Abstract
Introduction: Additive manufacturing has emerged as a promising solution for improving the accessibility and affordability of upper limb prostheses. Despite the growing need, traditional prosthetic devices remain costly and often inaccessible, particularly in underserved regions. This review examines the current landscape of 3D-printed upper limb prostheses, focusing on their design, functionality, and cost-effectiveness. It aims to assess the potential of 3D-printing upper limb prostheses in addressing current accessibility barriers. Methods: A two-phase approach was used to analyze the literature on 3D-printed upper limb prostheses. The first phase involved a literature search using keywords related to 3D printing and upper limbs prostheses. The second phase included data collection from online platforms such as Enabling the Future, Thingiverse, and NIH 3D Print Exchange. Studies focusing on the design, fabrication, and clinical application of 3D-printed prostheses were included. The results were organized into categories based on design characteristics, kinematic features, and manufacturing specifications. Results: A total of 35 3D-printed upper limb prostheses were reviewed, with the majority being hand prostheses. Devices were categorized based on their range of motion, actuation mechanism, materials, cost, and assembly complexity. The e-NABLE open-source platform has played a significant role in the development and dissemination of these devices. Prostheses were classified into cost categories (low, moderate, and high), with 64% of models costing under USD 50. Most designs were rated as easy to moderate in terms of assembly, making them accessible for non-specialist users. Conclusions: Three-dimensional printing offers an effective, low-cost alternative to traditional prosthetic manufacturing. However, variability in design, a lack of standardized manufacturing protocols, and limited clinical validation remain challenges. Future efforts should focus on establishing standardized guidelines, improving design consistency, and validating the clinical effectiveness of 3D-printed prostheses to ensure their long-term viability as functional alternatives to traditional devices.
1. Introduction
Upper limb amputations affect individuals of all age groups, from children to adults, with causes ranging from trauma and cancer to vascular diseases, congenital disorders, and infections [1]. The scope of this issue is vast. In 2005, approximately 541,000 Americans had undergone upper limb amputations, a figure projected to double by 2050 [2]. Among these, over 32,500 children, in the United States alone, have experienced upper limb amputations, and an additional 1500 children are born each year with upper limb reductions, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) [3]. Globally, the prevalence of upper limb amputation is estimated at 4–5 per 10,000 live births, with some studies citing rates as high as one per 100 live births [3].
Despite the significant need, access to prosthetic devices remains alarmingly inadequate. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that nearly 40 million individuals worldwide require prosthetic limbs, yet only 5–15% can access them [1]. This disparity is due to several barriers, including high costs, limited availability, a shortage of qualified professionals, and insufficient infrastructure [1,2]. Upper limb prostheses are particularly expensive, with conventionally manufactured models costing between USD 4000 and USD 75,000, while body-powered alternatives range from USD 4000 to USD 20,000 [3,4]. For children, these costs are further magnified by the need for frequent replacements to accommodate their growth [3]. Furthermore, the acquisition process often involves extensive time commitments, requiring numerous appointments for measurements, fittings, and consultations with specialists, adding another layer of complexity to prosthetic care accessibility for patients and families [5].
Three-dimensional printing has emerged as a transformative solution to these challenges, offering a faster, more cost-effective, and highly customizable approach to prosthetic manufacturing [6]. Unlike traditional methods, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, allowing the production of devices tailored to individual needs without the need for retooling [4]. Over the past decade, this technology has seen remarkable progress, with the development of numerous prosthetic designs made accessible through open-source platforms. This expansion is largely driven by the emergence of collaborative communities such as E-nable, providing low-cost, personalized prosthetic solutions for both children and adults, significantly enhancing accessibility [4,7].
Modern upper limb prostheses fall into two main categories based on their operational mechanisms: mechanical actuated and externally powered systems. In mechanical actuation systems, the user’s residual limb provides the energy needed to generate movement, often through a network of cables and harnesses connecting the prosthesis to the intact limb. Externally powered prostheses, on the other hand, utilize an external energy source, such as batteries, to create movement. Among these, electromyographic (EMG) prostheses stand out for their ability to translate muscle signals from the user’s residual limb into precise movements. This allows for enhanced control and advanced functionalities, such as fine grasping and manipulation, offering users a more natural and seamless experience [8].
The primary challenge remains the limited accessibility of upper limb prostheses, largely driven by their high costs. To address this issue, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of current 3D-printed upper limb prostheses, focusing on their design, cost, and potential to overcome current accessibility barriers. This review aims to provide an up-to-date overview of 3D-printing upper limb prostheses, as no standardized guidelines currently exist. By synthesizing these insights, we highlight innovative approaches, identify existing gaps, and propose opportunities for advancing prosthetic development to improve accessibility and affordability.
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
The review followed a two-phase approach to ensure a thorough synthesis of available literature, addressing the limited availability of peer-reviewed research on 3D-printed prostheses. The initial phase involved an extensive literature search to identify relevant studies on the topic. This was complemented by a supplementary data collection phase, using online resources and specialized platforms dedicated to 3D printing.
Key platforms consulted included Enabling the Future (www.enablingthefuture.org, accessed 10/01/2025), recognized as the largest source of up-to-date 3D-printed prostheses for the upper extremity, and the NIH 3D Print Exchange (https://3d.nih.gov accessed 10/01/2025), an open-access, community-driven library featuring bioscientific and medical 3D models. Additionally, the 3D print website (www.3dprint.com accessed 10/01/2025) was also explored, using the keyword “prosthesis” to identify pertinent 3D-printed advancements. The Thingiverse platform (https://www.thingiverse.com accessed 10/01/2025) which contains user-generated digital design files for advanced technologies such as 3D printing, laser cutting, and milling, was also used to expand the dataset and gather insights into emerging innovations.
