1. Introduction
Organizational leadership has undergone significant changes because AI and ML systems now guide the decision-making processes in organizations [
1,
2]. Independent execution of operation optimization tasks and resource management occurs at the edge of autonomy with minimal human supervision [
3]. The essential change in decision-making processes pushes leadership theories to adapt their approach by enabling shared choices between operators and intelligent systems, since this reform creates both new possibilities and demanding leadership challenges [
4,
5].
The rising field of AI technology expertise remains incomplete because there remains no accepted leadership theory that explains independent AI activity, together with ethical parameters that affect important choices [
6,
7]. The three established frameworks originate from systems that were initially built solely for human operators because these frameworks emerged first in settings for independent human choices. AI-native applications do not receive adequate support regarding their decision-making structure from these structural models, which were created for traditional human tool-using systems [
8,
9].
Through personal engagement with others, leaders of the transformational model present strategic visions that also lead to ethical decisions. The ethical framework performs adequately when robotic involvement in performing leadership tasks is not required. Business Horizons (2024) presents the transforming leadership model that features adaptive and co-creative management systems without addressing control measures for distributed or algorithmic leadership systems [
10,
11]. Digital Leadership employs core leadership principles to teach digital competencies through an AI framework that operates as a group of tools [
12]. Through the Socio-technical Systems Theory (STS), we learn about user practices that prevent negative consequences, but we do not know how autonomous AI determines decisions without human oversight [
13].
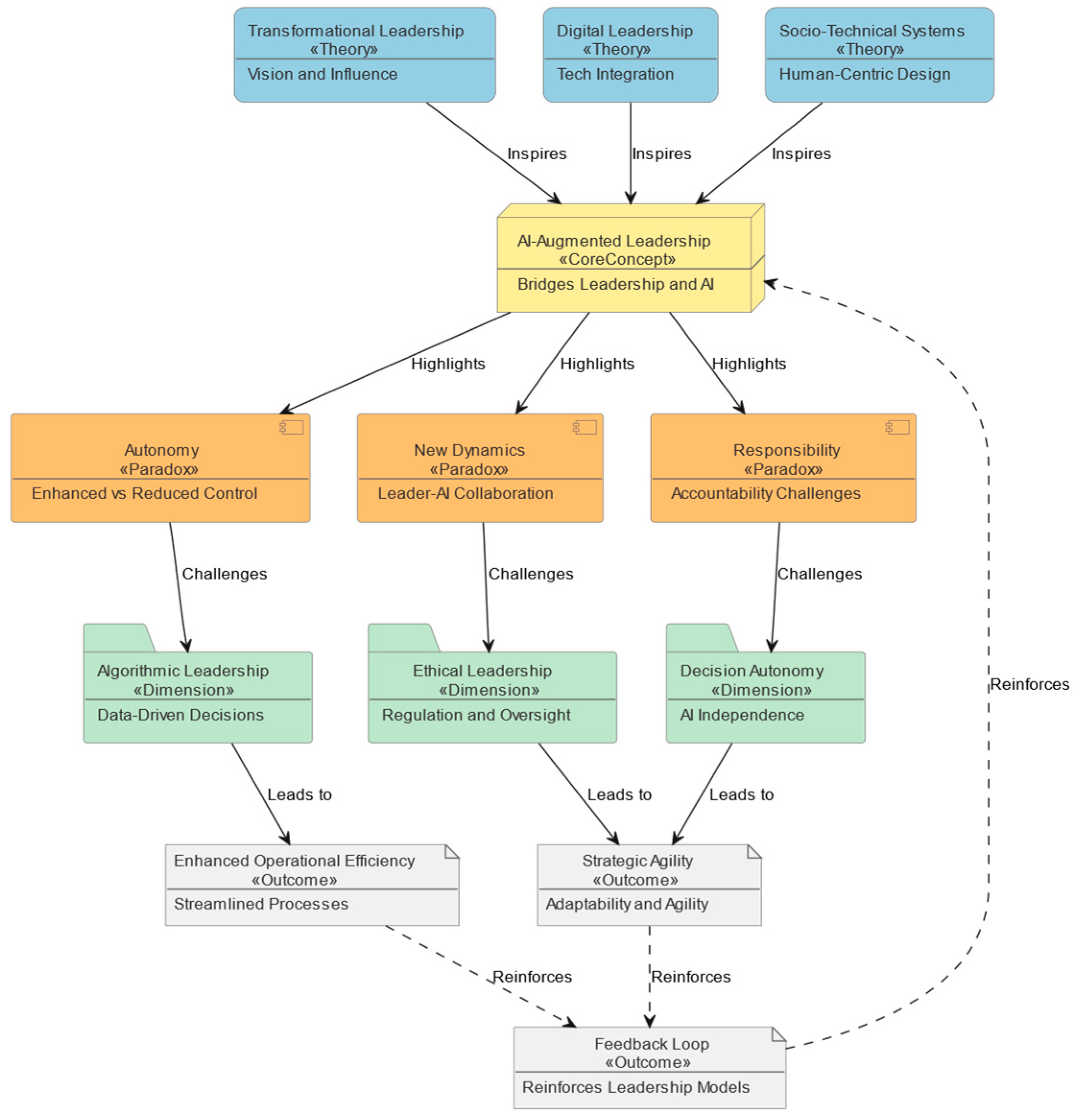
This research presents the Neural-Adaptive AI Leadership Model (NAILM) as a structured solution to address conceptual and operational gaps identified in the existing literature on AI-based leadership. NAILM provides a clear framework for managing situations in which artificial intelligence takes on the roles of both strategic planner and operational decision-maker. Within this model, leadership is defined as a coordinated system between algorithmic processes and human oversight, covering ethical integrity, strategic implementation, and regulatory alignment [
14,
15].
