Molecular Diagnosis of Osteoarticular Implant-Associated Infection: Available Techniques and How We Can Use Them
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Homemade PCR-Based Techniques
3. Commercial PCR-Based Techniques
3.1. Adapted Kits
3.2. Specifically Designed Kits
4. Next-Generation Sequencing and Metagenomics
5. How Can the Molecular Diagnosis Techniques Be Used in a Routine Setting?
5.1. In What Type of Patients Can These Techniques Be Used?
5.2. What Type of Technique Must Be Used?
5.2.1. Time
5.2.2. Complexity
5.2.3. Cost
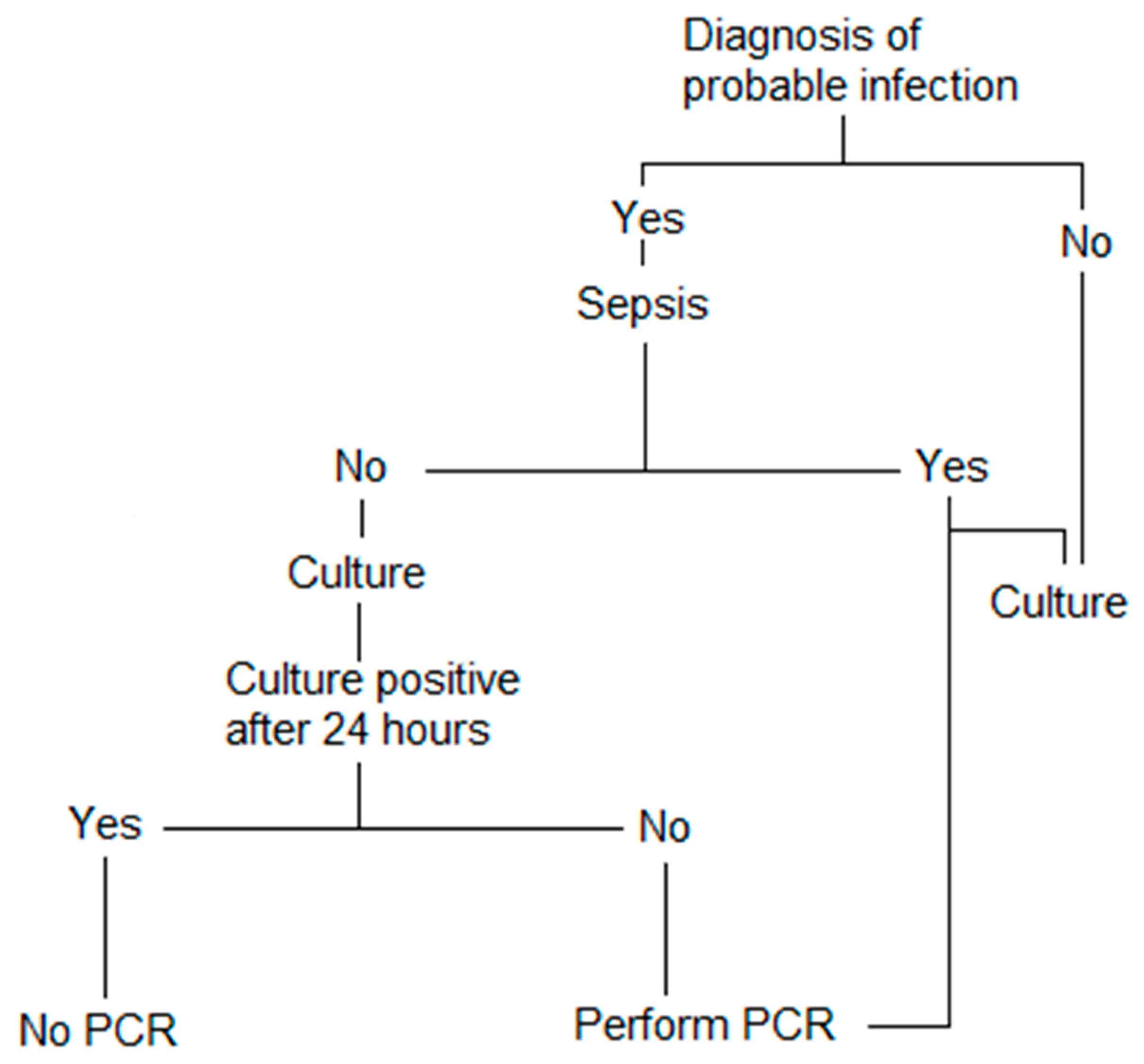
5.3. How Can We Use These Methods?
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tande, A.J.; Patel, R. Prosthetic joint infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 302–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Lau, E.; Watson, H.; Schmier, J.K.; Parvizi, J. Economic burden of periprosthetic joint infection in the United States. J. Arthroplast. 2012, 27, 61–65.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lora-Tamayo, J.; Murillo, O.; Iribarren, J.A.; Soriano, A.; Sánchez-Somolinos, M.; Baraia-Etxaburu, J.M.; Rico, A.; Palomino, J.; Rodríguez-Pardo, D.; Horcajada, J.P.; et al. A large multicenter study of methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic joint infections managed with implant retention. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.; Ribera, A.; Mavrogenis, A.F.; Rodriguez-Pardo, D.; Bonnet, E.; Salles, M.J.; Dolores Del Toro, M.; Nguyen, S.; Blanco-García, A.; Skaliczki, G.; et al. Multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Gram-negative prosthetic joint infections: Role of surgery and impact of colistin administration. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora-Tamayo, J.; Senneville, É.; Ribera, A.; Bernard, L.; Dupon, M.; Zeller, V.; Li, H.K.; Arvieux, C.; Clauss, M.; Uçkay, I.; et al. The Not-So-Good Prognosis of Streptococcal Periprosthetic Joint Infection Managed by Implant Retention: The Results of a Large Multicenter Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1742–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusejko, K.; Aunon, A.; Jost, B.; Natividad, B.; Strahm, C.; Thurnheer, C.; Pablo-Marcos, D.; Slama, D.; Scanferla, G.; Uckay, I.; et al. The Impact of Surgical Strategy and Rifampin on Treatment Outcome in Cutibacterium Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, e1064–e1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, N.; Franco, M.; Ribera, A.; Soriano, A.; Rodriguez-Pardo, D.; Sorlí, L.; Fresco, G.; Fernández-Sampedro, M.; Dolores del Toro, M.; Guío, L.; et al. Time trends in the aetiology of prosthetic joint infections: A multicentre cohort study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 732.e1–732.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, N.; Mur, I.; Ribera, A.; Soriano, A.; Rodríguez-Pardo, D.; Sorlí, L.; Cobo, J.; Fernández-Sampedro, M.; Del Toro, M.D.; Guío, L.; et al. The Different Microbial Etiology of Prosthetic Joint Infections according to Route of Acquisition and Time after Prosthesis Implantation, Including the Role of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellova, P.; Knop-Hammad, V.; Königshausen, M.; Mempel, E.; Frieler, S.; Gessmann, J.; Schildhauer, T.A.; Baecker, H. Sonication of retrieved implants improves sensitivity in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, J. Microbiologial diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection: Is there a need for standardization? Enferm. Infecc. Y Microbiol. Clin. 2022, 40, 287–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, E.; Suh, G.A.; Tande, A.J. Enhancing Diagnostics in Orthopedic Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2022, 60, e0219621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicenti, G.; Bizzoca, D.; Nappi, V.; Pesce, V.; Solarino, G.; Carrozzo, M.; Moretti, F.; Dicuonzo, F.; Moretti, B. Serum biomarkers in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection: Consolidated evidence and recent developments. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solarino, G.; Bizzoca, D.; Moretti, L.; Vicenti, G.; Piazzolla, A.; Moretti, B. What’s New in the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infections: Focus on Synovial Fluid Biomarkers. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzoca, D.; Moretti, L.; Gnoni, A.; Moretti, F.L.; Scacco, S.; Banfi, G.; Piazzolla, A.; Solarino, G.; Moretti, B. The Usefulness of Synovial Fluid Proteome Analysis in Orthopaedics: Focus on Osteoarthritis and Periprosthetic Joint Infections. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2022, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, E.; Roschka, C.; Esteban, J.; Raglio, A.; Tisler, A.; Willems, P.; Kramer, T.S. The State of Microbiology Diagnostic of Prosthetic Joint Infection in Europe: An In-Depth Survey among Clinical Microbiologists. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 906989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falces-Romero, I.; Rico-Nieto, A. Processing of osteoarticular samples for microbiological diagnosis: Results of a national multi-center survey. Enferm. Infecc. Y Microbiol. Clínica 2013, 31, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo, J.L.; Patel, R. Clinical practice. Infection associated with prosthetic joints. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, J.; Sorli, L.; Alentorn-Geli, E.; Puig, L.; Horcajada, J.P. Conventional and molecular diagnostic strategies for prosthetic joint infections. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trampuz, A.; Osmon, D.R.; Hanssen, A.D.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Patel, R. Molecular and antibiofilm approaches to prosthetic joint infection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2003, 414, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, M.; Garcia-Lechuz, J.M.; Alonso, P.; Villanueva, M.; Alcalá, L.; Gimeno, M.; Cercenado, E.; Sánchez-Somolinos, M.; Radice, C.; Bouza, E. Role of universal 16S rRNA gene PCR and sequencing in diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, E.; Cazanave, C.; Cunningham, S.A.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Uhl, J.R.; Hanssen, A.D.; Karau, M.J.; Schmidt, S.M.; Osmon, D.R.; et al. Prosthetic joint infection diagnosis using broad-range PCR of biofilms dislodged from knee and hip arthroplasty surfaces using sonication. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3501–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bémer, P.; Plouzeau, C.; Tande, D.; Léger, J.; Giraudeau, B.; Valentin, A.S.; Jolivet-Gougeon, A.; Vincent, P.; Corvec, S.; Gibaud, S.; et al. Evaluation of 16S rRNA gene PCR sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection: A prospective multicenter cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3583–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plouzeau, C.; Bémer, P.; Valentin, A.S.; Héry-Arnaud, G.; Tandé, D.; Jolivet-Gougeon, A.; Vincent, P.; Kempf, M.; Lemarié, C.; Guinard, J.; et al. First experience of a multicenter external quality assessment of molecular 16S rRNA gene detection in bone and joint infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achermann, Y.; Vogt, M.; Leunig, M.; Wüst, J.; Trampuz, A. Improved diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection by multiplex PCR of sonication fluid from removed implants. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo, M.E.; Salvadó, M.; Sorli, L.; Alier, A.; Martínez, S.; Trampuz, A.; Gómez, J.; Puig, L.; Horcajada, J.P. Multiplex PCR of sonication fluid accurately differentiates between prosthetic joint infection and aseptic failure. J. Infect. 2012, 65, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, J.; Alonso-Rodriguez, N.; del-Prado, G.; Ortiz-Perez, A.; Molina-Manso, D.; Cordero-Ampuero, J.; Sandoval, E.; Fernandez-Roblas, R.; Gomez-Barrena, E. PCR-hybridization after sonication improves diagnosis of implant-related infection. Acta Orthop. 2012, 83, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubouix-Bourandy, A.; de Ladoucette, A.; Pietri, V.; Mehdi, N.; Benzaquen, D.; Guinand, R.; Gandois, J.-M. Direct detection of Staphylococcus osteoarticular infections by use of Xpert MRSA/SA SSTI real-time PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 4225–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasoo, S.; Cunningham, S.A.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Hanssen, A.D.; Abdel, M.P.; Osmon, D.R.; Berbari, E.F.; Patel, R. Evaluation of the FilmArray Blood Culture ID Panel on Biofilms Dislodged from Explanted Arthroplasties for Prosthetic Joint Infection Diagnosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2790–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metso, L.; Mäki, M.; Tissari, P.; Remes, V.; Piiparinen, P.; Kirveskari, J.; Tarkka, E.; Anttila, V.-J.; Vaara, M.; Huotari, K. Efficacy of a novel PCR- and microarray-based method in diagnosis of a prosthetic joint infection. Acta Orthop. 2014, 85, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, A.-K.; Laakso, S.; Piiparinen, P.; Aittakorpi, A.; Lindfors, M.; Huopaniemi, L.; Piiparinen, H.; Mäki, M. Rapid identification of bacterial pathogens using a PCR- and microarray-based assay. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Borja, L.; Rodriguez-Sevilla, G.; Aunon, A.; Perez-Jorge, C.; Sandoval, E.; Garcia-Canete, J.; Gadea, I.; Fernandez-Roblas, R.; Blanco, A.; Esteban, J. Evaluation of a commercial multiplex PCR (Unyvero i60((R))) designed for the diagnosis of bone and joint infections using prosthetic-joint sonication. Enferm. Infecc. Y Microbiol. Clin. 2017, 35, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borde, J.P.; Häcker, G.A.; Guschl, S.; Serr, A.; Danner, T.; Hübner, J.; Burrack-Lange, S.; Lüdke, G.; Helwig, P.; Hauschild, O.; et al. Diagnosis of prosthetic joint infections using UMD-Universal Kit and the automated multiplex-PCR Unyvero i60 ITI(®) cartridge system: A pilot study. Infection 2015, 43, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hischebeth, G.T.R.; Gravius, S.; Buhr, J.K.; Molitor, E.; Wimmer, M.D.; Hoerauf, A.; Bekeredjian-Ding, I.; Randau, T.M. Novel Diagnostics in Revision Arthroplasty: Implant Sonication and Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2017, 130, 55147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renz, N.; Feihl, S.; Cabric, S.; Trampuz, A. Performance of automated multiplex PCR using sonication fluid for diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection: A prospective cohort. Infection 2017, 45, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malandain, D.; Bémer, P.; Leroy, A.G.; Léger, J.; Plouzeau, C.; Valentin, A.S.; Jolivet-Gougeon, A.; Tandé, D.; Héry-Arnaud, G.; Lemarié, C.; et al. Assessment of the automated multiplex-PCR Unyvero i60 ITI® cartridge system to diagnose prosthetic joint infection: A multicentre study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 83.e1–83.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, C.; Cabric, S.