Regenerated Bone Quality as a Determinant of Bone Turnover and Prognosis in Short Plateau Implants: A Finite Element Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
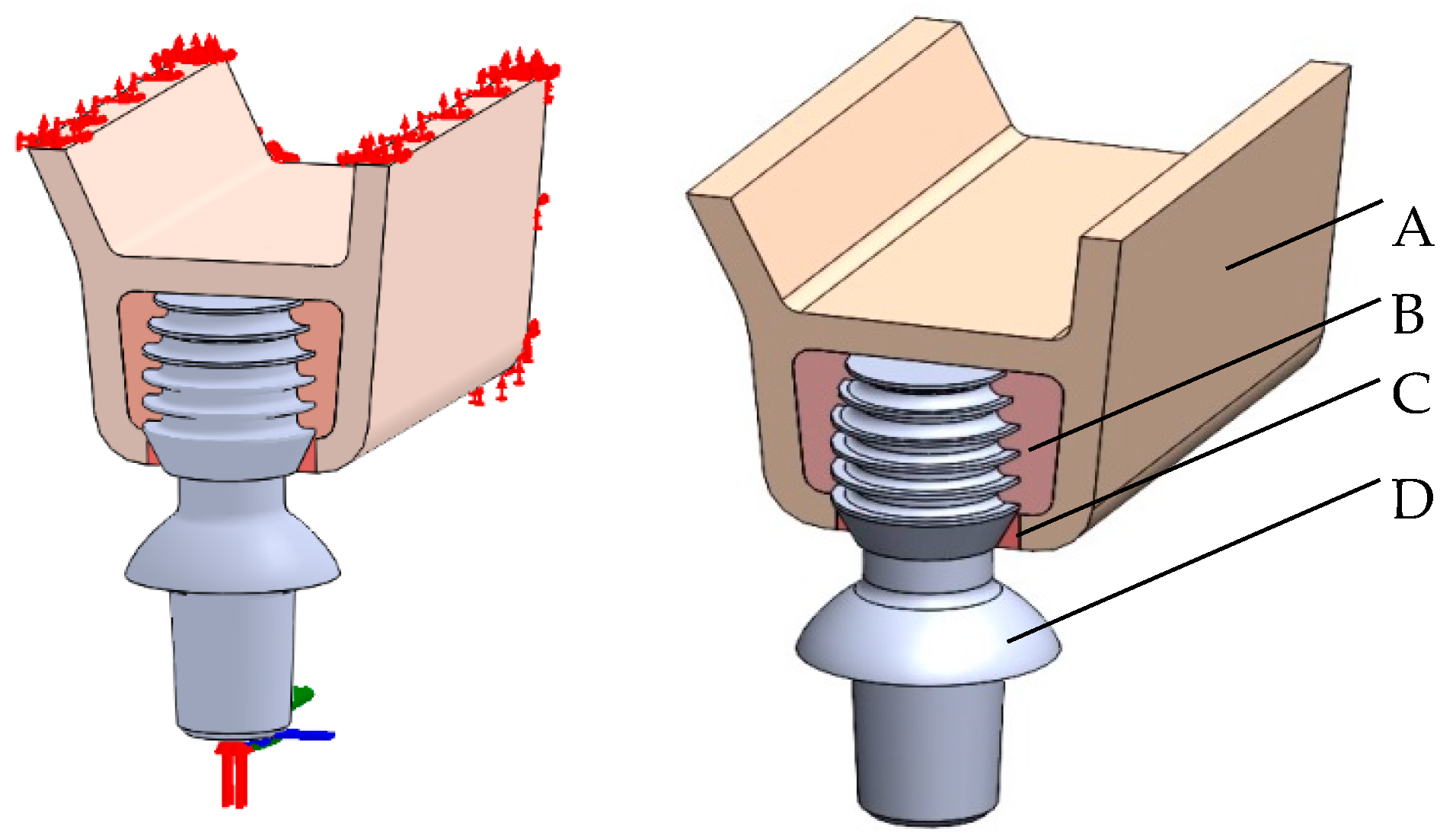
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
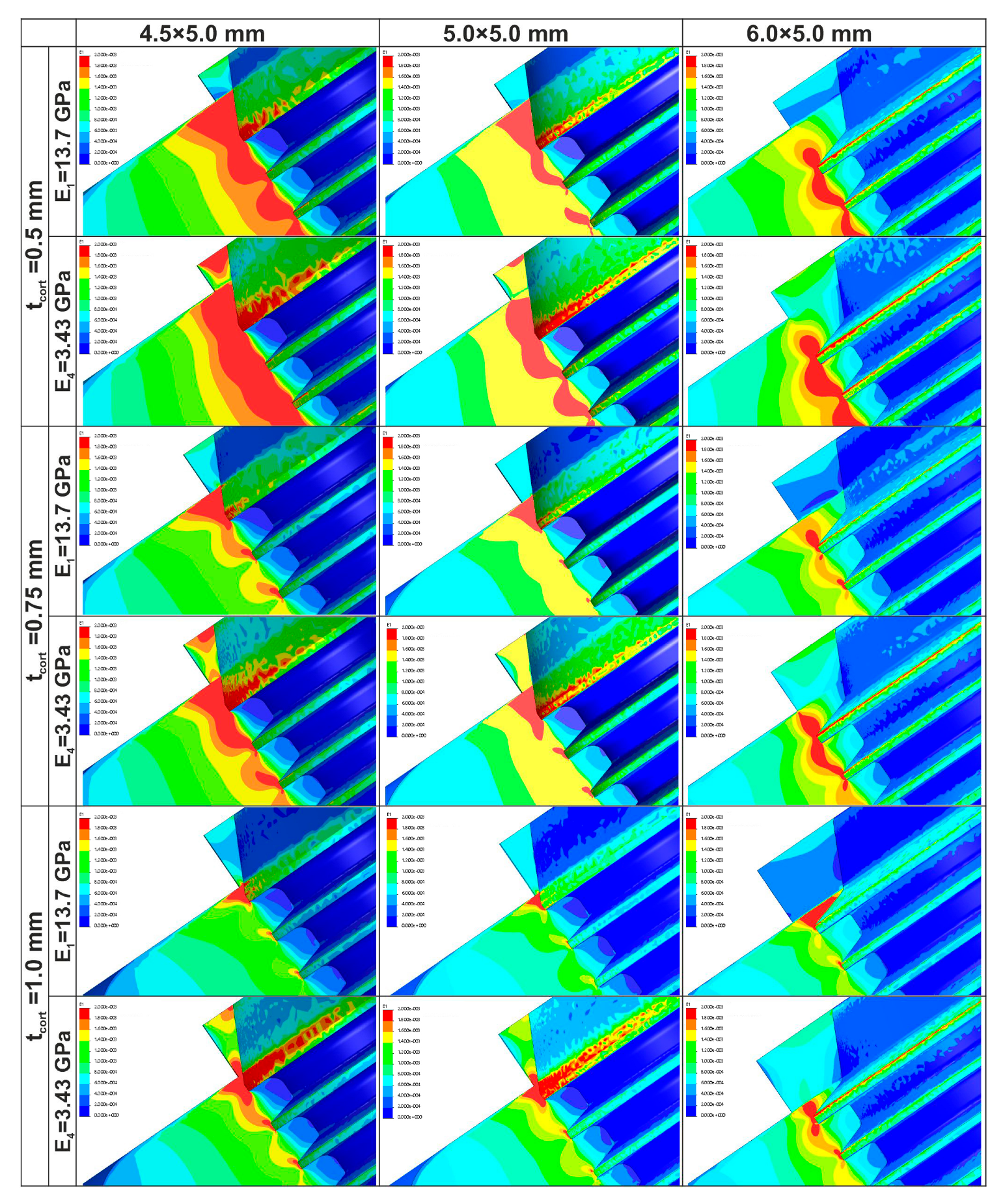
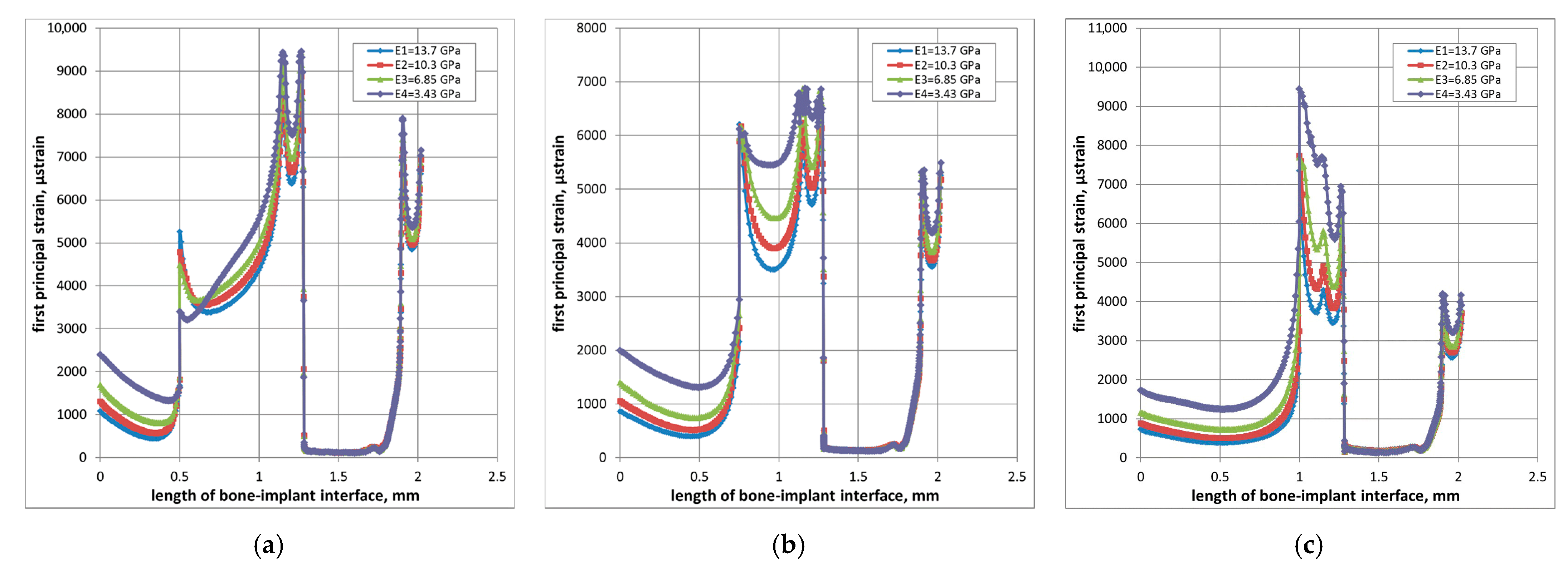
