Abstract
This investigation compared the fatty acid (FA) levels found in erythrocyte (RBC) membranes, plasma, whole blood (WB), and blubber from wild Alaskan (Bristol Bay) belugas (Delphinapterus leucas) (BBB, n = 9) with oceanaria-based belugas (OBB, n = 14) fed a controlled diet consisting of primarily herring (Clupea harengus) and capelin (Mallotus villosus). FA patterns in RBCs, WB, and plasma varied considerably between BBB and OBB animals. Focusing on RBC FA levels of known dietary origin, the OBBs had markedly higher levels of 20:1n9,11 and 22:1n9,11. RBC levels of these fatty acids were 1% and 0.2% in the BBBs, but 8.2% and 4.5%, respectively, in the OBBs (p < 0.05 both). These long-chain mono-unsaturated FAs (LC-MUFAs) are rich in herring and capelin but not in the prey species (i.e., salmonids, smelt, cod, and shrimp) generally available to BBBs. As for the marine omega-3 poly-unsaturated fatty acids [PUFAs; 20:5n3 (eicosapentaenoic acid) and 22:6n3 (docosahexaenoic acid)], the former was higher in the OBBs vs. BBBs (16% vs. 11%, p < 0.05), but the latter was low and similar in both (3.8% vs. 4%). Similar patterns were seen in the other sample types, except that DHA% was higher in BBB than OBB animals in both plasma (12.6% vs. 8.7%) and in blubber (12% vs. 4.9%) (p < 0.05). A physiologically important omega-6 PUFA, 20:4n6 (arachidonic acid) was approximately 2× higher in BBB than OBB within RBC (22% vs. 12%), WB (16% vs. 7%), plasma (11.5% vs. 4.6%) and blubber (4.6% vs. 2.4%), respectively. While blubber FAs have been evaluated historically and relatively easy to procure with biopsy darts in the field, this study proposes that blood-based FAs collected during health assessments or subsistence hunts, especially RBC or WB FAs, may be more convenient to handle using dried blood spot cards (DBS) with limited cold storage and simplifies shipping requirements, and may more accurately reflect tissue FA status.
1. Introduction
Tissue fatty acid (FA) composition is one method used to characterize and infer feeding habits in wild animals. In marine mammals, blubber FA content has been used primarily for this purpose, but the extent to which blubber is representative of dietary FAs and metabolism is still being determined [1,2]. The blubber layer in odontocetes plays an important role in thermoregulation and is stratified for different thermal habitats and body size with varying composition of lipids [3,4]. Species occupying colder ecological niches are observed to have greater stratification of blubber FAs than temperate odontocete species [3]. In addition, higher concentrations of dietary FAs are characteristically found in the metabolically active innermost blubber layers, while endogenous FAs remain in the outer layer of blubber [3,5]. These metabolic FA stores can be depleted or mobilized with periods of fasting or changes in prey availability [6]. For belugas that have a blubber depth of 5–15 cm along the dorsum, a blubber biopsy sample extending only 1–3 cm deep may not adequately sample the innermost layer of blubber, which is the most metabolically relevant [5,7]. Therefore, the analysis of superficial blubber biopsies from free-ranging cetaceans may not reflect short-term variations in FA intake [5].
Red blood cells (RBCs, erythrocytes) provide a readily accessible model membrane with a FA composition reflective of major organs (e.g., heart, liver, intestine, etc.) [8]. Thus, it is more likely than blubber to mirror metabolically important processes since blubber is primarily a depot for lipid energy reserve and insulation. RBC FAs may reflect true dietary FA patterns without the confounding factors of age, sex, body site, body condition, tissue lipid stratification, and thermal niche that exist for localized blubber FAs. The RBC has been widely used in human research to reflect tissue FA composition, with most work focusing on the two major marine long-chain omega-3 (ω-3) FAs present in RBC membranes, 20:5n3 (eicosapentaenoic acid, EPA) and 22:6n3 (docosahexaenoic acid, DHA) to measure risk of cardiac disease in humans [9]. Dietary supplements of marine ω-3 poly-unsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are ultimately derived from cold-water fish or krill and contain high levels of EPA and DHA. Certain plants, on the other hand, contain the shorter-chain ω-3 FA, α-linolenic (ALA) [10]. Dietary marine ω-3 PUFAs do not require the complex conversion of ALA to EPA and DHA and can directly exert effects on biologic pathways or be further metabolized to bioactive lipids [10]. Upon absorption, increased ω-3 PUFAs can profoundly alter the composition of mammalian membrane lipids which then serve as a source of cellular mediators for cell growth, metabolism, inflammation, and regulation of the immune response [11,12]. In the cell membrane, ω-3 PUFAs compete directly with ω-6 PUFAs, primarily 20:4n6 (arachidonic acid, ARA) for enzymatic pathways and can limit the production of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids such as prostaglandins, thromboxanes and leukotrienes [13]. Characterizing RBC or whole blood (WB) FAs may impart a better understanding of the net metabolic effects from PUFAs that are present in wild and managed odontocete populations, including belugas, the focus of the present research.
The controlled fish diet [herring (Clupea pallasii), capelin (Mallotus villosus), and mackerel (Scomber japonicus)] of oceanaria-based belugas (OBB, Delphinapterus leucas), is precisely known and determined for each individual animal based on body weight. Hence, FA content of such diets can be analyzed with precision allowing for a direct comparison of dietary FAs with RBC, WB, plasma, and blubber FA patterns. Unfortunately, the diets of wild belugas are not known with the same certainty, as they include a variety of species that can vary with season. Diets of wild populations of Arctic beluga have been estimated from stomach content studies which showed multiple types of prey, including benthic invertebrates, squid, and estuarine and large pelagic fish [1,14,15,16]. Based on former analyses, belugas from Bristol Bay, Alaska (BBB) feed primarily on salmonid and some smelt species, as the salmon runs in Bristol Bay begin in May and last until August [15].
