Oceanic Environmental Impact in Seaports
Abstract
1. Introduction
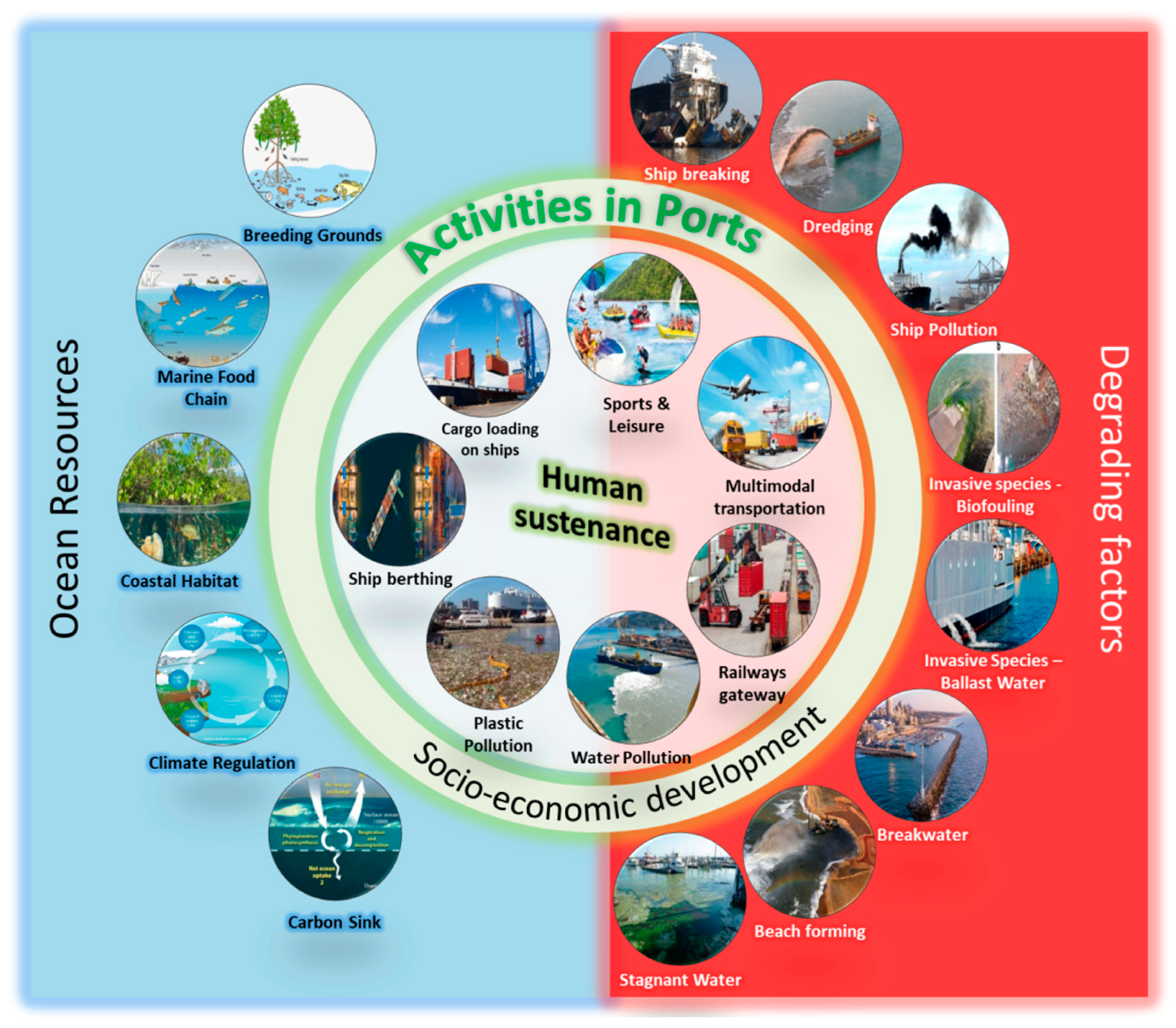
2. Understanding Ports, Port Activities, and Their Correlation with Human Sustenance
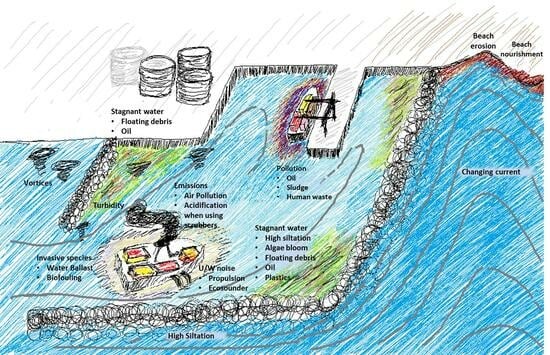
3. Seaports and Their Oceanic Environmental Impacts
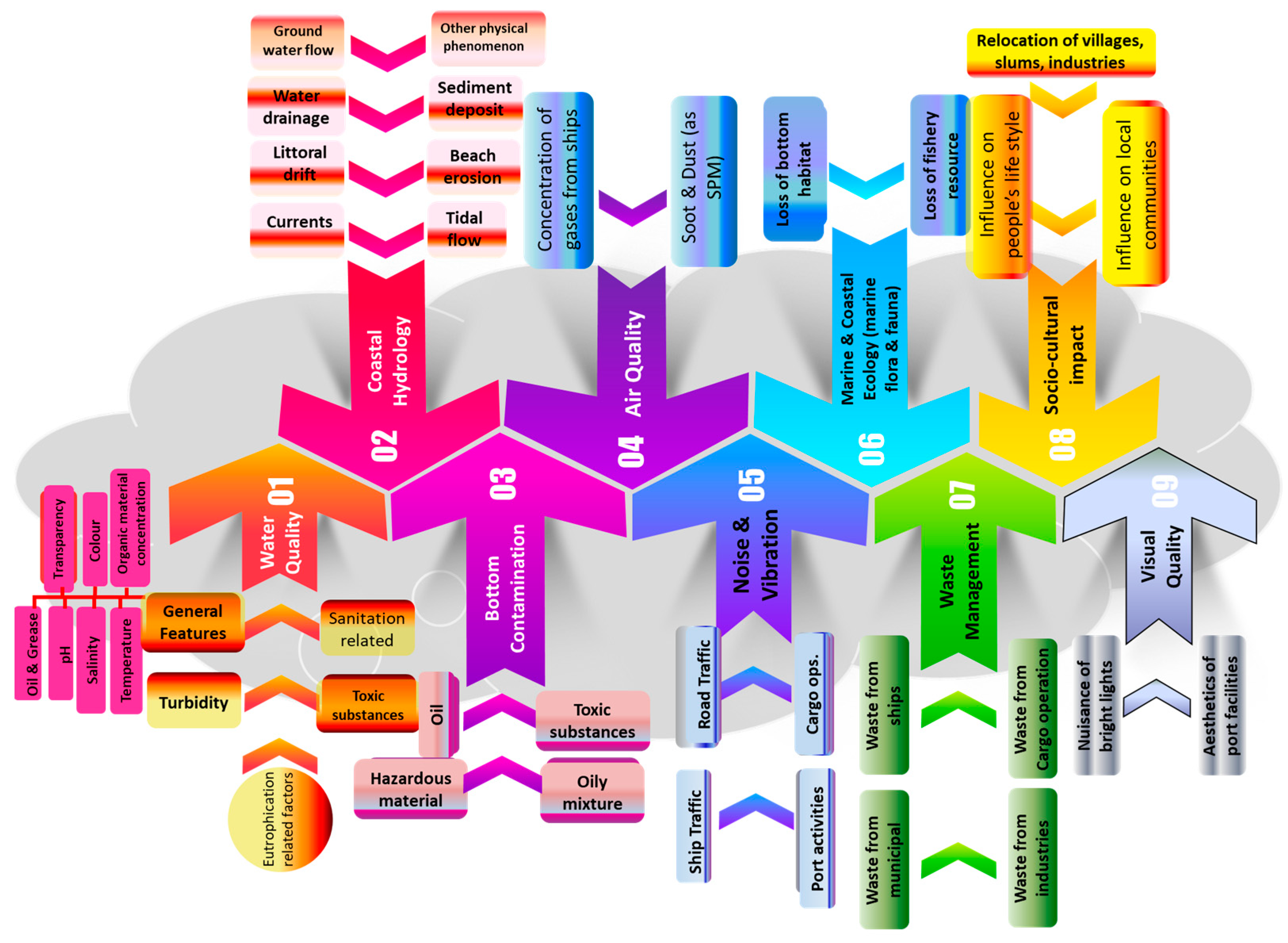
3.1. Physical Seascape Alterations and Their Impacts
3.1.1. Water Quality within the Port Basin
3.1.2. Sediment Quality within the Port Basin
3.1.3. Impact on Coastline
3.2. Biological Impacts
3.2.1. Impacts on Marine Mammals
3.2.2. Impacts on Turtles
3.2.3. Impacts on Benthic Habitats
3.2.4. Factors Impacting Marine Life in Ports
Water Quality
- (a)
- Due to nutrients: Nutrient accumulation as a result of discharge in ports causes eutrophication. This eutrophication depletes oxygen levels, causing the death of fishes and other species [61] due to higher chlorophyll-a concentrations [57]. The impact of chlorophyll-a concentration was found to be high in a 6 km radius from the ports, beyond which the impact reduced [62]. For a newly constructed port, the chlorophyll-a concentration was found to increase during the final two months before starting operations. However, this effect was too small to create an algal bloom that could cause the death of fishes [47].
- (b)
- Due to non-native species from ballast water: The exchange of ballast water by a ship occurs as a requirement for maintaining stability during the passage of the ship and the loading and unloading of cargo. When a ship moves from one port to another without adequate cargo and consumes fuel and water, it is forced to take in seawater as ballast to ensure its transverse stability. This ballast water carries species local to the region from which the ballast water was taken and is eventually transported to a foreign oceanic space, where the ballast water is discharged. This mechanism allows the migration of species from one oceanic space to another. The species introduced in this way are referred to as bioinvaders, exotic species, alien species, or non-indigenous species. Studies have shown that nearly 10 billion tons of ballast water is transported each year [69]. When these species are released, the temperature, salinity, resources available, existing competition for food, and the presence of predators determine whether these species will survive in the new conditions. If the non-indigenous species survive, they become invasive to the existing species, thereby creating an imbalance in the food chain.
