Underwater Reverberation Suppression Using Wavelet Transform and Complementary Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We constructed a simplified active sonar dataset and validated the simulated signal. It provides reliable experimental data support for subsequent research and facilitates the comparison and testing of various dereverberation methods.
- We proposed an ERCL strategy, which simultaneously learns the target echo and reverberation through two complementary predictors. The final target echo is reconstructed using the features extracted by these two predictors, thereby improving the model’s dereverberation performance. This strategy enables better recovery of the target echo in complex environments and reduces reverberation interference.
- We propose a wavelet transform-based attention feature extraction method that replaces the traditional STFT with CWT. It balances time–frequency resolution and better handles the non-stationary nature of reverberation. Instead of recovering the magnitude and phase spectra, we focus on recovering the real and imaginary parts, simplifying the phase recovery process. Additionally, introducing an attention mechanism helps the network to focus on important regions of the time–frequency spectrogram, especially in complex reverberation environments.
2. Materials and Methods
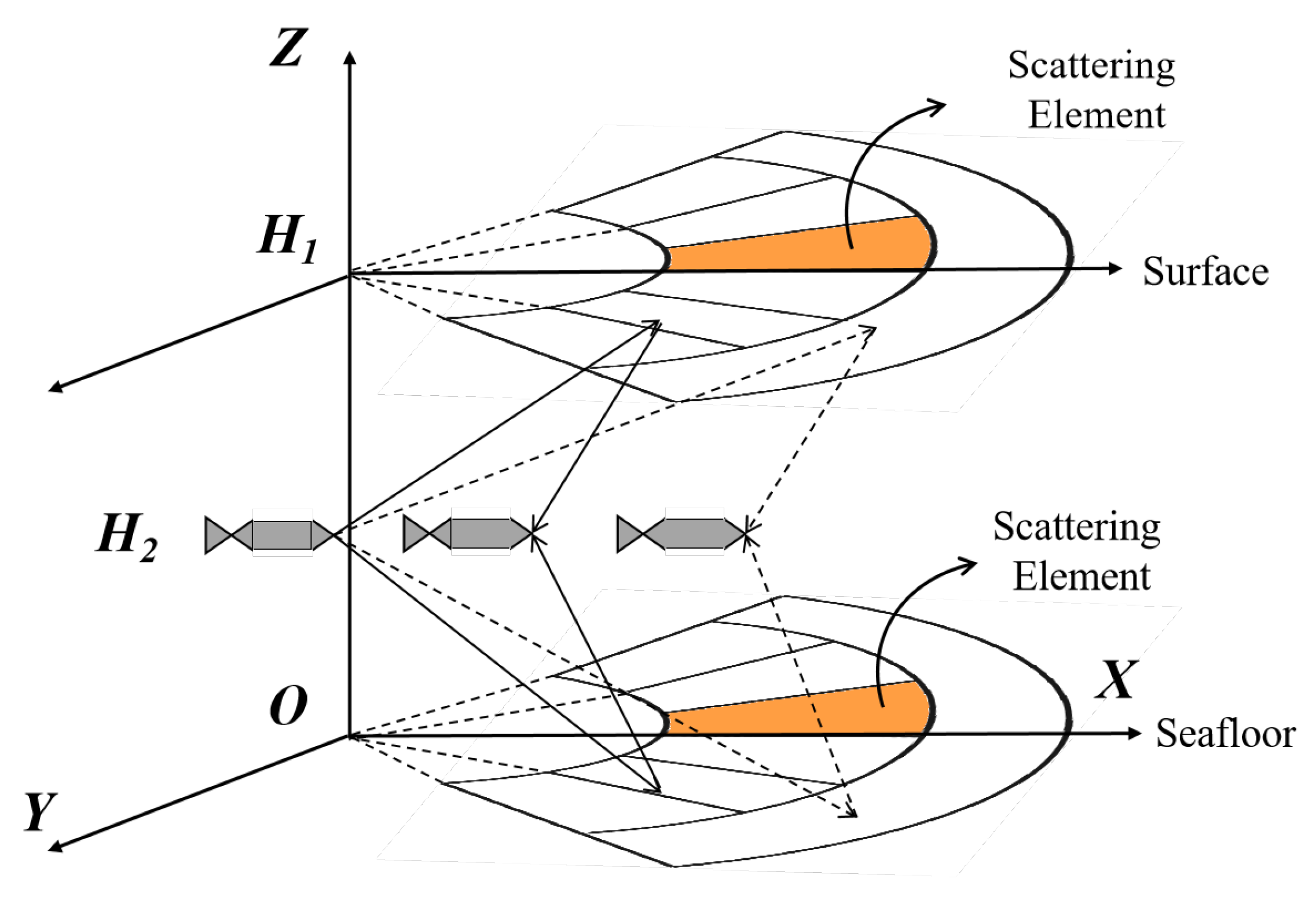
2.1. Data Modeling
2.2. Preprocessing
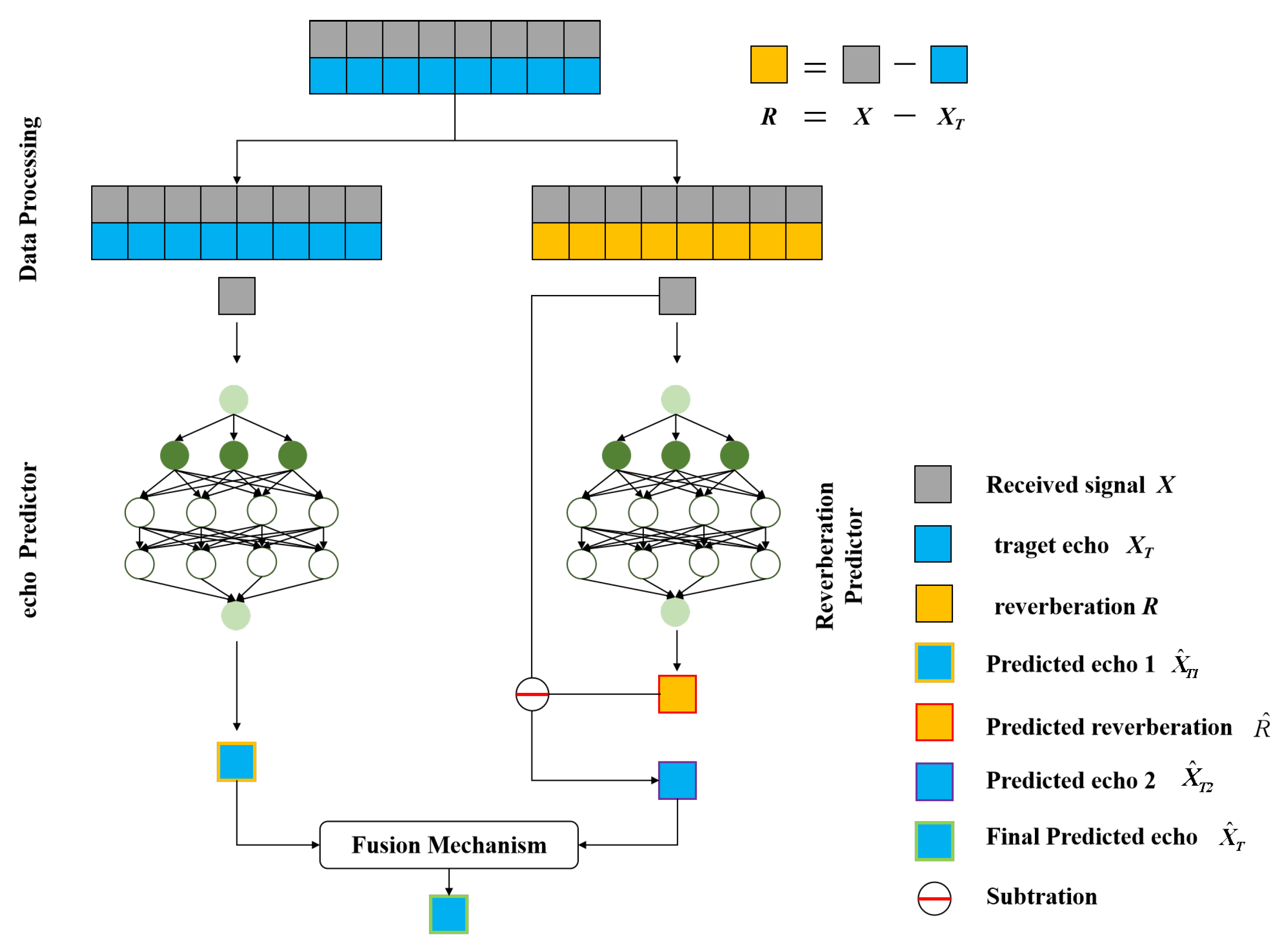
2.3. Echo–Reverberation Complementary Learning Strategies
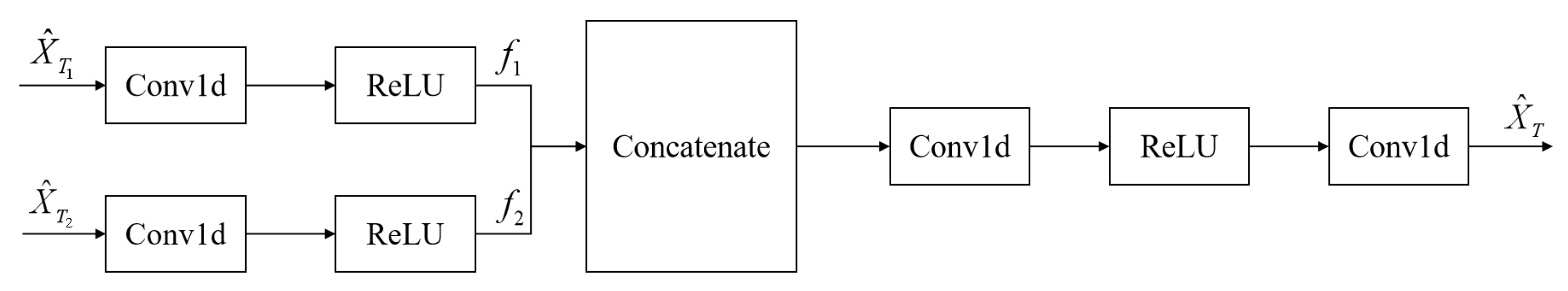
2.4. ERCL-AttentionNet
2.4.1. Overall Architecture
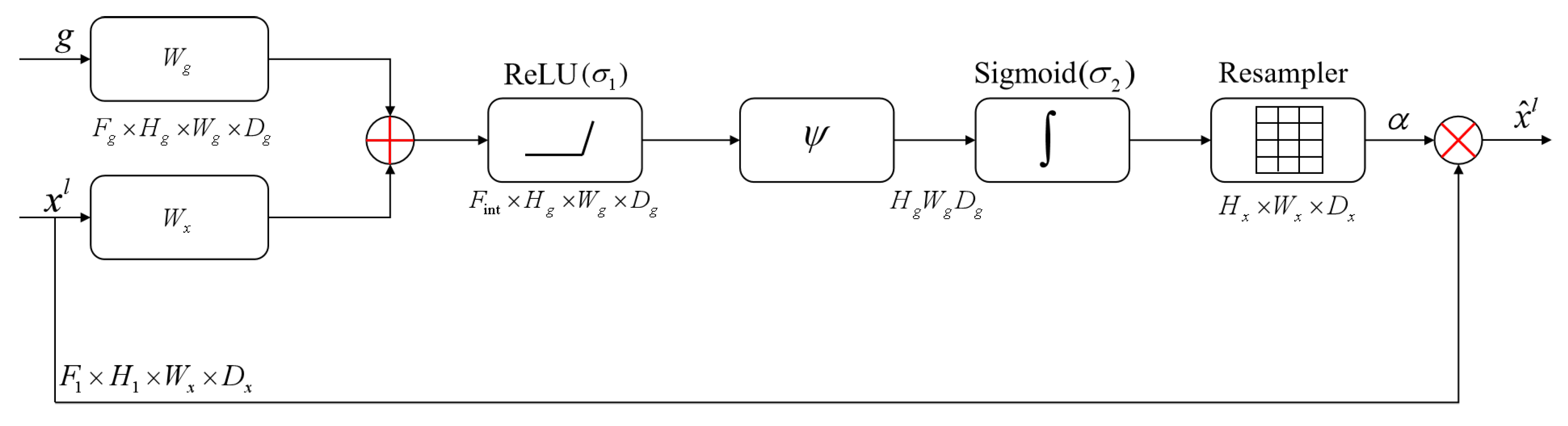
2.4.2. Attention Gate
2.4.3. Loss Function
3. Dataset Construction and Experimental Setup
3.1. Dataset Construction
3.2. Experimental Setup
4. Results
4.1. Evaluation Metrics
4.1.1. PSRR
4.1.2. SSIM
4.1.3. PAR
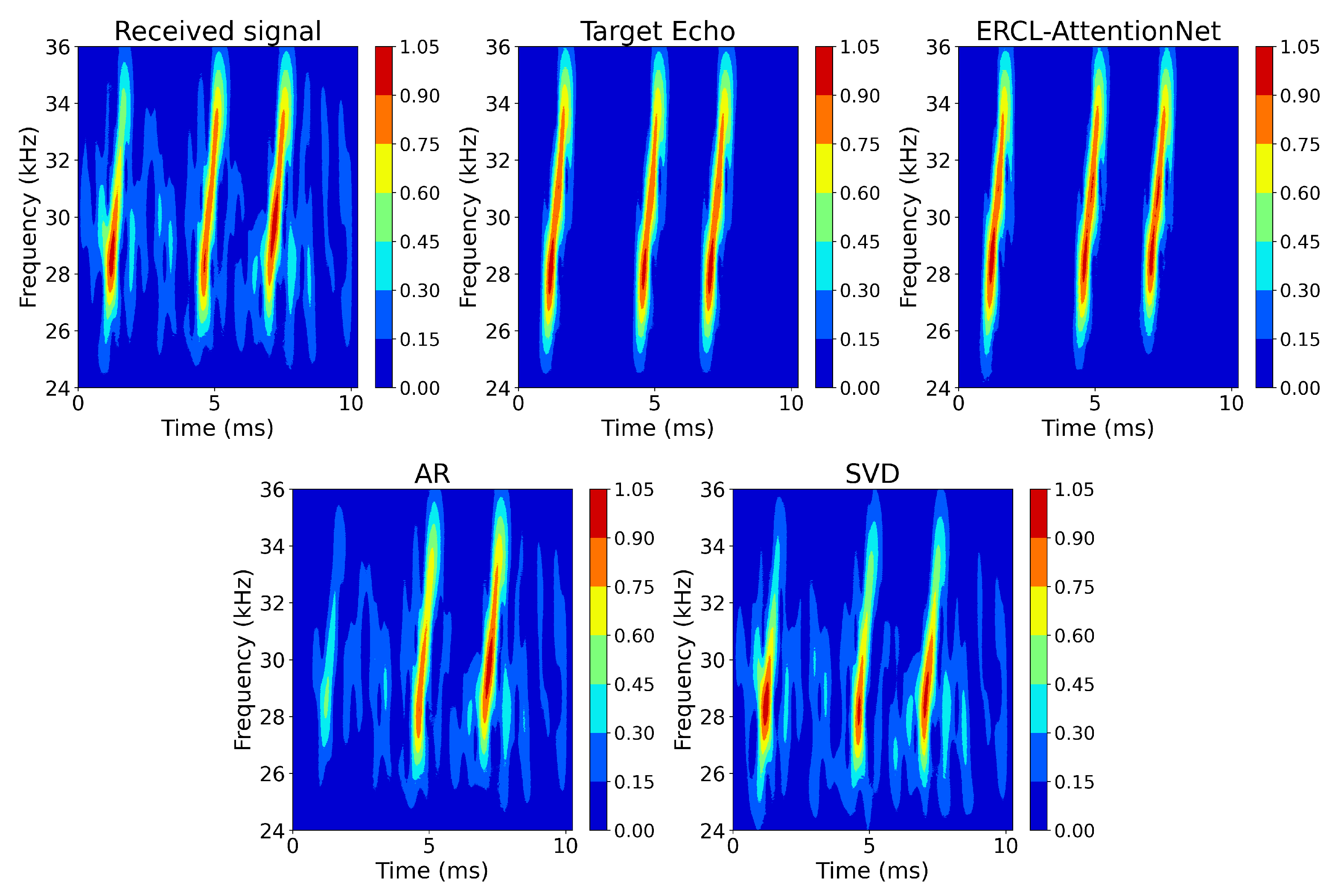
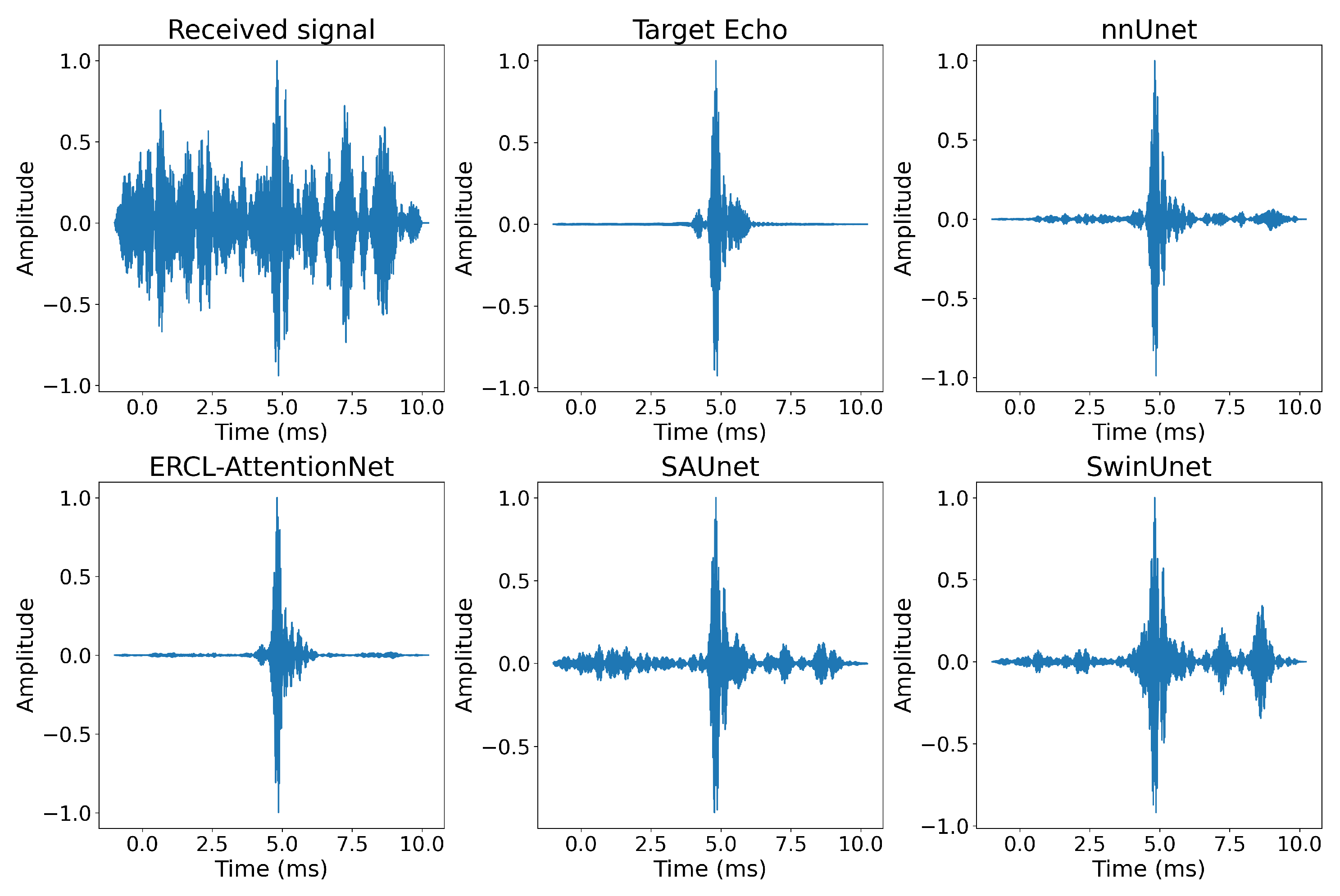
