Abstract
The precision of the luting protocol plays a crucial role in the success and survival rate of porcelain laminate veneers (PLVs). This in vitro study aimed to evaluate the influence of different luting techniques on the positioning of PLVs through a novel, noninvasive, scanning-based technique. A total of 45 ceramic PLVs were milled and cemented on human tooth replicas. Specimens were divided into three groups of 15, each subjected to a different luting protocol: flowable composite (Group A), dual-cure resin cement (Group B), and preheated composite resin (Group C). After luting procedures, specimens were scanned, and every STL file was superimposed with the original tooth design in Geomagic Control X version 2022.1 software to assess linear (incisal, mid, cervical) and angular discrepancies. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s HSD tests, and regression analysis. ANOVA results showed no statistically significant differences for incisal (F = 0.327, p = 0.723), mid (F = 0.287, p = 0.752), cervical (F = 0.191, p = 0.827), and angular (F = 0.026, p = 0.975) measurements. Tukey’s HSD post hoc tests confirmed the lack of significant pairwise differences between groups. The study demonstrated that the type of luting agent used does not significantly impact the final position of PLVs. This suggests flexibility in the choice of luting agents without compromising the accuracy of PLV placement.
1. Introduction
Porcelain laminate veneers (PLVs) are thin, bonded ceramic restorations that restore the facial, incisal, and part of the proximal surfaces of teeth requiring aesthetic restoration [1]. Developed in the 1980s by John Calamia, PLVs have become a preferred choice in aesthetic dentistry due to their ability to mimic natural tooth appearance and provide durable solutions for various dental issues, such as severe discolorations, enamel defects, diastemas, correcting malalignment, and mitigating wear [2,3].
Ceramic veneers offer several advantages, including excellent aesthetics, biocompatibility, and resistance to staining. However, they also present challenges such as different geometries of tooth preparation, potential for fracture, and risk of debonding [3,4,5].
The clinical success of veneers is heavily influenced by the quality of tooth preparation and luting techniques used. For instance, studies show that the survival rate of ceramic veneers can exceed 90% over ten years with proper clinical protocols. PLVs achieved survival rates of 97.6% [6], 98.8% [7], 91% [8], and 94.4% [5] after 5, 6, 10, and 12 years, respectively. The variations in these outcomes are largely attributed to differences in cementation protocols and materials used over the years.
Different preparation designs play a critical role in the success of ceramic veneers, influencing both the accuracy of veneer placement and their long-term performance [9,10]. Standard preparation designs involve minimal enamel removal to enhance bonding strength [11]. Common designs include feather edge, incisal overlap, and window preparations [12,13,14,15]. Feather edge is the most conservative, preserving tooth structure but potentially compromising veneer fit due to minimal incisal coverage [13]. In contrast, incisal overlap improves stability and seating accuracy by extending over the incisal edge, which is particularly beneficial for aesthetic results [14,15]. Window preparation, while preserving more tooth structure, may not offer the same mechanical support as incisal overlap, especially under functional stress [12,13]. The mechanical properties of each design vary, with incisal overlap providing better distribution of occlusal forces and reducing fracture risk, whereas feather edge, despite its conservation of tooth material, might result in thinner, more fragile veneers [13,14,15]. Therefore, the choice of preparation design must carefully balance aesthetic needs with mechanical durability to optimize the success and longevity of the restoration [13].