The literature search was conducted across PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library on 10 January 2025. The search strategy employed the following combination of MeSH terms and keywords: “Rapid prototyping” OR “3D-printing” OR “3D-printed” AND “hand” OR “upper limb” OR “arm” OR “finger” AND “prosthesis” OR “prosthetic’ OR “prosthetics”. To comply with the project’s innovative scope, the search was restricted to full-text articles published in English within the past 10 years.
2.2. Study Selection and Eligibility
All references were uploaded to the Covidence platform, where title, abstract, and full-text screening was performed by two reviewers following an initial deduplication process. Studies focusing on the design, fabrication, or clinical application of 3D-printed upper extremity prostheses, including those for the upper arm, forearm, hand, and fingers, were included. Patients of all ages, from children to adults, and regardless of the underlying etiology necessitating the prosthesis were considered eligible. Exclusion criteria included studies involving non-human models, splints, tool-specific prostheses, outdated versions, passive or cosmetic prostheses, or specific remixes of prosthesis designs, as well as systematic reviews and abstracts without full-text availability.
3. Results
The literature review initially identified 451 articles, of which 39 underwent full-text review. This process led to the inclusion of 13 studies, each presenting a distinct prosthesis. As for the internet search, it further identified an additional 22 models, bringing the total number of upper limb prostheses reviewed to 35. Findings are organized across three tables: the first outlines the design characteristics and mechanical properties of 3D-printed prostheses, the second highlights their kinematic features, and the third table details their manufacturing specifications.
4. Hand Designs
4.1. Type of Prosthesis
The prostheses reviewed are classified into four main categories: finger, hand, arm, and upper-arm designs. Finger prostheses are single-digit devices extending to the MCP joint, while hand prosthesis reach the wrist, arm prosthesis extend to the elbow and upper-arm designs span to the shoulder. Hand prostheses (54%, n = 19) represented the largest category, followed by 12 arm prostheses (34%). Notably, Zuniga et al. [9] describe a model that extends to the shoulder. Of the 35 models reviewed, seven were specifically designed for children or can be resized to accommodate pediatric use. Detailed design specifications and mechanical attributes of these 3D-printed prostheses are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Design specifications and mechanical attributes of 3D-printed prostheses.
4.2. Type of Actuation and Control
Actuation mechanisms in 3D-printed prostheses predominantly rely on body-powered (BP) systems or motorized options, such as servo motors (SM) and micro motors (MM), with BP systems being the most widely adopted. Of the body-powered devices, 11 are activated through wrist flexion, five by elbow flexion, three through shoulder movement, and one finger prosthesis is controlled by MCP joint action. Additionally, two models incorporate shoulder harnesses, while a single device utilizes passive activation via the unaffected limb. Figure 1 visually represents the proportional distribution of actuation types among the upper limb prostheses.
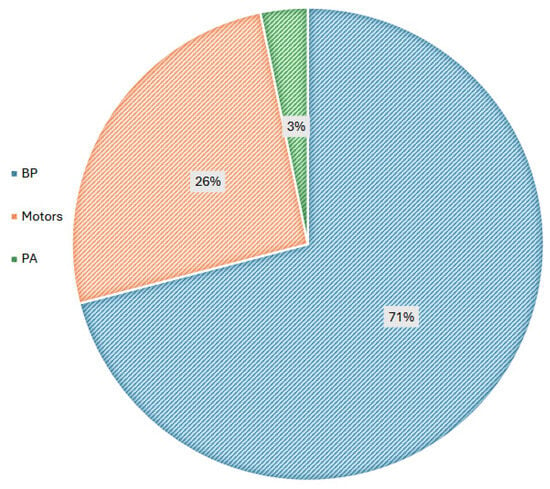
Figure 1.
Actuation mechanisms of 3D-printed prostheses.
Regarding other control methods, six prostheses use electromyographic (EMG) signals, while unique approaches include the integration of electroencephalographic (EEG) control in the Cyborg Beast forearm and force-myographic control (FMG) featured in the Federica hand. Interestingly, no voice-controlled prostheses were identified in this review. Figure 2 provides a visual breakdown of the control mechanisms used in 3D-printed prostheses.
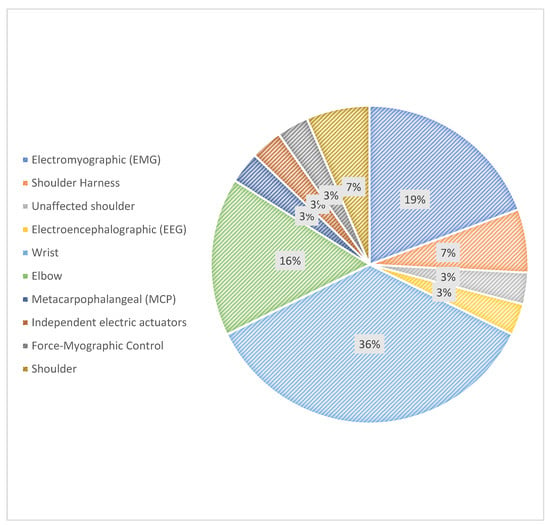
Figure 2.