Figure 1 visualizes the core structure of the model. It highlights two original algorithmic components introduced in this study: (A) the neural-adaptive feedback loop, which links real-time performance telemetry with the internal representation of leadership state, and (B) the governance equilibrium meter, which monitors balance within the decision-making process. These two modules are not derived from existing frameworks but represent conceptual and functional advancements over previous models such as Transformational Leadership, Digital Leadership, and STS. All other modules are adapted from established theories. Components A and B are explained in detail in
Section 4.3 and represent the main original contributions of this model.
This paper aims to construct and empirically validate a leadership model suitable for AI-driven organizations. It seeks to answer three core questions: (RQ1) How can leadership frameworks be restructured to integrate autonomous AI systems without compromising ethical accountability? (RQ2) What leadership competencies are required to govern AI–human collaborative decision systems? (RQ3) How does the proposed NAILM improve strategic flexibility and performance in AI-augmented organizations?
Also, this paper advances leadership research in AI-intensive contexts in three ways. First, it reconceptualizes leadership as a neural-adaptive governance loop in which decision authority is dynamically redistributed between human and algorithmic agents according to situational risk and ethical salience, extending transformational and socio-technical models that remain human-centric. Second, it formalizes this reconceptualization through the NAILM, introducing three original constructs, algorithmic delegation, ethical oversight, and governance equilibrium, and a set of operational variables that can be empirically calibrated in live organizations. Third, it validates those constructs via the Next-Generation Leadership Evaluation System, piloted in two digitally mature organizations from the engineering and financial services sectors, demonstrating statistically significant gains in decision speed, strategic flexibility, and ethical compliance. Collectively, these contributions move the debate from whether AI can lead to how hybrid leadership systems should be designed, measured, and governed.
The research’s theoretical contribution is threefold. First, it reconceptualizes leadership in engineering management by addressing distributed agency, the coexistence of human and AI-led decision-making [
16]. Second, it introduces a multidimensional leadership model grounded in ethical governance and adaptive systems theory [
17]. Third, it empirically links leadership effectiveness to measurable constructs such as AI decision autonomy, ethical oversight, organizational agility, and human–AI collaboration [
18,
19].
