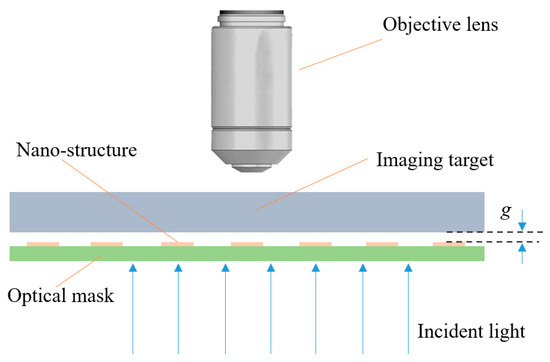
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of the super-resolution imaging system based on phase modulation. After the incident light passes through the optical mask, a specific phase difference can be obtained in adjacent areas. Thus, by using this phase-modulated light field to illuminate the sample in near-field, the two originally indistinguishable object points on the sample surface become distinguishable.
Typically, we use nano-grating structures to demonstrate the modulation of light phase, as shown in Figure 6a. A plane wave with a wavelength of 500 nm was set as the incident light, and the grating structures are composed of SiO2 substrate and a grating layer with a refractive index of 2, which has a period of 400 nm and a thickness of 250 nm. After passing through the substrate and the grating layer, the light rays reach the near-field monitor, and the light phase distribution at this monitor is demonstrated in Figure 6b. The phase difference between gratings and grooves is around π, which matches the theoretical value very well.
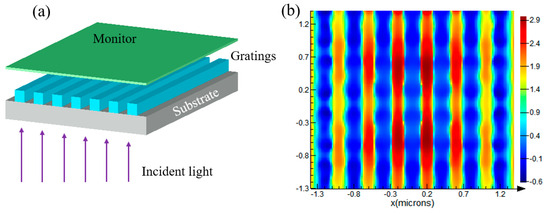
Figure 6.
Generation of phase difference through grating structures. (a) Schematic diagram; (b) light phase distribution on the near-field monitor.
To numerically verify the effectiveness of this scheme, we used a metal film etched with two-hole or three-bar structures as a transmission sample. The central distance between adjacent holes or lines is 400 nm, as shown in Figure 7a,e. When illuminating it with a plane wave (λ = 500 nm) and collecting results with an objective lens (NA = 0.9), neither the two-hole structure nor three-bar structure can be clearly distinguished, as shown in Figure 7b,f. If the optical masks, shown in Figure 7c,g, are installed below the sample, which ensures that the adjacent holes or lines can obtain a phase difference of π, then the originally indistinguishable two-hole and three-bar structures now can be clearly resolved, as shown in Figure 7d,h.
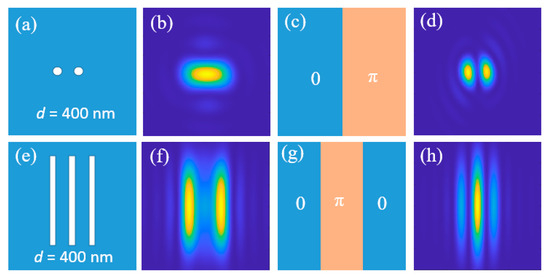
Figure 7.
Comparison of the imaging results for two-hole and three-bar structures without and with optical mask. (a,e) are the nano-structures on the sample’s surface; (b,f) are the imaging results without optical masks; (c,g) are the optical masks designed; (d,h) are the imaging results with these optical masks, which shows the resolution improvement with the phase modulation of incident light.
In the practical imaging process, there are two key parameters that should be investigated carefully prior to the widespread use of this scheme. The first parameter is the gap between the optical mask and the sample, denoted by g, which significantly influences the phase difference, as the light field changes continuously in the process of propagation from the sample surface to the far-field. Here, we use four near-field monitors to record the phase distribution above the grating structures, and the gap is set to 0 nm, 100 nm, 200 nm, and 300 nm, respectively. The recorded phase distributions are shown in Figure 8a–d, where the phase difference Δϕ gradually decreases with the increasing of the gap. When the imaging target of the three-hole structure with a period of 400 nm is located at these positions of the near-field monitors, the imaging results obtained are illustrated in Figure 8e–h. As the phase difference between two adjacent holes decreases, the imaging results deteriorate gradually, until the gap is 300 nm, at which point the three holes are completely indistinguishable. Therefore, a non-contact imaging mode is possible, but the gap between the optical mask and the sample’s surface should be less than half a wavelength.