Control mechanisms in 3D-printed prostheses.
4.3. Weight
Prosthesis weights were reported in 12 of the 35 studies reviewed. The lightest prosthetic hand, described by Cuellar et al. [11] weighed only 92 g, while the heaviest device, an arm prosthesis detailed by Cutipa-Puma et al. [7] reached 1000 g. Gretsch et al. [19] presented the lightest arm, weighing 240 g, designed specifically for individuals with transradial congenital or traumatic amputations.
On average, hand prostheses, including their actuation systems, weighed 274 g, whereas arm prostheses had a higher mean weight of 797 g. Adult arm models ranged from 962 g to 1000 g. Actuation systems alone accounted for weights between 675 g and 695 g, significantly outweighing the less than 300 g attributed to the 3D-printed components. This indicates that the printed elements contribute minimally to the overall weight of these prostheses. Figure 3 illustrates the weight distribution of 3D-printed prostheses.
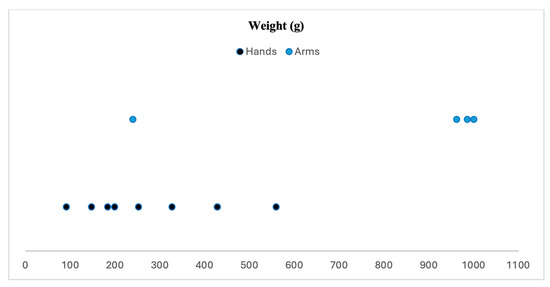
Figure 3.
Weight distribution of 3D-printed prostheses (based on 12 articles).
4.4. Type of Flexors and Extensors
Extensor and flexor mechanisms were described in 26 out of the 35 articles reviewed. Non elastic, generally nylon, cables or cords (15) and elastic cords or bands (7) are the most commonly used methods for flexion. Other flexion mechanisms include a gripper, an innovative four-bar linkage mechanism and the stainless steel internal phalange system featured in the Victoria Hand project for the VC300 [39] and VO300 [41] models.
For extension, elastic cords (9) and cables (6) are primarily employed, with springs also supporting extension in five models. Additionally, two models utilized elastic finger joints, known as compliant mechanisms. Figure 4 illustrates the various extensor and flexor types used in these prostheses.
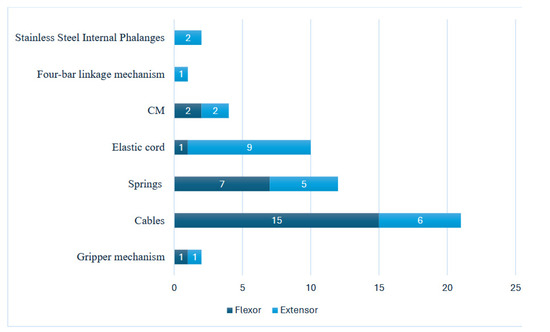
Figure 4.
Distribution of extensor and flexor types in 3D-printed prostheses.
5. Kinematic Specifications
Table 2 presents the kinematic features of the prostheses included in the review, detailing the range of motion (ROM) for the fingers and thumb, grip strength, and the various grasps types each model can perform. Grasp types were classified into two main groups: precision and power. The precision category includes three specific movements: pinch, tripod, and lumbrical, while the power category is further divided into cylindrical, spherical, and hook grasps. This classification aligns with the modern perspective on grasp types proposed by Yang et al. [44], visually illustrated in Figure 5. While some publications provided detailed kinematic specifications, many models found online, as well as several articles, did not include this information. As a result, much of the data presented in this review is based on estimates derived from published images, videos, and patient testimonials.

Table 2.
Kinematic features of 3D-printed prostheses.
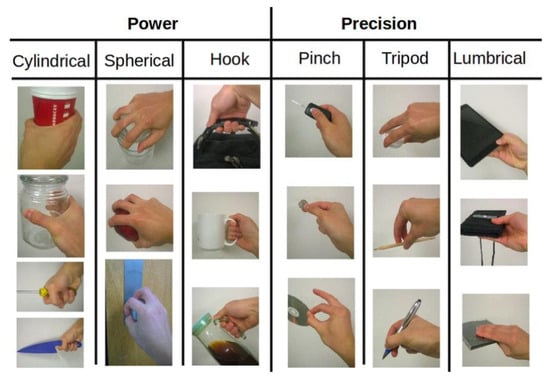
Figure 5.
Various grasp types as outlined by Yang et al. (2015) [44]. Image sourced from “Grasp Type. Revisited: A Modern Perspective on A Classical Feature for Vision”. The authors obtained the permission to reuse this figure from original authors.
5.1. Range of Motion
Normal values used to estimate the range of motion (ROM) are defined as follows: 0–90° for metacarpophalangeal joint (MCPJ) movement, 0–90° or 100° for proximal interphalangeal joint (PIPJ), and 0–70° for distal interphalangeal joint (DIPJ). For the thumb, cinterphalangeal joint (IPJ) movement was considered normal at 0–80°. The ability to rotate the thumb was also assessed.
The range of motion for fingers was evaluated in 34 out of 35 models; the exception was the prototype from Carmo et al. [10], for which no pictures or videos were available. All models achieved a minimum MCPJ flexion of 40°, with 20 models demonstrating full MCPJ flexion, six achieving 70–80°, and eight limited to 60° or less. For PIPJ flexion, all models achieved at least 45°, with nine limited to 60° or less, four achieving 70–80°, and the remaining 21 models reaching 90° or higher. In terms of DIPJ flexion, 11 models were restricted to 45° or less, with the lowest flexion recorded at 10°. Two models achieved 60°, while 20 models demonstrated flexion up to 80°. The DIPJ flexion of one model, Zúñiga et al.’s hand [43], could not be estimated.