3.1. Strain Localization
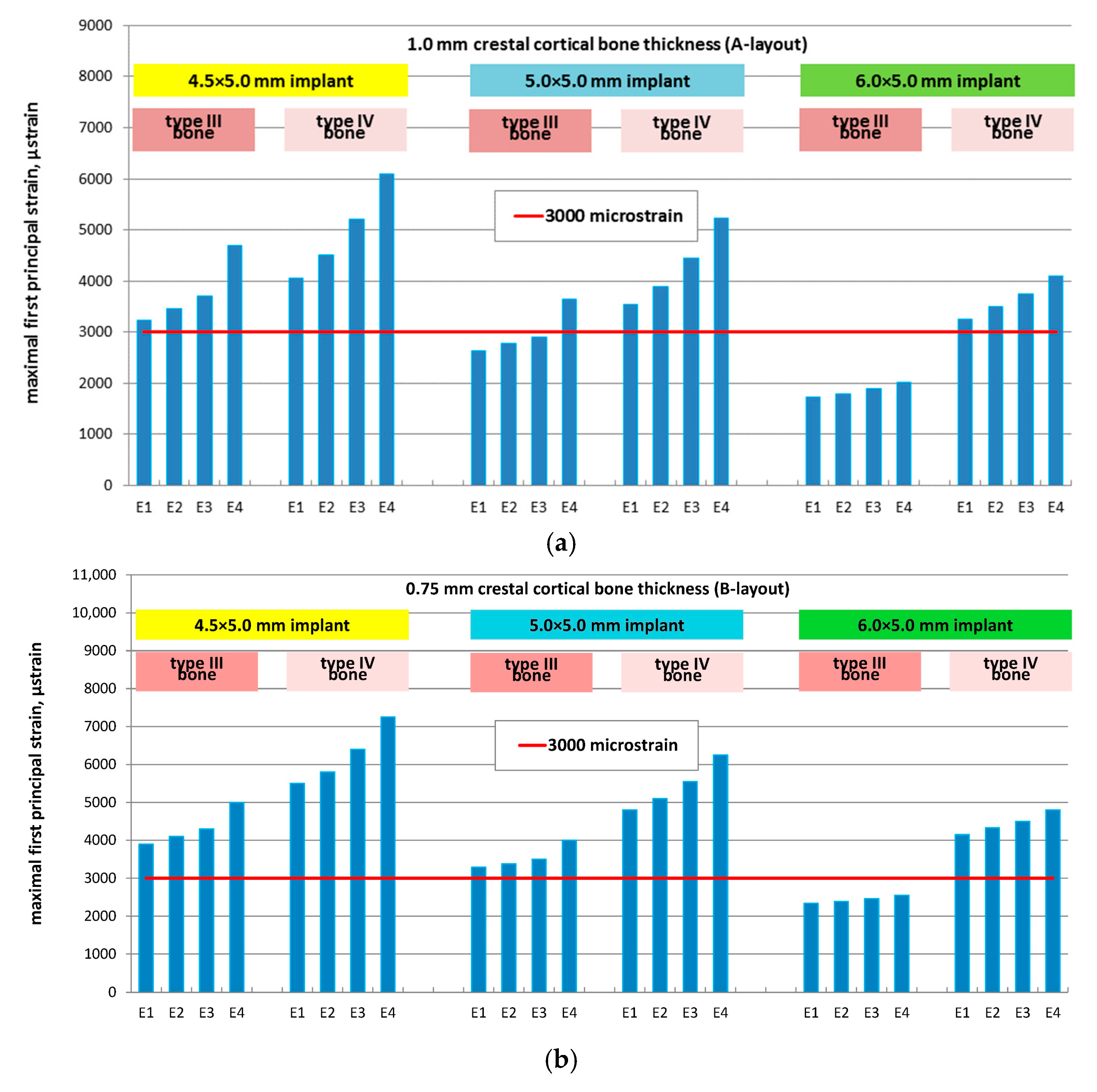
3.2. Effect of Implant Diameter
- A-layout (1.0 mm cortical): 47%, 48%, 50%, and 56%
- B-layout (0.75 mm cortical): 40%, 42%, 44%, and 49%
- C-layout (0.5 mm cortical): 38%, 39%, 40%, and 43%
- A-layout: 20%, 23%, 26%, and 32%
- B-layout: 24%, 26%, 29%, and 34%