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A.; Renz, N. Synovial fluid multiplex PCR is superior to culture for detection of low-virulent pathogens causing periprosthetic joint infection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 90, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renz, N.; Cabric, S.; Morgenstern, C.; Schuetz, M.A.; Trampuz, A. Value of PCR in sonication fluid for the diagnosis of orthopedic hardware-associated infections: Has the molecular era arrived? Injury 2018, 49, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, I.K.; Windhager, R.; Sevelda, F.; Staats, K.; Puchner, S.E.; Stenicka, S.; Thalhammer, F.; Holinka, J. Multiplex PCR Unyvero i60 ITI application improves detection of low-virulent microorganisms in periprosthetic joint infections. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suren, C.; Feihl, S.; Cabric, S.; Banke, I.J.; Haller, B.; Trampuz, A.; von Eisenhart-Rothe, R.; Prodinger, P.M. Improved pre-operative diagnostic accuracy for low-grade prosthetic joint infections using second-generation multiplex Polymerase chain reaction on joint fluid aspirate. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, F.; Toscano, M.; De Vecchi, E.; Bortolin, M.; Drago, L. Reliability of a multiplex PCR system for diagnosis of early and late prosthetic joint infections before and after broth enrichment. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2017, 307, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausmann, C.; Kolle, K.N.; Citak, M.; Abdelaziz, H.; Schulmeyer, J.; Delgado, G.D.; Gehrke, T.; Gebauer, M.; Zahar, A. How reliable is the next generation of multiplex-PCR for diagnosing prosthetic joint infection compared to the MSIS criteria? Still missing the ideal test. HIP Int. 2020, 30, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüdemann, M.; Sulastyanto, S.; Raab, P.; Schoen, C.; Rudert, M. Periprosthetic joint infection: Comparison of automated multiplex-PCR Unyvero i60 ITI cartridge system with bacterial culture and real-time PCR. Technol. Health Care 2022, 30, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graue, C.; Schmitt, B.H.; Waggoner, A.; Laurent, F.; Abad, L.; Bauer, T.; Mazariegos, I.; Balada-Llasat, J.-M.; Horn, J.; Wolk, D.; et al. 322. Evaluation of the BioFire® Bone and Joint Infection (BJI) Panel for the Detection of Microorganisms and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Synovial Fluid Specimens. Open Forum. Infect. 2020, 7, S233–S234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabichi, M.; Alvand, A.; Shohat, N.; Goswami, K.; Parvizi, J. Diagnosis of Streptococcus canis periprosthetic joint infection: The utility of next-generation sequencing. Arthroplast. Today 2018, 4, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indelli, P.F.; Ghirardelli, S.; Violante, B.; Amanatullah, D.F. Next generation sequencing for pathogen detection in periprosthetic joint infections. EFORT Open Rev. 2021, 6, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantouly, A.T.; Alzobi, O.; Toubasi, A.A.; Zikria, B.; Al Dosari, M.A.A.; Ahmed, G. Higher sensitivity and accuracy of synovial next-generation sequencing in comparison to culture in diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg. Sport. Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivy, M.I.; Thoendel, M.J.; Jeraldo, P.R.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Hanssen, A.D.; Abdel, M.P.; Chia, N.; Yao, J.Z.; Tande, A.J.; Mandrekar, J.N.; et al. Direct Detection and Identification of Prosthetic Joint Infection Pathogens in Synovial Fluid by Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00402-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, T.L.; Sanderson, N.D.; Atkins, B.L.; Brent, A.J.; Cole, K.; Foster, D.; McNally, M.A.; Oakley, S.; Peto, L.; Taylor, A.; et al. Molecular Diagnosis of Orthopedic-Device-Related Infection Directly from Sonication Fluid by Metagenomic Sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2334–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Lee, G.