A previous study from our group reported the FA composition of RBCs and plasma from bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from oceanaria and compared it with human FA patterns with the intent to both characterize blood FAs in dolphins and to evaluate its utility for cardiovascular health assessment in dolphins [17]. In the present report, we turn to the beluga to compare FA patterns from oceanaria-based animals, not with humans, but with wild Alaskan belugas. The purpose of the present investigation was to gain a better understanding of the potential utility of evaluating FA patterns from managed beluga RBCs, plasma, WB, and blubber to highlight similarities and differences in feed diversity with a wild population of belugas. In addition, this study will serve as a foundation for establishing methods for FA analysis from WB, which can be collected, stored and shipped as dried blood spots (DBS) during field health assessments conducted in remote areas with limited access to cold storage, and potentially provide data on wild beluga feeding habits in cooperation with subsistence hunts or stranding events.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
Fourteen healthy OBBs of both sexes aged 3 to 46 years were sampled during routine diagnostic evaluations at three public-display oceanaria (SeaWorld of California (SWC), SeaWorld of Florida (SWF) and SeaWorld of Texas (SWT)) in the spring of 2016. Blood samples were obtained under voluntary cooperation with venipuncture of the ventral fluke vein (perivascular rete) using a 1.07 mm (19 gauge) × 19 mm (0.75 inch) long butterfly needle set-up attached to a 20 mL syringe. Fasted whole blood samples were collected in the morning and placed immediately into a dried potassium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), citrate and thrombin Vacutainer® tubes (BD Vacutainer, Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) and processed in respective SeaWorld laboratories within an hour of collection. Four full-thickness blubber samples, separated from epidermis, (1 cm × 3–4 cm deep) were obtained from frozen (−20 °C) tissue archives from deceased belugas (2 SWC, 1 SWF, 1 SWT), after being stored 6 to 13 years. These were sectioned to size, placed in cryovials, and express mailed to OmegaQuant Analytics, LLC (Sioux Falls, SD, USA) for analysis.
Blood samples from nine BBBs with an approximate age range of 3 to 22 years of age, were collected in the same manner using manual restraint during a wild beluga health assessment project in the Nushigak Arm of Bristol Bay in late August and early September of 2014. The Alaskan beluga health assessment study was conducted under National Marine Fisheries Service marine mammal research permit #14245 and approved by NOAA Fisheries, Alaska Fisheries Science Center Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Belugas were captured by net in shallow water and held for up to two hours, as a physical exam was conducted. As part of the diagnostic evaluation, samples of blood, skin, and blubber were collected. In addition, blubber thickness was sonographically measured, auditory tests conducted, and satellite transmitters were attached to belugas following approved protocols [18,19]. The blood samples were obtained within the first 30 min after capture. WB was collected into EDTA and serum separator Vacutainer® tubes (BD Vacutainer, Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) and placed immediately into an ice-filled cooler and transferred to refrigerator storage within 8 h until shipment the following day. Aliquots of the WB samples (1.8 mL) were then placed in 2.0 mL polypropylene NALGENE® cryovials (Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA, USA) and express mailed on cold packs to SeaWorld of California Animal Health Laboratory (SWC) (San Diego, CA, USA) to coordinate processing of samples. Additionally, eight frozen-archived (in −80 °C) blubber samples were collected and sent on dry ice for analysis. Blubber samples were obtained from eight of the nine wild belugas sampled during the 2016 health assessment using biopsy punches, 6–8 mm wide × 1 cm deep, that included full skin and superficial blubber tissue. Blubber was separated from epidermis, and subsamples were placed in 2.0 mL cryovials and transferred to a liquid nitrogen shipper within 8 h of sampling, then transferred to a −80 °C freezer within 2 weeks’ time. Frozen blubber samples selected for this study were stored at −80 °C for four years before being shipped on dry ice to SWC and then shipped on dry ice to OmegaQuant for analysis.
2.2. Laboratory Processing and Analysis of PLASMA, RBC, WB, Blubber and Dried Blood Spots
At the respective SeaWorld Animal Health laboratories in California, Texas, and Florida, WB samples from OBB were processed in the following manner. Two 0.25 mL aliquots of WB were removed from the EDTA tube, one for hematological analysis and the other frozen in a cryovial at −80 until shipped, the remaining WB was centrifuged at 1000× g for 10 min at 4 °C to separate plasma from RBCs. Aliquots (0.25 mL) aliquot of both plasma and RBCs were frozen in 2.0 mL cryovials at −80 °C for less than 7 days until shipped (on dry ice) to OmegaQuant for analysis. For the dried-blood spot FA analysis, one drop of whole blood from the fresh EDTA tube was placed onto a sample collection card pre-treated with an antioxidant cocktail Fatty Acid Protection System (FAPS™) and allowed to dry [20]. DBS and liquid WB were compared in four OBB animals, from SWC, when WB was collected during a pilot study to evaluate the utility of DBS in 2017. The DBS cards were stored at −80° C for less than 7 days until shipped to OmegaQuant for analysis. Samples from BBBs were processed in a similar manner once received by SWC and then shipped overnight on dry ice to OmegaQuant in less than 7 days.
At OmegaQuant, plasma samples were thawed, and an aliquot was combined (1:40 parts) with the methylating mixture [boron trifluoride (BF3) in methanol (14%), toluene and methanol (35/30/35 v/v)], shaken and heated at 100 °C for 45 min. (Methanol provides the methyl group and BF3 is the catalyst). After cooling, 40 parts of both hexane and distilled water were added. After briefly vortexing, the samples were spun to separate layers, and an aliquot of the hexane layer which contained the FA methyl esters was taken for analysis by gas chromatography (GC) with flame ionization detection as described previously [20]. WB (whether liquid or dried on filter paper) was treated in the same manner [20]. RBC samples were methylated with only boron trifluoride in methanol (14%) and were heated for 10 min. Otherwise the methods were the same.
Blubber samples were also analyzed for FA composition at OmegaQuant. Tissue samples (10–30 mg) were weighed into a screw-cap glass vial which contained tritricosanoin as an internal standard (tri-23:0 TG) (NuCheck Prep, Elysian, MN, USA). The tissue samples were homogenized and then extracted with a modified Folch extraction (choloroform:methanol:water, 2:2:0.75 v/v) [21]. A portion of the organic layer was transferred to a screw-cap glass vial and dried in a speed vac. After samples were dried, a mixture of methanol containing 14% boron trifluoride, toluene, and methanol (35:30:35 v/v/v) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was added. The vial was briefly vortexed and heated in a hot bath at 100 °C for 45 min. After cooling, hexane (EMD Chemicals, Gibbstown, NJ, USA) and HPLC grade water was added, the tubes were recapped, vortexed and centrifuged help to separate layers. An aliquot of the hexane layer was transferred to a GC vial. GC was carried out using a GC-2010 Gas Chromatograph (Shimadzu Corporation, Columbia, MD, USA) equipped with an SP-2560, 100 m fused silica capillary column (0.25 mm internal diameter, 0.2 um film thickness; Supelco, Bellefonte, PA, USA).
