Convolutional Neural Networks with Transfer Learning for Recognition of COVID-19: A Comparative Study of Different Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
2.2. Architecture of Basic CNNs
2.3. Transfer Learning Using CNNs
2.4. Pre-Trained Deep Networks
3. Material and Methods
3.1. X-ray Image-Dataset
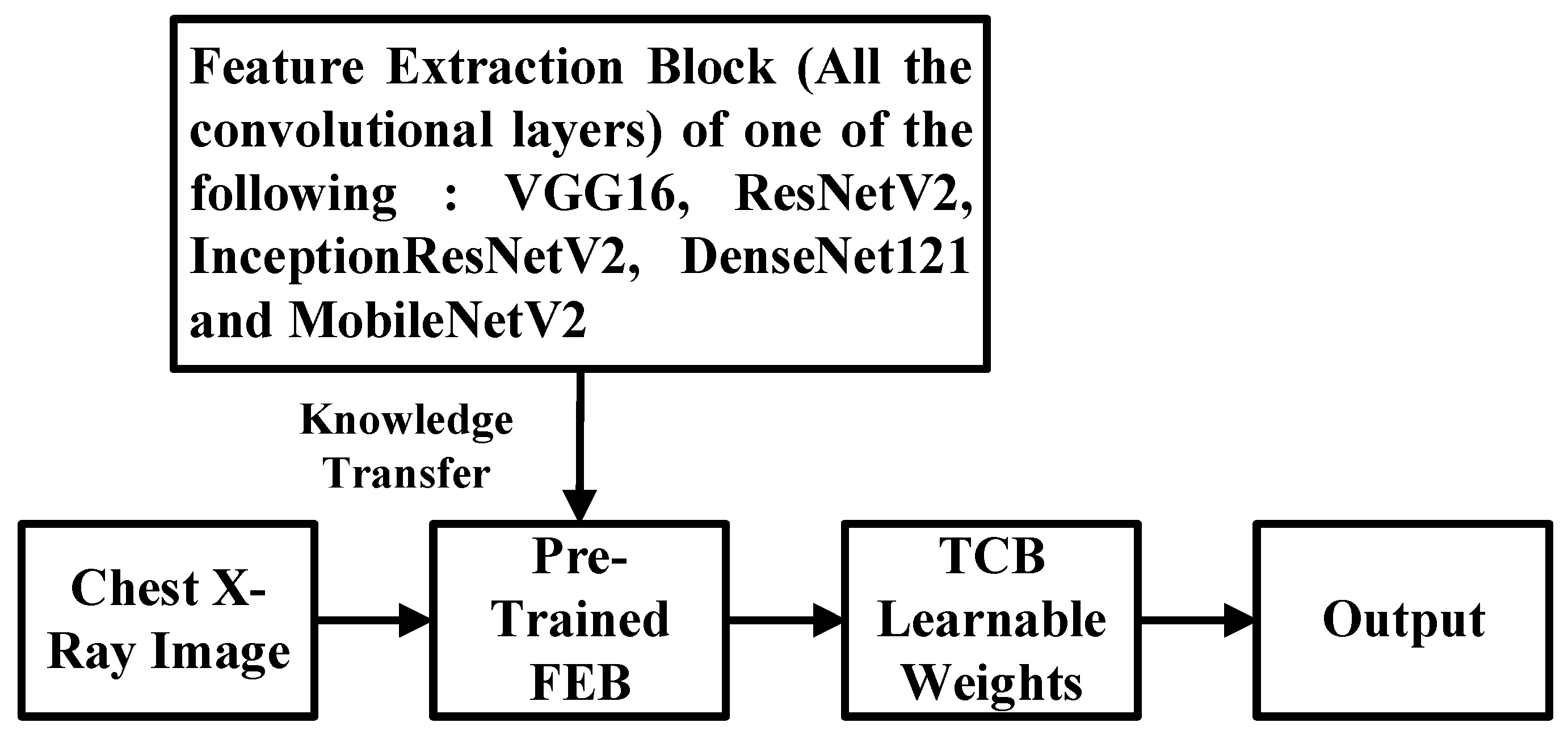
3.2. New CNN Model with Shallow Tuning and Its Training Procedure
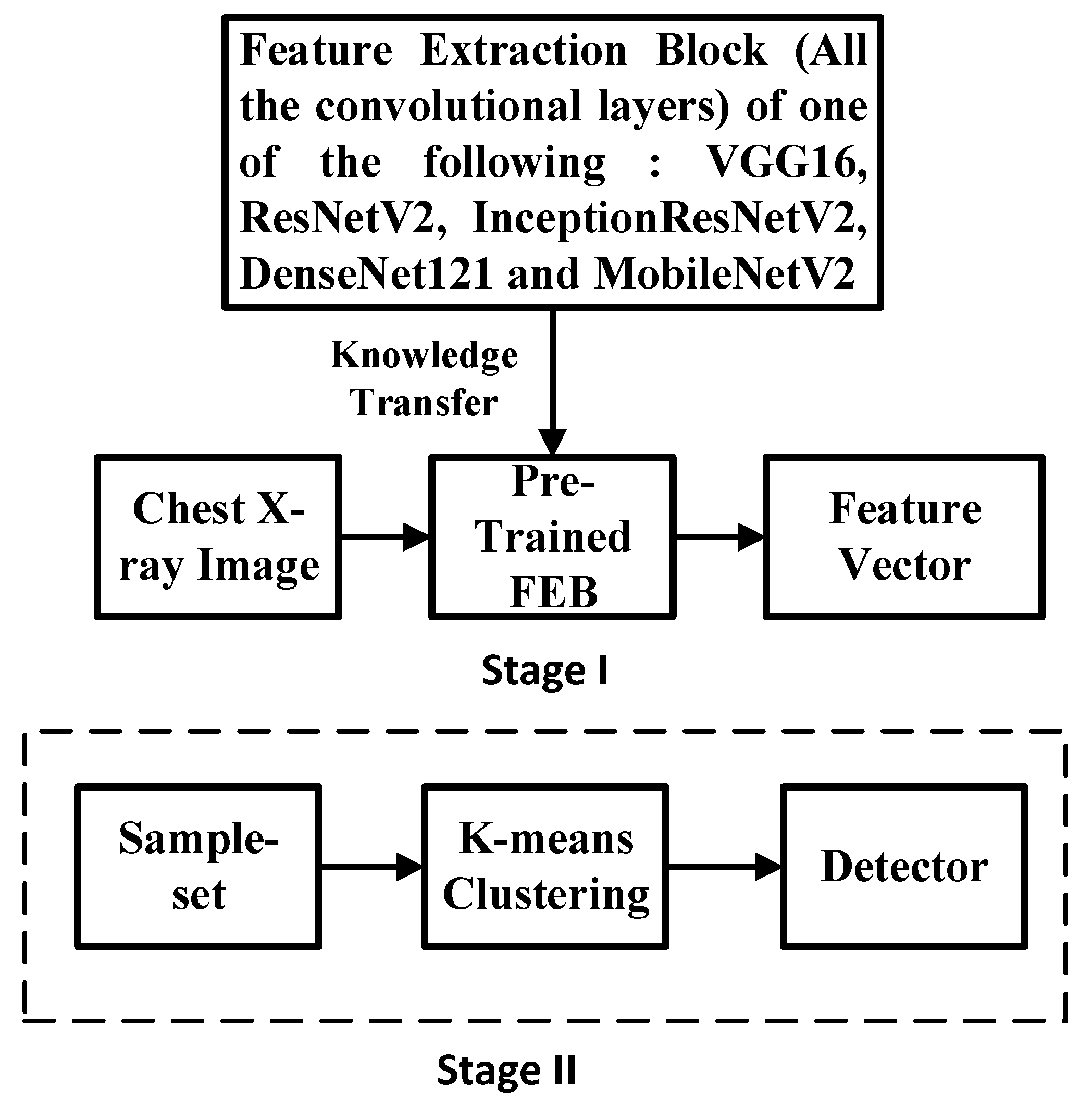
3.3. Semi-Supervised K-Means Detector
3.4. Simple Integrated Model (SIM)
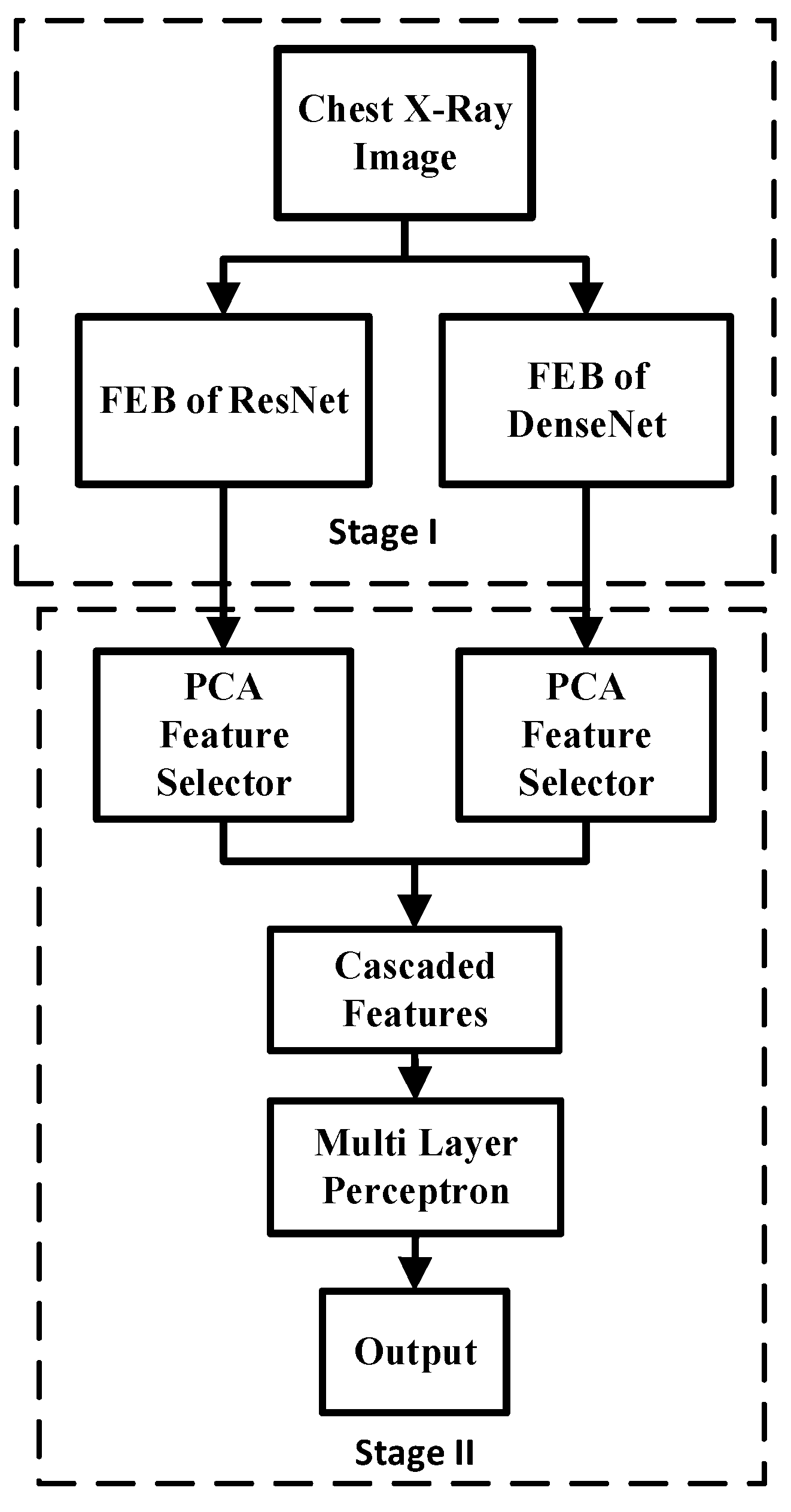
3.5. Fused Integrated Model (FIM)
3.6. Performance Measures
4. Simulation Results
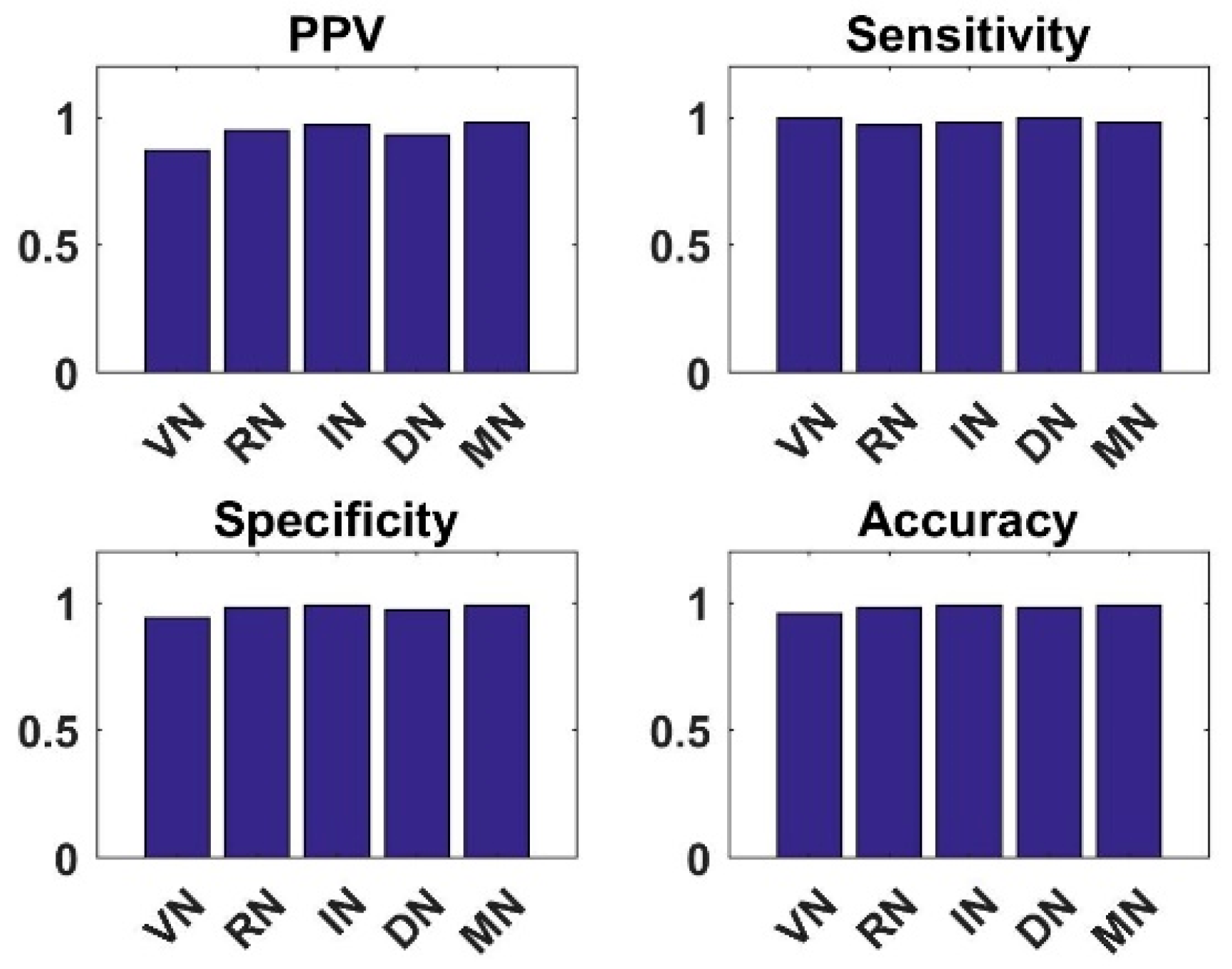
4.1. Analysis of New CNN Models with Shallow Tuning on Dataset1 and Dataset2
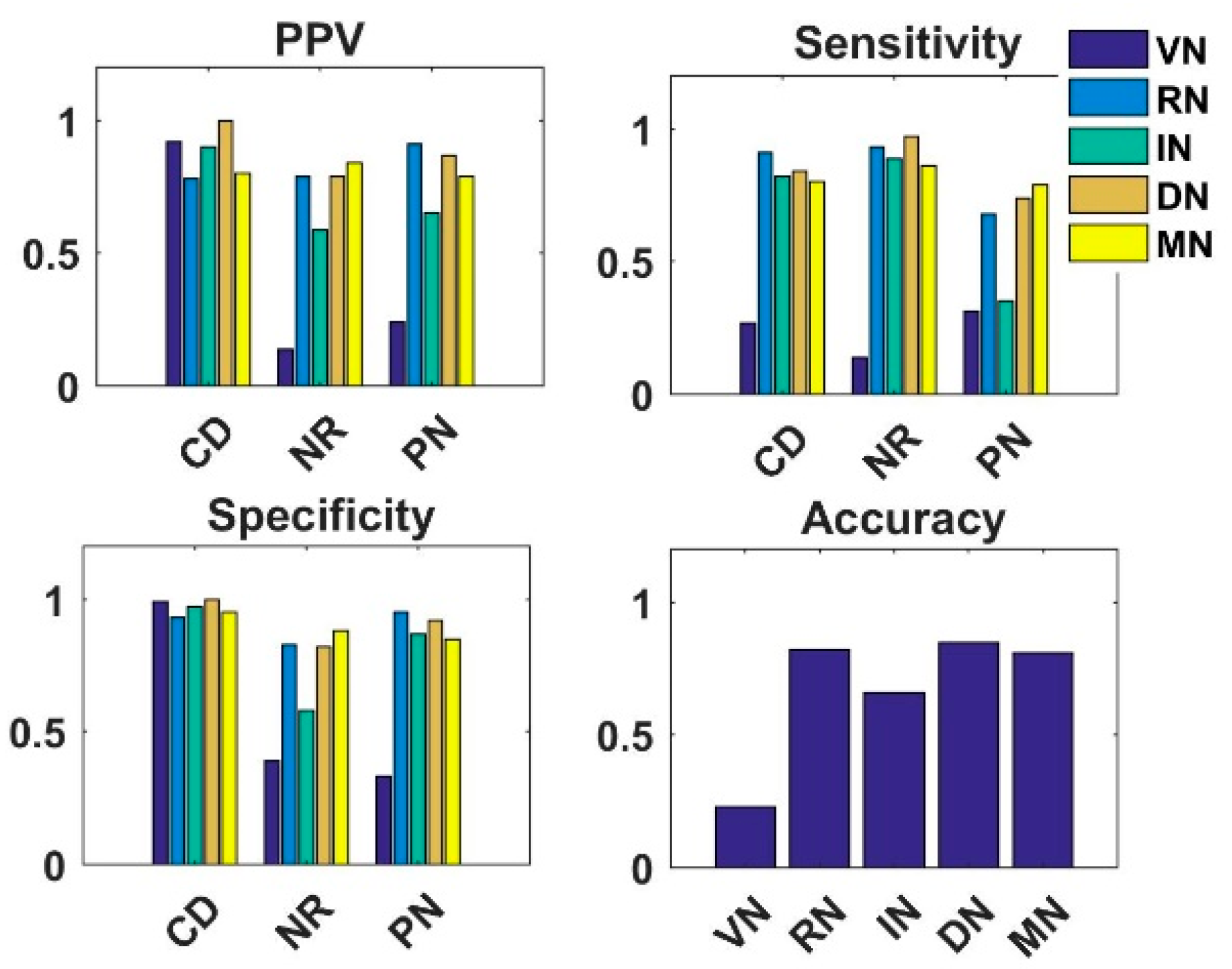
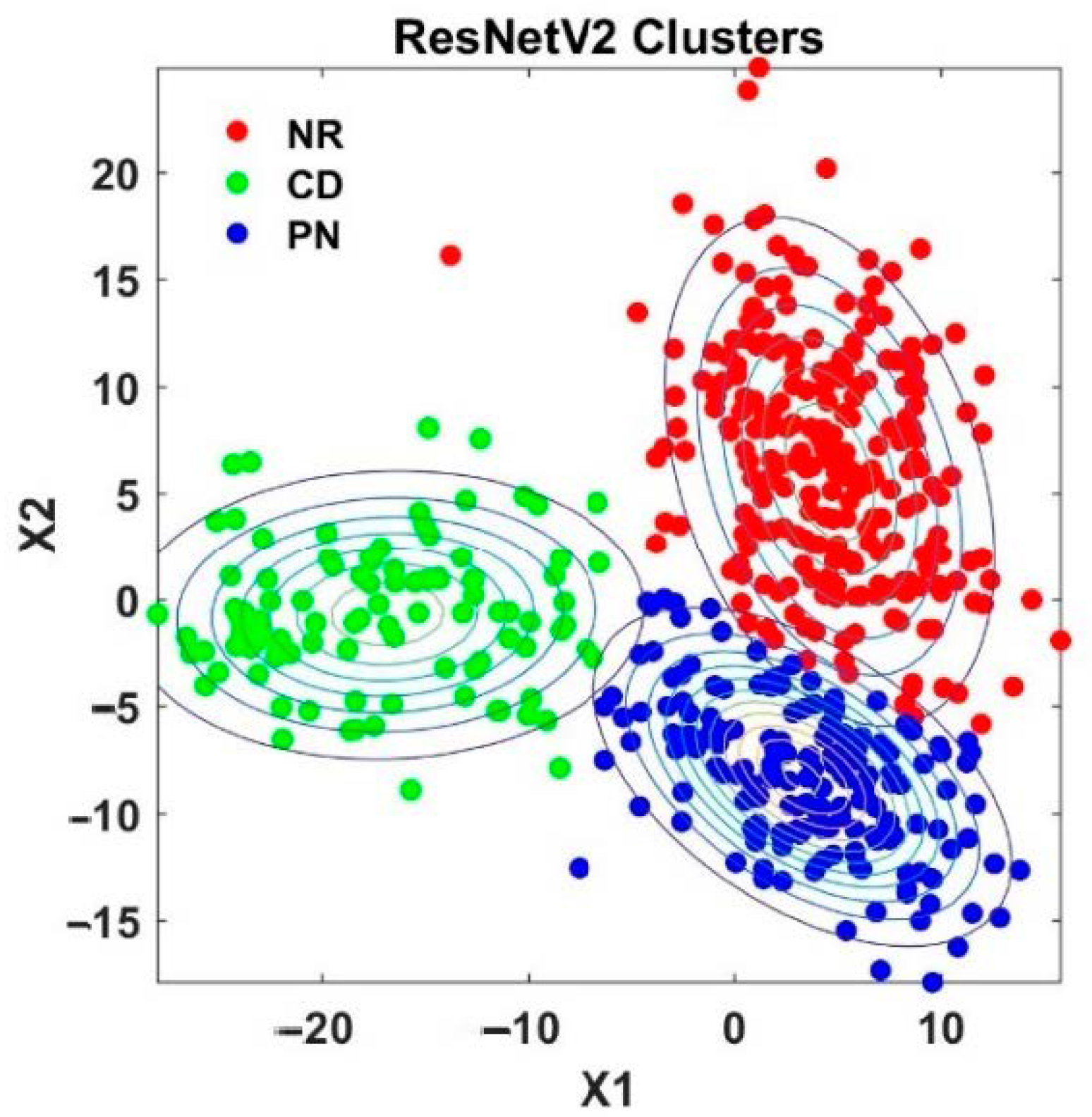
4.2. Analysis of Semi-Supervised K-Means Detector
4.3. Analysis of Simple Integrated Model (SIM)
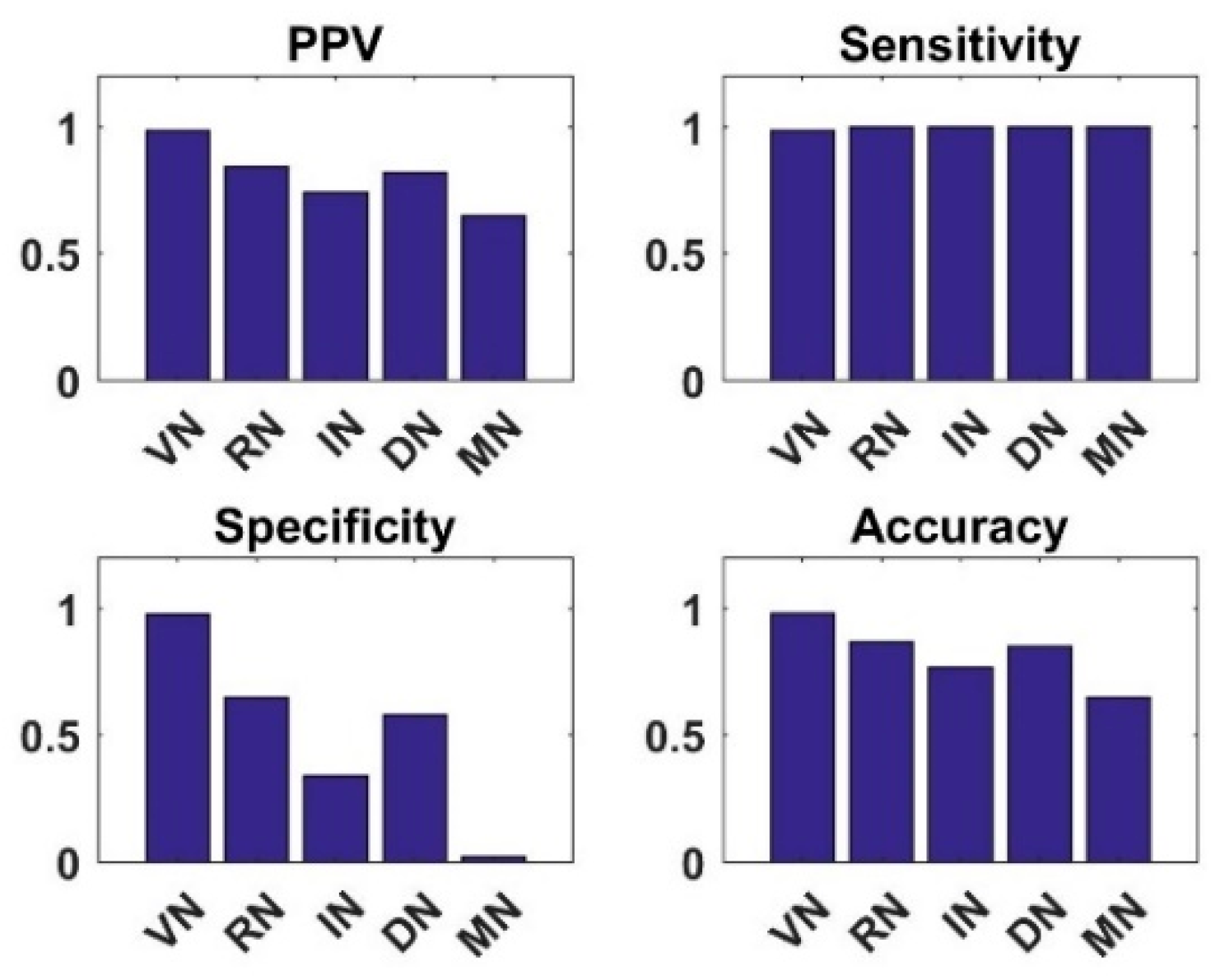
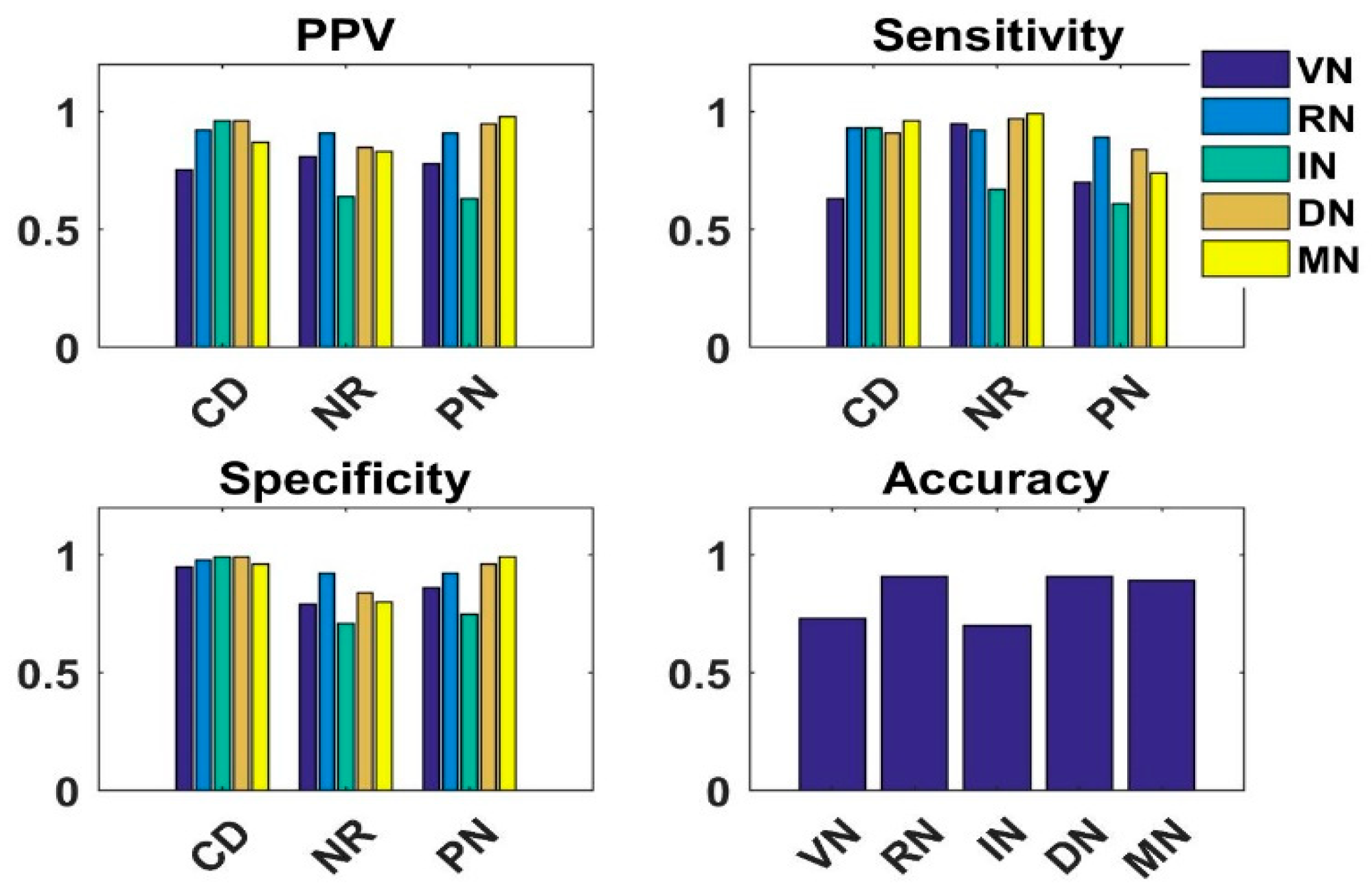
4.4. Analysis of Knowledge Transfer Capability of Different Pre-Trained CNN Models
4.5. Analysis of Fused Integrated Model
5. Comparison of Results with other Modeling Studies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allam, M.; Cai, S.; Ganesh, S.; Venkatesan, M.; Doodhwala, S.; Song, Z.; Hu, T.; Kumar, A.; Heit, J.; COVID-Nineteen Study Group; et al. COVID-19 diagnostics, tools, and prevention. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott. Abbott Launches Molecular Point-of-Care Test to Detect Novel Coronavirus in as Little as Five Minutes. Available online: https://abbott.mediaroom.com/2020-03-27-Abbott-Launches-MolecularPoint-of-Care-Test-to-Detect-Novel-Coronavirus-in-as-Little-as-Five-Minutes (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- Mitra, A.P.; Suri, S.; Goyal, T.; Misra, R.; Singh, K.; Garg, M.K.; Misra, S.; Sharma, P. Association of comorbidities with Coronavirus disease 2019: A review. Ann. Natl. Acad. Med. Sci. 2020, 56, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.D.; Ryerson, C.J.; Haramati, L.B.; Sverzellati, N.; Kanne, J.P.; Raoof, S.; Schluger, N.W.; Volpi, A.; Yim, J.