An 80° flexion was considered the normal range for thumb interphalangeal joint (IPJ). IPJ ROM was assessed in 29 models. Among these, 10 models achieved a flexion of 70° or more, four reached between 50° and 60°, and the remaining 15 were limited to 45° or less, with the flexion recorded at 15°.
Thumb rotation was also evaluated in 29 models. Three models did not allow thumb rotation, while four supported thumb rotation but without a measurable ROM. Among the remaining models, 12 were limited to 45°, six achieved between 60° and 90°, and four demonstrated a rotation of 120°.
Regarding finger flexion, 15 models achieved full ROM across all three finger joints, seven attained full ROM in two joints, and five had restricted flexion across all three joints. Figure 6 visually summarizes the ROM for each joint.
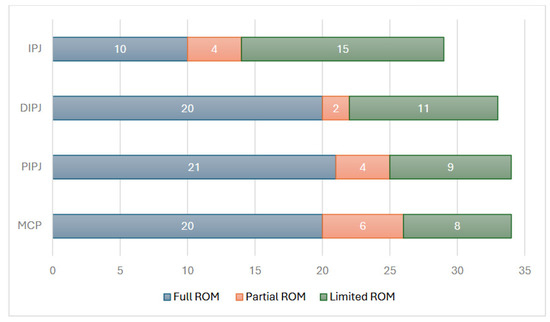
Figure 6.
Range of motion (ROM) achieved by 3D-printed prosthetic models for finger and thumb. joints. The data include metacarpophalangeal (MCP), proximal interphalangeal (PIP), distal interphalangeal (DIP), and thumb interphalangeal (IP) joints.
5.2. Grasp Type and Grip Strength
Power grasp was evaluated in 29 of the 35 models, while precision grasp was assessed in 27 prostheses. Among the grasp types, 29 models could achieve a cylindrical grasp, 26 could perform a spherical grasp, and 28 were able to perform a hook grasp. Additionally, 27 models could perform a pinch grip, 23 could achieve the tripod position, and only 18 models were able to successfully perform the lumbrical grip, the most challenging position. These findings are summarized in Figure 7.
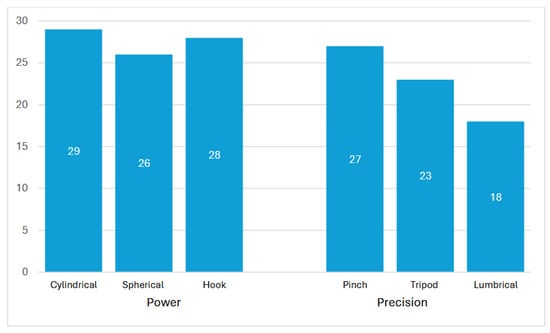
Figure 7.
Grasp types performed by 3D-printed prosthetic models.
Grip strength was classified into three levels based on the e-NABLE community’s guidelines, which were developed through a comparative analysis of different prosthetic models. In this review, grip strength was categorized as weak if below 10 N, moderate between 10 N and 20 N, and strong above 20 N. Data on grip strength were available for 30 models, with thirteen exhibiting strong grip strength, twelve demonstrating moderate strength, and five categorized as weak. Moderate grip strength is generally sufficient for performing routine daily tasks. The recorded grip strength ranged from 8.3 N (Zúñiga et al.’s hand [43]) to 23 N (Avilés-Mendoza et al.’s model [8]).
6. Manufacturing Specifications
Table 3 presents the manufacturing specifications, including the printer used, material costs, and printing and assembly difficulty. The classification follows the Device Ratings Guide from e-NABLE [45], which categorizes material costs into three levels: low (less than USD 50), moderate (between USD 50 and USD 100), and high (over USD 100). Similarly, the difficulty of printing and assembly is classified as easy, moderate, or difficult based on comparisons with other 3D-printed prostheses. The information provided is either directly sourced from the ratings given by the e-NABLE community or estimated by the authors, based on the model’s features when direct data were unavailable.

Table 3.
Manufacturing specifications of 3D-printed prostheses.
6.1. Printing Technology
The information regarding the 3D-printing technology used for prosthesis fabrication was infrequently detailed across the reviewed models. Out of the 35 models, only 13 specified the printers used. Among these, the MakerBot Ultimaker 2 was utilized for six models, while another six models were printed with the MakerBot Replicator 2. Other printers mentioned include the Ender 3 Max, MakerGear M2, Prusa i3 MK3S, Ultimaker S5, and FlashForge Guider II. Aiming to validate a cost-cutting methodology, Carmo et al. [3] used the Anet A8 printer, priced at under USD 200, and the student version of the Autodesk Inventor program for modeling, which proved to be a viable option.
6.2. Three-Dimensional Printing Material
The materials used in the fabrication of 3D-printed prostheses were documented for 20 models. Polylactic acid (PLA) emerged as the most commonly utilized material, featured in 15 models, followed by thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), each used in four models. Additional materials reported included polyethylene terephthalate glycol-modified (PETG), aluminum, nylon, UV resin, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and photopolymer resin.