Luting protocols are crucial for the survival rate and performance of veneers [16,17,18]. The choice is based on the thickness of the restorations, adhesive capabilities, marginal fit, and mechanical properties [19,20,21]. Various types of luting agents are used, each with specific advantages and limitations. Dual-cure cements are advantageous in cases where the ceramic material is too thick or too opaque to allow sufficient light transmission for polymerization. This can occur in the restoration of teeth post-endodontic treatment, in posts, and in full crowns [20]. It can also happen in veneers with overly aggressive preparation designs, such as in the treatment of discolored teeth where thickness and opacity are necessary to mask the underlying tooth [21]. However, dual-cure cements have a shorter working time and may lead to aesthetic issues if not properly cured, such as discoloration or chemical reactions [16,17,18,22,23]. On the other hand, light-cured luting composites are preferred for thinner veneers, as they offer longer working times, facilitating the removal of excess material and improving marginal adaptation and color stability [24]. Composite resins, including preheated composite, offer high strength and aesthetics but require careful handling and isolation during placement, especially in light of their high viscosity, which can challenge precise veneer seating [24,25]. Research by Tosco et al. in 2021 has demonstrated that preheated composites can achieve a higher degree of polymerization, which is crucial for the longevity and performance of restorations [26]. The higher degree of conversion in these materials enhances their mechanical properties, reducing the risk of microleakage and increasing the durability of the bond [25,26]. Additionally, flowable composites, while easier to handle and adaptable to tooth structures, typically lack the mechanical strength of more viscous composites [26]. Barceleiro et al. [22] found similar results when bonding feldspathic porcelain to bovine enamel using a dual-polymerized resin luting agent and a light-polymerized flowable composite resin. This study suggests the possibility of using flowable composite resins as a suitable alternative luting agent when bonding porcelain laminate veneers less than 2 mm in thickness [22]. Thus, the selection between dual-cure and light-cured cements should be tailored to the specific clinical scenario, balancing the need for mechanical strength with aesthetic considerations [22,27].
Despite extensive research on the adhesive strength, fracture resistance of different luting techniques, discoloration, and microscopical marginal gap, there is a notable gap in studies comparing cementation effects on the final position of PLVs. This gap highlights the need for comprehensive analyses to understand how various luting methods influence clinical outcomes. For instance, an imprecise seating of the veneer can lead to marginal discrepancies, resulting in an increased risk of microleakage, secondary caries, and periodontal disease [9,19,20]. Additionally, it can cause issues during the luting of multiple restorations, preventing the correct seating of multiple veneers or increasing the need for intraoperative adjustments [27].
Technological advancements in dentistry have significantly transformed monitoring and assessment techniques for both teeth and soft tissues [28]. Digital technologies now enable clinicians to perform multiple scans, allowing for precise tracking of changes over time or before and after specific dental procedures. This capability enhances the ability to evaluate clinical scenarios with greater accuracy, leading to improved treatment outcomes [29,30]. Among these, reverse engineering software plays a crucial role in precisely matching and evaluating the effects of different procedures. This capability allows for objective and quantifiable assessment of the changes achieved. To the best of our knowledge, there are no studies in the literature that compare quantitatively the effects of different luting protocols on the final positioning of restorations. Therefore, this study aims to compare quantitatively the interference of different luting techniques on the positioning of PLVs using a novel, noninvasive, scanning-based technique. The null hypothesis posits that there are no significant differences in the final position of veneers cemented using different techniques.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
The present in vitro study evaluated the effect of different luting procedures on the final position of PLVs using a novel, noninvasive, scanning-based technique. A total of 45 veneers were luted on 45 3D-printed tooth replicas. The 45 specimens were divided into three groups of 15, each subjected to different luting protocols, as described in the following paragraph. According to Mounajjed et al. [31], a sample size of 15 specimens per group was calculated to detect a minimum difference in marginal fit between the three groups with an expected standard deviation based on previous studies. The value of α was determined at 0.05, while the power of the test was 0.80. For the calculation, G*Power 3.1 software was used, specifically the ANOVA test.
2.2. Sample Preparation
An upper central incisor from an STL tooth library (Exocad, exocad GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany) was 3D printed (LightBuilder 4K, dental makers, Vallecorsa, FR, Italy). An experienced prosthodontist carried out the PLV preparations using magnifying loupes and a silicone index to standardize the preparation. A silicone index was generated on the 3D printed model to ensure uniform and accurate thickness for the veneer preparation. Each preparation was executed with diamond-coated burs (Komet, Gebr. Brasseler GmbH & Co. KG, Lemgo, Germany), specifically the depth marker bur 868B.314.018, the tapered diamond bur 868.314.016, and the finishing bur 8868.314.016, all under water spray. The specimens were prepared with a cervical mini-chamfer finish line, achieving a final veneer thickness of 0.5 mm. The preparation thicknesses were verified using the silicone index and a millimeter-periodontal probe (Offset Williams Probe, Hu-Friedy Mfg. Co., Chicago, IL, USA), under magnification. Adhering to the feather edge veneer preparation principle, the incisal margin was preserved. The prepared replica was scanned again with an intraoral scanner (Trios 3, 3shape, Copenhagen, Denmark). Using CAD software (Exocad DentalCAD 3.1 Rijeka, exocad GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany), the preparation was assessed for accuracy and margin suitability. The veneer was designed on the prepared tooth replica and milled, replicating the original tooth’s design prior to reduction. Subsequently, 45 3D-printed resin replicas of the prepared element were printed (LightBuilder 4K, dental makers, Vallecorsa, FR, Italy). The 45 PLVs in lithium disilicate were milled from a block (IPS e.max CAD LT, Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein). The 45 specimens (replicas and PLVs) were randomly allocated into three groups of 15, each subjected to different luting protocols:
- -
- Group A (FLOW): Veneers were luted using flowable composite resin (Tetric Evoflow, Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein).