FAs were identified by comparison with a standard mixture (GLC OQ-A, NuCheck Prep, Elysian, MN, USA) using LabSolutions Software (Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, INC., Kyoto, Japan). The standard mix was also used to construct individual FA calibration curves which were used to calculate concentrations and then percent composition. The following 27 FAs (by class) were identified: saturated (14:0, 15:0, 16:0, 17:0, 18:0, 20:0, 22:0 24:0); cis monounsaturated (16:1, 18:1, 20:1, 22:1, 24:1); trans [16:1, 18:1, 18:2); cis n-6 polyunsaturated (18:2, 18:3, 20:2, 20:3, 20:4, 22:4, 22:5); cis n-3 polyunsaturated (18:3, 20:5, 22:5, 22:6). FA composition was expressed as a percent of total identified FAs and concentrations as µg/mg of tissue. The Omega-3 Index (O3I) was defined as the EPA + DHA content of RBC membranes expressed as a percent of total RBC FAs [22]. Between run coefficients of variation from quality control, samples were 5%, 3% and 16% for EPA, DHA and the LC-MUFAs, respectively.
2.3. Fish FA Analysis
To determine the FA composition of the fish fed to the OBBs, samples of the previously frozen fish [capelin (Mallotus villosus), herring (Clupea pallasii), and mackerel (Scomber japonicus)] were also analyzed as described previously [17]. OBBs are fed a mixture of these three fish species daily (55 ± 15% herring, 43 ± 15% capelin, and 1.8 ± 3.9% mackerel, Supplemental Figure S1). The ratio of herring:capelin:mackerel fed varied by facility based on food fish inventory, dietary need, or husbandry practice per location. Supplementary Table S2 lists mean percents of total FAs in average diet from SWC_OBB based on percentages of fish type fed (Table S2). Additionally, the OBB diet included a vitamin supplement (Marine Mammal Vitamins containing B1-3, B5-7, B9, B12, E, K, and no Vitamin A; Mazuri Exotic Animal Nutrition, St. Louis, MO, USA) based on the amount of fish fed. It was beyond the scope of study to evaluate the effects of supplemental vitamins on blood-based fatty acid levels.
Statistical methods. t-tests were used to compare RBC, WB, and plasma FA levels between the OBB and BBB groups. A p-value of <0.05 was a statistically significant difference. The quantity (n = 4, OBB) and quality (n = 8, superficial BBB) of blubber samples precluded statistical comparisons, therefore only descriptive generalizations are given. Principal component analysis (PCA) was utilized to visualize variation of FA sample origin between OBB and BBB. In all, twenty-eight variables were used to construct the PCAs in all cases, with 27 total FAs and the Omega-3 Index. Of these, 80% of the total FA analyzed represent FAs derived primarily from dietary intake: C18:2n6, C18:3n3, C17:0, C20:1, C22:1, C20:5n3, and C22:6n3 [5,6]. Others have been found to have dietary sources or are biosynthesized: C16:1n7, C18:1n9, C18:0, C18:3n6, C20:4n6, C22:4n6, C22:5n6, C22:5n3, and C20:2n6 [6].
3. Results
In total, 26 FAs, plus O3I, were measured in RBCs, plasma, and WB; and 27 FAs (including 15:0) were measured in blubber for BBB and OBB groups (see Supplemental Table S1 which also includes the FA composition of average OBB diet). The mean values for blood-derived FAs that constituted ≥1% of total FAs for each sample type are presented in Figure 1. Although the levels of many FAs were statistically significantly different between BBB and OBB, a few were markedly different for RBC, WB and plasma. These included (for all three sample types) the LC-MUFAs [20:1n9,11 (eicosenoic and gadoleic acids) and 22:1n9,11 (erucic and cetoleic acids)], and the LC-PUFAs, ARA and EPA. The RBC levels of the two LC-MUFAs (20:1 and 22:1) were much higher in the OBBs compared with the BBBs (20:1, 8.2% vs. 1.0% and 22:1, 4.5% vs. 0.2%, respectively). RBC EPA was higher in OBBs compared with BBBs (16% vs. 11%), whereas the reverse was true for RBC ARA (OBB 12% vs. BBB 22%; Figure 1 and Table S1).
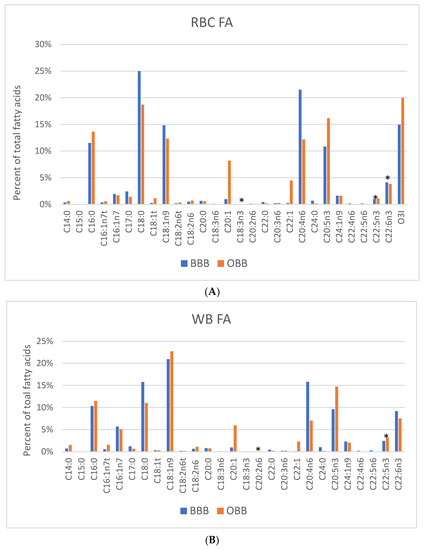
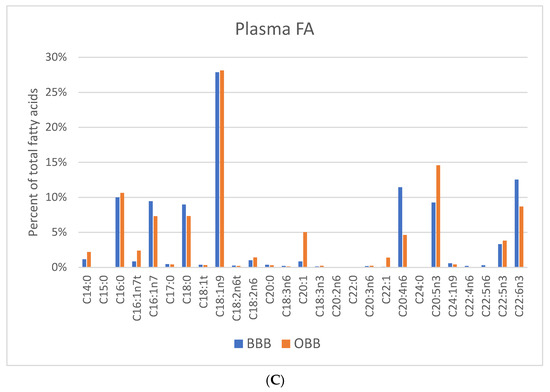
Figure 1.
FA profiles for (A) RBC, (B) Whole blood (WB), and (C) plasma for Bristol Bay belugas (BBB, n = 9) and oceanaria-based belugas (OBB, n = 14). Data are expressed as a percent of total FAs. * p > 0.05 between groups. O3I, Omega-3 Index only applies to RBC EPA + DHA and has not been validated in WB, plasma or blubber.
Mean levels from 13 FAs from BBB and 12 from OBB were found to be >1% of the total FAs in blubber (Table S1). The small sample sizes (n = 8 OBB and n = 4 BBB) precluded meaningful statistical analysis, however profile differences were observed in Figure 2. The primary FAs found were 14:0; 16:0; 16:1n7; 18:1n9; 20:1n9,11; 22:1n9,11; 20:5n3; 22:5n3; and 22:6n3. Similar to RBCs, blubber LC-MUFAs were generally greater in OBB than BBB, whereas blubber ARA, EPA, DPA and DHA were all higher in BBB than OBB (Figure 2).
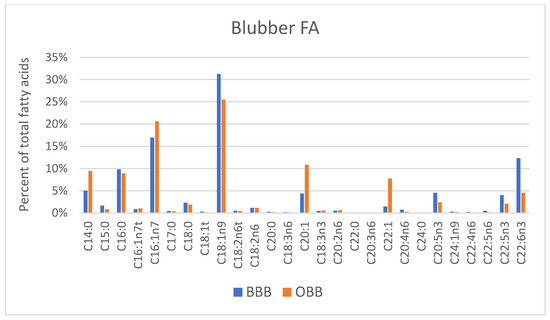
Figure 2.
