Feeding Ecology of Sicydium bustamantei (Greeff 1884, Gobiidae) Post-Larvae: The “Little Fish” of São Tomé Island
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Collection of Samples
2.2. Gut Content Analysis
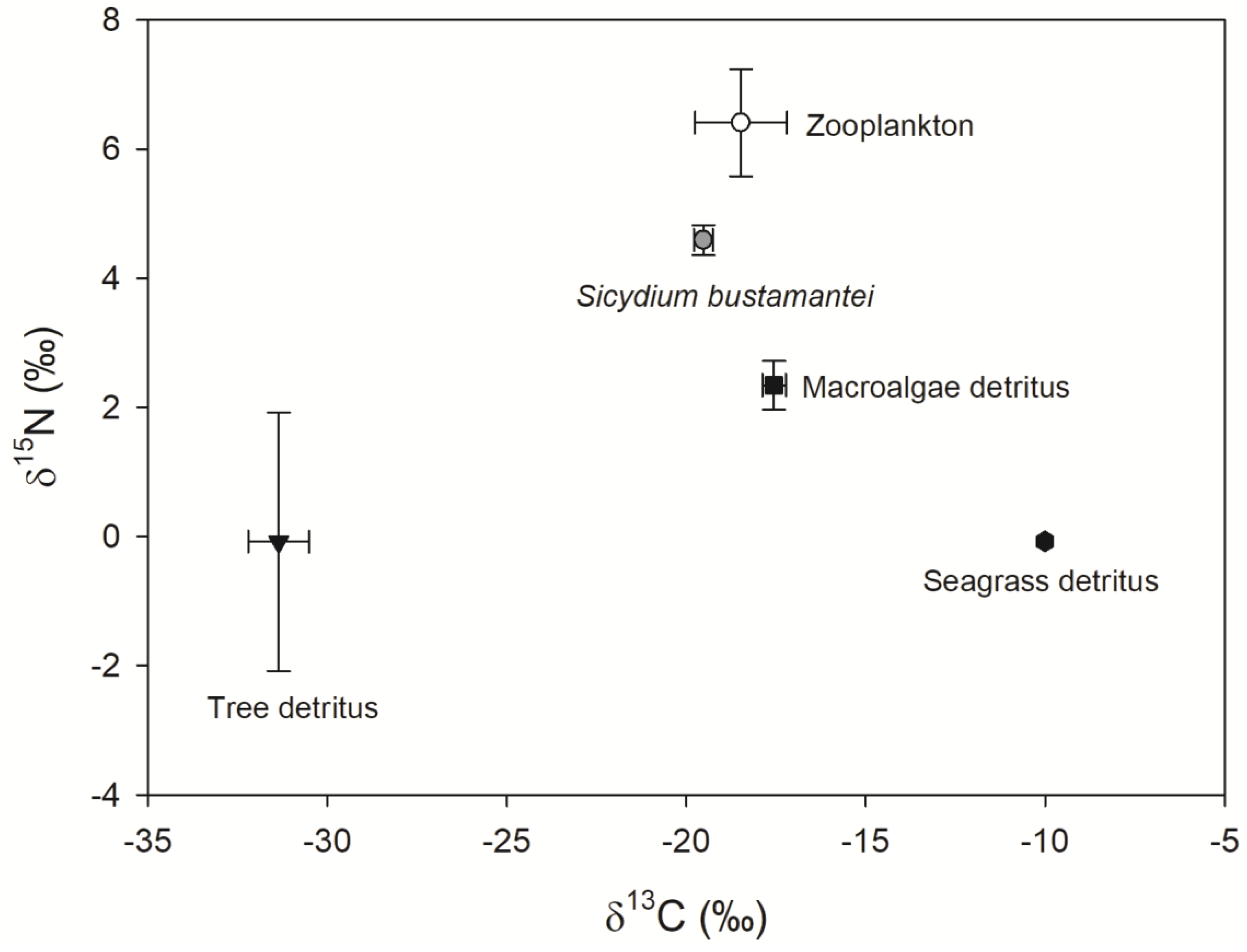
2.3. Stable Isotope Analyses
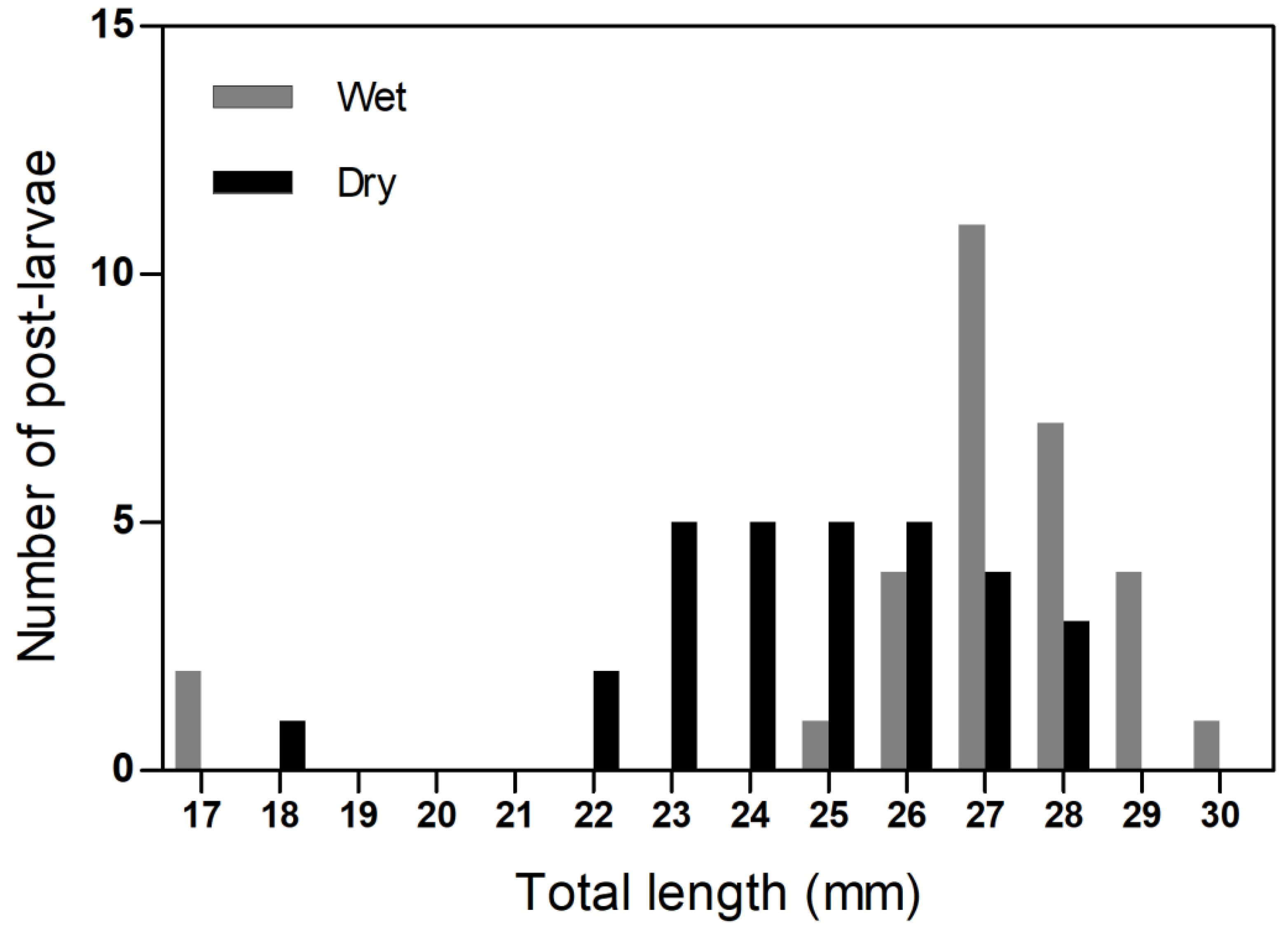
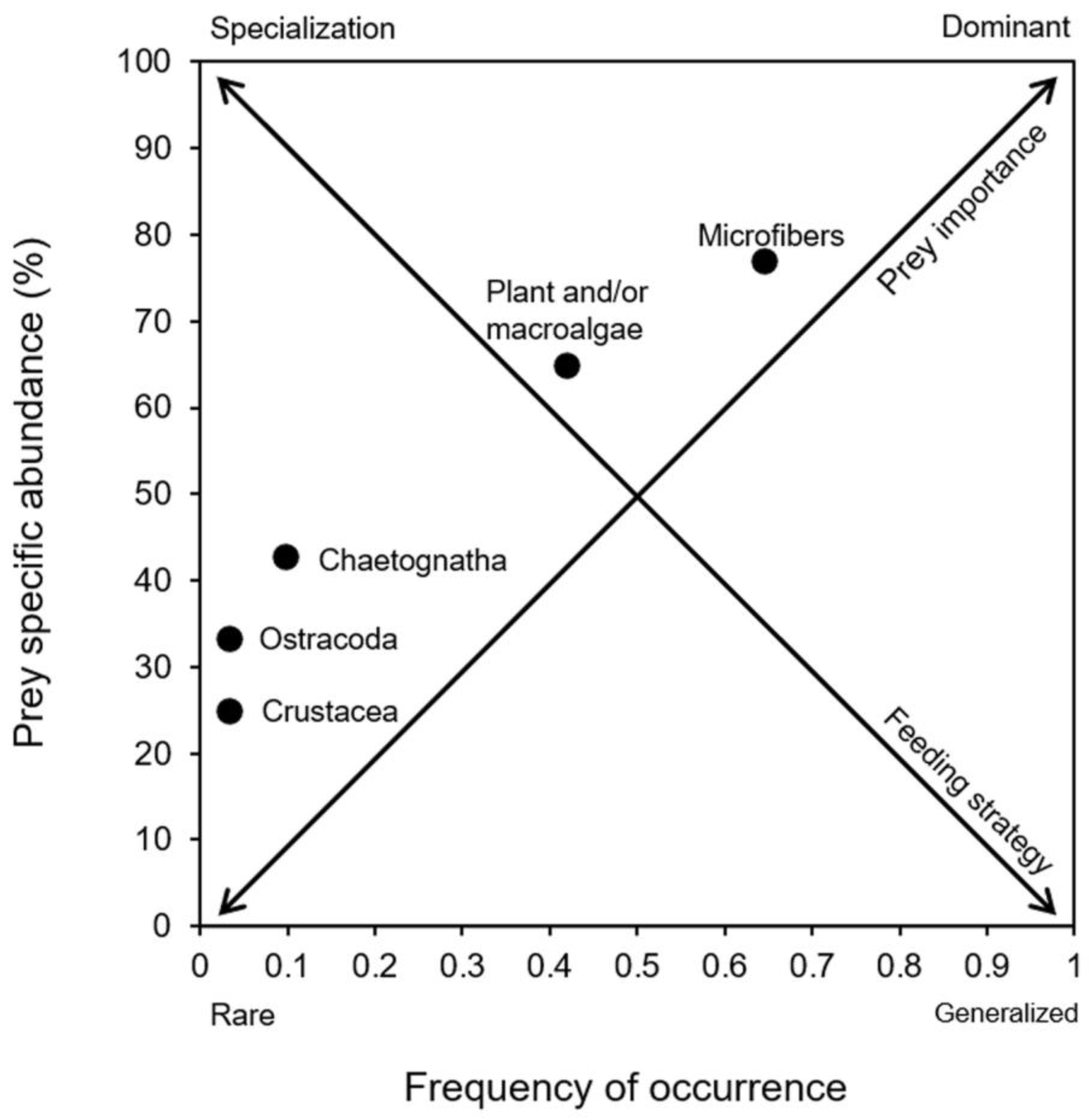
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morais, P.; Daverat, F. Definitions and concepts related to fish migration. In An Introduction to Fish Migration; Morais, P., Daverat, F., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Closs, G.P.; Warburton, M. Life histories of amphidromous fishes. In An Introduction to Fish Migration; Morais, P., Daverat, F., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 102–122. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, P. Biology and ecology of amphidromous gobiidae of the indo-pacific and the caribbean regions. J. Fish Biol. 2003, 63, 831–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowall, R.M. Early hatch: A strategy for safe downstream larval transport in amphidromous gobies. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2009, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.; Brun, C.; Hautecoeur, M.; Keith, P. Insights on endemism: Comparison of the duration of the marine larval phase estimated by otolith microstructural analysis of three amphidromous Sicyopterus species (Gobioidei: Sicydiinae) from Vanuatu and New Caledonia. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2010, 19, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, P.; Lord, C.; Lorion, J.; Watanabe, S.; Tsukamoto, K.; Couloux, A.; Dettal, A. Phylogeny and biogeography of Sicydiinae (Teleostei: Gobiidae) inferred from mitochondrial and nuclear genes. Mar. Biol. 2011, 158, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, K.N. An overview of goby-fry fisheries. Naga ICLARM Q. 1999, 22, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- McDowall, R.M. On amphidromy, a distinct form of diadromy in aquatic organisms. Fish Fish. 2007, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezold, F.; Iwamoto, T.; Harrison, I.J. Multivariate analysis of sicydiines of São Tomé and Príncipe with redescription of Sicydium brevifile and S. bustamantei (Teleostei: Gobiidae) and a key to west African sicydiines. The california academy of sciences gulf of guinea expedition (2001). Proc. Calif. Acad. Sci. 2006, 57, 965–980. [Google Scholar]
