Abstract
Background: A key point in assessing dental implant prosthetic joints is their mechanical strength and biological response under the masticatory loading. The aim of the present systematic review was to evaluate the marginal bone loss and prosthetic behaviour of different internal/external bi-phasic implants. Methods: Randomized Clinical Trials (RCTs) have been considered for analytic purposes. The article screening was conducted on the Pubmed/MEDLINE, EMBASE and Google Scholars databases through an electronic process. Eligibility and risk of bias assessments were conducted for an article to be included in the data process. A series of pairwise meta-regressions for continuous variables was conducted considering the mean differences and 95% CI at two different timepoints: baseline and 1-year follow-up. The meta-analysis was performed comparing the following groups: internal conical prosthetic joint with index (IC), external hexagon bone level position (EI), internal tri-channel connection bone level position (ITC), internal hexagon 1 mm below the bone level (HI), internal hexagon bone level position (HI crest), cone morse 1 mm below the bone level (CM), cone morse bone level position (CM crest) and internal octagon bone level position (IO). The following parameters were considered for descriptive data synthesis: sample size, implant manufacturer, prosthetic joint type, prosthetic complications, marginal bone loss, study outcomes. Results: A total of 247 papers were identified by the electronic screening and 241 were submitted for the full text assessment. The eligibility process excluded 209 articles, and 32 studies with a low risk of bias were considered for the qualitative synthesis and further statistical methods. At the baseline, the CM showed a more effective efficiency and reduced marginal bone loss compared to IC, EI, ITC, internal hexagon, cone morse and internal octagon (p < 0.05). CM showed the lower rate of prosthetic complications and structural device failure including abutments and joint components under the loading compared to other joint types. Conclusion: Within the limits of the present investigation, the heterogeneity, the weight of the study model considered and the inherent differences between the dental implant properties, the pure CM showed a more consistent control of marginal bone loss at short- and medium-term follow-up. Despite the low rate of cumulative complications for all joints considered, the CM abutment joints were less prone to prosthetic failure at an early and medium-term follow-up.
1. Introduction
The implant–abutment joint is a well-known factor in two stage implantology due to the related biological and biomechanical implications. A submerged implant is considered to be a supportive protocol to avoid early biofilm colonization and preserve the osteointegration process during the early healing phases from bacteria and local inflammatory stress [1,2]. On the contrary, immediate functional loading could emphasize solicitations at the level of the peri-implant marginal components and consequently produce a consistent instability in the peri-implant soft and hard tissues [3]. As such, the implant–abutment design, the length and the stability of the prosthetic joint and the platform components’ tolerance play a key role in the creation of a hypothetical bacterial reservoir and sustaining a chronic inflammatory status, triggering peri-implant marginal bone loss (MBL) [4]. In the literature, the implant’s success is considered with a −1.5 mm MBL during the first year after loading and afterwards <0.2 mm/year [5,6,7]. Different factors have been recognized as being correlated with peri-implant marginal bone resorption. The most extensively investigated factor is the peri-implant inflammation reaction that is recognized to be a consequence of bacteria colonization at the level of the dental implant interfaces [8]. The biofilm adhesion is determined a few seconds after the surface’s exposure to the oral cavity environment [8]. The prosthetic joint micro-gap could potentially generate a reservoir of bacteria and biofilm subproducts resulting in chronic inflammation at the level of the surrounding tissues [9]. In fact, the microleakage is able to produce a pump effect under the functional loading determined by the mismatch generated by the abutment joint prosthetic components [9,10]. At present, microleakage prevention seems to be the main challenge for transmucosal dental implants design. In the literature, many different prosthetic joint design have been investigated for this purpose [11,12]. The most common implant joint in the market are external connection, internal connection and conical/cone morse joint [7,13]. The aim of the present systematic review was to determine the more recent evidence regarding dental implant prosthetic joint design through a network meta-analysis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
The present study has been registered on International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) prot. n. CRD42024500303. The database screening has been performed following the PRISMA guidelines and checklist (Suppl. S1) (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses) [14] and was conducted on the Pubmed/MEDLINE database, Google Scholar, Scopus and Web of Science using the following keywords: (dental implant* OR dental prosth* OR implant-supported prosth* OR endosseous implant*) AND (conical OR tapper OR tapered OR fractional OR locking)) and (internal connection OR internal hexagon OR non conical OR non tapered OR internal tri-channel OR butt-joint)) AND (survival OR success OR bone loss OR bone level OR complications). The PICO question has been detailed:
- (1)
- P = Population/Patient/Problem—Subjects needing dental implant for prosthetic rehabilitations;
- (2)
- I = Intervention—dental implant treatment positioning and fixed oral rehabilitation;
- (3)
- C = Comparison—comparison between different internal, external and conical prosthetic joint;
- (4)
- O = Outcome—Marginal bone loss, major prosthetic complications.