FA profiles for blubber are presented for Bristol Bay belugas (BBB, n = 8) versus oceanaria-based belugas (OBB, n = 4), respectively. Data expressed as percent of total Fas.
FA profiles for blood and tissue components of BBB are shown in Figure 3. Mean ± SD values are provided, along with OBB values in Table S1. Whole blood FAs were identified to be an approximate average of RBC and Plasma FAs as expected since blood is an approximately 50:50 mix of these two pools.
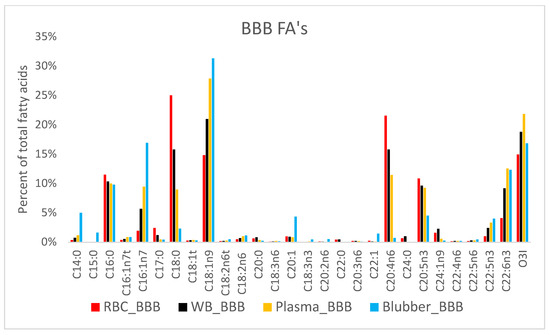
Figure 3.
FA profiles from Bristol Bay beluga (BBB, n = 9) by tissue compartment (RBC, WB, plasma and blubber).
For OBB FA comparison, blubber Fas profiles from archived OBB samples and select OBB dietary Fas were included with tissue components (Figure 4).
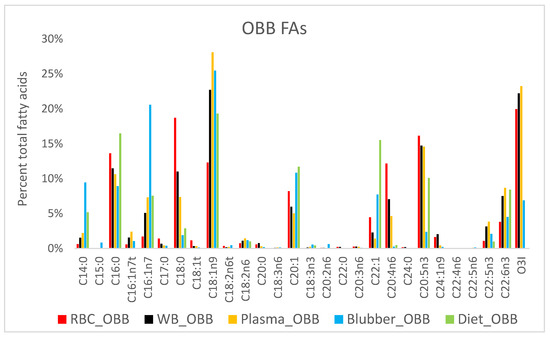
Figure 4.
FA profiles from Oceanaria-based belugas (OBB, n = 4) by tissue compartment (RBC, WB, plasma and blubber) and diet.
As expected, the FA profiles of four DBS samples from same OBBs sampled during a pilot study in 2017 were comparable to corresponding WB samples (Figure 5).
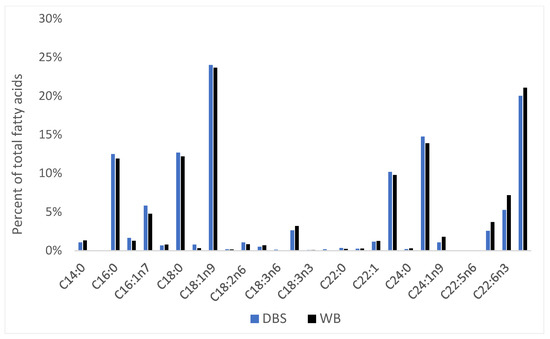
Figure 5.
Mean percent of dried blood spot (DBS) FA composition compared with WB from 4 OBBs analyzed during 2017 SWC pilot study.
The PCA results showed that BBB and OBB clustered separately (based on non-overlapping 95% CI ellipses) for RBC and plasma Fas but had overlap for blubber FA (Figure 6).
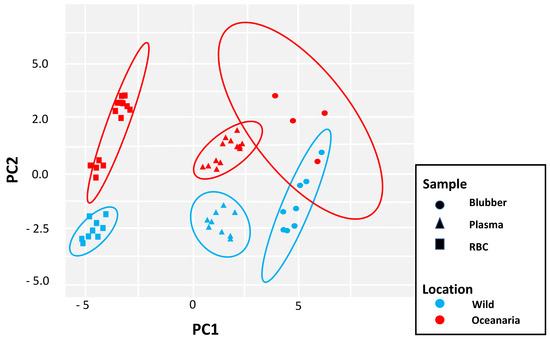
Figure 6.
Principal component analysis (PCA) of fatty acid signatures in blubber, plasma, and RBCs of 9 wild belugas (BBB; blue) and 14 oceanaria-based belugas (OBB; red). Ellipses show 95% confidence intervals (CIs) around each sample type. PC1 and PC2 explain 65% of the variance.
Variation in FA signatures were further evaluated based on park of origin and sample type (i.e., RBC, plasma, or blubber) (Supplemental Figure S3). Separate clusters were identified for BBB and whales at SWC, however SWT and SWF had more similarity and overlapped with each other. Blubber FAs were found to be more similar for BBB and OBB when evaluated by specific park location (Supplemental Figure S3). However, interpretation is limited due to the small number of archived blubber samples analyzed.
4. Discussion
This investigation found similarities and differences in the FA patterns of erythrocytes, WB, plasma, and blubber from oceanaria-based belugas and a subset of a wild Alaskan (Bristol Bay) beluga population. This was not unexpected as wild belugas are opportunistic migratory predators that feed on a variety of fish and crustaceans in various regions of the Arctic, whereas managed belugas are fed a uniform and consistent diet comprised of 3–4 feed species. Wild belugas consume different fish species that vary by trophic levels and season. For example, Greenland belugas are known to feed on capelin, halibut, Arctic cod and squid, while Hudson Bay belugas are reported to feed primarily on capelin [23,24]. Other research studies have found North Alaskan belugas to feed primarily on Arctic cod, and western Alaskan belugas to feed on salmon, smelt and crustacean species [14,15]. It was beyond the scope of this study, to evaluate dietary tracer models and calibration coefficients used by other mammal metabolic studies with feeding trials to estimate metabolic differences between the OBB and BBB [25]. Instead, the focus was to first characterize tissue FA components of OBBs (consuming a known diet) and opportunistically compare it with samples obtained from a subset of BBBs examined during a wildlife health assessment.
The principal differences between the populations were in LC-MUFAs, which were higher in OBBs than BBBs and is likely explained by the increased LC-MUFA content of the fish fed in the oceanarias (i.e., herring and capelin). Quakenbush et al. found that BBBs, a non-migratory population, were eating relatively little herring, capelin or other sources of the LC-MUFAs during the same months that the present study samples were acquired [15]. Instead, BBBs have historically been found to feed during the summer primarily on salmonids, with a limited contribution from rainbow smelt and invertebrates (shrimp, isopods, and bivalves), all of which contain lower levels of LC-MUFAs [15]. The LC-MUFAs originate primarily from the wax esters biosynthesized by certain calanoid copepod species, and concentrations can vary considerably between the trophic levels of predatory fish, but were found to be higher in Arctic Cod, herring and capelin, than smelt and salmon [23,26,27]. Marine carnivores accustomed to high dietary intake of C22:1 may have the ability to shorten or beta-oxidize these FAs in their peroxisomes, avoiding the potentially harmful cardiac lipidosis seen in terrestrial animals that consume diets high in these FAs [26,28]. There are no published reports of pathologic cardiac lipidosis in wild or oceanaria-based marine mammals.