- (c)
- Due to non-native species from biofouling: Yet another method by which invasive species may be introduced to ports is through biofouling on vessels. Biofouling is the colonization of marine species on a substrate when it comes into contact with water. Through prolonged contact with water, multiple colonization layers deposit on one another to eventually allow larger macro-fouling species to be deposited. If the structure is moving, the deposited layers are likely to be washed away. However, the problem becomes acute when the structure is stationary. The problem of biofouling is common to both stationary structures such as dykes, groins, jetties, and piers and moving structures such as ships, boats, and yachts. This biofouling causes corrosion of the adhering surface, and for moving structures it increases resistance, thereby increasing fuel consumption and blocking water intake, leading to engine damage due to overheating. However, the translocation of such invasive species through vessel biofouling has received little attention from researchers and policymakers [84].
- (d)
- Due to pollutants, e.g., chemicals, oil, human waste, plastics: Water quality in ports can be impacted by several pollutants, such as oil and chemicals, human waste, plastics, etc., which may be discharged accidentally or intentionally by ships, industries, or anthropogenic activities in the port, both terrestrial and marine. These pollutants may originate from land-based sources, marine traffic, port infrastructure, or neighboring coastal areas. The resulting contaminants include chemicals, metals, plastics, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which accumulate in the sediments and persist in the environment for prolonged durations. While the natural process of degradation of these pollutants is by bacteria, the presence of high concentrations of these pollutants and multiple of them at the same time exerts a toxic effect on the bacteria present [97], making them nearly ineffective. Similarly, untreated human sewage delivers pathogenic bacteria and viruses that may not be killed when exposed to seawater. Increased concentrations of these microbes make local seafood (such as clams and mussels) unsafe for consumption, transmit waterborne viruses such as cholera, and make the contaminated waters unsafe for bathing [98].
- (e)
- Due to the impact of climate change: Climate change is likely to have a severe impact on biodiversity by altering habitats. Since climate determines the distribution of species, it is possible that all existing plants and animals may not be able to accept the resulting climate change, which may lead to the extinction of some species, leading to biodiversity losses. With some species becoming extinct, those dependent on the extinct ones may not be able to survive, leading to further species becoming extinct or modifying their behavior. While the exact impacts of climate change have not been studied to date, an increase in temperature due to climate change would impact planktons and alter disease behavior, while an increase in sea level would impact certain species of frogs and toads, and increased acidification would impact living corals.
Noise and Vibration
Construction of Maritime and Coastal Structures
4. Existing Policies and Legal Provisions to Address These Pollutants
5. Discussion
6. The Way Ahead
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Efimova, E.G.; Gapochka, A.A. Seaports as drivers of regional economic development: The case of Saint Petersburg and Leningrad Province. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2020, 8, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, B.; Khan, S.A.; Raza, M. Econometric evidence of catalytic effect of seaport activity in OECD countries: Getting it right. Marit. Transp. Res. 2023, 4, 100090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayesu, E.K.; Sakyi, D.; Arthur, E.; Osei-Fosu, A.K. The impact of trade on African welfare: Does seaport efficiency channel matter? Res. Glob. 2022, 5, 100098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanques, A.; Guillén, J.; Puig, P.; Durán, R. Effects of long-lasting massive dumping of dredged material on bottom sediment and water turbidity during port expansion works. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2022, 223, 106113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žilinskas, G.; Janušaitė, R.; Jarmalavičius, D.; Pupienis, D. The impact of Klaipėda Port entrance channel dredging on the dynamics of coastal zone, Lithuania. Oceanologia 2020, 62, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prukpitikul, S.; Kaewpoo, N.; Ariffin, E.H. An evaluation of a new offshore breakwater at Sattahip Port, Thailand. Marit. Technol. Res. 2019, 1, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengsupavanich, C. A current Environmental Impact Assessment of a port in Thailand: Marine physical aspects. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2011, 54, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengsupavanich, C. Enhancing water circulation in a river port. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2019, 22, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, J.A.; Panaitescu, M.; Panaitescu, F.; Ghiță, S. Impact of coastal protection systems on marine ecosystems. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 85, 07011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.V.; Prakash, G. Assessment of environmental sustainability issues for South-Asian maritime ports. Aust. J. Marit. Ocean. Aff. 2023, 15, 154–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, A. Seaports participation in enhancing the sustainable development goals. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwarakish, G.S.; Salim, A.M. Review on the Role of Ports in the Development of a Nation. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, M.; Darbra, R.M. The Role of Ports in a Global Economy, Issues of Relevance and Environmental Initiatives. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 593–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Saz-Salazar, S.; García-Menéndez, L.; Merk, O. The Port and Its Environment: Methodological Approach for Economic Appraisal, OECD Regional Development Working Papers 2013, 2013/24; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trozzi, C.; Vaccaro, R. Environmental impact of port activities. In Maritime Engineering and Ports II; Brebbia, C.A., Olivella, J., Eds.; Wessex Institute of Technology: Southampton, UK, 2000; p. 400. [Google Scholar]
- Asariotis, R. Climate Change Impacts on Seaports: A Growing Threat to Sustainable Trade and Development, UNCTAD. Available online: https://unctad.org/news/climate-change-impacts-seaports-growing-threat-sustainable-trade-and-development (accessed on 4 June 2023).
