Fluctuations in Goat Milk Composition During Processing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Farm Characteristics
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Milk Proximate Composition Analyses
2.4. Goat Groups
2.5. Curd Firmness
2.6. Study Limitations
2.7. Data Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SCC | Somatic cell count |
| SCS | Somatic cell score |
| a30 | Curd firmness measured 30 min after rennet addition |
| k20 | Curd firming time to specified firmness |
| N | Newtons |
| RCT | Rennet coagulation time |
References
- Alhussien, M.N.; Dang, A.K. Milk somatic cells, factors influencing their release, future prospects, and practical utility in dairy animals: An overview. Vet. World 2018, 11, 562–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smistad, M.; Sølverød, L.; Inglingstad, R.A.; Østerås, O. Distribution of somatic cell count and udder pathogens in Norwegian dairy goats. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 11878–11888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocco, G.; Dadousis, C.; Vacca, G.M.; Pazzola, M.; Summer, A.; Dettori, M.L.; Cipolat-Gotet, C. Predictive formulas for different measures of cheese yield using milk composition from individual goat samples. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 5610–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.; Mora Garcίa, M.B. A 100-Year Review: Advances in goat milk research. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 10026–10044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, G.; Lavon, Y.; Matzrafi, Z.; Benun, O.; Bezman, D.; Merin, U. Somatic cell counts, chemical composition and coagulation properties of goat and sheep bulk tank milk. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 58, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podhorecká, K.; Borková, M.; Šulc, M.; Seydlová, R.; Dragounová, H.; Švejcarová, M.; Peroutková, J.; Elich, O. Somatic Cell Count in Goat Milk: An Indirect Quality Indicator. Foods 2021, 10, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, R.; Huau, C.; Caillat, H.; Fassier, T.; Bouvier, F.; Pampouille, E.; Clément, V.; Palhière, I.; Larroque, H.; Tosser-Klopp, G.; et al. Divergent selection on milk somatic cell count in goats improves udder health and milk quality with on nematode resistance. