Impact of Magnifying Loupes on the Finish Lines of Fixed Prosthesis Preparations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Hypothesis
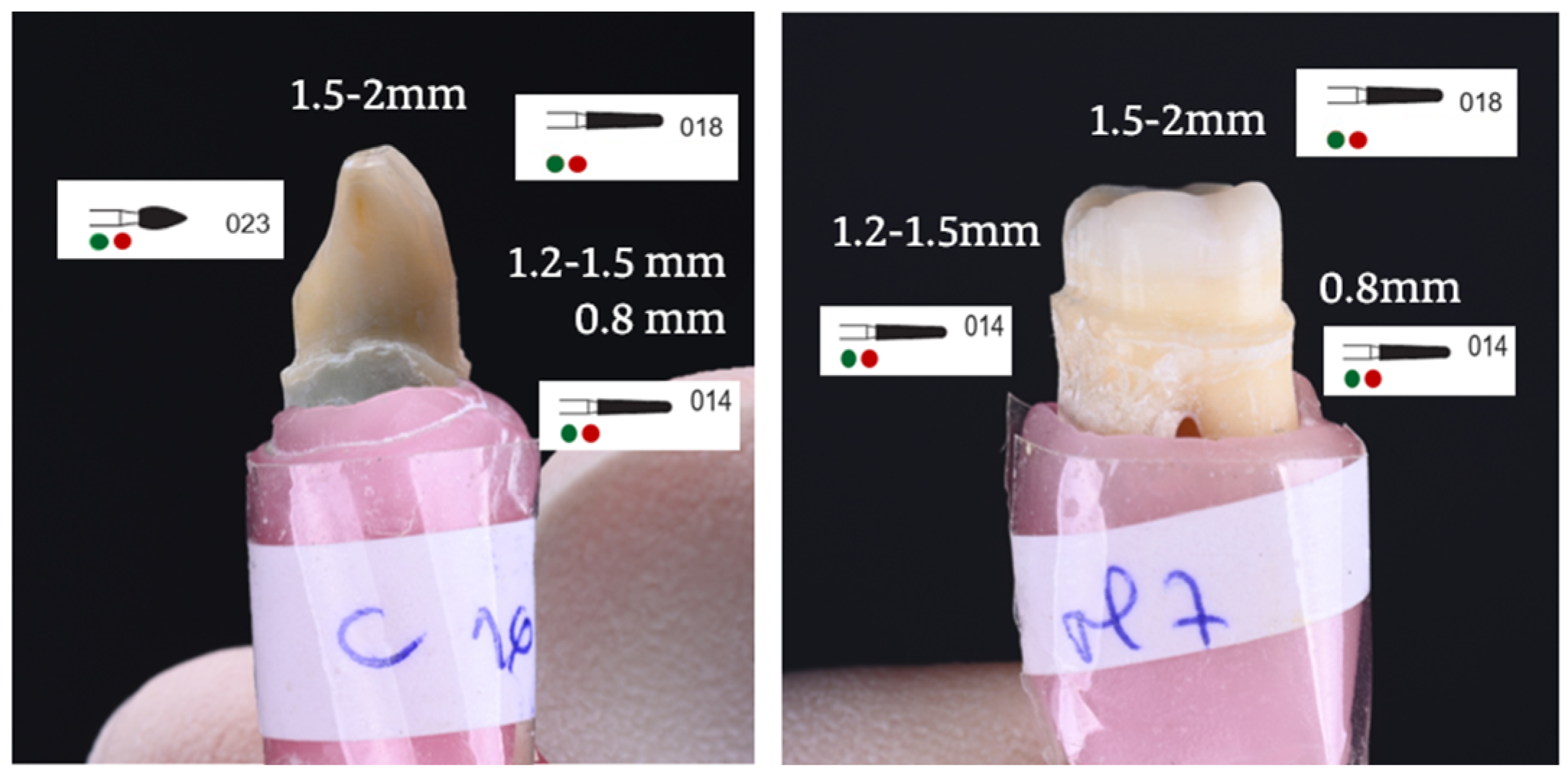
2.2. Research
2.3. Statistical Data Processing
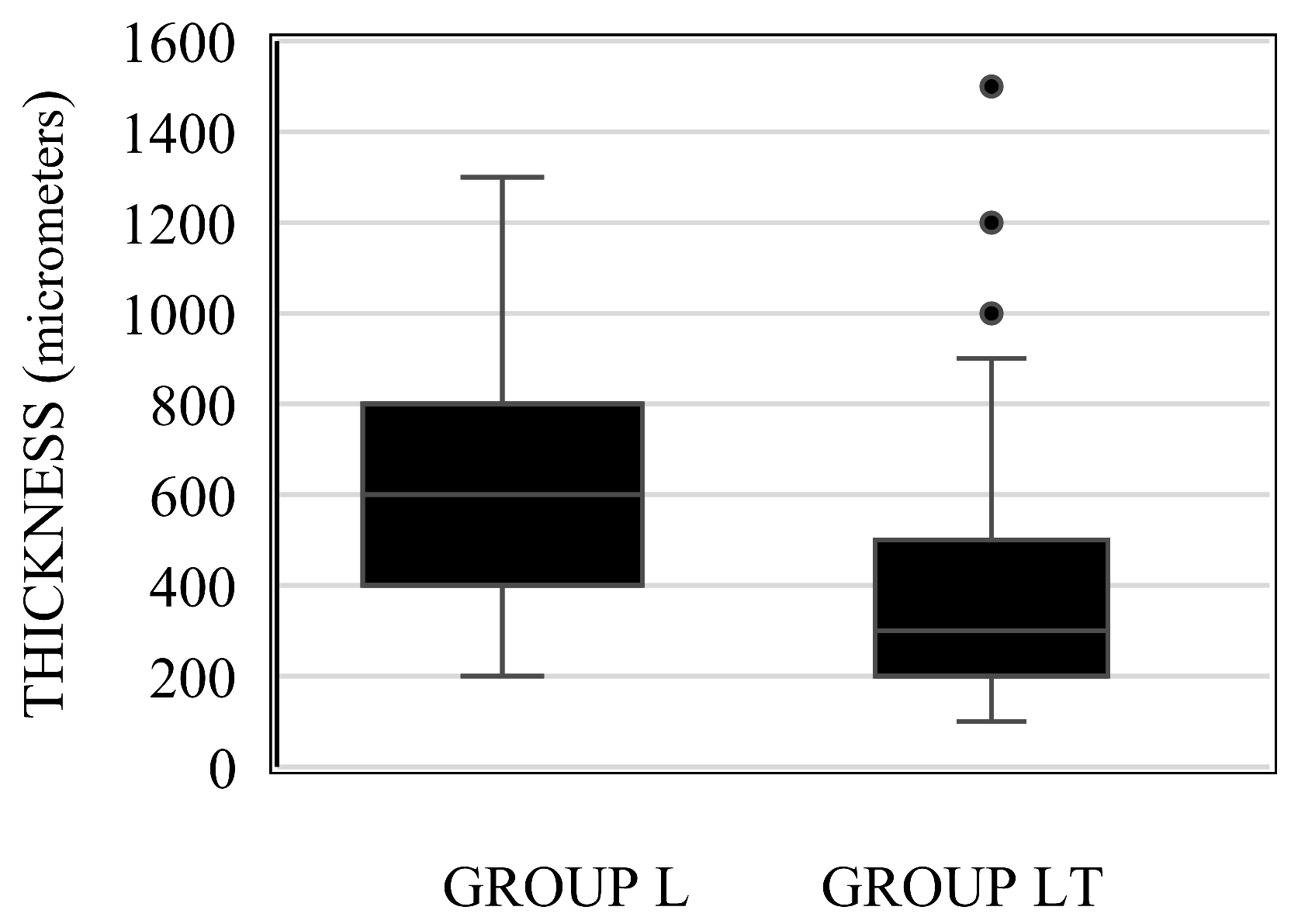
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Douglass, C.W.; Watson, A.J. Future needs for fixed and removable partial dentures in the United States. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2002, 87, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristina, A.; Queiroz, S.; Barreira, A.K.; Marcio, G.; Rodrigues, F. Preparos Dentais em Prótese Fixa: Revisão Integrativa da Literatura e Protocolo para Preparo. Arch. Health Investig. 2022, 11, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-dumaini, M.A.; Al-kadasi, B.A. Influence of Work Time Conditions on Quality of Tooth Preparation for Porcelain Fused to Metal Restoration Performed by Dental Students. Al-Andal. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2020, 59, 59–72. Available online: https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=a9h&AN=144337683&site=eds-live (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Hung, S.H.; Hung, K.-S.; Eick, J.D.; Chappell, R.P. Marginal fit of porcelain-fused-to-metal and two types of ceramic crown. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1990, 63, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pjetursson, B.E.; Tan, K.; Lang, N.P.; Bragger, U.; Egger, M.; Zwahlen, M. A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of fixed partial dentures (FPDs) after an observation period of at least 5 years. I. Implant-supported FPDs. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2004, 15, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.; Bennani, V.; Purton, D.; Chandler, N.; Lowe, B. The Effect of Ultrasonic Instruments on the Quality of Preparation Margins and Bonding to Dentin. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2012, 24, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, P.; Bennani, V.; Chandler, N.; Purton, D. Ultrasonic Margin Preparation for Fixed Prosthodontics: A Pilot Study. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2012, 24, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, T.F.; de Melo, M.P.; Pereira, J.R.; Takeshita, W.M.; Ceribelli, B.M.; Vessoni Iwaki, L.C. Subjective qualitative assessment of the finish line of prosthetic preparations submitted to different finishing instruments. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 116, 375–381. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002239131600144X (accessed on 15 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Winkelmeyer, C.; Wolfart, S.; Marotti, J. Analysis of tooth preparations for zirconia-based crowns and fixed dental prostheses using stereolithography data sets. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 116, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urlic, I.; Pavan, J.; Verzak, Z.; Karlovic, Z.; Negovetic Vranic, D. The best dentistry professional visual acuity measured under sim-ulated clinical conditions provides keplerian magnification loupe: A cross-sectional study. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, P.; Eichenberger, M.; Neuhaus, K.W.; Lussi, A. Visual acuity and magnification devices in dentistry. A review. Swiss Dent. J. SSO 2016, 126, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bud, M.; Jitaru, S.; Lucaciu, O.; Korkut, B.; Dumitrascu-Timis, L.; Ionescu, C.; Cimpean, S.; Delean, A. The advantages of the dental operative microscope in restorative dentistry. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2020, 94, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, D.J.; Glickman, G.N.; Solomon, E.S.; He, J. Magnification’s effect on endodontic fine motor skills. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setzer, F.C.; Kohli, M.R.; Shah, S.B.; Karabucak, B.; Kim, S. Outcome of endodontic surgery: A meta-analysis of the literature—Part 2: Comparison of endodontic microsurgical techniques with and without the use of higher magnification. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lussi, A.; Kronenberg, O.; Megert, B. The effect of magnification on the iatrogenic damage to adjacent tooth surfaces during class II preparation. J. Dent. 2003, 31, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenberger, M.; Biner, N.; Amato, M.; Lussi, A.; Perrin, P. Effect of Magnification on the Precision of Tooth Preparation in Dentistry. Oper. Dent. 2018, 43, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpoor, H.; Jamshidy, L. The Effect of Different Teaching Methods on the Quality of Tooth Preparation by Preclinical Students. Educ. Res. Med Sci. 2019, 8, e90960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, A.M.; Janyavula, S.; Elsabee, R.; Alper, E.; Isleem, W.F.; Bergler, M.; Setzer, F.C. Comparison of loupes versus microscope-enhanced CAD-CAM crown preparations: A microcomputed tomography analysis of marginal gaps. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, 131, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelhoff, D.; Sorensen, J.A. Tooth structure removal associated with various preparation designs for anterior teeth. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2002, 87, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindl, A.; Mörmann, W.H. Marginal and internal fit of all-ceramic CAD/CAM crown-copings on chamfer preparations. J. Oral Rehabil. 2005, 32, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadid-Zadeh, R.; Sahraoui, H.; Lawson, B.; Cox, R. Assessment of tooth preparations submitted to dental laboratories for fabrication of monolithic zirconia crowns. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hey, J.; Schweyen, R.; Kupfer, P.; Beuer, F. Influence of preparation design on the quality of tooth preparation in preclinical dental education. J. Dent. Sci. 2017, 12, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mubarak, N.; Abu-Bakr, N.; Omer, O.; Ibrahim, Y. Assessment of undergraduate students’ tooth preparation for full veneer cast restorations. Open J. Stomatol. 2014, 04, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhaus, K.W.; Jost, F.; Perrin, P.; Lussi, A. Impact of different magnification levels on visual cavities detection with ICDAS. J. Dent. 2015, 43, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taschieri, S.; Del Fabbro, M.; Testori, T.; Francetti, L.; Weinstein, R. Endodontic Surgery Using 2 Different Magnification Devices: Preliminary Results of a Randomized Controlled Study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renne, W.; Wolf, B.; Kessler, R.; McPherson, K.; Mennito, A.S. Evaluation of the Marginal Fit of CAD/CAM Crowns Fabricated Using Two Different Chairside CAD/CAM Systems on Preparations of Varying Quality. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2015, 27, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fouzan, A.F.; Tashkandi, E.A. Linear measurements of finish line length associated with various preparation designs using CAD/CAM technology. Saudi J. Dent. Res. 2016, 7, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Cohen’s Weighted Kappa | ICC | |
|---|---|---|
| Inter-rater reliability | ||
| Continuity | 0.471 | - |
| Roughness | 0.660 | - |
| Thickness | - | 0.825 |
| Intra-rater reliability | ||
| Continuity | 0.599 | - |
| Roughness | 0.686 | - |
| Thickness | - | 0.844 |
| Dental Pieces | Statistics | Group O | Group L | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | Median (P25; P75) | 600 (500; 800) | 600 (400; 800) | 0.482 |
| Mean ± StDev | 628.4 ± 213.5 | 619.3 ± 205.9 | ||