PLA is commonly chosen for upper-limb prostheses due to its affordability, strength, and durability [46]. Its lower printing temperature make it more user friendly, while its adaptability enables precise custom-fitting tailored to individual needs [47]. Notably, seven models incorporated more than one 3D-printed material, with the HandBot-Kid [20] standing out as the only model to include a non-plastic material—aluminum—in its design. TPU is often used, either entirely or in combination with other materials, to improve the prosthesis’ flexibility. As a flexible and elastic filament, TPU can stretch and return to its original shape, making it particularly suitable for components that require multidirectional movement [10]. Figure 8 illustrates the materials employed in the fabrication of included 3D-printed prostheses.
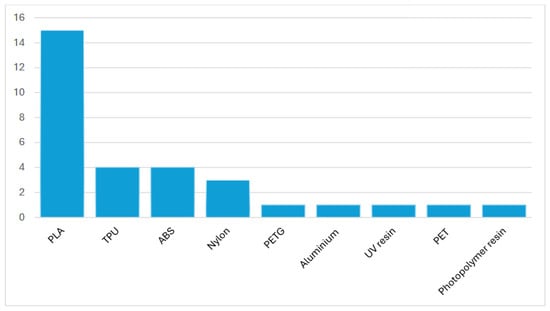
Figure 8.
Materials utilized in the fabrication of 3D-printed prostheses (based on 20 models).
6.3. Printing and Material Cost
Printing and material costs were reported in 28 studies. The model described by Avilés-Mendoza et al. [9] was the most expensive, costing over USD 600. In contrast, the Knick Finger was the least expensive finger model, with a total cost of USD 12, while the HandBot-Kid [20], a pediatric hand prosthesis, cost USD 20. The majority of models (18 out of 28) had a low production and material cost, priced at under USD 50, while six models exceeded USD 100. Production costs are visually represented in Figure 9.
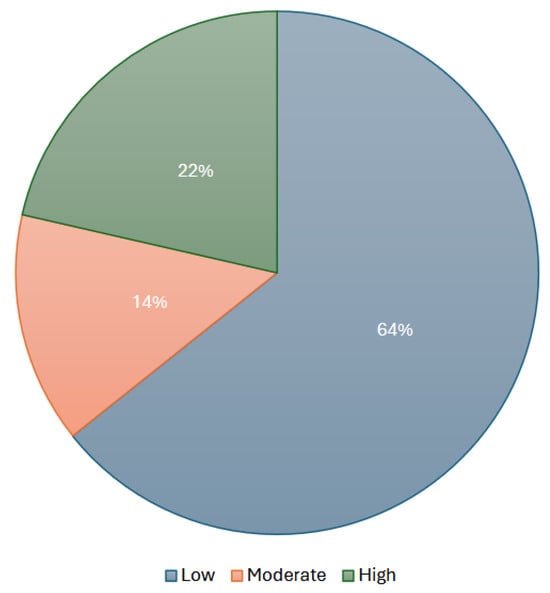
Figure 9.
Cost analysis of 3D-printed prostheses production (based on 28 models).
All models extracted from the e-NABLE website were classified by the organization into three cost categories: low (under USD 50), moderate (USD 50–100), and high (over USD 100). These estimates account for the materials used in 3D-printed parts and hardware components. Given that e-NABLE designs are open-source, users can freely download, modify, and print them, leading to cost variations. While e-NABLE provides a comparative cost analysis based on similar prosthetic features, determining an exact price remains challenging due to design modifications and material choices. Nevertheless, e-NABLE prostheses are significantly more affordable than traditional myoelectric devices, which can cost tens of thousands of dollars.
6.4. Printing and Assembly Difficulty
Printing and assembly difficulty were directly reported for models retrieved from the e-NABLE community. The e-NABLE device rating guide, which is widely recognized within the field categorizes models into easy, moderate, and difficult. Given e-NABLE’s extensive experience as the largest open-access platform for 3D-printed prostheses, their classification system provides a standardized benchmark informed by comparisons across various models and input from experienced designers. For other models that were well-described, printing and assembly difficulty were estimated by the authors by comparing them to similar designs from the e-NABLE community. This approach led to the classification of 29 models. Of these, 86% were categorized as easy to moderately difficult to print and assemble, meaning that they can typically be reproduced by individuals with limited experience in 3D printing. Many of these models also have multiple online tutorial videos available for assembly. Nevertheless, four models were considered difficult by their creators, indicating that specialized expertise is required for their conception or that the manufacturing process is typically handled by larger enterprises. Printing and assembly difficulty are visually represented in Figure 10.
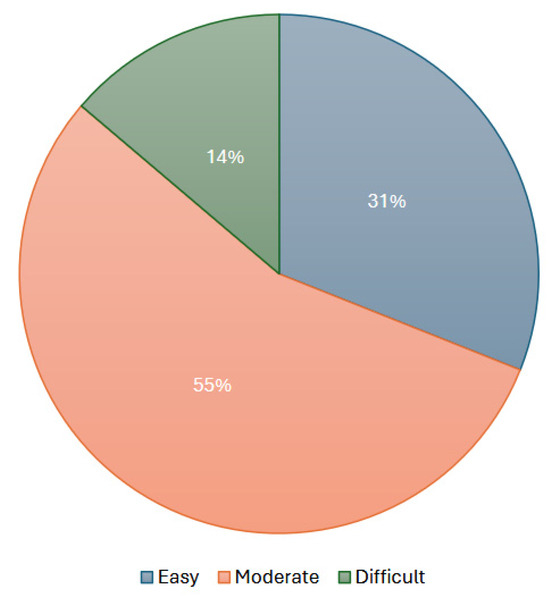
Figure 10.