-J.; Martin, I.B.; et al. The role of chest imaging in patient management during the COVID-19 pandemic. Chest 2020, 158, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, A.S.; Jana, M.; Naranje, P.; Manchanda, S. Role of chest radiographs during COVID-19 pandemic. Ann. Natl. Acad. Med Sci. 2020, 56, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xia, L. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Role of chest CT in diagnosis and management. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhong, Z.; Xie, X.; Yu, Q.; Liu, J. Relation between chest CT findings and clinical conditions of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia: A multicenter study. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Yao, D.; Shi, Y.; Song, Z. Computer-aided detection in chest radiography based on artificial intelligence: A survey. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Wu, G.; Suk, H. Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; Van Der Laak, J.A.W.M.; Van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ker, J.; Wang, L.; Rao, J.; Lim, T. Deep learning applications in medical image analysis. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 9375–9389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, O.; Hagiwara, Y.; Hong, T.J.; Lih, O.S.; Acharya, U.R. Deep learning for healthcare applications based on physiological signals: A review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 161, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murat, F.; Yildirim, O.; Talo, M.; Baloglu, U.B.; Demir, Y.; Acharya, U.R. Application of deep learning techniques for heartbeats detection using ECG signals-analysis and review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 120, 103726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topol, E.J. High-performance medicine: The convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteva, A.; Robicquet, A.; Ramsundar, B.; Kuleshov, V.; Depristo, M.; Chou, K.; Cui, C.; Corrado, G.; Thrun, S.; Dean, J. A guide to deep learning in healthcare. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermany, D.S.; Goldbaum, M.; Cai, W.; Valentim, C.C.S.; Liang, H.; Baxter, S.L.; McKeown, A.; Yang, G.; Wu, X.; Yan, F.; et al. Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell 2018, 172, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, L.; Ye, C.; Wang, C.; Zhou, S. Deep convolutional neural networks for WCE abnormality detection: CNN architecture, region proposal and transfer learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 30017–30032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M.; Campbell, J.P.; Beers, A.; Chang, K.; Ostmo, S.; Chan, R.P.; Dy, J.; Erdogmus, D.; Ioannidis, S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; et al. Automated diagnosis of plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity using deep convolutional neural networks. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018, 136, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-C.; Roth, H.R.; Gao, M.; Lu, L.; Xu, Z.; Nogues, I.; Yao, J.; Mollura, D.; Summers, R.M. Deep convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection: CNN architectures, dataset characteristics and transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oquab, M.; Bottou, L.; Laptev, I.; Sivic, J. Learning and Transferring Mid-level Image Representations Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1717–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, T.; Gandhi, T.K. Deep convolutional neural networks with transfer learning for automated brain image classification. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2020, 31, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajbakhsh, N.; Shin, J.Y.; Gurudu, S.R.; Hurst, R.T.; Kendall, C.B.; Gotway, M.B.; Liang, J. Convolutional neural networks for medical image analysis: Full training or fine tuning? IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Jiang, M.