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
The articles written in English language were included with no restrictions regarding the date publication. The titles and abstracts list were considered for a first-level initial screening by two independent reviewers (FL, IA). Clinical trials were included for descriptive synthesis and meta-regression.
2.3. Study Data Extraction
The following parameters were extracted from the selected studies: publication date, study model design, population size, age, marginal bone loss, prosthetic complications, follow-up. For the scope of this article, a specially designed electronic database form has been used (Excel, Microsoft Office 360, Redmont WA, USA).
2.4. Risk of Bias (RoB)
The Risk of Bias Rating Tool for Human and Animal Studies (OHAT) tool has been assessed to measure the risk of bias of the articles assessed. The assessment categories were “low risk”, “unclear risk” and “high risk” of bias [15].
The tool categories considered were: random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of patients and personnel, blinding of outcome assessment, attrition bias, reporting bias and other biases [15].
2.5. Heterogeneity and Meta-Analysis Assessment
The high heterogeneity is determined by the differences in articles’ publication year, study model design, healing duration period, and sample size. The meta-regression has been conducted through the dedicated statistical software package Review Manager (RevMan 5.0, The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, Copenhagen, Denmark) and the freely available MetaInsight v5.1.2 software (Shinyapps, Leicester, UK) for continuous variables with full R code [16].
2.6. Inconsistency Assessment
The node-splitting measurement has been conducted to evaluate the inconsistency of the variables’ comparison. No inconsistency was considered at p > 0.05. The level of evidence was assessed by the CINeMA (Confidence in Network Meta-Analysis) system [17,18].
2.7. Study Data Analysis
Bayesian NMA was performed using the Bayesian framework with random-effects hierarchical models through the freely available MetaInsight v5.1.2 software (Shinyapps, Leicester, UK) for continuous variables with full R code [16]. A forest plot of relative effects from Bayesian random effect has been calculated to evaluate the consistency model and the significance of the ranks. The I2 test considered a low heterogeneity with a value <40%. For I2 test > 40%, the heterogeneity was further investigated through meta-regressions. The data were presented considering the mean differences and the 95% CI of the means. The surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) rank-o-gram has been applied to assess the robustness of the comparison categories.
3. Results
3.1. General Parameters
The electronic search identified a total of 247 articles. A total of three duplicates and three articles written in a non-English language have been removed (Figure 1). A total of 241 papers were submitted to the eligibility process by two independent reviewers. The reasons for excluding papers were: ninety-one articles were off topic, eighty-four were conducted with the wrong study design (invitro/in silico/on animal model), seventeen were literature reviews, fourteen studies used the wrong sampling and three studies had incomplete reporting regarding the implant prosthetic joint type. A total of thirty-two articles were considered for the descriptive synthesis and meta-regression analysis.
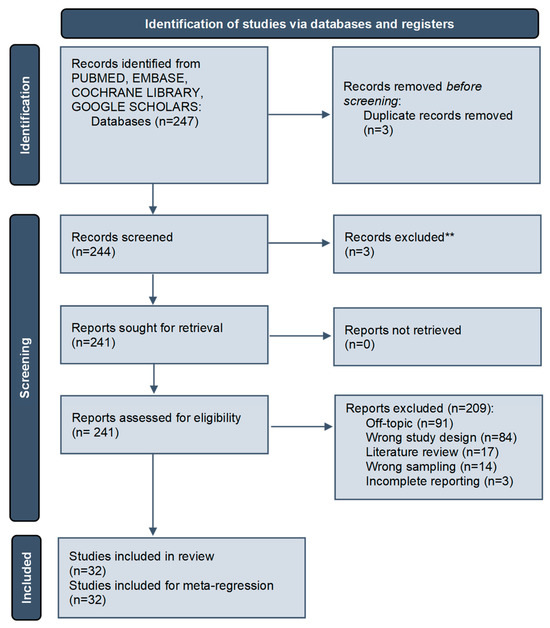
Figure 1.