- -
- Group B (DUAL): Veneers were luted using dual-cure composite resin cement (Variolink Esthetic DC, Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein).
- -
- Group C (COMPO): Veneers were luted using preheated composite resin (Tetric Evoceram, Ivoclar Vivadent AG). Composite was warmed to 55 °C by using a heating device (Ena Heat; Micerium, Micerium, Avegno, Genova, Italy).
A standardized luting protocol was implemented, as shown in Figure 1, altering only the final step concerning the type of cement used [22,25,32,33,34]. The initial steps were consistent throughout the process. Initially, the intaglio surfaces of the veneers were etched with 4.9% hydrofluoric acid (IPS Ceramic Gel, Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein) for 20 s. The acid was then removed using an air/water spray syringe, followed by an ultrasonic bath in 98% alcohol for 3 min to eliminate any residues. After drying, a single-component silane (Monobond S, Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein) was applied for one minute. Subsequently, a universal adhesive (Adhese Universal, Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein) was applied without polymerizing the contact surface between the intaglio surfaces of the veneers and the tooth. Finally, the different types of luting agent were applied inside the PLVs, which were then positioned on the replicas. Visual verification of proper seating was performed, followed by pre-polymerization for 5 s, and all excess cement was removed. Finally, complete curing (Bluephase G4, Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein) for 40 s on each surface was carried out. Margins were manually refined. Figure 2 shows the specimens luted.
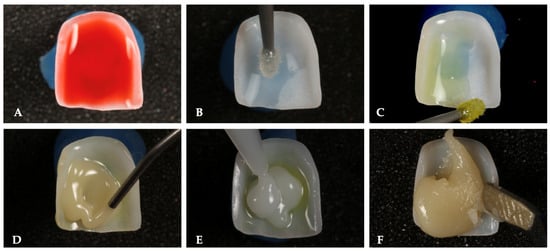
Figure 1.
Adhesive protocol applied to specimens. The sequence of the adhesive protocol includes the following steps: (A) etching of the veneer with 4.9% hydrofluoric acid for 20 s; (B) application of single-component silane for one minute; (C) application of universal adhesive without polymerization; (D) application of flowable composite resin luting agent in Group A; (E) application of dual-cure composite resin luting agent in Group B; (F) application of preheated composite resin in Group C.
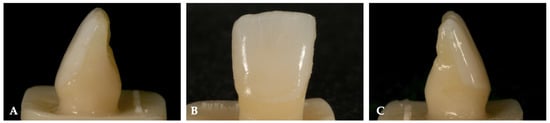
Figure 2.
Luted veneer on the specimens for in vitro testing. The image sequence represents a luted veneer on the specimens used for the in vitro test: (A) a lateral view showing one side of the luted veneer; (B) a frontal view of the luted veneer; (C) a lateral view from the opposite side. The complete cementation process is visible, including post-polymerization and the removal of excess luting agent.
2.3. Data Processing and Measurement
After luting, all specimens were scanned using an intraoral scanner (Trios 3, 3shape, Copenhagen, Denmark). The resulting STL files were utilized for comparison. Each obtained specimen was overlaid with the STL file of the unprepared tooth using the registration algorithm of the software to verify the correct positioning of each veneer compared to the planned ideal position, as shown in Figure 3. Utilizing the best-fit algorithm software, the image of the specimen was isolated and aligned with the corresponding project file to measure discrepancies (Geomagic version 2022.1, Geomagic, Morrisville, NC, USA). Each file pair underwent vertical sectioning precisely at the tooth’s midpoint. Transversely oriented, three linear measurements at three selected points (incisal, mid, cervical), and one angular measurement were performed and repeated for each specimen. Linear measurements assessed discrepancies in different portions of the tooth, while the angular measurement provided information on the rotation and translation of the veneer post-cementation.