- C-layout: 30%, 31%, 33%, and 36%
3.3. Effect of Cancellous Bone Quality
- A-layout: +25% (N), +34% (M), +88% (W)
- B-layout: +41% (N), +46% (M), +78% (W)
- C-layout: +53% (N), +57% (M), +73% (W)
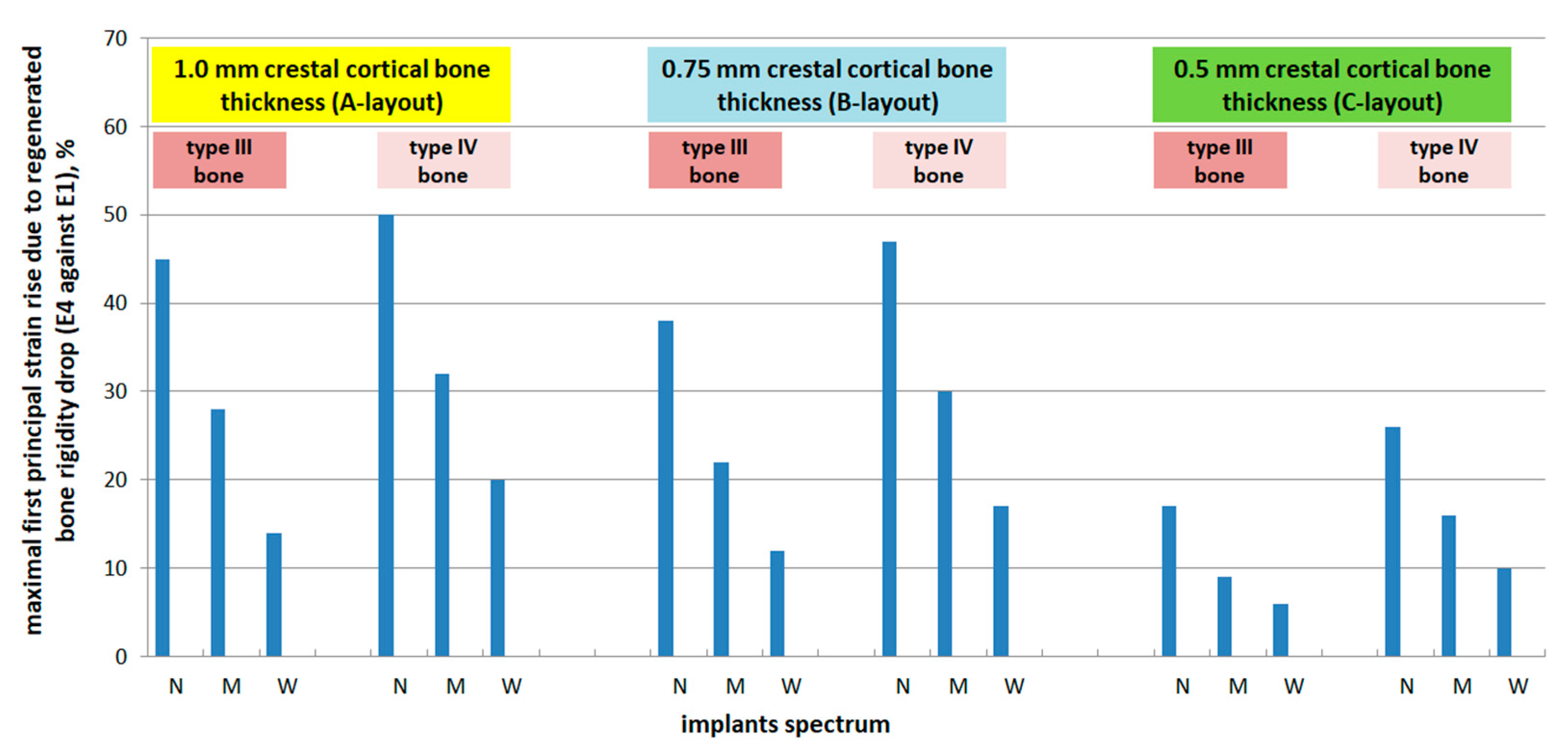
3.4. Effect of Regenerated Bone Elasticity
- A-layout: +45% (N), +28% (M), +14% (W)
- B-layout: +38% (N), +22% (M), +12% (W)