Article screening process following the PRISMA guidelines [**record exclusion performed by automated tool] [14].
A cumulative total of 2064 patients [mean: 64.5; sd: 45.2; 95 CI: 48.2-80.8] and 4943 implants [mean: 156.1 sd:149.1; 95 CI: 102.3-209.8] have been evaluated in the present analysis (Table 1).

Table 1.
Search strategy for the electronic database screening.
A total of eight different prosthetic joint connections have been considered: internal hexagonal joint 1 mm below the bone level position [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27], internal hexagonal joint at bone level position [19], external hexagonal joint at bone level position [23,25,26,28,29,30,31], Internal conical prosthetic joint with index [19,22,27,28,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46], cone morse 1 mm below the bone level position [23,24,25,26,30,47,48,49], cone morse at the bone level position [49], internal octagon [26] and internal tri-channel connection bone level position [49]. The median follow-up period was 12 months [range: 3-156 months] (Table 1).
3.2. Prosthetic Complications and Joint Failure
The most common prosthetic joint complications, including provisional/final crown debonding, provisional/final abutment screw loosening, provisional/final framework fracture, chipping/cracking of veneering material, no mechanical failure and prosthetic joint failure, have been detected for all included studies (Table 2 and Table 3).

Table 2.
Descriptive synthesis of the studies included.

Table 3.
Descriptive synthesis of the included study.
3.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
The risk of bias assessment is shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3. The randomization bias [43% wlr; 7% ur; 50% whr], selection bias [92% wlr; 8% ur; 5% whr], performance bias [28% wlr; 20% ur; 52% whr], detection bias [28% wlr; 20% ur; 52% whr], attrition bias [79% wlr; 21% ur; 0% whr], reporting bias [87% wlr; 13% ur; 0%whr] and other bias [100% wlr; 0% ur; 0% whr]. A total of twelve studies reported a low risk of bias [22,24,30,31,34,36,37,39,42,43,49,50].
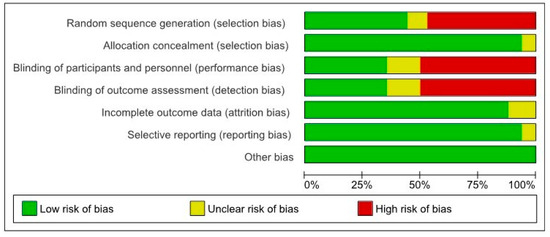
Figure 2.
Risk of bias graph: review authors’ judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies [wlr: weighted low risk; ur: unclear risk; weighted high risk: whr].

Figure 3.
Risk of bias summary: review authors’ judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study [19,20,21,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49].
3.4. Meta-Regression MBL
A plot of the relative effects from the Bayesian random effect consistency model is shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5. The higher SUCRA (Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve) values and cumulative ranking curves nearer the top left indicate better performance. The plot represents each data points’ contribution to the residual deviance in the NMA in terms of consistency (horizontal axis) and the unrelated mean effect (ume) inconsistency models (vertical axis) along with the line of equality, while the radial SUCRA plot showed that higher SUCRA values indicate better treatments; the size of nodes represents number of participants, and thickness of lines indicates the number of trials conducted. At the baseline, the CM positioned 1 mm under the bone level resulted in the most effective reduction in marginal bone resorption at the baseline. The forest plot for the baseline indicated that CM abutment joint showed a significant advantage in marginal bone loss reduction over HI crest group (MD: 0.74; 95% CI: −1.02, −0.56), HI group (MD: 1.23; 95% CI: 0.96, 1.59), CM crest (MD: −1.09; 95% CI: −1.50, −0.80) and EH (MD: −1.52; 95% CI: −1.81, −1.21) (Figure 4 and Figure 5)
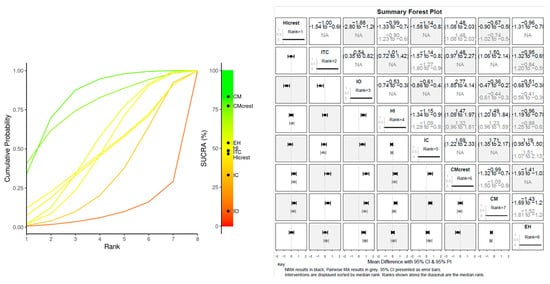
Figure 4.