-S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z. Automatic detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs based on deep learning algorithm. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, D.; Hao, L.; Liu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G.; Lin, H.; Liu, B.X.; Zeng, C.Y.; et al. Pulmonary image classification based on inception-v3 transfer learning model. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 146533–146541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mormont, R.; Geurts, P.; Maree, R. Comparison of Deep Transfer Learning Strategies for Digital Pathology. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wong, A. COVID-net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest radiography images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshar, P.; Heidarian, S.; Naderkhani, F.; Oikonomou, A.; Plataniotis, K.N.; Mohammadi, A. COVID-CAPS: A capsule network-based framework for identification of COVID-19 cases from X-ray images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 138, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, Z.; Islam, M.; Asraf, A. A combined deep CNN-LSTM network for the detection of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) using X-ray images. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 20, 100412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimzadeh, M.; Attar, A. A new modified deep convolutional neural network for detecting COVID-19 from X-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.08052. [Google Scholar]
- Alqudah, A.M.; Qazan, S.; Alquran, H.H.; Qasmieh, I.A.; Alqudah, A. Covid-2019 Detection Using X-ray Images and Artificial Intelligence Hybrid Systems. Available online: https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.16077.59362/1 (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- Ucar, F.; Korkmaz, D. COVIDiagnosis-Net: Deep Bayes-SqueezeNet based diagnosis of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from X-ray images. Med