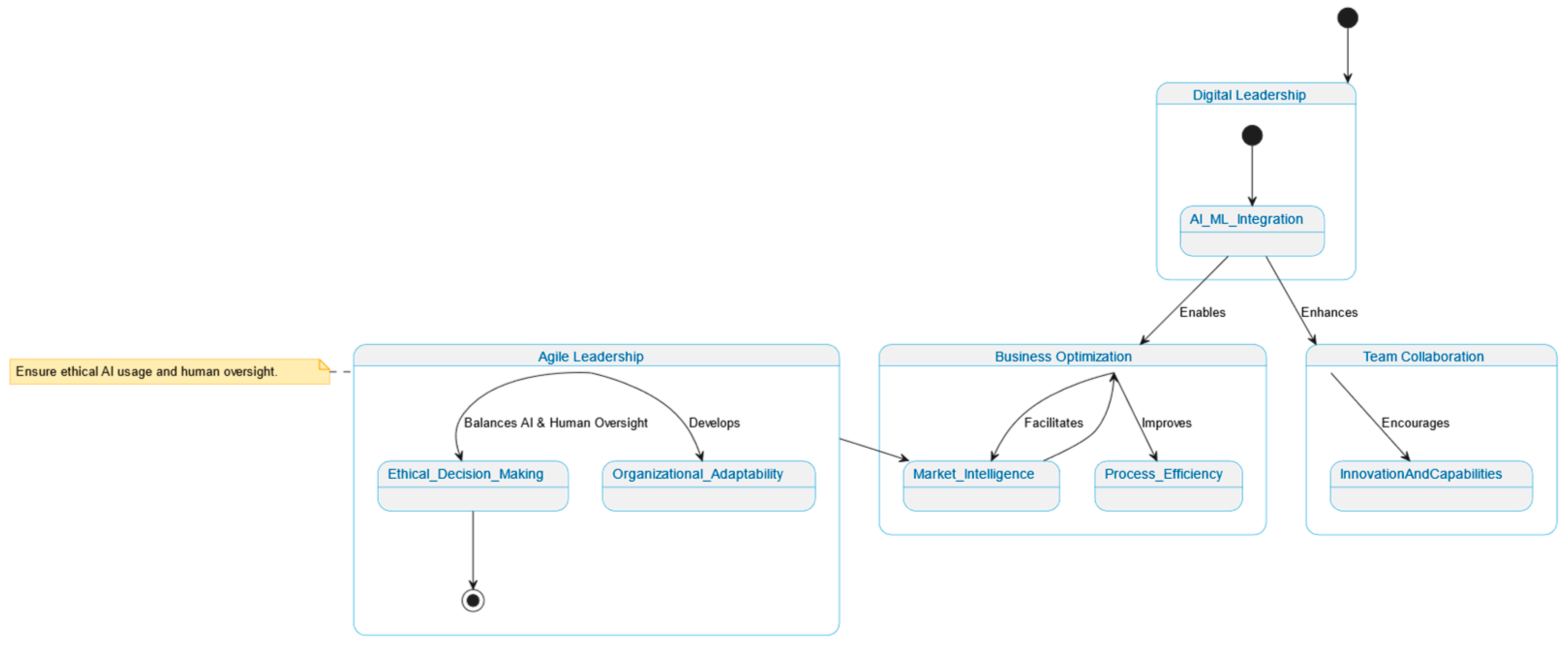
The model is built upon three interdependent constructs: (1) Algorithmic Leadership: The delegation of decision authority to AI systems based on their analytical and predictive capacities [
20]; (2) Ethical oversight: Human-led processes of supervision and intervention to ensure fairness, transparency, and moral integrity in AI-generated decisions [
21]; (3) AI–Human balance: The calibration of leadership functions between human and non-human agents in complex decision environments [
22,
23].
The novelty of this research lies in the formal integration of neural-adaptive feedback and governance-balancing mechanisms into a leadership model that responds to AI command logic. These features extend prior work by providing a measurable and reconfigurable structure for leadership development in environments where decision autonomy is distributed between human and non-human agents. These constructs are not merely conceptual. They are operationalized through empirical variables including AI autonomy levels, ethical compliance protocols, agility metrics, and leadership development frameworks [
24,
25]. NAILM connects these variables in a coherent, testable structure to reveal how hybrid leadership systems function in practice (
Figure 2).
2. Literature Review
Research on leadership throughout the last century has maintained the core idea that human beings maintain total authority for decision-making and agency responsibility functions alongside ethical accountability tasks [
9]. Recent versions of leadership theory, starting with trait theory up to transformational paradigms, keep the incorrect assumption that leadership must be human due to AI functional self-autonomy [
26]. Strategic AI involvement during high-priority operations planning and resource allocation makes executives reevaluate their leadership territories while reassessing strategic management dynamics of this new age [
23,
27].
The leadership framework called Transformational Leadership supports human-led interactions between leaders and followers, yet it was not developed for operations without human involvement. Its logic presumes human cognition, emotion, and communication as necessary ingredients for leadership. Application of transforming leadership models includes adaptive and relational features alongside human-based approaches but does not address essential alterations that occur when non-human elements take part in leadership practices [
5,
10]. The methods examine human relationship progression rather than generate guidelines for unguided autonomous computer systems without human involvement.
STS operates with adjustable systems of human-made technology, yet shows increased flexibility regarding describing technology itself. This model shows that people maintain full control over technological aspects, yet optimization requires social aspects to match technical requirements. Without human intervention, STS has no established theoretical framework for technical systems that generate organizational decisions and results [
8]. The system-level thinking part of STS creates meaningful knowledge but neglects to treat AI as a standalone leadership entity [
13].