-C.; Fang, X.; Xing, L.; Yang, B.; Lin, J.; Zhang, W. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of synovial fluid demonstrates high accuracy in prosthetic joint infection diagnostics: mNGS for diagnosing PJI. Bone Jt. Res. 2020, 9, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabichi, M.; Shohat, N.; Goswami, K.; Parvizi, J. Can next generation sequencing play a role in detecting pathogens in synovial fluid? Bone Jt. Res. 2018, 100-B, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoendel, M.J.; Jeraldo, P.R.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Yao, J.Z.; Chia, N.; Hanssen, A.D.; Abdel, M.P.; Patel, R. Identification of Prosthetic Joint Infection Pathogens Using a Shotgun Metagenomics Approach. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Fu, J.; Yu, B.; Sun, W.; Chen, J.; Hao, L. Meta-analysis of sonication prosthetic fluid PCR for diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, J.; Gómez-Barrena, E. An update about molecular biology techniques to detect orthopaedic implant-related infections. EFORT Open Rev. 2021, 6, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, M.; Sousa, R.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Chen, A.F.; Soriano, A.; Vogely, H.C.; Clauss, M.; Higuera, C.A.; Trebše, R. The EBJIS definition of periprosthetic joint infection. Bone Jt. Res. 2021, 103-B, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, J.; Tan, T.L.; Goswami, K.; Higuera, C.; Della Valle, C.; Chen, A.F.; Shohat, N. The 2018 Definition of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection: An Evidence-Based and Validated Criteria. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1309–1314.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohat, N.; Bauer, T.; Buttaro, M.; Budhiparama, N.; Cashman, J.; Della Valle, C.J.; Drago, L.; Gehrke, T.; Marcelino Gomes, L.S.; Goswami, K.; et al. Hip and Knee Section, What is the Definition of a Periprosthetic Joint Infection (PJI) of the Knee and the Hip? Can the Same Criteria be Used for Both Joints?: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, S325–S327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkins, J.M.; Kates, S.; Lange, J.; Lange, J.; Lichstein, P.; Otero, J.; Soriano, A.; Wagner, C.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M. General Assembly, Diagnosis, Definitions: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, S181–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Si, H.; Bao, X.; Shen, B. Performance of Sequencing Assays in Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 1514–1522.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, P.; Fink, B.; Sandow, D.; Margull, A.; Berger, I.; Frommelt, L. Prolonged bacterial culture to identify late periprosthetic joint infection: A promising strategy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo, M.E.; Corvec, S.; Borens, O.; Trampuz, A. Propionibacterium acnes: An Underestimated Pathogen in Implant-Associated Infections. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 804391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo, M.E.; Salvadó, M.; Alier, A.; Martínez, S.; Sorli, L.; Horcajada, J.P.; Puig, L. Advantages of sonication fluid culture for the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection. J. Infect. 2014, 69, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portillo, M.E.; Salvadó, M.; Trampuz, A.; Siverio, A.; Alier, A.; Sorli, L.; Martínez, S.; Pérez-Prieto, D.; Horcajada, J.P.; Puig-Verdie, L. Improved diagnosis of orthopedic implant-associated infection by inoculation of sonication fluid into blood culture bottles. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1622–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, A.; Miele, M.C.; Al Ismail, D.; Di Timoteo, F.; De Angelis, M.; Rosa, L.; Cutone, A.; Venditti, M.; Mascellino, M.T.; Valenti, P.; et al. Challenges in the Microbiological Diagnosis of Implant-Associated Infections: A Summary of the Current Knowledge. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 750460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renz, N.; Mudrovcic, S.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A. Orthopedic implant-associated infections caused by Cutibacterium spp.—A remaining diagnostic challenge. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizi, J.; Gehrke, T. Proceedings of the Second International Consensus Meeting on Musculoskeletal Infection, 1st ed.; Data Trace Publishing Company: Brooklandville, MD, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-57400-157-0. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.; Chiu, C.; Rodino, K.G.; Miller, M.B. Point-Counterpoint: Should We Be Performing Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing for Infectious Disease Diagnosis in the Clinical Laboratory? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01739-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, S.; Yi, Q.; Xia, Y.; Geng, B. Diagnostic Value of Next-Generation Sequencing in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Liu, Y.; Ehnert, S.; Nüssler, A.K.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, T. The Effectiveness of Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing in the Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 875822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, R.; Viglietta, E.; Mazza, D.; Petrucca, A.; Borro, M.; Iolanda, S.; Simmaco, M.; Ferretti, A. Accuracy and Cost-Effectivenss of a Novel Method for Alpha Defensins Measurement in the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infections. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 3275–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.; Oyagüez, I.; Prieto, L.; Rodriguez, G.; Esteban, J. Costs Analysis Of Pcr Unyverotm I60-Iti Technique For Detecting Microorganisms In Patients With Suspected Chronic Infection At Musculoskeletal Implants. Value Health 2015, 18, A351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Auñon, Á.; Coifman, I.; Blanco, A.; Garcia-Canete, J.; Parron-Cambero, R.; Esteban, J. Usefulness of a Multiplex PCR Assay for the Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infections in the Routine Setting. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, G.; Taddei, F.; Brandolini, M.; Mancini, A.; Denicolò, A.; Congestrì, F.; Manera, M.; Arfilli, V.; Battisti, A.; Zannoli, S.; et al. Molecular Approach for the Laboratory Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salar-Vidal, L.; Auñón, Á.; Esteban, J. Molecular Diagnosis of Osteoarticular Implant-Associated Infection: Available Techniques and How We Can Use Them. Prosthesis 2023, 5, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis5010001
Salar-Vidal L, Auñón Á, Esteban J. Molecular Diagnosis of Osteoarticular Implant-Associated Infection: Available Techniques and How We Can Use Them. Prosthesis. 2023; 5(1):1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis5010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalar-Vidal, Llanos, Álvaro Auñón, and Jaime Esteban. 2023. "Molecular Diagnosis of Osteoarticular Implant-Associated Infection: Available Techniques and How We Can Use Them" Prosthesis 5, no. 1: 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis5010001
APA StyleSalar-Vidal, L., Auñón, Á., & Esteban, J. (2023). Molecular Diagnosis of Osteoarticular Implant-Associated Infection: Available Techniques and How We Can Use Them. Prosthesis, 5(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis5010001