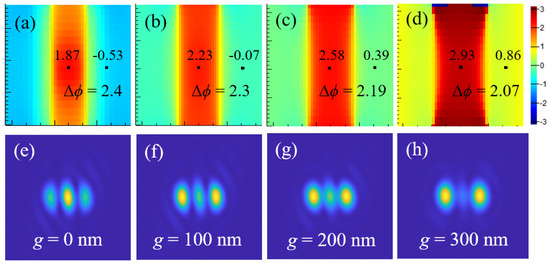
Figure 8.
The phase difference decreases as the gap increases. (a–d) Phase distributions at the four near-field monitors; (e–h) imaging results of the three-hole structure when the sample is located at the positions of four monitors, respectively. As the gap increases, the phase difference in the light field gradually decreases, so the imaging resolution also gradually decreases.
Another parameter is the dislocation between the phase boundary of the optical mask and the nanostructure at the imaging target, also known as the relative position of the phase boundary and the nanostructure. Here, five cases are considered: when the boundary is on the left side of the left hole; when the boundary is in the center of the left hole; when the boundary is on the right side of the left hole; when the boundary is in the center of the two holes; and when the boundary is on the left side of the right hole, as shown in Figure 9a–e, k–o. If the two holes are separated by 300 nm, they are unresolvable without the optical mask. Using an optical mask with π phase difference, we can obtain a series of imaging results by moving the phase boundary to the five particular positions given above, as shown in Figure 9f–j. Only when the two holes are on the same side of phase boundary are the two indistinguishable, which is consistent with the results obtained without an optical mask. In the remaining cases, the two are either barely distinguishable or completely distinguishable. For the two holes that can be resolved originally (separated by 500 nm), the imaging results do not change much with the assistance of the optical mask, as shown in Figure 9p–t. The above example shows that, for the structures that can be resolved originally, the phase modulation will slightly change the light intensity of its image, but will not make it unresolvable; for structures that cannot be distinguished, there is a great possibility to make them resolvable.

Figure 9.
Influence of phase boundary on the imaging results for the two-hole structure. (a–e,k–o) Positions of the phase boundary relative to the two-hole structure, represented by two yellow circles; (f–j) imaging results for the two-hole structure of 300 nm separation with different positions of phase boundary; (p–t) imaging results for the two-hole structure of 500 nm separation with different positions of phase boundary. These results show that, for object points that can be resolved originally, phase modulation does not affect the resolution results; however, for the undistinguishable object points, there is a great chance to distinguish it after phase modulation.
To further verify the feasibility of this scheme, we select a slightly more complex imaging target, which is composed of two lines with an included angle of 10°, as shown in Figure 10a. Here, a gridded optical mask was designed for general samples, whose structure is shown in Figure 10b. After passing through this optical mask, any two adjacent units will obtain a particular phase difference of π. If the size of the grid unit is 300 nm, it means that any two objects with more than 300 nm separation must be located in two different units, so they can be resolved. The imaging results are simulated in Figure 10c,d, with and without the optical mask, respectively. For this sample, the imaging resolution can be determined using the bifurcation position of the angle. In Figure 10c, the two lines can be distinguished precisely with a distance of 460 nm, while, in Figure 10d, the two lines can be distinguished precisely with a distance of 350 nm. The imaging results show that this type of optical mask is suitable for general samples.
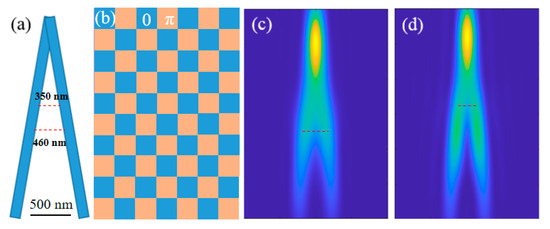
Figure 10.