Hypotheses 2020, 140, 109761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kumari, S. Detection of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Based on Deep Features. Available online: https://Www.Preprints.Org/Manuscript/202003.0300/V1 (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- Jain, R.; Gupta, M.; Taneja, S.; Hemanth, D.J. Deep learning based detection and analysis of COVID-19 on chest X-ray images. Appl. Intell. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Abdelsamea, M.M.; Gaber, M.M. Classification of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images using DeTraC deep convolutional neural network. Appl. Intell. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemdan, E.E.D.; Shouman, M.A.; Karar, M.E. COVIDX-net: A framework of deep learning classifiers to diagnose COVID-19 in X-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11055. [Google Scholar]
- Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Mpesiana, T.A. Covid-19: Automatic detection from X-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narin, A.; Kaya, C.; Pamuk, Z. Automatic detection of Coronavirus disease (COVID- 19) using X-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.10849. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, T.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, E.A.; Baloglu, U.B.; Yildirim, O.; Acharya, U.R. Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luz, E.; Lopes Silva, P.; Silva, R.; Moreira, G. Towards an efficient deep learning model for covid-19 patterns detection in x-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.05717. [Google Scholar]
- Ghoshal, B.; Tucker, A. Estimating uncertainty and interpretability in deep learning for coronavirus (COVID-19) detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.10769. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, C.; Xia, Y. COVID-19 screening on Chest X-ray images using deep learning based anomaly detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.12338. [Google Scholar]