- Radtke, R.L.; Kinzie, R.A.; Shafer, D.J. Temporal and spatial variation in length of larval life and size at settlement of the Hawaiian amphidromous goby Lentipes concolor. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 59, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoareau, T.B.; Lecomte-Finiger, R.; Grondin, H.-P.; Conand, C.; Berrebi, P. Oceanic larval life of La Réunion ‘bichiques’, amphidromous gobiid post-larvae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 333, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, K.N. What comes down must go up: The migration cycle of juvenile-return anadromous taxa. Am. Fish Soc. Symp. 2009, 69, 321–341. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Garcés, G.C. A review of amphidromous freshwater fishes of the Choco biogeographical region (Colombia and Ecuador): Diversity, ecology, fisheries and conservation. Cybium 2017, 41, 157–169. [Google Scholar]
- Lagarde, R.; Teichert, N.; Boussarie, G.; Grondin, H.; Valade, P. Upstream migration of amphidromous gobies of la Réunion Island: Implication for management. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2015, 22, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Becheler, E.; Trinh, A.M.; Ellien, C. Spatial variability in post-larval traits of Sicyopterus lagocephalus Pallas 1770 around Reunion Island. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2018, 101, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelo, R. Biogeographical considerations of fish diversity in Bioko. Biodivers. Conserv. 1994, 3, 808–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.J. Biodiversity in the Gulf of Guinea: An overview. Biodivers. Conserv. 1994, 3, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, P.; Ferreira, C.E.L.; Floeter, S.R.; Fricke, R.; Gasparini, J.L.; Iwamoto, T.; Roch, L.; Sampaio, C.L.S.; Schliewen, U.K. Coastal fishes of São Tomé and Principe islands, Gulf of Guinea (eastern Atlantic Ocean)—An update. Zootaxa 2007, 1523, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, K.N. Opportunities in stream drift: Methods, goby larval types, temporal cycles, in situ mortality estimation, and conservation implications. Bish. Mus. Bull. Cult. Environ. Stud. 2007, 3, 35–61. [Google Scholar]
