LiteCOD: Lightweight Camouflaged Object Detection via Holistic Understanding of Local-Global Features and Multi-Scale Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose LiteCOD, a lightweight COD architecture featuring Holistic Unification Modules (HUMs) for bilateral global–local feature enhancement and Enhanced Context Generation (ECG) for multi-scale contextual understanding, achieving SOTA performance with only 5.1M parameters and real-time inference at 76 FPS.
- We introduce an ultra-lightweight Efficient Spatial Attention (ESA) mechanism within the HUMs that captures long-range spatial dependencies with significant FLOPS reduction through shared query–key projections and streamlined attention computation, enabling comprehensive spatial relationship modeling while preserving computational efficiency.
- We design a multi-stage feature integration (MFI) strategy that incorporates progressive contextual guidance and region-aware spatial weighting, facilitating effective information propagation from coarse semantic features to fine-grained spatial details across the entire decoder hierarchy through systematic feature refinement.
- Comprehensive experiments on standard COD benchmarks (CAMO, COD10K, NC4K) demonstrate that our modular approach consistently outperforms existing lightweight methods while maintaining competitive performance against heavyweight approaches.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Camouflaged Object Detection
2.2. Deep Learning-Based COD Methods
2.2.1. Biologically Inspired Approaches
2.2.2. Supplementary Information-Based Approaches
2.2.3. Multi-Scale Feature Integration and Contextual Enhancement
2.2.4. Lightweight COD Methods
3. Proposed Methodology
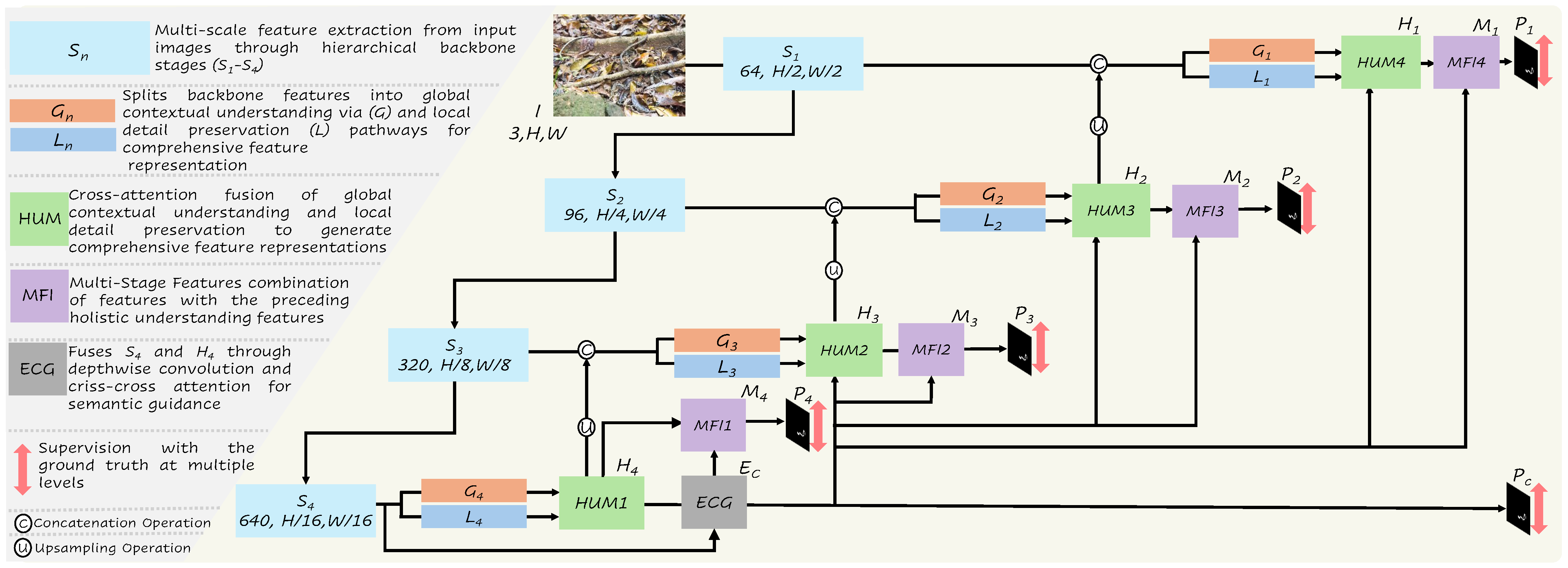
3.1. Overall Framework Architecture
3.2. Lightweight Backbone Feature Extraction
3.3. Global–Local Feature Processing Modules
3.3.1. Global Feature Extraction (G)
3.3.2. Local Feature Extraction (L)
3.4. Holistic Unification Modules (HUMs)
3.5. Enhanced Context Generation (ECG)
3.6. Multi-Stage Feature Integration (MFI)
3.7. Progressive Upsampling and Multi-Scale Supervision
4. Experiments and Discussion
4.1. Implementation Settings and Reproducibility
4.2. Datasets
4.3. Objective Function
4.4. Evaluation Metrics
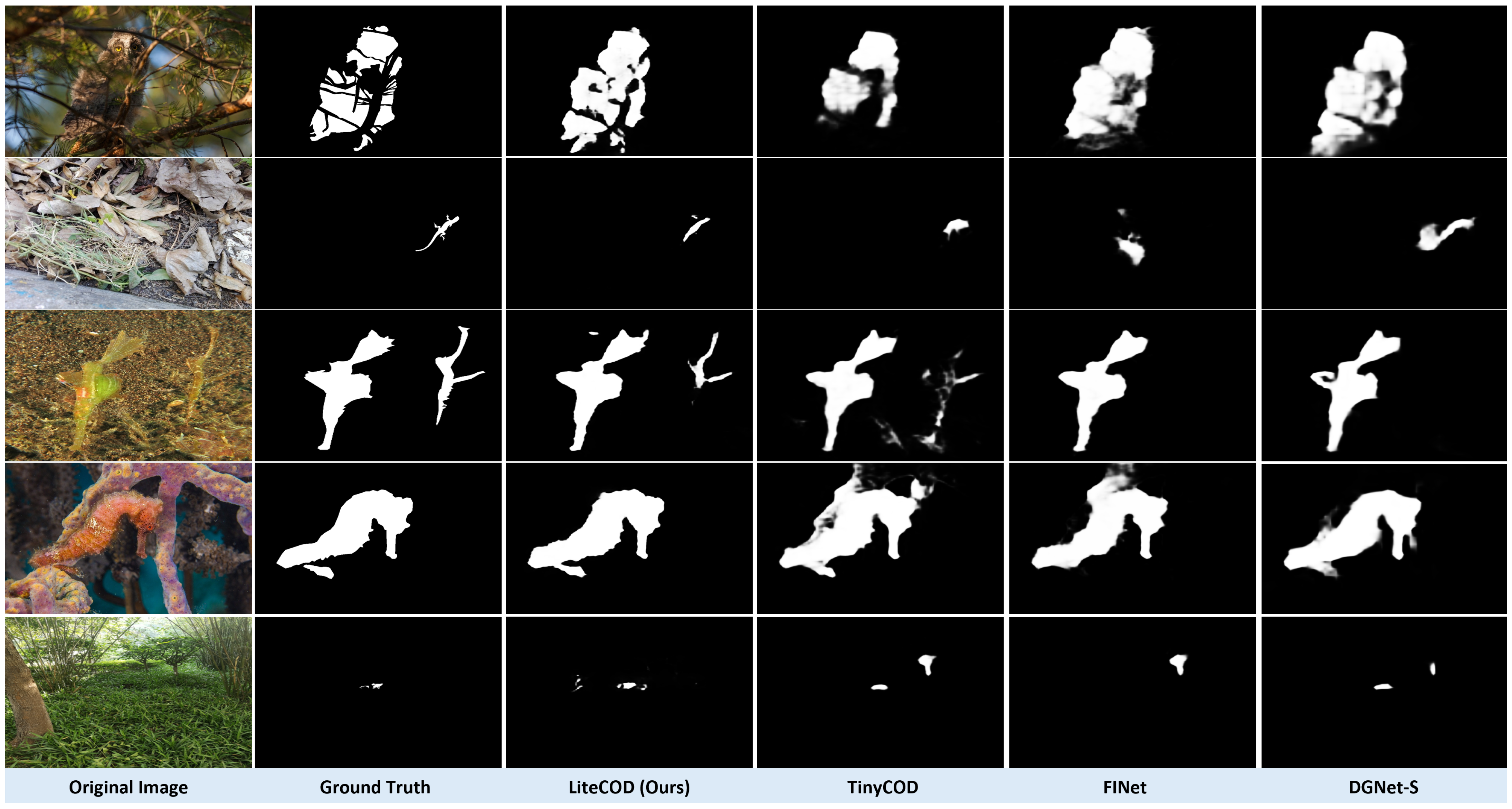
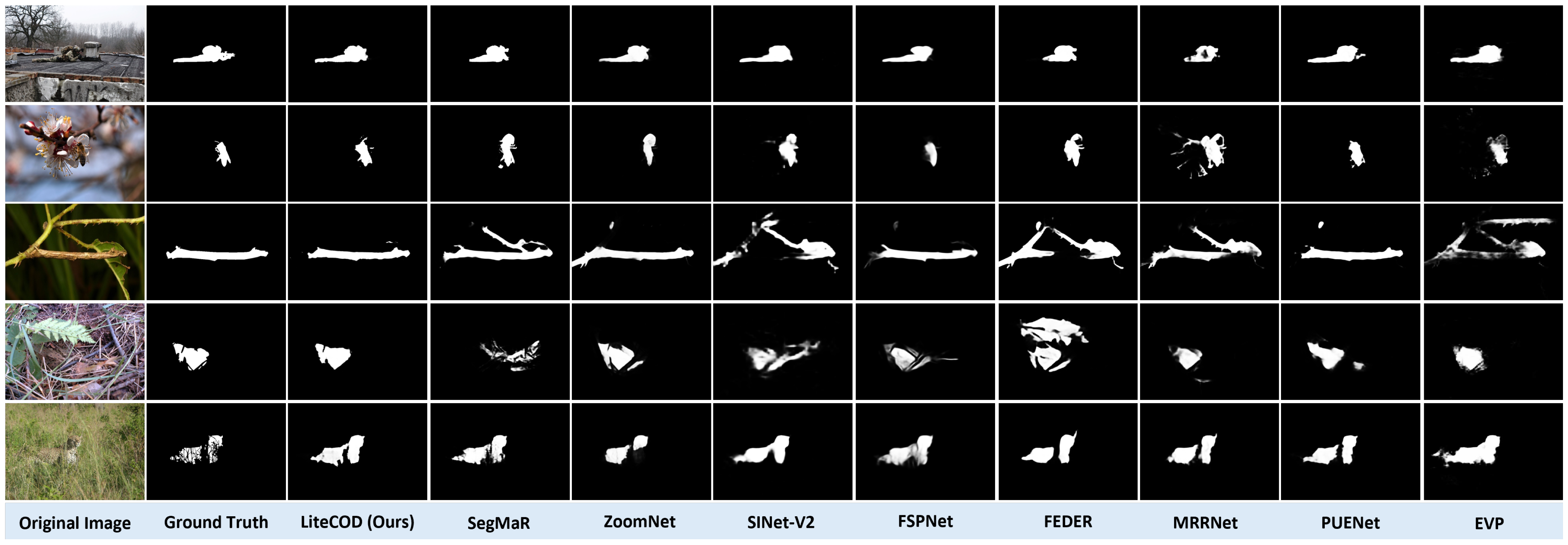
4.5. Qualitative and Quantitative Results
| Method | Publication | Param/M | FLOPs/G | FPS | CAMO (250) | COD10K (2026) | NC4K (4121) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | M↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | M↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | M↓ | |||||
| SINet [1] | CVPR’20 | 48.95 | 19.30 | 82 | 0.751 | 0.771 | 0.606 | 0.100 | 0.771 | 0.797 | 0.551 | 0.051 | 0.808 | 0.838 | 0.723 | 0.058 |
| PFNet [10] | CVPR’21 | 46.50 | 26.39 | 106 | 0.782 | 0.855 | 0.695 | 0.085 | 0.800 | 0.868 | 0.660 | 0.040 | 0.829 | 0.894 | 0.745 | 0.053 |
| LSR [29] | CVPR’21 | 50.94 | 17.36 | 150 | 0.793 | 0.859 | 0.743 | 0.080 | 0.804 | 0.883 | 0.678 | 0.037 | 0.840 | 0.904 | 0.666 | 0.048 |
| SINetV2 [28] | TPAMI’22 | 26.98 | 12.17 | 130 | 0.820 | 0.884 | 0.743 | 0.070 | 0.815 | 0.864 | 0.689 | 0.037 | 0.847 | 0.901 | 0.770 | 0.044 |