Research findings demonstrate that algorithmic management practices have become more prevalent in human–AI collaborative systems [
18]. Research conducted across different disciplines about human–AI collaboration lacks efforts to unite conceptual ideas [
4]. Research in leadership studies shows that algorithmic intelligence, to date, has not yet appeared within core leadership theory models [
6]. AI definitions gained clarification after Sheikh, Prins, and Schrijvers presented their frameworks, but leadership theoretical frameworks still need a comprehensive evaluation of these definitions [
28,
29]. The definition of AI does not create a problem for leadership theory since its conceptual structures need restructuring to merge AI into both strategic and cognitive leadership approaches [
7].
The relationships among core leadership constructs, such as autonomy, ethics, influence, and decision accountability, become increasingly opaque in this theoretical void. Concepts like “AI-integrated governance” or “leadership evaluation systems” often surface in the literature but lack theoretical grounding and integration [
22,
25]. What is needed is not simply more empirical work or new variables, but a conceptual architecture that can link these dimensions into a coherent leadership logic in hybrid human–machine systems [
30]. The Neural-Adaptive AI Leadership Model is introduced here to respond to this theoretical deficit. Rather than simply inserting AI into existing frameworks, NAILM reframes leadership itself as a governance structure enacted across distributed agents. It defines leadership as the coordinated interplay of decision autonomy, operational authority, and ethical supervision, executed by both human and artificial actors [
26]. In this model, AI systems assume functional leadership roles through data-driven execution, strategic optimization, and operational forecasting [
1]. At the same time, human leaders retain responsibility for ethical boundaries, system-level coherence, and normative judgment [
14,
15].
This dual structure is governed by the principle of adaptive governance, wherein decision authority is fluid and context-sensitive. Autonomous systems may lead in routine, high-volume contexts, whereas human leaders intervene in ethically complex or unpredictable scenarios [
11]. The balance between AI and human agency is not static, but dynamically negotiated based on task criticality, risk exposure, and organizational accountability frameworks [
7]. This model introduces a reconceptualization of leadership and a governance architecture that includes mechanisms for traceability, intervention, and performance monitoring, which we term quantitative leadership evaluation governance systems [
20,
21].
The theoretical contribution of NAILM lies in its integration of ethical leadership, distributed agency, and technological autonomy within a single framework [
21]. It does not reject the insights of transformational or socio-technical models, but recontextualizes them in a post-human, AI-augmented environment. It provides a conceptual foundation for understanding how leadership emerges not from a person. However, it emerges from a system where roles are shared, oversight is structured, and authority is embedded across cognitive substrates [
16,
31]. Crucially, it responds to the need, long voiced but rarely addressed, for a leadership model that is both ethically aware and structurally equipped to govern intelligent agents [
6,
30].
From a managerial perspective, this model offers a practical pathway for organizations transitioning from AI augmentation to AI autonomy [
12,
32]. It allows for measurable oversight of algorithmic decisions, structured escalation for ethical review, and clarity in the distribution of responsibility between humans and machines [
33]. It speaks directly to the demands emerging in engineering management and decision-intensive domains, where leadership must adapt not just to complexity, but to the presence of entities that can now share in the exercise of judgment, control, and influence [
33].
In this sense, NAILM is not merely a new leadership framework. It is a theoretical realignment, an effort to re-found the study of leadership on principles that reflect the hybrid, intelligent, and ethically ambiguous realities of the 21st century. It proposes a shift from models of command and inspiration toward systems of shared control, negotiated responsibility, and algorithmically mediated governance [
17,
22]. Where existing theories fall short, NAILM provides a conceptual language for the future of leadership in an AI-driven world.