4.2. Evaluation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, X.; Wang, N.; Yan, Y.; Yang, K. Underwater detection of small-volume weak target echo in harbor scene under multisource interference. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, N.; Ning, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Q.; Wu, D.; Hou, P. Acoustic source localization in a reverberant environment based on sound field morphological component analysis and alternating direction method of multipliers. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trucco, A. Experimental results on the detection of embedded objects by a prewhitening filter. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2001, 26, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.; Salisbury, J. Improved active sonar detection using autoregressive prewhiteners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 87, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Pan, Y.; Tang, J. Multi-Level Binary SVD for Sonar Reverberation Suppression. In Proceedings of the 2018 OCEANS-MTS/IEEE Kobe Techno-Oceans (OTO), Kobe, Japan, 28–31 May 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Wu, S.; Guo, S.; Peng, D. Study on an anti-reverberation method based on PCI-SVM. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 182, 108189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Qiu, H.A.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Miao, F. Research on reverberation cancellation algorithm based on empirical mode decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Information Technology, Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (ICIBA), Chongqing, China, 6–8 November 2020; Volume 1, pp. 941–945. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, L.; Feng, X.; Juan, Y.; Xudong, A. The bottom reverberation suppression algorithm for side scan sonar. In Proceedings of the 2014 Oceans-St. John’s, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 14–19 September 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, K.