- Moelants, T. Sicydium Bustamantei. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2010: E.T182284A7849800. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-3.RLTS.T182284A7849800.en (accessed on 7 October 2020).
- Carbery, M.; O’Connor, W.; Thavamani, P. Trophic transfer of microplastics and mixed contaminants in the marine food web and implications for human health. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, P.; Porteiro, F.M.; Santos, R.S.; Barreiros, J.P.; Worms, J.; Wirtz, P. Coastal marine fishes of São Tomé Island (Gulf of Guinea). Arquipel. Cienc. Biol. Mar. 1999, 17A, 65–92. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, M.J. Predator feeding strategy and prey importance: A new graphical analysis. J. Fish Biol. 1990, 36, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundsen, P.A.; Gabler, H.M.; Stald-Vik, F.J. A new approach to graphical analysis of feeding strategy from stomach contents data-modification of the Costello (1990) method. J. Fish Biol. 1996, 48, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyntek, P.M.; Teece, M.A.; Schulz, K.L.; Thackeray, S.J. A standard protocol for stable isotope analysis of zooplankton in aquatic food web research using mass balance correction models. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 2135–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuchtmayr, H.; Grey, J. Effect of preparation and preservation procedures on carbon and nitrogen stable isotope determinations from zooplankton. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 2605–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Zanden, J.; Rasmussen, J. Variation in 15N and 13C trophic fractionation: Implications for aquatic food web studies. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, A.C.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A.L. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too much variation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gallegos, C.L.; Jordan, T.E.; Correll, D.L. Event-scale response of phytoplankton to watershed inputs in a subestuary: Timing, magnitude, and location of blooms. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 813–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deegan, L.A.; Garritt, R.H. Evidence for spatial variability in estuarine food webs. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 147, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans-White, M.A.; Dodds, W.K.; Whiles, M.R. Ecosystem significance of crayfishes and stonerollers in a prairie stream: Functional differences between co-occurring omnivores. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2003, 22, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dodds, W.K.; Collins, S.M.; Hamilton, S.K.; Tank, J.L.; Johnson, S.; Webster, J.R.; Simon, K.S.; Whiles, M.R.; Rantala, H.M.; McDowell, W.H.; et al. You are not always what you think you eat: Selective assimilation across multiple whole-stream isotopic trace studies. Ecology 2014, 95, 2757–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Keith, P.; Hoareau, T.; Lord, C.; Ah-Yane, O.; Gimmoneau, G.; Robinet, T.; Valade, P. Characterisation of post-larval to juvenile stages, metamorphosis, and recruitment of an amphidromous goby, Sicyopterus lagocephalus (Pallas, 1767) (Teleostei: Gobiidae: Sicydiinae). Mar. Fresh Res. 2008, 59, 876–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, M.; Maeda, K.; Hirashima, K.; Tachihara, K. Comparative larval development of three amphidromous Rhinogobius species making reference to their habitat preferences and migration biology. Mar. Fresh Res. 2013, 64, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engman, A.C.; Kwak, T.J.; Cope, W.G. Do postlarval amphidromous fishes transport marine-derived nutrients and pollutants to Caribbean streams? Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2018, 27, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, P.W.; Hobson, K.A. Stable isotope analysis of amphidromous Hawaiian gobies suggests their larvae spend a substantial period of time in freshwater river plumes. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2005, 74, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, K.A.; Smith, R.J.F.; Sorensen, P.W. Applications of stable isotope analysis to tracing nutrient sources to Hawaiian gobioid fishes and other stream organisms. Bish. Mus. Bull. Cult. Environ.Stud. 2007, 3, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Lönnstedt, O.M.; Eklöv, P. Environmentally relevant concentrations of microplastic particles influence larval fish ecology. Science 2016, 352, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannetier, P.; Morin, B.; Le Bihanic, F.; Dubreil, L.; Clérandeau, C.; Chouvellon, F.; Arkelc, K.V.; Daniond, M.; Cachot, J. Environmental samples of microplastics induce significant toxic effects in fish larvae. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Galindo, G.A.; Sanchez, G.C.; Beltran-Leon, B.S.; Zapata, L. A goby-fry fishery in the northern Colombian Pacific Ocean. Cybium 2011, 35, 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, R.P.; Hogan, J.D.; Blum, M.J.; Gagne, R.B.; Hain, E.F.; Gilliam, J.F.; McIntyre, P.B. Climate change and conservation of endemic amphidromous fishes in Hawaiian streams. Endanger. Species Res. 2012, 16, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Seasons | Examined Guts (N) | Guts with Food (N) | Feeding Incidence (%) | Plant and/or Macroalgae Incidence (%) | Zooplankton Incidence (%) | Microplastic and Microfiber Incidence (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet | 30 | 16 | 53.3 | 46.7 | 16.7 | 20.0 |
| Dry | 30 | 6 | 20.0 | 20.3 | 0.0 | 23.3 |
| Food Items | Low 95% | High 95% | Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zooplankton | 0.42 | 0.71 | 0.56 |
| Macroalgae detritus | 0.16 | 0.50 | 0.35 |
| Tree detritus | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baptista, V.; Dias, E.; Cruz, J.; Branco, M.; Vieira, S.; Teodósio, M.A. Feeding Ecology of Sicydium bustamantei (Greeff 1884, Gobiidae) Post-Larvae: The “Little Fish” of São Tomé Island. Oceans 2020, 1, 300-310. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans1040020
Baptista V, Dias E, Cruz J, Branco M, Vieira S, Teodósio MA. Feeding Ecology of Sicydium bustamantei (Greeff 1884, Gobiidae) Post-Larvae: The “Little Fish” of São Tomé Island. Oceans. 2020; 1(4):300-310. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans1040020
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaptista, Vânia, Ester Dias, Joana Cruz, Maria Branco, Sara Vieira, and Maria Alexandra Teodósio. 2020. "Feeding Ecology of Sicydium bustamantei (Greeff 1884, Gobiidae) Post-Larvae: The “Little Fish” of São Tomé Island" Oceans 1, no. 4: 300-310. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans1040020
APA StyleBaptista, V., Dias, E., Cruz, J., Branco, M., Vieira, S., & Teodósio, M. A. (2020). Feeding Ecology of Sicydium bustamantei (Greeff 1884, Gobiidae) Post-Larvae: The “Little Fish” of São Tomé Island. Oceans, 1(4), 300-310. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans1040020