- Pettit, S.J.; Beresford, A.K.C. Port development: From gateways to logistics hubs. Marit. Policy Manag. 2009, 36, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, F.; Maugeri, S. Origin and taxonomy of conflicts in seaports: Towards a research agenda. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2013, 8, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. An Overview of Ports Planning and Operations to Support Community Participation. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/community-port-collaboration/ports-primer-71-environmental-impacts (accessed on 6 August 2023).
- UNESCAP. Assessment of the Environmental Impact of Port Development. Available online: https://www.unescap.org/sites/default/files/pub_1234_ch2.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2023).
- Cutroneo, L.; Carbone, C.; Consani, S.; Vagge, G.; Canepa, G.; Capello, M. Environmental complexity of a port: Evidence from circulation of the water masses, and composition and contamination of bottom sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Woo, S.; Lee, H.S.; Gu, B.; Kim, J.W.; Song, J.I. Baroclinic effect on inner-port circulation in a macro-tidal estuary: A case study of Incheon North Port, Korea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, T.; Jalil, Z.; Akhyar, A.; Husaini, H. Oceanographic factors as the indicators for shipyard industry development in Kutaraja Fishing Port: A preliminary study. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengsupavanich, C.; Ariffin, E.H.; Yun, L.S.; Pereira, D.A. Environmental impact of submerged and emerged breakwaters. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, S.; Chadwick, A.J.; Fleming, C. Investigation of detached breakwaters: Part I hydrodynamics. Marit. Eng. 2005, 158, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iouzzi, N.; Mouakkir, L.; Meftah, M.B.; Chagdali, M.; Loudyi, D. SWAN Modeling of Dredging Effect on the Oued Sebou Estuary. Water 2022, 14, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaan, M.; Lebleb, A.A.; ElZahar, M.M.H.; Iskander, M. Studying the tidal-induced water circulation pattern within EL-Burullus fishing harbor, Egypt, using CMS-PTM numerical modeling. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 180, 105726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonamano, S.; Madonia, A.; Piazzolla, D.; de Mendoza, F.P.; Piermattei, V.; Scanu, S.; Marcelli, M. Development of a predictive tool to support environmentally sustainable management in port basins. Water 2017, 9, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Shin, H.; Kim, Y.T.; Dellapenna, T.M.; Kim, K.J.; Williams, J.; Kim, S.; Figueroa, S.M. Field investigation of siltation at a tidal harbor: North Port of Incheon, Korea. Ocean. Dyn. 2019, 69, 1101–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallwork, J.T.; Pu, J.H.; Kundu, S.; Hanmaiahgari, P.R.; Pandey, M.; Satyanaga, A.; Khan, M.A.; Wood, A. Review of suspended sediment transport mathematical modelling studies. Fluids 2022, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Chen, C.; Tsai, M.; Wu, C.; Lin, Y.; Wang, M.; Albarico, F.P.J.B.; Chen, C.; Dong, C. Impacts of fishing vessels on the heavy metal contamination in sediments: A case study of Qianzhen Fishing Port in Southern Taiwan. Water 2022, 14, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas Alkarkhi, F.M.; Ismail, N.; Easa, A.M. Assessment of arsenic and heavy metal contents in cockles (Anadara granosa) using multivariate statistical techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.K.; Hossain, M.R.; Ghosh, G.C.; Ghosh, P.; Sadik, A.; Habib, A.; Zaman, S.; Enamul Kabir, A.H.M.; Khan, A.S.; Rahman, M.M. Distribution, source identification and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Mongla port area, Bangladesh. Toxin Rev. 2022, 41, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, N.P.C.; Ha, N.N.; Dong, N.V.; Nhan, D.T.; Tri, N.N. Heavy metal levels in blood cockle from south Vietnam coastal waters, New Zealand. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uda, T. Fundamental issues in Japan’s coastal management system for the prevention of beach erosion. Marit. Technol. Res. 2022, 4, 251788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengsupavanicha, C.; Seenprachawong, U.; Gallardo, W.G.; Shivakoti, G.P. Port-induced erosion prediction and valuation of a local recreational beach. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 67, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijamir, K.; Ameer, F.; Thennakoon, S.; Herath, J.; Iyoob, A.L.; Zahir, I.L.M.; Sabaratnam, S.; Jisna, M.V.F.; Madurapperuma, B. Geoinformatics application for estimating and forecasting of periodic shoreline changes in the east coast of Ampara District, Sri Lanka. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2023, 232, 106425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ayllón, S.; Gómez, F.; Bianco, F. Analysis of the spatial correlation between port areas configuration and alterations of the coastal shoreline: A multidisciplinary approach using spatiotemporal GIS indicators. Land 2022, 11, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandepitte, L.; Vanhoorne, B.; Decock, W.; Vranken, S.; Lanssens, T.; Dekeyzer, S.; Verfaille, K.; Horton, T.; Kroh, A.; Hernandez, F.; et al. A decade of the World Register of Marine Species—General insights and experiences from the Data Management Team: Where are we, what have we learned and how can we continue? PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Nielsen, D.A.; Kelleway, J.J.; Atwood, T.B.; Seymour, J.R.; Petrou, K.; Connolly, R.M.; Thomson, A.C.; Trevathan-Tackett, S.M.; Ralph, P.J. Can we manage coastal ecosystems to sequester more blue carbon? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2017, 15, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desforges, J.W.; Sonne, C.; Levin, M.; Siebert, U.; Guise, S.D.; Dietz, R. Immunotoxic effects of environmental pollutants in marine mammals. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakes, P.; Dall, S.R.X. Marine mammal behavior: A review of conservation implications. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckendorf, A.; Siebert, U.; Parmentier, E.; Das, K. Chemical pollution and diseases of marine mammals. In Marine Mammals; Brennecke, D., Knickmeier, K., Pawliczka, I., Siebert, U., Wahlberg, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulland, F.M.D.; Baker, J.D.; Howe, M.; LaBrecque, E.; Leach, L.; Moore, S.E.; Reeves, R.R.; Thomas, P.O. A review of climate change effects on marine mammals in United States waters: Past predictions, observed impacts, current research and conservation imperatives. Clim. Chang. Ecol. 2022, 3, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albouy, C.; Delattre, V.; Donati, G.; Frölicher, T.L.; Albouy-Boyer, S.; Rufina, M.; Pellissier, L.; Mouillot, D.; Leproeur, F. Global vulnerability of marine mammals to global warming. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutcavage, M.E. Human impacts on sea turtle survival. In The Biology of Sea Turtles, Volume I; Lutz, P.L., Musick, J.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas, M.L.; Rodríguez-Caballero, E.; Esteban, N.; Carpio, A.J.; Barrera-Vilarmau, B.; Fuentes, M.M.P.B.; Robertson, K.; Azanza, J.; León, Y.; Ortega, Z. Uncertain future for global sea turtle populations in face of sea level rise. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA, Benthic Communities and Habitats. Available online: https://www.epa.wa.gov.au/sites/default/files/Policies_and_Guidance/Guideline-Benthic-Communities-Habitats-131216_2.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Harris, P.T. Anthropogenic threats to benthic habitats. In Seafloor Geomorphology as Benthic Habitat, 2nd ed.; Harris, P.T., Baker, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 35–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijnders, P.J.H.; Aguilar, A.; Borrell, A. Pollution and marine mammals. In Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals, 2nd ed.; William, F.P., Würsig, B., Thewissen, J.G.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal-ur-Rehman, M. Polluted water borne diseases: Symptoms, causes, treatment and prevention. J. Med. Chem. Sci. 2019, 2, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogowska, J.; Namieśnik, J. Environmental implications of oil spills from shipping accidents. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Whitacre, D., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSRP. Filtration of Runoff from Pressure Washing Vessel Hull in Drydock. Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA445598.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2023).
- Hossain, M.S.; Fakhruddin, A.N.M.; Chowdhury, M.A.Z.; Gan, S.H. Impact of ship-breaking activities on the coastal environment of Bangladesh and a management system for its sustainability. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 60, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Österlund, H.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. The pollution conveyed by urban runoff: A review of sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.T. Thermal pollution and its control. Boston Coll. Environ. Aff. Law Rev. 1972, 2, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Le Moal, M.; Gascuel-Odoux, C.; Ménesguen, A.; Souchon, Y.; Étrillard, C.; Levain, A.; Moatar, F.; Pannard, A.; Souchu, P.; Lefebvre, A.; et al. Eutrophication: A new wine in an old bottle? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.; Stark, C.; Ridd, P.; Jones, R. Spatial patterns in water quality changes during dredging in tropical environments. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuchies, J.; Cox, T.J.S.; Van Itterbeeck, K.; Meysman, F.J.R.; Blust, R. The impact of scrubber discharge on the water quality in estuaries and ports. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madon, B.; David, R.; Torralba, A.; Jung, A.; Marengo, M.; Thomas, H. A review of biodiversity research in ports: Let’s not overlook everyday nature! Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2023, 242, 106623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménesguen, A.; Lacroix, G. Modelling the marine eutrophication: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudhistira, M.H.; Karimah, I.D.; Maghfira, N.R. The effect of port development on coastal water quality: Evidence of eutrophication states in Indonesia. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 196, 107415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.D.S.; Abessa, D.M.D.S.; Bainy, A.C.D.; Zaroni, L.P.; Gasparro, M.R.; Bícego, M.C.; Taniguchi, S.; Furley, T.H.; De Sousa, E.C.P.M. Integrated assessment of multilevel biomarker responses and chemical analysis in mussels from São Sebastião, São Paulo, Brazil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Yang, G.; Wang, N.; Lu, X. Relationship between environmental factors and plankton in the Bayuquan Port, Liaodong Bay. China: A five-year study. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2016, 34, 654–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Coastal Environmental Studies: Importance, Problem and Prospect. J. Geogr. Nat. Disasters 2012, 2, e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.M.S.; Tagde, J.P.; Singh, P.R.; Dutta, S.; Sangolkar, L.N.; Kumar, M.S. Impact of port and harbour activities on plankton distribution and dynamics: A multivariate approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 165, 112105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.L.; Pollard, A.I. Changes in the relationship between zooplankton and phytoplankton biomasses across a eutrophication gradient. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 2493–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korus, J. How Phytoplankton Endangers Fish Farms—and the Best Way to Combat the Threat, Innovasea. Available online: https://www.innovasea.com/insights/how-phytoplankton-endangers-fish-farms/#:~:text=Thus%2C%20in%20high%20concentrations%20phytoplankton,issues%20in%20a%20fish’s%20gills (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- Lymperopoulou, D.S.; Dobbs, F.C. Bacterial diversity in ships’ ballast water, ballast-water exchange, and implications for ship-mediated dispersal of microorganisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1962–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchin, D.; Lucy, F.; Sullivan, M. Zebra. Mussel: Impacts and spread. In Invasive aquatic species of Europe. Distribution, Impacts and Management; Leppäkoski, E., Gollasch, S., Olenin, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2002; pp. 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.M.; Elliott, J.A. Life history and population dynamics of green crabs (Carcinus maenas). Fishes 2020, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.C.; Woodfield, R.A.; Cohen, A.N.; Harris, L.H.; Goddard, J.H.R. First report of the Asian kelp Undaria pinnatifida in the Northeastern Pacific Ocean. Biol. Invasions 2002, 4, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.J.; Slaten, D.D.; Marano, N.; Tappero, J.W.; Wellman, M.; Albert, R.J.; Hill, V.R.; Espey, D.; Handzel, T.; Henry, A.; et al. Preventing maritime transfer of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1680–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saburova, M.; Al-Kandari, M.; Polikarpov, I.; Akbar, A.; Hussain, S.; Rahmeh, R.; Al-Zakri, W.; Al-Yamani, F. Alien toxic dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama from the Western Pacific in Kuwait, NW Indian Ocean. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2022, 196, 105027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, J.B.M.; de Oliveira, A.R.G.; da Costa, K.G.; Brito, E.P.; dos Santos Fernandes, F.D.; Nunes, Z.M.P.; Koening, M.L.; Pereira, L.C.C.; da Costa, R.M. Phytoplankton of the shipping sector of São Marcos Bay (Amazon Coast): A potential risk area for the establishment of non-indigenous species. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 49, 102121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempesti, J.; Langeneck, J.; Romani, L.; Garrido, M.; Lardicci, C.; Maltagliati, F.; Castelli, A. Harbour type and use destination shape fouling community and non-indigenous species assemblage: A study of three northern Tyrrhenian port systems (Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwigwe, T.I.; Kiyokazu, M. Investigation of ballast water quality in onne harbor-physiochemical assessment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 13799–13808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Shi, J.; Li, T.; Ren, L.; Tian, W.; Lu, X.; Han, Y.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, T. Deciphering the characterization, ecological function and assembly processes of bacterial communities in ship ballast water and sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 152721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valković, V.; Obhođaš, J. Sediments in the ship’s ballast water tank: A problem to be solved. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2717–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brickman, D.; Smith, P.C. Variability in invasion risk for ballast water exchange on the Scotian Shelf of eastern Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurniawan, S.B.; Pambudi, D.S.A.; Ahmad, M.M.; Alfanda, B.D.; Imron, M.F.; Abdullah, S.R.S. Ecological impacts of ballast water loading and discharge: Insight into the toxicity and accumulation of disinfection by-products. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, V.; Drake, L.A. Efficacy of open-ocean ballast water exchange: A review. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2016, 7, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.M.; El-naggar, M.M.A. Ballast water review: Impacts, treatments and management. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2012, 12, 976–984. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiades, E.; Scianni, C.; Davidson, I.; Tamburri, M.N.; First, M.R.; Ruiz, G.; Ellard, K.; Deveney, M.; Kluza, D. The Role of Vessel Biofouling in the Translocation of Marine Pathogens: Management Considerations and Challenges. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 660125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Hua, J.; Chuang, S.; Li, J. Preventative biofouling monitoring technique for sustainable shipping. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, P.; McKinley, A.; Kaur, P. Understanding biofouling and contaminant accretion on submerged marine structures. Npj Mater. Degrad. 2023, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oceanera. Available online: http://oceanic-project.eu (accessed on 3 August 2023).