| BGNet [16] | ICCAI’22 | 79.85 | 58.24 | 88 | 0.812 | 0.876 | 0.749 | 0.073 | 0.831 | 0.892 | 0.722 | 0.033 | 0.851 | 0.911 | 0.788 | 0.044 |
| SegMaR [12] | CVPR’22 | 56.97 | 33.49 | 85 | 0.815 | 0.881 | 0.753 | 0.071 | 0.833 | 0.869 | 0.724 | 0.034 | 0.861 | 0.905 | 0.781 | 0.046 |
| ZoomNet [11] | CVPR’22 | 32.28 | 101.35 | 41 | 0.820 | 0.883 | 0.752 | 0.066 | 0.838 | 0.893 | 0.729 | 0.029 | 0.853 | 0.907 | 0.784 | 0.043 |
| FEDER [15] | CVPR’23 | 44.13 | 35.80 | 42 | 0.802 | 0.877 | 0.738 | 0.071 | 0.822 | 0.901 | 0.716 | 0.032 | 0.847 | 0.913 | 0.789 | 0.044 |
| CamoFocus-P [56] | WACV’24 | 73.2 | 44 | 45 | 0.817 | 0.884 | 0.752 | 0.067 | 0.838 | 0.900 | 0.724 | 0.029 | 0.865 | 0.913 | 0.788 | 0.042 |
| FSEL [67] | ECCV’24 | 29.15 | 35.64 | - | 0.822 | 0.892 | 0.758 | 0.067 | 0.833 | 0.898 | 0.728 | 0.031 | 0.855 | 0.913 | 0.792 | 0.042 |
| CamoFormer [50] | TPAMI’24 | 36.11 | 34.20 | 87 | 0.817 | 0.884 | 0.752 | 0.067 | 0.838 | 0.900 | 0.724 | 0.029 | 0.865 | 0.913 | 0.788 | 0.042 |
| ESNet [68] | KBS’25 | 10.77 | 4.52 | 99 | 0.848 | - | - | 0.049 | 0.850 | - | - | 0.031 | 0.862 | - | - | 0.040 |
| Lightweight COD Techniques | ||||||||||||||||
| DGNet-S [21] | MIR’23 | 7.02 | 1.14 | 153 | 0.826 | 0.896 | 0.754 | 0.063 | 0.810 | 0.869 | 0.672 | 0.036 | 0.845 | 0.902 | 0.764 | 0.047 |
| ASBI [55] | CVIU’23 | 9.47 | 9.84 | 95 | 0.839 | 0.896 | 0.761 | 0.064 | 0.825 | 0.872 | 0.690 | 0.035 | 0.855 | 0.902 | 0.775 | 0.046 |
| ERRNET [39] | PR | 9.47 | 9.84 | 95 | 0.839 | 0.896 | 0.761 | 0.064 | 0.825 | 0.872 | 0.690 | 0.035 | 0.855 | 0.902 | 0.775 | 0.046 |
| CamoFocus-E [56] | WACV’24 | 4.76 | 5.54 | 78 | 0.817 | 0.884 | 0.752 | 0.067 | 0.838 | 0.900 | 0.724 | 0.029 | 0.865 | 0.913 | 0.788 | 0.042 |
| TinyCOD [18] | ICASSP’23 | 4.72 | 1.40 | 60 | 0.822 | 0.890 | 0.752 | 0.066 | 0.831 | 0.877 | 0.678 | 0.036 | 0.843 | 0.903 | 0.766 | 0.047 |
| FINet [20] | SPL’24 | 3.74 | 1.16 | 127 | 0.828 | 0.890 | 0.752 | 0.065 | 0.817 | 0.882 | 0.686 | 0.034 | 0.847 | 0.904 | 0.771 | 0.047 |
| LiteCOD(Ours) | - | 5.15 | 7.95 | 72 | 0.841 | 0.907 | 0.796 | 0.056 | 0.852 | 0.920 | 0.765 | 0.026 | 0.870 | 0.926 | 0.822 | 0.036 |
4.6. Ablation Study
4.7. Edge Computing Deployment Analysis
4.8. Discussion and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Sun, G.; Cheng, M.M.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Camouflaged Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, M.; Ruxton, G.D. The key role of behaviour in animal camouflage. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Hu, S.; Shen, Y.; Fang, C.; Huang, J.; He, C.; Tang, L.; Yang, Z.; Li, X. A survey of camouflaged object detection and beyond. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.14562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc Lan, P.; An, N.S.; Hang, D.V.; Long, D.V.; Trung, T.Q.; Thuy, N.T.; Sang, D.V. Neounet: Towards accurate colon polyp segmentation and neoplasm detection. In Proceedings of the Advances in Visual Computing: 16th International Symposium, ISVC 2021, Virtual, 4–6 October 2021; pp. 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Di, X. Extraordinary MHNet: Military high-level camouflage object detection network and dataset. Neurocomputing 2023, 549, 126466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Wu, J.; Sun, S.; Ren, P. TransCODNet: Underwater transparently camouflaged object detection via RGB and event frames collaboration. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 9, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Khan, M.; Gueaieb, W.; El Saddik, A.; De Masi, G.; Karray, F. SpotCrack: Leveraging a Lightweight Framework for Crack Segmentation in Infrastructure. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 6–8 January 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-de la Fuente, R.; Delclòs, X.; Peñalver, E.; Speranza, M.; Wierzchos, J.; Ascaso, C.; Engel, M.S. Early evolution and ecology of camouflage in insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21414–21419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Zhou, T.; Chen, G.; Fu, H.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Pranet: Parallel reverse attention network for polyp segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2020, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; pp. 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, H.; Ji, G.P.; Wei, Z.; Yang, X.; Wei, X.; Fan, D.P. Camouflaged object segmentation with distraction mining. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 8772–8781. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xiang, T.Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Zoom in and out: A mixed-scale triplet network for camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2160–2170. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Q.; Yao, S.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X.; Liu, R.; Luo, Z. Segment, magnify and reiterate: Detecting camouflaged objects the hard way. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4713–4722. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, F.; Chen, P.; Zheng, F. Depth-aided camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 3297–3306. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; He, C.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Shen, Y.; Chen, C.; Xu, G.; Li, X. Integrating extra modality helps segmentor find camouflaged objects well. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.14471. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, X. Camouflaged object detection with feature decomposition and edge reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22046–22055. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Xiang, T.Z. Boundary-guided camouflaged object detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.00794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, H.; Gao, S.; Tang, H.; Mok, T.Q.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, W. TINYCOD: Tiny and effective model for camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Khan, M.; Gueaieb, W.; El Saddik, A.; De Masi, G.; Karray, F. Recod: Resource-efficient camouflaged object detection for UAV-based smart cities applications. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Bucharest, Romania, 24–27 September 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Mu, X.; Xu, J. FINet: Frequency injection network for lightweight camouflaged object detection. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2024, 31, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.P.; Fan, D.P.; Chou, Y.C.; Dai, D.; Liniger, A.; Van Gool, L. Deep gradient learning for efficient camouflaged object detection. Mach. Intell. Res. 2023, 20, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xuan, H.; Yang, J.; Luo, L. Glconet: Learning multisource perception representation for camouflaged object detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 36, 13262–13275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galun; Sharon; Basri; Brandt. Texture segmentation by multiscale aggregation of filter responses and shape elements. In Proceedings of the Ninth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Nice, France, 13–16 October 2003; pp. 716–723. [Google Scholar]
- Bhajantri, N.U.; Nagabhushan, P. Camouflage defect identification: A novel approach. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Information Technology (ICIT’06), Bhubaneswar, India, 18–21 December 2006; pp. 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Geng, W. A new camouflage texture evaluation method based on WSSIM and nature image features. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Multimedia Technology, Ningbo, China, 29–31 October 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Boot, W.R.; Neider, M.B.; Kramer, A.F. Training and transfer of training in the search for camouflaged targets. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2009, 71, 950–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.N.; Nguyen, T.V.; Nie, Z.; Tran, M.T.; Sugimoto, A. Anabranch network for camouflaged object segmentation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2019, 184, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Cheng, M.M.; Shao, L. Concealed object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 6024–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, A.; Liu, B.; Barnes, N.; Fan, D.P. Simultaneously Localize, Segment and Rank the Camouflaged Objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 11591–11601. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Han, J. Integrating part-object relationship and contrast for camouflaged object detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 5154–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Xu, K.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Piao, H.; Wei, X.; Yang, X. Camouflaged object segmentation with omni perception. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2023, 131, 3019–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Le, T.N.; Nguyen, K.D.; Tran, M.T.; Do, T.T.; Nguyen, T.V. Mirrornet: Bio-inspired camouflaged object segmentation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 43290–43300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Zhang, J.; Lv, Y.; Li, A.; Zhong, Y.; Dai, Y. Exploring depth contribution for camouflaged object detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.13217. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; An, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Demonceaux, C.; Sun, G.; Timofte, R. Object segmentation by mining cross-modal semantics. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 3455–3464. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Paudel, D.P.; Fan, D.P.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Demonceaux, C.; Timofte, R.; Van Gool, L. Source-free depth for object pop-out. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 1032–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Jiang, P.T.; Shen, Z.H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.W.; Li, B. Chain of visual perception: Harnessing multimodal large language models for zero-shot camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Melbourne, Australia, 28 October–1 November 2024; pp. 8805–8814. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Lin, J.; Gong, S.; Cai, W. Relax image-specific prompt requirement in sam: A single generic prompt for segmenting camouflaged objects. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2025; Volume 38, pp. 12511–12518. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Liu, N.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Fan, D.P.; Khan, F.; Han, J. Vscode: General visual salient and camouflaged object detection with 2d prompt learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 17169–17180. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, G.P.; Zhu, L.; Zhuge, M.; Fu, K. Fast camouflaged object detection via edge-based reversible re-calibration network. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 123, 108414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yan, W. CFANet: A cross-layer feature aggregation network for camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Brisbane, Australia, 10–14 July 2023; pp. 2441–2446. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Sun, J.; Sun, F. Efficient camouflaged object detection network based on global localization perception and local guidance refinement. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 5452–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, C.; Xie, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z. You do not need additional priors in camouflage object detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.00702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, K.; Bi, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L. Camouflaged object detection via neighbor connection and hierarchical information transfer. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2022, 221, 103450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Hu, X.; Zhu, L.; Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Deng, Z.; Heng, P.A. Deep texture-aware features for camouflaged object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 33, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Bi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, S. D2C-Net: A Dual-Branch, Dual-Guidance and Cross-Refine Network for Camouflaged Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 5364–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, S.J.; Sun, Y.J.; Ji, G.P.; Wu, Y.F.; Zhou, T. Camouflaged object detection via context-aware cross-level fusion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 6981–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuge, M.; Lu, X.; Guo, Y.; Cai, Z.; Chen, S. CubeNet: X-shape connection for camouflaged object detection. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 127, 108644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xiao, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S. A bioinspired three-stage model for camouflaged object detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.12635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Zhang, P.; He, C.; Hu, R.; Liu, Y. Concealed object segmentation with hierarchical coherence modeling. In Proceedings of the CAAI International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Fuzhou, China, 22–23 July 2023; pp. 16–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, B.; Zhang, X.; Fan, D.P.; Jiao, S.; Cheng, M.M.; Van Gool, L.; Hou, Q. Camoformer: Masked separable attention for camouflaged object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 10362–10374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Dai, H.; Xiang, T.Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.X.; Qin, J.; Xiong, H. Feature shrinkage pyramid for camouflaged object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5557–5566. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Lu, F.; Xue, N.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; He, W. Cross-level attention with overlapped windows for camouflaged object detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.16618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, X. Weakly-supervised concealed object segmentation with sam-based pseudo labeling and multi-scale feature grouping. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 30726–30737. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y.; et al. Segment anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 4015–4026. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, X.; Chen, Y.; Ge, Y.; Bi, H. Attention-induced semantic and boundary interaction network for camouflaged object detection. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2023, 233, 103719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Khan, M.; Gueaieb, W.; El Saddik, A.; De Masi, G.; Karray, F. CamoFocus: Enhancing camouflage object detection with split-feature focal modulation and context refinement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 1434–1443. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M. MobileViT: Light-weight, General-purpose, and Mobile-friendly Vision Transformer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, H.; Chen, C.; Hu, X. COD-SAM: Camouflage object detection using SAM. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 168, 111826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32 (NeurIPS 2019), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pvt v2: Improved baselines with pyramid vision transformer. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.P.; Cheng, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Borji, A. Structure-measure: A new way to evaluate foreground maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4548–4557. [Google Scholar]
- Achanta, R.; Hemami, S.; Estrada, F.; Susstrunk, S. Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1597–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.P.; Gong, C.; Cao, Y.; Ren, B.; Cheng, M.M.; Borji, A. Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, C.; Yang, J.; Xuan, H.; Luo, L. Frequency-spatial entanglement learning for camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 343–360. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, P.; Bai, T.; Sun, F. ESNet: An Efficient Skeleton-guided Network for camouflaged object detection. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2025, 311, 113056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Category | Representative Methods | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Approaches | Galun et al. [23], Bhajantri & Latte [24], Song et al. [25] |