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, E. Noise reduction for sonar images by statistical analysis and fields of experts. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2021, 74, 102995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.M.; Yahya, N.; Kamel, N. Optimum order selection criterion for autoregressive models of bandlimited EEG signals. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE-EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES), Langkawi Island, Malaysia, 1–3 March 2021; pp. 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Libal, U.; Johansson, K.H. Yule-Walker equations using higher order statistics for nonlinear autoregressive model. In Proceedings of the 2019 Signal Processing Symposium (SPSympo), Krakow, Poland, 17–19 September 2019; pp. 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, Q. Spatio-Temporal Reverberation Suppression Method Based on Itakura Distance Segmental Pre-Whitening and Progressive Adaptive Binary SVD. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Bali, Indonesia, 19–22 August 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Qi, J.; Xu, F.; Ren, Z. Weakly-Supervised Depression Detection in Speech Through Self-Learning Based Label Correction. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2025, 33, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Wee, K. Multi-Noise Representation Learning for Robust Speaker Recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2025, 32, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.C.; Ai, Y.; Ling, Z.H. Incorporating Ultrasound Tongue Images for Audio-Visual Speech Enhancement. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2024, 32, 1430–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. Improving monaural speech enhancement by mapping to fixed simulation space with knowledge distillation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2024, 31, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoller, D.; Ewert, S.; Dixon, S.W.U. Wave-U-Net: A Multi-Scale Neural Network for End-to-End Audio Source Separation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.03185. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Mesgarani, N. Conv-tasnet: Surpassing ideal time–frequency magnitude masking for speech separation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 27, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; He, B.; Zhu, W.P. Caunet: Context-aware u-net for speech enhancement in time domain. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Daegu, Republic of Korea, 22–28 May 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, K.; Li, G.; Xie, X.; Wang, Z. Sonar Dereverberation via Independent Component Analysis and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 22nd IEEE Interregional NEWCAS Conference (NEWCAS), Sherbrooke, QC, Canada, 16–19 June 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. Learning spectral mapping for speech dereverberation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; pp. 4628–4632. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Woods, W.S.; Merks, I.; Zhang, T. Learning spectral mapping for speech dereverberation and denoising. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2015, 23, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, O.; Chazan, S.E.; Gannot, S.; Goldberger, J. Speech dereverberation using fully convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Rome, Italy, 3–7 September 2018; pp. 390–394. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Zhu, W.; Li, S.; Luo, H.; Zhang, X.L.; Rahardja, S. Multi-resolution convolutional residual neural networks for monaural speech dereverberation. IEEE/Acm Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2024, 32, 