BASELINE MBL: Litmus rank-o-gram SUCRA (left); forest plot of relative effects of Bayesian random effect consistency model (right).
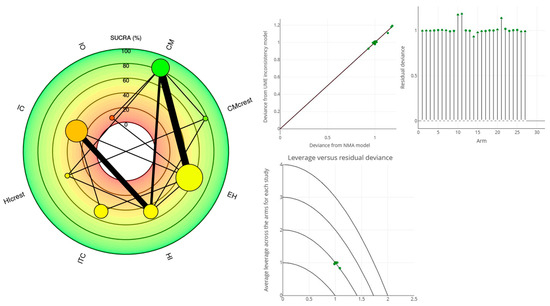
Figure 5.
BASELINE MBL: Radial SUCRA plot (left); The stem plot represents the posterior residual deviance per study arm. The total number of stems equals the total number of data points in the network meta-analysis (NMA). The square root plot showed the average leverage across the arms for each study (right).
The forest plot indicated that, after 1 year of loading, the CM abutment joint positioned 1 mm under the bone level showed a significant advantage in terms of marginal bone loss reduction over the IO crest group (MD: 0.94; 95% CI: −1.42, −0.63), HI group (MD: 1.72; 95% CI: 0.88, 3.33) and EH (MD: 1.43; 95% CI: −1.1, 1.64) (Figure 6 and Figure 7).
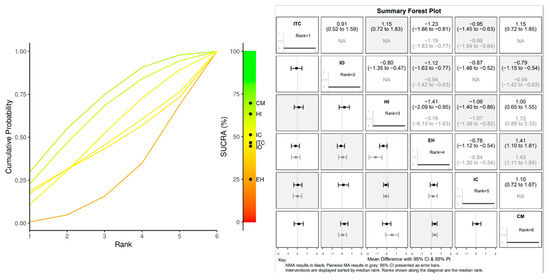
Figure 6.
1 YEAR MBL: Litmus rank-o-gram SUCRA (left); forest plot of relative effects of Bayesian random effect consistency model (right).
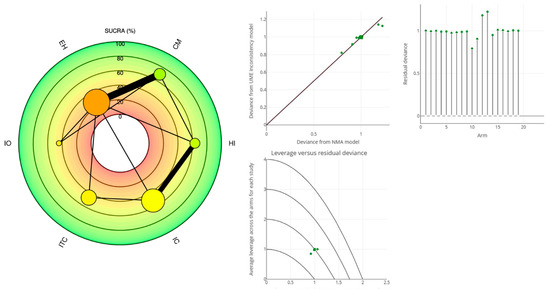
Figure 7.
1 YEAR MBL: Radial SUCRA plot (left); The stem plot represents the posterior residual deviance per study arm. The total number of stems equals the total number of data points in the NMA. The square root plot showed the average leverage across the arms for each study (right).
4. Discussion
This NMA evaluates the effect of different implant–abutment prosthetic joints on marginal bone loss through direct and indirect pairwise comparisons. A total of eight studies have been conducted from 2005 to 2015. The risk of bias represented one of the key assessments within the present investigation. A total of 36.36% of the articles included reported a low risk of bias while only 18 studies reported the adoption of a randomized approach for the population sample allocation. Due to the significance of the marginal bone loss for dental implant survival rate, we compared the early healing period of a submerged implant at the baseline (uncovering) and after 1 year. The CM abutment joint showed a significantly lower amount of marginal bone loss evidence compared to the other connections at the baseline. The same results emerged 1 year after the loading, except for the comparison between the HI and CM groups which revealed a similar resorption rate at the 1-year timepoint. Significantly higher resorption patterns for EH implants have been observed during the 1-year follow up. Several studies in the literature documented the internal flat-to-flat and conical press-fit joint as more favourable compared to an external abutment joint with a lower peri-implant resorption rate [27,30,51]. This evidence seems to support the findings observed in the present NMA. The reasons for peri-implant bone resorption are multifactorial, and they include surgical, mechanical and biological factors, including several comorbidities [32]. The bone level positioning vs. subcrestal implant’s effects on marginal bone loss resulted in non-clear evidence from the NMA due to the low effect size documented in the meta-regression. The abutment joint stability and interface micro-gaps could play a role in functional microleakage creating a critical bacterial reservoir at the level of the crestal bone interface [52,53]. In the literature, the press-fit joint has been proposed to reduce the micro-gaps and improve the stability of the implant–abutment joint [32,51]. A precise adaptation of the prosthetic components is certainly important to produce a higher stability at the implant interfaces avoiding the creation of gaps [54]. The prosthetic joint precision fit is also a theoretical critical point for external and internal flat-to-flat systems, where the loading and the bending impairment could produce a marginal decoupling of the components [51]. The presence of an interface is able to produce a physiological reaction determined by bacterial contamination and marginal micromovements [55]. This evidence is histologically accompanied by a chronic inflammatory infiltrate at the level of the peri-implant tissues [55]. The mechanical complications seem to be a heterogeneous occurrence that transversely affects all systems considered with a cumulative rate ranging from 0 to 8.53% including major and minor events and a cumulative prosthetic success rate >95%. The screw loosening/fracture is a common joint complication for both internal flat-to-flat and conical connections with index [12]. Despite the limited follow-up of the present investigation, no abutment joint decoupling has been documented for CM joints in any of the studies included. Although the implant prosthetic joint could be considered