- Sethy, P.K.; Behera, S.K.; Ratha, P.K.; Biswas, P. Detection of Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) based on deep features and support vector machine. Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2020, 5, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M. Machine learning for COVID-19 detection and prognostication using chest radiographs and CT scans: A systematic methodological review. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.06388. [Google Scholar]
- Majeed, T.; Rashid, R.; Ali, D.; Asaad, A. Issues associated with deploying CNN transfer learning to detect COVID-19 from chest X-rays. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubel, D.H.; Wiesel, T.N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction, and functional architecture in the cat’s visual cortex. J. Physiol. 1962, 160, 106–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Essen, D.C.; Maunsell, J.H. Hierarchical organization and functional streams in the visual cortex. Trends Neurosci. 1983, 6, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavian, A.S.; Azizpour, H.; Sullivan, J.; Carlsson, S. CNN Features Off-the-Shelf: An Astounding Baseline for Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 512–519. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollar, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated Residual Transformations for Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5987–5995. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.4729. [Google Scholar]
- Zewen, L.; Wenjie, Y.; Shouheng, P.; Fan, L. A survey of convolutional neural networks: Analysis, applications, and prospects. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.02806v1. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V. Inception-v4, Inception-Resnet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, PR, USA, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.P. COVID-19 image data collection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11597. Available online: https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- Kermany, D.; Zhang, K.; Goldbaum, M. Labeled Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and Chest X-ray Images for Classification Mendeley Data. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.17632/rscbjbr9sj.2 (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- Ruder, S. An overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.04747. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, A.C.; Roelofs, R.; Stern, M.; Srebro, N.; Recht, B. The marginal value of adaptive gradient methods in machine learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.08292. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Shete, D.; Lingayat, N.S.; Chouhan, V. K-means algorithm for the detection and delineation of QRS-complexes in Electrocardiogram. IRBM 2010, 31, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, T. Principal Component Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Murtagh, F. Multilayer perceptrons for classification and regression. Neurocomputing 1991, 2, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks and Learning Machines; Pearson Education: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]





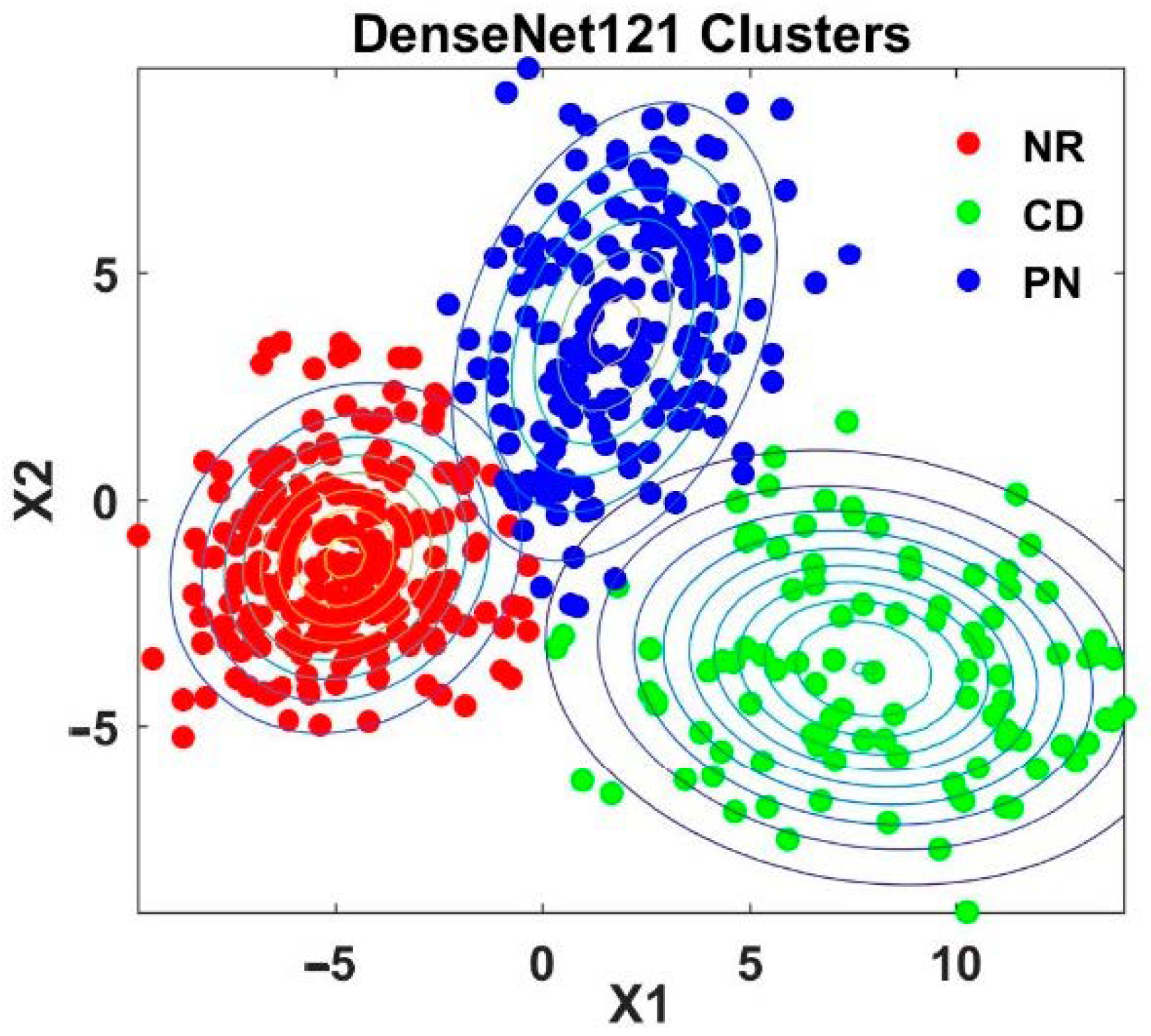
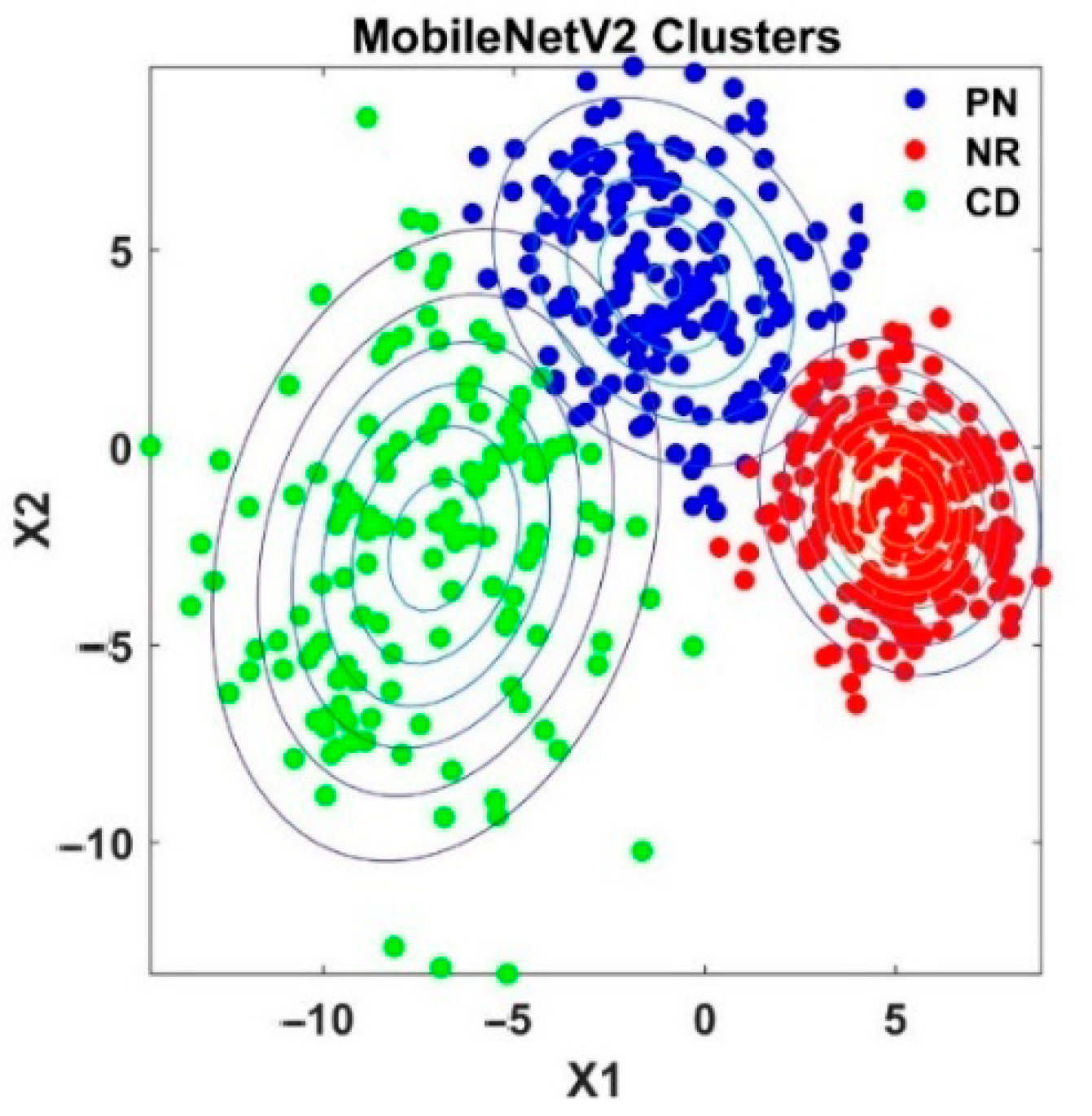

| Model | Top-1 val. Error (%) | Top-5 val. Error (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| MobileNetV2 | 25.3 | - | [54] |
| VGG16 | 25.6 | 8.1 | [49] |
| ResNet50V2 | 23.9 | - | [50] |
| InceptionResNetV2 | 19.9 | 4.9 | [53] |
| DenseNet121 | 23.61 | 6.66 | [55] |
| Images/Dataset | COVID | Normal | Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset1 | 142 | 300 | - |
| Dataset2 | 142 | 300 | 300 |
| Actual | Predicted | ||
| COVID-19 | Normal | ||
| COVID-19 | True Positive Values (TP) | False Negative Values (FN) | |
| NORMAL | False Positive Values (FP) | True Negative Values (TN) | |
| Actual | Predicted | |||
| CD-19 (A) | NR (B) | PN (C) | ||
| CD-19 | TPA | FAB | FAC | |
| NR | FBA | TPB | FBC | |
| PN | FCA | FCB | TPC | |