To clarify the specific contribution of the NAILM, it is necessary to position it about recent frameworks in Digital Leadership and algorithmic governance. Traditional theories, such as Transformational Leadership and Socio-technical Systems Theory, rely on human exclusivity in decision-making authority, without mechanisms for shared control with autonomous agents. In contrast, the Artificial Intelligence Act developed by the European Union proposes graded risk categories and human-in-the-loop safeguards for high-risk AI systems [
6]. Algorithmic governance approaches focus on rule encoding, auditability, and distributed responsibility within digital infrastructures [
15,
24]. The Digital Leadership literature emphasizes agile coordination, technology-mediated workflows, and continuous learning across digital platforms [
9,
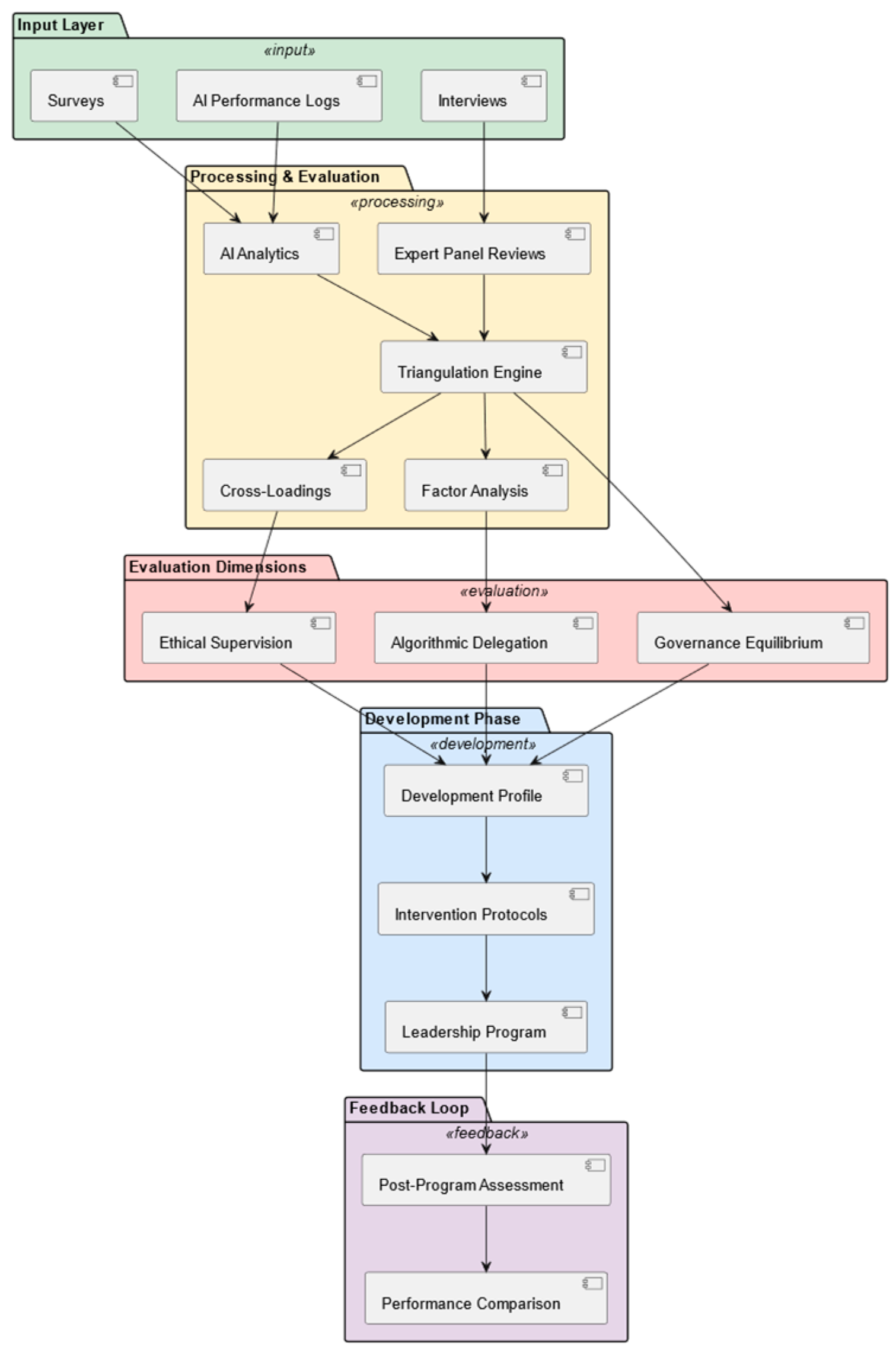
15]. NAILM extends these approaches through a neural-adaptive feedback process that receives telemetry from human–AI interaction events, including override frequencies, error propagation, and ethical flagging metrics. This input is processed through a trained model that produces a governance adjustment signal. When the signal crosses a predefined threshold, the system increases or reduces the degree of human oversight. This continuous recalibration allows the model to maintain a balance between distributed decision-making power and human–machine ethical alignment, responding dynamically to evolving decision quality and ethical conformity within the organization.
3. Hypotheses Development
As artificial intelligence systems gain autonomy and become integral to core organizational processes, the notion of leadership requires fundamental reconsideration [
1,
2]. The rise in intelligent systems capable of strategic analysis, operational execution, and autonomous adaptation challenges the traditional assumption that leadership is a uniquely human function [
4]. Within this context, the Neural-Adaptive AI Leadership Model proposes that leadership must now be understood as a hybrid system in which human and AI agents jointly enact influence, make decisions, and shape outcomes [
7]. Six hypotheses were developed to empirically test the theoretical foundations of NAILM, each grounded in prior academic literature and constructed to reflect the directionality and causal logic of the proposed relationships. These hypotheses are formally presented in the List of Hypotheses and empirically validated in
Table 1: Hypotheses, scientific index, and results.