Printing and assembly difficulty of 3D-printed prostheses (based on 29 models).
7. Discussion
This review analyzed a total of 35 upper-limb prosthesis, 13 identified from published literature and an additional 22 models found online. The findings highlight the transformative potential of 3D printing in addressing the persistent challenges associated with upper limb prostheses, particularly regarding accessibility and affordability. A diverse range of innovative designs was identified, including finger, hand, arm, and upper-arm prostheses, with hand prostheses being the most prevalent.
Notably, 71% of the 3D-printed prostheses were body-powered, using the residual limb to generate power through the wrist, elbow, or shoulder, with wrist mechanisms being the most common. Weight was reported in 12 studies, ranging from 92 g to 1000 g, with an average of 274 g for hand prostheses and 797 g for arm prostheses. For flexion, cables were the most commonly employed mechanism, while elastic cords and springs were the primary methods for extension. The use of lightweight materials such as PLA and the increased availability of open-source designs significantly reduced production costs, with 64% of the models costing under USD 50 and an additional 14% costing under USD 100. These cost reductions are particularly beneficial for children, who require frequent replacements due to growth, thereby reducing the financial burden on families. Furthermore, 86% of the models were rated as easy to moderately easy to print and assemble, thanks to the accessibility of designs and numerous instructional resources, which enhances their practical availability.
This study also extensively evaluated the range of motion offered by these prostheses, including the flexion capabilities of the MCP, PIPJ, and DIPJ of the fingers, as well as the IPJ and rotational capacities of the thumb. Fifteen models achieved full flexion across all three finger joints, while five demonstrated significantly limited functionality. Thumb rotation ranged from 30° to 120° in 26 models. The prostheses could perform three types of power grasps and three types of precision grasps, with up to 29 models supporting power grasps and 27 models accommodating precision grips.
Building upon the foundational work of Ten Kate et al.’s 2017 review [48], this study provides updated insights, revealing that many prostheses previously described are now obsolete. For instance, limitations of earlier models, such as the Raptor Hand’s reduced performance in pinching tasks, have led to contemporary designs like the Osprey Hand, which offers improved functionality [49]. Additionally, while Ten Kate et al. [48] reported that all hand prostheses in their study were body-powered, our review highlights a shift, with some prostheses now utilizing motor-powered systems, marking a significant advancement in technology. Moreover, pressurized air, once used as an actuation method, has also fallen out of favor. Unlike the prior review, this study includes finger prostheses, further broadening the scope of analysis.
Upper limb prostheses are becoming increasingly being utilized beyond their traditional role in long-term limb replacement. Thomas et al. describe a rehabilitation protocol involving a 3D-pinted prosthetic hand for pediatric use. In their case study, the impact of a 4-week home exercise program combined with a 3D-printed prosthetic hand on the upper extremity function of a 6-year-old boy with a congenital upper limb deficiency was assessed [50]. The findings revealed significant improvements, including enhanced strength in all movements except radial deviation, increased wrist flexion and extension, and improved forearm pronation. Additionally, coordination and sensory integration were notably enhanced. These results highlight the expanding role of 3D-printed prostheses in clinical settings.
Despite these advancements, significant challenges persist. Since the publication of Ten Kate et al.’s review in 2017, the persistent challenges of accessibility in upper limb prostheses remain largely unaddressed. While open-source platforms like e-NABLE have greatly increased access to prosthetic designs, the lack of standardized guidelines for design, manufacturing, and testing continues to limit the generalization of progress. As a result, prostheses are often created by individual designers to meet specific patient needs, relying on techniques based on personal experience, subjective perspectives, and implicit knowledge, which contribute to inconsistencies in methodology [51,52,53]. Furthermore, critical details regarding materials, printing technologies, costs, and other key aspects are often underreported, also making it challenging to generalize findings and implement these solutions on a broader, global scale.
The Victoria Hand Project was established to tackle the challenge of accessibility by providing high-quality, affordable prosthetic hands to individuals in need [54]. Operating across 11 countries, this initiative utilizes 3D printing technology to produce two functional prosthetic models: the Voluntary Close (VC) and the Voluntary Open (VO) designs. Additionally, a specialized adaptation of the VC, known as the Small Hand, is available for pediatric patients. By partnering with local healthcare providers and establishing clinics worldwide, the project accelerates the production and distribution of prosthetic devices, enabling broader access. The Victoria Hand Project is dedicated to empowering amputees and advancing equitable healthcare through innovative and sustainable solutions.
Given that the demand for lower-limb prostheses is more significant than for upper-limb prostheses and considering the complexity and uniqueness of upper-limb characteristics and needs, it is understandable that there is no single method prescribed for creating upper-limb prostheses [55,56]. To overcome these challenges, future efforts should prioritize developing quality control protocols, to increase the standardization and application of 3D-printed prostheses. Collaborative efforts between researchers, engineers, healthcare providers, and prosthetic users are essential to drive innovation and improve the quality and accessibility of these devices.
8. Conclusions
Upper limb prosthetic devices are essential for improving the quality of life for individuals with amputations, yet their accessibility remains limited by high costs and limited availability. This review highlights the transformative potential of 3D printing in addressing the accessibility and affordability challenges of upper limb prostheses. Through an analysis of 35 models, we identified key trends in design, actuation, material selection, and cost-effectiveness. The majority of reviewed prostheses were body-powered, lightweight, and made from polylactic acid (PLA), with 64% costing under USD 50, making them significantly more affordable than traditional myoelectric prostheses.