|
|
| Biologically Inspired Methods | SINet [1], PFNet [10], ZoomNet [11], MirrorNet [32] |
|
|
| Supplementary Information Methods | FEMNet, FEDER [15], DCE [33], XMSNet [34], CoVP [36] |
|
|
| Multi-Scale Feature Integration | ERRNet [39], CamoFormer [50], FSPNet [51], OWinCANet [52] |
|
|
| Lightweight COD Methods | TinyCOD [18], DGNet-S [21], FINet [20], CamoFocus [56] |
|
|
| Model Variant | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | M↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backbone | 0.811 | 0.678 | 0.713 | 0.876 | 0.916 | 0.036 |
| + HUM module | 0.831 | 0.719 | 0.747 | 0.896 | 0.923 | 0.030 |
| + HUM + MFI w/o ECG | 0.849 | 0.758 | 0.785 | 0.916 | 0.926 | 0.027 |
| + HUM + MFI (Ours) | 0.852 | 0.765 | 0.790 | 0.920 | 0.928 | 0.026 |
| Backbone | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) | FPS | COD10K | NC4K | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ||||||
| PVT-V2 [62] | 63.55 | 34.2 | 46 | 0.859 | 0.791 | 0.929 | 0.023 | 0.884 | 0.846 | 0.933 | 0.031 |
| ResNet-50 [61] | 31.34 | 15.8 | 62 | 0.830 | 0.777 | 0.922 | 0.025 | 0.872 | 0.829 | 0.924 | 0.035 |
| MobileVit-S [57] | 5.13 | 7.95 | 76 | 0.852 | 0.765 | 0.920 | 0.026 | 0.870 | 0.822 | 0.926 | 0.036 |
| Image Size | FLOPs (G) | FPS | COD10K | NC4K | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | |||||||
| 384 × 384 | 4.47 | 88 | 0.844 | 0.759 | 0.912 | 0.915 | 0.032 | 0.861 | 0.814 | 0.917 | 0.924 | 0.039 |
| 416 × 416 | 5.28 | 83 | 0.847 | 0.761 | 0.919 | 0.921 | 0.029 | 0.863 | 0.817 | 0.923 | 0.928 | 0.033 |
| 512 × 512 | 7.95 | 76 | 0.852 | 0.765 | 0.920 | 0.928 | 0.026 | 0.870 | 0.822 | 0.926 | 0.930 | 0.036 |
| Input Resolution | FLOPs (G) | GMACs | FPS (Jetson) | ↑ | ↑ | M↓ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 384 × 384 | 4.47 | 4.6 | 0.846 | 0.753 | 0.914 | 0.922 | 0.028 | |
| 416 × 416 | 5.28 | 5.61 | 0.849 | 0.759 | 0.917 | 0.925 | 0.027 | |
| 512 × 512 | 7.95 | 9.44 | 0.852 | 0.765 | 0.920 | 0.928 | 0.026 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.; Ullah, H.; Munir, A. LiteCOD: Lightweight Camouflaged Object Detection via Holistic Understanding of Local-Global Features and Multi-Scale Fusion. AI 2025, 6, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6090197
Khan A, Ullah H, Munir A. LiteCOD: Lightweight Camouflaged Object Detection via Holistic Understanding of Local-Global Features and Multi-Scale Fusion. AI. 2025; 6(9):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6090197
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Abbas, Hayat Ullah, and Arslan Munir. 2025. "LiteCOD: Lightweight Camouflaged Object Detection via Holistic Understanding of Local-Global Features and Multi-Scale Fusion" AI 6, no. 9: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6090197
APA StyleKhan, A., Ullah, H., & Munir, A. (2025). LiteCOD: Lightweight Camouflaged Object Detection via Holistic Understanding of Local-Global Features and Multi-Scale Fusion. AI, 6(9), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6090197