- Vinagre, P.A.; Simas, T.; Cruz, E.; Pinori, E.; Svenson, J. Marine biofouling: A European database for the marine renewable energy sector. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEPC. 2011 Guidelines for the Control and Management of Ships’ Biofouling to Minimize the Transfer of Invasive Aquatic Species. Available online: https://wwwcdn.imo.org/localresources/en/KnowledgeCentre/IndexofIMOResolutions/MEPCDocuments/MEPC.207.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- GEF-UNDP-IMO GloFouling Partnerships Project. Biofouling Management for Recreational Boating: Recommendations to Prevent the Introduction and Spread of Invasive Aquatic Species. 2022. Available online: https://www.imo.org/en/MediaCentre/Pages/WhatsNew-1769.aspx (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Alghamdi, S.A.; Cordova, R.A.Q. The Impact of Biofouling on Marine Environment: A Qualitative Review of the Current Antifouling Technologies. World Maritime University Dissertations, 1201. Available online: https://commons.wmu.se/all_dissertations/1201 (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Bressy, C.; Lejars, M. Marine fouling and overview. J. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 9, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, W.Y.; Huang, Z.K. Marine Biofouling and Fisheries. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/144566296.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Seaward, K.; Acosta, H.; Inglis, G.J.; Wood, B.; Riding, T.A.C.; Wilens, S.; Gould, B. The marine biosecurity porthole—A web-based information system on non-indigenous marine species in New Zealand. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2015, 6, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Azevedo, J.; Antunes, J.T.; Machado, A.M.; Vasconcelos, V.; Leão, P.N.; Froufe, E. Monitoring of biofouling communities in a Portuguese port using a combined morphological and metabarcoding approach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valchev, J.; Coraddu, A.; Kalikatzarakis, M.; Geertsma, R.; Oneto, L. Numerical methods for monitoring and evaluating the biofouling state and effects on vessels’ hull and propeller performance: A review. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 251, 110883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, E.; Doni, L.; Lussu, R.; Meloni, F.; Cappai, G.; Carucci, A.; Casalone, E.; Mastromei, G.; Vitali, F. Impacts of anthropogenic pollutants on benthic prokaryotic communities in Mediterranean touristic ports. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalli, C.M.; Parsons, T.R. Human impacts on marine biota. In Biological Oceanography: An introduction, 2nd ed.; Lalli, C.M., Parsons, T.R., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, N. Reducing plastic litter for a cleaner planet. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 80, 1456–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, V.L.; Cutrim, C.H.G.; Koch, E.B.D.A.; Araújo, V.A. Anthropogenic threats associated with mortality and biomass of stranded sea turtles on the northern coast of São Paulo State, Brazil. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 80, 1912–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum. The New Plastics Economy—Rethinking the Future of Plastics. Available online: http://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/publications (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Agarwala, N.; Nair, E.M.S. Effect of inplane loading on sound radiation of a floating runway when an airplane is taking off. J. Nav. Archit. Mar. Eng. 2013, 10, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunc, H.P.; McLaughlin, K.E.; Schmidt, R. Aquatic noise pollution: Implications for individuals, populations, and ecosystems. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zhao, X.; Liu, G. Noise in the sea and its impacts on marine organisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12304–12323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, R.; Day, R.; Swadling, K.; Fitzgibbon, Q.P.; Watson, R.A.; Semmens, J.M. Widely used marine seismic survey air gun operations negatively impact zooplankton. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 0195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCauley, R.; Fewtrell, J.; Popper, A.N. High intensity anthropogenic sound damages fish ears. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 113, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popper, A.N.; Smith, A.E.; Cott, P.A.; Hanna, B.W.; MacGillivray, A.O.; Austin, M.E.; Mann, D.A. Effects of exposure to seismic airgun use on hearing of three fish species. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 3958–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlberg, M.; Westerberg, H. Hearing in fish and their reactions to sounds from offshore wind farms. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 288, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocki, L.E.; Dittami, J.P.; Ladich, F. Ship noise and cortisol secretion in European freshwater fishes. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 128, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, R.M.; Parks, S.E.; Hunt, K.E.; Castellote, M.; Corkeron, P.J.; Nowacek, D.P.; Wasser, S.K.; Kraus, S.D. Evidence that ship noise increases stress in right whales. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 2363–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahouri, A.; Elouahmani, N.; Ouchene, H. Recent progress in marine noise pollution: A thorough review. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbe, C.; Marley, S.A.; Schoeman, R.P.; Smith, J.N.; Trigg, L.E.; Embling, C.B. The Effects of Ship Noise on Marine Mammals—A Review. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Bertasi, F.; Colangelo, M.A.; De Vries, M.; Frost, M.; Hawkins, S.J.; Macpherson, E.; Moschella, P.S.; Satta, M.P.; Thompson, R.C.; et al. Ecological impact of coastal defence structures on sediments and mobile fauna: Evaluating and forecasting consequences of unavoidable modifications of native habitats. Coast. Eng. 2005, 52, 1027–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airoldi, L.; Abbiati, M.; Beck, M.W.; Hawkins, S.J.; Jonsson, P.R.; Martin, D.; Moschella, P.S.; Sundelof, A.; Thompson, R.C.; Aberg, P. An ecological perspective on the deployment and design of low-crested and other hard coastal defence structures. Coast. Eng. 2005, 52, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speybroeck, J.; Bonte, D.; Courtens, W.; Gheskiere, T.; Grootaert, P.; Maelfait, J.P.; Mathys, M.; Provoost, S.; Sabbe, K.; Stienen, E.W.M.; et al. Beach nourishment: An ecologically sound coastal defence alternative? A review. Aquat. Conserve Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2006, 16, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R.A. Panama Canal Port Projects Threaten Mangroves, Mongabay. Available online: https://news.mongabay.com/2007/03/panama-canal-port-projects-threaten-mangroves/ (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Pranoto, A.K.; Haryani, E.B.S.; Tanjung, A. The impact of coastal degradation on mangrove ecosystem in North Karawang coastal area. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 278, 012061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paling, E.; Humphreys, G.; McCardle, I. The effect of a harbour development on mangroves in northwestern Australia. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 11, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carugati, L.; Gatto, B.; Rastelli, E.; Martire, M.L.; Coral, C.; Greco, S.; Danovaro, R. Impact of mangrove forests degradation on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.T.; Ngo, V.T.; Pham, T.T.; Bui, T.T.; Nguyen, T.L.G. The Role of Mangroves in Supporting Ports and the Shipping Industry to Reduce Emissions and Water Pollution; Center for International Forestry Research: Bogor, Indonesia, 2022; p. 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandilyan, S.; Kathiresan, K. Mangrove conservation: A global perspective. Biodivers. Conserv. 2012, 21, 3523–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, M.J.; Mayer-Pinto, M.; Airoldi, L.; Firth, L.B.; Morris, R.L.; Loke, L.H.L.; Hawkins, S.J.; Naylor, L.A.; Coleman, R.A.; Chee, S.Y.; et al. Effects of ocean sprawl on ecological connectivity: Impacts and solutions. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2017, 492, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, R.B.; Wool, T.A.; Connolly, J.P. WASP4, A Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Model, EPA/600/3-87/039; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1988.