For LC-PUFAs, RBC, WB and plasma EPA was found to be higher in OBB than BBB. There are 4 possible explanations for higher EPA: higher intakes of EPA, a higher rate of conversion of ALA to EPA, or a higher intake of ALA with the same conversion rate. Mean EPA levels in fish fed to OBBs were 10%, compared to estimated levels in BBB of 7.5%, whereas ALA intakes were ~0.6%, which is within the estimated range of (0.4–1%) from salmonid and smelt from Western Alaska [6,15]. A novel hypothesis for the higher EPA levels in the OBB relates to their aforementioned higher intake of 22:1. Ostbye et al. (2019) reported that cetoleic acid stimulated endogenous production of EPA and DHA from ALA in human and salmon hepatocytes [29]. The possible mechanisms involved in this are unclear. EPA, to a lesser extent DHA, can inhibit formation of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids, like thromboxane A2 (TxA2) and leukotriene B (LTB4) from ARA, and be further synthesized to less-active eicosanoids [30]. It was beyond the scope to measure circulating levels of eicosanoids in OBB and BBB, but further investigation may provide greater understanding for the regulatory role of immune-mediated PUFAs with normal health and inflammatory disease.
LC-PUFA levels in blubber were higher in BBB than OBB. These findings may in part be derived from dietary differences or from vertical stratification storage into blubber. Other marine mammal species (ringed seal, killer whale, porpoise) have shown varying concentrations of FAs in inner and outer layers of blubber, with low-molecular short-chain MUFAs occupying the outer blubber layer, and saturated FAs and LC-MUFAs in the innermost blubber layer [3,5,31]. Similar to ring seals in the Arctic, differences in water temperature may influence the distribution of these FAs in belugas in addition to dietary differences [31].
ARA from BBB was found to be 1.8× higher in RBC, 2.3× higher in WB, 2.5× higher in plasma, and 3.1× higher in blubber than OBB levels. ARA is obtained by direct consumption or through metabolism of the parent molecule, linoleic acid, LA (18:2n6) [32]. As one of the most important PUFAs, ARA is released from cell membranes and transformed into powerful chemical mediators (prostaglandins, leukotrienes, thromboxanes) that regulate the inflammatory response among many other effects [12]. There are four possible explanations for higher ARA levels in BBBs: higher ARA intake, a higher rate of conversion of LA to ARA (possibly secondary to an EPA-induced inhibition of ARA synthesis), ARA replacing EPA on membrane phospholipids, or a higher LA intake. The most likely explanation would be higher ARA intake or a higher rate of LA to ARA conversion and/or EPA-driven displacement of ARA from the membrane. A study by Choy et al. found dietary ARA was quite low, in managed beluga fed sockeye salmon, 0.6% of total fatty acids [25]. In the same study, Choy et al. measured LA in salmon fed to study belugas to account for 9% of the FA composite in the diet, compared to 1% and 0.7% for herring and capelin, respectively [25]. As noted above, the stomach content survey of belugas in Bristol Bay by Quakenbush et al. (2015), reported the frequency of occurrence of about 81% salmonid species, 21% shrimp, 4% isopods, and 3% bivalves [15]. Therefore, dietary intake of salmonidae spp. with higher levels of LA than were present in the oceanaria food fish (about 1%) combined with invertebrate ARA content could account for increased dietary ARA in wild belugas. Studies in humans consuming supplemental ARA have shown no significant changes in platelet aggregation or blood coagulation, and human ARA levels were comparable to those in wild belugas [33,34]. Further research is needed to understand the role ARA has in neurologic development, blood coagulation and compensatory relationships with other FAs (i.e., EPA and DHA) in marine mammals.
DHA, the most prominent long-chain omega-3 PUFA found in RBC membranes, was not significantly different between groups, but tended to be higher in BBB vs. OBB for WB, plasma and blubber. Choy et al. reported mean DHA levels in salmon (5.27%) fed to beluga in their study to be less than herring (8.68%) and half the level of capelin (17.1%) [25]. In our study, mean DHA percentages in the average model diet were capelin (6.3%), herring (8.7%), and mackerel (23.8%). However, a higher DHA intake in the BBBs could explain this trend.
4.1. The Omega-3 Index
The Omega-3 Index (RBC EPA + DHA) is a risk factor biomarker for cardiovascular disease in humans. Levels in our study for OBB and BBB are very high (20% vs. 15.3% of total fatty acids). These levels are high (relative to the human, which is typically <8%) and yet RBC DHA levels in both beluga populations were only 4%, very close to average human levels [35]. The relatively small differences found between BBB and OBB in ω-3 index levels are unlikely to have significant health consequences, perhaps because they are well above levels viewed as optimal for human health (i.e., >8%) [22]. Therefore, humans who have higher ω-3 index levels (either from fish consumption or fish oil supplement use) have increased longevity and reduced risk of cardiovascular and immune-mediated diseases [30,36,37,38]. Whales and dolphins are long-lived animals that consume diets rich ω-3 FAs, so it is not surprising that there are rare reports of cardiovascular disease or immune-mediated disease in cetaceans.
4.2. Potential Utility of Dried Blood Spot Testing in Marine Research
A drop of WB dried on filter paper may be a convenient method to obtain samples from remote exams in the field. In belugas, WB FAs were found to closely match DBS FAs (as they should since one is liquid and the other dried) (Figure 6). The same has been shown using human blood samples (See Supplementary Figure S2). Studies in humans and animals have documented the validity (i.e., stability, accuracy, and precision) of DBS collection systems [20,39]. When collected on antioxidant-treated paper, human samples are known to be stable (i.e., minimal loss of PUFAs) for at least 4 weeks at room temperature and for up to two years at −20 °C. DBS sampling has been used in human field studies in Mexico, Ghana, and Tanzania, and in Bangladesh, dried breast milk FA composition was analyzed [40,41,42,43]. DBS samples are obviously easier to transport than blood tubes especially in remote areas that may have limited access to freezers or ability to ship samples for analysis. Therefore, using DBS sample collection has many advantages for field work, animal stranding events, subsistence hunts, or with fresh necropsy specimens.