2338–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.F.; Falk, T.H. Speech dereverberation with context-aware recurrent neural networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2018, 26, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, B.; Zhang, T. Late reverberation suppression using recurrent neural networks with long short-term memory. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5434–5438. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Du, J.; Chai, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lee, C.H. A LSTM-based joint progressive learning framework for simultaneous speech dereverberation and denoising. In Proceedings of the 2019 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Lanzhou, China, 18–21 November 2019; pp. 274–278. [Google Scholar]
- Kothapally, V.; Xia, W.; Ghorbani, S.; Hansen, J.H.; Xue, W.; Huang, J. Skipconvnet: Skip convolutional neural network for speech dereverberation using optimally smoothed spectral mapping. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.09131. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Wang, K.; Zhu, W.P. Se-dptunet: Dual-path transformer based u-net for speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2022 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 7–10 November 2022; pp. 696–703. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Du, S.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y. Underwater target recognition method based on multi-domain active sonar echo images. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Xi’an, China, 17–20 August 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; He, Q.; Zhu, S.; Li, X.; Fan, X.; Xin, Y. Multi-scale fusion and efficient feature extraction for enhanced sonar image object detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 256, 124958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.H.; Wu, C.H. Memory-Efficient Multi-Step Speech Enhancement with Neural ODE. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, INTERSPEECH 2022, Incheon, Republic of Korea, 18–22 September 2022; pp. 961–965. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Li, A.; Zheng, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Dual-branch attention-in-attention transformer for single-channel speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 7847–7851. [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim, A.V.; Lim, J.S. The importance of phase in signals. Proc. IEEE 1981, 69, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Saif, A.; Lu, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, T.; Kingsbury, B.; Saon, G. Joint Unsupervised and Supervised Training for Automatic Speech Recognition via Bilevel Optimization. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.06980. [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi, S.; De Fréin, R. Elevato-CDR: Speech Enhancement in Large Delay and Reverberant Assisted Living Scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2024 9th International Conference on Frontiers of Signal Processing (ICFSP), Paris, France, 12–14 September 2024; pp. 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Nguyen, B.T.; Geng, Y.; Iwai, K.; Nishiura, T. Joint Deep Neural Network for Single-channel Speech Separation on Masking-based Training Targets. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 152036–152044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.C.M.; Silva, D.F.; Marcacini, R.M. Artist Similarity based on Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks. Ieee/Acm Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2024, 32, 3717–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothapally, V.; Hansen, J.H. SkipConvGAN: Monaural speech dereverberation using Generative Adversarial Networks via complex time-frequency masking. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2022, 30, 1600–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Deng, J.; Geng, M.; Jin, Z.; Wang, T.; Hu, S.; Cui, M.; Meng, H.; Liu, X. Audio-visual end-to-end multi-channel speech separation, dereverberation and recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2023, 31, 2707–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, F.; Yang, J. Restoration of bone-conducted speech with U-net-like model and energy distance loss. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 31, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, N.; Hansen, J.H. Speech enhancement for cochlear implant recipients using deep complex convolution transformer with frequency transformation. IEEE/Acm Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2024, 32, 2616–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chitre, M.; Stojanovic, M. Underwater acoustic communications. Nat. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2024, 2, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Ghosh, D.; Mandal, N. Unveiling the Dynamics of Mantle Plumes Initiated by Rayleigh-Taylor Instabilities: Impact of Layer-Parallel Global Flows. Authorea Preprints 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bjørnø, L. Chapter 5—Scattering of Sound. In Applied Underwater Acoustics; Neighbors, T.H., Bradley, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 297–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y. CWT-based method for extracting seismic velocity dispersion. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 7502205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, M.E. Some statistical properties of lake surface reverberation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1978, 64, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urick, R.J. Principles of Underwater Sound, 3rd ed.; Peninsula Publishing: Westport, CT, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]


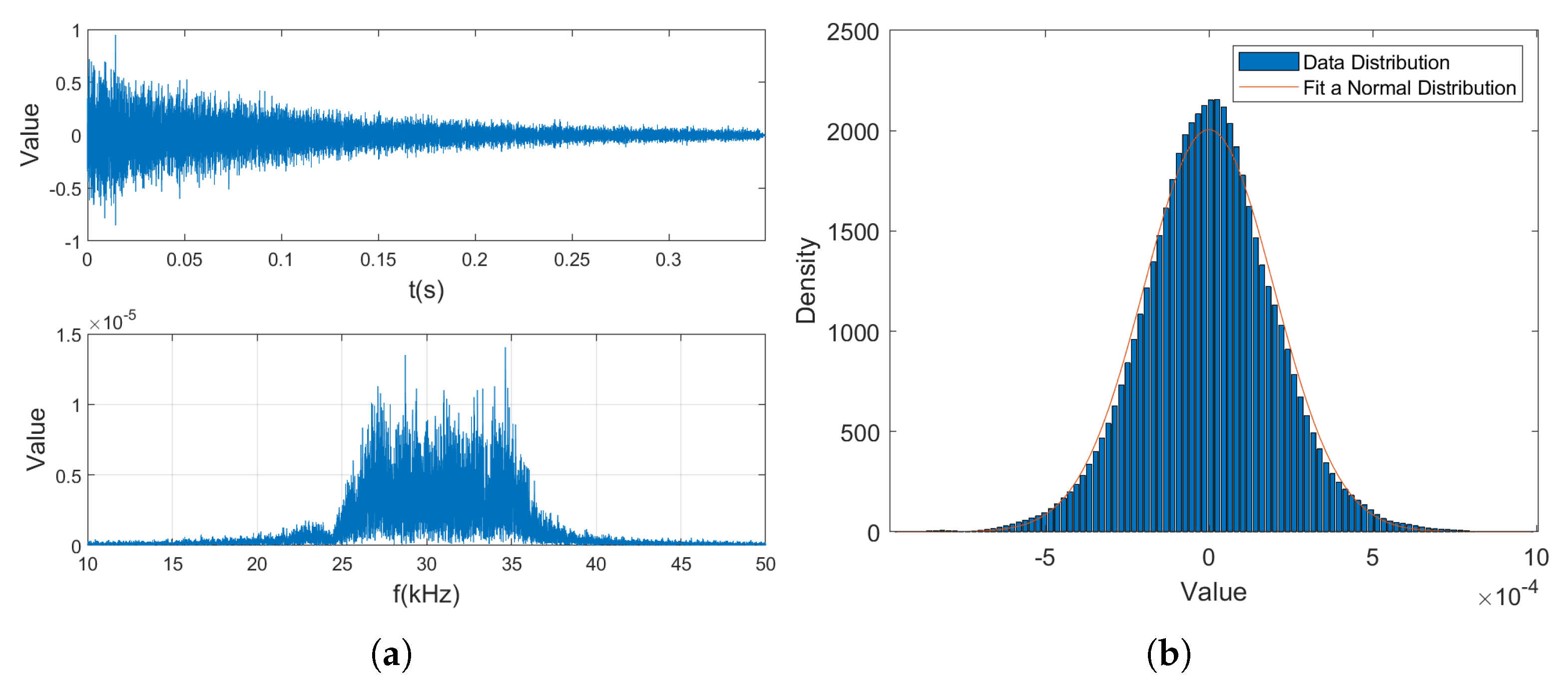
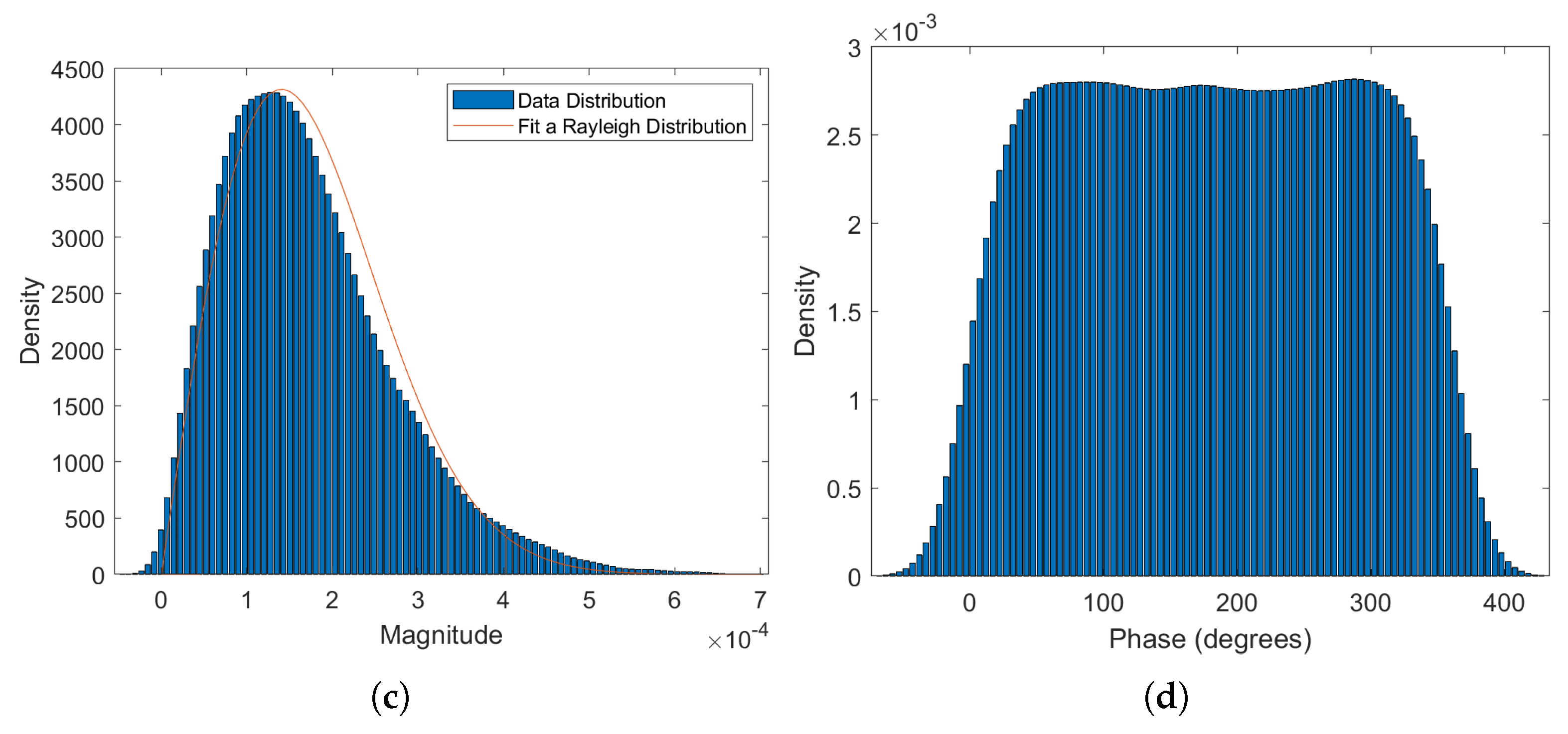
