Linear Quadratic Tracking Control of Car-in-the-Loop Test Bench Using Model Learned via Bayesian Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
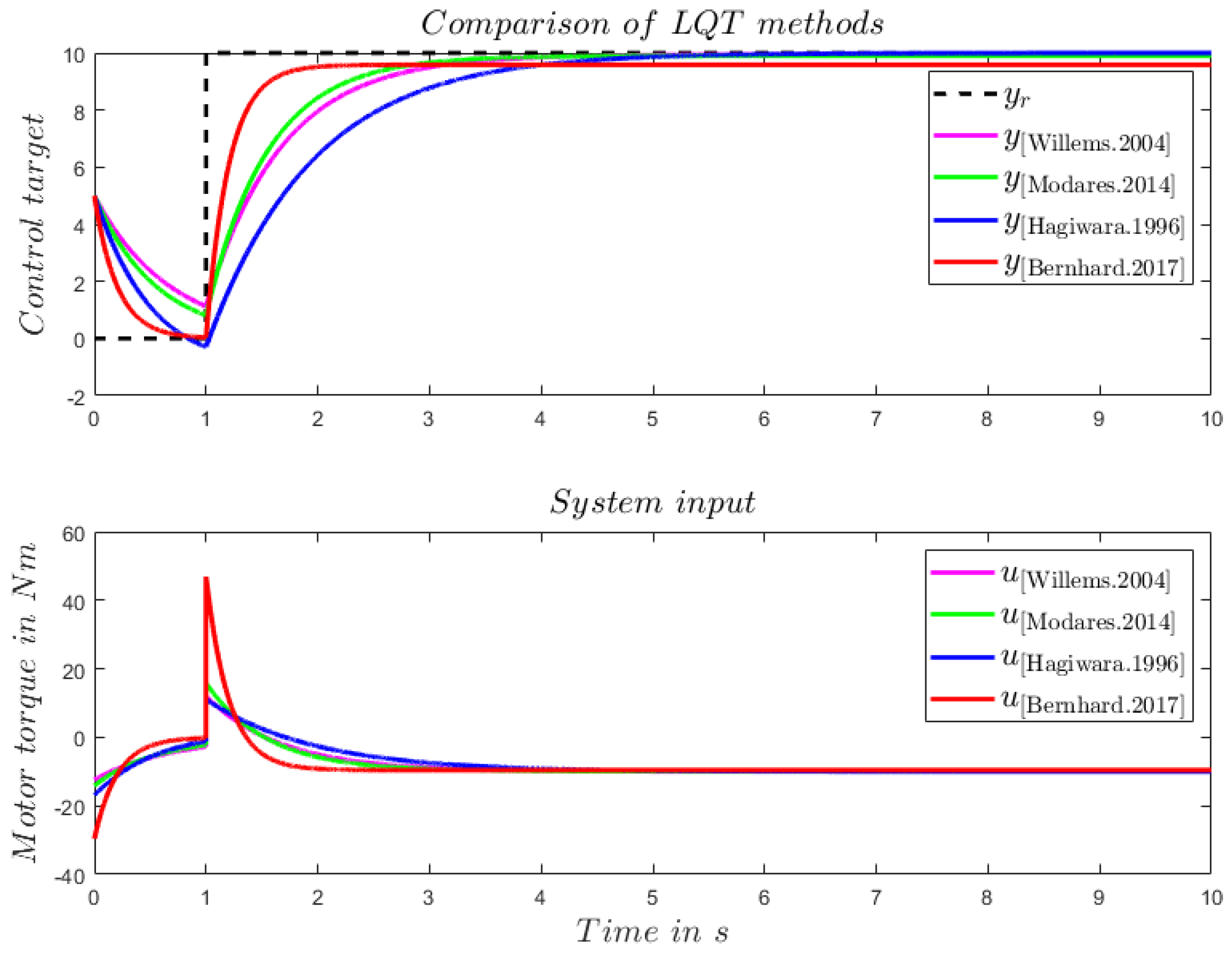
2.1. Linear Quadratic Tracking Methods
2.2. Bayesian Optimization for Dynamic System Control
3. Augmented LQT Framework and Fundamentals of Bayesian Optimization
3.1. LQT with Augmented State
3.1.1. Problem Description
3.1.2. General LQT Control Framework
3.1.3. Augmented LQT Control Framework
3.1.4. Simple Numerical Example
3.2. Bayesian Optimization with Gaussian Process
| Algorithm 1: Model learning via Bayesian optimization | |
| Step | Procedure |
| 1 | Initialize GP with |
| 2 | for |
| find , apply | |
| conduct closed-loop experiment with | |
| measure and ; | |
| compute cost function | |
| update GP and D with | |
| 3 | Compute optimal parameter , where . |
4. LQT Implementation for Car-in-the-Loop
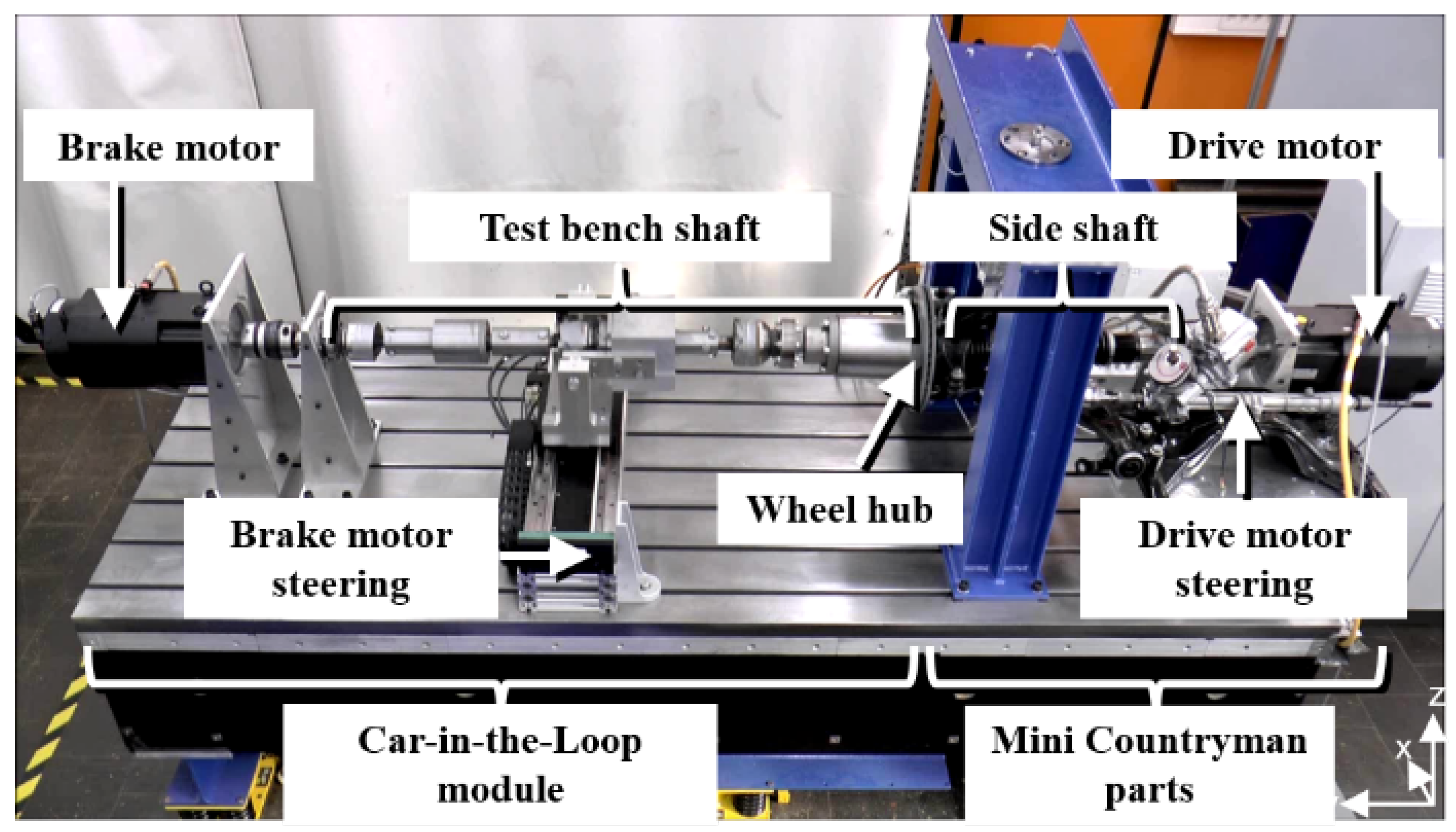
4.1. Car-in-the-Loop Test Bench Prototype
4.2. Augmented LQT Control with Perfect Model
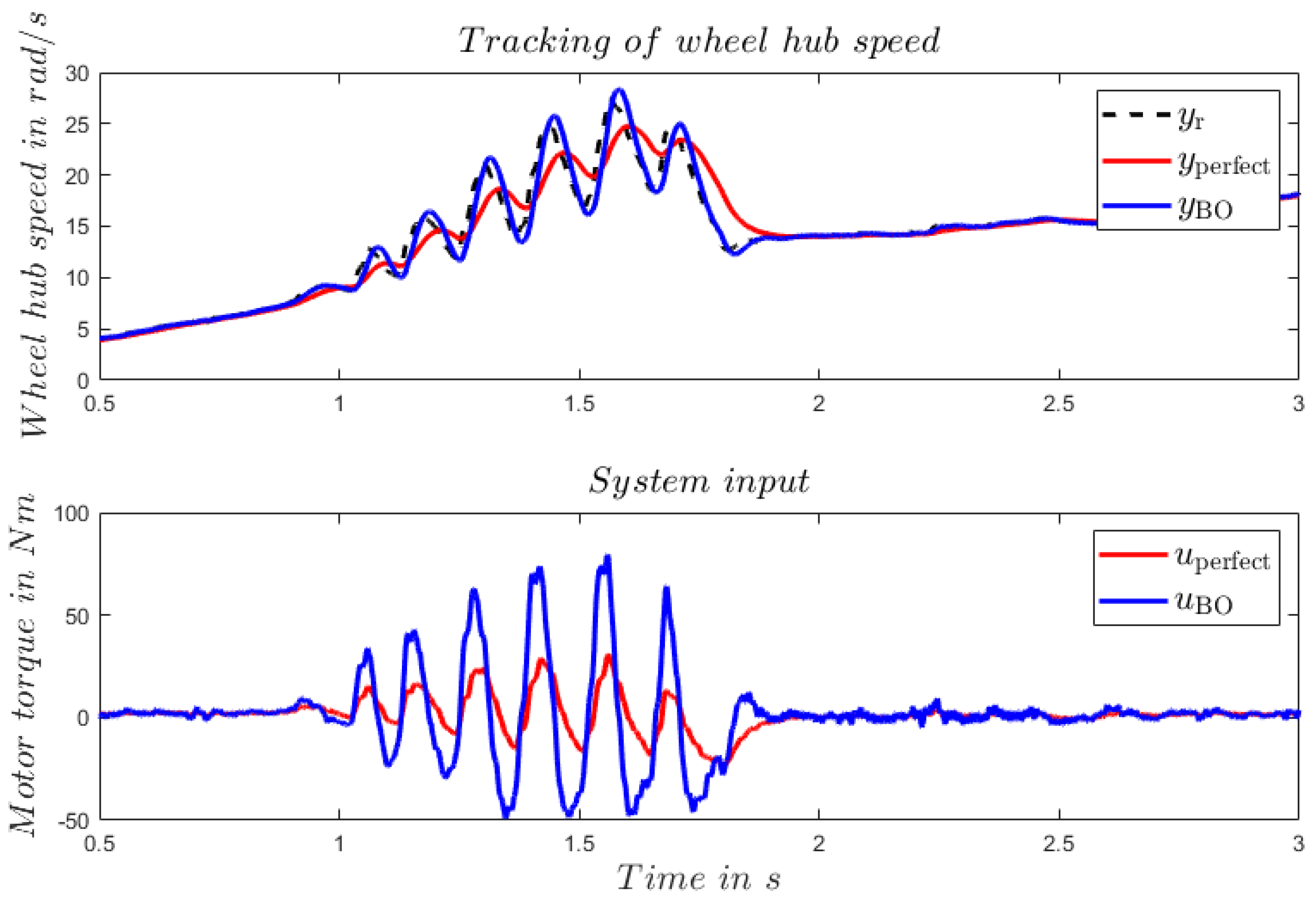
4.3. Augmented LQT Control with Model Learned via Bayesian Optimization
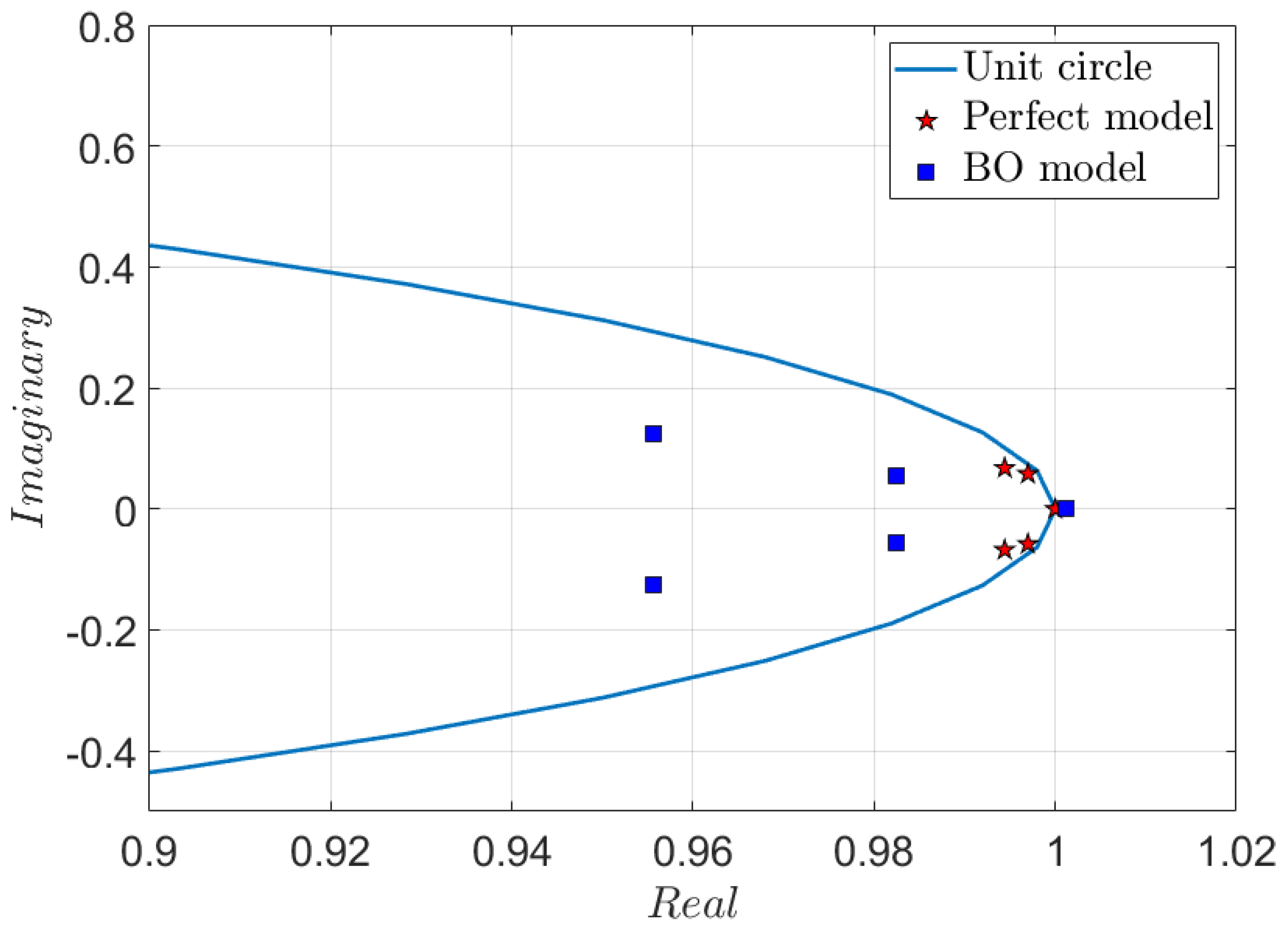
4.4. Discussion on the Model Learned via Bayesian Optimization
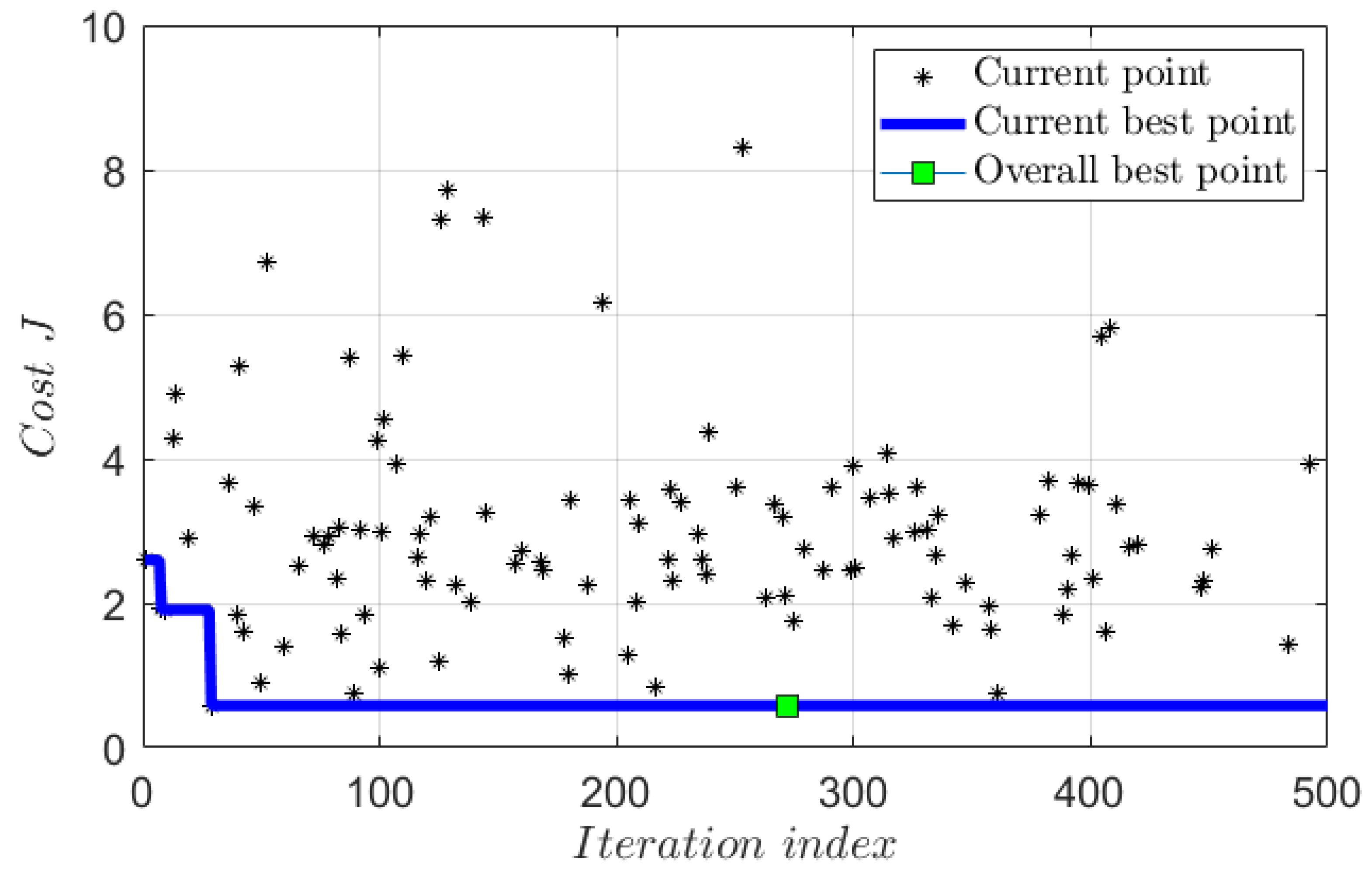
4.5. Effectiveness of Bayesian Optimization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahlert, A. Ein Modellbasiertes Regelungskonzept für Einen Gesamtfahrzeug Dynamikprüfstand; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Wang, W. An Indoor Vehicle-in-the-Loop Simulation Platform Testing Method for Autonomous Emergency Braking. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 2021, 8872889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegl, S.; Ratz, S.; Düser, T.; Hettel, R. Vehicle-in-the-Loop at Testbeds for ADAS/AD Validation. Atzelectronics Worldw. 2021, 16, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schyr, C.; Inoue, H.; Nakaoka, Y. Vehicle-in-the-Loop Testing—A Comparative Study for Efficient Validation of ADAS/AD Functions. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Connected Vehicle and Expo (ICCVE), Lakeland, FL, USA, 7–9 March 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fietzek, R. Modellbildung, Regelung und Realisierung eines Neuartigen Konzepts für Einen Gesamtfahrzeugprüfstand; Forschungsberichte Mechatronische Systeme im Maschinenbau, Shaker: Aachen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht, S.; Fietzek, R.; Meier, T. Control Strategy for the Longitudinal Degree of Freedom of a Complete Vehicle Test Rig; Technical report; SAE Technical Paper: Detroit, MI, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard, S. Time-Invariant Control in LQ Optimal Tracking: An Alternative to Output Regulation. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 50, 4912–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.; Bokor, J. Development and performance evaluation of an infinite horizon LQ optimal tracker. Eur. J. Control 2018, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Han, S.; Kwon, W.H. LQ tracking controls with fixed terminal states and their application to receding horizon controls. Syst. Control Lett. 2008, 57, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, J.L.; Mareels, I.M. A rigorous solution of the infinite time interval LQ problem with constant state tracking. Syst. Control Lett. 2004, 52, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modares, H.; Lewis, F.L. Linear Quadratic Tracking Control of Partially-Unknown Continuous-Time Systems Using Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2014, 59, 3051–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, T.; Yamasaki, T.; Araki, M. Two-degree-of-freedom design method of LQI servo systems: Disturbance rejection by constant state feedback. Int. J. Control 1996, 63, 703–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, E.; Alba-Flores, R. On the infinite-horizon LQ tracker. Syst. Control Lett. 2000, 40, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochu, E.; Cora, V.M.; De Freitas, N. A tutorial on Bayesian optimization of expensive cost functions, with application to active user modeling and hierarchical reinforcement learning. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1012.2599. [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi, M.; Koenig, C.; Maier, M.; Smith, R.S.; Lygeros, J.; Rupenyan, A. Safety-Aware Cascade Controller Tuning Using Constrained Bayesian Optimization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, L.P.; Küttel, C.; Arcari, E.; Hewing, L.; Zeilinger, M.N.; Carron, A. Contextual tuning of model predictive control for autonomous racing. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 10555–10562. [Google Scholar]