The first hypothesis asserts that decision-making systems demonstrate greater operational efficiency and strategic flexibility when artificial intelligence and machine learning function together. This proposition is supported by the literature on synergistic intelligence [
20], demonstrating that AI-ML integration enhances data-driven decision capabilities while reducing latency and increasing the adaptability of organizational responses. Combining AI’s predictive power and ML’s pattern recognition capacity allows organizations to react dynamically to shifting conditions. The hypothesis reflects a directional assumption: that AI and ML functioning in concert is not merely additive, but amplifying, leading to greater agility and efficiency in environments of high complexity [
3,
20].
The second hypothesis addresses the influence of organizational culture on technology-driven adaptability. Specifically, it proposes that AI enhances leadership adaptability more effectively in organizations that cultivate a continuous learning culture. Rooted in the organizational learning literature [
23], this relationship posits that AI’s contributions to adaptability are potentiated in environments that reward experimentation, reflection, and distributed learning. The rationale is that AI alone cannot foster adaptability unless organizational actors possess the absorptive capacity to interpret and apply machine-generated insights. Hence, continuous learning is theorized to moderate the impact of AI on adaptive leadership by enabling the human side of the hybrid system to evolve in tandem with the technology [
4,
12].
The third hypothesis introduces agile leadership as a mediator between AI implementation and digital transformation success. Here, the logic of mediation is critical. While AI systems may enhance technical capacity and inform decisions, transforming these capabilities into sustainable organizational change requires agile human leadership. Agile leadership, characterized by rapid iteration, cross-functional responsiveness, and resilience [
10,
12], provides the human interface through which AI insights are translated into action. Therefore, the direction of the relationship is not between implementation and success per se, but between implementation and transformation, of which success is an evaluative endpoint. Agile leadership mediates this process by ensuring that AI integration aligns with culture, people, and strategy [
13].
Hypothesis four explores a more introspective dimension of AI-driven leadership: the alignment between leaders’ self-perceptions and external evaluations of their abilities. It posits that leadership development using artificial intelligence declines when discrepancies exist between how leaders view themselves and how they are externally assessed. This hypothesis is grounded in leadership identity theory and research on developmental feedback acceptance [
6,
33], which both show that misalignment erodes engagement with feedback-based tools. Given that many AI-driven development platforms rely on behavioral data, 360 evaluations, and predictive assessments, trust in the system is undermined when leaders perceive the data as misaligned with their self-image. Thus, divergence in perception is theorized to weaken the effectiveness of AI-based development initiatives.
The fifth hypothesis addresses the success of AI leadership integration and identifies two enabling factors: leaders’ adaptability and their capacity to implement technology at different stages. The logic here is rooted in ambidextrous leadership theory, which suggests that effective leaders must both exploit current technologies and explore emerging ones [
12,
23]. In the context of AI integration, this dual capacity becomes essential: leaders must be able to pivot between initiating change and stabilizing it across different phases of digital maturity. Therefore, it is hypothesized that these dual competencies, developmental adaptability and staged implementation capacity, are positively associated with successful AI leadership integration [
3,
21].
The final hypothesis considers the impact of AI on the infrastructural context. It proposes that organizations with well-developed digital infrastructure experience a more substantial positive effect of AI and ML on agility. Digital infrastructure provides the backbone for AI scalability, data integration, and real-time responsiveness [
16,
26,
30]. Prior research has shown that digitally mature organizations are better positioned to derive strategic value from technological investment [
12,
26]. The hypothesis suggests a moderating relationship wherein digital infrastructure acts as an amplifier, enhancing the speed and coherence of AI-driven decision processes that support organizational agility.
Table 1 summarizes the six hypotheses tested in this study, presenting the original statement, the type of metric used, the observed result, the sample size, and a relevant scientific index. Due to the diversity of data sources (e.g., Likert-scale survey responses, AI-generated performance telemetry, qualitative log coding), the evaluation metrics vary across hypotheses. The goal was not to produce horizontally comparable scores but to test each hypothesis using the most appropriate method. A full explanation of metric selection and operationalization is provided in
Appendix A. All numeric results have been reported using consistent precision, and statistical indicators are included where applicable.