| Incisor | Median (P25; P75) | 700 (500; 800) | 500 (400; 800) | 0.040 |
| Mean ± StDev | 671.9 ± 211.3 | 562.5 ± 205.960 | ||
| Canine | Median (P25; P75) | 600 (500; 675) | 500 (400; 800) | 0.553 |
| Mean ± StDev | 581.3 ± 183.9 | 556.3 ± 228.512 | ||
| Premolar | Median (P25; P75) | 500 (400; 700) | 500 (300; 600) | 0.231 |
| Mean ± StDev | 533.3 ± 176.7 | 495.8 ± 182.1 | ||
| Molar | Median (P25; P75) | 700 (500; 875) | 800 (525; 900) | 0.073 |
| Mean ± StDev | 701.6 ± 224.3 | 771.9 ± 268.1 |
| Continuity | NC n (%) | PC n (%) | C n (%) | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group O | 12 (6.8) | 62 (35.2) | 102 (58.0) | 0.165 |
| Group L | 16 (9.1) | 46 (26.1) | 114 (64.8) |
| Dental Pieces | Result | Group O | Group L | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | R | 54 (30.7) | 51 (29.0) | 0.727 |
| P | 122 (69.3) | 125 (71.0) | ||
| Incisor | R | 10 (31.3) | 12 (37.5) | 0.599 |
| P | 22 (68.8) | 20 (62.5) | ||
| Canine | R | 13 (40.6) | 19 (59.4) | 0.434 |
| P | 10 (31.3) | 22 (68.8) | ||
| Premolar | R | 15 (31.3) | 33 (68.8) | 0.519 |
| P | 18 (37.5) | 30 (62.5) | ||
| Molar | R | 16 (25.0) | 48 (75.0) | 0.279 |
| P | 11 (17.2) | 53 (82.8) |
| Continuity | Roughness | Thickness | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC n (%) | PC n (%) | C n (%) | R n (%) | P n (%) | Median (P25; P75) | Mean ± St Dev. |
| 52 (57.8) | 32 (35.6) | 6 (6.7) | 81 (90) | 9 (10) | 300 (200; 500) | 405.6 ± 301.1 |
| p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nóbrega, C.; Manso, M.C.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Gil, J.; Ribeiro, P. Impact of Magnifying Loupes on the Finish Lines of Fixed Prosthesis Preparations. Prosthesis 2024, 6, 631-642. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis6030044
Nóbrega C, Manso MC, Herrero-Climent M, Gil J, Ribeiro P. Impact of Magnifying Loupes on the Finish Lines of Fixed Prosthesis Preparations. Prosthesis. 2024; 6(3):631-642. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis6030044
Chicago/Turabian StyleNóbrega, Catarina, Maria Conceição Manso, Mariano Herrero-Climent, Javier Gil, and Paulo Ribeiro. 2024. "Impact of Magnifying Loupes on the Finish Lines of Fixed Prosthesis Preparations" Prosthesis 6, no. 3: 631-642. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis6030044
APA StyleNóbrega, C., Manso, M. C., Herrero-Climent, M., Gil, J., & Ribeiro, P. (2024). Impact of Magnifying Loupes on the Finish Lines of Fixed Prosthesis Preparations. Prosthesis, 6(3), 631-642. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis6030044