as a relevant risk factor for late implant failure, no significant evidence in this NMA has been detected. A consistent critical point in the present NMA is that implant success could be determined by the type of rehabilitation. In fact, the present investigation considered no limitations for either provisional or final restoration. In addition, the surrounding bone loss is mainly influenced by many factors other than prosthetic joint type, including gingival biotype and thickness, bone width, bone density, biologic width around the implant and other factors related to prosthetic provision. These aspects could be considered a relevant limitation of the present study and the methodology. On the other hand, the lack of homogeneity of the study data represented a critical factor for the network meta-analysis where bone level position data were not available after 1 year for the CM and HI groups, but only at the baseline. These data could be useful for improving the relevance of the findings in relation to the biomechanical behaviour of the different prosthetic joints and the bone level depth.
The biomechanical behaviour could significantly affect the MBL, creating a confounding factor for the NMA calculations and masking the effects of the variables. On the other hand, a rigid inclusion criteria approach could reduce the sample size leading to the investigation making more assumptions. Another limitation of the present study is determined by the follow-up, where very few studies carried out more than 24 months of follow-up. Further long-term randomized clinical trials including implants with similar macro-/and micro-topography are necessary for an equal and comparative evaluation.
5. Conclusions
Within the limits of the present systematic review and NMA, the CM implant joint showed significantly lower MBL after 1 year compared with external hexagonal and internal flat-to-flat and conical connections. On the other hands, the CM joint reported a lower rate of prosthetic complications and implant–abutment decoupling events.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/prosthesis6010015/s1, Suppl. S1. Checklist according to the PRISMA guidelines. Reference [56] is cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S., F.L. and I.A.; methodology, A.S., I.A. and F.L.; software, F.L.; validation, A.S., F.L., I.A., S.A.G., M.D.C. and S.R.T.; formal analysis, A.S., F.L., S.A.G. and M.D.C.; investigation, A.S., F.L., I.A., S.A.G., M.D.C. and S.R.T.; data curation, F.L., A.S. and I.A.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S., F.L. and I.A.; writing—review and editing, A.S., F.L. and I.A.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All experimental data to support the findings of this study are available by contacting the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hamada, Y.; Shin, D.; John, V. Peri-Implant Disease--A Significant Complication of Dental Implant Supported Restorative Treatment. J. Indiana Dent. Assoc. 2016, 95, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Koutouzis, T. Implant-abutment Connection as Contributing Factor to Peri-implant Diseases. Periodontology 2000 2019, 81, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardes, S.R.; da Gloria Chiarello de Mattos, M.; Hobkirk, J.; Ribeiro, R.F. Loss of Preload in Screwed Implant Joints as a Function of Time and Tightening/Untightening Sequences. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Influences of Microgap and Micromotion of Implant–Abutment Interface on Marginal Bone Loss around Implant Neck. Arch. Oral Biol. 2017, 83, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrektsson, T.; Zarb, G.; Worthington, P.; Eriksson, A.R. The Long-Term Efficacy of Currently Used Dental Implants: A Review and Proposed Criteria of Success. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1986, 1, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Romeo, E.; Ghisolfi, M.; Murgolo, N.; Chiapasco, M.; Lops, D.; Vogel, G. Therapy of Peri-Implantitis with Resective Surgery: A 3-Year Clinical Trial on Rough Screw-Shaped Oral Implants. Part I: Clinical Outcome. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2004, 16, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.; Koo, K.-T.; Kim, T.-I.; Seol, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.-M.; Ku, Y.; Rhyu, I.-C. Comparison of Marginal Bone Loss between Internal- and External-Connection Dental Implants in Posterior Areas without Periodontal or Peri-Implant Disease. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2018, 48, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellakany, P.; Mahrous, A.; Eraky, D.; Albarrak, A.; AlJindan, R.; Fouda, S. Evaluation of Bacterial Leakage in Platform-Switching Dental Implant with Morse Taper Connection Under Thermocycling and Loading Effects: In Vitro Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2021, 36, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assenza, B.; Tripodi, D.; Scarano, A.; Perrotti, V.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G.; D’Ercole, S. Bacterial Leakage in Implants with Different Implant-Abutment Connections: An in Vitro Study. J. Periodontol. 2012, 83, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.F.; Grenho, L.; Fernandes, M.H.; Sampaio-Fernandes, J.C.; Gomes, P.S. Microgap and Bacterial Microleakage during the Osseointegration Period: An in Vitro Assessment of the Cover Screw and Healing Abutment in a Platform-Switched Implant System. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 130, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrucea, C.; Conrado, A.; Olivares, D.; Padilla, C.; Barrera, A.; Lobos, O. Bacterial Microleakage at the Abutment-Implant Interface, in Vitro Study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, C.; Ayyildiz, S. Correlation between Microleakage and Screw Loosening at Implant-Abutment Connection. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2014, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, M.R. An in Vitro Evaluation of the Strength of an Internal Conical Interface Compared to a Butt Joint Interface in Implant Design. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1997, 8, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA Extension Statement for Reporting of Systematic Reviews Incorporating Network Meta-Analyses of Health Care Interventions: Checklist and Explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, R.K.; Bradbury, N.; Xin, Y.; Cooper, N.; Sutton, A. MetaInsight: An Interactive Web-Based Tool for Analyzing, Interrogating, and Visualizing Network Meta-Analyses Using R-Shiny and Netmeta. Res. Synth. Methods 2019, 10, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolakopoulou, A.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Papakonstantinou, T.; Chaimani, A.; Del Giovane, C.; Egger, M.; Salanti, G. CINeMA: An Approach for Assessing Confidence in the Results of a Network Meta-Analysis. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, T.; Nikolakopoulou, A.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Egger, M.; Salanti, G. CINeMA: Software for Semiautomated Assessment of the Confidence in the Results of Network Meta-Analysis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2020, 16, e1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceruso, F.M.; Ieria, I.; Tallarico, M.; Meloni, S.M.; Lumbau, A.I.; Mastroianni, A.; Zotti, A.; Gargari, M. Comparison between Early Loaded Single Implants with Internal Conical Connection or Implants with Transmucosal Neck Design: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial with 1-Year Clinical, Aesthetics, and Radiographic Evaluation. Materials 2022, 15, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceruso, F.M.; Ieria, I.; Martelli, M.; Lumbau, A.I.; Xhanari, E.; Gargari, M. New Generation of Fixture–Abutment Connection Combining Soft Tissue Design and Vertical Screw-Retained Restoration: 1-Year Clinical, Aesthetics and Radiographic Preliminary Evaluation. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Nakano, T.; Shimomoto, T.; Kabata, D.; Shintani, A.; Yatani, H. Multivariate Analysis of the Influence of Prosthodontic Factors on Peri-Implant Bleeding Index and Marginal Bone Level in a Molar Site: A Cross-Sectional Study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2020, 22, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corvino, E.; Pesce, P.; Camodeca, F.; Moses, O.; Iannello, G.; Canullo, L. Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Implants with Two Different Connection Configurations: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 2020, 13, 355–368. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminaka, A.; Nakano, T.; Ono, S.; Kato, T.; Yatani, H. Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Horizontal and Vertical Dimensional Changes in Buccal Peri-Implant Alveolar Bone and Soft Tissue: A 1-Year Prospective Clinical Study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, e576–e585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieri, F.; Aldini, N.N.; Marchetti, C.; Corinaldesi, G. Influence of Implant-Abutment Interface Design on Bone and Soft Tissue Levels around Immediately Placed and Restored Single-Tooth Implants: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2011, 26, 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Oda, Y.; Mori, G.; Honma, S.; Ito, T.; Iijima, T.; Yajima, Y. Marginal Bone Loss and the Risk Indicators of Fixed Screw-Retained Implant-Supported Prostheses and Fixed Telescopic-Retained Implant-Supported Prostheses in Full Arch: A Retrospective Case-Control Study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2021, 32, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.