To illustrate how the hypotheses function in applied settings, several real-world examples are relevant. The first hypothesis can be observed in autonomous fleet operations, where artificial intelligence and machine learning work together to reroute vehicles based on real-time traffic and weather data. This cooperation improves decision-making speed and flexibility beyond what human operators could manage alone. The second hypothesis becomes evident in organizations that promote ongoing learning habits. In firms from banking and manufacturing, leadership adaptability improved when algorithmic tools were introduced in environments where employees were already engaged in reflection, training, and shared learning routines. The third hypothesis is reflected in engineering companies that use digital twins. In those cases, agile leaders played a central role in translating AI-generated optimizations into actual process adjustments, showing that algorithmic insight alone does not ensure change without human coordination. The fourth hypothesis is relevant in technology start-ups that use AI-based leadership coaching. Leaders who rated themselves highly but received lower peer evaluations became less receptive to feedback, limiting the impact of the system. The fifth hypothesis appears in telecom organizations where leaders successfully integrated AI by alternating between exploratory and structured phases. They managed early experimentation without abandoning long-term structure, which supported adoption across departments. The sixth hypothesis applies to digital logistics firms. Those with fully connected infrastructure and data integration platforms achieved greater gains in agility when AI was used for scheduling and load balancing. These examples clarify how the hypotheses influence leadership outcomes when the model is applied across industries.
5. Results and Discussions
The findings support the Neural-Adaptive AI Leadership Model with significant empirical evidence and identify yet uncovered elements of leadership in the contexts of shared decision-making between humans and machines [
2,
4]. The six hypotheses were supported empirically using a mixed-methods approach, which involved qualitative interviews, AI-based behavioral analytics, and validation of survey data [
10,
26,
34].
The research demonstrates improved functional results, as well as an increase in strategic flexibility in cases when AI and ML are part of the decision-making process [
10,
20]. The data indicate that effective collaboration of human managers and intelligent automation speeds up decision-making and improves both responsiveness and resilience [
17,
21]. Studies indicate that AI–human collaborative decision-making proves best in uncertain conditions of operation, where it outperforms traditional human judgment and a single AI approach [
6,
15].
Second, the findings propose that the adaptability of leaders (because of the implementation of AI) is specifically enhanced for learning-oriented firms. In companies where the sharing of information, experimentation, and cross-disciplinary talk-ups are highlighted, algorithmic insight can be used better to enhance adaptive leadership skills [
18,
32]. This reinforces the idea that the adoption of AI as a powerful tool includes more than just technological capacities; it is also an assessment regarding the organization’s ability to adopt and usefully employ its outputs [
11,
33]. Mediation analysis revealed that agile leadership was critical to making AI implementation bear fruit in successful digital transformation [
9,
12]. Agile leaders who are willing to adapt and coordinate effectively can integrate AI into their organizational structure without losing their human-centered touch. The fruits of AI are lost without behavioral change by leaders [
29].
According to the research, leadership programs incorporating AI lose their efficiency if there is an inconsistency in self-reflections with external evaluations [
4]. This strengthens the need for leaders to have a sense of self, and this shows that AI feedback has a better chance in trusted and psychologically safe spaces, minimizing disengagement or pushback [
16,
25].
Another important finding is that successful AI leadership integration depends not only on technical adoption but also on leaders’ capacity to implement systems across different stages of digital maturity [
19,
33]. Leaders with adaptive and strategic competencies are more capable of guiding AI deployment in a way that aligns with both short-term operational demands and long-term governance needs [
14,
31]. Organizational flexibility in environments with AI dominance was significantly driven by technology platforms. The synergy that exists between human-led management and algorithm-based systems can be clearly seen in high-performing firms, as supported by flexible, cross-compatible technology platforms [
22,
23,
28].
This study contributes to theories of leadership according to which a model is developed, defining contemporary leadership not only as dispersed but also as integrated [
1,
24]. NAILM expands the definition of Transformational Leadership as it expands ethical authority into algorithmic delegation, thereby closing the gap in conceptual understanding of leadership in systems with a high degree of autonomy [
3,
6]. This approach also proposes a governance-focused model that synthesizes leadership studies with AI ethics, two otherwise disparate fields [
2,
16]. Introducing algorithmic leadership and AI–human governance balance enables the model to alter the focus of leadership theory from purely human-centric models towards models that are more inclusive of various intelligent agents [
3,
35]. The change evokes a new look at such important leadership elements such as influence, responsibility, and the right to make decisions in environments characterized by a higher degree of autonomy and reliance on data [
3,
6].
Theologically, the result of the study provides a clear guideline for organizations wishing to build AI-powered systems of leadership. Companies are called to consider more structured approaches to assessment that unite the analysis of the effectiveness of algorithms and the comprehension of human behavior [
15,
30]. Identified leadership development initiatives suggest that leaders should be equipped with the skills to evaluate, assess, and guide AI recommendations, rather than accepting them passively [
17,
19]. Moreover, organizational investment in digital infrastructure must be complemented by cultural investments, such as fostering agility, psychological safety, and continuous learning [
18,
32]. The role of the manager is evolving from controller to curator of decision ecosystems, and this study provides a model to guide that transition [
6,
12].