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 102, 5242–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, A.C.; Vigalo, V.; De Marchi, M.; Lopez-Villalobos, N.; Loveday, S.M.; Weeks, M.; McNabb, W. Effect of protein polymorphisms on milk composition, coagulation properties, and protein profile in dairy sheep. Int. Dairy J. 2025, 160, 106102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Prendes, R.; Crooijmans, R.P.M.A.; Dibbits, B.; Laport, K.; Breunig, S.; Keijzer, P.; Pellis, L.; Bovenhulis, H. Genetic and environmental factors shaping goat milk oligosaccharide composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 11214–11223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desidera, F.; Skeie, S.B.; Devold, T.G.; Inglingstad, R.A.; Porcellato, D. Fluctuations in somatic cell count and their impact on individual goat milk quality throughout lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 108, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lianou, D.T.; Michael, C.K.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Liagka, D.V.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Caroprese, M.; Fthenakis, G.C. Association of Breed of Sheep or Goats with Somatic Cell Counts and Total Bacterial Counts of Bulk-Tank Milk. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, W.D., Jr.; Marinho do Monte, D.F.; Gomes Cardoso de Leon, C.M.; Paulino de Moura, J.F.; Vieira da Silva, N.M.; Ramos do Egypto Queiroga, R.d.C.; Neto, S.G.; Naves Givisiez, P.E.; Pereira, W.E.; Bruno de Oliveira, C.J. Logistic regression model reveals major factors associated with total bacteria ans somatic cell counts in goat bulk milk. Small Rumin. Res. 2021, 198, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocco, G.; Dadousis, C.; Vacca, G.M.; Pazzola, M.; Paschino, P.; Dettori, M.L.; Ferragina, A.; Cipolat-Gotet, C. Breed of goat affects the prediction accuracy of milk coagulation properties using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 104, 3956–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsiou, K.; Andreadis, M.; Manessis, G.; Lazaridou, A.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Basdagianni, Z.; Bossis, I.; Moschakis, T. Effects of farming system on rheological behaviour of rennet-induced coagulation in milk from Skopelos breed goats. Foods 2025, 14, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margatho, G.; Rodrίguez-Estévez, V.; Medeiros, L.; Simões, J. Seasonal variation of Serrana goat milk contents in mountain grazing system for cheese manufacture. Rev. Med. Vet. 2018, 169, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Pazzola, M.; Amalfitano, N.; Bittante, G.; Dettori, M.L.; Vacca, G.M. Composition, coagulation properties, and predicted cheesemaking traits of bulk milk from different farming systems, breeds, and stages of production. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 6724–6738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smistad, M.; Inglingstad, R.A.; Skeie, S. Seasonal dynamics of bulk milk somatic cell count in grazing Norwegian dairy goats. Short Communication. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 5, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdid, A.; Martί-De Olives, A.; Fernández, N.; Rodrίguez, M.; Peris, C. Effect of stress on somatic cell count and milk yield and composition in goats. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 125, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desidera, F.; Skeie, S.B.; Devold, T.G.; Inglingstad, R.A.; Porcellato, D. Impact of somatic cell count and lactation stage on coagulation properties of milk from Norwegian individual goats. Int. Dairy J. 2025, 162, 106161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geus, Y.de.; Scherpenisse, P.; Smit, L.A.M.; Bossers, A.; Stegeman, J.A.; Benedictus, L.; Spieβ, L.; Koop, G. Total bacterial count and somatic cell count in bulk and individual goat milk around kidding: Two longitudinal observational studies. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 5427–5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Delger, M.; Dave, A.; Singh, H.; Ye, A. Acid and rennet gelation properties of sheep, goat, and cow milks: Effects of processing and seasonal variation. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 106, 1611–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 Laying down Specific Hygiene Rules for Food of Animal Origin; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2004.
- Cipolat-Gotet, C.; Cecchinato, A.; Malacarne, M.; Bittante, G.; Summer, A. Variations in milk protein fractions affect the efficiency of the cheese-making process. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8788–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzola, M.; Stocco, G.; Paschino, P.; Dettori, M.L.; Cipolat-Gotet, C.; Bittante, G.; Vacca, G.M. Modeling of coagulation, curd firming, and syneresis of goat milk from 6 breeds. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 7027–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocco, G.; Cipolat-Gotet, C.; Cecchinato, A.; Calamari, L.; Bittante, G. Milk skimming, heating, acidification, lysozyme, and rennet affect the pattern, repeatability, and predictability of milk coagulation properties and of curd-firming model parameters: A case study of Grana Padano. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 98, 5052–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbo, T.; Cipolat-Gotet, C.; Bittante, G.; Cecchinato, A. The nonlinear effect of somatic cell count on milk composition, coagulation properties, curd firmness modelling, cheese yield, and curd nutrient recovery. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 99, 5104–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfatti, V.; Ribeiro de Freitas, D.; Lugo, A.; Vicario, D.; Carnier, P. Effects of the detailed protein composition of milk on curd yield and composition measured by model micro-cheese curd making of individual milk samples. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 102, 7863–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breunig, S.; Crooijmans, R.P.M.A.; Bovenhuis, H.; Hettinga, K.; Bijl, E. Linking variation in the casein fraction and salt composition to casein micelle size in milk of Dutch dairy goats. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 6474–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadousis, C.; Cipolat-Gotet, C.; Stocco, G.; Ferragina, A.; Dettori, M.L.; Pazzola, M.; Rangel, A.H.d.N.; Vacca, G.M. Goat farm variability affect milk Fourier-transform infrared spectra used for predicting coagulation properties. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 104, 3927–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scano, P.; Caboni, P. Seasonal variation of milk composition of Sarda and Saanen dairy goats. Dairy 2022, 3, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocco, G.; Pazzola, M.; Dettori, M.L.; Paschino, P.; Bittante, G.; Vacca, G.M. Effect of composition on coagulation, curd firming, and syneresis of goat milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9693–9702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutz, M.M.; Hansen, L.B.; Steuernagel, G.R.; Reneau, J.K.; Kuck, A.L. Genetic parameters for somatic cells, protein, and fat in milk of Holsteins. J. Dairy Sci. 1990, 73, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvarožková, K.; Tančin, V.; Uhrinčat, M.; Oravcová, M.; Hleba, L.; Gancárová, B.; Mačuhová, L.; Ptáček, M.; Marnet, P.G. Pathogens in milk of goats and their relationship with somatic cell count. J. Dairy Res. 2023, 90, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovska, S.; Jonkus, D.; Zagorska, J.; Ciprovica, I. The influence of k-casein genotype on the coagulation properties of milk collected from the local Latvian cow breeds. Agr. Res. 2017, 15, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Marcinkoniene, L.; Ciprovica, I. The influence of milk quality and composition on goat milk suitability for cheese production. Agr. Res. 2020, 18, 1796–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomone-Caballero, M.; Fresno, M.; Álvvarez, S.; Torres, A. Effects of parity and somatic cell count threshold on udder morphology, milk ability traits, and milk quality in Canarian goats. Animals 2024, 14, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjajevis, N.V.; Tomasevic, I.B.; Miloradovic, Z.N.; Nedeljkovic, A.; Miocinovic, J.B.; Jovanovic, S.T. Seasonal variations of Saanen goat milk composition and the impact of climatic conditions. J. Food. Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.M.; Tedeschi, L.O.; Atzori, A.S. The comparison of the lactation and milk yield and composition of selected breeds of sheep and goats. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2017, 1, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacca, M.G.; Stocco, G.; Dettori, L.M.; Pira, E.; Bittante, G.; Pazzola, M. Milk yield, quality, and coagulation properties of 6 breeds of goats: Environmental and individual variability. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 7236–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šlyžius, E.; Anskienė, L.; Palubinskas, G.; Juozaitienė, V.; Šlyžienė, B.; Juodžentytė, R.; Laučienė, L. Associations between somatic cell count and milk fatty acid and amino acid profile in Alpine and Saanen goat breeds. Animals 2023, 13, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenc, B.; Malovrh, Š.; Paveljšek, D.; Rozman, V.; Simčič, M.; Treven, P. Correlation of goat milk coagulation properties between dams and daughters. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 143, 105644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglingstad, R.A.; Eknæs, M.; Brunborg, L.; Mestawet, T.; Devold, T.G.; Vegarud, G.E.; Skeie, S.B. Norwegian goat milk composition and cheese quality: The influence of lipid supplemented concentrate and lactation stage. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 56, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michlová, T.; Dragounová, H.; Seydlová, R.; Hejtmánková, A. The hygienic and nutritional quality of milk from Saanen goats bred in the Moravian-Silesian region. Agr. Res. 2016, 14, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Currò, S.; De Marchi, M.; Claps, S.; Salzano, A.; De Palo, P.; Manuelian, C.L.; Neglia, G. Differences in the detailed milk mineral composition of Italian local and Saanen goat breeds. Animals 2019, 9, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicovery, I.M.C.; Rodrigues, T.C.G.d.C.; Tosto, M.S.L.; Bittencourt, R.F.; Mariz, L.D.S.; Azevedo, J.A.G.; Pinto de Carvalho, G.G.; Santos, S.A. Nutritional attributes of goat milk obrained from Anglo Nubian, Moxoto, and Saanen breeds in different lactation phases. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 145, 105720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.C.G.d.C.; Nicovery, I.M.C.; Alba, H.D.R.; Carvalho, G.G.P.d.C.; Tosto, M.S.L.; Bittencourt, R.F.; Azevedo, J.A.G.; Mariz, L.D.S.; Santos, S.A. Lactation curve, milk composition and metabolic status of goats from different genetic groups under propical conditions. J. Livest. Sci. Teh. 2023, 11, 01–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