-I.; Shen, Y.-W.; Huang, H.-L.; Hsu, J.-T.; Fuh, L.-J. A Retrospective Study of Implant–Abutment Connections on Crestal Bone Level. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 202S–207S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannata, M.; Grandi, T.; Samarani, R.; Svezia, L.; Grandi, G. A Comparison of Two Implants with Conical vs Internal Hex Connections: 1-Year Post-Loading Results from a Multicentre, Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 10, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Arnhart, C.; Kielbassa, A.M.; Martinez-de Fuentes, R.; Goldstein, M.; Jackowski, J.; Lorenzoni, M.; Maiorana, C.; Mericske-Stern, R.; Pozzi, A.; Rompen, E.; et al. Comparison of Variable-Thread Tapered Implant Designs to a Standard Tapered Implant Design after Immediate Loading. A 3-Year Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 5, 123–136. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, L.A.; Souza, M.B.C.; Barbosa, G.A.S.; Carreiro, A.D.F.P. Peri-Implant Bone Loss of External Hexagon and Morse Taper in Patients Wearing Immediately Loaded Overdentures. Braz. Dent. J. 2017, 28, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machtei, E.E.; Oved-Peleg, E.; Peled, M. Comparison of Clinical, Radiographic and Immunological Parameters of Teeth and Different Dental Implant Platforms. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2006, 17, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, A.; Agliardi, E.; Tallarico, M.; Barlattani, A. Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Two Implants with Different Prosthetic Interfaces and Neck Configurations: Randomized, Controlled, Split-Mouth Clinical Trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lops, D.; Stocchero, M.; Motta Jones, J.; Freni, A.; Palazzolo, A.; Romeo, E. Five Degree Internal Conical Connection and Marginal Bone Stability around Subcrestal Implants: A Retrospective Analysis. Materials 2020, 13, 3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Moreno, P.; León-Cano, A.; Ortega-Oller, I.; Monje, A.; Suárez, F.; ÓValle, F.; Spinato, S.; Catena, A. Prosthetic Abutment Height Is a Key Factor in Peri-Implant Marginal Bone Loss. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 80S–85S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyszkowski, A.; Kozakiewicz, M. Effect of Implant-Abutment Connection Type on Bone Around Dental Implants in Long-Term Observation: Internal Cone Versus Internal Hex. Implant Dent. 2019, 28, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Moreno, P.; Ravidà, A.; Catena, A.; O’Valle, F.; Padial-Molina, M.; Wang, H.L. Limited Marginal Bone Loss in Implant-Supported Fixed Full-Arch Rehabilitations after 5 Years of Follow-Up. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2022, 33, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moergel, M.; Rocha, S.; Messias, A.; Nicolau, P.; Guerra, F.; Wagner, W. Clinical and Radiographic Performance of Self-Locking Conical Connection Implants in the Posterior Mandible: Five-Year Results of a Two-Centre Prospective Study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2021, 32, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moergel, M.; Rocha, S.; Messias, A.; Nicolau, P.; Guerra, F.; Wagner, W. Radiographic Evaluation of Conical Tapered Platform-Switched Implants in the Posterior Mandible: 1-Year Results of a Two-Center Prospective Study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Moreno, P.; Concha-Jeronimo, A.; Lopez-Chaichio, L.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, R.; Sanchez-Fernandez, E.; Padial-Molina, M. Marginal Bone Loss around Implants with Internal Hexagonal and Internal Conical Connections: A 12-Month Randomized Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toia, M.; Stocchero, M.; Galli, S.; Papia, E.; Wennerberg, A.; Becktor, J.P. The Use of Implant-Level Connection in Screw-Retained Fixed Partial Dentures: A 3-Year Randomised Clinical Trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2022, 33, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, A.; Tallarico, M.; Moy, P.K. Immediate Loading with a Novel Implant Featured by Variable-Threaded Geometry, Internal Conical Connection and Platform Shifting: Three-Year Results from a Prospective Cohort Study. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 8, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, T.; Berton, F.; Salgarello, S.; Barbalonga, E.; Rapani, A.; Piovesana, F.; Gregorio, C.; Barbati, G.; Di Lenarda, R.; Stacchi, C. Factors Influencing Early Marginal Bone Loss around Dental Implants Positioned Subcrestally: A Multicenter Prospective Clinical Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualini, F.; Salina, S.; Rigotti, F.; Mazzarini, C.; Longhin, D.; Grigoletto, M.; Trullenque-Eriksson, A.; Sbricoli, L.; Esposito, M. Subcrestal Placement of Dental Implants with an Internal Conical Connection of 0.5 Mm versus 1.5 Mm: Outcome of a Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial 1 Year after Loading. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 10, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pozzi, A.; Mura, P. Immediate Loading of Conical Connection Implants: Up-to-2-Year Retrospective Clinical and Radiologic Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lops, D.; Romeo, E.; Stocchero, M.; Palazzolo, A.; Manfredi, B.; Sbricoli, L. Marginal Bone Maintenance and Different Prosthetic Emergence Angles: A 3-Year Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, K.L.; Barth, T.; Cacaci, C.; Kistler, S.; Schlee, M.; Stiller, M. Clinical and Patient-Reported Outcome of Implant Restorations with Internal Conical Connection in Daily Dental Practices: Prospective Observational Multicenter Trial with up to 7-Year Follow-Up. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2020, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fügl, A.; Zechner, W.; Pozzi, A.; Heydecke, G.; Mirzakhanian, C.; Behneke, N.; Behneke, A.; Baer, R.A.; Nölken, R.; Gottesman, E.; et al. An Open Prospective Single Cohort Multicenter Study Evaluating the Novel, Tapered, Conical Connection Implants Supporting Single Crowns in the Anterior and Premolar Maxilla: Interim 1-Year Results. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 21, 2133–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Galindo-Moreno, P.; León-Cano, A.; Monje, A.; Ortega-Oller, I.; O’Valle, F.; Catena, A. Abutment Height Influences the Effect of Platform Switching on Peri-Implant Marginal Bone Loss. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Ayukawa, Y.; Koyano, K. A 3-Year Prospective Study on Radiographic Marginal Bone Evaluation Around Platform-Shifting Implants with Internal Conical Connections. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2021, 36, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaska, I.; Tsaousoglou, P.; Vouros, I.; Konstantinidis, A.; Menexes, G. Influence of Placement Depth and Abutment Connection Pattern on Bone Remodeling around 1-Stage Implants: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, e47–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanos, G.E.; Biltucci, M.T.; Kokaras, A.; Paster, B.J. Bacterial Composition at the Implant-Abutment Connection under Loading in Vivo: Bacteria at Implant-Abutment Interface under in Vivo Loading Conditions. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camps-Font, O.; Rubianes-Porta, L.; Valmaseda-Castellón, E.; Jung, R.E.; Gay-Escoda, C.; Figueiredo, R. Comparison of External, Internal Flat-to-Flat, and Conical Implant Abutment Connections for Implant-Supported Prostheses: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 130, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, A.; Perrotti, V.; Piattelli, A.; Iaculli, F.; Iezzi, G. Sealing Capability of Implant-Abutment Junction under Cyclic Loading: A Toluidine Blue in Vitro Study. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2015, 13, e293–e295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, A.; Mortellaro, C.; Mavriqi, L.; Pecci, R.; Valbonetti, L. Evaluation of Microgap With Three-Dimensional X-Ray Microtomography: Internal Hexagon Versus Cone Morse. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2016, 27, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naser Mostofy, S.; Jalalian, E.; Valaie, N.; Mohtashamrad, Z.; Haeri, A.; Bitaraf, T. Study of the Effect of GapSeal on Microgap and Microleakage in Internal Hex Connection After Cyclic Loading. J. Res. Dentomaxillofac. Sci. 2019, 4, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, G.; Fanali, S.; Scarano, A.; Petrone, G.; di Silvestro, S.; Piattelli, A. Tissue Reactions, Fluids, and Bacterial Infiltration in Implants Retrieved at Autopsy: A Case Report. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2000, 15, 283–286. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).