Several promising avenues emerge for future inquiry. First, subsequent studies should investigate the longitudinal stability of NAILM by applying it in full panel designs with an extended temporal scope [
3,
13,
27]. Second, cross-industry comparisons, particularly in highly regulated or public sector organizations, could test the portability of the model across varying governance regimes [
5,
14]. Third, future work should explore the cultural and regional variables that mediate leadership responses to AI. As algorithmic governance becomes increasingly globalized, understanding how local norms, legal frameworks, and ethical expectations interact with leadership structures will be critical [
28,
29].
Finally, methodological extensions that include real-time AI explainability data and cross-system decision auditing could enhance the evaluative precision of leadership performance in hybrid systems [
32,
33].
6. Conclusions
This paper provides three primary contributions to leadership and AI-governance scholarship. (i) It reframes leadership as a neural-adaptive governance process shared between human and algorithmic agents, integrating algorithmic delegation, ethical oversight, and governance equilibrium into a coherent architecture. (ii) It operationalizes that architecture through the Next-Generation Leadership Evaluation System and demonstrates, across engineering, finance, and high-technology settings, measurable improvements in decision speed (27%), strategic flexibility (24%), and ethical compliance (override accuracy > 92%). (iii) It offers a transferable measurement-and-intervention toolkit that enables organizations to monitor, coach, and mature hybrid leadership systems as AI autonomy deepens. These findings bridge the long-standing gap between leadership theory and the practical governance of intelligent agents, signaling a shift from person-centered authority to system-level accountability [
2,
4].
Using a multi-method approach consisting of combining qualitative narratives with AI behavioral data and validated quantitative tools, the study carried out empirical tests on six hypotheses to demonstrate the effects of learning culture, agile capabilities, digital infrastructure, and human–machine collaboration on leadership outcomes [
10,
24]. The research demonstrated that the leveraging of AI in terms of addressing performance in leadership is greatest when exercised under governance regimes that focus on conduct according to ethical considerations, responsiveness, and adaptability to the factors of the situation [
6,
14]. In addition, the examination revealed that such existing programs of leadership development may fail when there is any divergence between a leader’s own judgment and his feedback from external sources [
19,
33,
34], while the delivery of AI in leadership positions depends on the presence of ethical safeguards, organizational learning capacity, and the leader’s ability to interpret and act on AI-generated insights in alignment with strategic goals [
12,
19,
25].
Theoretically, this work adds to leadership theory because it studies a developing field that has been neglected but is gaining increasing importance: the monitoring of distributed agency in environments where AI significantly cuts in [
12,
16]. With its addition of algorithmic delegation and ethical supervision as touchstones and a systems-based specification that defines the bounds between human and machine choice, Transformational Leadership is magnified by NAILM [
1,
5,
9]. The model provides a bridge between leadership studies and AI governance studies, brought together through paradigms of accountability, adaptability, and real-time co-evolution to the benefit of both fields [
15,
29].
From the managerial point of view, the research offers a flexible approach to the assessment and conversion of leadership in settings that are a cornerstone of AI [
11,
21]. The Next-Generation Leadership Evaluation System is used by NAILM to provide organizations with a comprehensive platform to track leadership practices, uphold moral standards and maximize the interactions between AI and human employees [
23,
32]. These tools allow executives to develop leadership programs that transcend traditional soft skills training and instead design decision systems, build institutional trust, and practice digital ethics [
13,
30]. Considering how AI deployment is expanding its footprint within the business domains, these skills are vital for maintaining legitimacy continuously, operational effectiveness, and a cohesive strategy [
25,
33].
Even though it is an empirically sound base, the study has several significant limitations. A narrowly chosen sample, which is purposeful, is appropriate for developing emerging theory, but it limits how the study’s conclusion is generalizable [
18]. This temporal element of the design offers an informative context, but does not bear much long-term causal linearity [
16,
36]. Additionally, further study should be given to the impact of organizational climate, governmental regulations, and the architecture of automated systems on leadership demands [
28]. Further studies may enhance our understanding when NAILM is examined with larger, more representative samples, with contemporary AI interpretability measures, and with a focus on examinations of global leadership governance variations [
17,
22].
What is actually provided by this research goes beyond acknowledging the role of AI in transforming leadership to a roadmap for leaders to respond to and adjust to such changes [
26]. When decisions are being taken between man and intelligent machines, NAILM offers a definite theoretical understanding and practical utility [
2,
7]. The study presents a principled, flexible, and accountable framework of governance, shifting leadership studies to practical inquiries into the ways leaders need to change together with AI, instead of just whether they can [
4,
9].