The findings emphasize the increasing role of open-source platforms like e-NABLE in increasing access to prosthetic solutions. Their classification systems provide valuable insights into cost estimation and assembly complexity, enabling both individuals and clinicians to make informed choices. However, despite these advancements, challenges remain, including the lack of standardized design protocols, variability in print quality, and the limited clinical validation of many 3D-printed models.
To bridge these gaps, future efforts should focus on establishing quality control guidelines, improving the biomechanical performance of 3D-printed prostheses, and enhancing interdisciplinary collaboration among engineers, healthcare professionals, and end-users. By addressing these challenges, 3D printing can continue to provide innovation in prosthetic care, ultimately improving accessibility and quality of life for individuals with upper limb amputations.
While progress has been made, particularly in the development of advanced actuation and control systems, the widespread adoption of 3D-printed prostheses faces challenges.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/prosthesis7020039/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.D. and J.E.; methodology, S.D. and J.E.; software, S.D. and J.E.; validation, S.D. and J.E.; formal analysis, S.D., N.D. and J.E.; investigation, S.D., N.D. and J.E.; resources, S.D., N.D., C.X., H.H. and J.E.; data curation, S.D., N.D., C.X., H.H. and J.E.; writing—original draft preparation, S.D., N.D., C.X., H.H. and J.E.; writing—review and editing, S.D.; visualization, S.D.; supervision J.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are disclosed in this article, no more new data created.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cuellar, J.S.; Smit, G.; Breedveld, P.; Zadpoor, A.A.; Plettenburg, D. Functional evaluation of a non-assembly 3D-printed hand prosthesis. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2019, 233, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendo, K.; Barbier, O.; Bollen, X.; Schubert, T.; Lejeune, T.; Raucent, B.; Olszewski, R. Open-source 3D printing in the prosthetic field—The case of upper limb prostheses: A review. Machines 2022, 10, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuniga, J.; Katsavelis, D.; Peck, J.; Stollberg, J.; Petrykowski, M.; Carson, A.; Fernandez, C. Cyborg beast: A low-cost 3D-printed prosthetic hand for children with upper-limb differences. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, I.; Lee, G.K.; Park, C.Y.; Lee, J.; Jeong, E. Clinical outcomes of a low-cost single-channel myoelectric-interface three-dimensional hand prosthesis. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2019, 46, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, J.; Day, S.; Dupan, S.; Nazarpour, K.; Dyson, M. 3D-printing and upper-limb prosthetic sockets: Promises and pitfalls. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.J.; Pierce, J.E.; Zuniga, J.M. Assessment of body-powered 3D printed partial finger prostheses: A case study. 3D Print. Med. 2019, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutipa-Puma, D.R.; Paredes-Madrid, L.; Paredes-Madrid, W. A low-cost robotic hand prosthesis with apparent haptic sense controlled by electroencephalographic signals. HardwareX 2023, 14, e00439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés-Mendoza, K.; Gaibor-León, N.G.; Asanza, V.; Lorente-Leyva, L.L.; Peluffo-Ordóñez, D.H. A 3D-printed, bionic hand powered by EMG signals and controlled by an online neural network. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuniga, J.M.; Carson, A.M.; Peck, J.M.; Kalina, T.; Srivastava, R.M.; Peck, K. The development of a low-cost three-dimensional printed shoulder, arm, and hand prostheses for children. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2017, 41, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tothy, J. Adjustowrap Gripper Arm (3DPX-020278). NIH 3D Print Exchange. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020278 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- do Carmo, T.A.; Cabette, R.E.S.; Gomes, R.G. Prototype of robotic mechanical prosthesis of upper limb at low cost. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2020, 7, 22–26. Available online: https://journal-repository.com/index.php/ijaers/article/view/1820 (accessed on 20 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Cuellar, J.S.; Plettenburg, D.; Zadpoor, A.A.; Breedveld, P.; Smit, G. Design of a 3D-printed hand prosthesis featuring articulated bio-inspired fingers. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2021, 235, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tothy, J. Cyborg Beast (3DPX-020267). NIH 3D Print Exchange. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020267 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- University of Nebraska Omah. Cyborg Beast. College of Education, Health, and Human Sciences, Biomechanics Core Facility. Available online: https://www.unomaha.edu/college-of-education-health-and-human-sciences/biomechanics-core-facility/research/cyborg-beast/index.php (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Tothy, J. e-NABLE Phoenix Hand v3. NIH 3D Print Exchange. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020260 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Tothy, J. El Medallo Bionic Arm (3DPX-020276). NIH 3D Print Exchange. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020276 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Tothy, J. Flexy Arm (3DPX-020281). NIH 3D Print Exchange. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020281 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Tothy, J. Flexy-Hand 2 (3DPX-020268). NIH 3D Print Exchange. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020268 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Tothy, J. Forefinger Gripper Hand (3DPX-020275). NIH 3D Print Exchange. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020275 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Gretsch, K.F.; Lather, H.D.; Peddada, K.V.; Deeken, C.R.; Wall, L.B.; Goldfarb, C.A. Development of novel 3D-printed robotic prosthetic for transradial amputees. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2016, 40, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Coello, P.; Salvador-Domínguez, B.; Badesa, F.J.; Rodríguez Corral, J.M.; Plastrotmann, H.; Morgado-Estévez, A. Anthropomorphic robotic hand prosthesis developed for children. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tothy, J. K1 Hand (3DPX-020271). NIH 3D Print Exchange. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020271 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- e-NABLE. Introducing the New 3D-printed Kinetic Hand Design. e-NABLE. Available online: http://enablingthefuture.org/2020/11/13/introducing-the-new-3d-printed-kinetic-hand-design/ (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Thingiverse. 3D Printed Kinetic Hand. Available online: https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:4618922 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- NIH 3D Print Exchange. Kinetic Hand (3DPX-020261). Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020261 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Tothy, J. Knick Finger. NIH 3D Print Exchange. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020290 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- NIH 3D Print Exchange. Kwawu Arm (3DPX-020299). Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020299 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- O’Neal, B. Designer Creates 3D Printed Elbow & Upper Arm Prosthetic with Hand Actuation for Boy Without Elbow. 3DPrint.com. Available online: https://3dprint.com/90944/3d-printed-elbow-prosthetic/ (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- e-NABLE Hub. Ody Hand. Available online: https://hub.e-nable.org/s/e-nable-devices/wiki/Ody+Hand (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- NIH 3D Print Exchange. Osprey Hand (3DPX-020262). Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020262 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- e-NABLE. Osprey Hand. e-NABLE Hub. Available online: https://hub.e-nable.org/s/e-nable-devices/wiki/Osprey+Hand (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Tothy, J. Phoenix Reborn Arm (3DPX-020277). NIH 3D Print Exchange. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020277 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- NIH 3D Print Exchange. Po Arm. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020282 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Tothy, J. Talon Hand (3DPX-020273). NIH 3D Print Exchange. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020273 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Esposito, D.; Savino, S.; Andreozzi, E.; Cosenza, C.; Niola, V.; Bifulco, P. The “Federica” hand. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tothy, J. The Paraglidar (3DPX-020270). NIH 3D Print Exchange. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020270 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Tothy, J. The UnLimbited Arm v2.1 (3DPX-020264). NIH 3D Print Exchange. Available online: https://3d.nih.gov/entries/3DPX-020264 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Printables. e-NABLE UnLimbited Phoenix Hand. Available online: https://www.printables.com/model/129817-e-nable-unlimbited-phoenix-hand (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- 3D-Creator. UnLimbited Phoenix Hand. Thingiverse. Available online: https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:1674320 (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Victoria Hand Project. The Victoria Hand Project Overview. Available online: https://www.victoriahandproject.com/_files/ugd/4add4b_5a1b2ae776144eb796cdff1caa110a32.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Vijayan, A.; Bhatia, V.; Arora, S.; Gupta, S. Completely digitally fabricated custom functional finger prosthesis. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2023, 23, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victoria Hand Project. Victoria Hand Project: Summer 2024 Overview. Available online: https://www.victoriahandproject.com/_files/ugd/4add4b_f3ad92ce9e8045e88c87ba3698395386.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Mohammadi, A.; Lavranos, J.; Zhou, H.; Mutlu, R.; Alici, G.; Tan, Y.; Choong, P.; Oetomo, D. A practical 3D-printed soft robotic prosthetic hand with multi-articulating capabilities. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fermüller, C.; Li, Y.; Aloimonos, Y. Grasp type revisited: A modern perspective on a classical feature for vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Francisco, CA, USA, 18–20 June 2015; pp. 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- e-NABLE. Device ratings guide. e-NABLE Hub. Available online: https://hub.e-nable.org/s/e-nable-devices/wiki/Device+Ratings+Guide (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Ultimaker. How to 3D Print with PLA and Which Materials to Choose. Available online: https://ultimaker.com/learn/how-to-3d-print-with-pla-and-which-materials-to-choose (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Instructables. Thermoforming 3D Printed PLA for use in Prosthetic Devices. Available online: https://www.instructables.com/Thermoforming-3D-Printed-PLA-for-Use-in-Prostethic/ (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Ten Kate, J.; Smit, G.; Breedveld, P. 3D-printed upper limb prostheses: A review. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2017, 12, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J. Raptor Reloaded. e-NABLE Hub. 2022. Available online: https://hub.e-nable.org/s/e-nable-devices/wiki/Raptor+Reloaded (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Thomas, A.; Muñecas, T. A rehabilitation protocol for the use of a 3D-printed prosthetic hand in pediatrics: A case report. J. Hand Ther. 2023, 36, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, M.R.; Rowe, P.; McFadyen, A.; Buis, A. Hands-off and hands-on casting consistency of amputee below-knee sockets using magnetic resonance imaging. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 486146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, F.E.H.; Manna, M.A.; Liu, L.X. A CASD/CASM method for prosthetic socket fabrication using the FDM technology. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2002, 8, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterno, L.; Ibrahimi, M.; Gruppioni, E.; Menciassi, A.; Ricotti, L. Sockets for limb prostheses: A review of existing technologies and open challenges. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 1996–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victoria Hand Project. The Project. Available online: https://www.victoriahandproject.com/the-project (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Esquenazi, A. Amputation rehabilitation and prosthetic restoration: From surgery to community reintegration. Disabil. Rehabil. 2004, 26, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Orthotic & Prosthetic Association. Amputation Data from Community Hospitals. Almanac. 2016. Available online: https://issuu.com/americanoandp/docs/april_2016_almanac (accessed on 20 December 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).