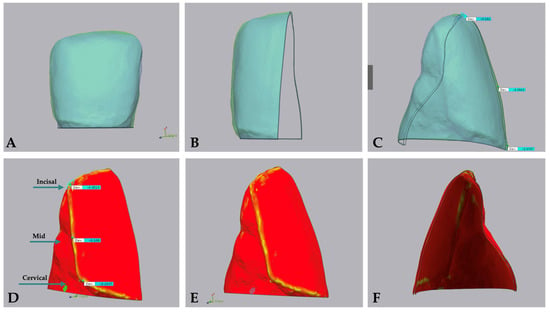
Figure 3.
Analysis procedure for veneer positioning. After luting, all specimens were scanned using an intraoral scanner. The resulting STL files were compared with the unprepared tooth. Linear measurements were taken at the incisal, mid, and cervical points, and an angular measurement assessed veneer rotation and translation. (A) Overlay of specimens with the reference tooth in a frontal view; (B) vertical sectioning along the tooth’s long axis; (C) example of measurements at incisal, mid, and cervical regions; (D) positioning of measurement points as indicated by the arrows. The same three points were used across all samples to ensure repeatable measurements and minimize bias associated with potential variations in measurement locations. (E) Overlay without measurements showing veneer alignment. (F) Lateral view with vertical sectioning showing luting discrepancies.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed to evaluate the differences in the final position of veneers. Data normality was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. A one-way ANOVA was employed to compare the mean variations across the three groups for each region and degree. Post hoc analysis using Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference (HSD) test was conducted to identify specific group differences. Correlation analysis was performed within each group to evaluate the relationships between the different regions and degrees. Additionally, regression analysis was utilized to determine the influence of variations in the incisal, mid, and cervical regions on the degree.
All statistical analyses were conducted using Python 3.8 (Python Software Foundation, Beaverton, OR, USA) and its associated libraries. Statistical significance was set at a p-value of <0.05 for all tests.
3. Results
The study aimed to compare the performance of three different types of dental luting agent used for veneer cementation: flowable luting agent (Group A), dual-cure luting agent (Group B), and pre-heated composite resin (Group C). A Shapiro–Wilk test was conducted to assess the normality of the data distributions. Figure 4 shows the quantitative analysis performed, while Table 1 shows the descriptive statistics. The overall means of deviation were 0.0904 ± 0.04 for Group A, 0.0830 ± 0.031 for Group B, and 0.0946 ± 0.052 for Group C. A one-way ANOVA was performed to compare the mean variations across the three groups for each region and degree. The results showed no significant differences between the groups in the incisal (F = 0.327, p = 0.723), mid (F = 0.287, p = 0.752), cervical (F = 0.191, p = 0.827), and degree (F = 0.026, p = 0.975). Additionally, the overall combined means of incisal, mid, and cervical were compared for each group. The comparison showed that there were no significant differences in the combined means across the groups (F-statistic = 0.292, p = 0.748). A box plot of the results is shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
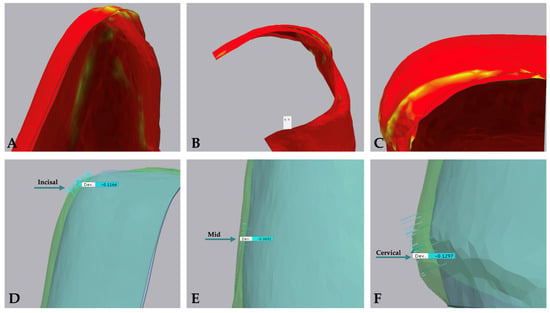
Figure 4.
Visualization of the study results. (A) Detail of incisal discrepancy; (B) mid-region discrepancy, showing a cross-sectional view of the crowns; (C) detail of cervical region; (D) measurement at the incisal level; (E) measurement at the mid-level; (F) measurement at the cervical level.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistical analysis.
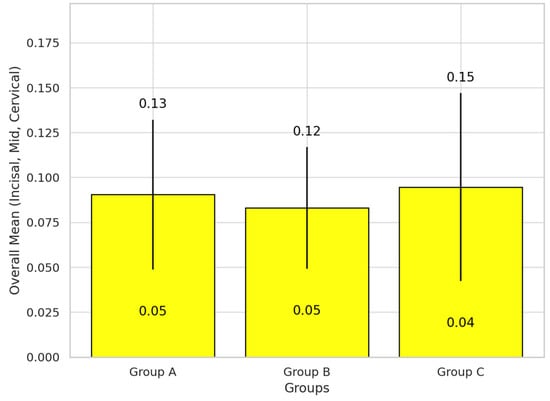
Figure 5.