Imaging results for a particular sample with a gridded optical mask. (a) Imaging target; (b) gridded optical mask with a unit size of 300 nm; (c) the imaging result without the optical mask; (d) the imaging result obtained with the gridded optical mask.
4. Conclusions
To further investigate the influence of light phase on the resolution of a coherent illumination microscope, we built a complete simulation model for the microscopic imaging system, and verified the impact of the phase difference on the imaging resolution with dipole sources. The results indicate that, as the phase difference increases, the imaging resolution improves gradually. To apply this conclusion into practical microscopic systems, we proposed a new super-resolution imaging scheme based on phase modulation with a gridded optical mask, which generates a π phase difference for adjacent points. Through some simple samples, we preliminarily verified the feasibility of this super-resolution imaging scheme, and analyzed the influence of the two most critical parameters on the imaging resolution. The results show its resolution improvement ability and its optimizable characteristics, which could be applied in many nano-imaging fields, such as material analysis and semiconductor defect detection, after further research and scheme optimization.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and X.W.; methodology, J.L. and X.L.; software simulation, Y.L. and J.G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L. and Y.L.; writing—review and editing, J.L.; funding acquisition, J.L., J.G., and X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62075176, 62005206, 51802243), the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (2024JC-YBMS-460), and the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics (SKLST202208).
Data Availability Statement
Data underlying the results presented in this paper are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lee, D.R. Progresses in implementation of STED microscopy. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 102002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, W.; Liu, X. Recent research on stimulated emission depletion microscopy for reducing photobleaching. J. Microsc. 2018, 271, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, B.; Chou, K. Review of super-resolution fluorescence microscopy for biology. Appl. Spectrosc. 2011, 65, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Tehrani, K.; Kner, P. Multicolor 3D super-resolution imaging by quantum dot stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2917–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haji, B.; Beheiry, M.E.; Dahan, M. PSF engineering in multifocus microscopy for increased depth volumetric imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izeddin, I.; Beheiry, M.E.; Andilla, J.; Ciepielewski, D.; Darzacq, X.; Dahan, M. PSF shaping using adaptive optics for three-dimensional single-molecule super-resolution imaging and tracking. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 4957–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, M. Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy. J. Microsc. 2000, 198, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Kner, P.; Rego, E.; Gustafsson, M. Super-resolution 3D microscopy of live whole cells using structured illumination. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 1044–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, E.; Lindberg, J.; ROY, T.; Savo, S.; Chad, J.; Dennis, M.; Zhwludev, N. A super-oscillatory lens optical microscope for subwavelength imaging. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, F.; Huang, K.; Wu, J.; Jiao, J.; Luo, X.; Qiu, C.; Hong, M. Shaping a subwavelength needle with ultra-long focal length by focusing azimuthally polarized light. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 09977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willig, K.; Rizzoli, S.; Westphal, V.; Jahn, R.; Hell, S. STED microscopy reveals that synaptotagmin remains clustered after synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Nature 2006, 440, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ash, E.A.; Nicholls, G. Super-resolution aperture sanning microscope. Nature 1972, 237, 510–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, W.; Li, L.; Luk’yanchuk, B.; Khan, A.; Chen, Z.; Hong, M. Optical virtual imaging at 50 nm lateral resolution with a white-light nanoscope. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yu, M.; Urbach, H.P.; Wu, Y. Effects of whispering gallery mode in microsphere super-resolution imaging. Appl. Phys. B 2017, 123, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Moullan, N.; Auwerx, J.; Gijs, M.A.M. Super-resolution biological microscopy using virtual imaging by a microsphere nanoscope. Small 2014, 10, 1712–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Durant, S.; Lee, H.; Pikus, Y.; Fang, N.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X. Far-Field optical superlens. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Kuang, C.; Hao, X.; Pang, C.; Xu, P.; Li, H.; Yu, C.; Xu, Y.; Nan, D. Fluorescent nanowire ring illumination for wide-field far-field subdiffraction imaging. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 076101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Liu, X.; Kuang, C.; Li, Y.; Ku, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Tong, L. Far-field super-resolution imaging using near-field illumination by micro-fiber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 013104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Resolution improvement of dark-field microscopy via micro-particle near-field illumination. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).