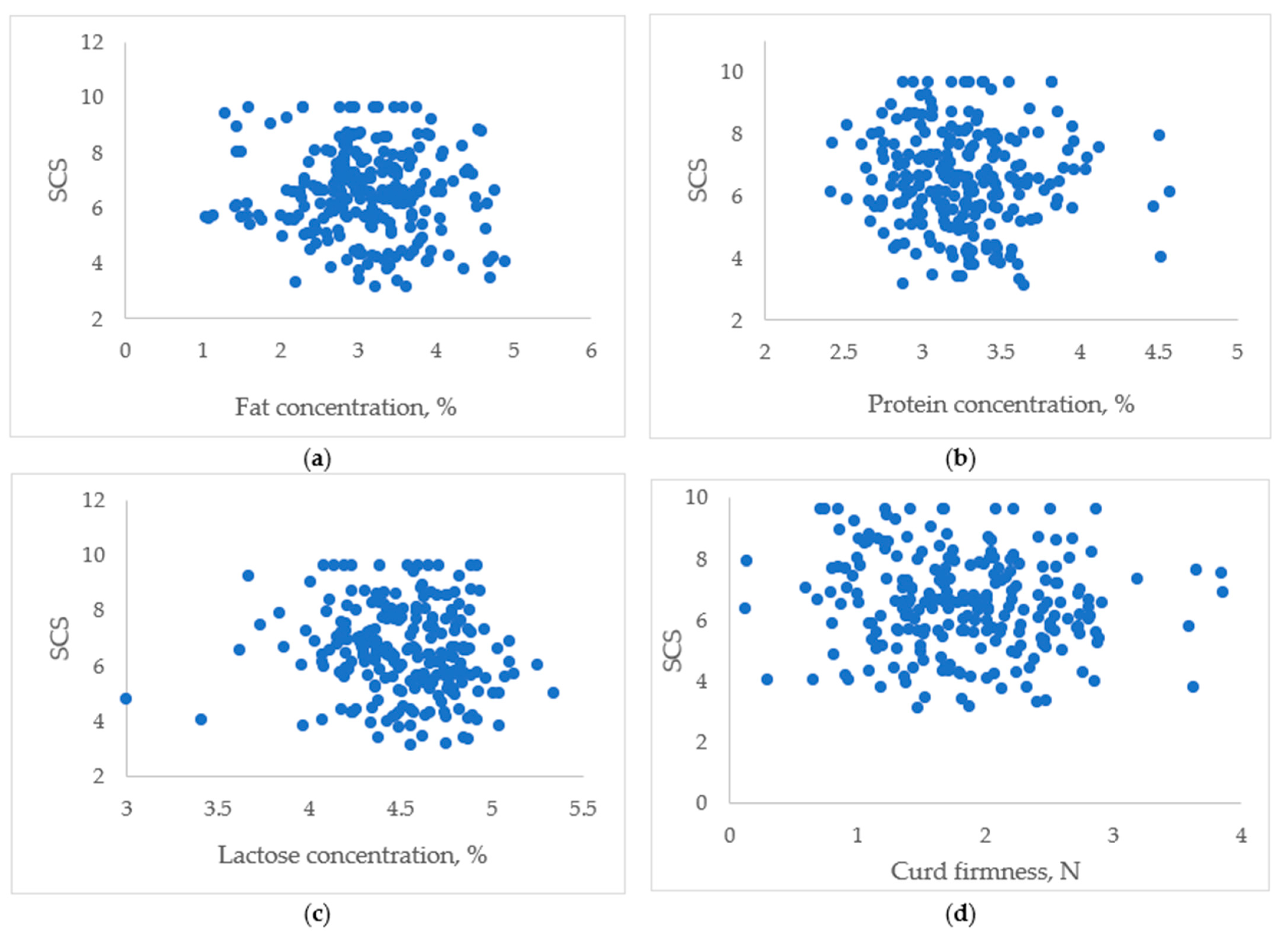
| Group | SCC, ×103 Cells/mL | SCS |
|---|---|---|
| I | <500 | <5.32 |
| II | 500–2000 | 5.32–7.32 |
| III | 2000–4000 | 7.32–8.32 |
| IV | >4000 | >8.32 |
| Parameter | Group I (n = 52) | Group II (n = 117) | Group III (n = 40) | Group IV (n = 31) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat, % | 3.34 ± 0.71 a | 2.97 ± 0.78 b | 3.12 ± 0.63 c | 3.03 ± 0.82 bc |
| Protein, % | 3.29 ± 0.31 bc | 3.26 ± 0.38 bc | 3.32 ± 0.53 b | 3.20 ± 0.31 c |
| Fat-to-protein ratio | 1.02 ± 0.20 c | 0.92 ± 0.24 d | 0.96 ± 0.22 dc | 0.95 ± 0.26 dc |
| Lactose, % | 4.56 ± 0.38 d | 4.51 ± 0.30 d | 4.50 ± 0.26 d | 4.51 ± 0.31 d |
| Dry matter, % | 11.28 ± 1.06 e | 10.92 ± 1.38 f | 10.98 ± 0.92 f | 10.73 ± 1.20 g |
| Freezing point, °C | −0.491 ± −0.038 f | −0.489 ± −0.033 f | −0.484 ± −0.026 f | −0.477 ± −0.028 f |
| SCS | 4.39 ± 0.60 g | 6.35 ± 0.54 h | 7.82 ± 0.28 i | 9.08 ± 0.48 j |
| Curd firmness, N | 1.81 ± 0.64 h | 1.89 ± 0.63 h | 1.88 ± 0.75 h | 1.56 ± 0.61 i |
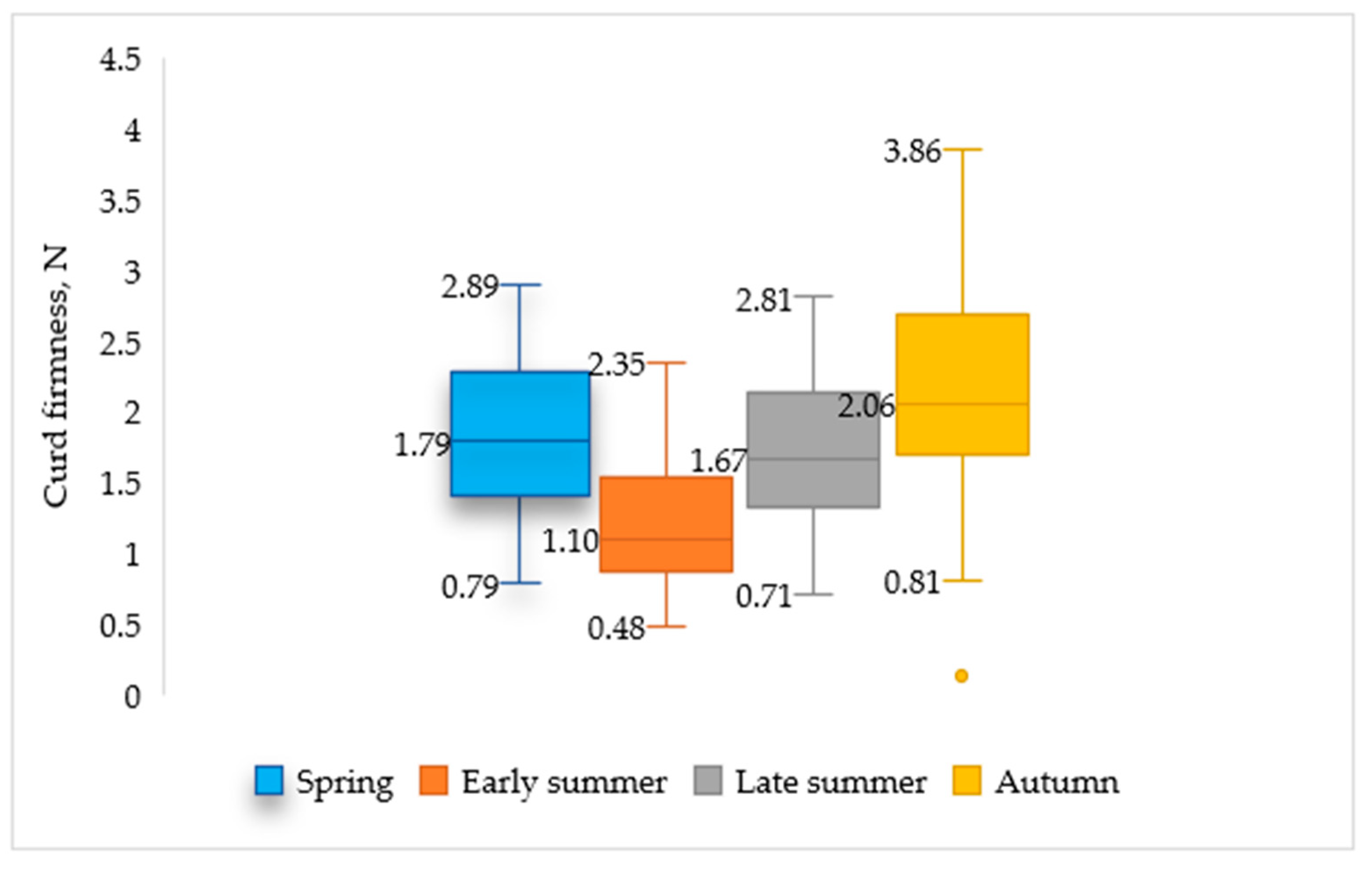
| Parameter | Spring (n = 66) | Early Summer (n = 74) | Late Summer (n = 55) | Autumn (n = 45) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat, % | 2.69 ± 0.81 a | 3.29 ± 0.74 b | 3.29 ± 0.70 b | 3.07 ± 0.54 c |
| Protein, % | 3.26 ± 0.40 bc | 3.23 ± 0.31 b | 3.30 ± 0.29 c | 3.29 ± 0.55 c |
| Fat-to-protein ratio | 0.83 ± 0.26 c | 1.02 ± 0.24 d | 1.00 ± 0.19 d | 0.95 ± 0.17 d |
| Lactose, % | 4.59 ± 0.30 d | 4.55 ± 0.33 d | 4.48 ± 0.32 e | 4.41 ± 0.27 e |
| Dry matter, % | 10.80 ± 1.59 e | 11.17 ± 1.07 f | 11.15 ± 1.03 f | 10.74 ± 1.03 e |
| Freezing point, °C | −0.500 ± −0.035 f | −0.489 ± −0.032 g | −0.485 ± −0.029 g | −0.469 ± −0.024 h |
| SCS | 6.21 ± 1.42 g | 6.52 ± 1.63 h | 6.74 ± 1.55 h | 6.70 ± 1.54 h |
| Curd firmness, N | 1.84 ± 0.56 h | 1.80 ± 0.56 h | 1.61 ± 0.63 i | 2.12 ± 0.85 j |
| Group | Breed | Protein, % | Fat, % | Fat-to-Protein Ratio | Curd Firmness, N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group I | Latvian Native (n = 13) | 3.32 ± 0.22 aA | 3.07 ± 0.72 aA | 0.92 ± 0.22 aA | 1.96 ± 0.66 aA |
| Saanen (n = 15) | 3.28 ± 0.27 abB | 3.33 ± 0.72 aC | 1.01 ± 0.18 aC | 1.91 ± 0.66 aC | |
| Cross-breed (n = 24) | 3.27 ± 038 aC | 3.50 ± 0.68 aD | 1.08 ± 0.19 aD | 1.66 ± 0.60 aE | |
| Group II | Latvian Native (n = 26) | 3.27 ± 0.26 bA | 2.52 ± 0.75 bB | 0.78 ± 0.24 bB | 2.02 ± 0.75 bA |
| Saanen (n = 34) | 3.20 ± 0.39 bB | 3.10 ± 0.74 cC | 0.97 ± 0.21 cC | 1.86 ± 0.57 bC | |
| Cross-breed (n = 57) | 3.28 ± 0.42 bC | 3.09 ± 0.76 cE | 0.95 ± 0.24 cD | 1.85 ± 0.61 bE | |