- C-layout: +17% (N), +9% (M), +6% (W)
- A-layout: +50% (N), +32% (M), +20% (W)
- B-layout: +47% (N), +30% (M), +17% (W)
- C-layout: +26% (N), +16% (M), +10% (W)
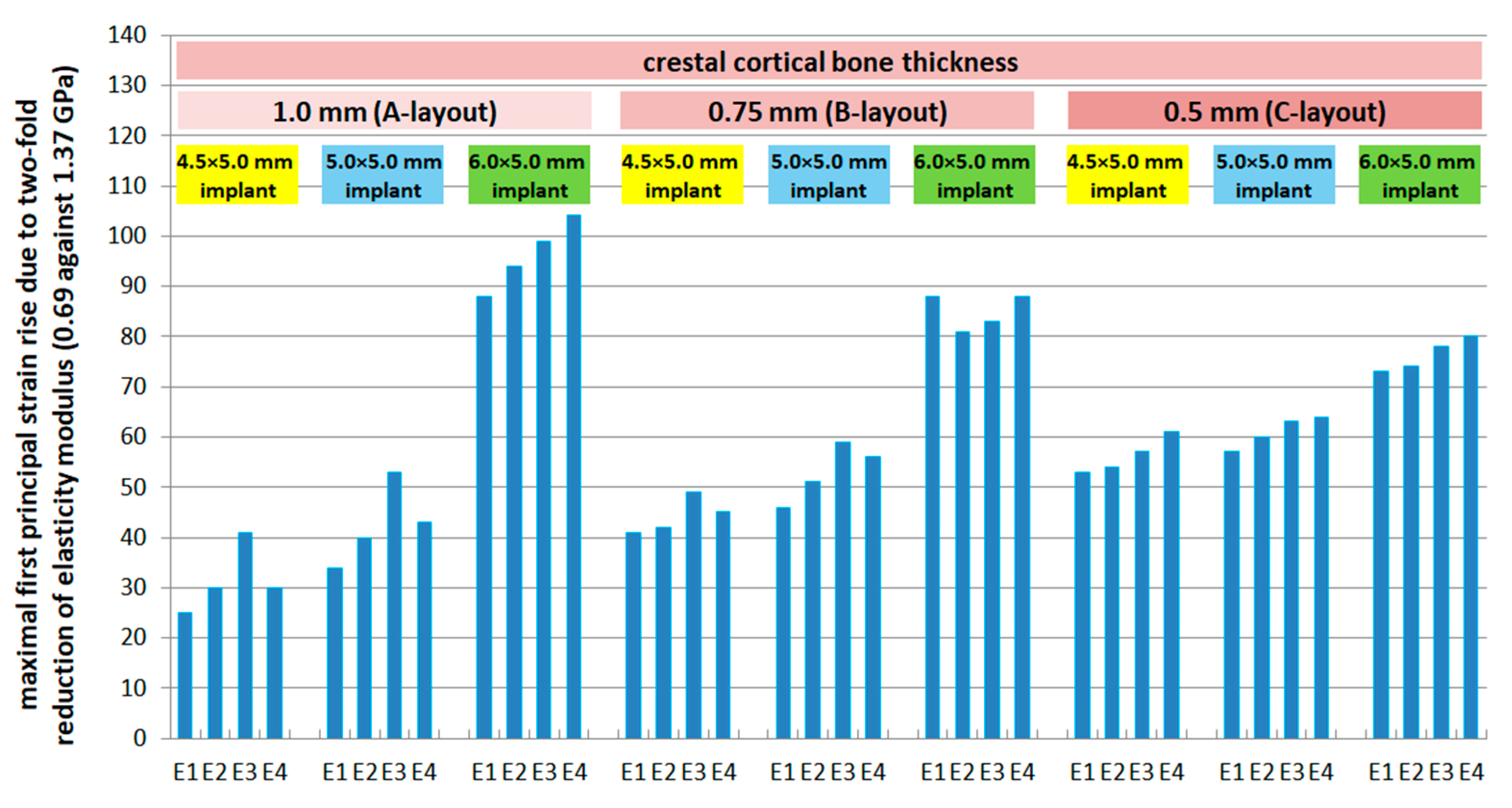
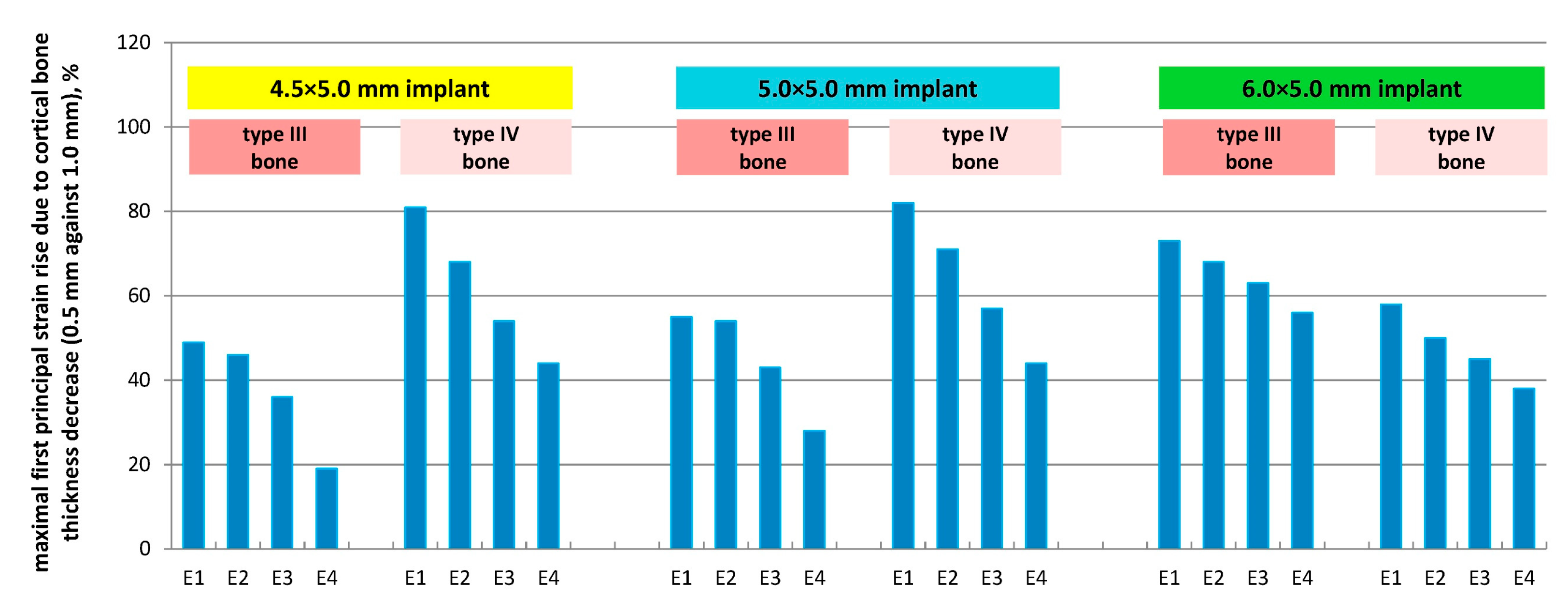
3.5. Effect of Cortical Bone Thickness
- E1: +49% (N), +55% (M), +73% (W)
- E2: +46% (N), +54% (M), +68% (W)
- E3: +36% (N), +43% (M), +63% (W)
- E4: +19% (N), +28% (M), +56% (W)
- E1: +81% (N), +82% (M), +58% (W)
- E2: +68% (N), +71% (M), +50% (W)
- E3: +54% (N), +57% (M), +45% (W)
- E4: +44% (N), +44% (M), +38% (W)
4. Discussion
- The isotropic material assumption, which does not capture anisotropy-related local strain variations.