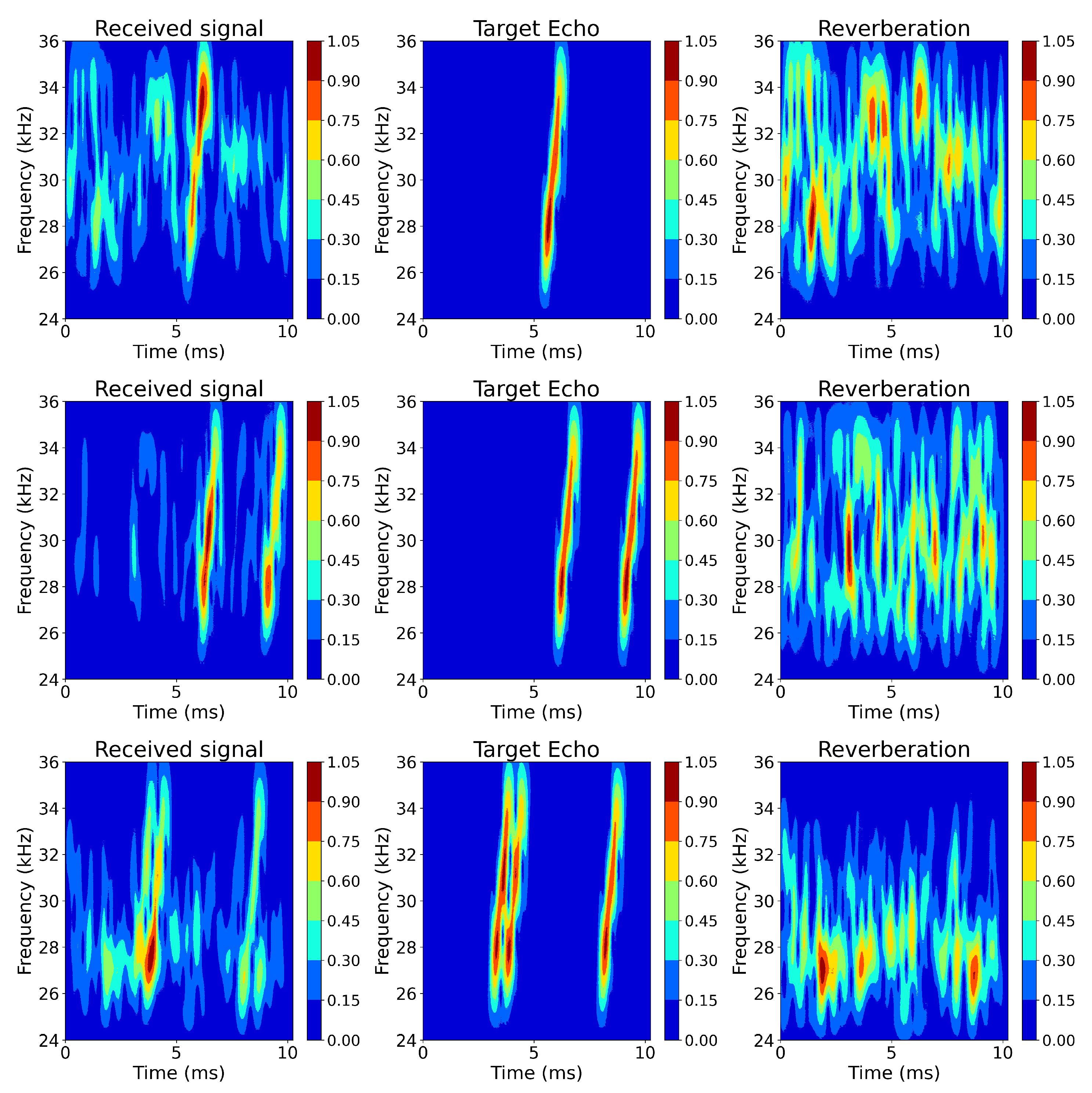

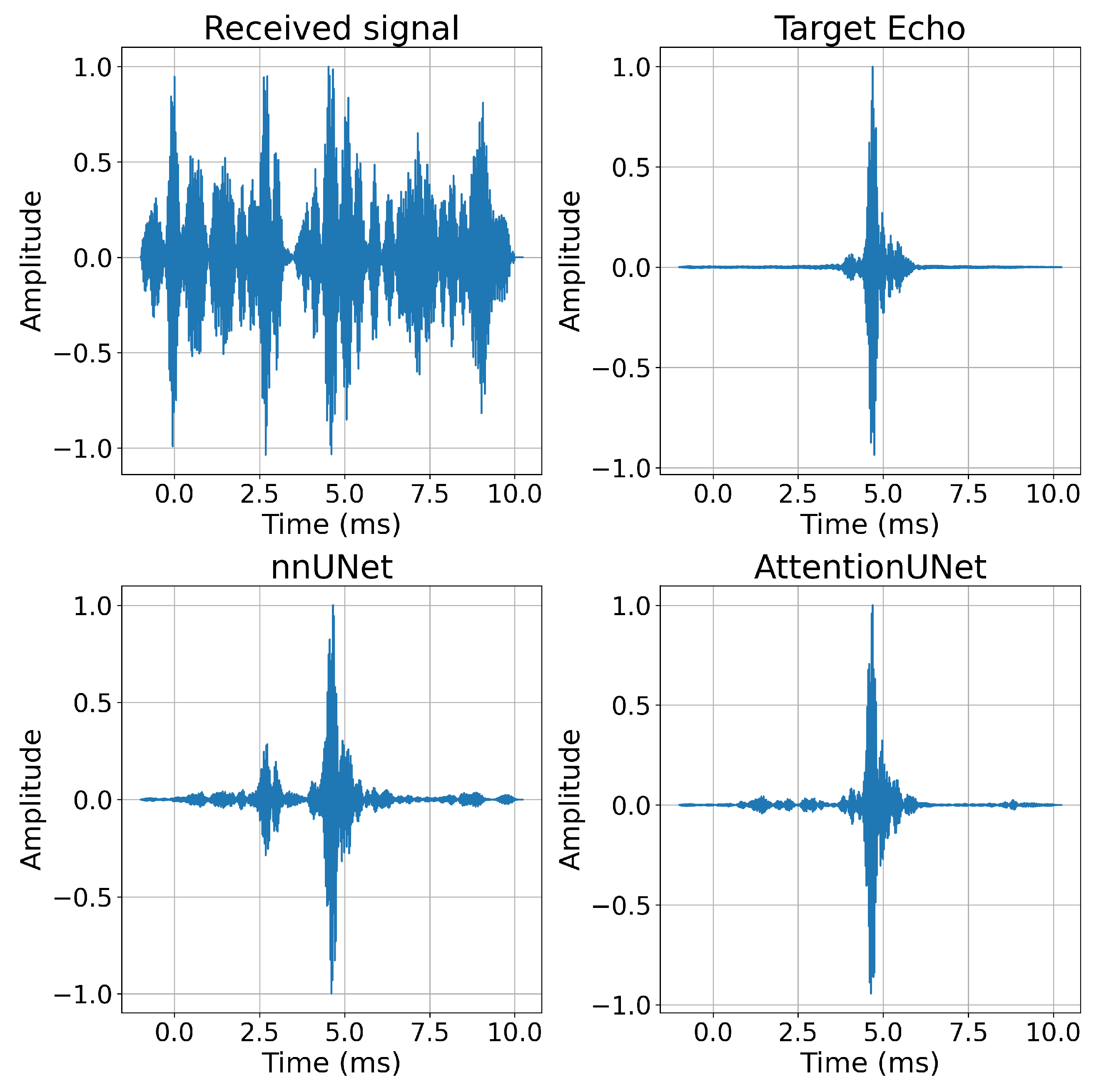




| Attribute | Number |
|---|---|
| Transmitted Signals | 9 |
| Targets | 3 |
| Target Angles | 60 |
| SRR | 9 |
| Entries | 14,580 |
| Model | PSRR (dB) | SSIM | PAR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unet for echo learning | 31.681 | 0.864 | 27.035 |
| AttentionUnet for echo learning | 34.583 | 0.925 | 29.982 |
| AttentionUnet for reverberation learning | 33.677 | 0.918 | 27.405 |
| ERCL-AttentionNet | 35.208 | 0.948 | 31.018 |
| Method | PSRR (dB) | SSIM | PAR |
|---|---|---|---|
| AR (p = 2) | 26.821 | 0.673 | 21.526 |
| SVD | 25.327 | 0.625 | 21.064 |
| ERCL-AttentionNet | 35.208 | 0.948 | 31.018 |
| Model | PSRR (dB) | SSIM | PAR |
|---|---|---|---|
| nnUnet | 31.681 | 0.864 | 27.035 |
| AttentionUnet | 34.583 | 0.925 | 29.982 |
| SAUnet | 27.568 | 0.654 | 23.025 |
| SwinUnet | 29.756 | 0.803 | 26.014 |
| ERCL-AttentionNet | 35.208 | 0.948 | 31.018 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, X.; Tang, C.; Pu, Z. Underwater Reverberation Suppression Using Wavelet Transform and Complementary Learning. Oceans 2025, 6, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6020036
Liu J, Zhang Q, Cui X, Tang C, Pu Z. Underwater Reverberation Suppression Using Wavelet Transform and Complementary Learning. Oceans. 2025; 6(2):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6020036
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiajie, Qunfei Zhang, Xiaodong Cui, Chencong Tang, and Zijun Pu. 2025. "Underwater Reverberation Suppression Using Wavelet Transform and Complementary Learning" Oceans 6, no. 2: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6020036
APA StyleLiu, J., Zhang, Q., Cui, X., Tang, C., & Pu, Z. (2025). Underwater Reverberation Suppression Using Wavelet Transform and Complementary Learning. Oceans, 6(2), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6020036