Box plot of the results. The box plot illustrates the cumulative mean and standard deviation of the average deviation between the incisal, mid, and cervical regions for each group.
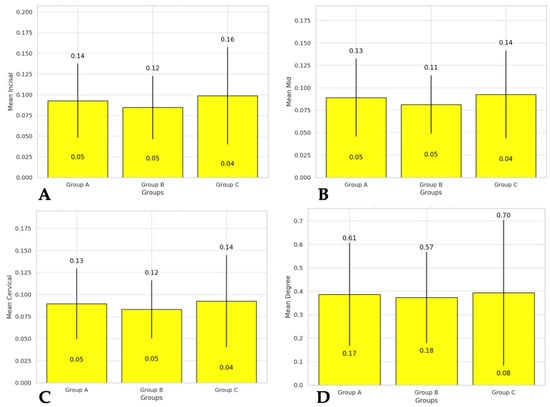
Figure 6.
Individual box plots. This figure presents the individual box plots for each measured region and angle: (A) the mean and standard deviation for the incisal region; (B) the mean and standard deviation for the mid region; (C) the mean and standard deviation for the cervical region; (D) the mean and standard deviation for the angle.
Post hoc analysis using Tukey’s HSD test confirmed that there were no significant differences between any pair of groups in all regions and degrees. The pairwise comparisons in the incisal, mid, cervical regions, and degree yielded p-values greater than 0.05, supporting the ANOVA results. Correlation analysis within each group revealed moderate to strong correlations between the different regions and degrees. In Group A, the incisal region showed a correlation of 0.497 with the mid region and 0.463 with the cervical region. Group B exhibited correlations of 0.530 and 0.618 between the incisal and mid, and incisal and cervical regions, respectively. Group C showed correlations of 0.782 and 0.712 between the incisal and mid, and incisal and cervical regions, respectively. Degree correlations in Groups A, B, and C with the other regions were also moderate. These correlations indicate that changes in one area of the veneer are moderately to strongly associated with changes in another area. Further regression analysis was performed to evaluate the influence of variations in the incisal, mid, and cervical regions on the degree. The regression model explained 71.8% of the variability in the degree (R-squared = 0.718), with the incisal region showing a significant impact on the degree (coefficient = 2.9141, p-value = 0.014). For the other regions, the regression analysis showed low coefficients, indicating a low to moderate correlation between changes in the mid and cervical areas and the degrees of veneer displacement.
4. Discussion
Results revealed no significant differences in the performance of flowable, dual-cure, and pre-heated composite luting agents regarding variations in the final position of PLVs. Therefore, the null hypothesis was not rejected. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to evaluate the final positioning of veneers post-luting using this innovative and non-invasive technique. This represents a novelty both methodologically and in terms of content. In contrast, many studies have focused on the performance of PLVs after adhesive luting, specifically assessing marginal fit as the marginal discrepancy post-cementation [20,33,35]. For example, studies by Mounajjed et al. [20] and Johnson et al. [33] reported minimal impact of luting agent type on marginal fit when appropriate protocols were followed. Mounajjed et al. [20] found that the mean marginal discrepancy for flowable luting agent was 42 ± 11 µm, 45 ± 29 µm for dual-cure luting agent, and 116 ± 47 µm for preheated composite luting agent. Albeit all within clinically acceptable limits, statistically significant differences were present using a preheated composite [20]. Although different outputs were evaluated, these results can be compared with those obtained in this study. Indeed, the results show a mean discrepancy in the position of the veneers of 0.09 mm in the flowable group, 0.083 mm in the dual-cure group, and 0.095 mm in the preheated composite group. These results are consistent with the data related to marginal discrepancies and are compatible with generally accepted clinical acceptability values. The literature reports that the normal acceptable marginal gap should be below 120 μm [36,37].