4.3. Fatty Acid Composition of Blubber
RBC or membrane FAs are likely more representative of an animal’s steady-state status for the very metabolically active LC-PUFAs profile, unlike blubber samples that store FAs for energy. Using PCA analysis, our investigation found individual clusters of OBB and BBB RBC and plasma FAs, yet there was overlap of blubber FAs from wild and managed belugas confirming that there are more shared FAs in blubber (Figure 6). Blubber is a complex tissue that varies by body site location, age and may not be fully sampled with field biopsy darts or punches [3,4,5]. This study provides FA data obtained from superficial blubber samples (i.e., blubber sampled to 1–1.5 cm depth with punch biopsy device) from subset of BBBs, whereas OBB blubber was obtained from frozen skin/blubber block specimens up to 6 cm thick). Therefore, FA results for BBB may not be representative of the total FA content of the full blubber layer for this stock in Bristol Bay. While RBC sampling may require hands-on examination, blood samples may provide a better alternative for complete FA signature analysis. A few studies have used full-thickness biopsies, generally obtained with permission during subsistence hunts or live-capture events for health assessments. Smith (2009) found that LC-MUFAs, PUFAs and saturated fatty acids (SFAs) < C:13, were higher in the outer versus inner blubber layers in Alaskan belugas. [4]. Blubber FA profiles have also shown FA differentiation between different beluga populations (ie., Bristol Bay, Cook Inlet, Beaufort Sea, Svalbard) [1,14,44]. Full-thickness blubber samples collected from belugas near Svalbard, Norway were analyzed to find FA signatures similar to dietary prey of polar cod, capelin, and possibly shrimp [1]. The elevated blubber LC-MUFAs, eicosenoic (C20:1n9, 11.9%) and erucic (C22:1n9, 2.9%), acids are most consistent with a calanoid copepod diet, of which polar cod and capelin are known to forage on [1]. Elevated levels of these LC-MUFAs (19.3% and 26.6%, respectively) were identified in commercially available Newfoundland capelin fed to OBB in this study [1] (Table S2).
The identity of dietary tracer FAs for belugas may not be plausible given the variety of prey items found in the Arctic waters. However, it appears that LC-MUFAs from fat esters found in calanoid copepods are prevalent in the food web of Arctic predators, so they may provide a key FA to monitor. Further investigations utilizing RBC FAs in correlation with full-thickness blubber FA levels will aid with determining which FAs are important for metabolic changes with physiologic demand or dietary shifts. If blubber samples are being used to estimate dietary sources, the innermost layer of blubber should be analyzed, and this may not be possible in some species due to depth of blubber layer. Establishing FA baselines for certain threatened populations of beluga (i.e., Cook Inlet, St. Lawrence, etc.) may help identify prey deficiencies and FA changes that may identify threats to populations at risk. Additionally, research is needed with health assessments of individuals from managed and wild populations to bolster health data and determine what changes are significant and reflective of metabolic challenges.
4.4. Potential Health Consequences of Fatty Acids
The potential health consequences of these varying levels of FAs in wild vs. oceanaria-based belugas is unclear. Increased consumption of marine FAs, EPA and DHA, is known to be anti-inflammatory in humans, and higher RBC EPA and DHA levels are associated with lower levels of circulating inflammatory biomarkers [13,30,45,46]. Eicosanoids produced from EPA generally have lower biological potency in humans than those produced from ARA [13]. Cytokines, TNF, interleukins (1, 6, and 8) are often elevated with inflammatory disease. Humans and mice fed fish oil had decreased production of TNF and interleukins (1, 6, and 8) with endotoxin-stimulated mononuclear cells and increased production of IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine [13]. Additional studies have also demonstrated that increased EPA and DHA can reduce adhesion molecule interaction on leukocytes and endothelial cells, chemotaxis and limit the potentiation of inflammation from the start [13]. Therefore, further research is needed to understand the role of both the omega-3 and omega-6 LC-PUFAs on the immune response in belugas.
4.5. Ecological Dietary Differences
Oceanaria-based belugas are clearly eating a different diet than the wild animals, one that contains much more of the LC MUFAs and more of the LC-PUFAs. However, the diet is not too dissimilar to other beluga stocks in the Arctic where prey species are also different than western Alaskan beluga stocks. Quakenbush et al. (2015) found that diets of wild beluga populations differ significantly based on geographic regions of the Alaskan coast, ocean currents and trophic levels where prey is found [15]. Different life stages of fish prey may also account for variation in calanoid wax ester accumulation, exemplified by Arctic and polar cod species being found pelagically and near bottom or capelin migrating north during summer months from Newfoundland [1,23]. Trophic level fish distribution can also affect predator forage habits, as Marcoux et al. (2012) found that nitrogen isotopes were higher in older beluga than younger individuals, suggesting that older belugas may feed at a higher trophic level [47]. Sexual habitat segregation may also exist for certain beluga populations and result in diet differences throughout the year [47]. Our study is limited in scope because only a subset of one population of beluga stock was sampled and diet estimates of BBB are based off historic observations. With belugas being a sentinel species in the Arctic, periodic surveillance of FA signature profiles may aid with assessing the prey distribution and overall health of beluga populations in the future.