| Study | Type | Model | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ioannis et al. [36] | Chest X-ray | VGG19 (3-Class) VGG19 (2-Class) | 93.48 98.75 |
| Sethy and Behera [42] | Chest X-ray | ResNet +SVM (3-Class) | 95.38 |
| Hemdan et al [35] | Chest X-ray | COVIDX-Net (2-Class) | 90 |
| Narin et al. [37] | Chest X-ray | Deep CNN ResNet- 50 (2-Class) | 98 |
| Afshar et al. [27] | Chest X-ray | COVID-CAPS (3-Class) | 95.7 |
| Eduardo et al. [39] | Chest X-ray | Efficient Net (3-Class) | 91.4 |
| Tulin et al. [38] | Chest X-ray | Darknet (3-Class) (2-Class) | 87.02 98.08 |
| Proposed: | |||
| Chest X-ray | Shallow Tuning VGG (3-Class) VGG (2-Class) | 87 98 | |
| Chest X-ray | SIM DenseNet (3-Class) DenseNet (2-Class) | 85 99 | |
| Chest X-ray | FIM DenseNet+ResNet (3-Class) | 94 | |
| Chest X-ray | K-Means DenseNet (3-Class) DenseNet (2-Class) | 91 99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garg, T.; Garg, M.; Mahela, O.P.; Garg, A.R. Convolutional Neural Networks with Transfer Learning for Recognition of COVID-19: A Comparative Study of Different Approaches. AI 2020, 1, 586-606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai1040034
Garg T, Garg M, Mahela OP, Garg AR. Convolutional Neural Networks with Transfer Learning for Recognition of COVID-19: A Comparative Study of Different Approaches. AI. 2020; 1(4):586-606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai1040034
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarg, Tanmay, Mamta Garg, Om Prakash Mahela, and Akhil Ranjan Garg. 2020. "Convolutional Neural Networks with Transfer Learning for Recognition of COVID-19: A Comparative Study of Different Approaches" AI 1, no. 4: 586-606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai1040034
APA StyleGarg, T., Garg, M., Mahela, O. P., & Garg, A. R. (2020). Convolutional Neural Networks with Transfer Learning for Recognition of COVID-19: A Comparative Study of Different Approaches. AI, 1(4), 586-606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai1040034