However, the new data presented here suggest a quantitative variation in the final position of the veneer. As seen, this is not influenced by the luting technique but is intrinsic to the workflow. Our observation that the incisal region significantly affects the degree suggests that certain areas of the veneer may respond differently depending on the luting agent, warranting further investigation. This finding aligns with the results of other studies emphasizing the critical role of precise fit to ensure survival rate and aesthetic outcomes [37,38,39]. These authors underscore the challenges associated with the freehand luting of veneers, particularly related to the management of multiple veneer placements and the luting technique used. Specifically, they propose a solution involving guide templates to assist in positioning. However, these publications primarily describe the operational technique and do not quantify the actual benefits and improvements achieved [38,39]. The results reported here objectively and quantitatively highlight the real discrepancies encountered during the luting of restorations.
Several studies have examined the impact of different luting agents, related to other factors, on the marginal fit and adaptation of dental restorations [40,41]. For instance, Falacho et al. [40] demonstrated that preheating and ultrasonic vibration significantly reduce the film thickness of different resin cements, potentially enhancing clinical outcomes. In contrast, the systematic review by Badami et al. [42] found no significant differences in the marginal adaptation between CAD-CAM and conventional feldspathic veneers, suggesting that the fabrication method may be less critical than other factors like luting technique and material properties [42]. Conversely, in in vitro conditions, different studies confirmed better results from traditional veneer compared to CAD-CAM [42,43,44]. Aboushelib et al. [44] reported that pressed ceramics exhibited better marginal fidelity compared to CAD-CAM veneers, with marginal discrepancies of 50 µm for pressed ceramics versus 75 µm for CAD-CAM veneers. Other factors should be considered to fully understand the elements that influence the final position of the veneer. Studies have shown that preparation designs significantly affect marginal fit, with shoulder and modified shoulder designs offering better outcomes compared to feather edge designs [11,12]. For example, a study comparing feather edge or designs that overlap incisal edge-like shoulder and a shoulder with wings preparation found that the shoulder with wings design produced the smallest cervical absolute margin discrepancy and overhang [41].
The absence of significant differences in our study indicates that dental practitioners have flexibility in choosing luting agents based on factors other than marginal fit, such as handling properties, restoration thickness, design, margin design, and other specific clinical scenarios. However, it is crucial to consider that the significant impact of the incisal region on the degree highlights the importance of careful attention to specific veneer areas during luting to ensure optimal outcomes [11,41]. Indeed, the results show how a greater incisal discrepancy can influence the positioning angle of the veneer. This study has several limitations, including its in vitro nature, which may not fully replicate the complex conditions of the oral environment. Additionally, the sample size was relatively small, limiting the generalizability of the results. Future studies with larger sample sizes and in vivo conditions are necessary to confirm these findings and explore the long-term performance of different luting agents. Future research should focus on evaluating the long-term effects of different resin luting agents on veneer stability and patient outcomes. Additionally, in vivo studies or research on extracted teeth could provide further insights into the mechanical properties and shear bond strength of veneers, depending on the cementation protocol used. Studies should also investigate the impact of various luting techniques and advanced fabrication methods like CAD-CAM and 3D printing on the clinical performance of veneers. Moreover, the interactions between different resin luting agents and these advanced techniques warrant further exploration to optimize veneer restorations. Additionally, the proposed methodology opens new perspectives for long-term monitoring of restorations, allowing the analysis of modifications, chipping, and dental movements.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study found no significant differences in the final position of veneers luted using flowable, dual-cure, and pre-heated composite cements. These findings suggest that the choice of luting agent may not significantly impact the final position of veneers under controlled conditions. Overall, dental practitioners can select resin luting agents based on other factors such as handling properties, design, and thickness of restoration without compromising the clinical outcomes of veneer restorations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.D. and B.S.; methodology, F.A. and G.T.; software, M.S. and G.D.; validation, G.B., F.A., and B.S.; formal analysis, G.D. and M.S.; investigation, G.D. and F.A.; resources, B.S. and F.M.; data curation, G.T. and M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, G.D. and F.A.; writing—review and editing, B.S. and G.T.; visualization, G.B.; supervision, B.S. and F.M.; project administration, B.S.; funding acquisition, F.