5. Conclusions
This comparative study of the FA composition of several sample types in OBB and BBB strongly suggests that these two populations consume different diets, particularly with respect to the LC-MUFAs. RBC, plasma and WB FAs may provide more reliable results when compared with blubber FAs levels obtained from dart biopsy or biopsy punches. Future studies are needed with greater sample size, age and reproductive demographics in order to evaluate statistical and metabolic differences in FAs between wild beluga stocks. Further examination of immune-mediated indices and products of FA metabolism during differing states of age, health and disease in OBB may aid with interpretation of wild beluga population health assessment data, that may also be used in threatened species recovery plans. Additional surveys of FAs from prey for wild marine mammals will help catalogue dietary FA signatures. Finally, this study provides a methodology for blood FA sampling and preliminary baseline FA data against which to compare for future changes in FA levels in the BBBs. In concert with periodic health assessment data, these FA biomarkers may help track and alert biologists of prey diversity changes in wild populations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/oceans3040031/s1, Table S1: Mean ± fatty acid levels (mass % of total) for blood components from Bristol Bay belugas (BBB, n = 9) and Oceanaria-based beluga (OBB, n = 14); Table S2: Mean percent of fatty acids in composite diet from percentage of FA in fish fed, example OBB_SWC; Figure S1: OBB diet percentages based on fish type, per location, SeaWorld of California (SWC), SeaWorld of Texas (SWT), and SeaWorld of Florida (SWF); Figure S2: A comparison of mean fatty acid patterns in 30 random samples of human blood comparing whole (liquid) blood (WB) to dried blood spots (DBS); Figure S3: PCA of fatty acid signatures in blubber, plasma, and RBCs of 9 wild belugas (blue) and 14 oceanaria-based belugas from different locations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.L.S. and W.S.H.; methodology, T.L.S. and W.S.H.; software, W.S.H. and H.B.; validation, T.L.S., H.B. and W.S.H.; formal analysis, T.L.S., W.S.H. and H.B.; investigation, T.L.S. and W.S.H.; resources, T.L.S., C.E.C.G., R.C.H., S.O. and S.D.; data curation, T.L.S., C.E.C.G. and W.S.H.; writing—original draft preparation, T.L.S.; writing—review and editing, T.L.S., W.S.H., C.E.C.G., R.C.H., S.O. and S.D.; visualization, T.L.S.; supervision, R.C.H. and W.S.H.; project administration, T.L.S.; funding acquisition, T.L.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The primary fatty acid sample analysis and research received no external funding. The blood and tissue samples were collected and banked during the 2016 wild beluga health assessments supported by funds from Georgia Aquarium, NOAA/AFSC/MML and Shedd Aquarium. Field work was supported by the Alaska SeaLife Center, NOAA/AFSC/MML, Alaska Department of Fish and Game, Georgia Aquarium, Mystic Aquarium, Shedd Aquarium and WHOI Ocean Life Institute with logistical support from the Bristol Bay Native Association, USFWS Togiak National Wildlife Refuge, the Kanakanak Hospital and the City of Dillingham.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study utilized routine samples for animal health assessment and was approved by the SeaWorld Parks and Entertainment Research Committee. Wild beluga activities were authorized by NMFS Scientific Research Permits (782-1719; 932-1489; and 14245), ADF&G IACUC (06-16), NOAA/MML IACUC (AFSC/NWFC 2012-1) and the Bristol Bay Marine Mammal Council (BB MMC).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to permit and Corporate policy.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the veterinary hospital staff (veterinarians, veterinary technicians, clinical lab scientists) and Wild Arctic trainers and White Whale and Dolphin trainers at respective SeaWorld parks in Orlando, San Antonio, and San Diego, for their help with collection, processing and storage of samples from oceanaria-based belugas. Additionally, the authors would like to acknowledge and thank the members of the research and capture crews. Special thanks go to Helen Aderman, Bristol Bay Native Association (BBNA), for helping to coordinate boat captains and other local participants including Ben Tinker, Richard Hiratsuka, Albie Roehl, William and Daniel Savo, Danny Togiak, William Norbert and their respective first mates. We appreciate the substantial assistance in animal handling and sample and data collection by Brett Long, Natalie Rouse, Russ Andrews, Renae Sattler, Eric Gaglione, Dennis Christen, George Biedenbach, William Hurley III, Tracy Romano, Tracey Spoon, Mandy Keogh, Laura Thompson, Justin Richards, Tim Binder, Lisa Naples, Amanda Moors, Jennifer Trevillian, Leslie Cornick, Jen Godfrey, Lindsey Saxon Kendall and Stephanie Norman. Additionally, we greatly appreciate the guidance, suggestions, and support of T. Rowles (NOAA). This is a SeaWorld Parks and Entertainment Technical Contribution number 2022-01.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dahl, T.M.; Lydersen, C.; Kovacs, K.M.; Falk-Petersen, S.; Sargent, J.; Gjertz, I.; Gulliksen, B. Fatty acid composition of the blubber in white whales (Delphinapterus leucas). Polar Biol. 2000, 23, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, D.P.; Burrow, D.G.; Wade, P.R.; Durban, J.W.; Matkin, C.O.; LeDuc, R.G.; Barrett-Lennard, L.G.; Krahn, M.M. Feeding ecology of eastern North Pacific killer whales Orcinus orca from fatty acid, stable isotope and organochlorine analyses of blubber biopsies. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 302, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, H.N. Phylogenetic, ecological, and ontogenetic factors influencing the biochemical structure of the blubber of odontocetes. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.R. Fatty Acid Variation in Beluga (Delphinapterus leucas) Blubber: Implications for Estimating Diet Using Fatty Acids. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bourque, J.; Dietz, R.; Sonne, C.; St Leger, J.; Iverson, S.; Rosing-Asvid, A.; Hansen, M.; McKinney, M.A. Fedding habits of a new Arctic predator: Insight from full-depth blubber fatty acid signatures of Greenland, Faroe Islands, Denmark, and managed-care killer whales Orcinus orca. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 603, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, S.J.; Field, C.; Bowen, W.D.; Blanchard, W. Quantitative fatty acid signature analysis: A new method of estimating predator diets. Ecol. Monogr. 2004, 74, 211–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornick, L.A.; Quakenbush, L.T.; Norman, S.A.; Pasi, C.; Maslyk, P.; Burek, K.A.; Goertz, C.E.C.; Hobbs, R.C. Seasonal and developmental differences in blubber stores of beluga whales in Bristol Bay, Alaska, using high-resolution ultrasound. J. Mammal. 2016, 97, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, J.I.; Gurzell, E.A.; Davidson, E.A.; Harris, W.S. Red blood cell PUFAs reflect the phospholipid PUFA composition of major organs. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2016, 112, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.H.; Harris, W.S. Blood fatty acid profiles: New biomarkers for cardiometabolic disease risk. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2018, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.W. Omega Fatty-Acids. 2019. Available online: themedicalbiochemistrypage.org (accessed on 18 December 2019).