- Frazier, P.I. A tutorial on Bayesian optimization. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.02811. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Jin, Y.; Schmitt, S.; Olhofer, M. Recent Advances in Bayesian Optimization. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, J.A.; Tsay, C. Bayesian optimization as a flexible and efficient design framework for sustainable process systems. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.16373. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, J.P.; Santos, L.O.; Reis, M.S. Bayesian Optimization for automatic tuning of digital multi-loop PID controllers. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2023, 173, 108211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, C.; Ozols, M.; Makarova, A.; Balta, E.C.; Krause, A.; Rupenyan, A. Safe risk-averse bayesian optimization for controller tuning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 8208–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wabersich, K.P.; Taylor, A.J.; Choi, J.J.; Sreenath, K.; Tomlin, C.J.; Ames, A.D.; Zeilinger, M.N. Data-Driven Safety Filters: Hamilton-Jacobi Reachability, Control Barrier Functions, and Predictive Methods for Uncertain Systems. IEEE Control Syst. 2023, 43, 137–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenger, D.; Ay, M.; Abel, D. Robust Parametrization of a Model Predictive Controller for a CNC Machining Center Using Bayesian Optimization. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 10388–10394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann-Brosig, M.; Marco, A.; Schwarzmann, D.; Trimpe, S. Data-Efficient Autotuning with Bayesian Optimization: An Industrial Control Study. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2020, 28, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorourifar, F.; Makrygirgos, G.; Mesbah, A.; Paulson, J.A. A Data-Driven Automatic Tuning Method for MPC under Uncertainty using Constrained Bayesian Optimization. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2021, 54, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, A.; Benosman, M. Safe learning-based observers for unknown nonlinear systems using Bayesian optimization. Automatica 2021, 133, 109860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, R.C.; Chowdhary, G.; How, J.P. Experimental validation of Bayesian nonparametric adaptive control using Gaussian processes. J. Aerosp. Inf. Syst. 2014, 11, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doekemeijer, B.M.; van der Hoek, D.C.; van Wingerden, J.-M. Model-based closed-loop wind farm control for power maximization using Bayesian Optimization using Bayesian optimization: A large eddy simulation study. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE Conference on Control Technology and Applications, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China, 19–21 August 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkenkamp, F.; Schoellig, A.P. Safe and robust learning control with Gaussian processes. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE European Control Conference (ECC), Linz, Austria, 15–17 July 2015; pp. 2496–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevers, M. Identification for Control: From the Early Achievements to the Revival of Experiment Design. Eur. J. Control 2005, 11, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjalmarsson, H. From experiment design to closed-loop control. Automatica 2005, 41, 393–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.; Calandra, R.; Xiao, T.; Levine, S.; Tomlin, C.J. Goal-driven dynamics learning via Bayesian optimization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 56th Annual Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Melbourne, Australia, 12–15 December 2017; pp. 5168–5173. [Google Scholar]
- Young, P.C.; Willems, J.C. An approach to the linear multivariable servomechanism problem. Int. J. Control 1972, 15, 961–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkapure, H.G.; Chidambaram, M. Comparison of Two Methods of Incorporating an Integral Action in Linear Quadratic Regulator. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2014, 47, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Pal, B.C. An extended linear quadratic regulator for LTI systems with exogenous inputs. Automatica 2017, 76, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Bai, H.; Chakrabortty, A. Model-based and model-free designs for an extended continuous-time LQR with exogenous inputs. Syst. Control Lett. 2021, 154, 104983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piga, D.; Forgione, M.; Formentin, S.; Bemporad, A. Performance-Oriented Model Learning for Data-Driven MPC Design. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2019, 3, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J. Guaranteed margins for LQG regulators. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1978, 23, 756–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanwar, A.; Stürz, Y.; Johansson, K.H. Robust data-driven predictive control using reachability analysis. Eur. J. Control 2022, 68, 100666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, G.; Jardin, P.; Rinderknecht, S. Linear Quadratic Tracking Control of Car-in-the-Loop Test Bench Using Model Learned via Bayesian Optimization. Vehicles 2024, 6, 1300-1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles6030062
Gao G, Jardin P, Rinderknecht S. Linear Quadratic Tracking Control of Car-in-the-Loop Test Bench Using Model Learned via Bayesian Optimization. Vehicles. 2024; 6(3):1300-1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles6030062
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Guanlin, Philippe Jardin, and Stephan Rinderknecht. 2024. "Linear Quadratic Tracking Control of Car-in-the-Loop Test Bench Using Model Learned via Bayesian Optimization" Vehicles 6, no. 3: 1300-1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles6030062
APA StyleGao, G., Jardin, P., & Rinderknecht, S. (2024). Linear Quadratic Tracking Control of Car-in-the-Loop Test Bench Using Model Learned via Bayesian Optimization. Vehicles, 6(3), 1300-1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles6030062