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- The Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms: Ninth Edition. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, e1–e105. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calamia, J.R. Etched porcelain veneers: The current state of the art. Quintessence Int. 1985, 16, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gresnigt, M.; Özcan, M.; Kalk, W. Esthetic rehabilitation of worn anterior teeth with thin porcelain laminate veneers. Eur. J. Esthet. Dent. 2011, 6, 298–313. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, F.J. Survival rates for porcelain laminate veneers with special reference to the effect of preparation in dentin: A literature review. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2012, 24, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fradeani, M.; Redemagni, M.; Corrado, M. Porcelain laminate veneers: 6- to 12-year clinical evaluation—A retrospective study. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2005, 25, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Guess, P.C.; Stappert, C.F. Midterm results of a 5-year prospective clinical investigation of extended ceramic veneers. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fradeani, M. Six-year follow-up with Empress veneers. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 1998, 18, 216–225. [Google Scholar]
- Dumfahrt, H.; Schaffer, H. Porcelain laminate veneers. A retrospective evaluation after 1 to 10 years of service: Part II—Clinical results. Int. J. Prosthodontics 2000, 13, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Blunck, U.; Fischer, S.; Hajtó, J.; Frei, S.; Frankenberger, R. Ceramic laminate veneers: Effect of preparation design and ceramic thickness on fracture resistance and marginal quality in vitro. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 2745–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alothman, Y.; Bamasoud, M.S. The success of dental veneers according to preparation design and material type. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 2402–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, R.; Ruggiero, G.; Borelli, B.; Barlattani, A.; Zarone, F. Dentin Exposure after Tooth Preparation for Laminate Veneers: A Microscopical Analysis to Evaluate the Influence of Operators’ Expertise. Materials 2022, 15, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, A.; Kaiwar, A.; Shubhashini, N.; Ashwini, P.; Naveen, D.; Adarsha, M.; Shetty, M.; Meena, N. Survival rates of porcelain laminate restoration based on different incisal preparation designs: An analysis. J. Conserv. Dent. 2011, 14, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, S.Y.; Bennani, V.; Aarts, J.M.; Lyons, K. Incisal preparation design for ceramic veneers: A critical review. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2018, 149, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanesi, R.B.; Pigozzo, M.N.; Sesma, N.; Laganá, D.C.; Morimoto, S. Incisal coverage or not in ceramic laminate veneers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2016, 52, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, N.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; Li, Y. Effect of preparation designs on the prognosis of porcelain laminate veneers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oper. Dent. 2017, 42, E197–E213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, C.J.; Soares, P.V.; Pereira, J.C.; Fonseca, R.B. Surface treatment protocols in the cementation process of ceramic and laboratory-processed composite restorations: A literature review. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2005, 17, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archegas, L.R.; Freire, A.; Vieira, S.; Caldas, D.B.; Souza, E.M. Colour stability and opacity of resin cements and flowable composites for ceramic veneer luting after accelerated ageing. J. Dent. 2011, 39, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaf, A.; Azer, S.S.; Sfeir, A.; Al-Haj Husain, N.; Özcan, M. Risk Factors with Porcelain Laminate Veneers Experienced during Cementation: A Review. Materials 2023, 16, 4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shorman, H.M.; Abu-Naba’a, L.A.; Sghaireen, M.G.; Alam, M.K. The Effect of Various Preparation and Cementation Techniques of Dental Veneers on Periodontal Status: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Dent. 2024, 18, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounajjed, R.; Salinas, T.J.; Ingr, T.; Azar, B. Effect of different resin luting cements on the marginal fit of lithium disilicate pressed crowns. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiee Dehpagaee, A.; Tavakol, O. Laboratory Study of Fracture Resistance and Failure Mode of Porcelain Laminate Veneers with Different Preparation Depths in Endodontically Treated Teeth. Am. J. Dent. 2024, 37, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barceleiro, M.O.; De Miranda, M.S.; Dias, K.R.; Sekito, T., Jr. Shear bond strength of porcelain laminate veneer bonded with flowable composite. Oper. Dent. 2003, 28, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aykor, A.; Ozel, E. Five-year clinical evaluation of 300 teeth restored with porcelain laminate veneers using total-etch and a modified self-etch adhesive system. Oper. Dent. 2009, 34, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peumans, M.