- Agarwala, N. Role of policy framework for disruptive technologies in the maritime domain. Aust. J. Marit. Ocean. Aff. 2022, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMO. International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL); IMO: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, P.G. The iconic Torrey Canyon oil spill of 1967-marking its legacy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, C.F.; McMullen, C.; Howe, V. Environmental management of ports and harbours—Implementation of policy through scientific monitoring. Mar. Policy 1999, 23, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbra, R.M.; Pittam, N.; Royston, K.A.; Darbra, J.P.; Journee, H. Survey on environmental monitoring requirements of European ports. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwala, P.; Chhabra, S.; Agarwala, N. Using digitalisation to achieve decarbonisation in the shipping industry. J. Int. Marit. Saf. Environ. Aff. Shipp. 2021, 5, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, N. Is LNG the solution for decarbonised shipping? J. Int. Marit. Saf. Environ. Aff. Shipp. 2022, 6, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, N. Promoting Circular Economy in the Shipping Industry. Int. J. Marit. Saf. Environ. Aff. Shipp. 2023, 7, 2276984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, N. Managing marine environmental pollution using Artificial Intelligence. Marit. Technol. Res. 2021, 3, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EcoPorts. Self Diagnosis Method (SDM): The User-Friendly Environmental Checklist. Available online: https://www.ecoports.com/sdm (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- EcoPorts. Port Environmental Review System (PERS): The Only Port Sector Specific Environmental Management Standard. Available online: https://www.ecoports.com/pers (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Green Marine. Available online: https://green-marine.org/about-us/ (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Široka, M.; Piličić, S.; Milošević, T.; Lacalle, I.; Traven, L. A novel approach for assessing the ports’ environmental impacts in real time—The IoT based port environmental index. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsch, W.J. What is ecological engineering? Ecol. Eng. 2012, 45, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesshöver, C.; Assmuth, T.; Irvine, K.N.; Rusch, G.M.; Waylen, K.A.; Delbaere, B.; Haase, D.; Jones-Walters, L.; Keune, H.; Kovacs, E.; et al. The science, policy and practice of nature-based solutions: An interdisciplinary perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strain, E.M.; Steinberg, P.D.; Vozzo, M.; Johnston, E.L.; Abbiati, M.; Aguilera, M.A.; Airoldi, L.; Aguirre, J.D.; Ashton, G.; Bernardi, M. A global analysis of complexity-biodiversity relationships on marine artificial structures. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkol-Finkel, S.; Hadary, T.; Rella, A.; Shirazi, R.; Sella, I. Seascape architecture-incorporating ecological considerations in design of coastal and marine infrastructure. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 120, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Promises of Ecological Rehabilitation in Port Areas, Encyclopedia of the Environment. Available online: https://www.encyclopedie-environnement.org/en/life/promises-ecological-rehabilitation-port-areas/ (accessed on 19 July 2023).
- Agarwala, N. Using robotics to achieve ocean sustainability during the exploration phase of deep seabed mining. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2023, 57, 130–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, N. Project Green Ports: Are Indian ports on the right track? Marit. Aff. J. Natl. Marit. Found. India 2022, 18, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agarwala, N.; Saengsupavanich, C. Oceanic Environmental Impact in Seaports. Oceans 2023, 4, 360-380. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans4040025
Agarwala N, Saengsupavanich C. Oceanic Environmental Impact in Seaports. Oceans. 2023; 4(4):360-380. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans4040025
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgarwala, Nitin, and Cherdvong Saengsupavanich. 2023. "Oceanic Environmental Impact in Seaports" Oceans 4, no. 4: 360-380. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans4040025
APA StyleAgarwala, N., & Saengsupavanich, C. (2023). Oceanic Environmental Impact in Seaports. Oceans, 4(4), 360-380. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans4040025