- The assumption of complete osseointegration, which may overestimate load transfer efficiency in poor-quality bone.
- The use of static rather than cyclic loading, which may underestimate long-term fatigue-related effects.
5. Conclusions
- Strains in the cortical layer remained within physiological limits in all scenarios, whereas cancellous bone in type IV maxillae frequently exceeded Frost’s pathological threshold (MESp = 3000 με), particularly with smaller implant diameters and reduced regenerated bone stiffness.
- Implant diameter had a major effect on strain distribution: increasing the diameter from 4.5 mm to 6.0 mm lowered MFPS by up to 56% in type III bone and up to 36% in type IV bone. The protective effect of wider implants was most evident in cases with thicker cortical bone and lower regenerated bone elasticity.
- The mechanical quality of regenerated bone proved critical: when elasticity was reduced (E3–E4), cancellous strains rose substantially, especially with cortical thicknesses < 0.75 mm. Under these conditions, only 6.0 mm implants maintained strains within safe ranges in most cases.
- From a clinical standpoint, biomechanical risk is jointly determined by implant diameter and regenerated bone quality. Wide-diameter short implants (6.0 mm) are particularly advantageous when bone quality is uncertain and cortical thickness is limited, whereas narrower implants may only be advisable if regenerated bone elasticity approaches cortical levels.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Overmann, A.L.; Aparicio, C.; Richards, J.T.; Mutreja, I.; Fischer, N.G.; Wade, S.M.; Potter, B.K.; Davis, T.A.; Bechtold, J.E.; Forsberg, J.A.; et al. Orthopaedic osseointegration: Implantology and future directions. J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.; Costa, B.; Trindade, H.F.; Castilho, R.M.; Fernandes, J. Comparative analysis between extra-short implants (≤6 mm) and 6 mm-longer implants: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial. Aust. Dent. J. 2022, 67, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuda, S.; Martins, B.G.D.S.; Castro, F.C.; Heboyan, A.; Gehrke, S.A.; Fernandes, J.C.H.; Mello-Moura, A.C.V.; Fernandes, G.V.O. Marginal Bone Level and Clinical Parameter Analysis Comparing External Hexagon and Morse Taper Implants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, A.R.; Desai, S.R.; Patel, J.R.; Alqhtani, N.R.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Heboyan, A.; Fernandes, G.V.O.; Mustafa, M.; Karobari, M.I. Investigating the impact of diameters and thread designs on the biomechanics of short implants placed in D4 bone: A 3D finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meslier, Q.; Shefelbine, S.J. Using Finite Element Modeling in Bone Mechanoadaptation. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2023, 21, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratiev, A.; Demenko, V.; Linetskiy, I.; Weisskircher, H.-W.; Linetska, L. Evaluation of bone turnover around short finned implants in atrophic posterior maxilla: A finite element study. Prosthesis 2024, 6, 1170–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jansen, J.A.; Walboomers, X.F.; van den Beucken, J.J. Mechanical aspects of dental implants and osseointegration: A narrative review. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 103, 103574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.C.; Marques, M.D.C.; Vidal, M.G.; Tolentino, P.H.M.P.; Dinelli, R.G.; Fernandes, G.V.d.O.; Shibli, J.A. Is the facial bone wall critical to achieving esthetic outcomes in immediate implant placement with immediate restoration? A systematic review. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 33, 979–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingsammer, L.; Pommer, B.; Hunger, S.; Stehrer, R.; Watzek, G.; Insua, A. Influence of implant length and associated parameters upon biomechanical forces in finite element analyses: A systematic review. Implant. Dent. 2019, 28, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenkoglu, B.G.; Balcioglu, N.B.; Ozdemir, T.; Mijiritsky, E. The Effect of the Length and Distribution of Implants for Fixed Prosthetic Reconstructions in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla: A Finite Element Analysis. Materials 2019, 12, 2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Buti, J.; Barausse, C.; Gasparro, R.; Sammartino, G.; Felice, P. Short implants versus longer implants in vertically augmented atrophic mandibles: A systematic review of randomised controlled trials with a 5-year post-loading follow-up. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 2019, 12, 267–280. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, P.; Cao, R.; Li, Z.; Fan, Z. A comprehensive biomechanical evaluation of length and diameter of dental implants using finite element analyses: A systematic review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Larrazabal Saez de Ibarra, N.; Morales Martín, I.; Saracho Rotaeche, L. Influence of Dental Implant Diameter and Bone Quality on the Biomechanics of Single-Crown Restoration. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calì, M.; Zanetti, E.M.; Oliveri, S.M. Influence of thread shape and inclination on the biomechanical behaviour of plateau implant systems. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, P.G.; Suzuki, M.; Marin, C.; Granato, R.; Gil, L.F.; Tovar, N.; Jimbo, R.; Neiva, R.; Bonfante, E.A. Osseointegration of Plateau Root Form Implants: Unique Healing Pathway Leading to Haversian-Like Long-Term Morphology. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 881, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, G.J.; Gjengedal, H.; Harkin, J.; Holland, N.; Moore, C.; Srinivasan, M. Effect of autogenous bone graft site on dental implant survival and donor site complications: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2022, 22, 101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linetska, L.; Kipenskyi, A.; Demenko, V.; Linetskiy, I.; Kondratiev, A.; Yefremov, O. Finite element study of biomechanical behavior of short dental implants with bone loss effects—Evaluation of bone turnover. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 4th KhPI Week on Advanced Technology (KhPIWeek), Kharkiv, Ukraine, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zeng, C.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, T.; Wang, Y. Optimization of stress distribution of bone-implant interface (BII). Biomater. Adv. 2023, 147, 213342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misch, C.E. (Ed.) Chapter 32—Progressive bone loading: Increasing the density of bone with a prosthetic protocol. In Dental Implant Prosthetics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 913–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreve, S.; Ferreira, I.; da Costa Valente, M.L.; Dos Reis, A.C. Relationship between dental implant macro-design and osseointegration: A systematic review. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, H.M. A 2003 update of bone physiology and Wolff’s Law for clinicians. Angle Orthod. 2004, 74, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, H.M. Bone mass and the mechanostat: A proposal. Anat. Rec. 1987, 219, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Singh, S.V.; Arya, D.; Shivakumar, S.; Chand, P. Mechanical failures of dental implants and supported prostheses: A systematic review. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2023, 13, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saab, X.E.; Griggs, J.A.; Powers, J.M.; Engelmeier, R.L. Effect of abutment angulation on the strain on the bone around an implant in the anterior maxilla: A finite element study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2007, 97, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcinelli, C.; Valente, F.; Vasta, M.; Traini, T. Finite element analysis in implant dentistry: State of the art and future directions. Dent. Mater. 2023, 39, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisiak-Myszke, M.; Marciniak, D.; Bieliński, M.; Sobczak, H.; Garbacewicz, Ł.; Drogoszewska, B. Application of Finite Element Analysis in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery-A Literature Review. Materials 2020, 13, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linetskiy, I.; Sutcliffe, M.; Kondratiev, A.; Demenko, V.; Linetska, L.; Yefremov, O. A novel method of load bearing ability analysis of short plateau implants placed in compromised bone. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 4th KhPI Week on Advanced Technology (KhPIWeek), Kharkiv, Ukraine, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.Y.; Müftü, S.; Bozkaya, D. Combined effects of implant insertion depth and alveolar bone quality on periimplant bone strain induced by a wide-diameter, short implant and a narrow-diameter, long implant. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2010, 104, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Horita, S.; Murakami, K.; Tsutsumi, S.; Kirita, T. The effects of bone density and crestal cortical bone thickness on micromotion and peri-implant bone strain distribution in an immediately loaded implant: A nonlinear finite element analysis. J. Periodontal. Implant. Sci. 2016, 46, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demenko, V.; Linetskiy, I.; Linetska, L.; Sutcliffe, M.; Kondratiev, A. Prognosis of crestally placed short plateau implants in posterior maxilla. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Engng. 2025, 41, e70025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkaya, D.; Muftu, S.; Muftu, A. Evaluation of load transfer characteristics of five different implants in compact bone at different load levels by finite elements analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 92, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, C.A.A.; Verri, F.R.; Noritomi, P.Y.; Kemmoku, D.T.; Souza Batista, V.E.; Cruz, R.S.; de Luna Gomes, J.M.; Pellizzer, E.P. Effect of bone quality and bone loss level around internal and external connection implants: A finite element analysis study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 125, 137.e1–137.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soodmand, I.; Becker, A.K.; Sass, J.O.; Jabs, C.; Kebbach, M.; Wanke, G.; Dau, M.; Bader, R. Heterogeneous material models for finite element analysis of the human mandible bone—A systematic review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodoso-Torrecilla, I.; Konka, J.; Kreuzer, M.; Jimenez-Pique, E.; Espanol, M.; Ginebra, M.-P. Quality assessment of regenerated bone in intraosseous and intramuscular scaffolds by spectroscopy and nanoindentation. Biomater. Adv. 2024, 164, 213982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez-Carmona, P.; Mora-Macías, J.; Pajares, A.; Mármol, Á.; Reina-Romo, E. On the influence of structural and chemical properties on the elastic modulus of woven bone under healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1476473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mericske-Stern, R.; Zarb, G.A. In vivo measurements of some functional aspects with mandibular fixed prostheses supported by implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1996, 7, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, S.; Cehreli, M.C.; Yalçin, E. The influence of functional forces on the biomechanics of implant-supported prostheses—A review. J. Dent. 2002, 30, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstunov, L. Implant zones of the jaws: Implant location and related success rate. J. Oral Implantol. 