| Group III | Latvian Native (n = 15) | 3.18 ± 0.39 cA | 2.84 ± 0.74 dAB | 0.91 ± 0.25 dA | 1.77 ± 0.56 cB |
| Saanen (n = 11) | 3.26 ± 0.34 cB | 3.10 ± 0.43 deC | 0.96 ± 0.17 dC | 2.14 ± 0.90 dC | |
| Cross-breed (n = 14) | 3.51 ± 0.72 cC | 3.44 ± 0.52 eD | 1.02 ± 0.23 dD | 1.79 ± 0.82 cE | |
| Group IV | Latvian Native (n = 6) | 3.19 ± 0.30 dA | 3.00 ± 0.45 fAB | 0.95 ± 0.16 eA | 1.47 ± 0.73 eB |
| Saanen (n = 10) | 3.14 ± 0.30 dB | 2.97 ± 0.88 fC | 0.95 ± 0.29 eC | 1.59 ± 0.62 eD | |
| Cross-breed (n = 15) | 3.24 ± 0.33 dC | 3.07 ± 0.94 fE | 0.95 ± 0.29 eD | 1.58 ± 0.60 eE |
| Group | Lactation | Protein, % | Fat, % | Fat-to-Protein Ratio | Curd Firmness, N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group I | 2nd lactation (n = 19) | 3.38 ± 0.43 aA | 3.40 ± 0.78 aA | 1.00 ± 0.21 aA | 1.75 ± 0.74 aA |
| 3rd lactation (n = 24) | 3.24 ± 0.21 aB | 3.30 ± 0.64 aC | 1.02 ± 0.20 aB | 1.80 ± 0.56 aB | |
| 4th lactation (n = 9) | 3.21 ± 0.21 aC | 3.34 ± 0.81 aE | 1.04 ± 0.23 aC | 1.67 ± 0.62 bD | |
| Group II | 2nd lactation (n = 46) | 3.35 ± 0.37 bA | 2.86 ± 0.83 bB | 0.86 ± 0.27 bA | 1.97 ± 0.51 cA |
| 3rd lactation (n = 52) | 3.17 ± 0.36 cB | 2.98 ± 0.76 bD | 0.95 ± 0.23 bB | 1.81 ± 0.69 cBC | |
| 4th lactation (n = 19) | 3.27 ± 0.41 bcC | 3.17 ± 0.71 bE | 0.97 ± 0.18 bC | 1.93 ± 0.74 cD | |
| Group III | 2nd lactation (n = 13) | 3.53 ± 0.58 cdA | 3.12 ± 0.63 cAB | 0.91 ± 0.24 cA | 2.08 ± 0.93 dA |
| 3rd lactation (n = 20) | 3.24 ± 0.54 cB | 3.01 ± 0.63 cCD | 0.97 ± 0.22 cB | 1.78 ± 0.72 eBC | |
| 4th lactation (n = 7) | 3.13 ± 0.25 dC | 3.25 ± 0.73 cE | 1.03 ± 0.19 cC | 1.78 ± 0.44 eD | |
| Group IV | 2nd lactation (n = 7) | 3.42 ± 0.36 eA | 2.90 ± 0.91 dAB | 0.85 ± 0.25 dA | 1.58 ± 0.65 fA |
| 3rd lactation (n = 16) | 3.13 ± 0.24 fB | 3.17 ± 0.87 dCD | 1.01 ± 0.27 dB | 1.49 ± 0.61 fC | |
| 4th lactation (n = 8) | 3.15 ± 0.34 fC | 2.85 ± 0.68 dE | 0.92 ± 0.26 dC | 1.68 ± 0.66 fD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Marcinkoniene, L.; Ciprovica, I. Fluctuations in Goat Milk Composition During Processing. Dairy 2026, 7, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy7010005
Marcinkoniene L, Ciprovica I. Fluctuations in Goat Milk Composition During Processing. Dairy. 2026; 7(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy7010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarcinkoniene, Liga, and Inga Ciprovica. 2026. "Fluctuations in Goat Milk Composition During Processing" Dairy 7, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy7010005
APA StyleMarcinkoniene, L., & Ciprovica, I. (2026). Fluctuations in Goat Milk Composition During Processing. Dairy, 7(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy7010005