- Saini, R.K.; Keum, Y.-S. Omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids: Dietary sources, metabolisms and significance—A review. Life Sci. 2018, 203, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surette, M.E. The science behind dietary omega-3 fatty acids. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2008, 178, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammation. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2006, 75, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loseto, L.; Stern, G.; Connelly, T.L.; Deibel, D.; Gemmill, B.; Prokopowicz, A.; Fortier, L.; Ferguson, S. Summer diet of beluga whale inferred by fatty acid analysis of eastern Beaufort sea food web. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 374, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quakenbush, L.T.S.; Suydam, R.S.; Bryan, A.L.; Lowry, L.F.; Frost, K.J.; Mahoney, B.A. Diet of beluga whales (Delphinapterus leucas) in Alaska from stomach contents, March–November. Mar. Fish. Rev. 2015, 77, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaman, G.A.; Lowry, L.F.; Frost, K.J. Foods of belukha whales (Delphinapterus leucas) in western Alaska. Cetology 1982, 44, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, W.S.; Schmitt, T.L. Unexpected similarity in RBC, DHA and AA levels between bottlenose dolphins and humans. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2014, 90, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citta, J.J.; Quakenbush, L.T.; Frost, K.J.; Lowry, L.; Hobbs, R.C.; Aderman, H. Movements of beluga whales (Delphinapterus leucas) in Bristol Bay, Alaska. Mar. Mammal. Sci 2016, 32, 1272–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, S.A.; Goertz, C.E.; Burek, K.A.; Quakenbush, L.T.; Cornick, L.A.; Romano, T.A.; Spoon, T.; Miller, W.; Beckett, L.A.; Hobbs, R.C. Seasonal hematology and serum chemistry of wild beluga whales (Delphinapterus leucas) in Bristol Bay, Alaska, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.S.; Polreis, J. Measurement of the Omega-3 Index in Dried Blood Spots. Ann. Clin. Lab. Res. 2016, 4, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane-Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.S.; Von Schacky, C. The Omega-3 Index: A new risk factor for death from coronary artery disease? Prev. Med. 2004, 39, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, T.C.; Loseto, L.L.; Stewart, R.E.A.; Yurkowski, M.; Ferguson, S.H. Importance of eating capelin: Unique dietary habits of Hudson Bay beluga. In A Little Less Arctic; Ferguson, S.H., Loseto, L.L., Mallory, M.L., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 53–70. [Google Scholar]
- Louis, M.; Skovrind, M.; Garde, E.; Heide-Jorgensen, M.P.; Szpak, P.; Lorenzen, E.D. Population-specific sex and size variation in long-term foraging ecology of belugas and narwhals. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 202226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, E.S.; Sheehan, B.; Haulena, M.; Rosenberg, B.; Roth, J.D.; Loseto, L.L. A comparison of diet estimates of captive beluga whales using fatty acid mixing models with their true diets. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2019, 516, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.H.; Iverson, S.J.; Rouvinen-Watt, K. Metabolism of dietary cetoleic acid (22:1n-11) in mink (Mustela vison) and gray seals (Halichoerus grypus) studied using radiolabeled fatty acids. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2006, 79, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, J.R.; Falk-Petersen, S. The lipid biochemistry of calanoid copepods. Hydrobiologia 1988, 167, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, J.; Norum, K.R. Metabolism of very long-chain monounsaturated fatty acids (22:1) and the adaptation to their presence in the diet. J. Lipid Res. 1982, 23, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostbye, T.K.; Berge, G.M.; Nilsson, A.; Romarheim, O.H.; Bou, M.; Ruyter, B. The long-chain monounsaturated cetoleic acid improves the efficiency of the n-3 fatty acid metabolic pathway in Atlantic salmon and human HepG2 cells. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 122, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvevoll, E.O.; Eilertsen, K.-E.; Brox, J.; Dragnes, B.T.; Falkenberg, P.; Olsen, J.O.; Kirkhus, B.; Lamglait, A.; Osterud, B. Seafood diets: Hypolipidemic and antiatherogenic effects of taurine and n-3 fatty acids. Atherosclerosis 2008, 200, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandberg, U.; Kakela, A.; Lydersen, C.; Kovacs, K.M.; Grahl-Nielsen, O.; Hyvarinen, H.; Kakela, R. Stratification, composition, and function of marine mammal blubber: The ecology of fatty acids in marine mammals. Phys. Biochem. Zool. 2008, 81, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hana, V.S.; Hafez, E.A.A. Synopsis of arachidonic acid metabolism: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 11, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumoto, A.; Ishikura, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Kiso, Y.; Takai, S.; Miyazaki, M. Effects of arachidonate-enriched triacylglycerol supplementation on serum fatty acids and platelet aggregation in healthy male subjects with a fish diet. Br. Nutr. J. 2007, 98, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G.J.; Schmidt, P.C.; Bartolini, G.; Kelley, D.S.; Phinney, S.D.; Kyle, D.; Silbermann, S.; Schaefer, E.J. The effect of dietary arachidonic acid on plasma lipoprotein distributions, apoproteins, blood lipid levels, and tissue fatty acid composition in humans. Lipids 1997, 32, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, W.S.; Pottala, J.V.; Varvel, S.A.; Borowski, J.J.; Ward, J.N.; McConnell, J.P. Erythrocyte omega-3 fatty acids increase and linoleic acid decreases with age: Observations from 160,000 patients. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2013, 88, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Caterina, R. N-3 fatty acids in cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, K. Fatty acids as modulators of the immune response. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2006, 26, 45–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, J.; Rust, C. Innovative dietary sources of N-3 fatty acids. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2006, 26, 75–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.; Minter, L.J.; Bibus, D.; Stoskopf, M.K.; Fellner, V.; Ange-van Heugten, K. Comparison of African savanna elephant (Loxodonta africana) fatty acid profiles in whole blood, whole blood dried on blood spot cards, serum, and plasma. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge, A.; Harris, W.S.; Ortiz-Panozo, E.; Yunes, E.; Cantu-Brito, C.; Catzin-Kuhlmann, A.; Lopez-Ridaura, R.; Lajous, M. Whole Blood omega-3 Fatty Acids Are Inversely Associated with Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Indigenous Mexican Women. Nutr. J. 2016, 146, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjepong, M.; Yakah, W.; Harris, W.S.; Annan, R.A.; Pontifex, M.B.; Fenton, J.I. Whole blood n-3 fatty acids are associated with executive function in 2-6-year-old Northern Ghanaian children. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 57, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumbe, T.; Comstock, S.S.; Harris, W.S.; Kinabo, J.; Pontifex, M.B.; Fenton, J.I. Whole-blood fatty acids are associated with executive function in Tanzanian children aged 4-6 years: A cross-sectional study. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, U.; Kanungo, S.; Zhang, D.; Ross Colgate, E.; Carmolli, M.P.; Dey, A.; Alam, M.; Manna, B.; Nandy, R.K.; Kim, D.R.; et al. Influence of maternal and socioeconomic factors on breast milk fatty acid composition in urban, low-income families. Matern. Child Nutr. 2017, 13, e12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahn, M.M.; Herman, D.P.; Ylitalo, G.M.; Sloan, C.A.; Burrows, D.G.; Hobbs, R.C.; Mahoney, B.A.; Yanagida, G.K.; Calambokidis, J.; Moore, S.E. Stratification of lipids, fatty acids and organochlorine contaminants in blubber of white whales and killer whales. J. Cetacean Res. Manag. 2004, 6, 175–189. [Google Scholar]
- Fontes, J.D.; Rahman, F.; Lacey, S.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; Harris, W.S.; Robins, S.J. Red blood cell fatty acids and biomarkers of inflammation: A cross-sectional study in a community-based cohort. Atherosclerosis 2015, 240, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Harris, W.S.; Chung, M.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Balk, E.M.; Kupelnick, B.; Jordan, H.S.; Lau, J. N-3 fatty acids from fish or fish-oil supplements, but not α-linolenic acid, benefit cardiovascular disease outcomes in primary- and secondary-prevention studies: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcoux, M.; McMeans, B.C.; Fisk, A.T.; Ferguson, S.H. Composition and temporal variation in the diet of beluga whales, derived from stable isotopes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 471, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).