2007, 33, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, R.A.; Rozental, T.D. Bone graft substitutes. Hand Clin. 2012, 28, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiasa, K.; Abe, Y.; Okazaki, Y.; Nogami, K.; Mizumachi, W.; Akagawa, Y. Preoperative computed tomography-derived bone densities in hounsfield units at implant sites acquired primary stability. ISRN Dent. 2011, 2011, 678729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.; Brizuela Velasco, A.; Ríos-Santos, J.V.; Sánchez Lasheras, F.; Lemos, B.F.; Gil, F.J.; Carvalho, A.; Herrero-Climent, M. Effect of Different Implant Designs on Strain and Stress Distribution under Non-Axial Loading: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Guo, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. Effect of different implant angulations on the biomechanical performance of prosthetic screws in two implant-supported, screw-retained prostheses: A numerical and experimental study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023, 130, 240.e1–240.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, X.; Chi, W.; Ai, H.; Wu, L. Comparing the influence of crestal cortical bone and sinus floor cortical bone in posterior maxilla bi-cortical dental implantation: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2015, 73, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, N.; Stegaroiu, R.; Kitamura, E.; Kurokawa, K.; Nomura, S. Influence of maxillary cortical bone thickness, implant design and implant diameter on stress around implants: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2010, 54, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.T.; Zanatta, L.C.S.; de Souza Rendohl, E.; Gehrke, S.A. Comparative analysis of stress distribution in one-piece and two-piece implants with narrow and extra-narrow diameters: A finite element study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.E.; Ellis, B.J.; Weiss, J.A. Verification, validation and sensitivity studies in computational biomechanics. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 10, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Matos, J.D.M.; Queiroz, D.A.; Nakano, L.J.N.; Andrade, V.C.; Ribeiro, N.D.R.; Borges, A.L.S.; Bottino, M.A.; Lopes, G.D.S. Bioengineering tools applied to dentistry: Validation methods for In Vitro and In Silico analysis. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tretto, P.H.W.; Dos Santos, M.B.F.; Spazzin, A.O.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Bacchi, A. Assessment of stress/strain in dental implants and abutments of alternative materials compared to conventional titanium alloy. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 23, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratiev, A.; Gaidachuk, V.; Nabokina, T.; Tsaritsynskyi, A. New Possibilities of Creating the Efficient Dimensionally Stable Composite Honeycomb Structures for Space Applications. In Integrated Computer Technologies in Mechanical Engineering. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Karl, M.; Wendler, F. Finite Element Analysis on Stress Development in Alveolar Bone During Insertion of a Novel Dental Implant Design. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, H.K.; Koc, S.; Kustarci, A.; Rennie, A.E. A literature review on the linear elastic material properties assigned in finite element analyses in dental research. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 30, 103087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.J.; Cheong, S.Y.; Han, J.H.; Heo, S.J.; Chung, J.P.; Rhyu, I.C.; Choi, Y.C.; Baik, H.K.; Ku, Y.; Kim, M.H. Evaluation of design parameters of osseointegrated dental implants using finite element analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2002, 29, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravani, M.R. Mechanical behavior of restorative dental composites under various loading conditions. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 93, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordin, D.; Castro, M.B.; Carvalho, M.A.; Araujo, A.M.; Cury, A.A.D.B.; Lazari-Carvalho, P.C. Different treatment modalities using dental implants in the posterior maxilla: A finite element analysis. Braz. Dent. J. 2021, 32, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.H.; Seo, J.H.; Cho, R.Y.; Yi, S.M.; Kim, L.K.; Han, H.S.; On, S.W.; Kim, W.H.; An, H.W.; Yang, B.E. Finite Element Analysis of a New Non-Engaging Abutment System for Three-Unit Implant-Supported Fixed Dental Prostheses. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demenko, V.; Linetskiy, I.; Yefremov, O.; Linetska, L.; Smetankina, N.; Kondratiev, A. Regenerated Bone Quality as a Determinant of Bone Turnover and Prognosis in Short Plateau Implants: A Finite Element Study. Prosthesis 2025, 7, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7050123
Demenko V, Linetskiy I, Yefremov O, Linetska L, Smetankina N, Kondratiev A. Regenerated Bone Quality as a Determinant of Bone Turnover and Prognosis in Short Plateau Implants: A Finite Element Study. Prosthesis. 2025; 7(5):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7050123
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemenko, Vladislav, Igor Linetskiy, Oleg Yefremov, Larysa Linetska, Natalia Smetankina, and Andrii Kondratiev. 2025. "Regenerated Bone Quality as a Determinant of Bone Turnover and Prognosis in Short Plateau Implants: A Finite Element Study" Prosthesis 7, no. 5: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7050123
APA StyleDemenko, V., Linetskiy, I., Yefremov, O., Linetska, L., Smetankina, N., & Kondratiev, A. (2025). Regenerated Bone Quality as a Determinant of Bone Turnover and Prognosis in Short Plateau Implants: A Finite Element Study. Prosthesis, 7(5), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7050123