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Lambrechts, P.; Vanherle, G. Porcelain Veneers: A Review of the Literature. J. Dent. 2000, 28, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Arcangelo, C.; De Angelis, F.; Vadini, M.; D’Amario, M. Clinical evaluation on porcelain laminate veneers bonded with light-cured composite: Results up to 7 years. Clin. Oral Investig. 2012, 16, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosco, V.; Monterubbianesi, R.; Orilisi, G.; Sabbatini, S.; Conti, C.; Özcan, M.; Putignano, A.; Orsini, G. Comparison of Two Curing Protocols during Adhesive Cementation: Can the Step Luting Technique Supersede the Traditional One? Odontology 2021, 109, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam Hepdeniz, O.; Temel, U.B. Clinical survival of No-prep indirect composite laminate veneers: A 7-year prospective case series study. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexhepi, I.; Santilli, M.; D’Addazio, G.; Tafuri, G.; Manciocchi, E.; Caputi, S.; Sinjari, B. Clinical Applications and Mechanical Properties of CAD-CAM Materials in Restorative and Prosthetic Dentistry: A Systematic Review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, L.; Galarraga-Vinueza, M.E.; Barootchi, S.; Tavelli, L. 3D surface defect map for characterising the buccolingual profile of peri-implant tissues. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 2023, 16, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- D’Addazio, G.; Xhajanka, E.; Traini, T.; Santilli, M.; Rexhepi, I.; Murmura, G.; Caputi, S.; Sinjari, B. Accuracy of DICOM-DICOM vs. DICOM-STL Protocols in Computer-Guided Surgery: A Human Clinical Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2336. [Google Scholar]
- Mounajjed, R.; Salinas, T.J.; Ingr, T.; Hillstead, M.B.; DeJesus, M.J.; Munoz, C.A. Effect of Cement Type on the Marginal Fit of Lithium Disilicate Pressed Crowns. J. Prosthodontics 2016, 25, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- D’Addazio, G.; Santilli, M.; Rollo, M.L.; Cardelli, P.; Rexhepi, I.; Murmura, G.; Al-Haj Husain, N.; Sinjari, B.; Traini, T.; Özcan, M.; et al. Fracture Resistance of Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Ceramic Crowns Cemented with Conventional or Adhesive Systems: An In Vitro Study. Materials 2020, 13, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, G.H.; Lepe, X.; Patterson, A.; Schäfer, O. Simplified cementation of lithium disilicate crowns: Retention with various adhesive resin cement combinations. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatz, M.B.; Conejo, J.; Alammar, A.; Ayub, J. Current Protocols for Resin-Bonded Dental Ceramics. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 66, 603–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, M.R.; Akbar, A.A.; Sabti, M.Y.; Behbehani, Z. Evaluation of Marginal and Internal Fit of a CAD/CAM Monolithic Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Porcelain Laminate Veneer System. J. Prosthodontics 2022, 31, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.W.; von Fraunhofer, J.A. The estimation of cement film thickness by an in vivo technique. Br. Dent. J. 1971, 131, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, N.; Ding, M.; Jing, J.; Xi, Q.; Wu, G. A digital guiding device to facilitate cementation of porcelain laminate veneers. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 124, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, R.; Ruggiero, G.; Di Mauro, M.I.; Breschi, L.; Leuci, S.; Zarone, F. Optical behaviors, surface treatment, adhesion, and clinical indications of zirconia-reinforced lithium silicate (ZLS): A narrative review. J. Dent. 2021, 112, 103722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; Liang, S. A digital guide device to facilitate CAD-CAM veneer cementation for mandibular incisors: A dental technique. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falacho, R.I.; Marques, J.A.; Palma, P.J.; Roseiro, L.; Caramelo, F.; Ramos, J.C.; Guerra, F.; Blatz, M.B. Luting indirect restorations with resin cements versus composite resins: Effects of preheating and ultrasound energy on film thickness. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2022, 34, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennani, V.; Aarts, J.M.; Senthilkumar, A. Effect of a modified laminate veneer preparation design on absolute margin discrepancy and marginal overhang. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2024, 131, 252.e1–252.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badami, V.; Satya Priya, M.; Vijay, L.; Kethineni, H.; Akarapu, S.; Agarwal, S. Marginal Adaptation of Veneers: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e31885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.M.; Liu, P.R.; Ramp, L.C.; Essig, M.E.; Givan, D.A.; Pan, Y.H. Fracture resistance and marginal discrepancy of porcelain laminate veneers influenced by preparation design and restorative material in vitro. J. Dent. 2012, 40, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboushelib, M.N.; Elmahy, W.A.; Ghazy, M.H. Internal adaptation, marginal accuracy and microleakage of a pressable versus a machinable ceramic laminate veneers. J. Dent. 2012, 40, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).